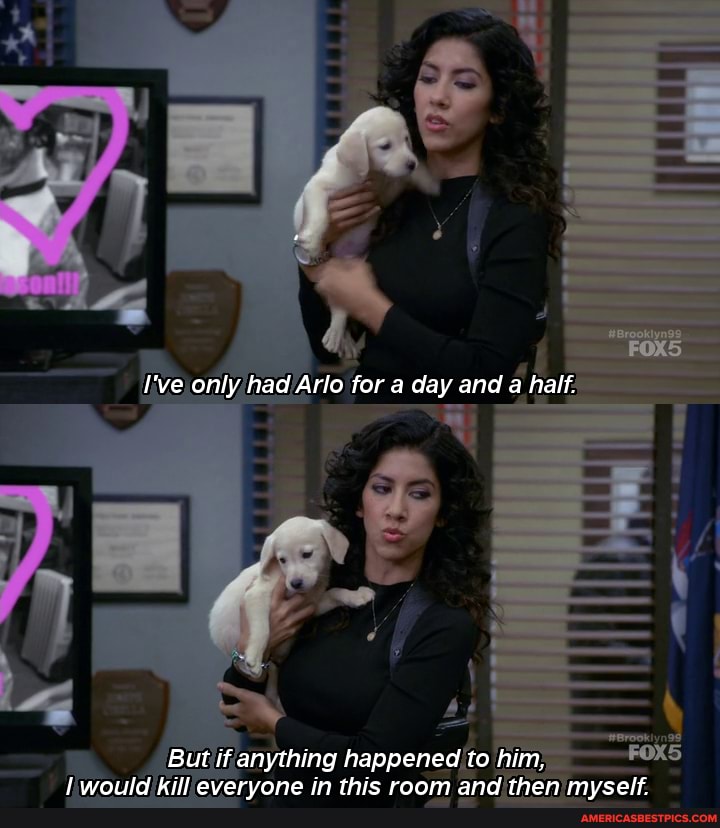
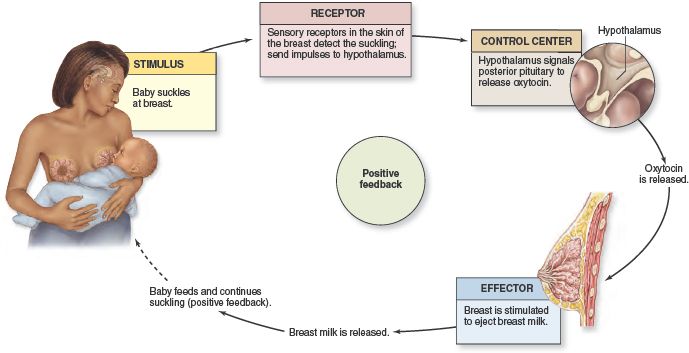
Baby only feeding 5 times a day
Guest blog: Breastfeeding: The dangerous obsession with the infant feeding interval
This guest blog from breastfeeding counsellor Emma Pickett discusses the dangers of promoting a strict feeding schedule at the expense of responsive, flexible infant feeding.
Add your voice to Unicef UK’s Change the Conversation campaign, calling on UK governments to take urgent action to protect, promote and support breastfeeding.
Somehow, somewhere, new mothers got the message that the gap between when a baby stops a breastfeed and the time they start to need another one matters a very very great deal. 24 hours a day.
It seems to matter beyond all logic and reason. They see this magic number – 90 minutes, 2 hours, 3 hours – as a measure of something sacred.
And it’s crap.
There are mums sitting at home, relaxing and nesting with their gorgeous new baby. There’s a disk from a box set in the DVD player, a cup of tea on the go, a recent chat with a friend. Breastfeeding is going well. Weight gain is fine. Baby is content. But when baby shows hunger cues after only 40 minutes instead of the hoped for 1 hr 30 minutes, their heart sinks and they feel a sense something is fundamentally wrong. They aren’t ‘doing it right’. Their friend’s baby ‘goes longer’. Doubts creep in.
As adults, we grab a cup of tea, a glass of water, a sweet, a snack. We respond to our personal cues and we’re flexible depending on time of day, the temperature, our mood, our energy levels. Many go to bed with a glass of water or sip from a bottle throughout the day. I don’t know any adults that look at their watch and say, “Only 30 minutes till my next sip of water or mint! Not long now”. But yet we expect teeny growing babies to be governed by this artificial notion of time.
Basic misconceptionsI spoke to a new mother last week who was perfectly happy with her feeding routine but wondered if she should start to stretch her baby’s intervals because ‘that’s what you do’. When I explained that it wasn’t necessarily, she said she was more than happy to go on as she was.
When I explained that it wasn’t necessarily, she said she was more than happy to go on as she was.
Where do these ideas come from? They don’t come from anyone with any breastfeeding education, nor antenatal classes with breastfeeding professionals, nor books written by those trained to support breastfeeding.
They come from popular baby care books and relatives and peers.
They seem to come from a fundamental misunderstanding of the science of breastfeeding and breastmilk production. Often they come from mid-20th century ideas based around the norms of formula-feeding and pseudo-science. And that’s all incredibly dangerous.
There are still people out there, surrounded by breastfeeding, who believe that a baby who feeds after 4 hours rather than 3 hours will ‘take more milk’. There are people who believe that you need to wait and hold a baby off to let your breasts ‘refill’. There are people who believe that when a baby does want to return to the breast after only an hour that must reflect a ‘problem’ and perhaps the mother even has a supply issue.
It’s scary and extremely frustrating that basic messages about how milk production works don’t reach the people who need them.
Searching for “normal”So what is normal? Well, how long have you got? Because there’s a lot of normal. A newborn should feed a minimum of 8-12 times in 24 hours. That means some might be going every 3 hours and others will be feeding more frequently than 2 hourly. Some babies may feed every 10 minutes every hour. Some may feed for 10 minutes every 2 hours. Some may feed for 40 minutes every 2 hours. For periods in the day, a younger baby will often cluster feed and not be happy away from the breast for any longer than a few minutes at a time. This natural cluster feeding may dominate an evening.
A very common call to the National Breastfeeding Helpline goes like this: “My baby used to sleep in the evenings and now he’s awake for 3-4 hours. The only thing that seems to settle him is the breast. I feel like I must not have enough milk as he’s on there for ages.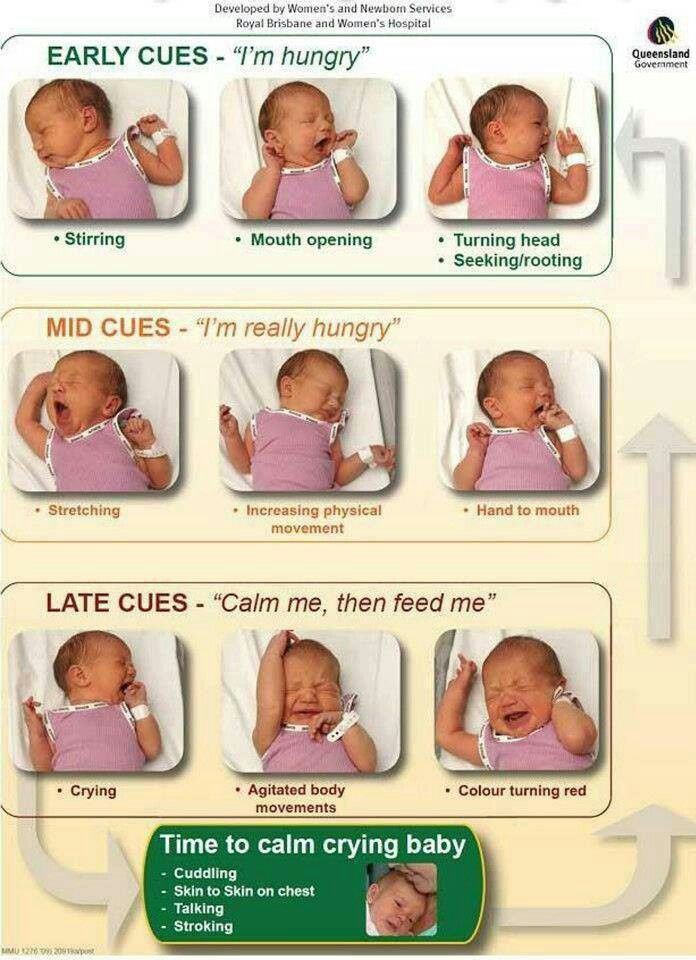 Surely there can’t be anything there.” As the baby swaps from breast to breast, getting small quantities of very high fat content milk and decompressing at the end of a long day, they know exactly what they are doing.
Surely there can’t be anything there.” As the baby swaps from breast to breast, getting small quantities of very high fat content milk and decompressing at the end of a long day, they know exactly what they are doing.
And soon their patterns will change again. Some babies will start to longer intervals in the day as the months go by. But not all will.
One of the most popular babycare books (which I better not name) gives a strong direction that while frequent feeding might be occasionally acceptable during growth spurts, this holy cow of the interval between feeds matters greatly. A 3 month old baby might be going 3 hourly intervals but if this isn’t increasing at 4 months, then oh dear. This same writer believes a woman can measure her milk supply by doing a yield test and using a pump to extract milk which apparently will be the equivalent amount to what her baby extracts during a feed using an entirely different process. What this woman doesn’t know about breastfeeding could fill an encyclopaedia.
What I find particularly dangerous about her message that longer intervals are ‘better’ and ‘correct’, is that is means new mothers doubt their milk supply with absolutely no justification. And I know from having spent time on the message boards associated with this writer, many mothers will end up supplementing with formula to try and reach these magic numbers of minutes.
Why?
Babies are no longer being exclusively breastfed and parents are not following Department of Health recommendations because of incorrect information in a baby care book.
There are parents who choose to use formula for a whole host of complex reasons. Some do so happily and some do so miserably. But to do so, merely because you have read a lie in a book, seems tragic to me.
Our knowledge about breasts has been transformed over the last 20 years. Much of the pioneering work has been done in Australia by scientists like Professor Peter Hartmann and Dr Donna Geddes, Steven Daly and their teams.
We used to think most women had a pretty similar number of milk ducts but the ultrasound research revealed there were less than previously thought and the range was big. One woman had 4 ducts at the nipple. One had 18.
But it’s the findings about breast storage capacity that we need to talk about here. When a baby feeds, some milk is manufactured during the feed itself and some is taken from milk that has been stored in the breasts between feeds.
Ultrasound revealed that a mother’s storage capacity cannot be guessed from breast size. Breast size is obviously not just about glandular tissue. The range in breast storage capacity was huge.
One mother was able to store about 2.6oz per breast. Another woman stored more than 20oz. That’s not a typo.
Women with a smaller breast storage capacity had a healthy milk production over a 24 hr period and their babies had good weight gain. But their babies might need to feed more frequently to access this healthy milk production.
Is this a mother with a supply problem?
No, it is not.
Her baby may continue to feed 2 hourly or even more frequently for a few months during the day, cluster feed at certain points and perhaps continue to wake a couple of times hungry at night. Her friend’s baby may settle into a pattern of feeding less frequently over a 24 hour period. This friend’s baby may not be receiving more milk overall.
When breasts are fuller, milk production slows. When breasts are emptier, we make more milk. When babies feed more frequently and from emptier breasts, they receive milk with a higher fat content. Frequent feeding has value. And as human milk has a fat content of around 3-5% compared to some mammals who have a fat content of 40% +, it seems pretty clear we’re designed as a species to need feeding more frequently.
But let’s imagine the mother with the smaller breast storage capacity has read this baby care book. She might become distressed that her baby still wants to feed 2 hourly. She might even try and stretch the interval between feeds in the mistaken belief this will increase her baby’s intake. And in doing so, her breasts spend longer at full storage capacity and their milk production slows and her breasts receive the signal to decrease milk supply.
She might even try and stretch the interval between feeds in the mistaken belief this will increase her baby’s intake. And in doing so, her breasts spend longer at full storage capacity and their milk production slows and her breasts receive the signal to decrease milk supply.
So in her attempt to stretch between feeds as the advice she is reading suggests she does, she may actually be decreasing her overall milk production in 24 hours and be doing some actual harm.
So what should we suggest to this mum who never seems to be able to stretch her baby to longer intervals in the ways that her friends seem able?
First off, we should congratulate her for responding to her baby’s cues. Thankfully she knew not to try and impose some routine early on and therefore her milk supply is at its maximum capacity. Let’s check breastfeeding is otherwise going well: that feeds are comfortable for her, baby does settle for periods of contentment after a feed (though it may only be an hour or even less, rather than 3), weight gain and nappies are fine and latching and positioning is at maximum efficiency.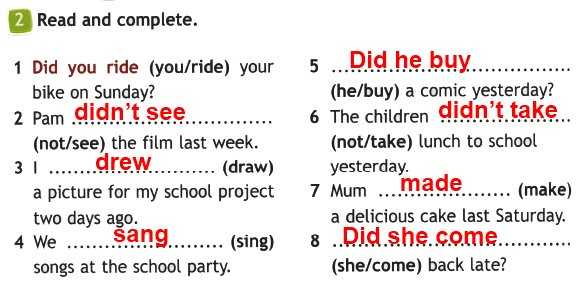 If all this is true, and never reaching a magic ‘interval’ is her only concern, then we need to make sure she knows as much as possible about how milk production works. It is possible she is one of the mothers who has a minimal breast storage capacity and she will need to feed more in 24 hours to maximise the volume of milk her baby receives. And there might be nothing she can do about that. What happens next is about acceptance and support and attitude.
If all this is true, and never reaching a magic ‘interval’ is her only concern, then we need to make sure she knows as much as possible about how milk production works. It is possible she is one of the mothers who has a minimal breast storage capacity and she will need to feed more in 24 hours to maximise the volume of milk her baby receives. And there might be nothing she can do about that. What happens next is about acceptance and support and attitude.
She has to keep that up for ideally around 6 months if her baby is going to get the full benefits of exclusive breastfeeding. She might need greater support with feeding outside the home – perhaps learning how to feed in a sling or experiment with different positions for different environments. It’s possible she may be woken at night more than her friend with the longer intervals – though we would expect night time intervals to be longer and for her to get a block of longer rest. She may benefit from support on safe bed-sharing practices.
And it is just a matter of months. After solids have been established, patterns will change. It’s surprising what we can cope with for just a few months. We have jars of pickle in our fridge significantly older than that. We may even have toothbrushes that are around that long. In terms of an adult lifetime, it’s a blink of an eye.
What won’t help these mothers is the relentless message that they just need to stretch their baby a little more. That if they leave him to cry for 15 minutes, magically he will take more milk and life will change. That just isn’t what science tells us is true for all women.
Responsive feeding: So much more than milkOf course breastfeeding isn’t just about milk anyway. Apparently there are people who think that a baby comes to a breast primarily to get milk but I’ve not met a parent of a baby who thinks that’s true. Just as we don’t measure our sips of water, sweets and snacks, we also don’t measure every time our family smiles warmly at us, communicates with us, looks for comfort, hugs us, checks in, helps us to feel safe. No smart phone app can measure all the complexities of our relationship with our baby and all the things that responsive feeding can do. You are trying to count and measure love.
No smart phone app can measure all the complexities of our relationship with our baby and all the things that responsive feeding can do. You are trying to count and measure love.
And I’m talking about myself here, by the way. My children under 6 months never went longer than 2 hours between feeds in the day and not much longer at night. My red record book records me feeding at 3 months every 90 minutes or so. So I learnt to feed while babywearing. I went to friendly groups and friendly places and met up with people at home. I read about safe co-sleeping practices which I know beyond a shadow of a doubt saved my bacon. And thankfully, I never felt anything was ‘wrong’. I just trusted my body. I trusted my baby and we worked as a beautiful team. I sat at home on the sofa and fed relatively frequently, enjoyed my box sets and my healthy and not-so-healthy snacks and that was OK.
It really wasn’t for long. But the benefits of exclusive breastfeeding will be.
Why should a watch or clock tell me how to be a mother? I’d rather pay attention to my baby.
Sources
- Anatomy of the lactating human breast redefined with ultrasound imaging. DT Ramsay, JC Kent, RA Hartmann, and PE Hartman. 2005.
- The magic number and long-term milk production. Nancy Mohrbacher IBCLC
- Studies on Human Lactation: Development of the computerized breast measurement system. D.B Cox, R.A Owens, Peter E. Hartmann
Breastfeeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Breastfeeding is a natural thing to do, but it still comes with its fair share of questions. Here's what you need to know about how often and how long to breastfeed your baby.
How Often Should I Breastfeed?
Newborn babies should breastfeed 8–12 times per day for about the first month. Breast milk is easily digested, so newborns are hungry often. Frequent feedings helps stimulate your milk production during the first few weeks.
By the time your baby is 1–2 months old, he or she probably will nurse 7–9 times a day.
In the first few weeks of life, breastfeeding should be "on demand" (when your baby is hungry), which is about every 1-1/2 to 3 hours. As newborns get older, they'll nurse less often, and may have a more predictable schedule. Some might feed every 90 minutes, whereas others might go 2–3 hours between feedings.
Newborns should not go more than about 4 hours without feeding, even overnight.
How Do I Count the Time Between Feedings?
Count the length of time between feedings from the time your baby begins to nurse (rather than at the end) to when your little one starts nursing again. In other words, when your doctor asks how often your baby is feeding, you can say "about every 2 hours" if your first feeding started at 6 a.m., the next feeding was around 8 a.m., then 10 a.m., and so on.
Especially at first, you might feel like you're nursing around the clock, which is normal. Soon enough, your baby will go longer between feedings.
How Long Does Nursing Take?
Newborns may nurse for up to 20 minutes or longer on one or both breasts. As babies get older and more skilled at breastfeeding, they may take about 5–10 minutes on each side.
As babies get older and more skilled at breastfeeding, they may take about 5–10 minutes on each side.
How long it takes to breastfeed depends on you, your baby, and other things, such as whether:
- your milk supply has come in (this usually happens 2–5 days after birth)
- your let-down reflex (which causes milk to flow from the nipple) happens right away or after a few minutes into a feeding
- your milk flow is slow or fast
- the baby has a good latch, taking in as much as possible of your areola (the dark circle of skin around your nipple)
- your baby begins gulping right away or takes it slow
- your baby is sleepy or distracted
Call your doctor if you're worried that your baby's feedings seem too short or too long.
When Should I Alternate Breasts?
Alternate breasts and try to give each one the same amount of nursing time throughout the day. This helps to keep up your milk supply in both breasts and prevents painful engorgement (when your breasts overfill with milk).
You may switch breasts in the middle of each feeding and then alternate which breast you offer first for each feeding. Can't remember where your baby last nursed? It can help to attach a reminder — like a safety pin or small ribbon — to your bra strap so you'll know which breast your baby last nursed on. Then, start with that breast at the next feeding. Or, keep a notebook handy or use a breastfeeding app to keep track of how your baby feeds.
Your baby may like switching breasts at each feeding or prefer to nurse just on one side. If so, then offer the other breast at the next feeding. Do whatever works best and is the most comfortable for you and your baby.
How Often Should I Burp My Baby During Feedings?
After your baby finishes on one side, try burping before switching breasts. Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Some infants need more burping, others less, and it can vary from feeding to feeding.
If your baby spits up a lot, try burping more often. While it's normal for infants to "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, a baby should not vomit after feeding. If your baby throws up all or most of a feeding, there could be a problem that needs medical care. If you're worried that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
While it's normal for infants to "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, a baby should not vomit after feeding. If your baby throws up all or most of a feeding, there could be a problem that needs medical care. If you're worried that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
Why Is My Baby Hungrier Than Usual?
When babies go through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt), they want to eat more than usual. These can happen at any time. But in the early months, growth spurts often happen when a baby is:
- 7–14 days old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
During these times and whenever your baby seems extra hungry, follow your little one's hunger cues. You may need to breastfeed more often for a while.
How Long Should I Breastfeed My Baby?
Experts recommend that babies be breastfed exclusively (without formula, water, juice, non–breast milk, or food) for the first 6 months. Then, they recommend continuing to breastfeed for 2 years (and beyond) if it works for you and your baby. Any length of time your baby can be breastfed is beneficial.
Any length of time your baby can be breastfed is beneficial.
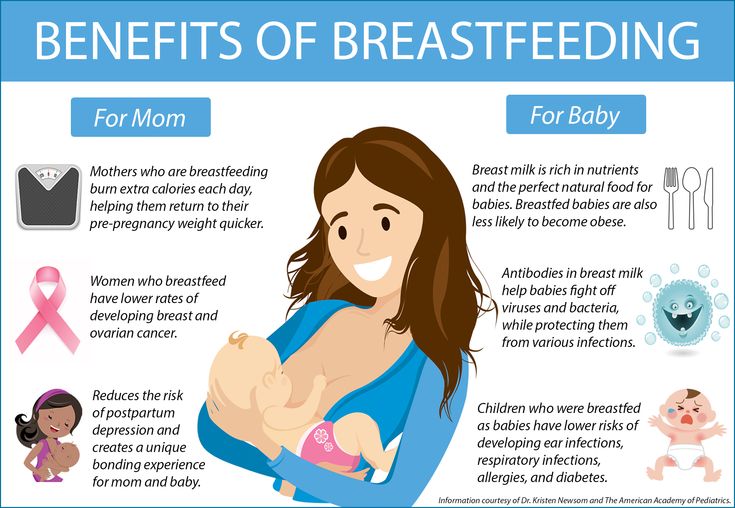
Breastfeeding has many benefits for mom and baby both. Studies show that it can lessen a baby's chances of diarrhea, ear infections, and bacterial meningitis, or make symptoms less severe. Breastfeeding also may protect children from sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), diabetes, obesity, and asthma.
For moms, breastfeeding burns calories and helps shrink the uterus. In fact, breastfeeding moms might return to their pre–pregnancy shape and weight quicker. Breastfeeding also helps lower a woman's risk of diseases like:
- breast cancer
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
- heart disease
It also might help protect moms from uterine cancer and ovarian cancer.
Reviewed by: Kristen Littleton, IBCLC and Jamila H. Richardson, BSN, RN, IBCLC
Date reviewed: November 2019
4. Diet:
6 hours - "NAN" 200 ml
10 hours - cereal porridge with fruits 200 ml
14 hours - "NAN" 200 ML
18 hours - vegetable puree 200 ml 22 hours - "NAH" 200 ml.
Additionally during the day up to 60 ml of fruit juice between feedings.
TASK 6
Child 5.5 months. The mother went to the doctor for feeding recommendations. Child receives breast milk up to 750-800 ml per day, vegetable puree, fruit puree, yolk. Feeds 6 times a day maintains 4-hour intervals between feedings. Weight 7400 g, height 66 cm (weight at birth 3100 g, height 51 cm).
1. Rational is the child fed? Give advice,
2. Does the mother have enough milk?
3. Estimate the child's weight and height,
4. Calculate daily and one-time volumes feeding, give recommendations on the regimen feeding,
5. Indicate the need for basic food ingredients and energy.
6. Make a diet for 1 day.
REFERENCE 6
1. Generally rational, but follows transfer the child to 5 meals a day with an interval between feedings of 4 hours.
Generally rational, but follows transfer the child to 5 meals a day with an interval between feedings of 4 hours.
2. Mother's milk is sufficient, it follows calculated (see below)
3. Due Height: 51 + (3X3) + (2.5X 2) + 1 = 66 cm;
due mass: 3100 + (800 X 5) + 400 = 7500 g
Weight and growth correspond age.
4. Daily volume nutrition - 1 liter, 7.5 x 115 kcal x 1000 ml: 700 kcal = 1230 ml. Feeding regimen: 5 times a day through 4 hours for 200 ml. One breastfeed mothers is replaced by complementary foods - vegetable puree, therefore, it is necessary 800 ml breast milk per day.
5. The need for basic food ingredients in g/kg masses body and energy per day: protein - 2.6; fat -6.0; carbohydrates - 13.0; kcal - 115.
6. Diet:
6 hours - breast milk 200 ml;
10 hours - vegetable puree 200 ml yolk 1/4 pc, rast. oil 3.0 g;
oil 3.0 g;
14 hours - breast milk 200 ml;
18 hours - breast milk 150 ml, apple puree 50 g;
22 hours - breast milk 200 ml
Between feeds to give Fruity juice (mashed) to 50 ml per day.
TASK 7
Child 6 months. Skin pink, velvety, tu r g op soft tissue is good. Withstands 4-hour intervals between feedings. Feeds 5 times: 4 times breastfeeding mother and 1 once receives complementary foods with vegetable puree.
1. Calculate the required mass and the growth of the child, considering the fact that with birth weight 3100 g, height 50 cm.
2. Provide recommendations for future child nutrition.
3. What are the daily and single meals most appropriate for this child? Is the feeding schedule correct?
4.
 Indicate the need for basic food ingredients and energy.
Indicate the need for basic food ingredients and energy. 5. Make a diet for 1 day.
REFERENCE 7
1. Due Growth: 50 + (3X3) + (2.5X 3) = 66.5 cm
due mass: 3100 + (800 X 5) = 7900g
2. The introduction of the 2nd complementary food in the form of rice porridge, cottage cheese, child can receive Fruit puree, yolk.
3. The feeding schedule is correct. Daily volume - 1000 ml, single - 200 ml.
4. The need for basic food ingredients in g/kg masses body and energy per day: squirrels - 2.9; fats -5.5; carbohydrates - 13.0; kcal - 110.
5. Diet:
6 hours - breast milk 200 ml
10 hours - 5% rice porridge 30 ml (bring to 200 ml per week) + breast milk 170 ml
14 hours - breast milk 150 ml + apple puree 50 g
18 hours - vegetable puree 200 ml + vegetable oil 5.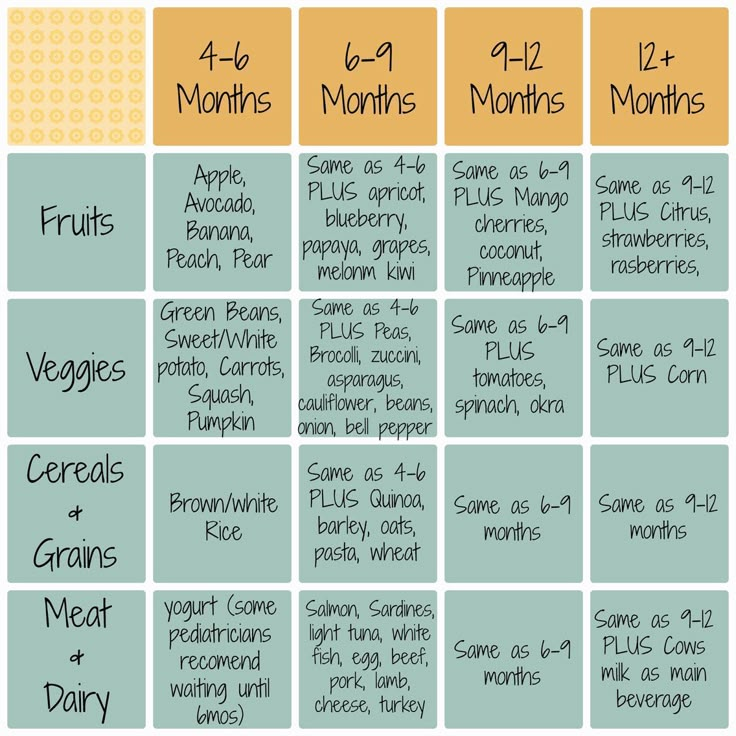 0 g + yolk (start with 1/4 and work up to 1/2)
0 g + yolk (start with 1/4 and work up to 1/2)
22 hours - breast milk 200 ml
Between feeds to give Fruit (vegetable) juices (puree) up to 60 ml per day.
TASK 8
Child 7 months. Feeds 5 times a day, daily receives breast milk 550-600 ml, vegetable puree 150-200g 1 time, fruit puree 50 g, rice porridge 150-200 ml 1 time, meat broth 150 ml 1 time, yolk 1 pc.
Mother consulted a doctor for advice on child nutrition. Child weight 8600 g, height 69cm (weight at birth 3200 g, height 51 cm).
1. Assess the child's weight and height.
2. Specify daily and one-time volumes feeding, feeding schedule.
3. Is the mother rationally feeding the child? Does the mother have enough milk? Give recommendations.
4. Indicate the daily need for basic facial ingredients and energy.
5. Make a diet for 1 day.
REFERENCE 8
1. Due Growth: 51 + (3 X 3) + (2.5 X 2) + 1.5 = 69 cm
due weight: 3200 + (800 X 6) + 400 = 8400 g
Weight and height is age appropriate.
2. daily volume 1000 ml, single - 200 ml, feed after 4 hours 5 times a day.
3. milk mothers enough as 2 feeds will get mixed up food dishes. Irrational is the excess of meat broth and egg yolk. Recommended at 7 months up to 20 ml of meat broth and 1/2 yolk. It is also recommended to introduce meat puree from beef - start with 5 g, bring to 30 g and alternating cereals: rice, oat, buckwheat.
4. The need for basic food ingredients in g/kg of body weight and energy per day: proteins - 2.9; fats -5.5; carbohydrates - 13.0; kcal - 110.
Sitemap
State autonomous professional
educational institution
Republic of Bashkortostan
Salavat Medical College
453261 Republic of Bashkortostan
Salavat, st. Furmanova, 4
Furmanova, 4
Phone/fax: (3476)-38-78-83
e-mail: [email protected]
- College information
- Basic information
- Structure and governing bodies of the college
- Documents
- Education
- Educational standards and requirements
- Manual. Teaching staff
- Logistics and equipment of the educational process
- Scholarships and other types of financial support
- Paid educational services
- Financial and business activities
- Number of students
- Vacancies for reception (transfer)
- Personal data processing
- Anti-corruption
- Legal framework for combating extremism and terrorism
- Vacancies
- Information security
- Olympics
- Mentoring
- Accessible environment
- International cooperation
- Employment of graduates
- Applicant
- Applicant
- Control figures for the reception of citizens
- Admission Rules
- Individual Achievement Regulations
- Local regulations
- List of specialties
- Document acceptance schedule
- Terms of admission under contracts for the provision of paid educational services
- Information on the need for applicants to undergo a mandatory preliminary medical examination (examination)
- Approximate tests of entrance examinations
- Features of conducting entrance examinations for disabled people and persons with disabilities
- Information about the possibility of filing documents by mail
- Submission of documents by e-mail
- List and deadlines for submission of documents
- Information on the availability of a hostel and the number of places in hostels allocated for nonresident applicants
- Enrollment Orders
- Number of applications submitted
- Filing and reviewing appeals
- College Application
- Citizens' appeal on admission issues
- Targeted training
- Consent to the processing of personal data
- Entrance examinations
- Rating of applicants
- student
- Fundamentals
- Regulations
- Culture and sports
- Dormitory
- Student Council
- Life safety
- Teaching materials
- Graduate Accreditation
- Page of educational psychologist
- Student Union
- Scholarship of the Head of the Republic of Bashkortostan
- teacher
- Reference
- Educational and methodical work
- Additional education
- Republican information and training pedagogical seminars
- Competitions and olympiads
- Contacts
- Hotline
- Feedback
- Contacts of controlling organizations
This page does not exist.