Feed baby solids first time
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.
- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Introducing solids: why, when, what & how
Solid foods: why babies need them
As babies get older, they need solid food to get enough nutrients for growth and development. These essential nutrients include iron, zinc and others.
These essential nutrients include iron, zinc and others.
For the first 6 months of life, babies use iron stored in their bodies from when they were in the womb. They also get some iron from breastmilk and/or infant formula. But babies’ iron stores go down as they grow. By around 6 months, babies need to start having solid food.
Introducing solids is also important for helping babies learn to eat, giving them experience of new tastes and textures from a range of foods. It develops their teeth and jaws, and it builds other skills that they’ll need later for language development.
Signs that it’s time to introduce solids
Signs your baby is ready for solids include when your baby:
- has good head and neck control and can sit upright when supported
- shows an interest in food – for example, they look at what’s on your plate
- reaches out for your food
- opens their mouth when you offer them food on a spoon.

Most babies start to show these signs by around 6 months, although this can vary.
It’s recommended not to introduce solids before 4 months.
If your baby is nearing 7 months of age and hasn’t started solids, you might like to get some advice from your child and family health nurse or GP.
The best times of day to introduce solids
When you’re first introducing solids, it’s good to offer solids when you and your baby are both happy and relaxed.
This is often after a feed of breastmilk or formula. Babies will still have room in their tummies for a taste of new foods after a feed of breastmilk or formula. But if they’re really hungry before a feed, they just want the breastmilk or formula that they know satisfies their hunger.
As time passes, you’ll learn when your baby is hungry or full, not interested or tired.
Signs of hunger include your baby:
- getting excited when they see you getting their food ready
- leaning towards you while they’re sitting in the highchair
- opening their mouth as you’re about to feed them.

Signs your baby is no longer interested include:
- turning their head away
- losing interest or getting distracted
- pushing the spoon away
- clamping their mouth shut.
Your baby’s appetite can vary from day to day.
How much food to offer when introducing solids
When you’re first introducing solids, try offering 1-2 teaspoons of food once a day. At first, your baby might have only a small taste and probably won’t swallow much.
As your baby grows, you can increase the amount according to your baby’s appetite and signs.
By 12 months, your baby should be eating around 3 small meals a day, plus breastmilk or infant formula.
The right textures for first foods
When your baby is ready for solids, first foods might be smooth or finely mashed, depending on what baby likes. Over the next weeks and months, your baby can move on to roughly mashed or minced foods and then chopped foods.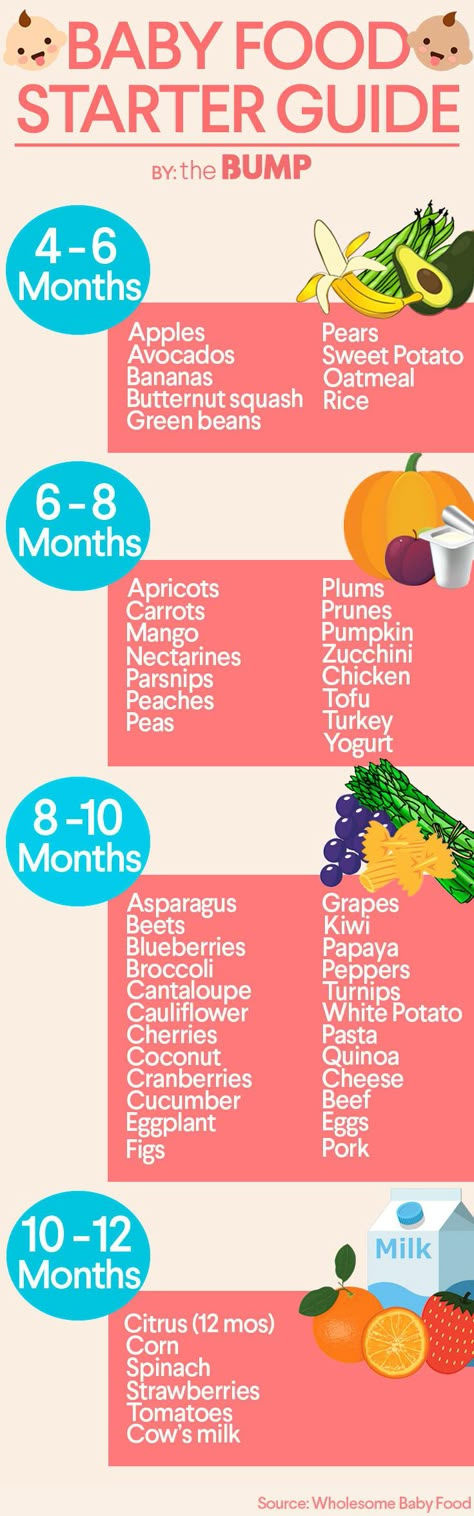 All foods should be very soft.
All foods should be very soft.
Your baby needs a variety of food textures. This helps your baby learn how to chew, and chewing helps with speech development and self-feeding. It also helps to prevent feeding difficulties as your baby develops. Babies can chew even before they get their first teeth.
By the time your baby is 12 months old, they should be eating the same foods that the rest of the family is eating. But you might still need to chop some foods into smaller pieces and cook vegetables until they’re soft.
To prevent choking, always supervise babies and young children while they’re eating solid food. Avoid nuts, take special care with pieces of meat and check fish for small bones, because these are choking hazards. And if your baby can move around, make sure baby is sitting down while they’re eating. If you sit with your baby while they’re eating, baby is less likely to move around.
Types of food to offer when introducing solids
All new foods are exciting for your baby.
The key is to include iron-rich foods of the right texture in your baby’s first foods. Iron-rich foods include:
- iron-fortified infant cereal
- minced meat, poultry and fish
- cooked tofu and legumes
- mashed, cooked egg (avoid raw or runny egg).
To these iron-rich foods, you can add other healthy foods of the right texture like:
- vegetables – for example, cooked potato, pumpkin, sweet potato, carrot, broccoli or spinach
- fruit – for example, banana, apple, pear, melon or avocado
- grains – for example, oats, bread, rice and pasta
- dairy foods – for example, yoghurt and full-fat cheese.
You can introduce any number of new foods at a time and in any order. When you offer your baby a variety of foods, they can try plenty of new tastes and get a range of nutrients.
Read our tips for introducing solid foods to learn how to get your baby interested in new foods and manage mealtime mess and play.
Breastmilk and infant formula while introducing solids
You should keep breastfeeding or using infant formula until at least 12 months.
When you start introducing solids, breastmilk or infant formula should still be the main source of your baby’s nutrition. Over the next few months, your baby will start having more solids and less milk or formula. The rate that this happens will vary.
By around 9 months, babies have generally developed enough chewing and swallowing skills to move from having milk before solids to having milk after solids.
Here are some signs that your baby is getting enough nutrition from both solids and breastmilk or formula during this time. Your baby:
- has plenty of wet nappies – at least 6-8 wet cloth nappies or 5 very wet disposables in 24 hours
- is alert and mostly happy after and between feeds
- is gaining weight at about the right rate – your child and family health nurse will weigh your baby at your regular check-ups.
From 12 months onwards, solids should be the main source of your baby’s nutrition. Your baby doesn’t need infant formula after 12 months, but you can keep breastfeeding for as long as you and your baby like.
If solid food replaces breastmilk and/or infant formula too quickly, babies can miss out on important nutrition. If you have any concerns about your baby’s feeds or weight, talk to your midwife, child and family health nurse, lactation consultant or GP.
Introducing water
Once your baby has reached 6 months, you can start to offer baby cooled, boiled water in a cup at mealtimes and at other times during the day. This is so your baby can practise drinking from a cup, but baby still doesn’t really need fluids other than breastmilk or formula at this age.
Once your baby has reached 12 months, you can offer fresh tap water without boiling it.
Foods and drinks to avoid while introducing solids
There are some foods to avoid until your baby is a certain age:
- Honey until 12 months – this is to avoid the risk of infant botulism.

- Raw or runny eggs and foods containing raw eggs like home-made mayonnaise until 12 months – bacteria in raw eggs can be harmful to babies.
- Reduced-fat dairy until 2 years – babies need full-fat dairy for growth.
- Whole nuts and similar hard foods until 3 years – these are choking hazards.
There are some drinks to avoid until your baby is a certain age:
- pasteurised full-fat cow’s milk as a main drink until 12 months
- dairy alternatives like soy, goat’s, sheep’s, rice, oat, almond and coconut milk until 2 years, unless your GP or child and family health nurse has recommended these for a particular reason
- unpasteurised milks at all ages
- tea, coffee or sugar-sweetened drinks at all ages
- fruit juice – this should be limited at all ages (whole fruits are better because they have fibre and help babies develop chewing and feeding skills).
Your baby doesn’t need added salt or sugar. Processed or packaged foods with high levels of fat, sugar and/or salt aren’t good for babies and children. These foods include cakes, biscuits, chips and fried foods.
Processed or packaged foods with high levels of fat, sugar and/or salt aren’t good for babies and children. These foods include cakes, biscuits, chips and fried foods.
Food allergy and introducing solids
Introducing allergenic foods early can reduce the risk of your child developing food allergy. Allergenic foods are foods that might cause allergies.
All babies, including babies with a high allergy risk, should try solid foods that might cause allergies from around 6 months of age. These foods include well-cooked egg, peanut butter and other nut butters, wheat (from wheat-based breads, cereals and pasta) and cow’s milk (but not as a main drink).
Once you’ve introduced an allergenic food, it’s a good idea to regularly include it in your baby’s diet.
It’s a good idea to get advice from your GP, child and family health nurse, dietitian, paediatrician or allergy and immunology specialist for the following reasons:
- Your baby already has a food allergy.

- Your baby has severe eczema.
- Your family has a history of food allergy and you’re concerned about starting solids.
- You’re worried about reactions to foods.
Complementary foods. When and where to start?
Turganova Elena
Published: 01/16/2023
Reading time: 5 minutes
8025
The purpose of complementary foods is to supplement the child's diet with nutrients and switch from breast milk (infant formula) to common table foods. In order for this transition to be harmonious and help the child develop comprehensively, the introduction of complementary foods begins with homogenized forms (mashed potatoes) with a gradual transition to a thicker and firmer consistency, from finely chopped to larger, pieces. It is important not only to feed the child, but also to instill new skills: biting, chewing and owning cutlery. The texture and consistency of complementary foods should be appropriate for the child's developmental level.
The texture and consistency of complementary foods should be appropriate for the child's developmental level.
When pieces are introduced into complementary foods
Pieces of complementary foods (12-23 months) can be started after passing through the following stages:
In addition to age, one should also focus on the child's psychophysical readiness: his interest, the presence of teeth, the ability to sit and hold objects in his hand.
After 1.5 years, purees are actively replaced with thick and coarsely ground food, the degree of mechanical and culinary processing is reduced to develop chewing skills, strengthen the muscles of the oral cavity and develop the ability to control the organs of articulation (lips, tongue, jaw).
Complementary foods. Where to begin?
Start introducing pieces with foods that the child is already familiar with.
- Porridges are well boiled, but not prepared from cereal flour, not rubbed or ground in a blender
- Prepare vegetable and cereal casseroles
- Vegetables and fruits are chopped or sliced rather than finely grated
- Meat and fish are prepared as cutlets or stews from finely chopped pieces
Industrial complementary foods can also help with pieces labeled for children from 1 year to 3 years.
Modern packaging such as pouch helps develop motor skills and independent skills.
What size pieces should be for the first feeding?
Purees and porridges made from grain flour are the best form for the first feeding.
Further, the consistency changes towards thicker and denser, cooked foods (dishes) are finely chopped or crushed. For cereals from 8 months, you can use muesli with pieces of berries and fruits to enhance the sensory experience.
The size of food pieces increases gradually, from grains to "peas" and "hazelnuts".
How do you know when your baby is ready for solid foods?
This discovery may be unexpected when a child accidentally takes food from the table, bites off a piece and chews it calmly.
In other cases, give the child the opportunity to take the initiative at the table, allowing him to take food from the table, taste it and “tooth”, bite and chew it.
From 8 months, start offering more solid, finely ground food. Let your child bite off food (vegetables, fruits, meatballs, etc.). Active spitting or vomiting are signs of unpreparedness. Normal perception, chewing and calm swallowing mean that the baby is completely ready to eat in pieces.
It is important to remember that prolonged feeding of mashed foods is an abuse of ease of use that limits the development of the child, inhibits the development of motor skills and adversely affects the child's eating behavior. 8-10 months is a critical period for changing the consistency of food towards dense, to pieces.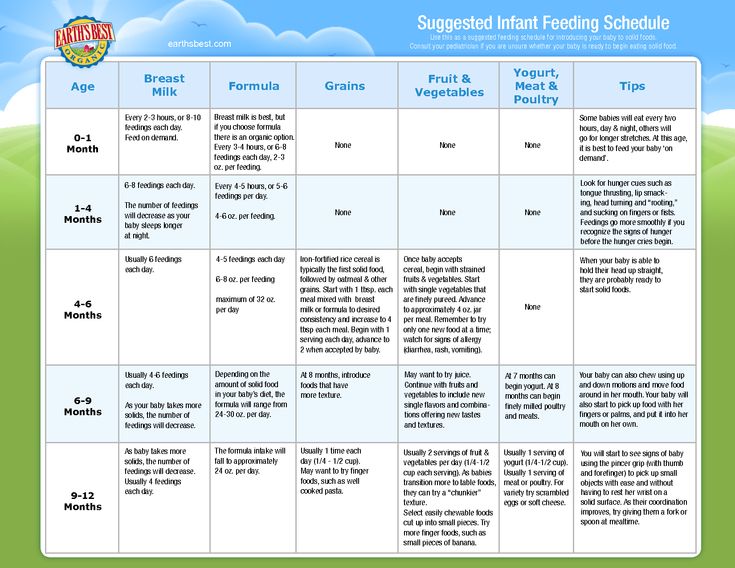
Author of the article
Turganova Elena
Pediatrician
About the author
Share on Vkontakte Telegram
Contents of the article
- When pieces are added to complementary foods
- Complementary foods. Where to begin?
- What size pieces should be for the first feeding?
- How do you know when a baby is ready for solid foods?
Products from article
Procereals baby milk porridge with apple and raspberry
From 6 months
Procereals baby porridge dairy-free oatmeal
From 5 months
Procereals baby porridge dairy-free buckwheat
Procereals baby porridge dairy-free multi-cereal
For children from 6 months
May be interesting
- Complementary milk porridge
- How to introduce complementary foods?
- Food allergy
How to transition a child from mashed potatoes to regular food
The introduction of dense food with pieces improves satiety and teaches the baby to chew, prepares him for the transition to a common table and trains speech skills. We are discussing how to transfer a child to solid food with puree and at the same time not provoke a refusal to eat, which can lead to health problems, with a pediatrician, medical consultant of the SMART-MAMA project, Polina Aleksandrovna Kizino.
We are discussing how to transfer a child to solid food with puree and at the same time not provoke a refusal to eat, which can lead to health problems, with a pediatrician, medical consultant of the SMART-MAMA project, Polina Aleksandrovna Kizino.
— Polina Alexandrovna, why do they start with pureed foods first?
— Classic complementary foods are introduced around 6 months or earlier. At this age, it is quite difficult for babies to coordinate the work of all the muscles of the oral cavity and chew hard pieces. Other than breast milk or formula, the baby has not tried anything yet. Therefore, if you give him hard pieces right away, he may not figure out what to do with them. In addition, for good absorption and easier swallowing, of course, pureed food is more suitable - cereals or mashed potatoes.
If, for some reason, a child begins to receive complementary foods at 7-8 months (that is, later than the recommended 4-6 months), it is acceptable to introduce products with very soft and small pieces, similar to mashed potatoes.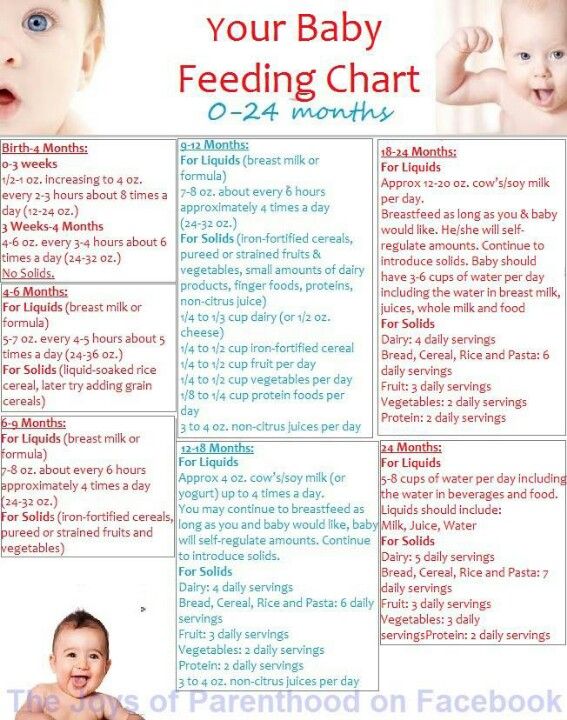 Even if a child swallows such a piece without chewing, it will happen without discomfort and does not threaten to refuse food with pieces in the future.
Even if a child swallows such a piece without chewing, it will happen without discomfort and does not threaten to refuse food with pieces in the future.
— What should be the consistency of food in the first year of a baby's life?
- At the stage of introducing the first or second complementary foods, the nutritional consistency is required to be homogeneous, that is, completely homogeneous, without pieces, veins of vegetables or cereal flakes. As the baby matures, he is already able to eat vegetables mashed with a fork. Gradually, the pieces may become harder and larger. However, even if the baby eats pieces, this does not mean that homogeneous foods should be immediately excluded when learning to chew. He can get both.
— Why is solid food obligatory for children under one year old?
— It is necessary to transfer a child to solid food only because he will not eat homogeneous purees and cereals all his life. And as soon as the physiological ability to chew appears, the baby begins to chew soft food, even if he does not yet have teeth. If the baby remains on homogeneous food and does not learn to chew, then it will be difficult for him to switch to other foods, he will not want to eat in a new way.
If the baby remains on homogeneous food and does not learn to chew, then it will be difficult for him to switch to other foods, he will not want to eat in a new way.
When chewing, the oral apparatus develops: jaws, muscles, teeth. The skill of chewing is closely related not only to the maxillofacial system and food processing, but also to the formation of bite and the development of speech in a child.
— When should a child be moved to a common table with hard pieces?
- This happens differently for all children, but on average about 7-8 months. At the same time, solid pieces do not mean those products that need to be gnawed, but precisely what is different from homogeneous food.
All changes in the child's diet are introduced gradually. Imagine if he suddenly bites off a large piece that he cannot chew and starts swallowing - as a result, there is a risk of severe choking and choking. Or, at best, experience discomfort, so you don’t want to try this product again. In order not to provoke such situations, all transitions in a child's life must be carried out very smoothly.
In order not to provoke such situations, all transitions in a child's life must be carried out very smoothly.
— How do parents know when a child is ready for solid food?
— Apart from the age and positive reaction of the child to the proposed product, there are no other signs. Even teeth will not be a readiness factor for solid foods. But if parents delay the introduction of solid pieces and a child at 9-10 months old is not yet familiar with them, then he will not want to eat this and will demand mashed potatoes.
Constant choking on food, regurgitation, restlessness of the baby are adverse reactions to the introduction of solid food. It makes sense to consult a pediatrician.
Remaining undigested food in the stool may be normal and should not be a concern for parents. In order for food to begin to be fully absorbed, the body needs time to adapt to complementary foods. It is important to monitor the condition of the baby.
— How to transfer a child to a common table if he refuses solid food?
- Unfamiliar and "unpleasant" foods should be offered at the start of a feed while the baby is still hungry. If the baby starts breakfast or lunch with his favorite dish, then, having been a little full and realizing that he got what he wanted, he, of course, will refuse other food.
If the baby starts breakfast or lunch with his favorite dish, then, having been a little full and realizing that he got what he wanted, he, of course, will refuse other food.
It is necessary to interest the child in literally all suitable ways:
- demonstrate interest in the product by example, praise its taste;
- offer "baby" food from your own plate;
- put food on a pretty children's plate;
- beautifully decorate food on a plate, make “pictures”;
- praise for the eaten pieces.
All this does not distract from the process of eating, like cartoons, and does not disguise eating as a game. The food will be interesting for the child, and he will get pleasure and satisfaction from what he eats.
Praise from parents is especially important for babies over one year old. For the sake of keeping the parents happy, the child is sometimes ready to do something that he does not like.
— What food to offer first and what does the child's menu depend on?
- This can be any food, and not necessarily new dishes. But you need to gradually change the density and hardness of food, the size of the pieces. To help in getting to know the pieces, but not with chewing, a nibbler can. Let not all children love it, but this accessory is important for the safety of the child: with it, the baby will not swallow too large a piece and will not choke.
How to start introducing solid food
| Products | Familiar products, but no longer homogeneous, but of a different consistency - you just need to mash the vegetables with a fork, grind them larger, chop a piece on a fork or invite the baby to take the vegetable with his hand and bite off him on his own. |
| Quantity | Look at the child's reaction, his desire and ability. |
| Consistency | The softness of the product should be the same as, for example, a ripe banana, so that when swallowing, even without chewing, the baby does not experience pain, gag reflex and other unpleasant sensations. |
| Administration order | One new product is administered over three to four days to monitor the response. Moreover, it should be exactly the same for the same product in both hard and soft form. |
| Piece size | Start with pieces about the size of a pea. You need to pay attention to how the child will chew the boiled "peas" of food. With their softness, there is practically no risk of choking and it is unlikely that a piece will get stuck. |
— How often should there be hard pieces in the diet? A child can eat only homogeneous purees all day, and then all day - only pieces. In addition, food chopped in different ways can be mixed in one dish, but so that the baby understands that in the spoon he has not only mashed potatoes, but also pieces. Then he will count on what he will have to chew. Food should be washed down - WHO recommends the mandatory introduction of water at the start of complementary foods.
- Rusks, bagels or whole fruits - when can they be introduced?
- Hard crackers and fruits can be in the diet for up to a year, but at a time when the baby still has no or few teeth and he will definitely not bite off, but lick or procrastinate treats. The child rubs boiled potatoes, carrots, broccoli well with gums, but cannot chop solid foods from the adult menu. It is right to give them in pedagogical complementary foods in order to introduce the baby to different tastes.
Be aware that when the incisors appear, the child may bite off a large enough piece that he cannot chew. Therefore, it is better for parents not to take risks if they cannot control the size of the pieces. A large unchewed lump of food causes pain and vomiting when it cannot penetrate the esophagus due to its size.
— How to teach a child to chew hard pieces?
- Other than constantly offering to try pieces, there are no special exercises that would help a child learn to chew before the age of one.