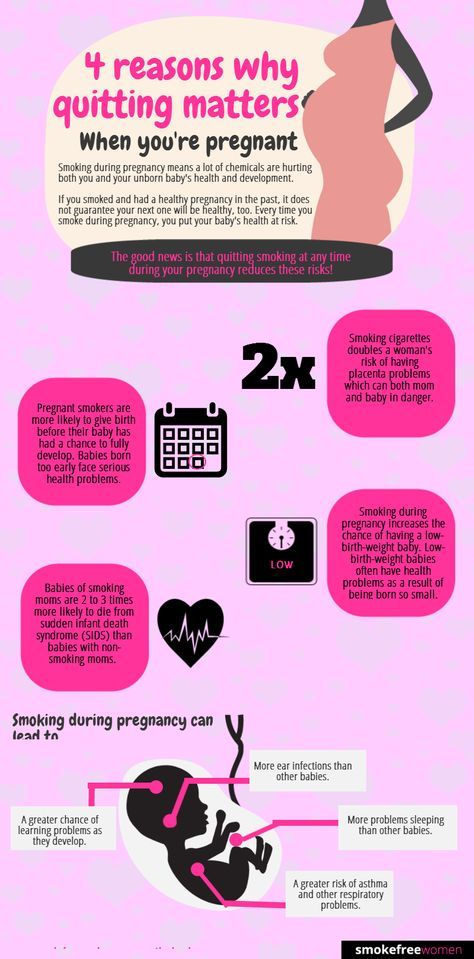
Can food poisoning hurt baby during pregnancy
Symptoms, treatment, dangers, and more
Pregnancy brings a greater chance of getting food poisoning. It can be a scary experience for expecting parents. There are many risks that come with food poisoning during pregnancy.
Hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy can alter a person’s immune system, leading them to be more susceptible to food poisoning.
Food poisoning can happen after a person eats or drinks something containing bacteria, a virus, parasites, or other contaminants.
Food poisoning in pregnancy can result in harm to the baby, early labor, pregnancy loss, or stillbirth. However, there are many ways to prevent it or treat it.
This article will explain what the symptoms of food poisoning during pregnancy are, explore its possible dangers, and discuss treatment and prevention methods.
General symptoms of food poisoning may include:
- upset stomach
- abdominal cramps
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- fever
The timing of symptoms may vary depending on when a person has eaten the contaminated food and what type of food poisoning a person has.
The type of food poisoning may also produce varying symptoms. According to the CDC, the following types of food poisoning have the following symptoms:
Listeria
Pregnant women are 10 times more likely to get a Listeria infection than the general population. Symptoms can take between a week to a month to develop. They may include:
- fever
- muscle ache
- headache
- fatigue
Salmonella
Salmonella symptoms can begin between 6 hours and 6 days after exposure to the contaminated food and may include:
- stomach pain
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- nausea
Norovirus
Norovirus symptoms usually start 12–48 hours after a person has consumed the contaminated food or drink. Norovirus symptoms include:
- stomach cramps
- diarrhea
- vomiting
- nausea
A person may start to experience E. coli symptoms 3–4 days after consuming the contaminated food or drink. These symptoms may include:
These symptoms may include:
- stomach cramps
- vomiting
- diarrhea
Staph (Staphylococcus aureus)
Staph symptoms may occur quickly, between 30 minutes and 8 hours after a person consumes the affected food. They can include:
- nausea
- vomiting
- stomach cramps
- diarrhea
There are some other conditions that can give a person similar symptoms to food poisoning.
Food poisoning or a stomach bug?
Gastroenteritis, or a stomach bug, is highly contagious and can spread easily from person to person. It is an inflammation of the intestines. Contaminated food or drink can cause gastroenteritis, but the main cause is usually a bacterial or viral infection.
Food poisoning is usually not contagious. People will only get it at the same time as someone else if they eat the same contaminated food.
Find out more about gastroenteritis here.
Food poisoning or morning sickness?
Morning sickness also presents similar symptoms to food poisoning. A person with morning sickness may experience symptoms during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, though they can occur at any time.
A person with morning sickness may experience symptoms during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, though they can occur at any time.
Food poisoning can be dangerous to the unborn child as well as the parent. It can cause serious health problems for the child, pregnancy loss, premature delivery, stillbirth, or even the death of the person carrying the child.
Developing fetuses need to get as many nutrients as possible from their parent carrying them. If the parent is unable to keep food in their body for long enough for their body to absorb the nutrients, the fetus may not grow appropriately.
A person with mild symptoms can pass an infection to their unborn child during pregnancy without the parent even knowing that they have food poisoning.
Newborns can also experience health issues, and can even be born with food poisoning if the person carrying the child has an infection.
While pregnant people should always visit a doctor if they have symptoms of food poisoning, there are some things that they can do at home to help too.
Foods
It can be difficult for a person to feel like eating anything when they have food poisoning. However, a pregnant person needs to eat to keep their strength up and ensure they are eating enough for themselves and the unborn child. It is best to eat bland, low-fat foods that will help keep the stomach as calm as possible.
Foods they can eat include:
- saltine crackers
- toast
- applesauce
- mashed potatoes
- boiled rice
Drinks
A person with food poisoning has a high risk of developing dehydration. Therefore, ensuring that they consume enough fluids is very important. Easy ways of replacing lost fluids include drinking:
- plain water
- fruit juices diluted with water
- sports drinks containing electrolytes
- broths
Oral rehydration solutions or salts can also help replace glucose and electrolytes. They are made up of water with extra salt and glucose that help the body rehydrate.
Natural remedies
Ginger has properties that ease nausea and vomiting. Ginger tea may help a person if they are experiencing these symptoms.
Find out more about the benefits of ginger tea here.
A person should contact a doctor if they are pregnant and suspect they have food poisoning. Even though most people will recover from food poisoning without needing to seek medical attention, a pregnant person must also consider the health of the unborn child.
A pregnant person should contact a doctor immediately if they have any of the following symptoms:
- a temperature of over 102°F
- blood in the stool
- diarrhea lasting longer than 3 days
- dizziness
- a dry mouth or throat
- frequent vomiting
Although the risks of food poisoning in pregnancy can be scary, there are ways to prevent it.
Food types to avoid
Food poisoning can come from a variety of different food products, but there are steps people can take to reduce their risk. For example:
For example:
Meat and poultry
Always make sure that these are cooked through. This will lower the risk of developing food poisoning. A meat thermometer can help a person check that their meat has reached a safe minimum internal temperature. For example, a person should cook beef, pork, steaks, and chops to at least 145°F (63°C), giving the meat a 3 minute rest time after cooking.
Vegetables
Unwashed vegetables and raw vegetables can cause a person to develop food poisoning. Make sure to carefully wash all vegetables.
Eggs
Consuming raw or undercooked eggs increases a person’s risk of foodborne illnesses. Pasteurized eggs carry a lower risk.
Milk
Unpasteurized milk can increase a pregnant person’s risk of food poisoning. This includes cheeses made with unpasteurized milk.
Seafood
Pregnant people should avoid raw or undercooked fish, like sushi. Cooked seafood and canned fish and seafood carry a lower risk of causing foodborne illnesses.
Other foods pregnant people should avoid include:
- raw sprouts
- deli salads
- pâtés
A pregnant person should also avoid deli meats and hot dogs unless cooked to a temperature of 165ºF (74ºC) or above.
Food safety tips
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend four food safety tips to try to avoid food poisoning:
Clean
Make sure that everything is clean before preparing food. This includes washing hands and working with clean utensils and cutting boards on freshly cleaned countertops. This lowers the risk of contamination.
Rinsing fresh fruits and vegetables under running water can remove the germs that may cause food poisoning.
Separate
Avoid cross-contamination by ensuring that all utensils that come into contact with raw foods do not then touch cooked or ready-to-eat foods.
Keep raw meat, poultry, seafood, and eggs separate from other foods when grocery shopping and after returning home, from storing them in the fridge to the preparation of meals.
Cook
Use a thermometer to determine if the internal temperature of their food is high enough to kill off germs that could cause food poisoning.
Chill
Chill perishable food as soon as possible, making sure the fridge stays at a temperature of 40°F (4°C) or below. Thaw frozen food in the refrigerator, in cold water, or in the microwave. When food is thawed on the counter, bacteria can multiply quickly in any parts of the food that reach room temperature.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 48 million people get sick from a foodborne illness each year. 128,000 of those people require hospitalization, and 3,000 of them pass away.
Pregnant people are more susceptible to food poisoning.
Food poisoning usually resolves itself after a few days, but in a pregnant person, it can be a serious and even fatal illness. Following food safety protocols can help pregnant people avoid food poisoning, have a safe and healthy pregnancy, and avoid any related issues for them and their child.
Food Poisoning During Pregnancy: What To Do
Written by Rachel Reiff Ellis
In this Article
- Types of Food Poisoning
- Symptoms of Food Poisoning During Pregnancy
- Home Remedies for Food Poisoning When Pregnant
- When to See a Doctor About Food Poisoning When Pregnant
- Complications of Food Poisoning When Pregnant
- Preventing Food Poisoning When Pregnant
It’s common to have morning sickness when you’re pregnant. But sometimes your symptoms might come from something else -- food poisoning.
How can you tell if it’s foodborne illness that’s making you sick? Once you know it is, how can you treat it safely when you have a baby on board?
Types of Food Poisoning
Your immune system is weaker than usual when you’re pregnant, so it’s harder for your body to fight off germs that might hitch a ride on food and make you feel bad.
You can get food poisoning when you eat foods contaminated with:
- Bacteria
- Parasites
- Viruses
- Certain chemicals
There are many types of food poisoning. Some are more common, and more dangerous, when you’re pregnant.
Some are more common, and more dangerous, when you’re pregnant.
- Listeriosis. This comes from listeria bacteria. Pregnant women are 13 times more likely to get listeriosis than other people. It can lurk in ready-to-eat meats like hot dogs and cold cuts. Poultry, seafood, and dairy products can have it, too, especially if they’re not pasteurized. It can grow even on foods that are cold in the refrigerator.
- Escherichia coli (E. coli). This bacteria lives in your gut naturally. Still, you can get sick if you eat contaminated fruits and vegetables, raw or undercooked meats, or unpasteurized milk and fruit juices with certain types of E. coli.
- Salmonella. This bacteria causes something called salmonellosis. Most often, you get it from undercooked or raw eggs, meats, poultry, or unpasteurized foods. You can also get it if you eat food that has touched soil or animal poop infected with salmonella.
- Campylobacter. You get this bacteria mainly through contaminated chicken or unpasteurized foods.
- Norovirus. This is the main cause of foodborne illness in the U.S. The virus spreads easily through contaminated food and drinks.
Symptoms of Food Poisoning During Pregnancy
It can be tricky to know when food poisoning is to blame for your sickness. Sometimes, germs from food can make you sick right away. Other times, they hang around in your body for days or even weeks before you have symptoms.
Usually, it causes:
It can be tricky to know when food poisoning is to blame for your sickness. Sometimes, germs from food can make you sick right away. Other times, they hang around in your body for days or even weeks before you have symptoms.
Usually, it causes:
- Stomach pain
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
- Dehydration
Often, food poisoning can feel like the flu, because you might have fever, headache, and body aches along with your other things.
- Stomach pain
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
Often, food poisoning can feel like the flu, because you might have fever, headache, and body aches along with your other things.
Home Remedies for Food Poisoning When Pregnant
When you’re pregnant, it’s more than just your health you’re protecting. Some bouts of food poisoning can pose problems for your baby, whose immune system isn’t strong enough yet to fight off germs.
When you start having symptoms that seem like food poisoning, call your doctor right away. They can help you figure out if it is food poisoning, and if so, what may have caused it.
You may be able to handle your symptoms at home with your doctor’s guidance. However, if you're vomiting and having diarrhea, you may need treatment at the doctor’s office or even a hospital. Don’t take any over-the-counter medications without talking to your doctor first.
If your case is mild enough to treat at home, work on rest and rehydration. Get fluids however you can: ice chips, small sips of water or clear liquids, or by drinking a sports drink with electrolytes in it. Wait until you’re sure your vomiting is over before you try to eat. Take your first foods slowly, and stick with bland, non-greasy foods.
Get fluids however you can: ice chips, small sips of water or clear liquids, or by drinking a sports drink with electrolytes in it. Wait until you’re sure your vomiting is over before you try to eat. Take your first foods slowly, and stick with bland, non-greasy foods.
When to See a Doctor About Food Poisoning When Pregnant
Your food poisoning needs professional treatment if you’re having:
- Signs of dehydration like excessive thirst, dry lips, little to no urine, or dizziness
- Vomiting or diarrhea that won’t stop
- Severe pain in your abdomen
- A fever higher than 101 F
- Blood or pus in your stool
- Black or tarry stool
Call your doctor right away if you have one or more of these problems. They’ll do tests on your blood or stool to find out what's making you sick. You may need treatment with antibiotics. They’ll also want to be sure your body has enough fluids. You may need an IV to help your body rehydrate.
Complications of Food Poisoning When Pregnant
Certain kinds of food poisoning are very dangerous for your unborn baby.
If you get listeriosis , you may have no symptoms at all. However, you can pass it on to your baby. That can cause serious health problems like:
- Paralysis
- Blindness
- Seizures
- Issues with the brain, heart, or kidneys
At worst case, listeriosis can cause preterm labor, low birthweight, and even miscarriage or stillbirth.
Salmonellosis can also pass to your baby and put them at risk of serious complications like meningitis.
Campylobacter can cause miscarriage if you get it early in your pregnancy. It’s also very dangerous if you have it at the time you give birth and pass it to your newborn. Infection in a new baby can be life-threatening.
For you, the most common complication from food poisoning in general is dehydration. Some foodborne illnesses, especially E. coli, can also cause kidney damage.
Preventing Food Poisoning When Pregnant
You can protect yourself from many kinds of food poisoning, whether you’re pregnant or not, by being careful about what you eat and how you handle it.
Safe food handling tips:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before and after you touch food.
- Don’t let raw meat come in contact with anything you’ll eat raw, like produce, or food that’s already prepared.
- Keep perishable foods refrigerated or frozen.
- Clean fruits and vegetables before you eat or cook them.
- Wash utensils and food prep surfaces after you use them.
- Cook food to a high enough temperature to kill germs.
- Refrigerate leftovers right away. Don’t eat food that’s been sitting out or that has expired.
Certain foods should be off the menu until after your baby is born. Don’t eat or drink:
- Unpasteurized dairy products, like raw milk and some brands of soft cheese
- Raw or undercooked meat, poultry, fish, or shellfish
- Runny or raw eggs, or things that contain them, like cookie dough and homemade eggnog. Pasteurized raw eggs are OK.
- Hot dogs or deli meat, unless heated to 165 degrees
- Refrigerated patés or meat spreads.
 Jarred or canned are OK.
Jarred or canned are OK. - Premade chicken, ham, or seafood salads from a deli
- Smoked fish, unless it came from a can or you cook it
- Unpasteurized juice or cider
- Sprouts
Also pay attention to food recalls. Companies have to tell the public if they find out something they’ve sold is making people sick.
Poisoning during pregnancy: treatment, prevention
Pregnancy is a magical time in every woman's life. A rounded figure, an unusual step, a happy glint in her eyes, all this makes the expectant mother especially beautiful and charming.
At the same time, a baby under the heart imposes on a woman a certain level of responsibility. She needs to take better care of herself, learn not to be nervous, get more rest and pay special attention to her diet.
It is important that the products that end up on the table are fresh and of high quality, the dishes are balanced and the emphasis is on useful microelements and vitamins. This approach to nutrition will be the key to the proper intrauterine development of the fetus.
This approach to nutrition will be the key to the proper intrauterine development of the fetus.
Sometimes in the position of girls, taste preferences change. Even if before that she had never eaten papaya and hated avocados, now a woman may want these particular foods in the middle of the night. And ask them to add marinated octopus and a couple of squids to them. Also during pregnancy, some desire to eat fresh vegetables and fruits more often increases. It would seem that there is nothing wrong here. Except for one "but".
Let's say you want plenty of vegetables and overseas fruits in winter. We must be aware that, firstly, our vegetables, which grew on their own, were not stuffed with antibiotics and other chemicals will be difficult to find. Secondly, any overseas products must retain an attractive appearance, despite the long journey. Therefore, you need to understand that they will also be stuffed with hazards.
So, if you used to eat all these goodies and nothing, then the pregnant woman’s body, which works according to other laws, can react to poisons and severe poisoning will develop.
Also, any other products of poor quality and with violation of the shelf life can cause poor health.
The main symptoms of poisoning
Poisoning during pregnancy looks exactly the same as in other people. That is, a person begins to experience:
-
nausea,
-
weakness,
-
dizziness,
-
malaise,
-
vomiting, diarrhea,
-
cramps in the stomach,
-
flatulence,
-
jumps in blood pressure may be observed.
As a rule, poisoning is caused by ingestion of E. coli. It acts only within the gastrointestinal tract and cannot cause any harm to the fetus through the placenta. It's a good news. But there is also bad news.
-
Food poisoning causes vomiting, which is a fast track to dehydration. It, in turn, will lead to thickening of the blood and a problem with blood flow.
 There is also a risk of blood clots.
There is also a risk of blood clots. -
The gag reflex is also bad because it causes uterine contractions, and if the uterus contracts often and strongly, then there is a threat of miscarriage.
-
With loose stools, vomit, useful vitamins and minerals leave the body, and then it will not be easy to replenish their supply.
-
General intoxication negatively affects the condition of the fetus.
Therefore, if you notice similar symptoms in yourself, you need to provide assistance in case of poisoning, preferably medical.
Help with poisoning - what to do
Why is it important to see a doctor during pregnancy if you are poisoned? After all, usually with diarrhea and vomiting, we prefer to just lie down. In fact, only a doctor can choose the right treatment and establish proper nutrition. Without his recommendations, it is better not to drink anything at all, except for sorbents.
A good option for enterosorbent during pregnancy will be Polysorb. Numerous studies have confirmed its safety and effectiveness. It carefully envelops toxins and poisons and gently brings them out. The drug does not enter the bloodstream and does not affect the organs. In case of poisoning, you need to stir the sorbent in water and drink. The dosage will depend on the weight of the patient. It is necessary to drink the suspension in small sips.
It is also important to monitor the sodium-potassium balance. If necessary, restore it with the help of special preparations.
After the attack subsides, you need to continue treatment and carefully monitor nutrition. It is necessary to remove from the diet:
-
milk and dairy products,
-
eggs,
-
heavy food - fried, fatty,
-
raw vegetables, fruits.
It is permissible to eat cereals on the water, cereals, broth. Do not lean on pastries and sweets. It is also better to exclude them from the diet for a week.
Do not lean on pastries and sweets. It is also better to exclude them from the diet for a week.
Prevention of food poisoning
Poisoning during pregnancy, what to do at this moment, and what to avoid, it became clear. It remains now to deal with the question of what prevention can be in this situation.
Best to avoid:
-
mushrooms, they are heavy for the stomach, can cause discomfort, and very often people feel bad after mushrooms,
-
canned food, still bet on the use of fresh products,
-
milk - milk poisoning is not uncommon, especially in cases where this product is purchased from the hands of farmers or grandmothers and is not subjected to additional heat treatment, it seems that everything is natural and there are no chemical additives, but different cases are known, in the end you don’t you know how the hostess takes care of the udder and how she stores the milk until it is sold,
-
fatty, fried - the body spends a huge amount of energy on digesting such dishes, but we do not add strength,
-
sausages, sausages - they are not healthy, not environmentally friendly and it is not clear what they actually consist of,
-
fast food and fast food restaurants are places that should be banned for pregnant women, cases of poisoning occur regularly here.

Neither are the banal rules that apply to regular hand washing, buying food with the correct expiration date, refusing to experiment in nutrition, no matter how much you want it.
You need to understand that during pregnancy you are responsible not only for your life, but also for the life, development and health of that little man whose heart is beating inside you.
He cannot take care of himself. And if you eat french fries or a burger, all the fat and carcinogens will enter your body. The baby will also get it. So you need to learn to look at your food differently in order to avoid problems and troubles.
Happy pregnancy!
Why is Polysorb right for you?
-
Recommended for use by people of all ages.
-
Does not contain preservatives, dyes and sweeteners. Neutral in taste.
-
Gently removes harmful and normalizes the intestinal microflora.

The dosage of the drug is calculated individually depending on its weight according to instructions .
If you have any difficulties in calculating the individual dose of Polysorb, you can get a free consultation by phone: 8-800-100-19-89 or in the consultation section .
- Where to buy?
- About
- Instruction
- Reviews
- Specialist consultation
- videos
Food poisoning during pregnancy. How it might affect your child
Find out what you need to watch out for, what treatment you need to get, and what can happen to your child if you have food poisoning.
It turns out that not only people, but also microbes love food. Once in food, pathogenic microorganisms feed on it, producing toxins. What are the types of infectious agents?
What are the types of infectious agents?
Staphylococcus
Most common. Reproduction of these microbes occurs with inappropriate storage of food.
Food intoxication is possible when drinking the milk of infected animals, as well as when hygiene rules are violated during food preparation.
Factory products become a source of staphylococcus in case of non-compliance with sanitary standards and lack of control over the health of employees, in particular, checking for skin diseases, acute inflammation of the upper respiratory tract (nose, throat, vocal cords, trachea).
Salmonella
Its source is raw eggs and other products that have not undergone sufficient heat treatment.
Salmonella can infect the entire digestive tract, from the stomach to the large intestine.
Proteus and clostridia
Their breeding medium is meat, fish, canned food, milk, sausages. One type of infection they cause is botulism.
One type of infection they cause is botulism.
Human susceptibility to foodborne infections is very high - more than 90%. It gets even higher during pregnancy.
You must learn to immediately distinguish early toxicosis from poisoning. It is important not to confuse one disorder with another.
Food intoxication during pregnancy - treatment
The first thing to do is to drink activated charcoal, which is allowed to be taken throughout the entire period of pregnancy.
Gastric lavage is possible only if the health condition of the pregnant woman requires it, and there is a doctor's recommendation for this.
The need for gastric lavage should be determined exclusively by a physician.
This procedure is carried out along with the obligatory control of blood pressure of both the mother and the unborn child.
Drink tea, fruit juices, and saline solutions.
If you have low blood pressure, consume caffeine to maintain normal blood flow to the placenta.
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics, but they are usually not needed.
If you have food intoxication during pregnancy, follow your doctor's nutritional advice.
For the first two days, only very sweet tea with biscuits and diluted currant or blueberry juice are allowed.
In the future, the list of approved products will expand. Over time, it is allowed to eat white bread, cream soup, fish meatballs or tender meat, low-fat meat soup, fresh cheese or soufflé.
Sweets, fruits and berries are allowed only in limited quantities.
Do not consume sauces, spices, snacks and alcohol after poisoning.
Food poisoning during pregnancy. What can happen to a child
With food poisoning, there is a risk of miscarriage. A sharp decrease in blood pressure, dehydration, failure of the ionic composition of the blood can lead to a delay in the development of the fetus and an undeveloped pregnancy.
Nevertheless, in general, the prognosis for both mother and child is quite comforting, since in most cases this disorder does not lead to any serious consequences.
Treatment approaches remain the same. Activated charcoal, plenty of fluids, light meals.
If necessary, take drugs that improve blood circulation in the placenta, but only on the advice of a doctor.
Consequences for the child:
- preterm birth;
- placental abruption;
- bleeding;
- miscarriage;
- fetal body weight deficiency;
- placental insufficiency with a lack of oxygen and nutrients in an infant.
These consequences occur in case of severe intoxication or when it is accompanied by various pathologies of pregnancy.
Treatment of salmonellosis during pregnancy
A visit to the doctor and tests will determine the course of action.
Hospitalization is necessary only when the state of health of the future mother requires it.
The consequences for the child and mother are similar to those described above.
Treatment of botulism during pregnancy
Botulism is very life threatening. In case of suspicion of intoxication during pregnancy, urgent hospitalization is required.
At the same time, procedures such as gastric lavage and enemas are mandatory.
During the first three days of illness, it is necessary to take therapeutic serum. In this case, it is vital, therefore it is prescribed, despite the pregnancy.
Antibiotics such as penicillin are prescribed for infectious complications (for example, in the case of pneumonia caused by the ingestion of stomach contents into the trachea).
All these complications are accompanied by the development of the disease. Therefore, drugs that stimulate urination may be required.
Complications for the fetus at an early stage of development are the same as for his mother, however, the death rate for him is much higher.