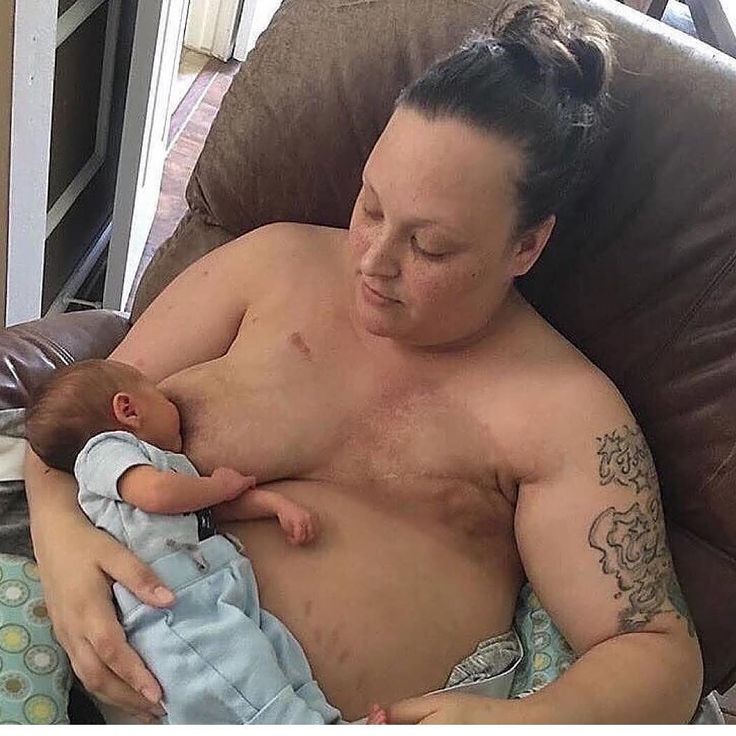
Baby squirming while feeding
16 Reasons Behind a Baby Squirming When Breastfeeding
Posts on The Breastfeeding Mama contain affiliate links, which I earn a small commission from. These are provided for your convenience, and the price is not increased at all.
Do you ever feel like your baby is constantly squirming when you’re breastfeeding? It can be really frustrating but don’t worry, you’re not alone. Many mothers experience this phenomenon. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the possible reasons why your baby is squirming and how to deal with it. We hope that this information will help make breastfeeding a more enjoyable experience for both you and your little one.
When breastfeeding, it’s normal for your baby to squirm and move around.
Babies often squirm when they’re breastfeeding because it feels good and they’re getting milk. However, if your baby is squirming a lot, seems to be in pain, or is just being a fussy baby, it may be a sign that something isn’t quite right.
In most cases, baby squirming is nothing to worry about. However, in this article, we’ll discuss possible causes behind squirminess during feeding time and important things you should keep in mind.
Table Of Contents
show
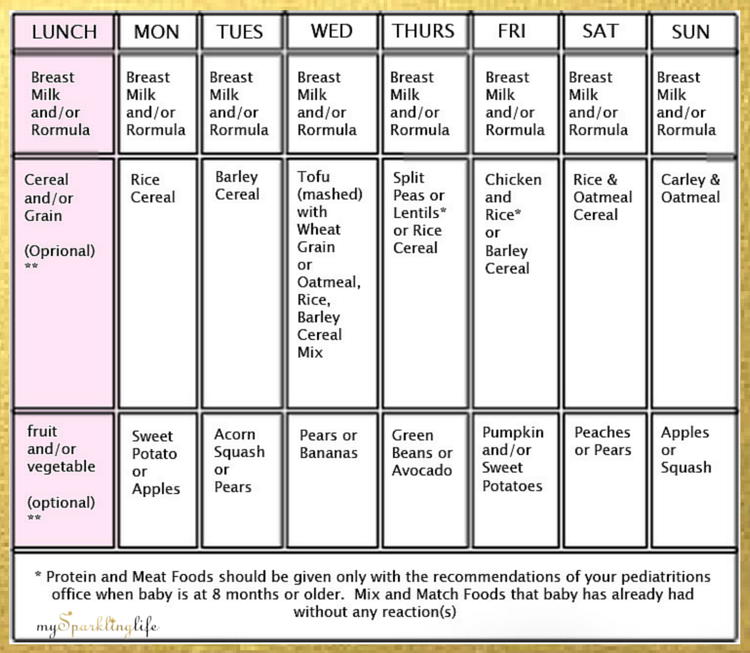
- Reasons Why a Baby Squirms While Breastfeeding
- Slow Letdown
- Fast letdown
- Gas
- Hunger
- Tiredness
- Overstimulation
- Growth Spurt/Developmental Leap
- Diaper
- Distracted
- Uneven Breasts
- Reflux
- Thrush
- Positioning
- Teething
- Illness
- Finished Eating
- Is baby squirming a cause for concern?
- How can I make breastfeeding more comfortable for my baby?
- What should I do if my baby is in pain while breastfeeding?
- More Articles You May Enjoy:
Reasons Why a Baby Squirms While Breastfeeding
There are some common reasons why breastfed babies squirm while breastfeeding. In most cases, baby squirming is just a sign that they’re comfortable and get all the milk they need. However, there are a few things that might be the culprit your baby is squirming excessively or seems to be in discomfort.
However, there are a few things that might be the culprit your baby is squirming excessively or seems to be in discomfort.
These are the top reasons:
- Gas
- Slow letdown
- Fast letdown
- Hunger
- Tiredness
- Overstimulation
- Growth Spurt/Developmental Leap
- Diaper
- Distracted
- Uneven Breasts
- Reflux
- Thrush
- Positioning
- Teething
- Illness
- Finished Eating
Slow Letdown
If your baby is squirming and seems frustrated, it could be because your milk is taking too long to let down. When the baby begins to nurse, they stimulate the release of oxytocin, which causes the milk to let down. In some cases, this process can take a few minutes. If baby gets impatient, they may start to squirm.
To help with a slower letdown, you can :
- Do breast compressions/massage before and during your nursing session
- Hand express to a letdown for a particularly fussy baby
- Switchback and forth every 1-2 minutes to keep baby engaged and to help elicit the letdown
Fast letdown
If your baby is squirming because of a fast or overactive letdown, it may be because the milk is coming out too quickly for them to handle. Managing a fast letdown can be tricky – sometimes they happen because of an oversupply of milk, while other times it just happens.
Managing a fast letdown can be tricky – sometimes they happen because of an oversupply of milk, while other times it just happens.
Certain positions can be better for a fast letdown than others. Some women find success with blocking off a milk duct by gently applying pressure in a “karate chop” position to the breast.
Gas
Another common reason baby is squirming might be because they have a lot of gas in their tummy. This can sometimes make the baby feel uncomfortable or bloated, which can lead to excessive squirming.
This is common in the early days of breastfeeding, due to infants having immature digestive systems. It can also happen if they have a poor latch which makes them bring in a lot of air, from a fast letdown where they get a fast flow of milk, or because of food allergies/intolerances.
Here is a great article about the different causes behind a gassy baby. But sometimes, all you need to do is help your baby get a good burp to help with gas issues.
Hunger
Your baby might just simply be hungry – which might make them more impatient for a letdown. If you find that this is happening frequently, you may want to pay closer attention to early hunger signs to ensure you are feeding your baby when they are in the early hunger stages – not the late.
Tiredness
If the baby is squirming and seems to be falling asleep, it could be a sign that they’re tired. When a baby is tired, they may start to fuss and squirm. They may settle and fall asleep as they start to nurse, or they may just not want to eat right then. Try giving them a short nap and try to feed them again later.
Overstimulation
Another common reason for baby squirming is overstimulation. When a baby is breastfeeding, they are also taking in all the sights and sounds around them. This can be overwhelming for them, causing them to squirm and try to escape the situation.
Growth Spurt/Developmental Leap
The baby may be squirming because of growth spurts or a developmental leap. During these times, babies may be extra hungry and need more milk to keep up with their growing bodies.
During these times, babies may be extra hungry and need more milk to keep up with their growing bodies.
During these times, they can be more interested in the world around them and have less patience. In this situation, just try and offer the breast as much as you can and be patient – this stage will pass!
Diaper
A wet or dirty diaper can also cause the baby to squirm. If a baby’s diaper is full, they will squirm and cry until you change it. Some babies are more sensitive to soiled diapers than others, so you may want to make a habit of making sure your baby has a clean diaper before feeding.
Distracted
Your baby may squirm if they’re getting distracted while breastfeeding. This is common if the baby is trying to look around the room or if there’s something else going on that’s grabbing their attention.
Here is some great advice on how to manage distracted nursing – 14 Tips for Surviving Distracted Nursing.
Uneven Breasts
Most women have a “slacker” side, or one side that seems to have a slower flow or produce less milk.![]() If your baby doesn’t like that side as much, they may squirm more to show their dissatisfaction.
If your baby doesn’t like that side as much, they may squirm more to show their dissatisfaction.
More on this topic – Lopsided Breastfeeding? How to Fix a Slacker Breast
Reflux
If a baby has gastroesophageal reflux disease, they may start to squirm and cry at the breast. This is because the acid from their stomach is coming back up, causing them to feel uncomfortable.
Laidback nursing can be helpful as it keeps your baby in a more upright position. Chiropractic adjustments can also be really helpful for helping with reflux.
Thrush
If a baby is squirming because of thrush, it’s important to take them to the doctor for treatment. Thrush can make the baby uncomfortable and fussy while breastfeeding, so it’s essential to get medical help right away.
Positioning
Sometimes your baby just doesn’t like the position they are in, and they are squirming to get more comfortable!
There are different positions you can try and experiment with. While a newborn baby can’t tell you why they are uncomfortable, sometimes a different position is just the trick. I am personally a fan of the cross-cradle hold and side-lying.
While a newborn baby can’t tell you why they are uncomfortable, sometimes a different position is just the trick. I am personally a fan of the cross-cradle hold and side-lying.
Teething
The baby may start to squirm and cry when they’re teething. This is because the pain from teething can be uncomfortable and the baby may want to find a way to relieve it.
Illness
If a baby seems to be fussy all the time, it could be a sign that they are sick. the baby may start to squirm if their illness is causing them discomfort or pain. Ear infections are one of the more common ailments to cause a disruption to breastfeeding.
Finished Eating
If the baby seems to be done nursing, it may be a sign that they are full and no longer need any more milk. In this case, you should try burping the baby and then putting them down for a nap or cuddle session. Ultimately, the best thing you can do is pay attention to the baby’s cues and respond accordingly to their needs.
Is baby squirming a cause for concern?
The good news is, this type of behavior while breastfeeding is not usually a cause for concern. However, if you have any concerns, make sure you reach out to a lactation professional or your child’s care provider.
Here are a few signs that maybe this squirming is more than just normal infant behavior:
- baby’s fussiness occurs all day long
- poor weight gain
- drop in diaper output
- frequently falling asleep at the breast before taking in a full feed
When you are trying to determine the cause of the squirming, here are a few questions to consider:
- Is it happening at the start, middle, or end of the feed
- Does it last the whole feed or just for a short time?
- Will they still nurse?
- Is it combined with other fussy behavior?
- Are you experiencing cracked or damaged nipples?
How can I make breastfeeding more comfortable for my baby?
There are a few things you can do to make breastfeeding more comfortable for your baby. Here are some things to try:
Here are some things to try:
- Try a new position
- Remove distractions
- Do skin-to-skin contact
- Nurse in a bath
- Burp baby
- Stop and try again later
- Ensure a good latch
- Determine underlying causes
What should I do if my baby is in pain while breastfeeding?
If baby squirming is accompanied by signs of pain or discomfort, such as increased agitation, pulling away from the breast, and grimacing, you should consider reaching out to a medical professional In some cases, baby squirming may be a symptom of an underlying condition that requires treatment.
To get help for your baby, speak to your doctor or a lactation consultant. They can help you identify the root cause of the baby’s discomfort and work with you to come up with an appropriate treatment plan.
If your baby is squirming a lot, it could be for any number of reasons. Hopefully, the tips in this post have given you some ideas on how to troubleshoot and alleviate the problem – most of the time, this is just a normal stage that will get better after a short time.
Always remember to consult with your pediatrician if you’re concerned about your baby’s health or well-being. And please share with us what solutions worked best for you in the comments below!
More Articles You May Enjoy:
Katie Clark, CLE, CBS
Katie Clark is a Certified Lactation Educator, Certified Breastfeeding Specialist, and IBCLC student. She has helped thousands of mothers and families around the globe navigate breastfeeding challenges and questions since 2015. She has a passion for creating research-based, helpful breastfeeding education and helping parents find a way to make breastfeeding work for them. Katie is a mom of three little boys and lives in the great state of Colorado. She also has a degree in Communications with an emphasis in print journalism.
10 Reasons Your Baby Squirms While Breastfeeding
Motherhood requires a lot of courage, education, and patience.
It takes a very strong woman to carry her baby to term, feed her, and take responsibility for everything that happens to her.
New mothers often analyze every move their little one makes, so if their baby squirms while breastfeeding most mothers will see it as a cause for concern.
There are various reasons a baby behaves this way, from tiredness to food sensitivity and uncomfortable nursing positions that cause poor latch and a fussy baby.
Of course, not every wiggle is a reason to be worried, but certain mistakes made during the first few months of nursing and other issues related to it may result in problems for both mother and baby.
Some of the most common issues are mastitis, poor milk production, sore nipples, etc.
Read on to discover more about baby squirming while breastfeeding and what you can do to help your baby nurse with ease.
10 Reasons Why Your Baby Squirms While Breastfeeding
Before we get into the details, I should note that squirming is a completely natural reaction that is common among healthy children at certain developmental phases.
However, babies can be fussy during feeding time for various reasons, so let’s take a look at some of the most common ones:
1. Slow let-down reflex
This is one of the most frequent reasons your baby squirms while breastfeeding.
Imagine someone taking away your food just as you started to eat – that’s how babies feel when the milk flow slows down.
Breastfeeding is all about following a particular pattern, which might cause occasional fussiness.
There can be several let-downs during one breastfeeding session, which are then followed by a slow flow of milk.
This can be quite irritating for the baby, so she’ll start fussing to try and get more milk out of the breast.
The baby is actually the one who establishes the breast milk supply and demand by drawing out more milk.
The harder she tries, the more milk you’ll have, which will result in a happier baby who doesn’t squirm during the feeding session.
Squirming is a completely natural reaction when the baby isn’t satisfied with the amount of milk she receives, and it can be easily solved.
For example, you can help your little one by applying pressure to your breast to stimulate the flow of milk, also known as breast compression, and do a gentle massage during breastfeeding.
You’ll notice how calm your little one becomes as soon as she gets enough milk without having to work too hard to get it.
Switching sides during breastfeeding is a good method to reduce squirming as it will increase milk supply in both breasts and your baby will be full and happy!
2. Growth spurt
New parents usually analyze every little detail of their babies, including her movements, crying, and facial expressions.
Growth spurts may cause certain confusion and worries among parents, although these are completely natural processes.
During these periods your little one goes through significant changes, so you might notice some physical alterations in growth or body size and a wider attention span and a curiosity about the world around her.
Your baby might start to squirm even during a feeding session because she can’t concentrate on it completely.
She’ll want to look at everything and react to every voice or noise she hears.
Fussiness isn’t always a sign of something bad, sometimes it’s just about a baby’s curiosity to explore the world around her and a reluctance to breastfeed for a long time.
The best way to prevent your little one from squirming during breastfeeding in these cases is to let your baby feed whenever she wants and for however long she’d like.
This might cause some minor changes to the feeding schedule, but it won’t take too long for the baby to settle into her old schedule again.
3. Tired baby
When a baby starts crying parents immediately start looking for possible causes, mostly because infants never cry without a reason.
The same applies to babies who squirm while being fed – there’s always a reason the baby behaves in such a way.
When babies cry parents try everything, from diaper changing to feeding the little one, but sometimes all they need is some rest.
RELATED: 8 Signs Of An Overtired Baby
If you notice your baby keeps touching her face or rubbing her eyes or her nose, she might not be hungry at all.
If she continues repeating these movements while being fed, it means she’s not really into breast milk and wants to take a nap instead.
You may try to feed your baby to sleep, there’s nothing wrong with that, but only if your baby doesn’t suffer from reflux.
However, some babies are not big fans of being breastfed to sleep and become fussy and upset at the breast.
If the baby keeps rejecting the breast or squirms, it’s time to find another way to help her fall asleep.
4. Breast size
Most mothers notice a certain difference between the left and right breast, especially during the breastfeeding stage.
However, we’re not the only ones who see the difference between them.
Your baby will learn which breast is bigger and fuller, so she might start to reject the smaller one.
If lopsided breasts don’t bother you esthetically, you can just continue using the breast your baby prefers, it won’t do her any harm and she’ll probably fuss far less.
Some mothers try to even them out as much as possible during the breastfeeding period by pumping out the milk after each feeding (in case the baby rejects the smaller-sized breast).
If you’re willing to continue breastfeeding your baby from both sides, you can do so by offering your baby the smaller-sized breast first.
However, if the baby squirms while breastfeeding from the smaller side, it might be better to switch to the fuller breast and pump out the other one or just wean from that breast and continue using the other one.
5. Possible infection or pain
Any type of pain can be a cause of great discomfort for people of all ages. However, adults can talk and express how they feel, but babies can’t, at least not in the typical way.
This is why parents usually analyze every movement of their baby to see any potential signal that something’s not right.
Unfortunately, if the baby squirms while breastfeeding there’s a high chance she’s in pain.
One of the most frequent causes of this is an ear infection.
Lots of babies go through this infection during the infancy period, so it’s no surprise if it happens to your little one as well.
If she suddenly starts squirming every time you feed her on one side, it could be a sign of an ear infection.
Other signs of an ear infection are:
• Pulling ears
• Fever
• Crying
• Difficulty hearing
• Excessive discharge from the ear
• Problems with sleeping
Try switching sides and check which side is causing fussiness. If this behavior repeats every time you feed your child it would be best to call your pediatrician.
6. Uncomfortable position
The nursing position is one of the most important aspects of successful breastfeeding for both mothers and their babies.
Infants already know how to nurse successfully and these “skills” are enhanced by skin-to-skin contact between a mother and her breastfed baby.
However, the baby’s instinct can’t help her to latch on properly, especially if she’s not positioned well.
Most first-time mothers aren’t aware of this positioning issue, which can also cause nipple cracking or soreness, mastitis, and fussiness.
They usually relate these problems to a lack of milk or low-quality breast milk, which is a myth – a mother’s milk fulfills all of the baby’s needs, especially during the first six months of life.
A proper nursing position will enable your little one to eat efficiently and develop in the healthiest way, and will save your nipples too.
There are some general guidelines regarding the right position for nursing, but the key is to make sure both you and the baby feel comfortable.
When latching on your little bundle of joy, make sure that at least an inch of the areola (and not just the nipple) is in the baby’s mouth.
If you notice that your baby is nursing efficiently without wriggling and crying, and that your nipples aren’t sore or cracked – congratulations, you have found the perfect feeding position!
While a newborn baby can’t speak, she can signal when something’s not right by wriggling and squirming, especially during feeding time.
However, if the baby typically nurses without any problems and this type of behavior suddenly begins, there might be another issue at hand, such as a wet diaper, sudden pain, or infection, but this doesn’t mean you should give up on nursing completely.
Many parents switch to bottle-feeding because of common misconceptions about nursing, such as thinking that nipple pain can be resolved only by switching to using a baby bottle, or that a difficult nursing start means the mother won’t be able to breastfeed her child at all.
Of course, a baby bottle is more than acceptable as an occasional replacement for the boob, but if a mother wants and has the ability to breastfeed it’s certainly one of the best choices for her and her little one.
If the latch becomes painful or uncomfortable and your baby squirms while breastfeeding, it’s time to switch positions until you find one that works the best for you and your baby.
However, if you have any worries regarding your breastfeeding baby and the process of nursing in general, you can always speak to a lactation consultant and get a piece of professional advice.
7. Fast let-down reflex
Although a faster flow of breast milk is desirable, it can become too fast, which might result in your baby fussing and wriggling because she can’t breathe properly.
A fast flow of milk might not be a problem for the majority of babies, but there are certain exceptions, especially in the case of a forceful let-down.
An infant can be overwhelmed by an extremely fast let-down, and the best way to recognize this is by noticing how fast your baby swallows milk during the first few minutes of feeding time.
If the baby swallows rapidly and starts squirming, it’s a clear sign the let-down is too fast for her.
Also, some mothers report having a tingling feeling during the first few minutes, while others describe it as a more painful experience, like a needle puncture type of feeling.
Mothers who have an oversupply of breast milk (hyperlactation) are prone to a fast let-down reflex, which directly affects the baby and causes:
• Wriggling and fussiness
• Crying
• Trapped wind
• Baby refusing the breast
• Spitting up
• Colic
When the baby eats too fast and keeps pulling away from the breast, she may swallow some air that can form an air bubble in your little one’s stomach.
This can cause gas, or even colic, which might be a reason for squirming.
The best way to avoid painful winds is to burp at least once after nursing because burping takes the excess air out of the system and helps your baby be more comfortable.
8. Teething
If you’ve ever had a toothache or sore gums, I’m sure the last thing on your mind was food.
Well, sore gums are equally painful for little babies, so it’s no surprise that your baby squirms while breastfeeding.
She might even reject nursing during this period, which is completely natural and shouldn’t be a cause for concern.
Although some people claim the baby should switch to the bottle during this period, it’s actually quite the opposite.
There is no better time to nurse a child than through these phases, because nothing can compare to a mother’s closeness and precious breast milk.
The mom is the main pacifier for the baby, and even though your baby might wriggle because of teething discomfort, you should try to continue to breastfeed through it.
In addition, you can offer your little one another type of teething remedy – cooled teething toys from the freezer.
This is a great way to ease the pain for babies who are still too young for solid foods.
Just keep in mind that teething is not a reason to stop nursing, just a small bump in the road.
9. Playtime
Parents usually underestimate the abilities of their young baby and aren’t aware of the things she can do during the first few months of her life.
Almost every month is a huge developmental milestone for a baby during the first six months of their life.
The baby starts rolling, making noises, observing the world around her, smiling, and playing.
Your baby can also try to play during breastfeeding sessions, so you might notice your baby squirming, wiggling, or even kicking while feeding.
While not a huge problem in and of itself, if you feel like your child isn’t getting enough milk you can minimize distractions during a feed.
For example, you can go into a room where there’s no TV, other people’s voices, or any strong lights.
Also, make sure you cover your other breast to avoid the baby twiddling your other nipple while nursing.
10. Thrush
Most breastfed babies get thrush on their tongue at least once during the nursing period.
This type of infection is an issue for both the mother and her child because it can cause damage to the nipple as well.
Essentially, thrush is a white build-up of a fungal infection known as candida albicans.
Most women mistake thrush for milk residue and don’t react until the infection transfers to the nipple or the baby shows obvious signs of discomfort during feeding time.
Thrush can make the baby nervous and irritated, which is why she might be fussy throughout the feeding time.
The best way to solve this infection is by taking the baby to the pediatrician, who will give you further instructions.
Other Reasons Why Your Baby Is Squirming While Breastfeeding
There are several other reasons your baby squirms during breastfeeding, which are deeply connected with certain processes that are going on in your body.
These are the most common reasons your baby might wriggle or reject the breast:
• Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle – First of all, breastfeeding is completely safe during all stages of the menstrual cycle and the milk is still nutritious enough for the healthy development of your baby.
However, some hormones go through a change during this cycle.
These changes might affect the taste of your breast milk and make it less sweet, i.e. saltier.
For example, ovulation can cause a rise of chloride and sodium as well as a drop in potassium and lactose levels in breast milk.
But, that doesn’t imply your breast milk isn’t good enough for your baby.
Therefore, it’s strongly recommended to continue nursing your baby through this period, as it’s beneficial for both mother and child.
• Pregnancy – Hormonal changes in a woman’s body during pregnancy can result in a different taste of breast milk. Some babies aren’t fond of the change and might wriggle as a result, but others don’t.
If your pregnancy is the cause of the baby’s squirming, I’m sure you will find out sooner or later!
• Medication – Certain medications can easily dissolve in breast milk and change its taste, the volume of milk production, or its color.
Antihistamines, hypertension medicines, diuretics, and decongestant medicines typically cause changes in milk taste, volume, and color.
If you’re supposed to use certain meds during the nursing period, make sure to check with your doctor or an IBCLC (International Board Certified Lactation Consultant) if the therapy is compatible with nursing.
Conclusion
Being a parent is an incredibly beautiful and challenging lifelong experience that completely alters the way you perceive the world.
Therefore, it’s completely natural that you’re watching and analyzing every movement and facial expression your little one makes.
The only way your baby can tell you something isn’t right is by crying or fussing, whether it’s during breastfeeding, playtime, bathtime, etc.
The majority of reasons babies squirm while breastfeeding are not a cause for great concern, but if the baby shows signs of intense pain or discomfort during feeding you can consult with a pediatrician or a lactation consultant just to make sure everything’s okay.
Remember to write down any other changes you’ve noticed in your baby’s behavior (if any) as this will help healthcare professionals give you more precise advice.
Like this post? Please share or pin it for later. You can also stay in the loop and follow us on Facebook, Instagram or Pinterest.
We love honesty! Find Your Mom Tribe is an Amazon Associate and we earn from qualifying purchases through affiliate links at no extra cost to you. Please see our full Amazon Affiliate disclosure for more information.
Sharing is caring!
1 shares
- Share
- Tweet
Frequent problems during breastfeeding: doctor's advice
Breastfeeding is a simple and natural process that does not require special training, skill, skills . ..
..
We can talk about the benefits of breast milk for babies for a very long time. Mother's milk is often called "white blood" because its composition and biological characteristics are as close as possible to the composition of placental blood, milk can carry nutrients and influence biochemical systems that increase immunity and destroy pathogenic microorganisms. In addition, breastfeeding is a process that allows you to establish the first contact between mother and child. For many mothers, these are happy moments of unity with the baby. But it is far from always possible to establish breastfeeding immediately and without problems. Often women experience difficulties that confuse, frighten and make them doubt the correctness of their own actions. Mammologist and breastfeeding specialist Anna Vanesyan talks about the most common problems faced by mothers who start breastfeeding. What to do if the baby fidgets at the chest? Should You Diet While Breastfeeding? And what if the baby has a tummy ache? The answers to these questions are in Anna Vanesyan's article.
First, the reasons depend on the age of the child . How old is the baby - a month, six months, a year? Secondly, at what stage of feeding does the baby begin to fidget - at the beginning, after 5 minutes, at the end?
If a completely newborn baby fidgets during the first month of life, it is likely that there are difficulties with grasping. The most important rule: make sure that not only the nipple, but the entire areola is in the mouth. There may also be problems with the bridle, but in this case, the baby should be examined by a specialist.
It is also very important to monitor the position of the child's body - the head and body should be located along the same line.
If the baby fidgets 5 minutes after the start of feeding, then, firstly, it is necessary to exclude the presence of mixed feeding. Children who have “tasted the bottle by mouth” understand that milk pours from a bottle into their mouths without much effort. And from the chest - only in the first 5 minutes. Next, you need to work. If there is no mixed feeding, then you need to look so that there are no beginning episodes of hypogalactia. At such moments, try to massage the breast from the periphery to the nipple with your free hand, try to lightly express milk into the baby’s mouth and thereby help.
And from the chest - only in the first 5 minutes. Next, you need to work. If there is no mixed feeding, then you need to look so that there are no beginning episodes of hypogalactia. At such moments, try to massage the breast from the periphery to the nipple with your free hand, try to lightly express milk into the baby’s mouth and thereby help.
If the child fidgets mainly at the end of feeding, in the evening hours, painfully leads to the stomach of the leg, screams piercingly, and he is 2.5-4 months old, then these may be the first signs of colic.
What should I do if my breastfed baby has a tummy ache?
The first thing a compassionate mother does when she notices that her baby has a tummy ache, conducts a thorough inspection of her diet and begins to live on bread and water, so as not to provoke another bout of colic in her child. Excessive mother's stress and worries, of course, lead to adrenaline surges, which in turn reduces the level of prolactin and oxytocin - and so on in a circle.
With a balanced mother's diet, the quality of milk does not depend on the mother's food. But how the baby eats at the breast is very important.
It is pleasant to distinguish between the so-called foremilk and hindmilk. Foremilk is thin, watery and rich in sugars, mainly intended to quench the thirst of the baby. The hindmilk is thick, rich in nutrients, proteins and fats, and promotes the growth of the baby. If a mother often changes breasts during feeding or the baby has an incorrect grip, then he can spend a long time at the breast and eat only foremilk. As a result, the stomach is filled, and the child still remains hungry. A large amount of sugar also affects the stool, leading to diarrhea, indigestion, sour smell and greenish color.
Another reason why a baby may have a stomach ache is colic. If the stomach hurts between 1.5-4 months, mostly in the evening, the child presses the legs to the stomach and screams, it is likely that these are signs of colic. In general terms, all you need to know about colic: the child is not sick at this moment, this is just a stage of intestinal maturation, to which different children react differently, depending on the sensitivity. There are no effective treatments for colic, but remember that at these moments there is no need to breastfeed the baby (quite the contrary, the longer the break, the more chances he has to calmly digest the previous portion of milk). Skin-to-skin contact and abdominal massage have a positive effect, and as for drug treatment, it is better to consult a pediatrician individually.
There are no effective treatments for colic, but remember that at these moments there is no need to breastfeed the baby (quite the contrary, the longer the break, the more chances he has to calmly digest the previous portion of milk). Skin-to-skin contact and abdominal massage have a positive effect, and as for drug treatment, it is better to consult a pediatrician individually.
Capture problems - what is the right way?
I repeated and repeat this every day: breastfeeding is a simple and natural process that does not require special training, skill, or skills. It is necessary to be able to relax in time and trust nature.
And the first and, undoubtedly, the most important step in this process is capture. A few simple principles for proper latch on:
1. Bring your baby to your breast, not the other way around. Moreover, if you carefully tickle the baby’s cheek or chin with the nipple, he will reflexively open his mouth wide and properly grasp the nipple.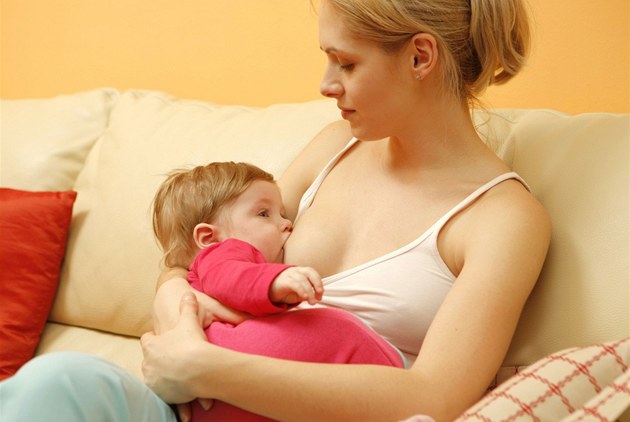
2. With proper grip in the mouth, the child has not only the nipple, but also the areola - the areola.
3. If the baby fidgets at the breast, eats too fast and vigorously, then gets tired and falls asleep, then wakes up again and sucks vigorously - it is necessary to check the grip. Incorrect latch also leads to nipple cracks and sores, blockages and mastitis.
12 reasons why a baby is anxious when breastfeeding. Why does baby cry while breastfeeding0001
In the first weeks after birth, a newborn and his mother are just getting used to each other, and much of the baby's behavior is incomprehensible to the mother. Why, for example, does a child worry at the breast during feeding? There are many reasons for this, and we decided to describe them and offer ways to overcome difficulties. Let's start with the cause of the child's anxiety, which mothers call the first, but which really exists least of all.
Lack of milk
This is the first thing that comes to the mind of a nursing mother whose baby cries a lot, including at the breast. One of the biggest challenges with breastfeeding, oddly enough, is that breastfeeding moms don't know exactly how much milk their babies are getting or if they're getting enough.
If your child is overly restless, most outside well-wishers will likely point out to you that the baby is probably hungry. Since you are a mother, such remarks can make you feel guilty. After all, it is your responsibility to feed the child! How to dispel doubts and fears associated with a lack of milk?
- Watch your baby urinate and defecate. After the sixth day of life, you should receive at least six wet diapers and one dirty diaper per day. If so, then your baby is getting enough milk.
- Frequent feedings are normal. In the first few weeks of life, a newborn usually needs 8-12 feedings per day.
 At the very beginning, you may at times have to keep it near your chest almost all the time. For several hours, he will demand it very often, and then fall asleep for four to five hours. As the baby learns to suckle more effectively, the number of feeds decreases.
At the very beginning, you may at times have to keep it near your chest almost all the time. For several hours, he will demand it very often, and then fall asleep for four to five hours. As the baby learns to suckle more effectively, the number of feeds decreases. - Keep track of your baby's weight. By two weeks, the baby should have regained the weight it was born with and gain at least 150 grams per week for the next two to three months.
If you are still worried that you are not getting enough milk, you may find it helpful to have a lactation consultant who will monitor and assess your baby's weight gain and suggest ways to increase your milk supply, if needed.
Breast swelling
Sometimes the child's restless behavior at the breast is caused by breast swelling. Excessive breast swelling most often occurs in the first weeks after childbirth. To reduce it, express some milk manually or with a quality breast pump to make the breast softer and easier for the baby to take it.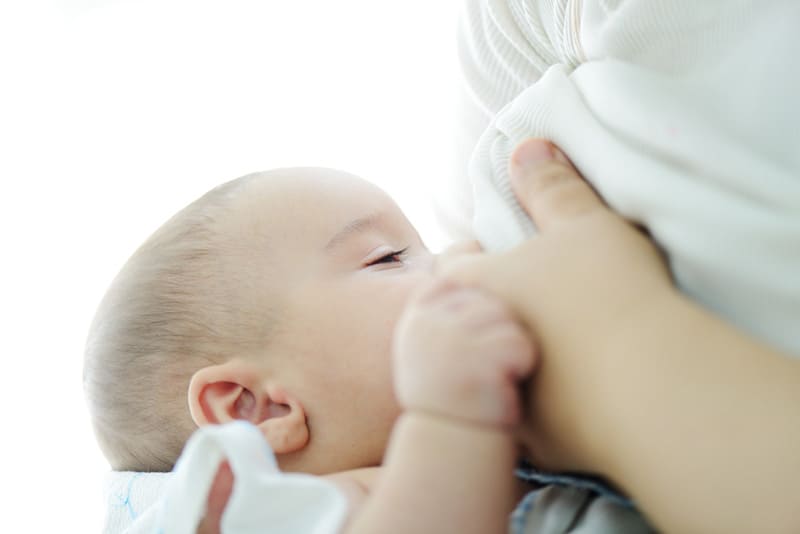 Don't express too much milk, as this can cause you to produce too much milk later on, which will only make the swelling worse. Apply cold compresses to your breasts between feedings to reduce swelling and soreness.
Don't express too much milk, as this can cause you to produce too much milk later on, which will only make the swelling worse. Apply cold compresses to your breasts between feedings to reduce swelling and soreness.
Flat or indented nipples
Also, the baby may be nervous to latch onto the breast if the mother has flat or indented nipples. To stretch them, you can wear special pads between feedings. Turning on the pump for a few minutes before putting the baby to the breast will help elongate the nipples and also start the flow of milk so that the baby will immediately receive it and is more likely to continue sucking instead of dropping the breast and crying.
In some cases, a woman has to use pads that encourage sucking until her nipples become more prominent. This should happen after about two to four weeks of breastfeeding. If you are having trouble with flat or sunken nipples, seek help from a lactation consultant as soon as possible.
Incorrect attachment, awkward posture
Another cause of restless behavior at the chest is incorrect position . Both the mother and the baby may be uncomfortable, due to which the effect on the breast is not as it should be, and a sufficient flow of milk is disturbed. If your baby is very nervous, your best bet is to use the underarm position (when you hold the baby to your side, holding him tightly against your nearest breast) or the "cradle" position (when you hold the baby horizontally at your chest), as these positions allow you to control his head.
Both the mother and the baby may be uncomfortable, due to which the effect on the breast is not as it should be, and a sufficient flow of milk is disturbed. If your baby is very nervous, your best bet is to use the underarm position (when you hold the baby to your side, holding him tightly against your nearest breast) or the "cradle" position (when you hold the baby horizontally at your chest), as these positions allow you to control his head.
These postures allow you to guide the baby to the breast and hold him there. The baby's nose and chin should be pressed into the mother's chest. As a rule, he suckles better when his mother holds him tightly. If something makes you feel uncomfortable while feeding, contact a consultant. Perhaps this is the reason for your baby's anxiety.
Gastroesophageal reflux
Almost all children have some degree of gastroesophageal reflux. This medical term refers to a condition in which the annular muscle (sphincter) that blocks the entrance to the stomach has not yet fully formed and does not always completely close the opening. Because of this, some milk, along with gastric juice, can flow back into the esophagus, causing a sensation that we call "heartburn."
Because of this, some milk, along with gastric juice, can flow back into the esophagus, causing a sensation that we call "heartburn."
As anyone who has ever experienced it knows, it is quite an unpleasant sensation. Just as an adult can relieve heartburn by sitting with a straight back, a child can also usually benefit from being held upright.
Sometimes reflux can occur during feeding. Its appearance can be prevented by holding the child more upright or periodically taking breaks so that the baby “stood” a little. As the child develops, so does the musculature, so that cases of reflux become rarer.
Sometimes the problem is so severe that the child is unable to eat normally due to reflux. In such cases, you must consult a doctor.
Increased flatulence
All newborns have flatulence . When a child begins to eat, he starts reflex gas production, which is necessary for the waste generated during nutrition to be removed from the body more quickly. This prevents constipation.
This prevents constipation.
Since breast milk is very easy to digest, it takes very little time for this food to pass through the baby's gastrointestinal tract. You can often hear characteristic sounds while the baby is still suckling. Although all children have gas, some tolerate it better than others. The time of day can also influence this. Apparently, the problem of flatulence becomes more noticeable at the end of the day. Traditionally, this time is considered the most hectic. The child seems to not want to let go of the breast at all, and this, in turn, can aggravate flatulence. This problem disappears on its own as the baby develops.
How to calm a crying baby
Many of the methods that promote calming are somehow related to the imitation of intrauterine conditions. Make sure that the air temperature is comfortable - not too hot and not too cool. Change diapers promptly. The baby can feel peace if he is held tightly to him or rocked. Swaddling or monotonous sounds - music or the buzzing of electrical appliances - may turn out to be effective.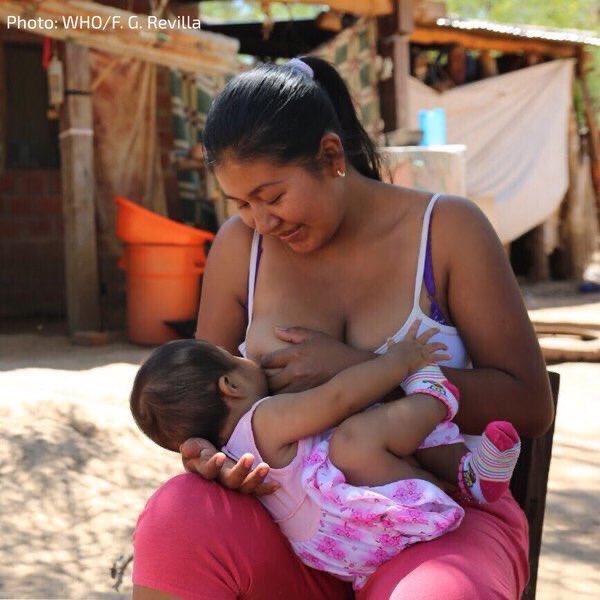 You can carry your baby in a sling, thereby providing him with comfort and getting the opportunity to do some business at the same time.
You can carry your baby in a sling, thereby providing him with comfort and getting the opportunity to do some business at the same time.
You can involve one of the family members in calming the child - for example, a father, grandmother or grandfather; in this case, the baby will not feel the smell of breast milk coming from the mother, which can excite him. In addition, this will give the mother the opportunity to devote some time to herself.
Physiological lactase deficiency
At the beginning of feeding, mother's milk is more saturated with milk sugar - lactose. It's called "front". After 10-15 minutes of feeding with the same breast, she begins to produce "hind" milk. It is richer in fats, which neutralize lactose and thereby reduce gas formation. If the baby is getting too much foremilk and not getting enough hindmilk, an excess of lactose and a lack of the lactase enzyme, which increases flatulence.
Try to have your baby suckle from one breast for at least 12-15 minutes to get the hind milk. When the baby grows up and sucks more efficiently, it will get to him in a shorter period of time after the start of feeding. Hindmilk has a calming effect and helps restless babies fall asleep. Most newborns naturally fall asleep at the end of a feed due to the calming action of hindmilk.
When the baby grows up and sucks more efficiently, it will get to him in a shorter period of time after the start of feeding. Hindmilk has a calming effect and helps restless babies fall asleep. Most newborns naturally fall asleep at the end of a feed due to the calming action of hindmilk.
The baby chokes on milk
While the baby is just learning to breastfeed, the so-called milk ejection reflex can be too powerful for him and lead to him choking. Because of this, the baby can drop the breast and start to get nervous. Press firmly on the breast for about a minute to stop the too rapid flow of milk, and then put the baby back on the breast. Try expressing some milk before feeding and see if you can trigger the ejection reflex before the baby takes the breast. Feed your baby in the underarm position. As the baby gets older, it will be able to cope with the consequences of the milk ejection reflex in any position for feeding without any problems.
Smell
In rare cases, the baby will become nervous and drop the breast because of soaps or creams you put on the breasts or nipples .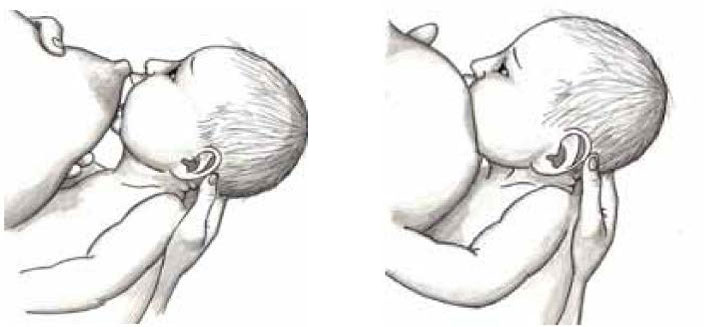 If you start using some new remedy, and the child becomes more nervous, wash it off and start feeding again.
If you start using some new remedy, and the child becomes more nervous, wash it off and start feeding again.
Thrush
The baby may develop a yeast infection in the mouth or on the nipples of the mother - the so-called thrush. You will see white spots in the child's mouth.
Your nipples may become bright red or itchy and burn after feeding. During feeding, the baby may be more restless than usual.
See a doctor. If he confirms that you have a fungal infection, both you and the child will have to undergo treatment.
Too noisy and too bright
In some children, excessive anxiety is associated with overstimulation. They can behave more calmly during feeding if it takes place in a darkened and quiet room.
Wants to calm down with the breast
Before 12 weeks, babies have little ability to soothe themselves and often reach for the breast just for comfort. They begin to suck to calm down, not experiencing at this moment the need for food.