Burping the baby after feeding
How and When to Burp a Newborn
NewbornPediatricsLactation Consultation
Reviewed By Melinda L. Winterscheid, M.D.
While it might not be the most glamorous of tasks, burping your baby is important for his or her comfort. When babies are feeding, they take in air, which can build up and make them uncomfortable, causing you to find yourself with a fussy, squirmy child.
When to Burp Your Baby
How much a baby needs to burp will vary from baby to baby. If you're burping a newborn after breastfeeding, the baby will typically burp less because they swallow less air. Most babies will outgrow the need to be burped by 4-6 months of age.
You can often tell that a baby needs to be burped if he or she is squirmy or pulling away while being fed. This being said, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that parents try to burp their baby:
- When a nursing mother switches breasts or
- Every 2-3 oz.
if being bottle-fed (60 – 90 mL)
Pausing to burp frequently slows feeding and reduces air intake. However, if your baby has not successfully burped after a few minutes of trying, switch methods or give up and continue with the feeding. It is possible that your baby doesn’t actually have to burp. The best method for burping will generally differ for babies and parents – use the method that works best for you.
Burping Methods
There are three popular methods for burping newborns and babies. All will require a burping cloth to protect from spit up or wet burps and a gentle patting motion across a baby’s back to coax out the burp. The main difference is how the baby is held. Take care to support the baby’s head and neck safely and move the baby slowly and gently.
- Leaning
- Place a burping cloth or towel on your shoulder and/or back.
- Rest your baby’s chin or belly on your shoulder. (If opting for the belly, make sure that your baby can breathe easily.
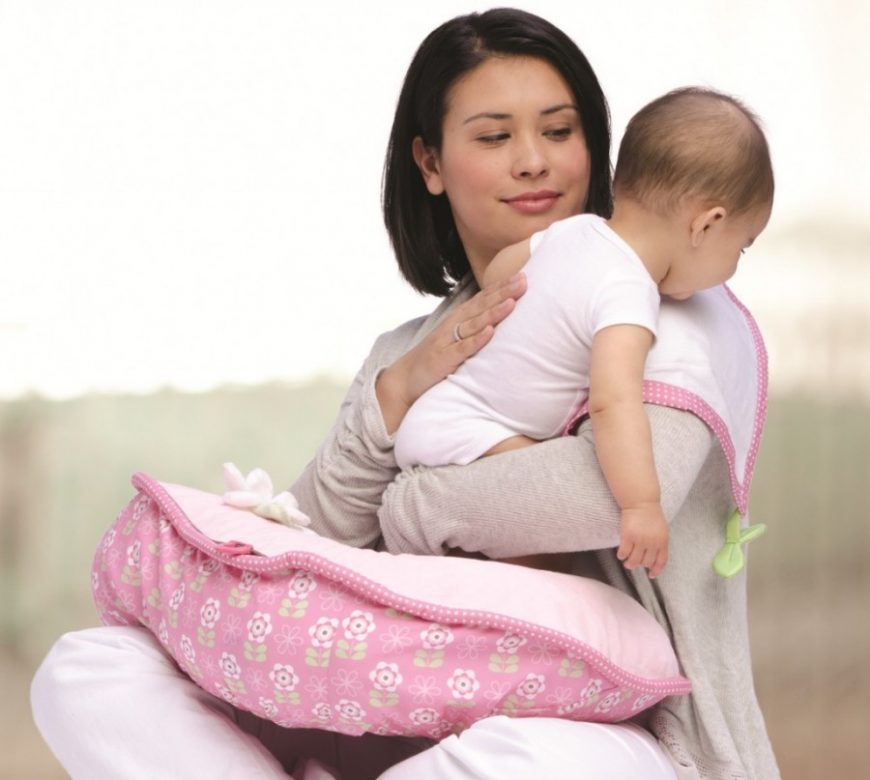 Parents may benefit from trying this option after their baby has better head/neck control.)
Parents may benefit from trying this option after their baby has better head/neck control.) - Support and hold your baby in place with one hand, while using the other to gently pat your baby on the back.
- Sitting
- Place a burping cloth or towel across your lap and put a bib on your baby.
- Using your palm to support your baby’s chest and your fingers to support his or her jaw (not throat), place your baby sitting on your lap, facing away from you.
- With your free hand, gently pat your baby on the back.
- Laying
- Place a burping cloth or towel across your lap.
- Lay your baby across your knees, perpendicular to your body.
- Use one hand to support your baby’s head so that it is higher than the chest. This will prevent blood from rushing to the head.
- With your free hand, gently pat your baby on the back.
More information about feeding and burping your newborn:
When to be Concerned About Spit Up
Feeding Your Newborn
Is My Baby Eating Enough?
Newborn Pediatrics;Lactation Consultation
It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled. Please turn on JavaScript and try again.
It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled. Please turn on JavaScript and try again.
Please turn on JavaScript and try again.
How to Burp a Sleeping Baby: Step-by-Step Guide
Some babies are gassier than others, but most babies will need to be burped at some point. Babies need to burp a lot more often than older kids and adults. They drink all of their calories, which means they can gulp a lot of air.
Burping a baby can be important day and night. Sometimes babies fall asleep while eating and you may need to find a way to burp them while they’re still asleep. It’s remarkable how much a newborn can sleep through.
Even if your baby falls asleep, try burping them for a few minutes before placing them back down to sleep. Otherwise, they make wake up in pain with trapped gas.
Not all babies burp, though, no matter if it’s on their own or with your help. If your baby is one that needs to be burped, read on for ways to do so even when they’re asleep.
It’s common for babies to fall asleep while eating, whether nursing or bottle-feeding. As their tummy fills and they start soothing sucking motions, they often become happy and relaxed and tend to drift off.
As their tummy fills and they start soothing sucking motions, they often become happy and relaxed and tend to drift off.
This is especially likely to happen at night when their sleep drive is strong. But even if your little one looks content and totally asleep, for some babies it’s important you try to get a burp out of them before lying them back down.
Burping a sleeping baby is basically the same as burping a baby who’s awake. You might move slower to help them stay asleep. Some burping positions are a bit easier to maneuver with a sleeping baby.
For example, many people sit a baby upright on their knee while supporting the baby’s head by cradling their chin. This position uses gravity and the baby’s own weight to get air up and out. However, this position is more likely to wake a baby, so you might not want to try it if your aim is to keep the baby asleep.
To burp a baby, they should be in a slightly upright position so you can put pressure on their tummy. If your baby doesn’t poop right after eating, you may want to change their diaper before feeding them at night so you don’t have to wake them up if they fall back to sleep while eating.
Here are some positions for burping a sleeping baby:
Burp between changing sides, or mid-bottle
A sleepy baby may enjoy their feeding so much that they overeat and don’t realize they need a pause to burp. Help your baby have a gentler burp and avoid any major gas pain by slowing down the feed.
Burp your baby between switching sides at the breast or before they finish their bottle. This will also help your baby make room for more milk instead of burping and spitting up any of their food.
Hold on your shoulder
If you feed your baby in a semi-upright position, you can gently move them all the way upright and onto your shoulder. Babies can keep sleeping in this cozy position while the pressure from your shoulder pushes on their tummy to release gas. Keep a burp rag over your shoulder if your baby tends to spit up.
Hold lower on your chest
Similar to the previous position, you can lift your baby from semi-upright to fully upright and keep them on your chest or sternum area. This may be most comfortable if you’re on a couch. Babies like to curl up with their legs in a frog position (a bonus move to release more gas from their bottoms) and you can support their head and wait for the burp to come.
This may be most comfortable if you’re on a couch. Babies like to curl up with their legs in a frog position (a bonus move to release more gas from their bottoms) and you can support their head and wait for the burp to come.
Rock on your arm (“sloth hold”)
After feeding, you can slowly turn them away from you at 45 degrees so their tummy rests on your forearm. Support their head in the crook of your elbow. Their legs may dangle on either side of your arm. This position puts pressure on their belly and you can gently pat their back until they burp. You can do this position while sitting or standing.
Lay on your knees
If you’re sitting in a chair, simply move your baby to a laying position on their tummy on your knees. You can move your legs side to side to rock them and gently pat or rub their back until a burp comes. A baby can remain asleep here as long as you want to stay sitting.
Burping is one of the many tasks parents have until their child grows into being more self-sufficient.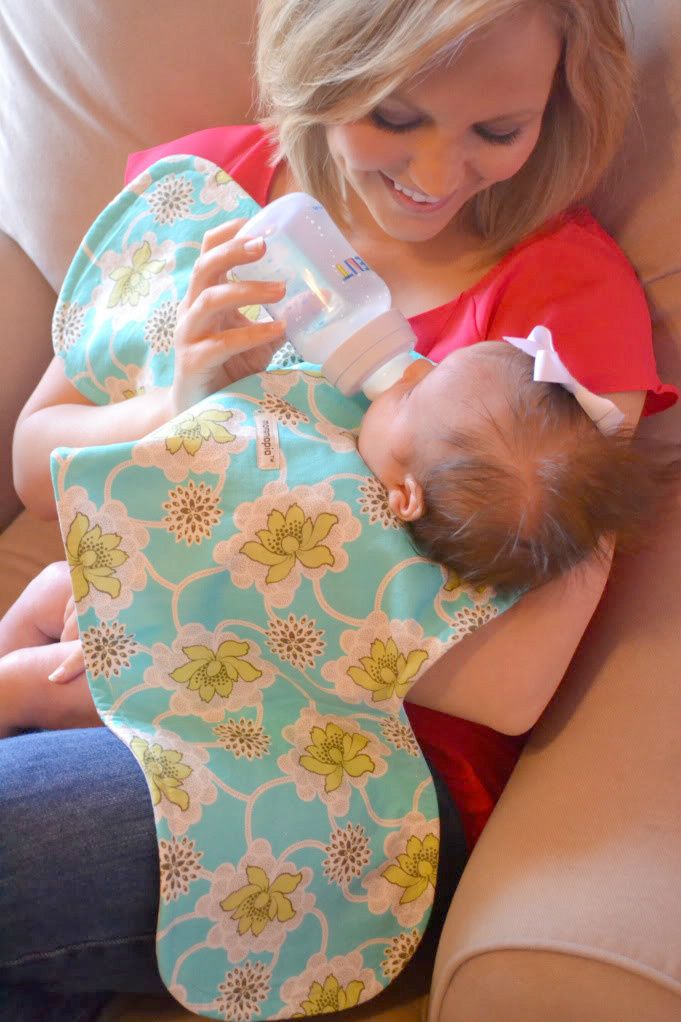 Kids and adults can easily release their own gas, but many babies need help because they have so little control over how their bodies are positioned.
Kids and adults can easily release their own gas, but many babies need help because they have so little control over how their bodies are positioned.
You’ll figure out pretty quickly if your baby is the type who can eat without burping or if they need to be burped every time. If your baby has a lot of gas or spit-up, you should talk to your doctor about reflux.
If you do have a colicky baby but you can’t seem to get them to burp, focus on any comfort measures that work and don’t worry too much about getting burps out. One study suggests that burping won’t help decrease colic.
Whether your baby burps a lot during the day, it may be worth it to burp them after every nighttime feeding. Since you’re already up feeding the baby, make the most of your time by giving a solid attempt at burping. This may get everyone a long stretch of sleep after the feeding.
Gas drops and gripe water are readily available at pharmacies but ask your doctor first before using any of them.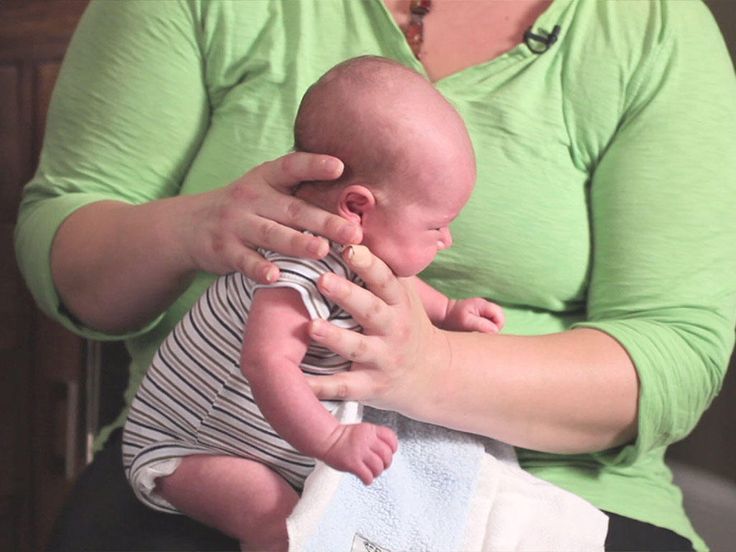 These supplements aren’t regulated for safety and may contain dangerous ingredients. If you have a very fussy and gassy baby — whether or not they spit up often — ask a doctor for coping skills. Most babies grow out of this after a few months.
These supplements aren’t regulated for safety and may contain dangerous ingredients. If you have a very fussy and gassy baby — whether or not they spit up often — ask a doctor for coping skills. Most babies grow out of this after a few months.
Risk of choking on spit-up is very rare. It’s still important not to overfeed your baby and to try to burp them after every feeding if they seem to benefit from it.
Burping usually only takes a minute or two. Sometimes a burp will come up as soon as you move your baby upright, and sometimes you have to wait a little while and help things with a gentle pat or tummy pressure.
Another helpful strategy is to get your baby in the habit of falling asleep in their crib rather than while feeding. When you notice them getting sleepy at the breast or bottle, stop the feeding, burp them for a minute or so, and then put them down to sleep. The younger you start this, the easier it is to do.
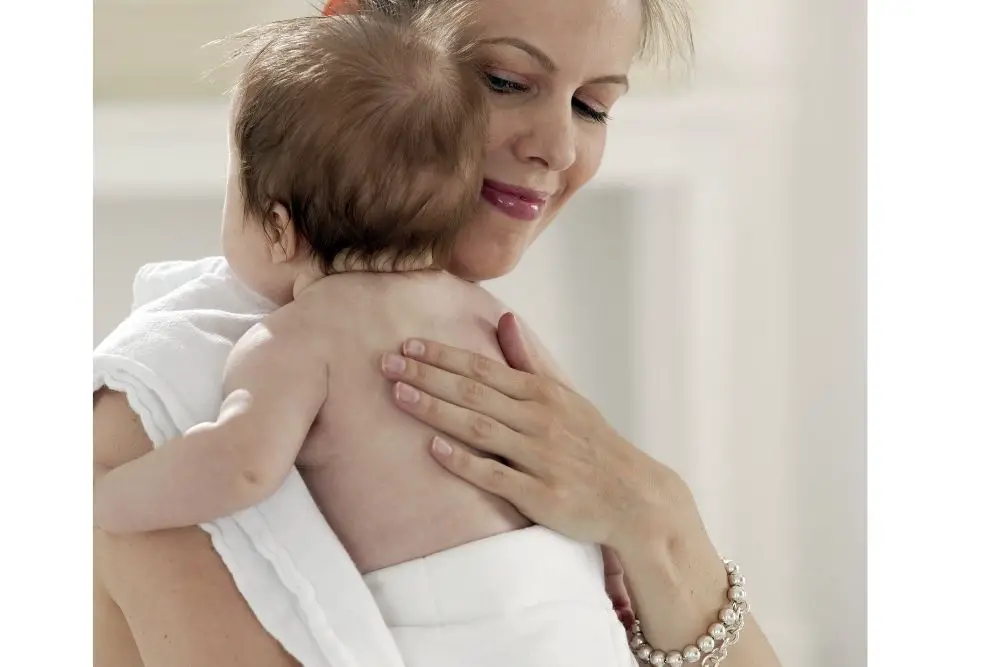
If your baby is often stiff and uncomfortable, talk with their doctor about more help for relieving gas.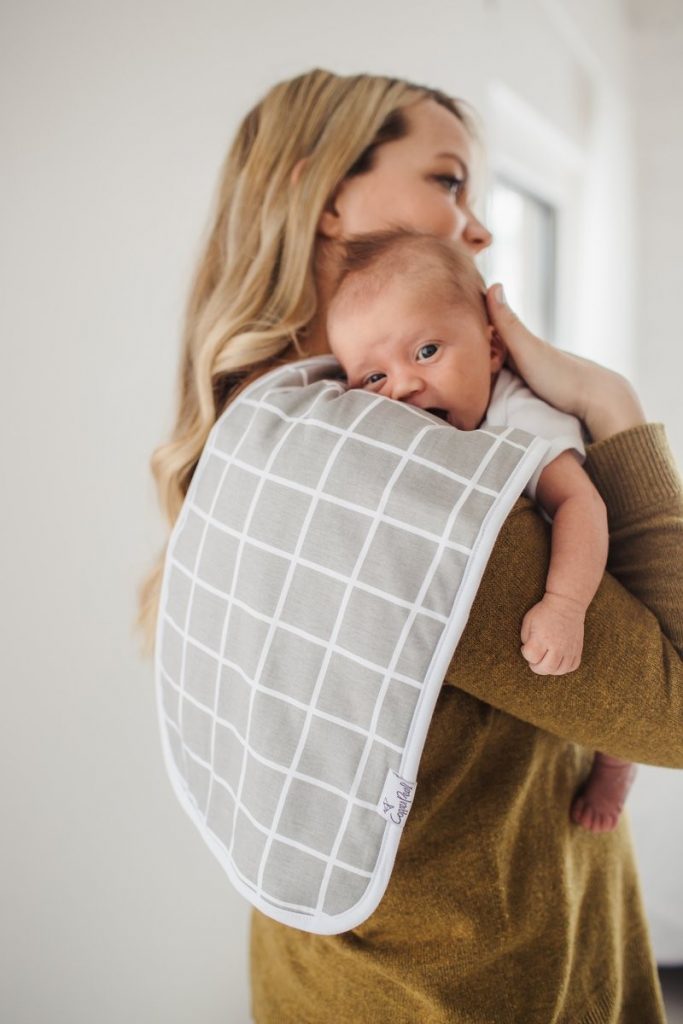 Some babies with bad reflux may need to stay upright for 30 minutes after eating, day or night.
Some babies with bad reflux may need to stay upright for 30 minutes after eating, day or night.
If your baby is asleep, try burping them for a minute before you lay them back down. Sometimes babies don’t need to burp as much at nighttime because they eat slower and don’t get as much air while feeding.
If they wake up crying, soothe them, check to see if they need a clean diaper, feed them again if it’s time, and try to burp them after that feeding.
Some people believe that bottle-fed babies are more likely to get gassy, but evidence of this is only anecdotal. Bottles may expose babies to more air as they gulp and may make it easier to overfeed your baby. But every baby is different and even breastfed babies can be very gassy — sometimes because they’re sensitive to food in their mother’s diet.
Though uncommon, a breastfeeding mother may have to experiment a lot before figuring out exactly what they ate to cause their baby’s upset stomach. There’s no solid research to tell a mother what exactly causes her baby’s excess gas. Also, many babies with gas aren’t bothered by it.
Also, many babies with gas aren’t bothered by it.
Burping is a basic but important way you can take care of your baby and keep them comfortable. Even if your baby is asleep, burping may be helpful to allow them to relieve gas so they don’t get uncomfortable or wake up too soon.
Why does the baby spit up after feeding?
search support iconSearch Keywords
Regurgitation is a common condition in newborns and infants and is most often a normal variant. However, it is not uncommon for parents to worry if their baby is spitting up frequently, believing that it is due to nutritional or health problems in general. Sometimes these fears are not unfounded, and regurgitation really has a pathological origin. What is its cause and when should you really consult a doctor about this?
Regurgitation - Return of a small amount of food (uncurdled or partially curdled milk) from the stomach up the digestive tract: into the esophagus and further into the oral cavity. According to statistics, at least 1 time during the day, at least 50% of babies from 0 to 3 months old can spit up, more than 60% of children 3-4 months old, and in 5% of children spit up continues up to the year 1 .
According to statistics, at least 1 time during the day, at least 50% of babies from 0 to 3 months old can spit up, more than 60% of children 3-4 months old, and in 5% of children spit up continues up to the year 1 .
Regurgitation in newborns is considered a physiological process. It is caused by a number of factors, including:
- Features of the structure of the upper digestive tract in babies
- In newborns and infants up to a year of life, the stomach has a spherical shape. It holds a small amount of food, besides, the release from it into the duodenum is slower in comparison with children after the year 2 .
- Weakness of the lower esophageal sphincter that separates the esophagus from the stomach
- Normally, the lower esophageal sphincter should tightly "close" the esophagus, allowing food to pass into the stomach and not allowing it to enter back into the upper digestive tract. However, in young children (up to a year), the muscles of the esophageal sphincter are poorly developed, and it does not do its job very well 2 .

- Slow movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract
- The neuromuscular system of newborns is immature. It does not ensure the proper movement of food through the esophagus, causing regurgitation.
One of the important risk factors contributing to regurgitation in newborns is aerophagia. This is the swallowing of large amounts of air during feedings. This happens when the baby is not properly attached to the breast, the mother has a lack of breast milk, or the bottle is in the wrong position in the child who receives the mixture. The size of the opening in the nipple also matters - if it is too large, the newborn swallows a lot of air 3 .
With aerophagia, the baby becomes capricious, restless immediately after feeding. Noticeable bloating. If the baby spits up immediately after a feed, the milk (or formula) remains practically fresh, uncurdled 3 .
Promotes regurgitation after feeding and a predominantly horizontal position of the baby during the day, combined with relatively high intra-abdominal pressure 4 . Therefore, the correct position of the baby after feeding is so important. To avoid regurgitation of an excessive amount of stomach contents, after feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in an upright “column” position for some time (10-20 minutes), lightly patting on the back and allowing excess air to “exit”.
Therefore, the correct position of the baby after feeding is so important. To avoid regurgitation of an excessive amount of stomach contents, after feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in an upright “column” position for some time (10-20 minutes), lightly patting on the back and allowing excess air to “exit”.
Regurgitation in many newborns can be provoked by other situations in which pressure in the abdominal cavity increases and stomach contents are thrown into the esophagus, in particular 3 :
- tight swaddling;
- stool disorders, in particular constipation;
- long, forced cry and some others.
Want to avoid common feeding problems?
Start with a baby bottle with an anti-colic system that helps you avoid common feeding problems such as colic, gas and spitting up*
How can you tell the difference between normal spitting up and vomiting?
Sometimes regurgitation is considered a manifestation of disorders in the digestive tract of children.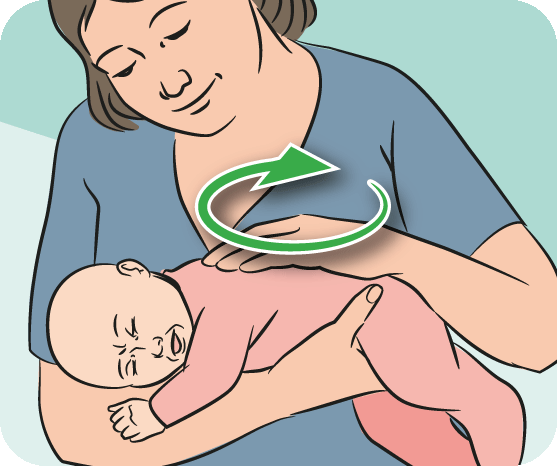 Due to the constant reflux of acidic stomach contents into the upper sections, inflammation and other complications may develop, including growth retardation, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and others. Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
Due to the constant reflux of acidic stomach contents into the upper sections, inflammation and other complications may develop, including growth retardation, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and others. Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
If the mother is worried that her baby is spitting up, keep track of when this happens and count the total number of spit ups per day. Normally, regurgitation usually occurs after eating (the child burps after each feeding), lasts no more than 20 seconds and repeats no more than 20-30 times a day. With pathology, the problem manifests itself at any time of the day, regardless of when the baby was fed. Their number can reach 50 per day, and sometimes more 1 .
The amount of discharge during regurgitation also matters. With normal, physiological regurgitation, it is approximately 5 - 30 ml. If this volume fluctuates between 50 and 100 ml, it is already defined as profuse vomiting. When the range of the jet of vomit is up to 50 cm, doctors talk about "vomiting a fountain." A variant of atonic vomiting is possible, when the contents of the stomach flow "sluggishly". It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
When the range of the jet of vomit is up to 50 cm, doctors talk about "vomiting a fountain." A variant of atonic vomiting is possible, when the contents of the stomach flow "sluggishly". It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
Vomiting in babies is a warning sign. Doctors are especially alarmed by repeated vomiting, a fountain, with an admixture of bile, in combination with constipation. Vomiting can lead to the development of dehydration, acid-base imbalance and other consequences, therefore, if it occurs, you should urgently contact a pediatrician to find out the cause and begin treatment. A doctor's consultation is necessary if the child is spitting up a lot (more than 15-30 ml at a time), with a frequency of more than 50 episodes per day 1.3 .
Physiological regurgitation: symptoms
Regurgitation in newborns, which is considered a normal variant and does not cause concern to pediatricians 3 :
- usually continues for a certain period of time;
- is characterized by slow, "passive" leakage; if the baby spits up a fountain, it is better to consult a doctor;
- has a sour smell of curdled milk;
- occurs without the participation of muscles - the baby does not strain during regurgitation;
- does not affect the general well-being of the baby.

How to help a newborn who spit up often?
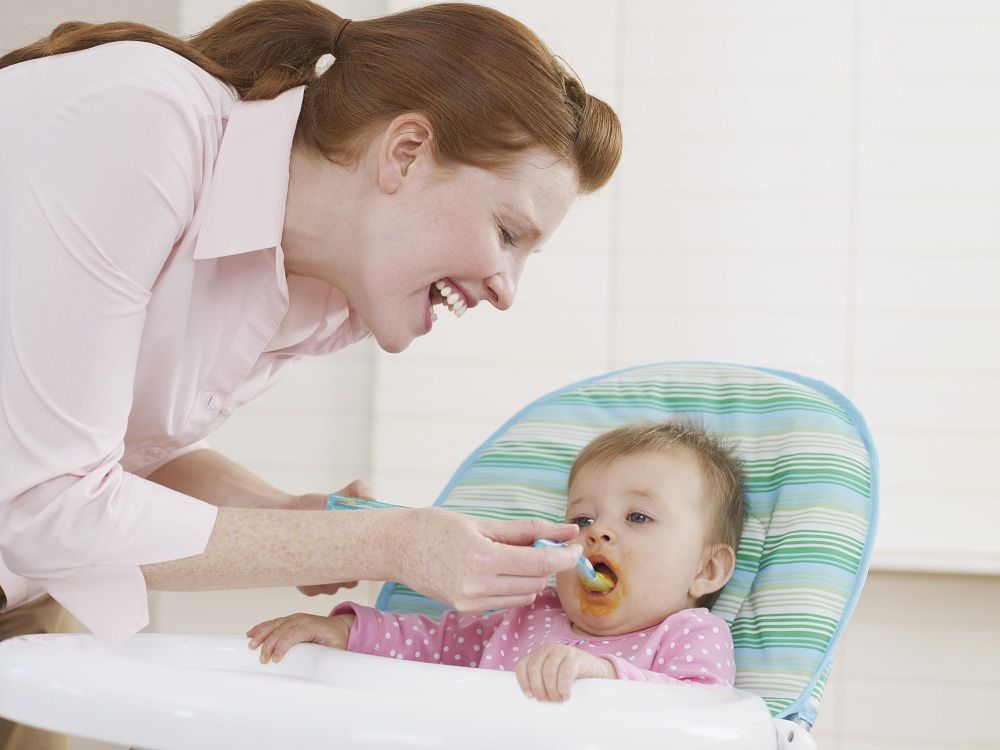
If the baby is healthy, no medication is prescribed for spitting up. To help the child allow simple measures based on lifestyle changes and feeding.
- Frequent feeding of the baby
It is known that the baby is more prone to spit up if his stomach is full. To improve the situation, it is recommended to feed the baby more often, avoiding oversaturation, best of all - on demand 5 .
- Correct feeding technique
Every feeding, the mother must ensure that the baby does not swallow too much air during suckling. When sucking, there should be no loud, smacking, clicking sounds. You also need to control that the baby captures the nipple along with the areola.
- Choosing the right bottle and nipple
If the newborn is bottle-fed and receiving formula, it is important to choose the right bottle and nipple. The hole in it should be such that the milk flows out in drops, and not in a stream. The nipple must not be filled with air
The hole in it should be such that the milk flows out in drops, and not in a stream. The nipple must not be filled with air New Anti-colic bottle with AirFree valve
The AirFree valve prevents air from entering the baby's stomach.
- Baby standing upright after eating
To allow air that has entered the digestive tract during meals to escape, it is important to keep the newborn upright for 10-20 minutes after feeding 4 .
- Ensure the correct position of the baby during sleep
To reduce the negative impact of the acidic contents of the stomach on the esophagus, it is necessary to put the baby to sleep in the supine position. The side or prone position, which many pediatricians used to recommend, is no longer recommended. It was found to be associated with an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome 5 .
If parents notice alarming symptoms, such as spitting up too often or large volume, etc.
 , it is important to consult a pediatrician without delay. This will allow you to identify the real problem in time and help the baby grow up healthy and happy.
, it is important to consult a pediatrician without delay. This will allow you to identify the real problem in time and help the baby grow up healthy and happy.
References1 Zakharova I. N., Andryukhina E. N. Regurgitation and vomiting syndrome in young children // Pediatric pharmacology, 2010. V. 7. No. 4.
Nagornaya 2900 V., Limarenko M. P., Logvinenko N. G. Experience with the use of domperidone in suspension in young children with regurgitation syndrome // Child Health, 2013. No. 5 (48).
3 Zakharova IN Regurgitation and vomiting in children: what to do? //Pediatrics. Supplement to Consilium Medicum, 2009. No. 3. S. 58-67.
4 Zakharova I. N., Sugyan N. G., Pykov M. I. Regurgitation syndrome in young children: diagnosis and correction // Effective pharmacotherapy, 2014. No. 3. P. 18-28.
5 Vandenplas Y. et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) //Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition.
 2009; 49(4): 498-547.
2009; 49(4): 498-547. You are leaving the Philips Healthcare (“Philips”) official website. Any links to third party websites that may be included on this site are provided solely as a convenience to you. Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain.
I understand
You are about to visit a Philips global content page
You are about to visit the Philips USA website.
How to help the baby when regulating
Support icon ofKeywords for searching
Home ›!! How to help a child in sprinkling
Home Home ›!! How to help a child in regurgitation
↑ Verki
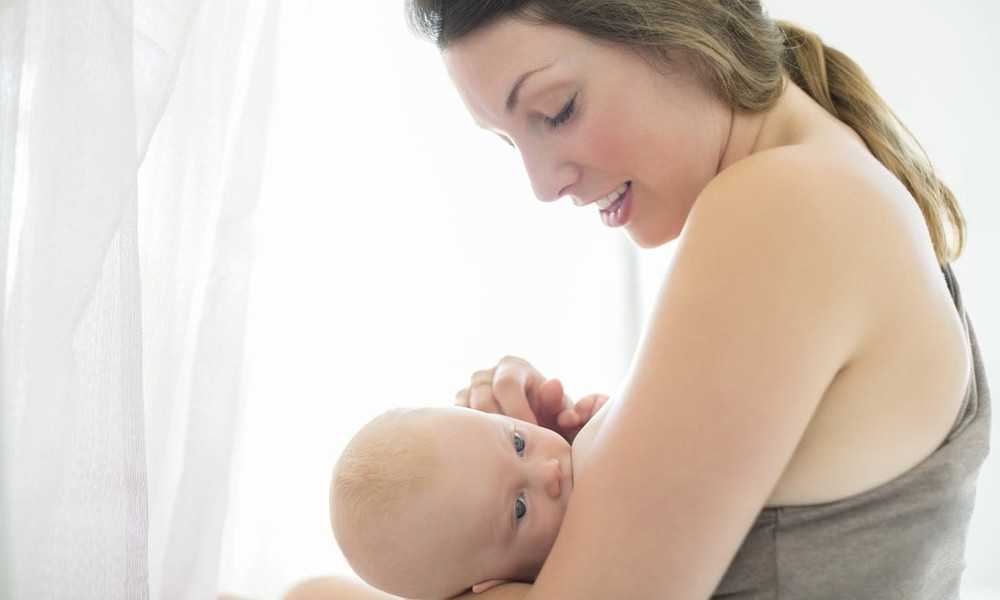
Breastal feed - breastfeeding a very special time for a mother and her newborn baby. Together with the feeling of closeness and affection that feeding brings, understanding its nuances cannot but raise many questions, including the question of how to help an infant spit up.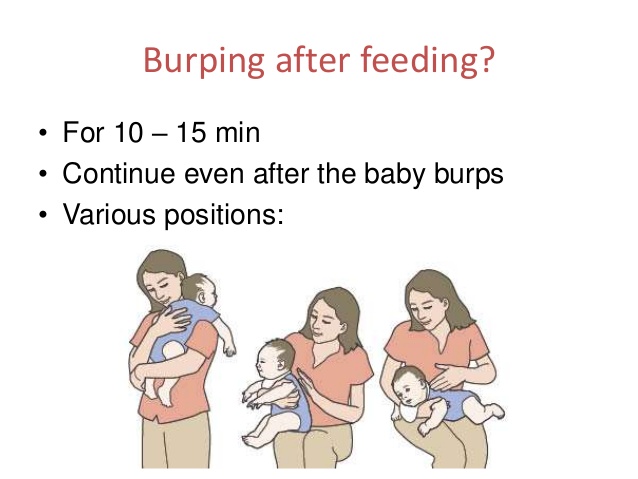 Regurgitation in a newborn is by no means always the result of a simple pat on his back.
Regurgitation in a newborn is by no means always the result of a simple pat on his back.
In this article, we'll talk about the basics of helping a newborn spit up, as well as other questions you may have about spitting up.
Why do babies spit up?Let's get this straight: Why do newborns need to burp in the first place? During feeding, children usually swallow extra air - this is called aerophagia. Spitting up helps prevent this air from entering the intestines, as well as vomiting, gas, and crankiness in the baby. To avoid the return of milk after feeding, you should give the baby the opportunity to burp more often.
How to help a newborn spit up?
During the first six months, the baby should be kept upright in a column for 10-15 minutes after each feed. This will help keep the milk in his stomach, but if the baby occasionally burps anyway, parents need not worry. While carrying your baby in an upright position, you can put a baby diaper or wipes on your shoulder to keep your clothes clean.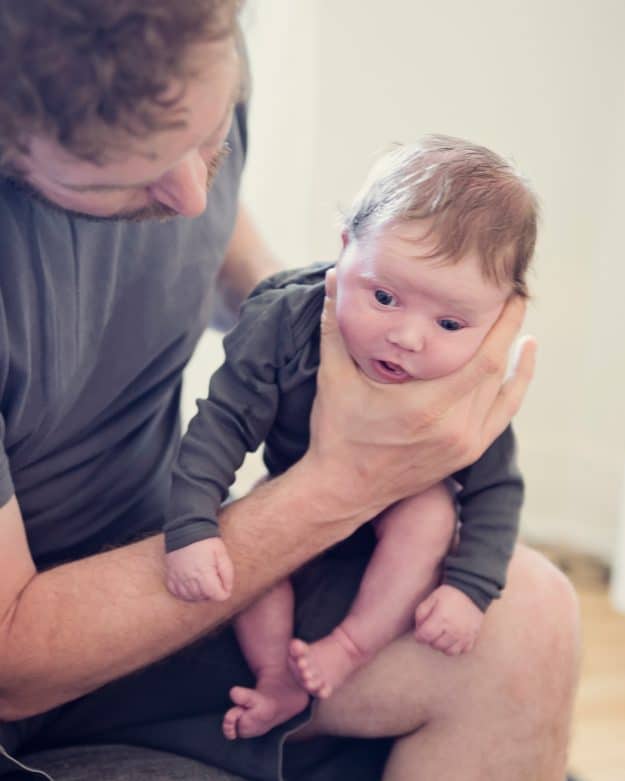
We've already seen why spitting up is important, now let's find out how to help your baby spit up. Parents should gently pat the baby on the back with a hand folded in a handful until he burps. Folding your hand into a handful is important because clapping with a flat palm may be too strong for an infant.
Every baby is different and there is no one right position for spitting up. To get started, you can try the following options:
- Sitting position with the baby on the chest. In this position, the parent puts the baby's head with his chin on his shoulder and with one hand supports the baby under the back. With the other hand, you can gently pat the baby on the back. This method is most effective in a rocking chair or when the baby is gently rocking.
- Holding a child upright on one's legs. With one hand, parents can hold the baby by the back and head, supporting his chin and placing his palm on the baby’s chest, with the other hand, you can gently pat him on the back.
 At the same time, it is important to be careful: do not press the child on the throat, but only gently support his chin.
At the same time, it is important to be careful: do not press the child on the throat, but only gently support his chin. - Holding a baby lying on his tummy in his lap. Make sure his head is above his chest and gently pat your baby on the back until he burps.
Here are some tips on how best to help your newborn spit up:
- Let your baby spit up during feeding. If the baby is restless or has swallowed air, it is worth giving him the opportunity to burp during feeding, and not just after.
- When bottle feeding, let the newborn burp after every 50-60 ml.
- When breastfeeding, let the baby burp at every breast change.
It is important to let your baby spit up after eating, even if he spit up during feeding!
If your baby is gassy, spit up more often. Also, if he vomits frequently or suffers from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), have him spit up after every 30 ml bottle-feeding or every five minutes while breastfeeding.

How long should a baby be held for it to burp? It's different for everyone, but generally keeping a newborn upright for 15 to 20 minutes after a feed helps the milk stay in the baby's stomach.
Minimize the amount of air you swallow. Gas production and regurgitation result from aerophagia during feeding. The baby will inevitably swallow air, but there are ways to prevent it from swallowing too much. Whether you bottle feed your baby or combine breastfeeding with bottle feeding, the Philips Avent anti-colic bottle with AirFree valve is designed so that the nipple is always filled with milk without excess air, even in a horizontal position, thus preventing the baby from swallowing excess air during feeding.
Reducing the amount of air your baby swallows can help reduce your baby's risk of colic, gas, and spitting up.
Breastfeeding is a wonderful time to strengthen the bond between parent and baby. Every mom and every baby is different, so learning to help your newborn burp properly can take time and practice.