Baby projectile spit up after feeding
Pyloric Stenosis (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
What Is Pyloric Stenosis?
Pyloric stenosis is a condition that can affect the gastrointestinal tract in babies. It can make a baby vomit forcefully and often, and can lead to other problems, such as dehydration. Pyloric stenosis needs medical care right away.
What Happens in Pyloric Stenosis?
Food and other stomach contents pass through the pylorus, the lower part of the stomach, to enter the small intestine. Pyloric stenosis (pie-LOR-ik stih-NOE-sis) is a narrowing of the pylorus. When a baby has pyloric stenosis, this narrowing of the pyloric channel prevents food from emptying out of the stomach.
Pyloric stenosis (also called infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis) is a type of gastric outlet obstruction, which means a blockage from the stomach to the intestines.
Pyloric stenosis affects about 3 out of 1,000 babies in the United States. It's more likely to affect firstborn male infants and also runs in families — if a parent had pyloric stenosis, then a baby has up to a 20% risk of developing it. Most infants who have it develop symptoms 3 to 5 weeks after birth.
What Causes Pyloric Stenosis?
It's thought that babies who develop pyloric stenosis are not born with it, but have progressive thickening of the pylorus after birth. A baby will start to show symptoms when the pylorus is so thick that the stomach can't empty properly.
The cause of this thickening isn't clear. It might be a combination of several things. For example, use of erythromycin (an antibiotic) in babies in the first 2 weeks of life or antibiotics given to moms at the end of pregnancy or during breastfeeding can be associated with pyloric stenosis.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Pyloric Stenosis?
Symptoms of pyloric stenosis typically begin when a baby is around 3 weeks old. They include:
- Vomiting.
 The first symptom is usually vomiting. At first it may seem that the baby is just spitting up often, but then it tends to become projectile vomiting, in which the breast milk or formula is ejected forcefully from the mouth, in an arc, sometimes over a distance of several feet. Projectile vomiting usually takes place soon after the end of a feeding, although in some cases it can happen hours later.
The first symptom is usually vomiting. At first it may seem that the baby is just spitting up often, but then it tends to become projectile vomiting, in which the breast milk or formula is ejected forcefully from the mouth, in an arc, sometimes over a distance of several feet. Projectile vomiting usually takes place soon after the end of a feeding, although in some cases it can happen hours later.The vomited milk might smell curdled because it has mixed with stomach acid. The vomit will not contain bile, a greenish fluid from the liver that mixes with digested food after it leaves the stomach.
Despite vomiting, a baby with pyloric stenosis is usually hungry again soon after vomiting and will want to eat. It's important to know that even with the vomiting, the baby might not seem to be in great pain or at first look very ill.
- Changes in stools. Babies with pyloric stenosis usually have fewer, smaller stools (poops) because little or no food is reaching the intestines.
 Constipation or poop with mucus also can happen.
Constipation or poop with mucus also can happen. - Failure to gain weight or weight loss. Most babies with pyloric stenosis will fail to gain weight or will lose weight. As the condition gets worse, they might become dehydrated.
Dehydrated infants are less active than usual, and they may develop a sunken "soft spot" on their heads and sunken eyes, and their skin may look wrinkled. Because less pee is made, they can go more than 4 to 6 hours between wet diapers.
- Waves of peristalsis. After feeds, increased stomach contractions may make noticeable ripples, which move from left to right over the baby's belly as the stomach tries to empty itself against the thickened pylorus.
It's important to call your doctor if your baby has any of these symptoms.
Other conditions can cause similar problems. For instance:
- gastroesophageal reflux (GER) usually begins before 8 weeks of age. GER involves lots of spitting up (reflux) after feedings, which can look like vomiting.
 But most babies with GER don't have projectile vomiting, and while they might have trouble gaining weight, they usually have normal poops.
But most babies with GER don't have projectile vomiting, and while they might have trouble gaining weight, they usually have normal poops. - a milk protein allergy also can make a baby spit up or vomit, and have diarrhea. But these babies don't have projectile vomiting.
- gastroenteritis (inflammation in the digestive tract that can be caused by viral or bacterial infection) also can cause vomiting and dehydration. But babies with gastroenteritis usually also have diarrhea with loose, watery, or sometimes bloody stools. Diarrhea usually isn't seen with pyloric stenosis.
How Is Pyloric Stenosis Diagnosed?
The doctor will ask detailed questions about the baby's feeding and vomiting patterns, including what the vomit looks like. The doctor will do an exam, and note any weight loss or failure to maintain growth since birth.
The doctor will check for a lump in the abdomen. If the doctor feels this lump, which usually is firm and movable and feels like an olive, it's a strong indication that a baby has pyloric stenosis.
If pyloric stenosis seems likely, the doctor probably will order an abdominal ultrasound. The enlarged, thickened pylorus will show on ultrasound images. The doctor may ask that the baby not be fed for several hours before an ultrasound.
Sometimes doctors order a barium swallow instead of an ultrasound. Babies swallow a small amount of a chalky liquid (barium). Then, special X-rays are done that let the doctor check the pyloric area for any narrowing or blockage.
The doctor also might order blood tests to check levels of electrolytes (minerals that help keep fluids balanced and vital organs working properly). An electrolyte imbalance often happens due to the ongoing vomiting of stomach acid and dehydration, and needs to be corrected.
How Is Pyloric Stenosis Treated?
When an infant is diagnosed with pyloric stenosis, either by ultrasound or barium swallow, the baby will be admitted to the hospital and prepared for surgery. Any dehydration or electrolyte problems in the blood will be corrected with intravenous (IV) fluids, usually within 24 hours.
Doctors do a surgery called pyloromyotomy (pie-lor-oh-my-OT-uh-me) to relieve the blockage. Using a small incision (cut), the surgeon examines the pylorus and separates and spreads the thick, tight muscles. This relaxes and opens those muscles.
The surgery can also be done through laparoscopy. This technique uses a tiny scope placed through a small cut in the belly button, letting the doctor see the area of the pylorus. Using other small instruments placed in nearby incisions, the doctor can complete the surgery.
Most babies return to normal feedings fairly quickly, usually 3 to 4 hours after the surgery. Because of swelling at the surgery site, a baby may still vomit small amounts for a day or so. If there are no complications, most babies who have had pyloromyotomy can return to a normal feeding schedule and go home within 24 to 48 hours of the surgery.
If you're breastfeeding, you might worry about continuing while your baby is hospitalized. The hospital staff should be able to provide a breast pump and help you use it so that you can continue to express milk until your baby can feed regularly.
The hospital staff should be able to provide a breast pump and help you use it so that you can continue to express milk until your baby can feed regularly.
After a successful pyloromyotomy, your baby won't need to follow any special feeding schedules. Your doctor will probably want to examine your child at a follow-up appointment to make sure the surgical site is healing properly and that your baby is feeding well and maintaining or gaining weight.
Pyloric stenosis should not happen again after a pyloromyotomy. If your baby still has symptoms weeks after the surgery, there might be another medical problem, such as gastritis or GER, so let your doctor know right away.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Pyloric stenosis is an urgent condition that needs immediate treatment. Call your doctor if your baby:
- has lasting or projectile vomiting after feeding
- is losing weight or not gaining weight as expected
- is less active than usual or is very sleepy
- has few or no stools (poops) over a period of 1 or 2 days
- show signs of dehydration, such as more than 4 to 6 hours between wet diapers, a sunken "soft spot" on the head, or sunken eyes
Spitting Up - Reflux
Is this your child's symptom?
- Spitting up small amounts of breastmilk or formula.
 Also called reflux.
Also called reflux. - Spitting up 1 or 2 mouthfuls of milk at a time
- No effort or crying
- Normal symptom in half of young babies
Symptoms of Normal Spitting Up
- Smaller amounts often occur with burping ("wet burps")
- Larger amounts can occur after overfeeding
- Most often seen during or shortly after feedings
- Occurs mainly in children under 1 year of age
- Begins in the first weeks of life
- Caution: normal reflux does not cause any crying
Complications of Spitting Up (GERD)
- Most infants are "happy spitters." Normal spitting up (normal reflux) occurs in half of babies. It does not cause crying or colic.
- Normal crying occurs in all babies. Frequent crying (called colic) occurs in 15% of babies. Crying and colic are not helped by heartburn meds. These meds also have side effects.
- If they develop complications, it's called GERD (gastro-esophageal reflux disease). This occurs in less than 1% of babies.

Symptoms of GERD
GERD problems occur in less than 1% of infants:
- Choking on spit up milk
- Heartburn from acid on lower esophagus. Infants with this problem cry numerous times per day. They also act very unhappy when they are not crying. They are in almost constant discomfort.
- Poor Weight Gain
Cause
- Poor closure of the valve at the upper end of the stomach (weak valve)
- Main trigger: overfeeding of formula or breastmilk
- More than half of all infants have occasional spitting up ("happy spitters")
Reflux Versus Vomiting: How to Tell
- During the first month of life, newborns with true vomiting need to be seen quickly. The causes of vomiting in this age group can be serious. Therefore, it's important to tell the difference between reflux and true vomiting.
Reflux
The following suggests reflux (normal spitting up):
- You've been told by a doctor your baby has reflux
- Onset early in life (85% by 7 days of life)
- Present for several days or weeks
- No pain or crying during reflux
- No effort with spitting up
- No diarrhea
- Your baby acts hungry, looks well and acts happy.
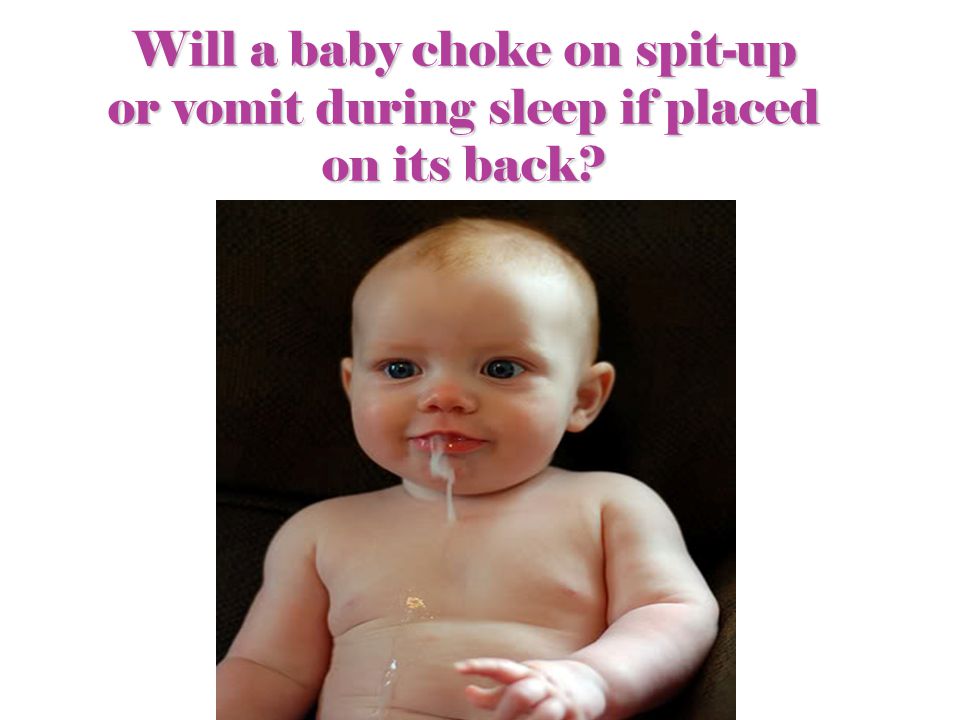
Vomiting
The following suggests vomiting:
- Uncomfortable during vomiting
- New symptom starting today or yesterday
- Forceful vomiting
- Contains bile (green color)
- Diarrhea is also present or
- Your baby looks or acts sick.
Pyloric Stenosis (Serious Cause)
- This is the most common cause of true vomiting in young babies.
- Onset of vomiting age 2 weeks to 2 months
- Vomiting is forceful. It shoots out of the baby's mouth. This is called projectile vomiting.
- Right after vomiting, the baby is hungry and wants to feed. ("hungry vomiter")
- Cause: the pylorus is the channel between the stomach and the gut. In these babies, it becomes narrow and tight.
- Risk: weight loss or dehydration
- Treatment: cured by surgery.
When to Call for Spitting Up - Reflux
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Blood in the spit up
- Choked on milk and turned blue or went limp
- Age less than 12 weeks and spitting up changes to vomiting (forceful or projectile)
- Age less than 1 month old and looks or acts abnormal in any way
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- You think your child needs to be seen, but the problem is not urgent
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- Chokes a lot on milk
- Poor weight gain
- Frequent crying
- Spitting up is getting worse
- Age more than 12 months old
- Spitting up does not get better with this advice
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home
- Normal reflux (spitting up) with no problems
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
Care Advice for Spitting Up (Reflux)
- What You Should Know About Spitting Up:
- Spitting up occurs in most infants (50%).
- Almost always doesn't cause any pain or crying.
- Spitting up does not interfere with normal weight gain.
- Infants with normal reflux do not need any tests or medicines.
- Reflux improves with age.
- Here is some care advice that should help.

- Feed Smaller Amounts:
- Skip this advice if age less than 1 month or not gaining weight well.
- Bottlefed Babies. Give smaller amounts per feeding (1 ounce or 30 mL less than you have been). Keep the total feeding time to less than 20 minutes. Reason: Overfeeding or completely filling the stomach always makes spitting up worse.
- Breastfed Babies. If you have a good milk supply, try nursing on 1 side per feeding. Pump the other side. Switch sides you start on at each feeding.
- Longer Time Between Feedings:
- Formula. Wait at least 2½ hours between feedings.
- Breastmilk. Wait at least 2 hours between feedings.
- Reason: It takes that long for the stomach to empty itself. Don't add more milk to a full stomach.
- Loose Diapers:
- Do not put the diaper on too tight. It puts added pressure on the stomach.

- Don't put pressure on the stomach right after meals.
- Also, do not play too hard with your baby during this time.
- Do not put the diaper on too tight. It puts added pressure on the stomach.
- Upright Position:
- After meals, try to hold your baby in the upright (vertical) position.
- Use a front-pack, backpack, or swing for 30 to 60 minutes after feedings.
- Decrease the time in a sitting position (such as infant seats).
- After 6 months of age, a jumpy seat is helpful. The newer ones are stable.
- During breast or bottle feeds, hold your baby at a slant. Try to keep your baby's head higher than the stomach.
- Less Pacifier Time:
- Frequent sucking on a pacifier can pump the stomach up with swallowed air.
- So can sucking on a bottle with too small a nipple hole.
- The formula should drip 1 drop per second when held upside down. If it doesn't, the nipple hole may be clogged. Clean the nipple better. You can also make the nipple hole slightly bigger.

- Burping:
- Burping is less important than giving smaller feedings. You can burp your baby 2 or 3 times during each feeding.
- Do it when he pauses and looks around. Don't interrupt his feeding rhythm in order to burp him.
- Burp each time for less than a minute. Stop even if no burp occurs. Some babies don't need to burp.
- Add Rice Cereal to Formula:
- If your baby still spits up large amounts, try thickening the formula. Mix it with rice cereal.
- Start with 1 level teaspoon of rice cereal to each ounce of formula.
- Acid Blocking Medicines:
- Prescription medicines that block acid production are not helpful for normal reflux.
- These medicines also can have side effects.
- They do not reduce excessive crying from colic.
- They are only useful for symptoms of heartburn.
- What to Expect:
- Reflux gets better with age.
- After learning to sit well, many babies are better by 7 months of age.
- Reflux gets better with age.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Spitting up changes to vomiting (forceful or projectile)
- Poor weight gain
- Your baby does not get better with this advice
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 12/09/2022
Last Revised: 01/13/2022
Copyright 2000-2022. Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Why does the baby spit up after feeding?
search support iconSearch Keywords
Regurgitation is a common condition in newborns and infants and is most often a normal variant. However, it is not uncommon for parents to worry if their baby is spitting up frequently, believing that it is due to nutritional or health problems in general. Sometimes these fears are not unfounded, and regurgitation really has a pathological origin. What is its cause and when should you really consult a doctor about this?
Sometimes these fears are not unfounded, and regurgitation really has a pathological origin. What is its cause and when should you really consult a doctor about this?
Regurgitation - Return of a small amount of food (uncurdled or partially curdled milk) from the stomach up the digestive tract: into the esophagus and further into the oral cavity. According to statistics, at least 1 time during the day, at least 50% of babies from 0 to 3 months old can spit up, more than 60% of children 3-4 months old, and in 5% of children spit up continues up to the year 1 .
Regurgitation in newborns is considered a physiological process. It is caused by a number of factors, including:
- Features of the structure of the upper digestive tract in babies
- In newborns and infants up to a year of life, the stomach has a spherical shape. It holds a small amount of food, besides, the release from it into the duodenum is slower in comparison with children after the year 2 .

- Weakness of the lower esophageal sphincter that separates the esophagus from the stomach
- Normally, the lower esophageal sphincter should tightly "close" the esophagus, allowing food to pass into the stomach and not allowing it to enter back into the upper digestive tract. However, in young children (up to a year), the muscles of the esophageal sphincter are poorly developed, and it does not do its job very well 2 .
- Slow movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract
- The neuromuscular system of newborns is immature. It does not ensure the proper movement of food through the esophagus, causing regurgitation.
One of the important risk factors contributing to regurgitation in newborns is aerophagia. This is the swallowing of large amounts of air during feedings. This happens when the baby is not properly attached to the breast, the mother has a lack of breast milk, or the bottle is in the wrong position in the child who receives the mixture. The size of the opening in the nipple also matters - if it is too large, the newborn swallows a lot of air 3 .
The size of the opening in the nipple also matters - if it is too large, the newborn swallows a lot of air 3 .
With aerophagia, the baby becomes capricious, restless immediately after feeding. Noticeable bloating. If the baby spits up immediately after a feed, the milk (or formula) remains practically fresh, uncurdled 3 .
Promotes regurgitation after feeding and a predominantly horizontal position of the baby during the day, combined with relatively high intra-abdominal pressure 4 . Therefore, the correct position of the baby after feeding is so important. To avoid regurgitation of an excessive amount of stomach contents, after feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in an upright “column” position for some time (10-20 minutes), lightly patting on the back and allowing excess air to “exit”.
Regurgitation in many newborns can be provoked by other situations in which pressure in the abdominal cavity increases and stomach contents are thrown into the esophagus, in particular 3 :
- tight swaddling;
- stool disorders, in particular constipation;
- long, forced cry and some others.
Want to avoid common feeding problems?
Start with a baby bottle with an anti-colic system that helps you avoid common feeding problems such as colic, gas and spitting up*
How can you tell the difference between normal spitting up and vomiting?
Sometimes regurgitation is considered a manifestation of disorders in the digestive tract of children. Due to the constant reflux of acidic stomach contents into the upper sections, inflammation and other complications may develop, including growth retardation, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and others. Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
If the mother is worried that her baby is spitting up, keep track of when this happens and count the total number of spit ups per day. Normally, regurgitation usually occurs after eating (the child burps after each feeding), lasts no more than 20 seconds and repeats no more than 20-30 times a day.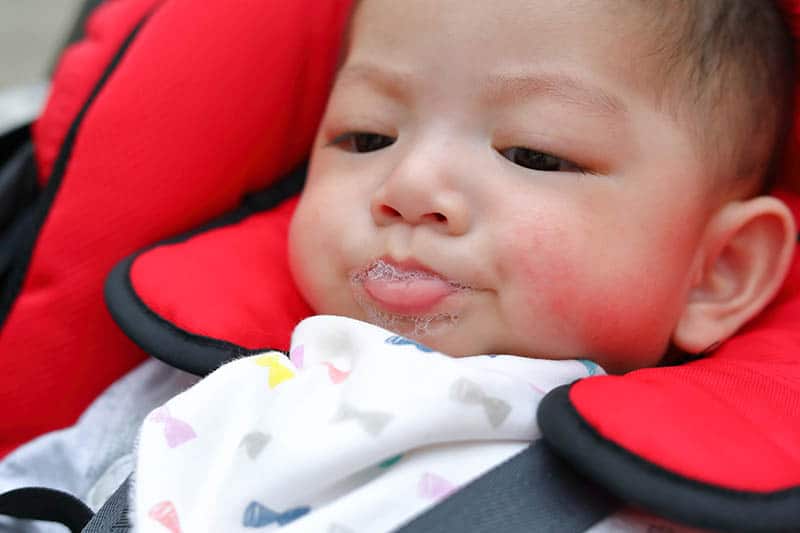 With pathology, the problem manifests itself at any time of the day, regardless of when the baby was fed. Their number can reach 50 per day, and sometimes more 1 .
With pathology, the problem manifests itself at any time of the day, regardless of when the baby was fed. Their number can reach 50 per day, and sometimes more 1 .
The amount of discharge during regurgitation also matters. With normal, physiological regurgitation, it is approximately 5 - 30 ml. If this volume fluctuates between 50 and 100 ml, it is already defined as profuse vomiting. When the range of the jet of vomit is up to 50 cm, doctors talk about "vomiting a fountain." A variant of atonic vomiting is possible, when the contents of the stomach flow "sluggishly". It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
Vomiting in babies is a warning sign. Doctors are especially alarmed by repeated vomiting, a fountain, with an admixture of bile, in combination with constipation. Vomiting can lead to the development of dehydration, acid-base imbalance and other consequences, therefore, if it occurs, you should urgently contact a pediatrician to find out the cause and begin treatment. A doctor's consultation is necessary if the child is spitting up a lot (more than 15-30 ml at a time), with a frequency of more than 50 episodes per day 1.3 .
A doctor's consultation is necessary if the child is spitting up a lot (more than 15-30 ml at a time), with a frequency of more than 50 episodes per day 1.3 .
Physiological regurgitation: symptoms
Regurgitation in newborns, which is considered a normal variant and does not cause concern to pediatricians 3 :
- usually continues for a certain period of time;
- is characterized by slow, "passive" leakage; if the baby spits up a fountain, it is better to consult a doctor;
- has a sour smell of curdled milk;
- occurs without the participation of muscles - the baby does not strain during regurgitation;
- does not affect the general well-being of the baby.
How to help a newborn who spit up often?
If the baby is healthy, no medication is prescribed for spitting up. To help the child allow simple measures based on lifestyle changes and feeding.
- Frequent feeding of the baby
It is known that the baby is more prone to spit up if his stomach is full. To improve the situation, it is recommended to feed the baby more often, avoiding oversaturation, best of all - on demand 5 .
To improve the situation, it is recommended to feed the baby more often, avoiding oversaturation, best of all - on demand 5 .
- Correct feeding technique
Every feeding, the mother must ensure that the baby does not swallow too much air during suckling. When sucking, there should be no loud, smacking, clicking sounds. You also need to control that the baby captures the nipple along with the areola.
- Choosing the right bottle and nipple
If the newborn is bottle-fed and receiving formula, it is important to choose the right bottle and nipple. The hole in it should be such that the milk flows out in drops, and not in a stream. The nipple must not be filled with airNew Anti-colic bottle with AirFree valve
The AirFree valve prevents air from entering the baby's stomach.
- Baby standing upright after eating
To allow air that has entered the digestive tract during meals to escape, it is important to keep the newborn upright for 10-20 minutes after feeding 4 .

- Ensure the correct position of the baby during sleep
To reduce the negative impact of the acidic contents of the stomach on the esophagus, it is necessary to put the baby to sleep in the supine position. The side or prone position, which many pediatricians used to recommend, is no longer recommended. It was found to be associated with an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome 5 .
If parents notice alarming symptoms, such as spitting up too often or large volume, etc., it is important to consult a pediatrician without delay. This will allow you to identify the real problem in time and help the baby grow up healthy and happy.
References1 Zakharova I. N., Andryukhina E. N. Regurgitation and vomiting syndrome in young children // Pediatric pharmacology, 2010. V. 7. No. 4.
Nagornaya 2900 V., Limarenko M. P., Logvinenko N. G. Experience with the use of domperidone in suspension in young children with regurgitation syndrome // Child Health, 2013.
 No. 5 (48).
No. 5 (48). 3 Zakharova IN Regurgitation and vomiting in children: what to do? //Pediatrics. Supplement to Consilium Medicum, 2009. No. 3. S. 58-67.
4 Zakharova I. N., Sugyan N. G., Pykov M. I. Regurgitation syndrome in young children: diagnosis and correction // Effective pharmacotherapy, 2014. No. 3. P. 18-28.
5 Vandenplas Y. et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) //Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition. 2009; 49(4): 498-547.
You are leaving the Philips Healthcare (“Philips”) official website. Any links to third party websites that may be included on this site are provided solely as a convenience to you. Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain.

I understand
You are about to visit a Philips global content page
Continue
You are about to visit the Philips USA website.
I understand
Why does the baby spit up after feeding
Family and Children
close
100%
Moderate regurgitation in children of the first year of life is not considered a pathology, but worries many parents. Olga Nikolaevna Glushko, a pediatric gastroenterologist at the Semeynaya clinic network, told Gazeta.Ru about the dangers and prevention of regurgitation.
When spitting up should alert
After feeding, one or sometimes several times a day, curdled breast milk or formula may leak from the baby's mouth. This phenomenon is called regurgitation or regurgitation - involuntary reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus and mouth after eating.

How to put a child to sleep without tears: useful tips
Judging by the survey published on the website "Deti.Mail.ru", the least favorite activity of parents is...
May 22 09:59
The reason for such regurgitation is the peculiarities of the structure of the gastrointestinal tract of babies in the first year of life. As a rule, it does not bother children, does not affect their well-being, appetite and weight gain. But there are situations when regurgitation should alert and cause a visit to the doctor. These include:
• Profuse regurgitation in large volume several times a day.
• Poor weight gain - the baby is not getting better or even losing weight.
• Fewer than six urination times per day - baby's diaper is dry most of the time.
• High or low temperature, pale or bluish discoloration of the skin.
• Anxiety, refusal to breastfeed if baby is breastfed or bottle fed if baby is bottle fed.
• Vomiting in a fountain when there is no stool or after falling and hitting the head.

• Atypical color of contents when spitting up - yellow or bloody.
Regurgitation can be symptoms of diseases such as esophagitis (inflammation of the lining of the esophagus), anemia, diseases of the upper respiratory tract, aspiration pneumonia.
What is the rate of spitting up in an infant
The rate of spitting up in babies is about one to two tablespoons and from one to five times a day. Normally, regurgitation disappears by a year or earlier. If they become more frequent or suddenly begin in a child older than six months, this also requires contacting a pediatrician.
The dangers of spitting up in newborns and how to avoid it
If the baby is healthy, spitting up in itself is not dangerous to health, but if the baby is not in an upright position at the time of spitting up, he may choke. To prevent this from happening, take the following preventive measures:
• When feeding, hold your baby at a 45° angle to the breast or bottle.







/imgs/2020/05/29/12/3933015/7cf142452ac7f89551afc432db0e634f8b6b47e5.jpg)