Best early baby foods
The Best First Foods for Babies 6 to 9 Months – Happiest Baby
By Happiest Baby Staff
On This Page
- Best Baby Foods at 6 Months
- Best Baby Foods at 7 Months
- Best Baby Foods at 8 Months
- Best Baby Foods at 9 Months
You've spent the first six months of your baby's life making sure that they are nourished with breastmilk or formula. As they grow and thrive, you might notice that your little sprout shows you some signs that they are ready to graduate from the bottle or breast to solid foods. If your baby can sit up and hold their head up, that's a great first sign! What's more, if they bring objects to their mouth and show an interest in what you are eating, your curious kiddo might be ready to start eating solid foods.
But what should you feed your baby? Here’s a list of perfect starter foods for your baby from ages 6 to 9 months.
Best Baby Foods at 6 MonthsAt 6 months, babies may be starting to chew. Though this skill won’t be mastered just yet, they are typically ready to get messy with some mushy, pureed eats—helping them learn about flavor and texture. At this age, the goal is not to satiate your baby with full meals of solid foods but rather to get your child curious and excited about their culinary options.
Because babies are growing so fast, their needs for iron are high to prevent iron-deficiency and support their overall health. Offer your little one iron rich foods like—infant cereal (read up on why you may want to skip rice cereal), well-cooked meat, poultry, mashed beans, and lentils. To keep your baby safe from choking, avoid adding solids like cereal to baby bottles.
Here are some great first foods for Baby to try:
- Infant oat, grain, or barley cereals mixed with breastmilk or formula and spoon-fed to your baby
- Sweet potato puree
- Squash puree
- Pea puree
- Carrot puree
- Mashed banana
- Mashed avocado
- Mashed or pureed beans
- Mashed or pureed lentils
- Pureed meats (beef, chicken, or turkey)
- Soft, falling apart meats (salmon, beef, chicken, turkey)
Check out more of our favorite first food purees. Or, if purees aren’t your thing, read up on how to start baby-led weaning.
Or, if purees aren’t your thing, read up on how to start baby-led weaning.
By 7 months old, your baby will probably be eating more solids but not enough to replace breastmilk or formula as their primary source of food. The goal for this month is to keep introducing solid foods to your baby. What's fun is by 7 months, you can get more creative with mixing flavors and adding textures.
Here are a few nutritious and delicious food combos to try with your baby:
- Peas pureed with breastmilk (or formula), sweet potatoes, or squash
- Kale pureed with blueberry, squash, potatoes, sweet potatoes, peas, pears, or bananas
- Apples pureed with cauliflower, carrots, pears, prunes, or beets
- Beef pureed with broccoli
- Chicken pureed with carrots and potatoes
- Chickpeas pureed with bananas, apples, or sweet potato
- Sweet potatoes pureed with red bell pepper
Seven months is also the perfect age to start giving your baby a plate, bowl, and plastic utensils so they can begin to practice feeding themselves. If your baby is teething, you can place frozen chunks of fruit in a sieve feeder/mesh bag that allows them to gnaw on the fruit without choking. Learn more about helping your baby use a fork and spoon!
If your baby is teething, you can place frozen chunks of fruit in a sieve feeder/mesh bag that allows them to gnaw on the fruit without choking. Learn more about helping your baby use a fork and spoon!
By 8 months, your baby is likely eating more solids and relying a little less on milk as a primary meal (though it’s still where they get the bulk of their nutrition!). And they’re probably having lots of fun learning how to use their hands to feed themselves. Something else to consider: Babies should be exposed to potential allergen foods (like peanuts, tree nuts, eggs, and fish) before their first birthdays to help prevent future food allergies. Starting at 6 months of age, peanut butter is safe to introduce as long as you are comfortable giving it to your baby.
In fact, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans says that babies can begin having these foods when they start eating solids. But many families often feel more comfortable waiting to introduce these foods until around this age. Of course, consult with your little one’s pediatrician if you have concerns about potential allergen foods.
Of course, consult with your little one’s pediatrician if you have concerns about potential allergen foods.
Here are some foods to add to your repertoire:
- Whole eggs, scrambled
- Nut butter thinned out with water and mixed with cereal (nut butters are sticky and can cause choking)
- Fully cooked fish, like salmon or tuna
- Full-fat yogurt
Here are some preparation ideas:
- Well-cooked (think over-cooked until falling apart) pasta such as elbows or alphabet shapes
- Mashed meat with mashed or ground vegetables such as peas and potatoes or kale and squash
- Rainbow on a plate: Using tiny pieces of soft, strained, pureed, and mashed food options, look for a variety of colors to offer. Some fun options could include banana, avocado, sweet potato, peas, blueberry, raspberry, cheese, and chicken.
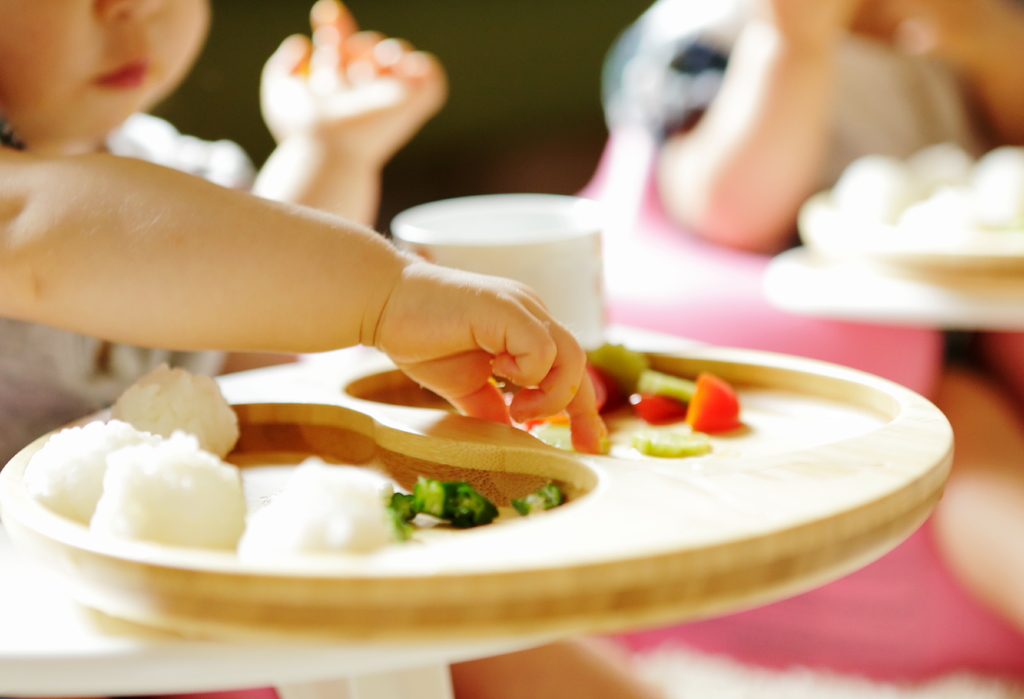
Though there’s a greater variety of foods babies eat now, formula or breastmilk continues to be their primary source of nutrition until age 1. At 9 months old, babies get more comfortable with self-feeding and eating the foods their families enjoy. After all, eating solid foods is a sensory wonderland of texture, smells, and tastes. Not to mention all that fun making messes with those adorably curious fingers.
At 9 months old, babies get more comfortable with self-feeding and eating the foods their families enjoy. After all, eating solid foods is a sensory wonderland of texture, smells, and tastes. Not to mention all that fun making messes with those adorably curious fingers.
As you begin to focus on meal planning for your baby, there are few things to keep in mind:
- Babies need four to five servings of fruits and vegetables a day. A serving size for a 9-month-old is less than a quarter cup.
- "Eat the rainbow" is excellent advice because it gives your baby exposure to lots of different fruits, vegetables, grains, and starches.
Here are a few menu ideas to help meal plan for your baby…
Breakfast Ideas for Babies
These morning meals pack a nutritional punch—and don’t forget to check out all of our favorite breakfast ideas for babies:
- Soft fresh fruit cut up in small pieces (think: banana, raspberries, or blueberries)
- Whole-grain waffles or pancakes
- Unsweetened oatmeal made with breastmilk or formula combined with cut-up and cooked apples and pears or banana slices.
 (It is essential to steam the apples or pears to make them soft enough for your baby to mash with their gums.)
(It is essential to steam the apples or pears to make them soft enough for your baby to mash with their gums.) - Full-fat yogurt mixed with mashed or pureed berries such as blueberries, blackberries, strawberries, or raspberries
- Soft scrambled eggs
- Veggie frittata
Lunch Ideas for Babies
- Spread hummus on soft crackers or bread
- Grilled cheese sandwich with cooled tomato soup
- Macaroni and cheese with cooked veggies like peas and carrots mixed in
- Pizza bites with chopped bits of spinach in the sauce and melted shredded cheese
- Quesadilla made with pureed spinach, squash, or beans
Snack Ideas for Babies
Babies this young won’t likely need to snack too much (remember, breastmilk or formula will provide the majority of your little one’s nutrition). Still, it’s not a bad idea to have snacks on hand for when your mini muncher needs something to eat that’s not quite a meal. A few baby snack ideas:
- Apple and carrot slaw
- Cheese slices
- Full-fat plain yogurt
- Hard-boiled egg
- Avocado slices
- Muffins made with fruits, veggies, and/or whole grains
- Fruit and veggie pouches
- Sugar-free, whole-grain cereal, like plain Cheerios
Dinner Ideas for Babies
To help your baby get and stay excited about eating solid foods, serve a version of whatever the family is having for dinner. Remember to steam or mash, grind or chop foods into appropriate softness and sizes to prevent choking. Some baby dinner ideas:
Remember to steam or mash, grind or chop foods into appropriate softness and sizes to prevent choking. Some baby dinner ideas:
- Pasta with softened vegetables
- Well-cooked rice, soft veggies, and chicken
- Baked sweet potato with butter or cheese
- Beans or lentils served with rice and veggies
- Flaky fish served with steamed zucchini
There are endless variations on what you can serve your baby for dinner. As long as your baby is safe and happy, try to encourage lots of food exploration!
You must not feed any child under the age of 1 year honey, cow’s milk, juice, hard foods like candy, raw vegetables, popcorn, or sticky foods like peanut butter, as these each present choking hazards.
Learn more about feeding your baby:
- The Happiest Baby Feeding Guide
- The Benefits of Homemade Baby Food
- The Best Store-Bought Baby Food
***
REFERENCES
- Unlocking Opportunities in Food Design for Infants, Children, and the Elderly: Understanding Milestones in Chewing and Swallowing Across the Lifespan for New Innovations.
 Journal of Texture Studies, August 2017
Journal of Texture Studies, August 2017 - Complementary Feeding: A Position Paper by the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) Committee on Nutrition, Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, January 2017
- Infant Formula Feeding Practices Associated With Rapid Weight Gain: A Systematic Review, Maternal & Child Nutrition, July 2018
- Solid Food Introduction and the Development of Food Allergies, Nutrients, November 2018
- US Department of Agriculture: Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020-2025
View more posts tagged, feeding
Have questions about a Happiest Baby product? Our consultants would be happy to help! Connect with us at [email protected].
Disclaimer: The information on our site is NOT medical advice for any specific person or condition. It is only meant as general information. If you have any medical questions and concerns about your child or yourself, please contact your health provider.
It is only meant as general information. If you have any medical questions and concerns about your child or yourself, please contact your health provider.
The Ultimate Guide to Baby’s First Foods from 4-6 Months Old
If you have a baby between 4 and 6 months old, you’re probably starting to think about what their first foods will be…which means you probably have questions about baby’s first foods, too! Things like: “When should I start?” “Do I need to stick to single-ingredient foods?” and “How do I safely introduce common allergens like peanut butter without freaking out?!” Chances are, you miiiiight be a little overwhelmed at the idea of first foods, too. I know it’s a lot to think about, but the good news is that you’ve found your way here! And now that you’re here, I can help.
As a mom of two and a pediatric dietitian, I’m writing this post to help you navigate the nerves and the new chapter that is buying, preparing, and serving up baby’s first foods! Whether you’re going for purees, baby-led weaning, or a combination of both, consider this your ultimate guide to what first foods to serve and how to introduce them to your baby safely.
P.S. Don’t forget to save this post! I know it’s one you’ll want to come back to again and again.
This post contains affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Skip right to the first foods info you’re looking for:
- When To Serve Baby Their First Foods
- Safety For Baby’s First Foods
- Purees vs. Baby-Led Weaning: What’s Right For You?
- The Best Foods To Introduce Baby To Between 4 & 6 Months Old
- The Ultimate Baby’s First Foods List
- Best Finger Foods & Baby-Led Weaning First Foods
- The Best Pureed First Foods
- The Best Easy-To-Make First Foods
- The Most Nutritious First Foods
- The Best Vegetarian First Foods
- Foods That Should Be Avoided
- Baby’s First Foods Chart: What, When & How To Serve Common First Foods to 4- to 6-Month-Old Babies
- First Foods For Babies With Allergies
When To Serve Baby Their First Foods
Although some people will serve baby’s first foods earlier, I recommend starting solids closer to the six-month mark. You want to avoid adding rice cereal or any other food to their bottle, and instead, begin solids when they display the signs of readiness listed below. By waiting to serve baby’s first foods until they’re truly ready, you increase their safety and chances of success as a new eater.
You want to avoid adding rice cereal or any other food to their bottle, and instead, begin solids when they display the signs of readiness listed below. By waiting to serve baby’s first foods until they’re truly ready, you increase their safety and chances of success as a new eater.
Signs of Eating Readiness
Your baby is ready to start solids if they:
- Can sit upright
- Can sit unsupported
- Have good head and neck control
- Have some practice bringing toys or objects from their hand to their mouth
- Show an interest in food (By reaching for what you’re eating, intently watching as others eat, etc.)
Can I Give My 4-Month-Old Baby Food?
Some pediatricians may okay solids around four months, but again, I generally recommend waiting until closer to six months, and when baby is displaying those signs of readiness.
There are more benefits to waiting than there are to starting earlier. Before six months, babies get everything they need from breastmilk or formula, so starting solids early won’t help them sleep better, grow faster, or, you know, become a professional athlete!
If you want to get your four- or five-month-old baby involved in mealtime, I recommend getting them acquainted with food and eating in these ways:
- Sit them near you while you’re eating
- Give them a silicone spoon to hold (I like NumNum GooTensils, EZPZ Tiny Spoons, and Olababy Training Spoons) and let them practice bringing it to their mouth
- Give them teething toys, like Sophie, or this elephant, to desensitize the gag reflex
FAQ: Do Formula- and Breast-Fed Babies Have Different Nutritional Needs?
Formula and breast milk are both completely nutritionally satisfactory for the first six months of life and beyond. So when it comes to starting solids, it doesn’t matter whether your baby has been receiving breast milk or formula.
So when it comes to starting solids, it doesn’t matter whether your baby has been receiving breast milk or formula.
That said, babies who are exclusively breastfed should receive a Vitamin D supplement, as levels in breastmilk are low. Formulas on the other hand are typically fortified with Vitamin D, so formula-fed babies don’t need one. Another thing to consider for a baby’s nutrition is iron. Babies build up an iron reserve from their mothers while in utero, but these stores begin to decline around six months of age for all babies.
Safety For Baby’s First Foods
Safety is a huge concern for parents when starting solids. Whether you start with baby foods, purees, or baby-led weaning, there are certain parameters to follow to make sure baby’s intro to food is safe and successful.
Choking Hazards for 4- to 6-Month-Old Babies
Choking hazards for babies ages four to six months old include any foods that are hard, crunchy, sticky, or chewy, as well those that are dangerous shapes.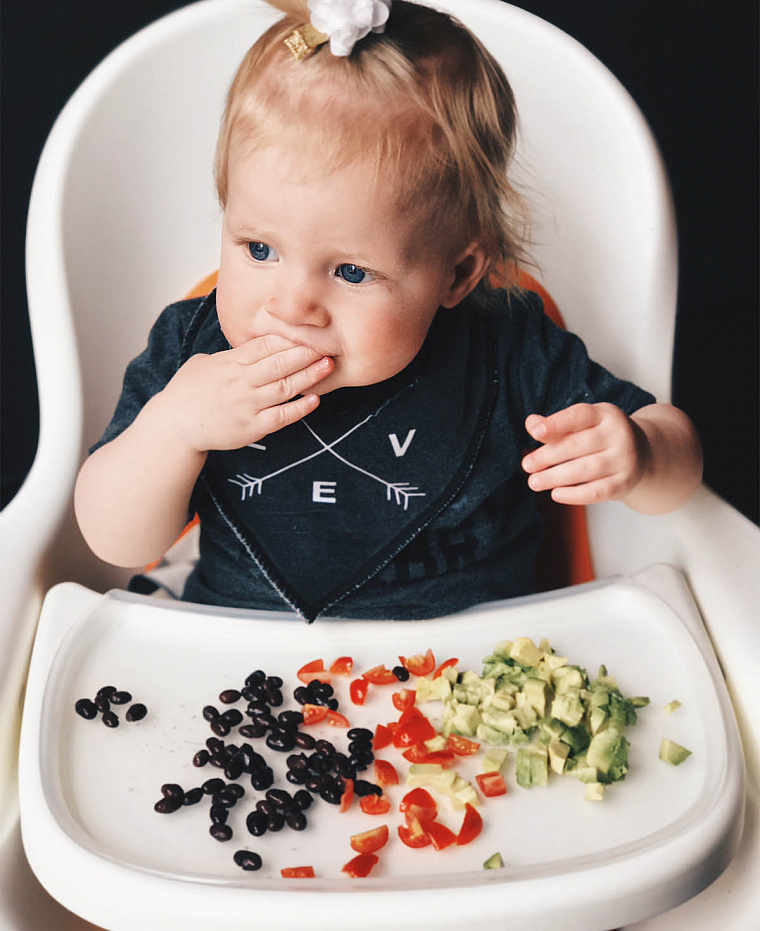
Common hazardous foods are:
- Chips
- Popcorn
- Pretzels
- Raw Apple
- Globs of Nut Butter
- Hot Dogs
- Grapes
- Large seeds (sunflower, pumpkin, for example)
- Whole nuts
Many of these foods can be prepared safely to minimize the risk of choking, but they remain a choking hazard if they’re in their “natural” states until children turn four years old.
You can minimize choking risks by making sure your child is seated upright and strapped in a high chair with good trunk support. Foot support on a high chair is also helpful when your baby is starting out because it reinforces their stability, and when they’re more stable, they can chew and swallow more safely!
AAP & CDC Recommendations
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommend starting solids around six months of age, but not before four months. Again, some pediatricians may okay solids around four months of age, but I usually recommend waiting until six months to make sure baby is showing the physical signs of readiness I outlined above.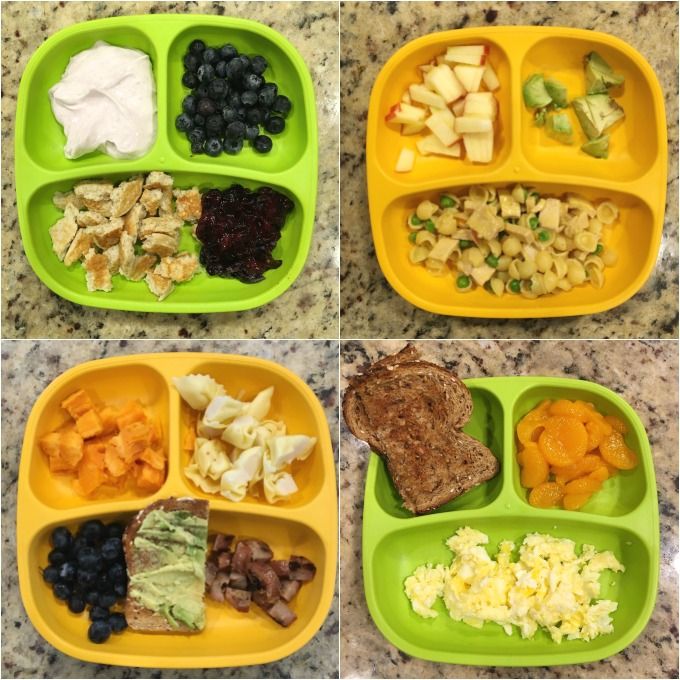
The one exception may be for introducing certain allergens to certain infants, depending on their inherent level of risk. Speak with your pediatrician or allergist to see if they want to start your baby on certain foods early.
Purees vs. Baby-Led Weaning: What’s Right For You?
Before you serve baby their first foods, you’ll need to decide what kinds of foods you want to offer. And while there’s a lot of dialogue and opinions about the “best” way to feed a baby, I want you to know there isn’t one right way to do this. You can start with purees or baby-led weaning, or you can do a combination of both.
Tip: If you take a puree approach, help them learn to self-feed by offering baby preloaded spoons and letting them bring the food to their mouth.
Babies are very intuitive about getting the nutrition they need, so full permission to opt for the feeding style that’s comfortable for you. They’ll be able to get enough to eat either way! If simple textures feel easier and lower-stress for you, start with purees. If you’re ready to tackle preparing foods in a way that’s safe for baby, go for baby-led weaning. And if you’re on the go a lot or need a caretaker to feed your baby sometimes, maybe a hybrid approach is best. It truly doesn’t matter as long as you’re helping them foster independence in eating, and offering a variety of different foods.
If you’re ready to tackle preparing foods in a way that’s safe for baby, go for baby-led weaning. And if you’re on the go a lot or need a caretaker to feed your baby sometimes, maybe a hybrid approach is best. It truly doesn’t matter as long as you’re helping them foster independence in eating, and offering a variety of different foods.
One thing that DOES matter when it comes to feeding your baby is letting them be in charge of how much they eat (while you learn to interpret their hunger and fullness cues). And you can do this whether you’re feeding them purees or finger foods.
Baby Signs Of Hunger:
- Reaching for food
- Moving toward the spoon
- Opening their mouth
- Pointing to food
- Excited at the sight of food
Baby Signs Of Fullness:
- Turning away from food
- Batting spoon away
- Clamping mouth shut
- Playing with/throwing food
- Significantly slowed pace of eating
- No longer showing interest
The Best Foods To Introduce Baby To Between 4 & 6 Months Old
A common question I get is, “What baby foods should I introduce first?” And really, there isn’t one “best” first food. You do not have to start with only baby cereal or only veggies or fruits. In fact, you shouldn’t! Research shows that introducing babies to a wide variety of foods early on is what’s most beneficial.
You do not have to start with only baby cereal or only veggies or fruits. In fact, you shouldn’t! Research shows that introducing babies to a wide variety of foods early on is what’s most beneficial.
That said, my favorite first food is avocado! It’s a wonderful source of healthy fat, and it’s loaded with vitamins and minerals. Fat is essential to the developing brain and central nervous system, so we want to prioritize it within a baby’s first foods and make sure it’s completely unrestricted during their first two years of life.
(We also want to prioritize iron, because it’s a common dietary deficiency, and our babies begin to run out of the iron stores they got in utero by about six months.)
It’s Okay If Baby’s First Foods Have Multiple Ingredients!
You may choose to serve solely single-ingredient foods like avocado or sweet potato, but know that it’s not necessary to do so. It can be really helpful to serve a variety of new foods together, so they get used to different tastes and textures. Plus, there are nutritional benefits to mixing foods. For example, yogurt—a common first food for babies—can be fortified with mashed fruit, nut butter, or hemp seeds to up the nutritional value. (But if you ever notice a reaction or suspect an allergy to a component of a food combination you’ve been serving, stop serving the suspected allergen and contact your pediatrician.)
Plus, there are nutritional benefits to mixing foods. For example, yogurt—a common first food for babies—can be fortified with mashed fruit, nut butter, or hemp seeds to up the nutritional value. (But if you ever notice a reaction or suspect an allergy to a component of a food combination you’ve been serving, stop serving the suspected allergen and contact your pediatrician.)
PSA: Skip The Baby Cereal
The recommendations from years past telling parents to start with rice-based infant cereals are outdated now. Rice cereals aren’t super nutritious, and we don’t want to rely too much on rice due to potential exposure to arsenic. So instead of cereals, offer new foods in safely-prepared forms. This is way more nutritious, and it exposes them to different flavors, textures, and nutrients which are beneficial for growth and development and can protect them against food allergies and picky eating.
The Ultimate List of Baby Foods
I’m covering allll the best kinds of baby foods separately, so you get all the juicy info and context you need. Then, I’m combining them all into one big, bad, comprehensive list of the best first foods for baby at the end.
Then, I’m combining them all into one big, bad, comprehensive list of the best first foods for baby at the end.
SKIP TO THE LIST
Best Finger Foods & Baby-Led Weaning First Foods
For baby’s first foods, I like to suggest approachable options like avocado, sweet potato, and banana. These can be prepared and served baby-led-weaning-style by cutting them in wedges or crescent shapes that can be gripped with a palmar grasp. Bananas can be served as halves or in thirds-long ways. Just stick to serving items in longer shapes, about the width of two adult fingers, for the first few months of BLW. This way, baby can hold them and bring them to their mouth. Once your baby is a little bit older—usually around 9 months—many foods can be served safely in smaller pieces.
The Best Pureed First Foods
If you’re going the puree route, you can start with many of the same foods. Just mash up the sweet potato, avocado, banana—or whatever else, really!—and serve those as purees. You may want to thin them some with breastmilk or formula.
You may want to thin them some with breastmilk or formula.
But shortly after starting with these foods, I would move on to introducing allergenic foods, because the early and repeated introduction of allergenic foods can be protective against the development of food allergies in babies, specifically for peanuts. Foods like yogurt and peanut butter may be good early options for allergenic introductions and are already in pureed form. Just start with small amounts.
The Best Easy-To-Make First Foods
Foods that are naturally soft are the easiest to prepare for young eaters. Banana, yogurt, apple sauce, and avocado are all great options that are easy to serve with little to no prep. You can also mix creamy nut butter with yogurt and incorporate other mashed fruits, like raspberries and blackberries, to ramp up the nutritional value while keeping prep extremely low.
Don’t feel like you need to shy away from foods that aren’t naturally soft, either! Many other fruits and veggies, like sweet potato, broccoli, and pears, can also be safely served with simple steaming or roasting techniques. Just make sure to cook these foods until they’re soft enough to be smashed between your fingers, so baby can safely enjoy them, and present them in a shape or style that they can safely navigate. (Soft foods can also be served to them on a pre-loaded spoon if they can’t be eaten by hand, yet.)
Just make sure to cook these foods until they’re soft enough to be smashed between your fingers, so baby can safely enjoy them, and present them in a shape or style that they can safely navigate. (Soft foods can also be served to them on a pre-loaded spoon if they can’t be eaten by hand, yet.)
Low-Prep First Food Options:
- Banana
- Yogurt (Can mix with mashed berries or nut butter)
- Apple Sauce
- Avocado
- Steamed Veggies (Soft enough to mash between your fingers)
The Most Nutritious First Foods
There are so many great, nutrient-dense choices for baby’s first foods that are safe by six months of age no matter what type of foods you serve. (But it’s true that, if you take a baby-led weaning approach, you’ll probably have more options.) Sardines and salmon (fresh or canned) are both loaded with omega-3 fatty acids, DHA, protein, and tons of vitamins and minerals, which make them highly nutritious first foods! From the plant kingdom, sweet potato and avocado are nutrient-dense foods with a wide variety of vitamins and minerals including vitamin A, vitamin B6, vitamin C, and magnesium.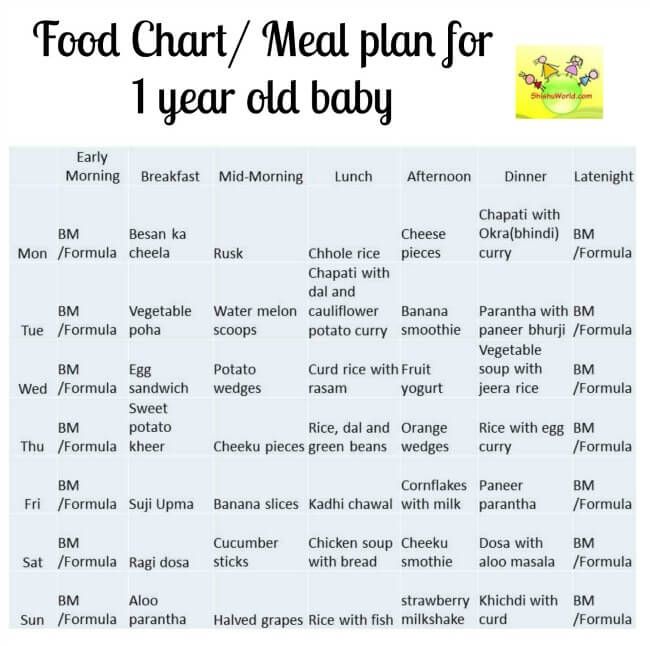
The Best Vegetarian First Foods
Vegetarian foods are some of the best first foods for baby! There are tons of wonderful and nutritious fruit and veggie options that suit young eaters, like berries, bananas, avocados, potatoes, broccoli, squash, and many others. Non-produce vegetarian items are great first foods for baby, too. Think tofu strips, eggs (yolk and white), beans, nut butter, and oatmeal.
Just be sure you serve these in safe shapes and forms, and that they’re soft enough to be mashed between your fingers. Always avoid serving things that are hard, sticky, or chewy, and keep in mind that many raw vegetables and fruits are choking hazards (like celery and apple).
Foods That Should Be Avoided
While most foods have a place in most diets, there are some foods to avoid serving your 4- to 6-month-old baby:
Added Sugar
To make sure our babies get the most nutrition possible during this important phase of growth and development, it’s best to avoid added sugar for children under two. Added sugar doesn’t have much nutritional value, so it’s best to limit it as much as possible and avoid it altogether if possible.
Added sugar doesn’t have much nutritional value, so it’s best to limit it as much as possible and avoid it altogether if possible.
Want to offer baby fun, homemade foods like cookies, bars, and muffins once they are fully established on solids? You still can! Just use the recipes in my No Sugar, Still Sweet cookbook, where everything is sweetened with fruit alone.
Honey
Babies should strictly avoid honey before 12 months of age. Honey can be contaminated with spores of a bacteria called clostridium botulinum. In babies under one, these spores can multiply and produce a dangerous toxin that causes infant botulism.
Related: Honey for Babies & Toddlers
Sodium
Finally, sodium should be limited. For babies ages four to six months, the recommended sodium limit intake for a day is 110 mg, which includes any sodium present in breast milk and/or formula.
Fruit Juice
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends no fruit juice before 1 year of age.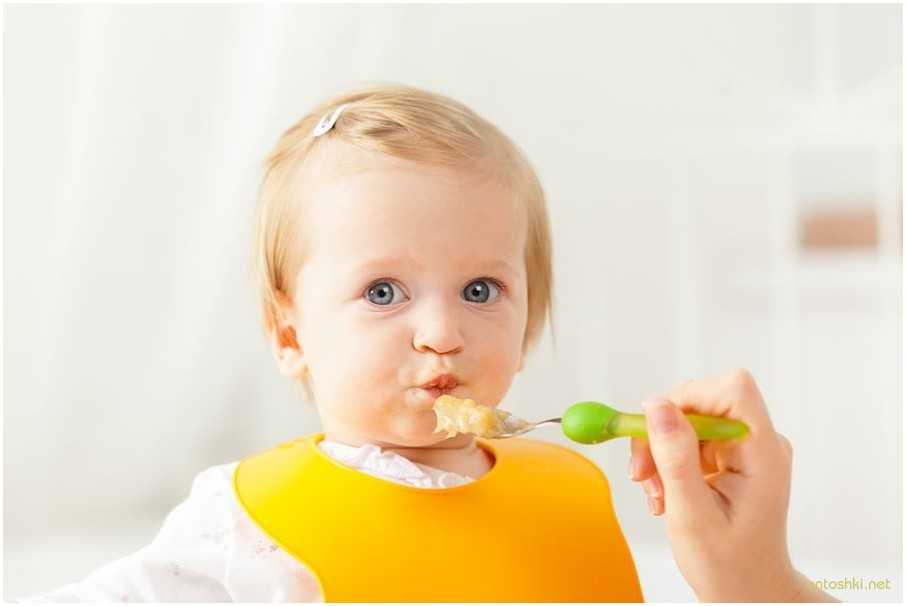 Juice offers very few nutritional benefits and therefore isn’t a helpful addition to a baby’s diet.
Juice offers very few nutritional benefits and therefore isn’t a helpful addition to a baby’s diet.
- Under 1: No Juice
- Age 1-3: 4 Oz Daily Max
- Age 4-6: 4-6 Oz Daily Max
- Age 7-18: 8 Oz Daily Max
The Ultimate Baby’s First Foods List
- Avocado
- Sweet Potato (Mashed or Steamed)
- Broccoli (Steamed or Roasted)
- Pears (Steamed or Roasted)
- Butternut Squash
- Mango
- Banana
- Yogurt*
- Nut Butter* (Mixed-In To Purees or Spread Thin on Toast)
- Oatmeal
- Apple Sauce
- Mashed Raspberries
- Mashed Blueberries
- Mashed Blackberries
- Canned Sardines*
- Canned Salmon*
- Potatoes (Mashed or Steamed)
- Squash (Steamed or Roasted)
- Tofu Strips*
- Baby-Safe Eggs* (Try omelet-style and cut into strips!)
- Beans (Mashed)
*Common Allergens
Baby’s First Foods Chart: What, When & How To Serve Common First Foods to 4- to 6-Month-Old Babies
| BABY’S FIRST FOOD | WHEN TO SERVE | HOW TO SERVE |
| Avocado | 6 Months or Later | Mashed, mixed-in to sauces, and purees, or in wedge shapes baby can grip (BLW). |
| Oatmeal | 6 Months of Later | Prepare with breastmilk or formula. Option to mix in yogurt, nut butter, mashed berries, or mashed banana. |
| Banana | 6 Months or Later | Mashed, mixed into sauces and purees, cut in halves or third-long pieces (BLW). |
| Sweet Potato | 6 Months or Later | Roasted or steamed so they’re soft enough to mash between your fingers. |
| Mango | 6 Months or Later | Cut into wedge-shaped pieces that baby can grip. Or, give baby the pit to work on! |
| Eggs (Common Allergen) | 6 Months or Earlier (If advised by a pediatrician or allergist) | Prepare eggs omelet-style and cut them into strips baby can grip. |
| Yogurt (Common Allergen) | 6 Months or Earlier (If advised by a pediatrician or allergist) | Serve yogurt as-is or mix it into sauces, oatmeals, or purees. |
| Nut Butter (Common Allergen) | 6 Months or Earlier (If advised by a pediatrician or allergist) | Mix nut butters into oatmeal or purees, or spread them thinly over toast. |
| Berries | 6 Months or Later | Mash berries into a thicker, jam-like consistency before serving. Consider mixing mashed berries into other foods. |
| Tofu (Common Allergen) | 6 Months or Earlier (If advised by a pediatrician or allergist) | Cut into thin strips that baby can grasp and fry them up in a pan. Serve cool or warm, not hot. |
| Broccoli | 6 Months or Later | Steamed or roasted so it’s soft enough to mash between your fingers. |
| Apple Sauce | 6 Months or Later | As-is or mixed in to oatmeal, yogurt, or purees. |
| Canned Sardines (Common Allergen) | 6 Months or Later | Whole piece or mashed with other foods. |
| Honey | 1 Year or Later | At 1 year or later, serve mixed-in to yogurt, sauces, or purees, or spread thinly on toast. |
| Fruit Juice | 1 year or Later | At 1 year or later, offer up to 4 oz per day. |
| Sugar | 2 Years or Later | Avoid added sugar before age two, then introduce it gradually and only as-needed. |
First Foods For Babies With Allergies
Food allergies have grown in prevalence over the last 50 years, and it’s now estimated that about 7% of babies have a food allergy! And while that can make choosing a baby’s first foods a little scary, the good news is that up to 80% of kids can grow out of their food allergies. (Especially when those allergies are milk and eggs!)
Important Information on Allergic Reactions & Introducing Allergens
For at least the last decade, parents were told to wait until 12 months or older to introduce the top eight allergens (peanut, tree nuts, eggs, milk, wheat, soy, fish, and shellfish) to their babies. Now, things are different. Today, we recommend introducing allergenic foods to your baby when they start solids, which, for most children, is around six months old.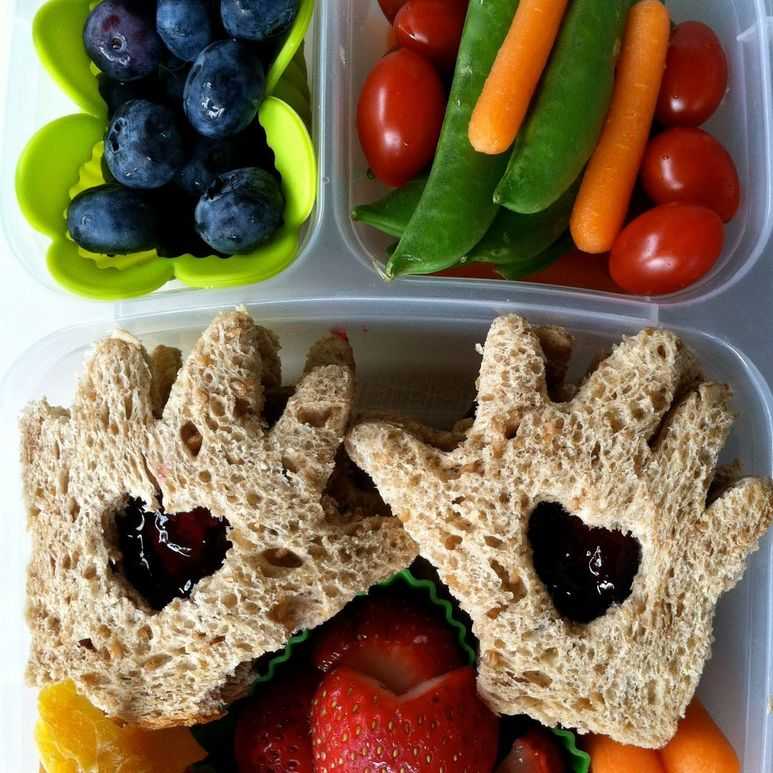 Introducing allergenic foods at this point in your baby’s development can reduce the risk of developing some food allergies—especially allergies to eggs and peanuts.
Introducing allergenic foods at this point in your baby’s development can reduce the risk of developing some food allergies—especially allergies to eggs and peanuts.
For Babies With Known Allergies
If your baby is already known to have a food allergy, do not introduce that food. But, if baby has certain risk factors WITHOUT a confirmed allergy (like eczema or a family member with a food allergy), consult the pediatrician. You may be referred to an allergist who will determine the best course of action with an introduction.
Introducing Allergens: What To Watch For
Mild allergic reactions may look like new hives around the mouth or face.
More severe reactions can include:
- Vomiting
- Lip Swelling
- Widespread Hives
- Face Or Tongue Swelling
- Difficulty Breathing
- Changes In Skin Color
- Sudden Lethargy Or Limpness
If you notice any of these severe signs, seek emergency medical help immediately.
Make Starting Solids Simple
I know that getting ready to start serving your baby their first foods is nerve-wracking. But with the right info (which you now have) and prep (which you’re equipped to do), I promise you it can be a great experience. Now that you know all the things about safety, allergic reactions, which foods to serve, and how to serve them, go in with your bases covered and just enjoy the time spent with your little one.
I also know that if you decide to go with solids, you might be a little extra nervous about things like gagging and making all foods baby-safe. And, I get it! These things can be intimidating the first few times. Lucky for you though, you’re not alone! You’ve got me in your corner. I’ve been there before, I’ve helped so many parents navigate through it, and I know you can do it, too.
To help you up your confidence, ditch the unnecessary doubts, and feed them well right from the start, I put together my research-backed Simply Solids guide. If you’re about to start—or already on—your baby-feeding journey, Simply Solids is a must-have.
If you’re about to start—or already on—your baby-feeding journey, Simply Solids is a must-have.
START THE CAR! Simply Solids Is Usually $15, But Right Now It’s Free
.Trust me, you’ll be kicking yourself if you don’t grab your copy right the heck now 👇
Get The Free Guide
Baby’s First Foods
Kacie Barnes, MCN, RDN, LD
Summary of baby first foods 4 to 6 months some ideas in case you want a printer friendly list!
No ratings yet
Print Recipe Pin RecipePrep Time 5 mins
Cook Time 5 mins
Total Time 10 mins
Course Breakfast, Dinner, lunch
Cuisine American
Servings 2 servings
Calories 50 kcal
- Avocado
- Oatmeal
- Banana
- Sweet Potato
- Mango
- Eggs (Common Allergen)
- Yogurt (Common Allergen)
- Nut Butter (Common Allergen)
- Berries
- Tofu (Common Allergen)
- Broccoli
- Apple Sauce
- Canned Sardines (Common Allergen)
Mashed, mixed-in to sauces or purees, or in wedge shapes baby can grip (BLW).

Prepare with breastmilk, formula, canned coconut milk or water. Option to mix in yogurt, nut butter, mashed berries, or mashed banana.
Mashed, mixed into sauces and purees, cut in halves or third-long pieces (BLW).
Roasted or steamed so they’re soft enough to mash between your fingers. Or, serve mashed with a spoon.
Cut into wedge-shaped pieces that baby can grip. Or, give baby the pit to work on!
Serve yogurt as-is or mix it into sauces, oatmeals, or purees.
Mix nut butters into oatmeal or purees, or spread them thinly over toast.
Mash berries into a thicker, jam-like consistency before serving.
 Consider mixing mashed berries into other foods.
Consider mixing mashed berries into other foods.
Cut into thin strips that baby can grasp and fry them up in a pan. Serve cool or warm, not hot.
As-is or mixed in to oatmeal, yogurt, or purees.
Calories: 50kcal
Keyword baby
Tried this recipe?Let me know how it was!
how to choose and what kind of baby food is better?
The ideal "baby food" for an infant is breast milk. However, not all mothers can breastfeed their baby, usually this is due to the health of the mother or child. It happens that the woman herself has a serious condition after childbirth and in the early postoperative period, reduced lactation or diseases in which breastfeeding is contraindicated. In such cases, the baby is given formula milk - this is the only alternative to mother's milk.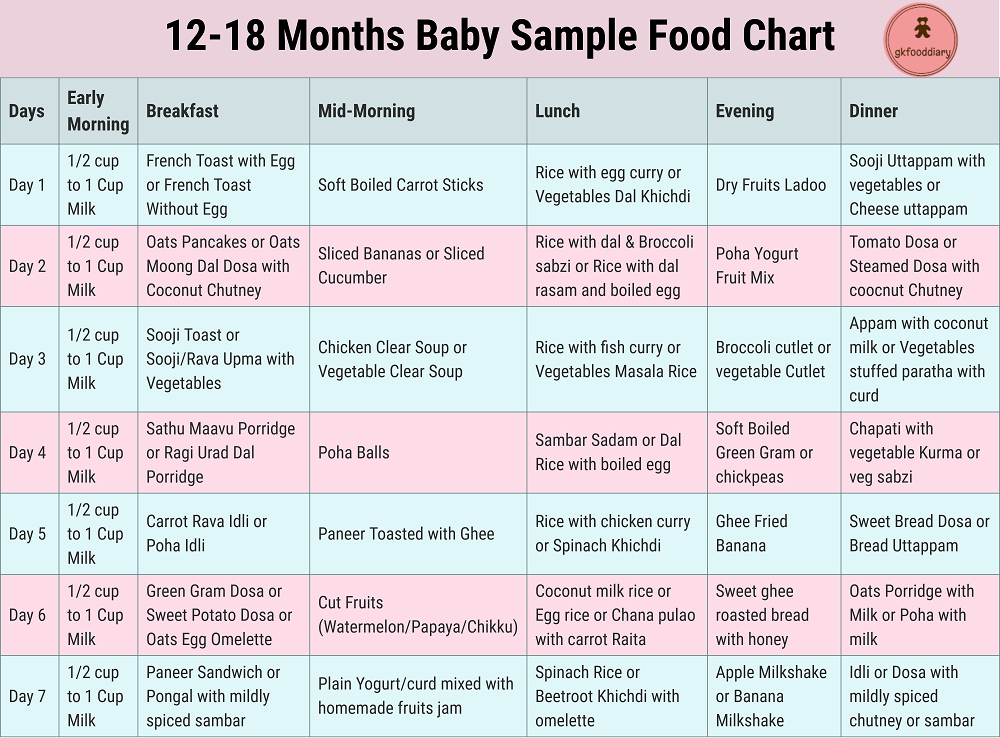 Subsequently, at four to seven months, complementary foods should be introduced into the child's diet, regardless of whether he is breastfed or artificial. The mother is faced with the task of choosing the right baby food for complementary foods. nine0005
Subsequently, at four to seven months, complementary foods should be introduced into the child's diet, regardless of whether he is breastfed or artificial. The mother is faced with the task of choosing the right baby food for complementary foods. nine0005
In this article, we will talk about what foods for babies are and how to choose the best baby food.
Legislation under "baby food" means food products that meet the physiological needs of the body of a child under 14 years of age. And nutrition for young children is food intended for children from birth to three years[1]. It is necessary to make a diet taking into account the age of the baby and the characteristics of his physical condition.
The Union of Pediatricians of Russia created the National Program for feeding children in the first year of life and the National Program for optimizing the nutrition of children from one to three years old [2]. They describe recommendations regarding what formula to feed the baby from birth, how to introduce complementary foods and expand the baby's diet. These programs provide detailed information on what nutrients and nutrients should be included in the diet of children of different ages. nine0007
These programs provide detailed information on what nutrients and nutrients should be included in the diet of children of different ages. nine0007
First you need to figure out what kind of baby food is[3]. Products for toddlers can be divided into two categories:
Infant formula. There are for children from birth to six months (formula 1 mixtures, or initial), from six months to a year (formula 2) and from a year (formula 3). The composition of such baby food is adapted, that is, as close as possible to the composition of breast milk.
- In the initial mixtures, the amount of protein is reduced to 1.2-1.5 g / 100 ml - in accordance with the composition of breast milk. They also changed the fat and mineral profile. The initial mixtures are enriched with such an essential amino acid as taurine, and micronutrients, probiotics, vitamins. nine0022
- After six months, the baby's need for protein increases, mother's milk changes its composition. And babies on artificial feeding begin to be fed with a more nutritious mixture of formula 2.
 Taurine is no longer always needed: the body of a baby aged from six months to a year is able to synthesize this amino acid itself. Meanwhile, the content of iron, calcium, zinc increases compared to the initial mixtures, because by this age the child's reserves of minerals received from the mother during pregnancy are depleted, and they need to be replenished. nine0022
Taurine is no longer always needed: the body of a baby aged from six months to a year is able to synthesize this amino acid itself. Meanwhile, the content of iron, calcium, zinc increases compared to the initial mixtures, because by this age the child's reserves of minerals received from the mother during pregnancy are depleted, and they need to be replenished. nine0022 - A child's diet changes after one year - he is already able to eat a variety of solid foods. However, it is advisable to continue to feed him with a mixture, though already formula 3. Pediatricians recommend it as a source of vitamins and minerals that the baby can easily absorb.
Complementary foods As we have already noted, it is introduced when the baby is four to seven months old. This interval is called the "critical window" and is considered optimal for the initiation of complementary foods for several reasons:
- The baby needs a wider range of minerals, vitamins and other nutrients.
 In addition, his baby's digestive system is already ready to accept more solid and complex foods than mother's milk or infant formula.
In addition, his baby's digestive system is already ready to accept more solid and complex foods than mother's milk or infant formula. - At this age, the child develops an interest in food, and it is necessary to offer him the right foods to develop his taste.
- During this period, the risk of developing a food allergy to a new product is lower.
- Timely introduction of complementary foods prevents the risk of micronutrient deficiencies and iron deficiency anemia. nine0022
Usually the first food is vegetable puree or monocomponent gluten-free cereals, dairy or dairy-free. Over time, cereals containing gluten, supplements from fruits and berries, and also consisting of several cereals are added. A six-month-old child can already be given several types of vegetables and cereals. Also, at about six months, they begin to give meat puree, then fruit, and from eight months - fish. A child from seven months is allowed the yolk.
From the age of 12 months, complementary foods already make up the majority of your baby's diet. At this age, it is especially important to diversify the child's diet: he can be given soups with small pieces of vegetables, meat, fish and cereals. nine0007
At this age, it is especially important to diversify the child's diet: he can be given soups with small pieces of vegetables, meat, fish and cereals. nine0007
Information
During the first feeding, the baby's eating habits are laid, and it depends on the parents how correct they will be. Often, mothers introduce fruit juices into complementary foods too early. And because babies have an innate preference for sweet tastes, they can become naughty and stop eating the unsweetened foods they need, especially vegetables. Unhealthy taste habits are formed, which can later provoke obesity. nine0005
Domestic doctors are concerned about such irrational nutrition of young children - due to the wrong approach to nutrition, many babies experience a deficiency of vitamins and an excess of fast carbohydrates.
How to choose baby foods
Finding the right foods for your baby is not an easy task. Store shelves are bursting with boxes, jars and bottles, and manufacturers write on every second package that the baby will be healthy, strong and cheerful after feeding. Of course, the baby will receive the necessary substances, no matter what product his parents choose, because all the production of baby food is strictly controlled by the state. By the way, Russia has some of the most stringent requirements for the quality of baby food in the world. nine0007
Of course, the baby will receive the necessary substances, no matter what product his parents choose, because all the production of baby food is strictly controlled by the state. By the way, Russia has some of the most stringent requirements for the quality of baby food in the world. nine0007
However, products for children differ in their properties. It is necessary to select food so that by the end of the first year of life the baby has actively developed chewing skills and an interest in independence, and the diet of complementary foods is reasonably varied.
For children from one to three years of age, the diet should be even more varied. It is important that the child receives daily something new from the main food groups: dairy, vegetables and fruits, meat and fish, cereals, butter and vegetable oil. Of course, the baby's diet should be expanded taking into account his state of health. nine0007
When organizing the nutrition of a child from the moment of introduction of complementary foods and up to three years, a mother needs not only to know what can be fed, but also to consider what foods should not be included in the diet. Among the prohibited products for children under three years of age:
Among the prohibited products for children under three years of age:
- any mushrooms, vegetables and fruits in a marinade;
- pickles, preserves in tomato sauce;
- commercial juice concentrates, carbonated drinks, coffee and strong tea;
- various condiments - mustard, ketchup, hot sauces, horseradish, pepper, vinegar, mayonnaise; nine0022
- products containing flavors, industrial colors, including chewing gum;
- margarine and refractory fats - lamb, pork;
- chocolates, sweets and other sweets.
To choose the right baby food, you need to know exactly what you should pay attention to and what you don't need to worry about.
When choosing mixtures, it is important to check:
- Absence of palm oil. Formula manufacturers may use palm oil (more specifically palm extract) because, like breast milk, it is rich in palmitic acid. However, in human milk, palmitic acid is in the beta position, while in palm oil it is in the alpha position.
 Such alpha-palmitic acid can interfere with the absorption of calcium and fats and is generally less well absorbed by the child's body. This can negatively affect the work of the intestines, lead to constipation, regurgitation. Milk fat is better suited for baby food as a source of palmitic acid[4][5]. nine0022
Such alpha-palmitic acid can interfere with the absorption of calcium and fats and is generally less well absorbed by the child's body. This can negatively affect the work of the intestines, lead to constipation, regurgitation. Milk fat is better suited for baby food as a source of palmitic acid[4][5]. nine0022 - Protein ratio. Breast milk protein is primarily whey proteins and casein. A child needs both types of protein, while proteins are easily digested, which cannot be said about casein. If baby food contains a lot of casein, it stays longer in the digestive tract, which can cause problems with the baby's stool.
- The presence of additional functional elements in the composition - lutein, nucleotides, pre- and probiotics. The task of lutein is to protect vision from ultraviolet rays. Nucleotides are low molecular weight compounds that promote the growth of beneficial bifidobacteria in the intestines. And pre- and probiotics in the composition of infant formulas help to establish comfortable digestion.
 nine0022
nine0022
When choosing complementary foods, pay attention to:
- Age appropriate. It is important that in the diet of a child under three years of age who receives complementary foods, special children's products predominate - in their composition the components are selected taking into account the age-related needs of the baby's body. It is impossible at an early age to transfer children to "adult" foods like pickles, smoked foods, fast food, and so on.
- Fortified products. nine0005 It is important that the composition contains vitamins and minerals. The National Child Nutrition Optimization Program recommends choosing complementary foods that contain elements designed to prevent anemia, rickets, and vitamin deficiencies.
- For a varied diet. The menu for a baby up to six months is quite monotonous. But as they grow older, the baby needs more various nutrients - proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals.

- For the individual reaction of the baby. nine0005 If the child is already receiving complementary foods, then it is worth introducing a new product only after the previous one has been fully introduced. If the baby is allergic to the product, then it should be administered carefully, carefully checking the reaction of the body.
Ingredient safety testing is optional. Of course, the content of any "chemistry" in the product for feeding a child, whether it be a mixture or complementary foods, is unacceptable. There is no need to worry about this: baby food is carefully checked. If it is registered on the territory of the Customs Union and hit the shelves, then it complies with SanPiN 2.3.2.1940-05 and there will be no "prohibited" components in its composition. Also, contrary to popular misconception, in Russia it is forbidden to use GMOs in children's products.
Note
Baby food in jars (usually mashed potatoes) has a short shelf life after opening because it does not contain preservatives. However, before the jar is opened, the products can stand for quite a long time on the shelves of stores or in the refrigerator at home. This is possible thanks to a special production technology, sterilization and vacuum packaging. If a soft pop is heard when opening the jar, this is a good sign: the puree is not spoiled. But products in jars with swollen lids or a protruding bottom should not be used: microorganisms already multiply in such food, it is not suitable for food. nine0005
However, before the jar is opened, the products can stand for quite a long time on the shelves of stores or in the refrigerator at home. This is possible thanks to a special production technology, sterilization and vacuum packaging. If a soft pop is heard when opening the jar, this is a good sign: the puree is not spoiled. But products in jars with swollen lids or a protruding bottom should not be used: microorganisms already multiply in such food, it is not suitable for food. nine0005
Features of the choice of dairy products
It is necessary to choose dairy products for babies, following the doctor's recommendations. The specialist will take into account the health of the baby, especially if he is allergic to cow protein. In Russia, such an allergy occurs in 30–40% of children [6]. Such a reaction may occur due to hereditary predisposition and immaturity of the organism. But most often, allergies go away when the child grows up.
Goat milk baby food may be a suitable option for young children with a predisposition to allergies. Its protein is perceived by the body better than cow's: alpha-s1-casein, contained in large quantities in cow's milk, makes a product based on it difficult to digest - food stagnates in the baby's gastrointestinal tract, motor skills are disturbed, as a result, allergies often occur. In goat milk, as in breast milk, there is practically no alpha-s1-casein [7]. Therefore, goat's milk, and hence the mixture based on it, are better absorbed. nine0007
Its protein is perceived by the body better than cow's: alpha-s1-casein, contained in large quantities in cow's milk, makes a product based on it difficult to digest - food stagnates in the baby's gastrointestinal tract, motor skills are disturbed, as a result, allergies often occur. In goat milk, as in breast milk, there is practically no alpha-s1-casein [7]. Therefore, goat's milk, and hence the mixture based on it, are better absorbed. nine0007
Of course, with the introduction of complementary foods, other dairy products will appear in the baby's diet. Unadapted fermented milk drinks, such as kefir, yogurt, biolact, can be introduced into the diet from eight months and in an amount not exceeding 200 ml. Also during this period, it is recommended to give cottage cheese - no more than 50 g per day, but according to indications, it can also be prescribed from the age of six months. Whole milk cannot be used as the main food, and it is advised to introduce it into the diet of babies no earlier than a year (in the amount of 100-150 ml per day) [8]. As mentioned above, it must be adapted infant milk or formula 3 formula.
As mentioned above, it must be adapted infant milk or formula 3 formula.
To choose the best baby food, it is necessary to take into account the health of the baby, his tastes, as well as individual reactions of the body. Therefore, before going to the store, you should consult a doctor. The specialist will not only tell you which baby food to choose, but also give recommendations on how to make the child's diet balanced and healthy.
Nutrition of young children
Of all environmental factors influencing human health, nutrition plays a leading role. nine0007
Breast milk is the best and only food that nature has created for a newborn baby. Mom's milk is not only all the necessary nutrients in the right quality and quantity that will ensure good growth and proper development of the baby. Breast milk is the ongoing mother's care and protection from an alien, sometimes aggressive environment for which the baby is not ready. Mom's support in the form of breastfeeding will be needed for the baby during the first year of life, while his immune system learns to recognize and fight all the harmful bacteria surrounding him. However, it happens that there is no breast milk or not enough. Then the child has to offer artificial feeding. It is necessary to rationally approach this issue. If there is a need to feed the baby with milk formula, give preference to mixtures with reduced protein, the presence of fatty acids and bifidobacteria. Remember that even after the introduction of complementary foods, you should continue to feed your baby with breast milk substitute until he is at least one year old. Be sure to check with your pediatrician before deciding whether to formula feed or formula supplement your baby, as only he or she can select the formula that best meets the baby's needs. If you are feeding your baby the formula recommended by the doctor and the baby is taking it well (no allergic reactions, no digestive problems), then there is no need to change the formula. Replacement of the mixture should be carried out only on the basis of the recommendations of a specialist. nine0007
However, it happens that there is no breast milk or not enough. Then the child has to offer artificial feeding. It is necessary to rationally approach this issue. If there is a need to feed the baby with milk formula, give preference to mixtures with reduced protein, the presence of fatty acids and bifidobacteria. Remember that even after the introduction of complementary foods, you should continue to feed your baby with breast milk substitute until he is at least one year old. Be sure to check with your pediatrician before deciding whether to formula feed or formula supplement your baby, as only he or she can select the formula that best meets the baby's needs. If you are feeding your baby the formula recommended by the doctor and the baby is taking it well (no allergic reactions, no digestive problems), then there is no need to change the formula. Replacement of the mixture should be carried out only on the basis of the recommendations of a specialist. nine0007
After 4 months, breast milk and formula remain on the baby's menu, but new products are added to them. We recommend starting complementary foods with dairy-free gluten-free porridge, which is enriched with vitamins and minerals, such as rice or buckwheat. Porridge is best diluted with breast milk, infant formula or water. After cereals, one-component vegetable, meat purees can be introduced, then fruit juices and purees between feedings.
We recommend starting complementary foods with dairy-free gluten-free porridge, which is enriched with vitamins and minerals, such as rice or buckwheat. Porridge is best diluted with breast milk, infant formula or water. After cereals, one-component vegetable, meat purees can be introduced, then fruit juices and purees between feedings.
In the first year of life, you have already carefully opened the door to the world of healthy and tasty products for him. At the age of one to three years, the child's diet gradually approaches the diet of an adult. But when compiling a menu, you need to know what products are necessary for its normal development. nine0007
The most important part of food is protein, the main building material for all tissues and cells. If there is not enough protein in the diet, protection against infectious diseases is reduced, liver activity is disrupted, growth and development slow down.
All essential amino acids are found in milk, eggs, meat. Meat dishes are best prepared from low-fat varieties - beef, veal, rabbit, turkey. Rational nutrition should include low-fat fish. In the third year of life, sausages can be introduced into the menu, but only high-quality and prepared specifically for children. An important source of protein is plant foods such as cereals and legumes. In addition to proteins, they contain a large amount of complex carbohydrates, fiber and vitamins. nine0007
Rational nutrition should include low-fat fish. In the third year of life, sausages can be introduced into the menu, but only high-quality and prepared specifically for children. An important source of protein is plant foods such as cereals and legumes. In addition to proteins, they contain a large amount of complex carbohydrates, fiber and vitamins. nine0007
For the normal absorption of proteins, as well as mineral salts and vitamins A and D, the body needs fats, so a balanced diet without eating fats is impossible. Fats are a kind of "fuel" that supplies the body with energy. In addition, thanks to fats, the taste of many foods improves. For young children, vegetable fats are useful, where there are a lot of useful polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Fat-like substance - lecithin has a positive effect on the development of the nervous system, and also improves blood formation and the body's resistance to toxic substances. There is a lot of lecithin in buckwheat, lettuce, soy and other legumes. nine0007
nine0007
Rational nutrition should also include the required amount of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are necessary for the functioning of the muscles, heart, liver, nervous system, as well as the normal absorption of fats. Most of the energy the body receives from vegetable carbohydrates. A lot of carbohydrates in bread, cereals, potatoes, sweet berries and fruits. Among animal products, they are found in milk. Non-food carbohydrate-fiber stimulates the intestines, it is important for normal digestion. A lot of fiber in wholemeal bread, vegetables, herbs and fruits. These products should be on the children's table. nine0007
Minerals are part of all body tissues. Bones are 2/3 composed of mineral salts. Their importance for a child, whose skeletal system is being formed, teeth are erupting, can hardly be overestimated. Almost all foods contain calcium salts, but they are far from being absorbed by all. Sources of easily digestible calcium are milk and dairy products, cottage cheese, cheese, egg yolks. Porfor is involved in the formation of bones and nervous tissue. There is a lot of it in fish, bread, cereals, meat, cheese, eggs, milk. nine0007
Porfor is involved in the formation of bones and nervous tissue. There is a lot of it in fish, bread, cereals, meat, cheese, eggs, milk. nine0007
Vitamins are needed for the normal functioning of the whole organism. In order for the child to receive all the necessary vitamins, give him vegetables, fruits, herbs, beans, peas.
The daily amount of food for young children is from 1000 to 1400 ml. The amount of sugar should not exceed 50 gr. per day.
Smoked products should not be given to children (they are harmful for adults as well), caviar and seafood (strong allergens) are also contraindicated. Exclude mushrooms from the children's menu, they are poorly digested up to 7 years. Sweets, sweetened juices, chocolate reduce appetite, contribute to the development of caries, overweight, allergies. Instead of sweets, it is better to give the baby dried fruits. nine0007
Healthy nutrition is the key to a full physical and spiritual life of a person. If you can forget about your own health or exchange it for the convenience and familiarity of “wrong” food, then taking care of the proper nutrition of your own child is your responsibility.