Baby very fussy after feeding
Baby Cries After Feeding: What Should I Do?
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.D. — By Chaunie Brusie on October 3, 2018
My daughter, the “crier”
My second daughter was what my oldest fondly referred to as a “crier.” Or, in other words, she cried. A lot. The crying with my baby girl seemed to intensify after every single feeding and particularly at night.
It was those hellish hours between darkness and dawn when my husband and I would take turns walking around the house with her in our arms, praying and, mostly in my case, sobbing because we couldn’t console our baby.
I didn’t know it then in my sleep-deprived state, but my daughter’s crying after feedings wasn’t that uncommon. In combination with her frequent spitting up, it was pretty much a classic textbook case of colic.
Colic
Colic, in technical terms, simply means a “crying, fussy baby that doctors can’t figure out.”
OK, so that’s not really the definition, but in essence, that’s what it boils down to. The British Medical Journal (BMJ) lists one criterion for colic: A baby that cries for at least three hours a day, three or more days a week, and is under 3 months old. Check, check, and check.
There isn’t one single known cause of colic. Even the actual clinical incidence of colic, estimated by BMJ to be around 20 percent of all babies, can be tricky.
Acid reflux
One of those causes of crying after feeding and spitting up in babies is actually acid reflux. This condition is known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) if it also causes significant symptoms such as poor weight gain.
When my “crier” daughter was 5, she frequently complained of her stomach hurting and as a result, had to undergo a series of testing with a gastroenterologist, a doctor that specializes in the GI system.
At our first appointment, the very first question he asked me was if she had colic as a baby and if she spit up a lot, to both of which I practically shouted, “Yes! How did you know?!”
He explained that acid reflux or GERD can manifest as symptoms similar to colic in babies, stomach pain in school-aged children, and later as actual heartburn pain in adolescents.
While many infants spit up, fewer have actual GERD, which can be caused by an underdeveloped flap between the esophagus and stomach or a higher-than-normal production of stomach acid.
In most cases, a diagnosis of infant reflux is simply based on your baby’s symptoms. If your doctor suspects a severe case however, there are several different tests that actually diagnose infant reflux.
Testing can involve taking a biopsy of your baby’s intestine or using a special type of X-ray to visualize any affected areas of obstruction.
Food sensitivities and allergies
Some babies, especially breastfed babies, may be allergic to certain food particles that their mothers are eating.
The Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine notes that the most common offender is cow’s milk protein in the mother’s milk, but even a true allergy is very rare. Only about 0.5 to 1 percent of exclusively breastfed babies are thought to be allergic to cow’s milk protein.
The other most common culprits, according to the ABM, are egg, corn, and soy, in that order.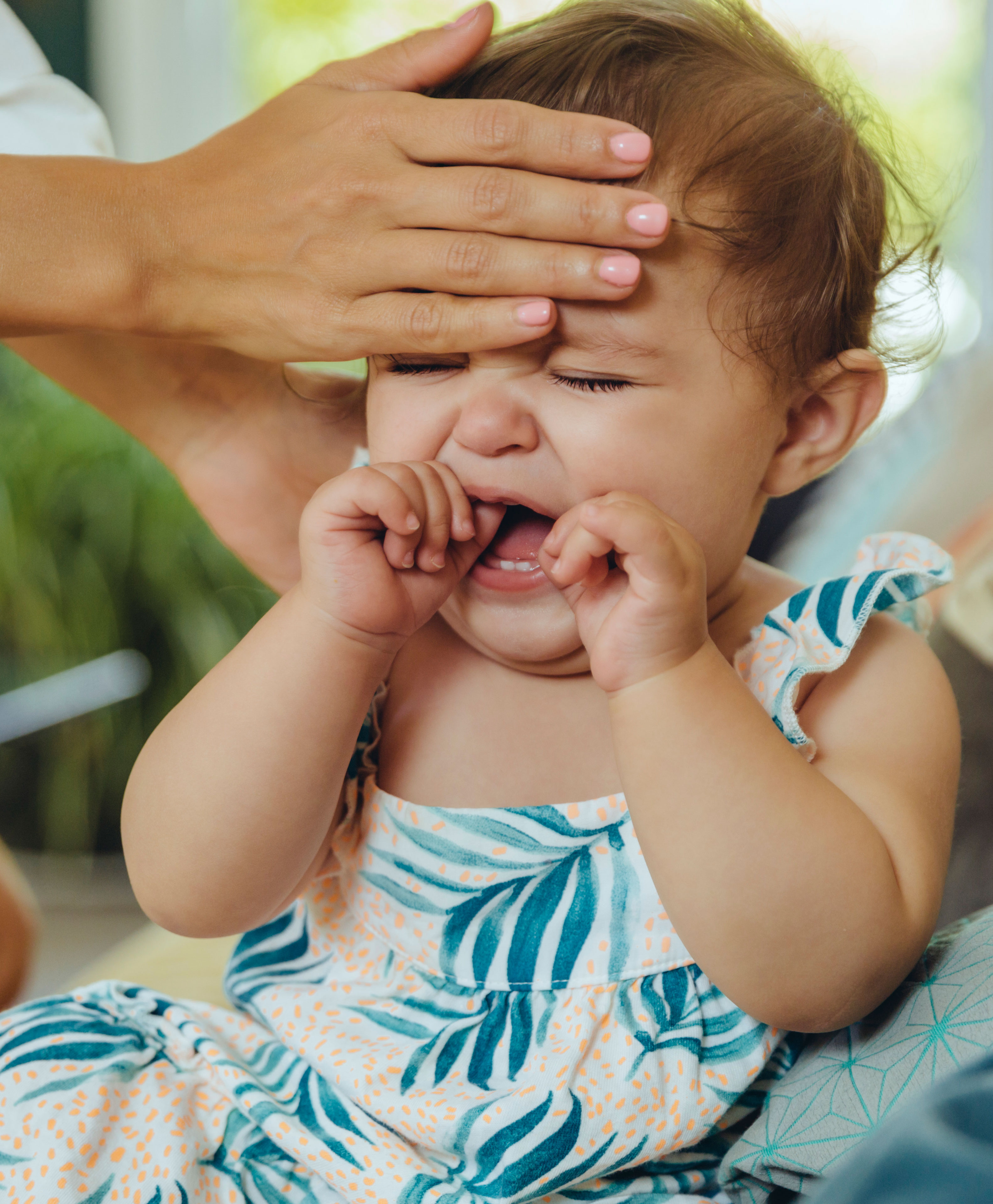
If your baby is displaying symptoms of extreme irritability after feedings and has other symptoms, such as bloody stools (poop), you should speak with your healthcare provider about getting them tested for allergies.
Aside from a true allergy, there’s also been some evidence that following a low allergen diet while breastfeeding (essentially avoiding those top allergy foods, such as dairy, eggs, and corn) may be beneficial for infants with colic.
Strict elimination diets can have their own risks, so speak with your doctor before significantly changing your diet.
In our situation, I found that dairy, caffeine, and certain seeded fruit exacerbated my daughter’s crying and spitting up. By eliminating those foods and substances from my diet, I was able to help lessen her discomfort.
If you have a baby with colic, you might want to try anything at all to help ease your baby’s crying. If you’re curious to see if your diet has any effect, you can start by logging your food in a food journal and writing down your baby’s reactions after each meal.
Next, you can eliminate one food at a time and see if reducing your intake of certain foods seems to make a difference in your baby’s behavior. If you hit on one you feel helps your baby to cry less, this does not mean they will not be able to eat that food in the future.
Just be sure to keep in mind that a true allergy is rare. Also, be sure to monitor for any additional symptoms, such as blood in your baby’s poop.
Gas
If your baby is crying a lot after every feeding, it may simply be a buildup of air swallowed while eating. It’s thought that bottle-fed babes in particular may be more prone to swallowing a lot of air during a feeding. This can trap gas in their stomachs and be uncomfortable.
In general, breastfed babies swallow less air while eating simply due to the way they eat. But every baby is different and even breastfed babies may need to be burped after a feeding.
Trying keeping your baby upright after a feeding and burping gently from the bottom of their back and up through the shoulders to work the gas bubbles up and out. Also check out this illustrated guide to burping a sleeping baby.
Also check out this illustrated guide to burping a sleeping baby.
Formula
If your baby is formula-fed, swapping out the formula you use may be a simple solution to a crying baby after feedings. Every formula is a little bit different and certain brands make formulas for more sensitive baby tummies.
If you decide to try this, talk to your baby’s pediatrician about whether an elemental formula would be a good choice to try for a week. If you try one different brand and you see no change in your baby’s fussiness, continuing to try different brands is unlikely to help.
Takeaway
Colic, along with a few other common conditions, might be the culprit if you too have a “crier” on your hands.
If your baby doesn’t find relief after dietary changes or additional burping, then make an appointment to see their doctor.
Share on Pinterest
Chaunie Brusie, BSN, is a registered nurse with experience in labor and delivery, critical care, and long-term care nursing. She lives in Michigan with her husband and four young children, and is the author of the book “Tiny Blue Lines.”
She lives in Michigan with her husband and four young children, and is the author of the book “Tiny Blue Lines.”
Last medically reviewed on October 3, 2018
- Parenthood
- Baby
- 06 Months
How we vetted this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- ABM clinical protocol #24: Allergic proctocolitis in the exclusively breastfed infant. (2011). DOI:
10.1089/bfm.2011.9977 - Harrel MC, et al. (2015). Is there a correlation between maternal diet in breastfeeding mothers and infantile colic? DOI:
10.1097/01.EBP.0000541032.94135.ca - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2018). Infant reflux.
mayoclinic. org/diseases-conditions/infant-acid-reflux/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351412
org/diseases-conditions/infant-acid-reflux/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351412 - Rosen LD, et al. (2007). Complementary, holistic, and integrative medicine.
pedsinreview.aappublications.org/content/28/10/381 - Saavedra MA, et al. (2003). Infantile colic incidence and associated risk factors: A cohort study. .
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14502331 - Sung V, et al. (2014). Treating infant colic with the probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri: Double blind, placebo controlled randomised trial. DOI:
10.1136/bmj.g2107 - Symptoms & causes of GER and GERD in infants. (2015).
niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/acid-reflux-ger-gerd-infants/symptoms-causes
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Oct 3, 2018
By
Chaunie Brusie
Edited By
Nizam Khan (TechSpace)
Medically Reviewed By
Karen Richardson Gill, MD
Share this article
Baby Cries After Feeding: What Should I Do?
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.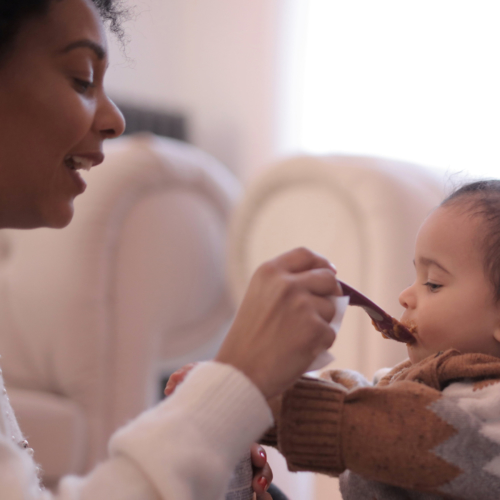 D. — By Chaunie Brusie on October 3, 2018
D. — By Chaunie Brusie on October 3, 2018
My daughter, the “crier”
My second daughter was what my oldest fondly referred to as a “crier.” Or, in other words, she cried. A lot. The crying with my baby girl seemed to intensify after every single feeding and particularly at night.
It was those hellish hours between darkness and dawn when my husband and I would take turns walking around the house with her in our arms, praying and, mostly in my case, sobbing because we couldn’t console our baby.
I didn’t know it then in my sleep-deprived state, but my daughter’s crying after feedings wasn’t that uncommon. In combination with her frequent spitting up, it was pretty much a classic textbook case of colic.
Colic
Colic, in technical terms, simply means a “crying, fussy baby that doctors can’t figure out.”
OK, so that’s not really the definition, but in essence, that’s what it boils down to. The British Medical Journal (BMJ) lists one criterion for colic: A baby that cries for at least three hours a day, three or more days a week, and is under 3 months old. Check, check, and check.
Check, check, and check.
There isn’t one single known cause of colic. Even the actual clinical incidence of colic, estimated by BMJ to be around 20 percent of all babies, can be tricky.
Acid reflux
One of those causes of crying after feeding and spitting up in babies is actually acid reflux. This condition is known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) if it also causes significant symptoms such as poor weight gain.
When my “crier” daughter was 5, she frequently complained of her stomach hurting and as a result, had to undergo a series of testing with a gastroenterologist, a doctor that specializes in the GI system.
At our first appointment, the very first question he asked me was if she had colic as a baby and if she spit up a lot, to both of which I practically shouted, “Yes! How did you know?!”
He explained that acid reflux or GERD can manifest as symptoms similar to colic in babies, stomach pain in school-aged children, and later as actual heartburn pain in adolescents.
While many infants spit up, fewer have actual GERD, which can be caused by an underdeveloped flap between the esophagus and stomach or a higher-than-normal production of stomach acid.
In most cases, a diagnosis of infant reflux is simply based on your baby’s symptoms. If your doctor suspects a severe case however, there are several different tests that actually diagnose infant reflux.
Testing can involve taking a biopsy of your baby’s intestine or using a special type of X-ray to visualize any affected areas of obstruction.
Food sensitivities and allergies
Some babies, especially breastfed babies, may be allergic to certain food particles that their mothers are eating.
The Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine notes that the most common offender is cow’s milk protein in the mother’s milk, but even a true allergy is very rare. Only about 0.5 to 1 percent of exclusively breastfed babies are thought to be allergic to cow’s milk protein.
The other most common culprits, according to the ABM, are egg, corn, and soy, in that order.
If your baby is displaying symptoms of extreme irritability after feedings and has other symptoms, such as bloody stools (poop), you should speak with your healthcare provider about getting them tested for allergies.
Aside from a true allergy, there’s also been some evidence that following a low allergen diet while breastfeeding (essentially avoiding those top allergy foods, such as dairy, eggs, and corn) may be beneficial for infants with colic.
Strict elimination diets can have their own risks, so speak with your doctor before significantly changing your diet.
In our situation, I found that dairy, caffeine, and certain seeded fruit exacerbated my daughter’s crying and spitting up. By eliminating those foods and substances from my diet, I was able to help lessen her discomfort.
If you have a baby with colic, you might want to try anything at all to help ease your baby’s crying. If you’re curious to see if your diet has any effect, you can start by logging your food in a food journal and writing down your baby’s reactions after each meal.
Next, you can eliminate one food at a time and see if reducing your intake of certain foods seems to make a difference in your baby’s behavior. If you hit on one you feel helps your baby to cry less, this does not mean they will not be able to eat that food in the future.
Just be sure to keep in mind that a true allergy is rare. Also, be sure to monitor for any additional symptoms, such as blood in your baby’s poop.
Gas
If your baby is crying a lot after every feeding, it may simply be a buildup of air swallowed while eating. It’s thought that bottle-fed babes in particular may be more prone to swallowing a lot of air during a feeding. This can trap gas in their stomachs and be uncomfortable.
In general, breastfed babies swallow less air while eating simply due to the way they eat. But every baby is different and even breastfed babies may need to be burped after a feeding.
Trying keeping your baby upright after a feeding and burping gently from the bottom of their back and up through the shoulders to work the gas bubbles up and out. Also check out this illustrated guide to burping a sleeping baby.
Also check out this illustrated guide to burping a sleeping baby.
Formula
If your baby is formula-fed, swapping out the formula you use may be a simple solution to a crying baby after feedings. Every formula is a little bit different and certain brands make formulas for more sensitive baby tummies.
If you decide to try this, talk to your baby’s pediatrician about whether an elemental formula would be a good choice to try for a week. If you try one different brand and you see no change in your baby’s fussiness, continuing to try different brands is unlikely to help.
Takeaway
Colic, along with a few other common conditions, might be the culprit if you too have a “crier” on your hands.
If your baby doesn’t find relief after dietary changes or additional burping, then make an appointment to see their doctor.
Share on Pinterest
Chaunie Brusie, BSN, is a registered nurse with experience in labor and delivery, critical care, and long-term care nursing. She lives in Michigan with her husband and four young children, and is the author of the book “Tiny Blue Lines.”
She lives in Michigan with her husband and four young children, and is the author of the book “Tiny Blue Lines.”
Last medically reviewed on October 3, 2018
- Parenthood
- Baby
- 06 Months
How we vetted this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- ABM clinical protocol #24: Allergic proctocolitis in the exclusively breastfed infant. (2011). DOI:
10.1089/bfm.2011.9977 - Harrel MC, et al. (2015). Is there a correlation between maternal diet in breastfeeding mothers and infantile colic? DOI:
10.1097/01.EBP.0000541032.94135.ca - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2018). Infant reflux.
mayoclinic. org/diseases-conditions/infant-acid-reflux/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351412
org/diseases-conditions/infant-acid-reflux/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351412 - Rosen LD, et al. (2007). Complementary, holistic, and integrative medicine.
pedsinreview.aappublications.org/content/28/10/381 - Saavedra MA, et al. (2003). Infantile colic incidence and associated risk factors: A cohort study. .
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14502331 - Sung V, et al. (2014). Treating infant colic with the probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri: Double blind, placebo controlled randomised trial. DOI:
10.1136/bmj.g2107 - Symptoms & causes of GER and GERD in infants. (2015).
niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/acid-reflux-ger-gerd-infants/symptoms-causes
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Oct 3, 2018
By
Chaunie Brusie
Edited By
Nizam Khan (TechSpace)
Medically Reviewed By
Karen Richardson Gill, MD
Share this article
The child is often psychotic and capricious
Author: Marfa Goncharova, magazine "My Baby and Me"; consultant: Yulia Andronnikova, pediatrician of the highest category, head of the pediatric department of the Center for Traditional Obstetrics and Family Medicine.
The expressed emotional state of the child is a message of discomfort. Leaving these messages unattended means ignoring the needs of the baby, which can be physical and psychological.
Inconsolable crying, screaming, stubbornness and irritation out of the blue - what upsets parents so much and outrages outsiders who have become unwitting witnesses to an unpleasant scene is usually called whims. In fact, if in an adult a completely unreasonable whim can be called a whim, then children's whims, as a rule, have a serious reason.
Yulia Andronnikova: "Children under one year old are not characterized by whims in their everyday sense. If a child suddenly starts behaving in an unusual way for him, this is always a signal for his mother, a message of discomfort. No doctor can say for sure: if a child cries for minutes ten - this is normal, and if longer, then this is a sign of illness. Mom's intuition should work here. After all, already in the first 2-3 months of life, being in close contact with the baby, the mother studies him so well that she knows perfectly well what is typical for her child and what goes beyond normal behavior. 0003
0003
If the baby is crying, the mother calms him down with the usual methods that suit him. Children love to be picked up, maintaining skin-to-skin contact, being rocked, talking in a low, calm voice, and being placed on their chest. Someone stops worrying in a warm bath, and someone better to undress for a while. The set of techniques may vary, but if the baby continues to cry despite the usual stress relief rituals, the mother should watch him more carefully. "
Infectious diseases
Unusually prolonged crying for a child or, conversely, lethargy, refusal to eat in children of any age are often the first sign of the development of an infectious disease. Like it or not, it becomes obvious in just a few hours: the temperature may begin to rise, a cough or runny nose will appear. For babies who still can neither say nor show that they are in pain, loud crying can be a sign of otitis media that has begun. If the ears hurt, there may be no fever or other signs of a cold, it is precisely the abruptly changed behavior that will cause suspicion: the child is inappropriately naughty, shakes his head, sometimes screams sharply, starts crying when the position of the head changes, refuses to eat, because it provokes pain. In such a situation, you should definitely call a doctor.
In such a situation, you should definitely call a doctor.
Meteosensitivity
The peculiarity of the response of the autonomic nervous system to changing environmental conditions is called meteosensitivity. Training the nervous system and blood vessels of the baby will help to cope with meteosensitivity. Thanks to hardening, the adaptive capabilities of the organism will grow, and the reaction to a change in the weather will become less violent or disappear altogether.
For toddlers, outdoor walks in any weather are the best hardening. Not only a change in pressure, rain, a thunderstorm, but also simply cloudy weather or a long absence of the sun in the sky can affect the body. In newborns, sudden changes in the weather are often worrisome. After a few months, the majority of such meteorological dependence disappears, but in children with a weakened autonomic nervous system, it can continue to manifest itself and even intensify against the background of stressful conditions.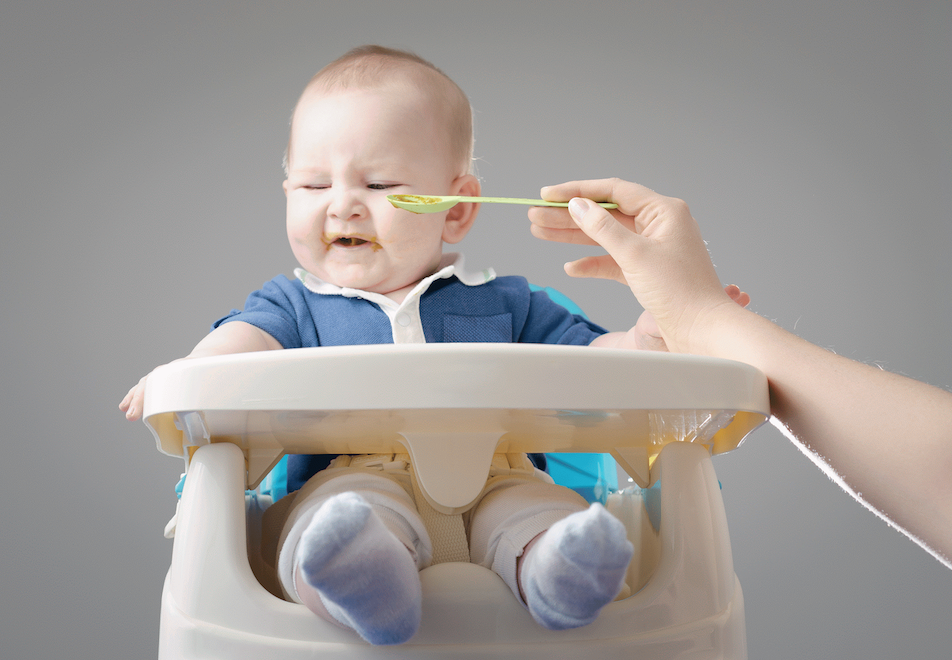
Chronic diseases
But what if the baby not only suddenly changed his behavior, but is constantly in a depressed state - he is lethargic, whimpering all the time and practically does not smile? Yulia Andronnikova: “The general well-being of a child is an important indicator of his health. A healthy baby may start to act up in the evening when he is tired, but he should wake up in a good mood - this is a signal to his mother that everything is in order with him.
If the child is naughty every day and is in a bad mood all the time, and you have ruled out the presence of any infections, it is worth bringing this to the attention of your pediatrician. Constant whims, pallor, lethargy, lack of a smile from birth, low weight gain and height are a set of symptoms characteristic of hormonal disorders. The earlier the diagnosis is made, the better, because with the timely initiation of treatment, the disease can be compensated and the life, health and intelligence of the child can be saved. If such diseases are suspected, the pediatrician will refer the child to an endocrinologist.
If such diseases are suspected, the pediatrician will refer the child to an endocrinologist.
Approximately the same symptoms can be with anemia or kidney problems. Routine blood and urine tests will help clarify the situation, confirming or dispelling such concerns.”
Overwork
If a child is naughty in the evening, mothers usually explain it like this: “I didn’t sleep well during the day” or “Went to class, he got too excited talking with other children there.” Perhaps here it will be enough to put the daily routine in order, give the baby more opportunities for rest, sleep and walks. If the child is excitable in itself, cannot sit still, control his emotions, and at the same time gets very tired, pedagogical problems are superimposed on physical ones, since parents literally do not keep up with the baby. A competent neurologist will help normalize the regimen and strengthen the nervous system, for example, with the help of massage and hardening techniques. A psychologist will advise parents about the features of proper communication with the child.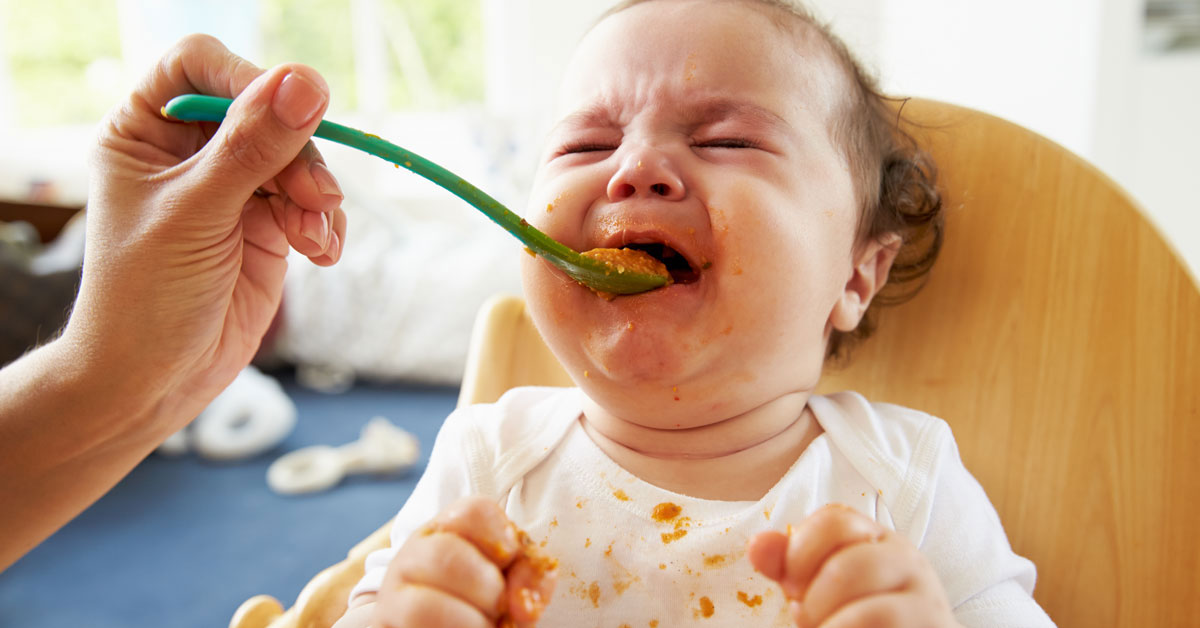
Caprice as a message to parents
Caprice is always a child's message about discomfort, which he cannot express in an acceptable form. If the child is naughty all the time, and you have excluded physical causes (malaise, fatigue), it is worth considering what state of mind he is in. Psychologists note that often the child's inappropriate behavior is a reaction to intra-family disharmony. The grandmother is unhappy with the way the young mother is raising the baby, she is constantly indignant and gives unsolicited advice. Or parents begin to quarrel every time the baby needs to be put to bed. Explicit or unspoken claims and conflicts, a tense situation in the family most affect the child. In this case, his “whims” are the materialization of the discontent and irritation surrounding him. And the situation can be corrected only by establishing relationships in the family.
Certain pedagogical disturbances in the family can also easily become a source of whims. If the parents allow the child absolutely everything, and he simply does not understand the word "no", any attempt to prohibit it leads him almost to hysterics. As a rule, parents are afraid of such a reaction and are ready to do anything to avoid its repetition, which means they continue to indulge the baby. And this inevitably deepens discord in the family and makes its members even more irritable. The opposite situation can also involve the whole family in a vicious circle: they behave with the child too strictly and literally stop all attempts to act independently and make decisions. The kid protests, parents become even stricter with him. The same effect occurs if different family members adhere to diametrically opposed parenting styles - for example, mom is very strict with the baby, and dad allows absolutely everything. All these situations are best dealt with by a family psychologist.
As a rule, parents are afraid of such a reaction and are ready to do anything to avoid its repetition, which means they continue to indulge the baby. And this inevitably deepens discord in the family and makes its members even more irritable. The opposite situation can also involve the whole family in a vicious circle: they behave with the child too strictly and literally stop all attempts to act independently and make decisions. The kid protests, parents become even stricter with him. The same effect occurs if different family members adhere to diametrically opposed parenting styles - for example, mom is very strict with the baby, and dad allows absolutely everything. All these situations are best dealt with by a family psychologist.
Struggle for independence
Parents often mistake the child's desire for independence for whims. From 8–9 months, the baby is already beginning to “test the strength” of the surrounding adults. They give him a toy, he throws it on the floor and immediately demands it back. This can be repeated many times in a row. The child finds out the boundaries of what is permitted, and when communicating with mom, dad or grandmother, the boundaries can be different. At the same time, it is quite easy to distinguish the crying of a real need from a “testing” cry: “checking”, the baby sometimes stops crying, looks around and listens in order to evaluate the effect produced. Such stops are a sign of the need for attention to oneself. This does not mean that in this case it should be ignored, it is better to talk softly with the child, give reasonable arguments, explain your actions, including the necessary refusals or prohibitions. Such verbal contact, if established at birth, makes it easier to distinguish what exactly caused unusual behavior, and to cope with the situation.
This can be repeated many times in a row. The child finds out the boundaries of what is permitted, and when communicating with mom, dad or grandmother, the boundaries can be different. At the same time, it is quite easy to distinguish the crying of a real need from a “testing” cry: “checking”, the baby sometimes stops crying, looks around and listens in order to evaluate the effect produced. Such stops are a sign of the need for attention to oneself. This does not mean that in this case it should be ignored, it is better to talk softly with the child, give reasonable arguments, explain your actions, including the necessary refusals or prohibitions. Such verbal contact, if established at birth, makes it easier to distinguish what exactly caused unusual behavior, and to cope with the situation.
At the age of 2–3 years, the time comes when the child literally answers everything: “I myself!”. Moreover, if attempts to do something on their own are not very successful (spilled, raked, broke, fell), the best strategy would be not to scold the baby, but to celebrate his achievements and offer to bring the matter to the end together.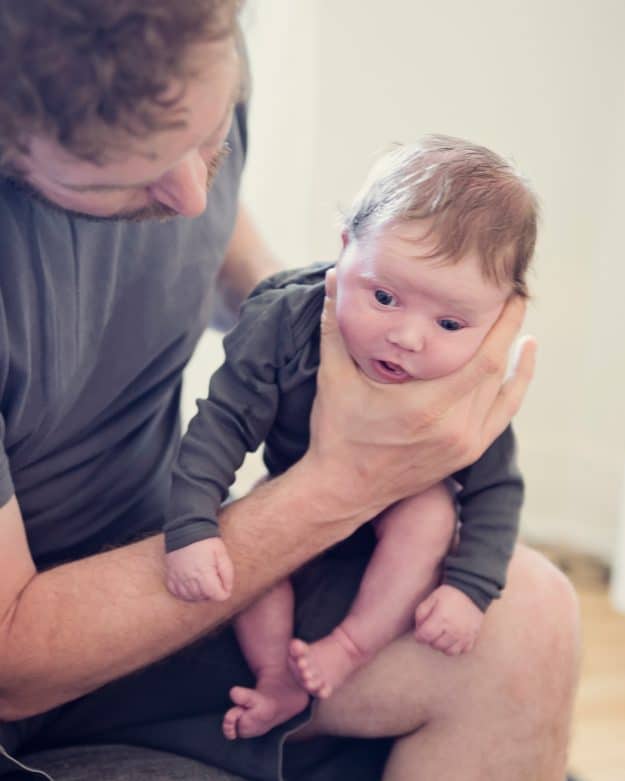 Often, the mere fact of recognizing the child's independent attempts to do something is already enough to live in harmony and reduce "whims" to a minimum.
Often, the mere fact of recognizing the child's independent attempts to do something is already enough to live in harmony and reduce "whims" to a minimum.
Stubborn facts
- Even if the baby likes to cry in principle, certain conditions should alert parents. These are the so-called emergencies.
- A child's loud, pronounced cry for two or more hours, in which no ordinary methods of calming help, is a signal to call a doctor. With problems such as intussusception (intestinal volvulus) or appendicitis, a young child may not have any other obvious external signs other than intense continuous crying. Only a doctor can diagnose the problem. It cannot be said that these cases are frequent. If a mother breastfeeds her baby and is well acquainted with the principles of introducing complementary foods, then volvulus, caused by a sharp transition to unfamiliar food in large quantities and at too early an age, does not threaten her child. Appendicitis in babies is also rare, but since the exact causes of this emergency are still unclear, it cannot be discounted.

Helpful Hints:
- Any inner feelings of a child (enrolling in a kindergarten or school, troubles in the family) can lead to stress. No need to try to protect the baby from difficult situations, but teach him to overcome difficulties. The kid will endure stress much easier if he knows that at home he will always be understood and supported, that for mom and dad he is the best in the world.
Your love and attention are the best "medicines" for stress. Talk with the baby, give him the opportunity to speak out, find out the reasons for the experiences. Play with him, draw, involve him in sports, but try to protect him from excessive loads.
The article was published in the magazine "My baby and I" (2014) and posted on the website krokha.ru.
Hyperactivity in a child | Children's City Hospital
There is a playground where my 4-year-old daughter and I go to play, one boy, Alyosha. He's 5. To say that he is very active is an understatement.
To say that he is very active is an understatement.
Just for the almost 2 years that we have been going there, I have never seen him calmly play in the sandbox, swing on a swing or just sit next to his mother for at least 2 minutes. This is a hurricane, a whirlwind, a tornado - such comparisons can be made. He doesn't walk, he runs. And always. Spinning, spinning, stumbling, falling, pushing, throwing, with anything, in the end, he is exhausted, and departs home with his mother in hysterics ...
When we see Alyosha on the playground, we try to wait for him to leave. Other mothers said among themselves that Alyosha had already been taken to a psychiatrist and diagnosed with hyperactivity...
What is attention deficit hyperactivity disorder?
There are generally two different options. This, in fact, is a painful condition in which the help of a specialist is necessary, and features of the character, temperament and upbringing of the child.
The disease is called Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and has distinct features:
- unable to maintain attention during play and tasks;
- often "does not hear" what is said to him, and has no hearing problems;
- does not finish what he started;
- often loses things that are needed every day - toys, school supplies;
- he finds it difficult to do anything on his own; easily distracted;
- is forgetful in familiar everyday situations;
- constantly on the move, even while eating;
- always does everything with noise; makes aimless movements;
- talks a lot; answers questions without hesitation;
- interferes with others, interferes with games and conversations;
- can't wait, stand in line.

If there are more than six of these signs and they are observed for six or more months in a row, it is highly likely that this is not a character and temperament, but a painful condition that requires the help of specialists.
In addition, children with ADHD simply cannot control themselves, cannot stop and calm down on their own, do not respond to prohibitions and remarks, are often impulsive and aggressive, do not finish anything, are quickly distracted and exhausted, speak quickly and a lot , ask millions of questions, but do not listen to the answers, are clumsy (dropping, breaking things), sleep poorly, they often have intestinal disorders and enuresis.
How to distinguish a simply active child from a hyperactive one
There is a simple way: if a child behaves the same EVERYWHERE - both at home, and at a party, and on the street, and in an unfamiliar environment, and in a children's team - this requires the help of specialists ( child neurologist, psychologist, psychiatrist). Consult, then either calm down and properly educate (more on this below), or confirm your doubts and be treated according to the recommendations of doctors.
Consult, then either calm down and properly educate (more on this below), or confirm your doubts and be treated according to the recommendations of doctors.
If a child is only noisy, restless and active at home, and sits “like a mouse” at a party, these are rather features of the character of such a child. This is exactly what happened to me with my child. The neurologist consulted, said that this is not a disease, but such a temperament; psychologist gave advice.
Why does this condition occur? Is it related to upbringing?
These are the questions that all parents worry about when a child is diagnosed. The number of children with ADHD, unfortunately, is growing every year. And now, according to various experts, they are from 3 to 10%. Boys among them are five times more than girls.
The causes of this condition are not fully known, but:
- environmental degradation;
- infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy;
- pathological childbirth;
- birth injuries
.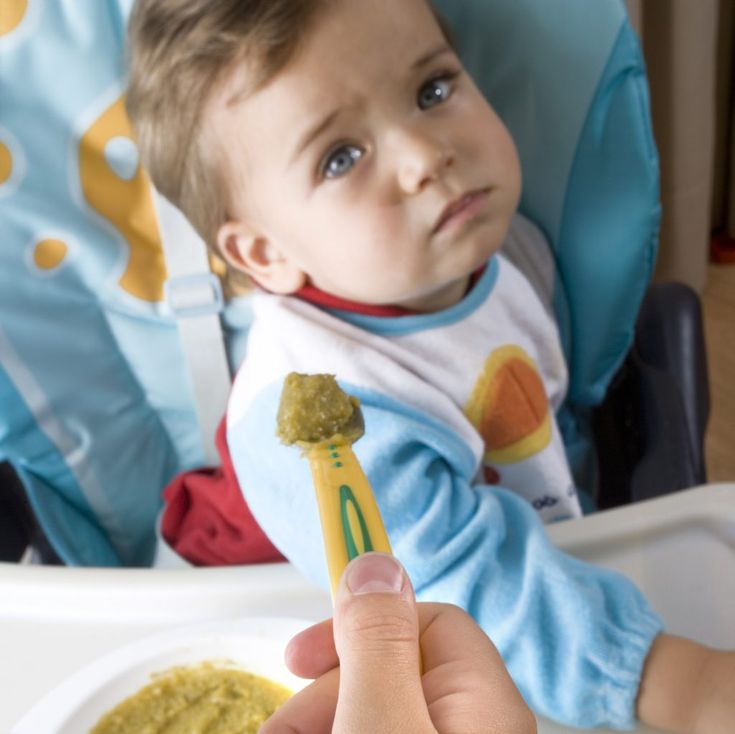 .. ... play an important role in the development of this condition.
.. ... play an important role in the development of this condition.
It is not connected with insufficiently tough upbringing (as some parents think, the child is not just “indulging” and “not obeying”), tougher penalties only worsen the situation with behavior.
"If you scold me and say I'm bad, then you'll know how bad I can be!" - this is the result.
What is the main problem of children with ADHD and what to do about it?
The main problem is that such children cannot adapt to society. Due to their impulsiveness, uncontrolled aggression, such children ignore the generally accepted rules of behavior, harming themselves and others. Which inevitably leads to problems. With development, study, communication.
And one more thing. According to statistics, 80% of people who are in prison were hyperactive children. Think about it and do not delay treatment. It won't go away on its own!
How can parents help such a child?
Dealing with Hyperactivity in a Child I have a very active child myself. This, thank God, is just such a temperament, but it is also suitable for children diagnosed with ADHD. And the psychologist taught us how to properly handle it, in order to live a little more ourselves.
This, thank God, is just such a temperament, but it is also suitable for children diagnosed with ADHD. And the psychologist taught us how to properly handle it, in order to live a little more ourselves.
- Try to establish contact with the child before demanding anything from the child. Touch, hold hands.
- Look into his eyes and then talk to him. Why do it? Because when a child is busy with something, passionate, playing - he is all there, in his experiences, and does not hear you. It really helps - I take my daughter by the hand, look into her eyes, tell her what I need her to do, and in most cases it helps.
- Set permanent rules. Stick to it strictly. The rules for the child should be clear and simple. For example, if today you can’t eat sweets before meals, touch someone else’s dog, jump from a swing, be rude to your grandmother, open a gas valve, then tomorrow it’s impossible.
- It is important to follow the sequence of actions, break complex tasks into several simple ones - this will make it easier for the child to cope.
 How do I apply it? I say: “Let's clean the children's room. First we make the bed. To do this, we straighten the sheets, pillows, cover with a bedspread. Then we collect toys. Cars - in a box, dolls - on a doll table, cubes - in a box. And so on, until we remove everything.
How do I apply it? I say: “Let's clean the children's room. First we make the bed. To do this, we straighten the sheets, pillows, cover with a bedspread. Then we collect toys. Cars - in a box, dolls - on a doll table, cubes - in a box. And so on, until we remove everything. - Always observe the regime in everything. Literally by the hour, get up, eat, walk, go to bed. Always, any day of the week. It really helps. And adults too.
- Praise. But wisely. Something done well - praise. Listened - praise. Find something that your child is best at and praise for it. My daughter, for example, loves to help prepare her dad's breakfast. And literally melts with pleasure when I praise her for it. And the mood is good for half a day.
- Try to spend excess energy. Excess energy goes away - the child becomes calmer. Checked on myself. It is important not just to run, but to “put energy in the right direction” - dancing, acrobatics, athletics, swimming pool ...
- If you are going somewhere (travel, guests, shop), prepare in advance.










