Can you feed a baby too much breast milk
Your breastfeeding questions answered - NHS
How often does my baby need to breastfeed?
All mothers and babies are different, and you and your baby will work out your own feeding pattern together. As a very rough guide, your baby should feed at least 8 times every 24 hours during the first few weeks.
Do not worry about feeding your baby whenever either of you wants to. You cannot overfeed a breastfed baby, and your baby will not become spoiled or demanding if you feed them whenever they're hungry or need comfort.
How long should each breastfeed last?
Every baby is different. Some babies want frequent short feeds, and others prefer feeding for longer, or a mixture of both. Let your baby finish the first breast, then offer the second.
If your baby feeds all the time and you're worried, speak to a midwife, health visitor or a breastfeeding specialist. You may need some help with positioning and attachment. You can also call the National Breastfeeding Helpline on 0300 100 0212.
How long should I breastfeed for?
Exclusive breastfeeding (breast milk only) is recommended for around the first 6 months of your baby's life. Breastfeeding alongside solid foods is best for babies from 6 months.
You and your baby can carry on enjoying the benefits of breastfeeding for as long as you like. Breastfeeding into your baby's 2nd year or beyond, alongside other foods, is ideal.
Lots of mothers carry on breastfeeding when they go back to work or college. Read more about breastfeeding after returning to work. You do not have to stop breastfeeding if you get pregnant again, either.
Find out more about deciding when to stop breastfeeding.
Why is "responsive feeding" so important?
A newborn baby's stomach is only the size of a walnut, so they need to feed little and often. Your baby can have a good feed and be hungry again quite quickly. This is why "responsive feeding" – also called "baby-led" or "on-demand" feeding – is so important.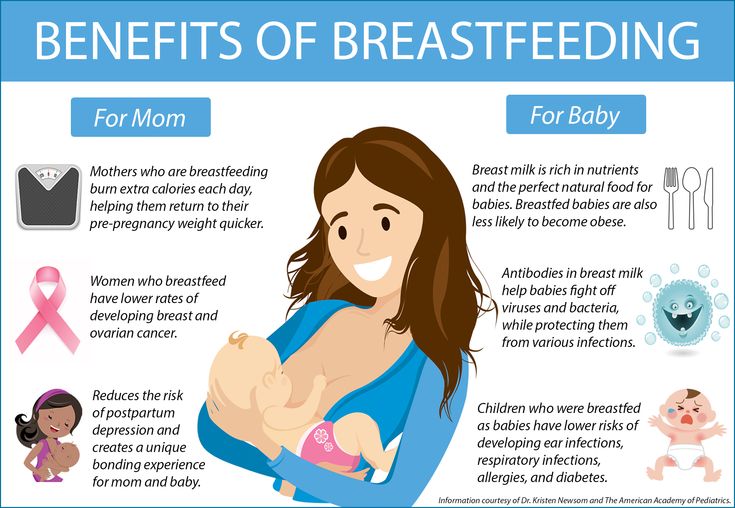
The idea is that you respond to your baby's cues. Breastfeeding is not only about your baby getting enough milk. Your baby feeds for comfort and reassurance, too.
Babies go through different patterns of feeding as they grow. Letting them feed when they need to will ensure they're content and getting the milk they need, when they need it, and will also stimulate your milk supply.
Responsive feeding is also to do with your needs. You may want to offer a breastfeed if your breasts are uncomfortably full, or if you need to fit in a feed around other commitments, or if you just want to sit down and enjoy spending some time with your baby.
Can I breastfeed after a caesarean?
Yes, you can. Make sure you get a skin-to-skin cuddle with your baby as soon as you're able to. A midwife may help you have a skin-to-skin cuddle while you're still in theatre, or in the recovery room.
If you keep your baby close to you and maintain lots of skin-to-skin contact, you'll be able to put them to the breast often and this will stimulate your milk supply.
After a caesarean, you might find the "rugby hold" (where the baby's body is around to the side of your body, supported by your arm on the same side) is preferable to having them lie against your stomach. Ask a midwife about pain relief so you can feed your baby more comfortably.
Are there any reasons why I should not breastfeed?
Very occasionally, there are sound medical reasons for not breastfeeding. For example, if you have HIV or, in rare cases, you're taking a medicine that could harm your baby, such as drugs for treating cancer.
If you're not sure whether you should breastfeed your baby, speak to a midwife or health visitor for information and support.
Can I still breastfeed with more than 1 baby?
Twins, triplets and other multiples can be breastfed. In fact, because multiple babies are more likely to be born prematurely and have a low birthweight, breast milk is especially important for them.
When you start breastfeeding, you may find it easier to feed each of your babies separately. When you feel more confident, you can feed them at the same time. This may take a few weeks.
It can be really helpful to talk to other mothers who have breastfed twins, either at an antenatal group or at a twins group in your area. Triplets can be breastfed, either 2 together and then 1 after, or all 3 rotated at each feed.
Read more about feeding twins or more.
Breastfeeding help and support
If you have any questions or concerns about breastfeeding, there is help and support available. You can:
- talk to a friend or family member who has breastfed
- ask a GP, midwife or health visitor
- call a helpline, such as the National Breastfeeding Helpline on 0300 100 0212
- look at reliable websites, such as The Breastfeeding Network
- join a local breastfeeding support group – ask a health visitor for details
Got a breastfeeding question?
Sign in with Facebook and message the Start4Life Breastfeeding Friend chatbot for fast, friendly, trusted NHS advice any time, day or night.
See more sources of help and support with breastfeeding.
Community content from HealthUnlockedHow Much Breastmilk for Newborn? Overfeeding and Choking While Breastfeeding – Happiest Baby
By Dr. Harvey Karp, MD, FAAP
How Much Milk Does a Newborn Need?
You may find that your baby starts feeding with regularity and zero fussiness. However, if your baby’s feeding habits change to the point where he is wailing and fussing during feedings, then you may have too much breastmilk for your newborn.
Too Much Breastmilk: A Real Life Example
At 7 weeks, Luca began to struggle with feedings. He had always eaten with gusto, but now after 2 minutes he’d arch and wail almost as if he hated being in his mom’s arms. But as soon as he was put down, he confused his poor parents by crying even harder!
Frustrated and demoralized, his mom wondered if her milk supply had dried up. Actually, Marija had plenty of milk—in fact, she had too much breastmilk.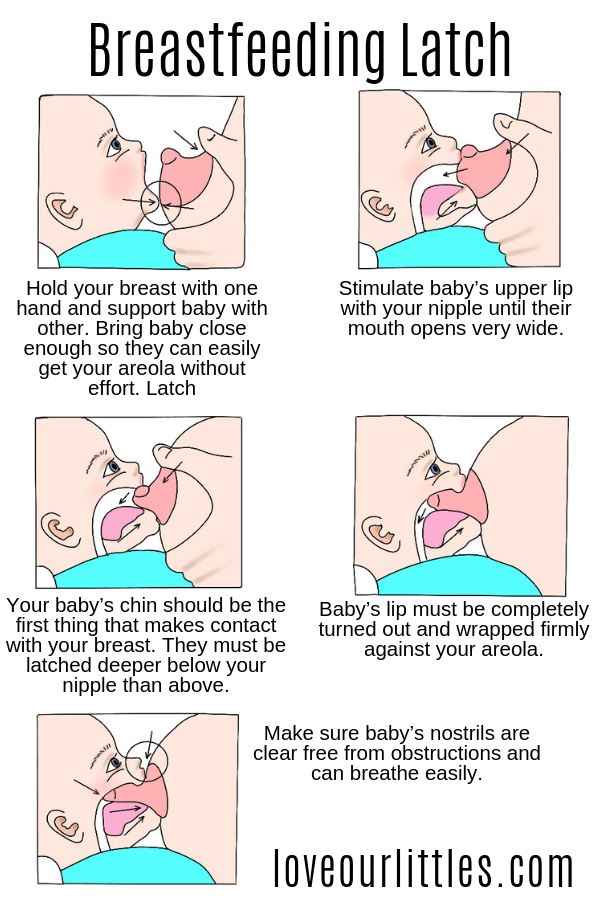
When Luca finished eating—and just wanted to suck for pleasure—Marija’s breasts continued spurting fast little streams of milk. Luca literally had to pull away to avoid choking, but he was in a pickle because he still wanted to suck.
Once Marija began holding her nipple like a cigarette—holding her ring and middle fingers in a V shape starting behind the areola and pressing together—she was able to slow the flow of the milk, and Luca became an easy feeder again.
Baby Choking While Breastfeeding
Some babies love milk so much, they overeat. They guzzle 4-8 ounces at a feed—gulping down a lot of air at the same time—and then vomit it all up. Other babies gobble not out of gluttony, but out of self-protection. Their mom’s milk pours out so fast, they’re gulping and sputtering simply trying not to choke.
Flooding can also happen with bottle-feeding.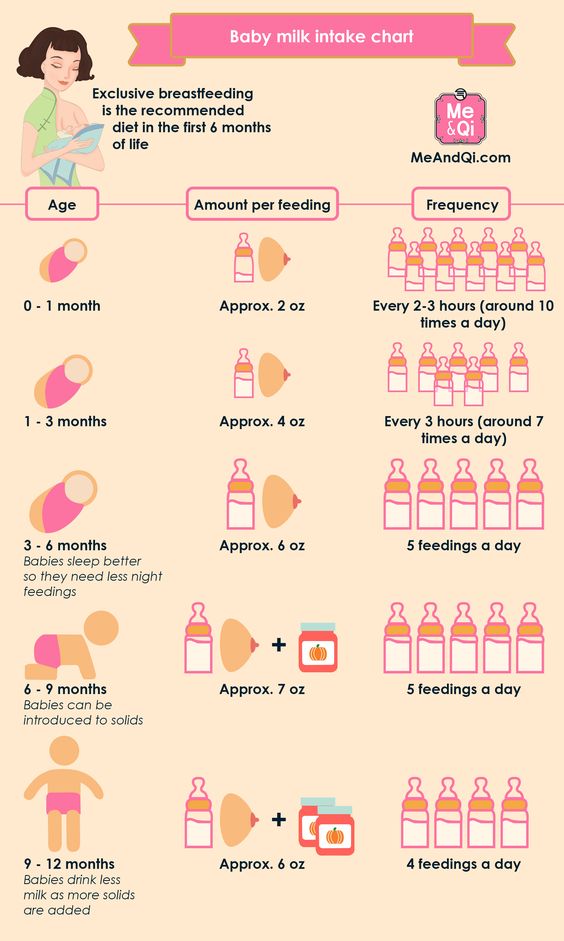 When the rubber nipple is too soft, or the holes in it are too large, infants can gag like they’re drinking from a running faucet.
When the rubber nipple is too soft, or the holes in it are too large, infants can gag like they’re drinking from a running faucet.
How to Know If Too Much Breastmilk Is an Issue
- Does your milk spray out of one breast when your baby is sucking on the other?
- Does your baby gulp and guzzle loudly?
- Does your infant struggle, cough or pull away as soon as the milk starts to flow into her mouth?
If you answered yes to these questions, try a little experiment to see if the crying stops when you slow the flow: Right before a feed, express one or two ounces out of each breast. Then, holding your nipple between your second and third fingers, like a cigarette, press your fingers inward—toward your ribs—while you feed your baby. Was there less sputtering and struggling? (You can also try nursing lying down—with your baby on top of you—to try to slow the flow.)
Can You Overfeed an Infant?
It is almost impossible to overfeed an infant while breastfeeding. Babies have a self-regulation system that tells them to eat when they’re hungry, and to stop when they’re full. Babies will tell you that they’re full or hungry by turning towards the nipple (begging for more), or by turning away to signal they’re full. If they’re gaining weight and your pediatrician is not concerned, then you don’t need to worry.
Babies have a self-regulation system that tells them to eat when they’re hungry, and to stop when they’re full. Babies will tell you that they’re full or hungry by turning towards the nipple (begging for more), or by turning away to signal they’re full. If they’re gaining weight and your pediatrician is not concerned, then you don’t need to worry.
About Dr. Harvey Karp
Dr. Harvey Karp, one of America’s most trusted pediatricians, is the founder of Happiest Baby and the inventor of the groundbreaking SNOO Smart Sleeper. After years of treating patients in Los Angeles, Dr. Karp vaulted to global prominence with the release of the bestselling Happiest Baby on the Block and Happiest Toddler on the Block. His celebrated books and videos have since become standard pediatric practice, translated into more than 20 languages and have helped millions of parents. Dr. Karp’s landmark methods, including the 5 S’s for soothing babies, guide parents to understand and nurture their children and relieve stressful issues, like new-parent exhaustion, infant crying, and toddler tantrums.
View more posts tagged, feeding
Have questions about a Happiest Baby product? Our consultants would be happy to help! Connect with us at [email protected].
Disclaimer: The information on our site is NOT medical advice for any specific person or condition. It is only meant as general information. If you have any medical questions and concerns about your child or yourself, please contact your health provider.
Too much milk? Reduced lactation
Sometimes you may feel like you are producing too much milk, especially in the first weeks of breastfeeding. After reading our article, you will find out if you really have too much milk, and what can be done to reduce it.
Share this information
Breast milk is very healthy, so it's good to have a lot of it, right? However, this is not always the case. Babies can sometimes have a hard time coping with the rapid rush of milk that usually accompanies excess lactation. And mothers who have too much milk often experience discomfort due to the constant leakage of milk and often suffer from mastitis. nine0003
Babies can sometimes have a hard time coping with the rapid rush of milk that usually accompanies excess lactation. And mothers who have too much milk often experience discomfort due to the constant leakage of milk and often suffer from mastitis. nine0003
Fortunately, there are a number of ways to help in this situation. But before you use them, answer two important questions:
Do I really have too much milk?
Some of the symptoms of over-lactation (listed below) may occur for very different reasons. You should not try to reduce the production of breast milk, if you are not sure that it is the overabundance of it that is the main problem. Otherwise, this can lead to the fact that your baby will produce less milk than your baby needs, especially in the critical first month when production is just being established. nine0003
Is being overweight a problem for me or my baby?
If you are sure that you have an excess of milk, but this does not cause problems for you and your baby, you do not need to do anything. In most cases, everything returns to normal within the first few months. As the baby grows, he will learn to better cope with the rapid flow of milk and will feed with pleasure.
In most cases, everything returns to normal within the first few months. As the baby grows, he will learn to better cope with the rapid flow of milk and will feed with pleasure.
Leakage is not always a sign of too much milk
During the first four to six weeks of your baby's birth, the level of prolactin, the hormone responsible for milk production, will rise each time the breast is emptied. In these first weeks, the breast learns to produce milk in the amount that the baby needs, depending on the time of day. Therefore, excessive leakage, rapid filling of the breast, and even splashing of milk during a rush are the norm. 1
At the same time, your baby is learning to suck and swallow milk, so you shouldn't be surprised if he suddenly coughs or chokes when he suckles. nine0003
After about four to six weeks, the spikes in prolactin levels will begin to fade and milk production will become more balanced, adjusting to your baby's needs on a supply and demand basis. 2 However, given the many hormonal changes that occur in the body of a young mother, such a restructuring may take some time. In some mothers, milk production is established quickly, in others a little longer.
2 However, given the many hormonal changes that occur in the body of a young mother, such a restructuring may take some time. In some mothers, milk production is established quickly, in others a little longer.
Behavior of the child, which may indicate an excess of milk
When overproduced, milk is usually released very quickly, especially during the first flush. As a result, the baby may cough or choke at the beginning of a feed, push back, or hold the breast loose in the mouth. The baby may pull away from the chest, frightened by a quick rush, and then cry because he hasn’t eaten. He can swallow milk in large volumes and with a lot of air, and after that he will spit up a lot. Try to be as careful as possible when you help him burp - sudden movements combined with a full tummy can cause the baby to vomit and scare him even more. nine0003
At the start of a feed, milk is relatively low in fat and consists mainly of lactose (sugar) and proteins. As the breast is fed and emptied, the fat content constantly increases. In the case of excess milk production, your baby may feel full before he completely empties his breast. This means that he will get a lot of lactose-rich milk, but not enough fat-rich milk that comes towards the end of a feed. Excess lactose instead of a balanced diet can make digestion difficult and cause hard, frothy, and greenish stools. nine0003
In the case of excess milk production, your baby may feel full before he completely empties his breast. This means that he will get a lot of lactose-rich milk, but not enough fat-rich milk that comes towards the end of a feed. Excess lactose instead of a balanced diet can make digestion difficult and cause hard, frothy, and greenish stools. nine0003
Oddly enough, in such a situation, the baby may constantly want to eat and behave restlessly between feedings. Despite the high calorie content, the low fat content of milk prevents it from being fully satiated. It is the fat contained in food that gives us a feeling of satiety. What happens if you eat a few dozen rice crackers or a slice of cheese with a cookie instead? You will fill up on cheese faster, as it is more saturated with fats.
However, all these symptoms can be caused by completely different problems, such as reflux, allergies, or even vice versa, insufficient milk production. An excess of breast milk can indeed cause these symptoms, but only if they are accompanied by excessive weight gain. Children usually dial around 900 g per month, but in the case of an excess of milk, they can gain much more, often almost twice as much. 1 If you feel like you are having too much milk but your baby is gaining weight normally, contact your lactation consultant or your healthcare provider.
Children usually dial around 900 g per month, but in the case of an excess of milk, they can gain much more, often almost twice as much. 1 If you feel like you are having too much milk but your baby is gaining weight normally, contact your lactation consultant or your healthcare provider.
Symptoms that may indicate an excess of milk in mothers
Mothers with an excess of breast milk often experience swelling and tightness in the breast, which constantly seems full. nine0029 3 As already noted, the leakage of breast milk in the first six weeks does not indicate its excess. However, if this continues at every feeding and after this period, it may be that the problem is in the overabundance.
A baby cannot always empty a full breast, so when there is an excess of breast milk, blockage of the milk ducts or periodic bouts of mastitis often occur. However, these problems can also be caused by other reasons.
How to reduce milk production
If you have found that you have too much breastmilk and this is causing you concern, here are a few simple things that can help. For some mothers, they are enough.
For some mothers, they are enough.
- Try feeding in a relaxed position. Reclining or lying down feeding will allow the baby to better control the process. In this position, the baby sets the rhythm of feeding himself and can always raise his head to take a break if the milk is released too quickly. Don't forget to put a towel over to soak up spilled milk. nine0066
- Release pressure. If full breasts make you uncomfortable, try expressing some milk by hand or with a breast pump, but try to express as little milk as possible. Every time you empty your breast, you send a signal to her to produce even more milk. Therefore, pumping provides short-term relief, but with prolonged use, it can only aggravate the situation. If you need to express and store milk to feed your baby when you are not around, it is best to address the problem of excess production first. nine0066
- Try bra pads. If you have milk leaks, put special pads or pads in your bra to collect milk* to keep your underwear dry.
 If your milk leakage is moderate and already decreasing, or your breasts leak slightly during pregnancy, ultra-thin disposable pads will help you feel confident in any life situation.
If your milk leakage is moderate and already decreasing, or your breasts leak slightly during pregnancy, ultra-thin disposable pads will help you feel confident in any life situation. - Avoid teas and lactation supplements. nine0014 If you have been drinking teas, eating special biscuits, or taking supplements to improve breast milk production, this should be stopped now to resolve the problem.
"Breast Watch" to reduce milk production
If all the above methods fail, you can try a technique called "Breast Watch", which allows you to better control milk production. However, before trying this method, check with a lactation consultant or healthcare provider. nine0003
On breastfeeding, you feed your baby on demand, but only on one breast for four hours. The second breast during this time is strongly filled. Since breast milk contains what is known as a "feedback lactation inhibitor", due to overfullness, the body sends a signal to that breast to slow down milk production. This is a natural way to protect the breast from endless filling.
This is a natural way to protect the breast from endless filling.
This technique must be applied for 24 hours, changing breasts every four hours. If the milk does not become less, try increasing the duration of the "watch" to six hours. nine0003
Complete emptying and “breast duty” technique
If after another day there is still a lot of milk produced,
you can try another version of this technique, which is recommended in cases of extreme overabundance. It is called "complete emptying and duty of the breast." 3
In this method, both breasts must be completely emptied in the morning with an electric breast pump and breastfeeding should be started immediately. The flow of milk will be weaker and allow the baby to eat calmly. In addition, he will get more fat-rich milk, which comes at the end of feeding, which means he will feel more full. nine0003
After that, you can continue the "breast watch" for four hours, as described above. If that doesn't help, try increasing the interval to six, eight, or twelve hours the next day, depending on the extent of the problem. Before using this technique, be sure to consult with your doctor.
Before using this technique, be sure to consult with your doctor.
You may not need to completely empty your breasts after the first use of this technique, but some mothers have to do this once or twice. Improvement usually occurs within the first two days or a little later, but in no case should "breast watch" be used for more than five days. nine0003
Literature
1 Morbacher N. Breastfeeding answers made simple. Amarillo TX , USA : Hale Publishing ; 2010. - Morbacher N., "Simple answers to questions about breastfeeding." Amarillo, Texas, USA: Publishing Hale 0106 et al . Blood and milk prolactin and the rate of milk synthesis in women. Exp Physiol. 1996;81(6):1007-1020. - Cox D.B. et al., Effects of blood and milk prolactin on milk production in women. Exp Physiol. 1996;81(6):1007-1020.
1996;81(6):1007-1020.
3 van Veldhuizen-Staas CG. Overabundant milk supply: an alternative way to intervene by full drainage and block feeding. Int Breastfeed J . 2007;2(1):11. - van Velhusen-Staas SJ, "Milk Overabundance: An Alternative Countermeasure by Total Drying and Blocking of Feeds." Int Brestfeed J (International Journal of Breastfeeding). 2007;2(1):11.
Read instructions before use. Consult a specialist about possible contraindications.
* RC № FZZ 2010/07352 dated 19.07.2010
What is normal breastfeeding? | Interview with Dr. Jacqueline Kent
It can be difficult for new mothers to understand if breastfeeding is going well, so we decided to ask the expert if it is possible to talk about the norms when it comes to breastfeeding.
Share this information
Dr Jacqueline Kent, Research Fellow, Hartmann Human Lactation Research Group:
Jacqueline joined the University of Western Australia research team in 1986 and received her PhD in 1999. She is currently researching the biochemical and physiological aspects of breast milk synthesis and release in search of scientific information to help mothers breastfeed longer.
She is currently researching the biochemical and physiological aspects of breast milk synthesis and release in search of scientific information to help mothers breastfeed longer.
Dr. Jacqueline Kent and her colleagues have been studying breastfeeding for many years. As it turned out, for all mothers and babies, this process occurs in its own way. nine0003
What were the most surprising results of your research?
Variety. It turns out that the limits of the norm are extremely wide.
We are used to textbooks that say that an infant should eat 8-12 times a day and gain 150 grams per week. But babies don't read textbooks and do things their own way! Some gain weight more slowly, others very quickly.
We followed exclusively breastfed infants aged one to six months. As our studies have shown, on average, a child is breastfed 4 to 13 times a day, and the duration of one feeding varies from 12 minutes to 1 hour. nine0029 1
How much milk do breastfed babies usually consume?
According to our research, the amount of milk consumed by baby
ranges from 54 to 234 ml per feeding. 1
1
Sometimes it seems to the mother that the baby ate well, but when weighed, it turns out that he ate very little milk. And it happens the other way around: the child is distracted, breastfeeds for only a few minutes and still eats 100 ml of milk. Even if the baby is restless, this does not mean at all that he is malnourished. nine0003
All babies are different, but they all get as much milk as they need in one way or another. One needs 500 ml of milk per day, while others eat up to 1356 ml!
By the way, boys on average eat 76 ml more milk per day than girls. The main thing is that you have enough milk, and the baby will decide when and how much he will eat.
Should I offer my baby a second breast?
I advise offering the second breast to the baby after the first has been completely emptied. If he accepts it, then he hasn't finished eating. If not, don't worry. Let the baby decide for himself - only he knows when he is full. According to our research, 30% of babies get enough milk from one breast, 13% eat from two breasts at each feed, and 57% from time to time. nine0029 1
nine0029 1
How do you know if a baby is getting enough milk?
In my experience, mothers often blame themselves for not producing enough milk. Ask yourself: Is my child growing? Is he putting on weight? Is he cheerful? Is his skin healthy? How often does he get diapers dirty? If the answer is “yes”, then the baby is getting enough milk, no matter if he eats a lot or a little.
What is the most common misconception about breastfeeding? nine0027
Mothers usually think that the older the child gets, the more often
he needs to be fed and the more milk he will eat. They are often surprised to learn that between the 4th and 26th weeks, total milk production normally does not change. 2
In the first few months, the baby grows very quickly and his metabolism is accelerated. The milk that the child consumes during this period is almost completely used for growth and maintenance of metabolism.
Between the ages of three and six months, metabolism slows down and growth slows, so the same amount of milk is sufficient for the baby. In other words, the baby does not have to consume more and more milk as they grow older. On the contrary, feedings become shorter and less frequent, but at the same time the child receives the same amount of milk, because he suckles better.
In other words, the baby does not have to consume more and more milk as they grow older. On the contrary, feedings become shorter and less frequent, but at the same time the child receives the same amount of milk, because he suckles better.
Do studies say anything about the age at which breastfed babies start sleeping through the night? nine0027
Most babies need to be fed at night.
A baby's stomach is not big enough to go all night without a feed, and breast milk is digested very quickly. Therefore, it is natural for the baby to wake up at night - and this usually continues for at least the first six months. Feeding at night is normal. When you feed your baby at night, do not even hesitate - all over the world at this moment other mothers of babies of the same age are doing the same. Be patient - it usually only lasts a few months. nine0029 1
What worries new mothers the most during the first few weeks of breastfeeding?
The most common concern is whether the baby latch on correctly, sucks well, and is full during feeding. Often mothers also worry about sore nipples. The main thing is to find the right position for feeding from the very beginning and ensure that the baby is latching on correctly. Practice shows that this significantly affects the flow of milk and the convenience of feeding. nine0003
Often mothers also worry about sore nipples. The main thing is to find the right position for feeding from the very beginning and ensure that the baby is latching on correctly. Practice shows that this significantly affects the flow of milk and the convenience of feeding. nine0003
What breastfeeding symptoms should be of concern?
Milk production usually returns to normal levels two weeks after delivery. If the child does not begin to gain weight on the fifth or sixth day of life, it's time to sound the alarm. You should contact your doctor to make sure that milk is being produced and that its composition is changing from colostrum to mature breast milk.
What advice would you give to a new breastfeeding mother?
Try to ensure skin-to-skin contact with the baby as soon as possible after delivery. If possible, feed your baby within the first hour of life, or at least breastfeed. As soon as possible, contact a specialist to correct the position and grip of the breast during feeding and thus avoid damage to the nipples.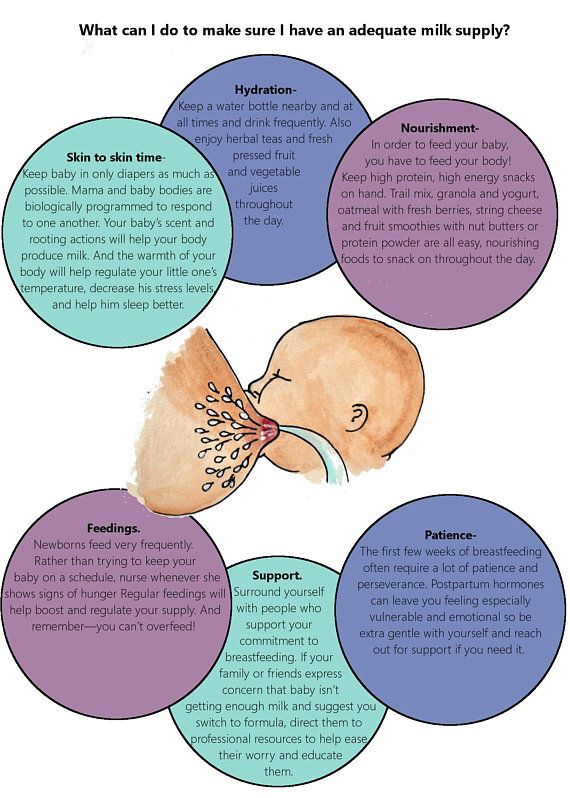 nine0003
nine0003
Feed frequently. Young mothers do not immediately succeed in correctly recognizing the signals that the child gives. Be sure to feed your baby on demand, and not at set intervals. Offer the breast as soon as you notice any signs of hunger - as a rule, the baby suckles better when he is calm. If he cries, it is more difficult for him to take the breast. If you are not sure what the child wants, offer him the breast. He decides whether he wants to eat or not.
To learn more about Dr. Kent's research, download infographic "How to determine the limits of normal when it comes to breastfeeding" or see it below.
Literature
1 Kent JC et al. Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics . 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics).
Learn more