Burping baby after bottle feeding
How to Burp a Sleeping Baby: Step-by-Step Guide
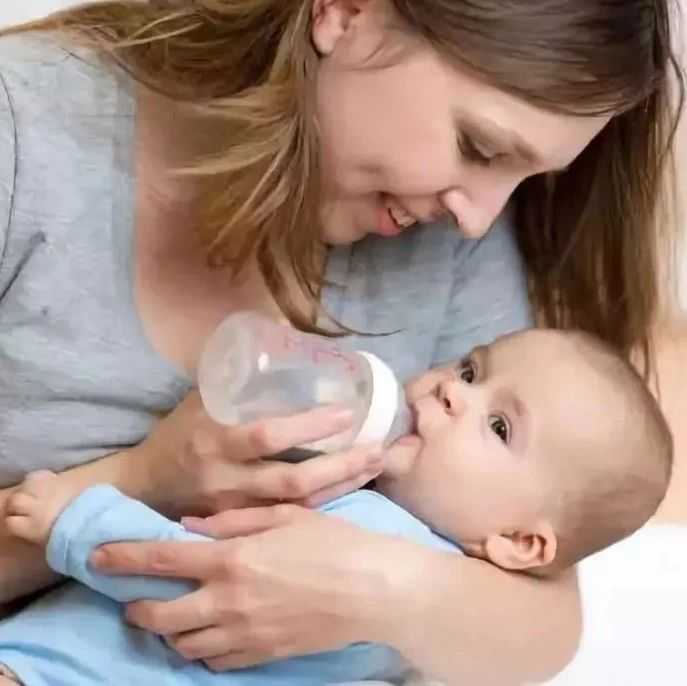
Some babies are gassier than others, but most babies will need to be burped at some point. Babies need to burp a lot more often than older kids and adults. They drink all of their calories, which means they can gulp a lot of air.
Burping a baby can be important day and night. Sometimes babies fall asleep while eating and you may need to find a way to burp them while they’re still asleep. It’s remarkable how much a newborn can sleep through.
Even if your baby falls asleep, try burping them for a few minutes before placing them back down to sleep. Otherwise, they make wake up in pain with trapped gas.
Not all babies burp, though, no matter if it’s on their own or with your help. If your baby is one that needs to be burped, read on for ways to do so even when they’re asleep.
It’s common for babies to fall asleep while eating, whether nursing or bottle-feeding. As their tummy fills and they start soothing sucking motions, they often become happy and relaxed and tend to drift off.
This is especially likely to happen at night when their sleep drive is strong. But even if your little one looks content and totally asleep, for some babies it’s important you try to get a burp out of them before lying them back down.
Burping a sleeping baby is basically the same as burping a baby who’s awake. You might move slower to help them stay asleep. Some burping positions are a bit easier to maneuver with a sleeping baby.
For example, many people sit a baby upright on their knee while supporting the baby’s head by cradling their chin. This position uses gravity and the baby’s own weight to get air up and out. However, this position is more likely to wake a baby, so you might not want to try it if your aim is to keep the baby asleep.
To burp a baby, they should be in a slightly upright position so you can put pressure on their tummy. If your baby doesn’t poop right after eating, you may want to change their diaper before feeding them at night so you don’t have to wake them up if they fall back to sleep while eating.
Here are some positions for burping a sleeping baby:
Burp between changing sides, or mid-bottle
A sleepy baby may enjoy their feeding so much that they overeat and don’t realize they need a pause to burp. Help your baby have a gentler burp and avoid any major gas pain by slowing down the feed.
Burp your baby between switching sides at the breast or before they finish their bottle. This will also help your baby make room for more milk instead of burping and spitting up any of their food.
Hold on your shoulder
If you feed your baby in a semi-upright position, you can gently move them all the way upright and onto your shoulder. Babies can keep sleeping in this cozy position while the pressure from your shoulder pushes on their tummy to release gas. Keep a burp rag over your shoulder if your baby tends to spit up.
Hold lower on your chest
Similar to the previous position, you can lift your baby from semi-upright to fully upright and keep them on your chest or sternum area. This may be most comfortable if you’re on a couch. Babies like to curl up with their legs in a frog position (a bonus move to release more gas from their bottoms) and you can support their head and wait for the burp to come.
This may be most comfortable if you’re on a couch. Babies like to curl up with their legs in a frog position (a bonus move to release more gas from their bottoms) and you can support their head and wait for the burp to come.
Rock on your arm (“sloth hold”)
After feeding, you can slowly turn them away from you at 45 degrees so their tummy rests on your forearm. Support their head in the crook of your elbow. Their legs may dangle on either side of your arm. This position puts pressure on their belly and you can gently pat their back until they burp. You can do this position while sitting or standing.
Lay on your knees
If you’re sitting in a chair, simply move your baby to a laying position on their tummy on your knees. You can move your legs side to side to rock them and gently pat or rub their back until a burp comes. A baby can remain asleep here as long as you want to stay sitting.
Burping is one of the many tasks parents have until their child grows into being more self-sufficient.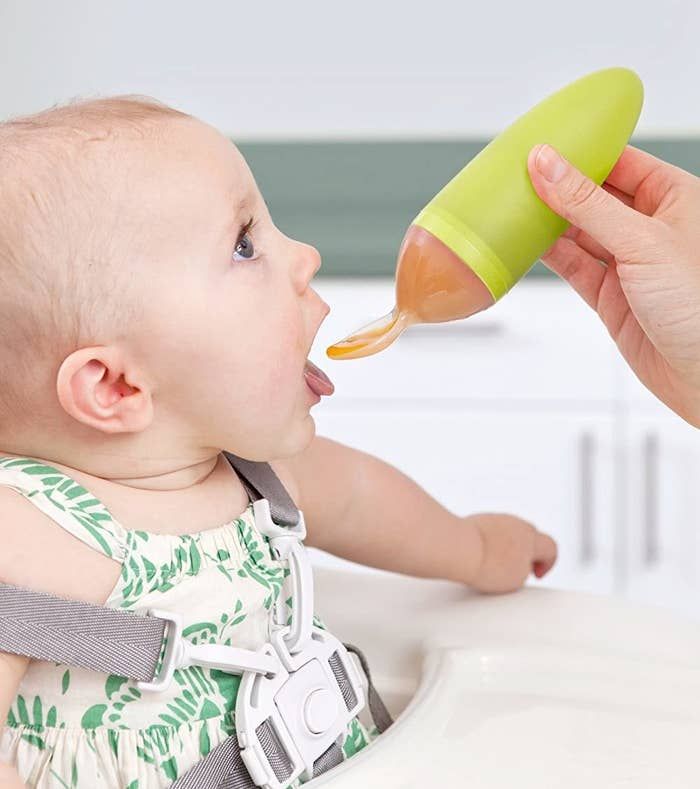 Kids and adults can easily release their own gas, but many babies need help because they have so little control over how their bodies are positioned.
Kids and adults can easily release their own gas, but many babies need help because they have so little control over how their bodies are positioned.
You’ll figure out pretty quickly if your baby is the type who can eat without burping or if they need to be burped every time. If your baby has a lot of gas or spit-up, you should talk to your doctor about reflux.
If you do have a colicky baby but you can’t seem to get them to burp, focus on any comfort measures that work and don’t worry too much about getting burps out. One study suggests that burping won’t help decrease colic.
Whether your baby burps a lot during the day, it may be worth it to burp them after every nighttime feeding. Since you’re already up feeding the baby, make the most of your time by giving a solid attempt at burping. This may get everyone a long stretch of sleep after the feeding.
Gas drops and gripe water are readily available at pharmacies but ask your doctor first before using any of them.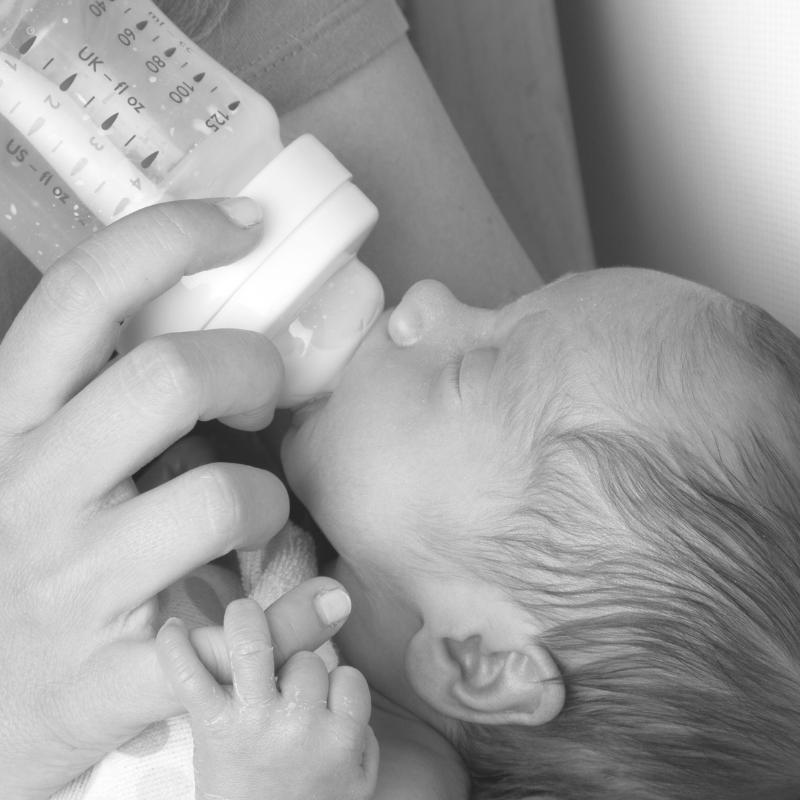 These supplements aren’t regulated for safety and may contain dangerous ingredients. If you have a very fussy and gassy baby — whether or not they spit up often — ask a doctor for coping skills. Most babies grow out of this after a few months.
These supplements aren’t regulated for safety and may contain dangerous ingredients. If you have a very fussy and gassy baby — whether or not they spit up often — ask a doctor for coping skills. Most babies grow out of this after a few months.
Risk of choking on spit-up is very rare. It’s still important not to overfeed your baby and to try to burp them after every feeding if they seem to benefit from it.
Burping usually only takes a minute or two. Sometimes a burp will come up as soon as you move your baby upright, and sometimes you have to wait a little while and help things with a gentle pat or tummy pressure.
Another helpful strategy is to get your baby in the habit of falling asleep in their crib rather than while feeding. When you notice them getting sleepy at the breast or bottle, stop the feeding, burp them for a minute or so, and then put them down to sleep. The younger you start this, the easier it is to do.
If your baby is often stiff and uncomfortable, talk with their doctor about more help for relieving gas. Some babies with bad reflux may need to stay upright for 30 minutes after eating, day or night.
Some babies with bad reflux may need to stay upright for 30 minutes after eating, day or night.
If your baby is asleep, try burping them for a minute before you lay them back down. Sometimes babies don’t need to burp as much at nighttime because they eat slower and don’t get as much air while feeding.
If they wake up crying, soothe them, check to see if they need a clean diaper, feed them again if it’s time, and try to burp them after that feeding.
Some people believe that bottle-fed babies are more likely to get gassy, but evidence of this is only anecdotal. Bottles may expose babies to more air as they gulp and may make it easier to overfeed your baby. But every baby is different and even breastfed babies can be very gassy — sometimes because they’re sensitive to food in their mother’s diet.
Though uncommon, a breastfeeding mother may have to experiment a lot before figuring out exactly what they ate to cause their baby’s upset stomach. There’s no solid research to tell a mother what exactly causes her baby’s excess gas.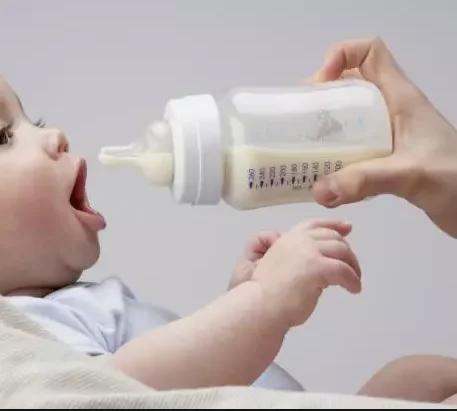 Also, many babies with gas aren’t bothered by it.
Also, many babies with gas aren’t bothered by it.
Burping is a basic but important way you can take care of your baby and keep them comfortable. Even if your baby is asleep, burping may be helpful to allow them to relieve gas so they don’t get uncomfortable or wake up too soon.
How to Hold a Baby: Step by Step
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
Now that your baby is here, you probably have a lot of questions about how to care for them. Even if you’re a seasoned parent, things like how to hold your newborn might feel foreign or downright scary at first.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to hold your newborn infant.
Always make sure your hands are clean before you pick up your baby. Baby’s immune system is still developing, so any germs you carry may make them sick. While lathering with soap and warm water works well, consider keeping hand sanitizer around for guests who also want to cuddle your little one. Clean your hands each time before holding your baby.
Clean your hands each time before holding your baby.
Comfort is one of the most important things about holding your baby. Not only do you want to feel physically comfortable, but you also want to feel confident in your hold. Seasoned fathers at the blog “Dads Adventures” suggest that it takes around five minutes to get comfortable with the idea of holding your newborn.
It’s OK to feel a bit freaked out at first. Give it time, and remember to breathe!
When holding a newborn, it’s very important to always have a hand to support the head and neck. After all, your baby’s head is the heaviest part of their body at birth. Pay special attention to baby’s fontanelles, which are the soft spots on the top of their head.
Newborns lack the critical neck muscle control to keep their heads supported on their own. This milestone isn’t usually reached until closer to the fourth month of life.
Holding starts with picking baby up. When you go to lift your baby, place one hand under their head and another under their bottom. From there, raise their body to your chest level.
From there, raise their body to your chest level.
As long as you’re supporting baby’s head and neck, the position is up to you. There are a variety of holds you and your baby might enjoy. Some of these positions are also great for breast-feeding or burping. Experiment by trying different ones to see what feels the best to both of you.
Cradle hold
Share on Pinterest
The cradle hold is one of the easiest and best ways to hold your newborn for the first several weeks of life:
- With your baby horizontal at your chest level, slide your hand from their bottom up to support their neck.
- Gently nudge baby’s head into the crook of your elbow.
- While still cradling their head, move your hand from the supporting arm to their bottom.
- Your free arm will be able to do other things or provide extra support.
Shoulder hold
Share on Pinterest
- With baby’s body parallel with your own, lift their head to shoulder height.

- Rest their head on your chest and shoulder so they can look out behind you.
- Keep one hand on their head and neck, and your other supporting baby’s bottom. This position may also allow baby to hear your heartbeat.
Belly hold
Share on Pinterest
- Lay your baby, stomach down, across your forearm with the head up toward your elbow.
- Their feet should land on either side of your hand, angled closer to the ground so the baby is at a slight angle.
- This position is helpful if baby is gassy and needs to be burped. Gently stroke baby’s back to work out the gas.
Lap hold
Share on Pinterest
- Sit in a chair with your feet firmly on the ground and place your baby in your lap. Their head should be at your knees, face up.
- Lift their head up with both of your hands for support and your forearms under their body. Baby’s feet should be tucked in at your waist.
Pay attention to baby’s mood while you’re holding them. If they’re fussy or crying, you might try another position to see if that makes them more comfortable. You can also try a gentle and slow rocking. Take note that baby’s head should always be turned out to allow them to breathe.
If they’re fussy or crying, you might try another position to see if that makes them more comfortable. You can also try a gentle and slow rocking. Take note that baby’s head should always be turned out to allow them to breathe.
- Try skin-to-skin contact while holding baby. It’s a great way to bond and keep them warm. You can strip baby down to their diaper, place them against your bare chest, and cover with a blanket.
- Choose a seated position if you feel nervous about holding baby. Sitting down is also a good idea for anyone who might not have the strength to support baby’s weight, like children and older individuals.
- Use a baby carrier, like a Boba Wrap, for hands-free holding. Follow all instructions on the carrier’s packaging. It suggests age-appropriate holds and positions.
- Use an infant support pillow, like a Boppy Pillow, when holding baby for extended periods of time or to help with breast-feeding.
- Do not cook or carry hot drinks while holding baby.
 Knives, flames, and excess heat are dangerous and could lead to injury by accident. Stay away from others who are working with those things near you.
Knives, flames, and excess heat are dangerous and could lead to injury by accident. Stay away from others who are working with those things near you. - Hold your baby with both hands while you’re going up and down the stairs for added safety.
- Do not ever shake your baby, whether to play or to express frustration. Doing so can cause bleeding in the brain and even death.
There’s really no right or wrong way to hold your baby if you keep these tips in mind. Though they’re tiny, newborns are less fragile than you might think. The key is to get comfortable and support your little one’s delicate head and neck. Even if holding your baby feels funny or frightening at first, it will soon become second nature with practice.
Q:
What are some helpful resources for new parents to learn about caring for an infant?
Anonymous patient
A:
There are many great resources. Your baby’s pediatrician can be helpful. A good book is “What to Expect the First Year” by Sandee Hathaway. Also visit http://kidshealth.org/ for more information.
Also visit http://kidshealth.org/ for more information.
University of Illinois-Chicago, College of Medicine
Answers represent the opinions of our medical experts. All content is strictly informational and should not be considered medical advice.
Share on Pinterest
Why does the baby spit up after feeding?
search support iconSearch Keywords
Regurgitation is a common condition in newborns and infants and is most often a normal variant. However, it is not uncommon for parents to worry if their baby is spitting up frequently, believing that it is due to nutritional or health problems in general. Sometimes these fears are not unfounded, and regurgitation really has a pathological origin. What is its cause and when should you really consult a doctor about this?
Regurgitation - Return of a small amount of food (uncurdled or partially curdled milk) from the stomach up the digestive tract: into the esophagus and further into the oral cavity. According to statistics, at least 1 time during the day, at least 50% of babies from 0 to 3 months old can spit up, more than 60% of children 3-4 months old, and in 5% of children spit up continues up to the year 1 .
According to statistics, at least 1 time during the day, at least 50% of babies from 0 to 3 months old can spit up, more than 60% of children 3-4 months old, and in 5% of children spit up continues up to the year 1 .
Regurgitation in newborns is considered a physiological process. It is caused by a number of factors, including:
- Features of the structure of the upper digestive tract in babies
- In newborns and infants up to a year of life, the stomach has a spherical shape. It holds a small amount of food, besides, the release from it into the duodenum is slower in comparison with children after the year 2 .
- Weakness of the lower esophageal sphincter that separates the esophagus from the stomach
- Normally, the lower esophageal sphincter should tightly "close" the esophagus, allowing food to pass into the stomach and not allowing it to enter back into the upper digestive tract. However, in young children (up to a year), the muscles of the esophageal sphincter are poorly developed, and it does not do its job very well 2 .

- Slow movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract
- The neuromuscular system of newborns is immature. It does not ensure the proper movement of food through the esophagus, causing regurgitation.
One of the important risk factors contributing to regurgitation in newborns is aerophagia. This is the swallowing of large amounts of air during feedings. This happens when the baby is not properly attached to the breast, the mother has a lack of breast milk, or the bottle is in the wrong position in the child who receives the mixture. The size of the opening in the nipple also matters - if it is too large, the newborn swallows a lot of air 3 .
With aerophagia, the baby becomes capricious, restless immediately after feeding. Noticeable bloating. If the baby spits up immediately after a feed, the milk (or formula) remains practically fresh, uncurdled 3 .
Promotes regurgitation after feeding and a predominantly horizontal position of the baby during the day, combined with relatively high intra-abdominal pressure 4 . Therefore, the correct position of the baby after feeding is so important. To avoid regurgitation of an excessive amount of stomach contents, after feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in an upright “column” position for some time (10-20 minutes), lightly patting on the back and allowing excess air to “exit”.
Therefore, the correct position of the baby after feeding is so important. To avoid regurgitation of an excessive amount of stomach contents, after feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in an upright “column” position for some time (10-20 minutes), lightly patting on the back and allowing excess air to “exit”.
Regurgitation in many newborns can be provoked by other situations in which pressure in the abdominal cavity increases and stomach contents are thrown into the esophagus, in particular 3 :
- tight swaddling;
- stool disorders, in particular constipation;
- long, forced cry and some others.
Want to avoid common feeding problems?
Start with a baby bottle with an anti-colic system that helps you avoid common feeding problems such as colic, gas and spitting up*
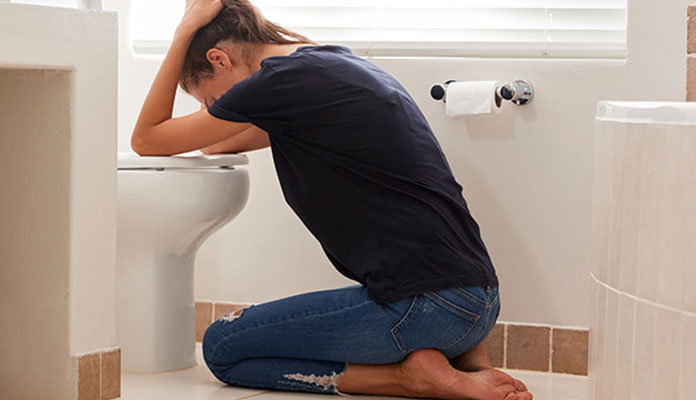
How can you tell the difference between normal spitting up and vomiting?
Sometimes regurgitation is considered a manifestation of disorders in the digestive tract of children. Due to the constant reflux of acidic stomach contents into the upper sections, inflammation and other complications may develop, including growth retardation, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and others. Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
Due to the constant reflux of acidic stomach contents into the upper sections, inflammation and other complications may develop, including growth retardation, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and others. Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
If the mother is worried that her baby is spitting up, keep track of when this happens and count the total number of spit ups per day. Normally, regurgitation usually occurs after eating (the child burps after each feeding), lasts no more than 20 seconds and repeats no more than 20-30 times a day. With pathology, the problem manifests itself at any time of the day, regardless of when the baby was fed. Their number can reach 50 per day, and sometimes more 1 .
The amount of discharge during regurgitation also matters. With normal, physiological regurgitation, it is approximately 5 - 30 ml. If this volume fluctuates between 50 and 100 ml, it is already defined as profuse vomiting. When the range of the jet of vomit is up to 50 cm, doctors talk about "vomiting a fountain." A variant of atonic vomiting is possible, when the contents of the stomach flow "sluggishly". It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
When the range of the jet of vomit is up to 50 cm, doctors talk about "vomiting a fountain." A variant of atonic vomiting is possible, when the contents of the stomach flow "sluggishly". It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
Vomiting in babies is a warning sign. Doctors are especially alarmed by repeated vomiting, a fountain, with an admixture of bile, in combination with constipation. Vomiting can lead to the development of dehydration, acid-base imbalance and other consequences, therefore, if it occurs, you should urgently contact a pediatrician to find out the cause and begin treatment. A doctor's consultation is necessary if the child is spitting up a lot (more than 15-30 ml at a time), with a frequency of more than 50 episodes per day 1.3 .
Physiological regurgitation: symptoms
Regurgitation in newborns, which is considered a normal variant and does not cause concern to pediatricians 3 :
- usually continues for a certain period of time;
- is characterized by slow, "passive" leakage; if the baby spits up a fountain, it is better to consult a doctor;
- has a sour smell of curdled milk;
- occurs without the participation of muscles - the baby does not strain during regurgitation;
- does not affect the general well-being of the baby.

How to help a newborn who spit up often?
If the baby is healthy, no medication is prescribed for spitting up. To help the child allow simple measures based on lifestyle changes and feeding.
- Frequent feeding of the baby
It is known that the baby is more prone to spit up if his stomach is full. To improve the situation, it is recommended to feed the baby more often, avoiding oversaturation, best of all - on demand 5 .
- Correct feeding technique
Every feeding, the mother must ensure that the baby does not swallow too much air during suckling. When sucking, there should be no loud, smacking, clicking sounds. You also need to control that the baby captures the nipple along with the areola.
- Choosing the right bottle and nipple
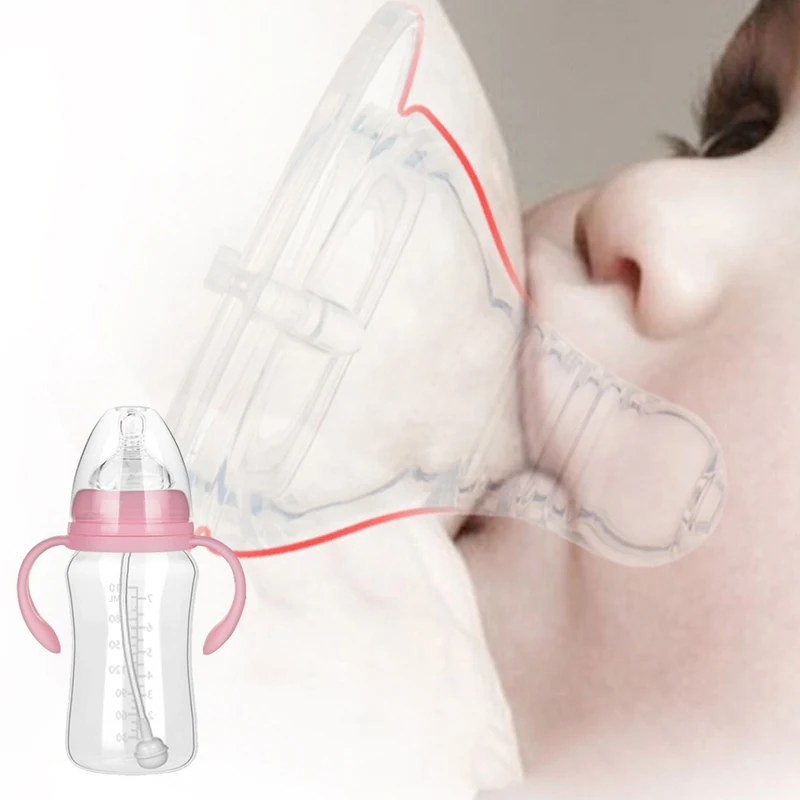
If the newborn is bottle-fed and receiving formula, it is important to choose the right bottle and nipple. The hole in it should be such that the milk flows out in drops, and not in a stream. The nipple must not be filled with air
The hole in it should be such that the milk flows out in drops, and not in a stream. The nipple must not be filled with air New Anti-colic bottle with AirFree valve
The AirFree valve prevents air from entering the baby's stomach.
- Baby standing upright after eating
To allow air that has entered the digestive tract during meals to escape, it is important to keep the newborn upright for 10-20 minutes after feeding 4 .
- Ensure the correct position of the baby during sleep
To reduce the negative impact of the acidic contents of the stomach on the esophagus, it is necessary to put the baby to sleep in the supine position. The side or prone position, which many pediatricians used to recommend, is no longer recommended. It was found to be associated with an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome 5 .
If parents notice alarming symptoms, such as spitting up too often or large volume, etc.
 , it is important to consult a pediatrician without delay. This will allow you to identify the real problem in time and help the baby grow up healthy and happy.
, it is important to consult a pediatrician without delay. This will allow you to identify the real problem in time and help the baby grow up healthy and happy.
References1 Zakharova I. N., Andryukhina E. N. Regurgitation and vomiting syndrome in young children // Pediatric pharmacology, 2010. V. 7. No. 4.
Nagornaya 2900 V., Limarenko M. P., Logvinenko N. G. Experience with the use of domperidone in suspension in young children with regurgitation syndrome // Child Health, 2013. No. 5 (48).
3 Zakharova IN Regurgitation and vomiting in children: what to do? //Pediatrics. Supplement to Consilium Medicum, 2009. No. 3. S. 58-67.
4 Zakharova I. N., Sugyan N. G., Pykov M. I. Regurgitation syndrome in young children: diagnosis and correction // Effective pharmacotherapy, 2014. No. 3. P. 18-28.
5 Vandenplas Y. et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) //Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition.
 2009; 49(4): 498-547.
2009; 49(4): 498-547. You are leaving the Philips Healthcare (“Philips”) official website. Any links to third party websites that may be included on this site are provided solely as a convenience to you. Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain.
I understand
You are about to visit a Philips global content page
You are about to visit the Philips USA website.
Why do newborns spit up? | Philips Avent
search support iconSearch Keywords
Home ›› Why is my baby spitting up and how can I help him?
Home ›› Why does my baby spit up and how can I help him?
↑ Top
Whether it's your first or third baby, you're bound to have questions about feeding. Reflux (spitting up) is a common topic among frequently discussed feeding topics, so you are not alone in finding the answer to the question “Why does my baby spit up so often?”.
So why do babies spit up? And is spitting up normal for babies? You have probably thought about this many times. After reading this article, you will receive important information that will explain the causes of infant spitting up, and you will learn how to act to help the child.
If you have any questions or your child has other symptoms, be sure to contact your doctor.
Why do babies spit up and when is it normal?
Let's look at why babies spit up and answer the frequently asked question "Why does my baby spit up so much?". Many newborns spit up after feedings or when burping because their digestive tract is not yet fully developed. However, in some situations, the likelihood of regurgitation in infants increases.So what causes reflux in babies? The following are some of the main causes of regurgitation in infants: 1
- The child has moved.
- The child was eating too fast.

- You help your baby spit up air, and with the air, the baby spit up part of the food.
- The child has too much air in the stomach.
- The child has excessive salivation.
So is spitting up normal in infants? In simple words: spitting up after some feeds, or even after each, is absolutely normal for a growing baby. However, there are points that need to be noted in order to distinguish ordinary regurgitation from vomiting. The two processes are very different, so you should check with your doctor if your baby is vomiting heavily after every or most feeds.
Also seek medical attention if your child has the following symptoms, which a doctor can help identify: 2
- The child spit up frequently, does not gain enough height or weight.
- Appears to be in pain, cries a lot, or arches his back.
- Coughing or difficulty breathing, which may be a symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease.

- Regurgitates even if he hasn't eaten anything.
- There is severe vomiting.
- Fever or diarrhea, which may be a sign of an intestinal infection and lead to dehydration.
If your baby spit up a small amount of milk after a feed and continues to grow and stay healthy, rest assured that this is normal and nothing to worry about. If you have any questions about reflux in infants, check out this article to learn about the symptoms of reflux and how to deal with it!
What to do
Now that you know that spitting up is a normal physiological process and what causes it, you are probably wondering what you can do to help your baby. After you have consulted with your pediatrician and he has determined that spitting up is not a cause for concern, there are a few things you can do to help you when you are confused: 11. Regular belching of air.
In addition to burping after feedings, try helping your baby burp when changing breasts. And when feeding from a bottle, try to have the child spit up air every 30-60 ml of the mixture. Consider using an anti-colic bottle with an AirFree valve. The AirFree valve prevents air from entering the nipple even when the bottle is in a horizontal position and the nipple remains completely filled with milk. The use of such a bottle will allow your baby to drink in an upright position, which will reduce the frequency of reflux, improve the digestion process and make the feeding process more comfortable for both you and the baby. Find out more about Philips Avent anti-colic bottles with AirFree valve here.
And when feeding from a bottle, try to have the child spit up air every 30-60 ml of the mixture. Consider using an anti-colic bottle with an AirFree valve. The AirFree valve prevents air from entering the nipple even when the bottle is in a horizontal position and the nipple remains completely filled with milk. The use of such a bottle will allow your baby to drink in an upright position, which will reduce the frequency of reflux, improve the digestion process and make the feeding process more comfortable for both you and the baby. Find out more about Philips Avent anti-colic bottles with AirFree valve here. 3. Avoid vigorous movement after feeding.
To avoid regurgitation after a feed, it is best to refrain from any bouncing, swaying or active play until the milk has been digested better.
4. Keep your baby's head up while feeding.
When you're trying to find the right feeding position that's comfortable for both your baby and you, try to avoid a position where your baby's head is down.
 In other words, it is necessary to ensure that in the process of feeding the head of the child is above the level of his legs.
In other words, it is necessary to ensure that in the process of feeding the head of the child is above the level of his legs. 5. Raise the mattress at the head of the bed
It is a good idea to roll up some towels or blankets and place them under the mattress (but not on top of the mattress) in the crib. Make sure that only the headboard is raised and that there are no creases in the middle of the mattress. There should be a very slight slope from which the baby will not slip.
It's a natural process
If you ever ask yourself the question "Why is my baby spitting up?" just remember that spitting up is a completely natural, sometimes troublesome process that is part of parenthood. There are various reasons for spitting up in babies, but if your baby looks calm after a feed and is actively developing, you have nothing to worry about. In truth, spitting up is more of a problem for the parents than for the child himself, who may not even notice it.











