Feeding an eight month old baby
Sample Menu for a Baby 8 to 12 Months Old
Log in | Register
Ages & Stages
Ages & Stages
Listen
Español
Text Size
Now that your baby is eating solid foods, planning meals can be more challenging. At this age, your baby needs between 750 and 900 calories each day, of which about 400 to 500 should come from
breast milk or formula (if you are not breastfeeding)—roughly 24 ounces (720 mL) a day. Breast milk and formula contain vitamins, minerals, and other important components for brain growth.
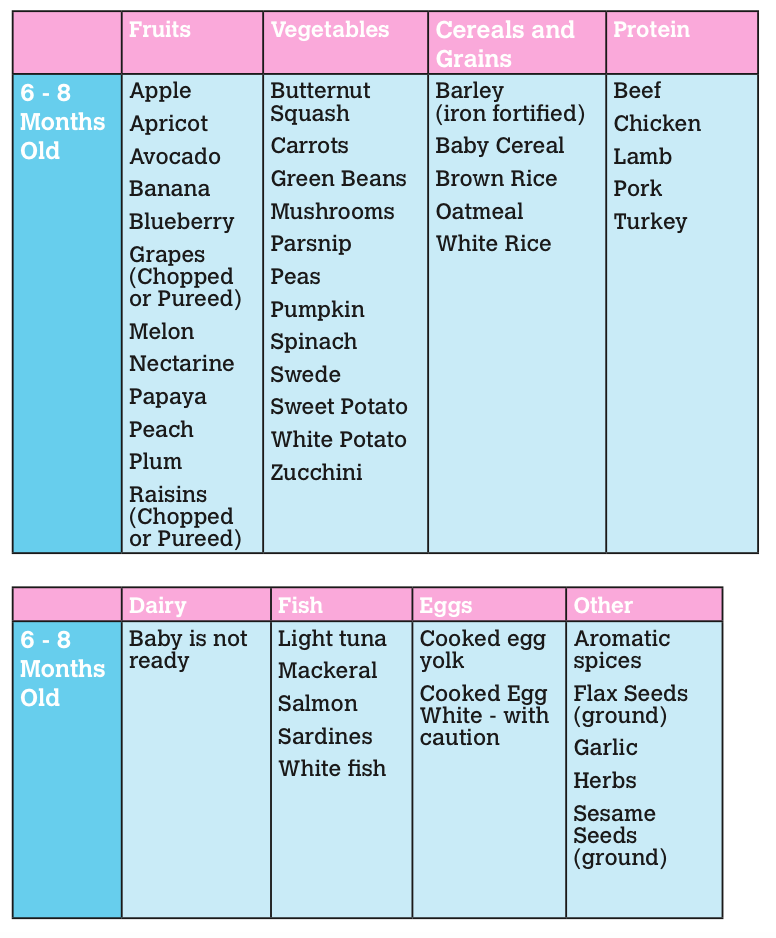
At about eight months, you may want to introduce foods that are slightly coarser than strained pureed foods. They require more chewing than baby foods. You can expand your baby's diet to include soft foods such as yogurt, oatmeal, mashed banana, mashed potatoes, or even thicker or lumpy pureed vegetables. Eggs (including scrambled) are an excellent source of protein, as are cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, and avocado.
Sample menu ideas for an 8- to 12-month-old baby:
1 cup = 8 ounces = 240 ml
¾ cup = 6 ounces = 180 ml
½ cup = 4 ounces = 120 ml
¼ cup = 2 ounces = 60 ml
Breakfast
2 to 4 ounces cereal, or 1 mashed or scrambled egg
2 to 4 ounces mashed or diced fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Lunch
2 to 4 ounces yogurt or cottage cheese, or pureed or diced beans or meat
2 to 4 ounces cooked pureed or diced yellow or orange vegetables
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Dinner
2 to 4 ounces diced diced poultry, meat, or tofu
2 to 4 ounces cooked green vegetables
2 to 4 ounces cooked soft-whole grain pasta or potato
2 to 4 ounces diced or mashed fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Before bedtime
Breastmilk or 6 to 8 ounces formula, or water.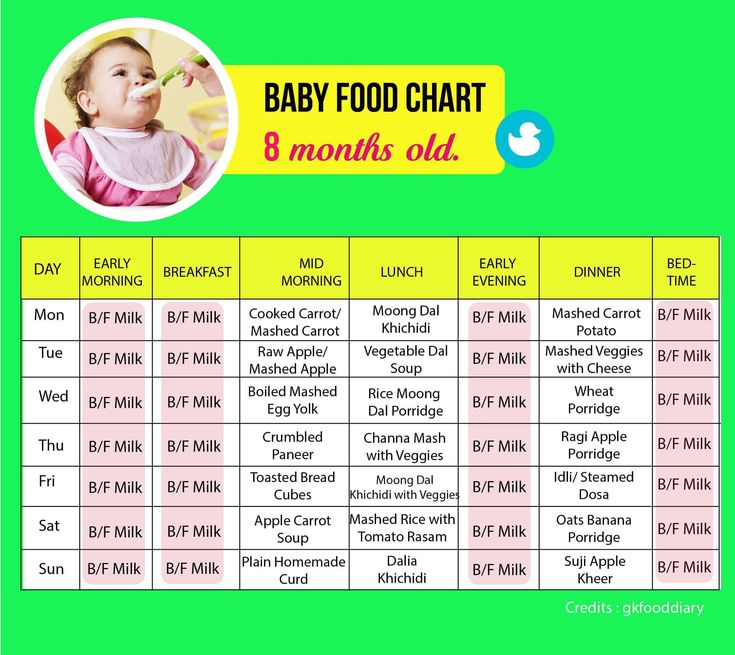 (If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
(If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
More information
- Sample Menu for a One-Year-Old
- Starting Solid Foods
- Breastfeeding Mealtime Milestones
- Ask the Pediatrician: Is it OK to make my own baby food?
- Last Updated
- 8/12/2022
- Source
- Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Feeding Your 8- to 12-Month-Old (for Parents)
By 8 months old, most babies are pros at handling the iron-fortified infant cereals and the puréed foods that are part of their diet, along with breast milk or formula.
Over the next few months, they will start to explore table foods.
Changing Eating Habits
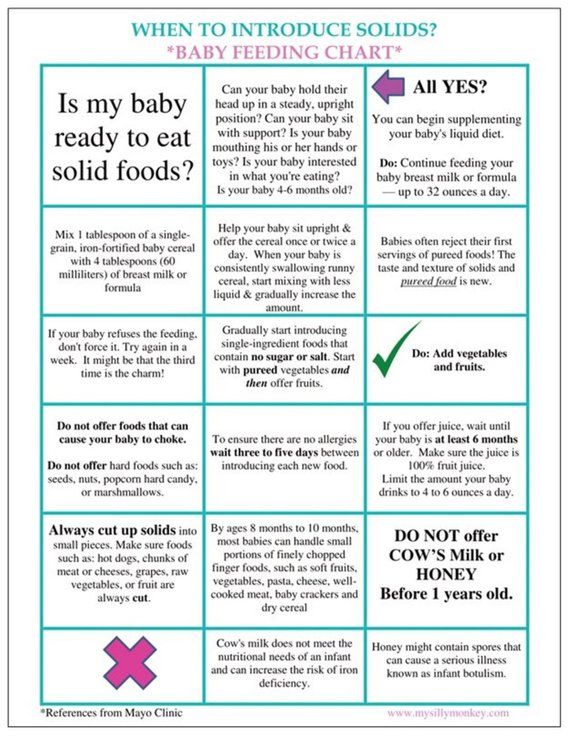
Offer your baby a variety of tastes and textures from all food groups. Start any new food with a trial run (a few days to a week) to look for any allergic reactions. Babies younger than 12 months old should not have:
- honey until after a baby's first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy drinks before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw vegetables, grapes, hard cheese, popcorn, and nuts
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
Babies this age are likely showing more interest in table foods. You can fork-mash, cut up, blend, or grind whatever foods the rest of the family eats.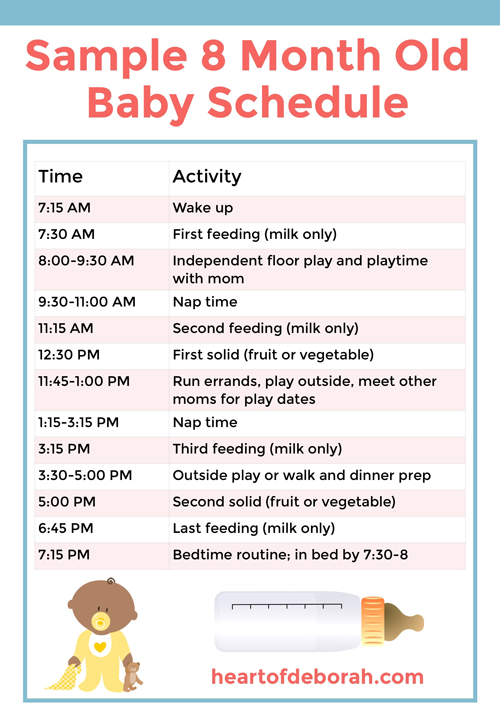 To prevent choking, cook table foods a little longer, until very soft, and cut or shred them into small pieces that your baby can handle safely.
To prevent choking, cook table foods a little longer, until very soft, and cut or shred them into small pieces that your baby can handle safely.
Around 9 months old, infant usually can pick food up between their finger and thumb so they can try feeding themselves.
If you haven't already, have your baby join the rest of the family at meals. They enjoy being at the table.
After the first birthday, babies are ready to switch to cow's milk. If you're breastfeeding, you can continue beyond 1 year, if desired. If you decide to stop breastfeeding before your baby's first birthday, give iron-fortified formula. If your baby is over 12 months, give whole milk.
Let your baby keep working on drinking from a cup, but do not give juice to infants younger than 12 months. After 12 months, you can serve whole milk in a cup, which will help with the move from the bottle.
Feeding Safety
Always supervise when your child is eating. Make sure your child sits up in a high chair or other safe place.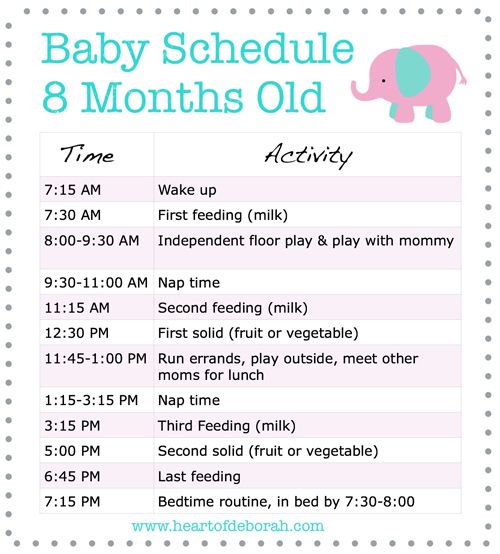 Don't serve foods that your baby could choke on.
Don't serve foods that your baby could choke on.
If you're unsure about whether a finger food is safe, ask yourself:
- Does it melt in the mouth? Some dry cereals will melt in the mouth, and so will light and flaky crackers.
- Is it cooked enough so that it mashes easily? Well-cooked vegetables and fruits will mash easily. So will canned fruits and vegetables. (Choose canned foods that don't have added sugar or salt.)
- Is it naturally soft? Cottage cheese, shredded cheese, and small pieces of tofu are soft.
- Can it be gummed? Pieces of ripe banana and well-cooked pasta can be gummed.
Making Meals Work
Keep your baby's personality in mind when feeding your baby. A child who likes a lot of stimulation may enjoy it when you "play airplane" with the spoon to get the food into their mouth. But a more sensitive tot might need the focus kept on eating with few distractions.
If your baby rejects new tastes and textures, serve new foods in small portions and don’t give up. It can take 8-10 tries before a baby accepts a new food.
It can take 8-10 tries before a baby accepts a new food.
How Much Should My Baby Eat?
Infant formula and breast milk continue to provide important nutrients for growing infants. But babies will start to drink less as they learn to eat variety of solid foods.
Watch for signs that your child is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your child stop when full. A child who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the breast or the bottle. With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
Let your baby finger feed or hold a spoon while you do the actual feeding. This is good preparation for the toddler years, when kids take charge of feeding themselves. And if you haven't already, set regular meal and snack times.
Diet for an 8-month-old baby
In the ninth month, fish can be introduced into the diet of children. Along with animal meat, fish is a source of complete protein with a well-balanced composition of amino acids, fat, vitamins B2, B12 and minerals. Compared to meat, fish contains 5 times less connective tissue, due to which it is quickly boiled soft, has a delicate texture after heat treatment and is easier to digest. Fish oil is characterized by a high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, including the ω-3 class. These substances are necessary for the child to mature the brain, retina, strengthen the cardiovascular and immune systems. Sea fish contains such important trace elements for the child's body as iodine and fluorine. The child should be given 1-2 times a week instead of meat, be sure to monitor how the child tolerates fish in general and its individual varieties. Preference should be given to oceanic fish, preferably white (cod, hake, pollock), red salmon can be recommended, river pike perch, carp.
Compared to meat, fish contains 5 times less connective tissue, due to which it is quickly boiled soft, has a delicate texture after heat treatment and is easier to digest. Fish oil is characterized by a high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, including the ω-3 class. These substances are necessary for the child to mature the brain, retina, strengthen the cardiovascular and immune systems. Sea fish contains such important trace elements for the child's body as iodine and fluorine. The child should be given 1-2 times a week instead of meat, be sure to monitor how the child tolerates fish in general and its individual varieties. Preference should be given to oceanic fish, preferably white (cod, hake, pollock), red salmon can be recommended, river pike perch, carp.
Self-cooked fish is given to a child with boiled and mashed vegetables. You can also offer your baby fish and vegetable canned food, but they contain only 10 - 20% of fish.
At this age, when all the main food groups have already been introduced, special attention should be paid to the diversity of the composition of dishes.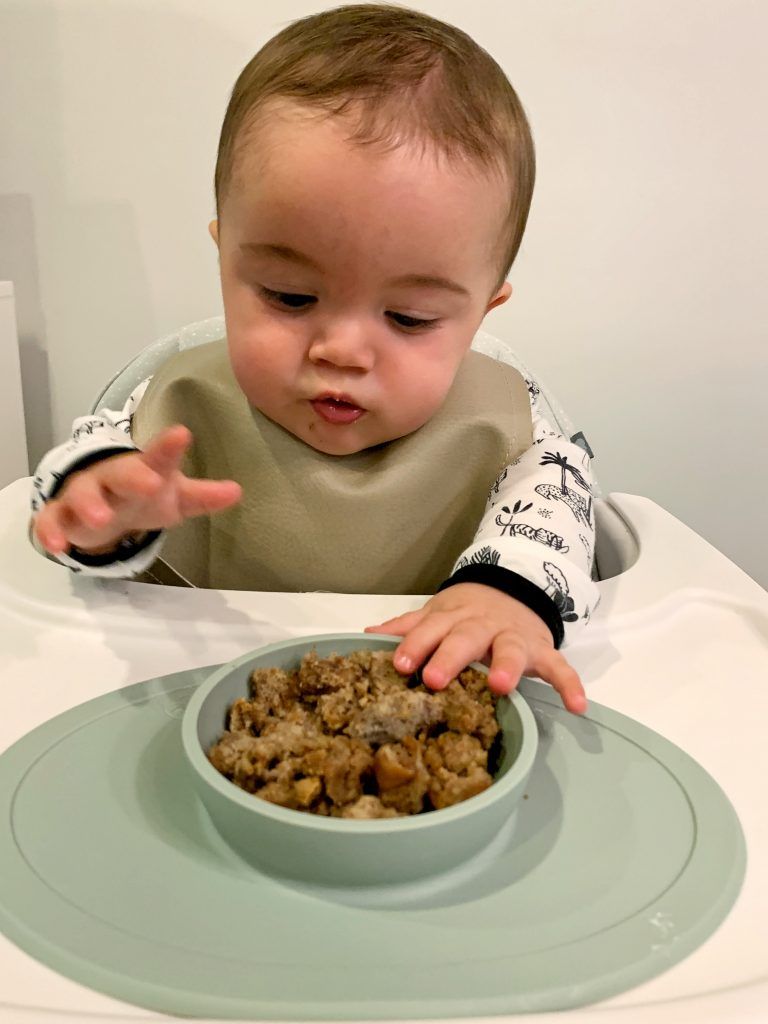 New, possibly combined products are introduced, for example, not only purees from various fruits and berries, but also their combinations with cottage cheese, cream, cereals, etc.
New, possibly combined products are introduced, for example, not only purees from various fruits and berries, but also their combinations with cottage cheese, cream, cereals, etc.
From the age of 8 months, the child's diet can be expanded to include fermented milk products (baby kefir, biokefir, bifidokefir, yogurt, bioyogurt, biolact). Fermented milk products are prepared using a special starter culture that breaks down milk protein, so that the baby can get an indispensable set of amino acids in a well-available form. Fermented milk products improve the composition of the intestinal microflora of the child, are rich in B vitamins and calcium. Their regular use favorably affects the functioning of the intestines, stimulates appetite, and increases the absorption of micronutrients. Children's dairy products are introduced into the baby's diet gradually, starting with 1 tsp. and with good tolerance increase their volume to 150-200 ml per day.
Sample menu for a healthy baby 8 months
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or infant formula | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free* or milk porridge Butter Boiled egg yolk Fruit puree Fruit juice | 180 g |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Vegetable oil Meat puree Fruit juice | 170 g 1/2 tsp 50 g 50 ml |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Cottage cheese Baby biscuits Fruit puree Supplementation with breast milk or baby kefir/yogurt | 40 g |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or infant formula | 200 ml |
* - diluted with breast milk, infant formula or water
Approximate daily ration for an 8 month old baby allergic to cow's milk proteins
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or formula for children allergic to cow's milk proteins | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 o'clock | Dairy-free* porridge Vegetable oil Fruit puree (apple, pear) | 120 g 1 tsp 80 g |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Vegetable oil Meat puree | 170 g 1 tsp 40 g |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Vegetable puree or porridge Vegetable oil Meat puree | 170 g 1 tsp 30 g |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or formula for children allergic to cow's milk proteins | 200 ml |
* - diluted with breast milk or a therapeutic formula for children with allergies to cow's milk proteins
optimal menu for an eight-month-old baby
01. 29.2019 diet of adult food and reduce the number of feedings. But I decided to study the issue and share with you. Let's find out how the eating behavior of an 8-month-old baby changes.
29.2019 diet of adult food and reduce the number of feedings. But I decided to study the issue and share with you. Let's find out how the eating behavior of an 8-month-old baby changes.
Important foods for an eight-month-old baby
At this age, breast milk or formula is still the main food for a baby. Their volume will reach up to 700-900 milliliters per day. But adult food is still in second place, although the composition of complementary foods is already expanding. The child becomes more and more familiar with new tastes, he develops food interest.
Let's see what can be added to the diet:
Cereals:
In addition to buckwheat, rice and corn, add oatmeal. Also, a child can already try pasta and vermicelli for soups. But it is better to introduce bread not earlier than a year.
Vegetables:
Broccoli and cauliflower, spinach, green beans are added in addition.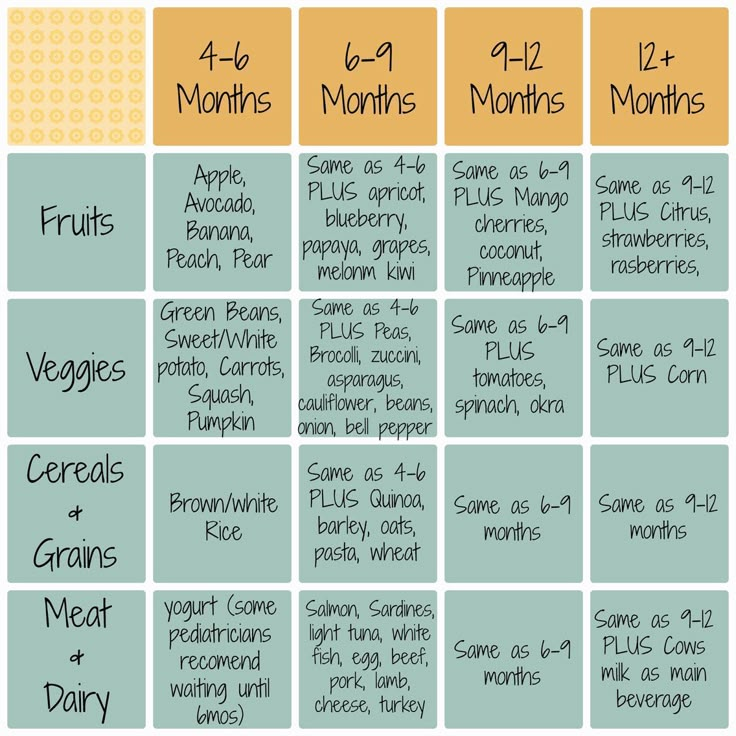
Fruit
The child can already taste bananas, prunes, plums, peaches, nectarines and apricots.
Meat
Add turkey, rabbit, chicken and veal to your menu. But soups with meat broth should be avoided for the time being.
Eggs
Since eggs can cause allergies, the hard-boiled yolk is given a taste first. A whole egg can be given after a year.
Fish
This is a new food item. For an eight-month-old baby to get acquainted with fish, cod is suitable.
Butter
Prefer butter, olive and sunflower oils.
Dairy products
Many mothers introduce them as early as possible to provide the baby with calcium. You can give pureed cottage cheese and yogurt.
Biscuits
Baby biscuits should be added in small portions if the child already chews well.
Drinks
In addition to breast milk or formula, offer your baby other liquids such as water, juice or compote.
How to cook and serve food
Cooked fruits and vegetables can be given to your child. We cook food mostly still in a soft and puree form. It is better to make porridge boiled to feed the baby.
At this age, the child begins to pick up food on his own and already knows how to chew better. To practice these skills, offer food in the form of pieces so that he can take them by hand. For example, bananas, pasta, meat and vegetables. Never leave your baby unattended while feeding. Do not give grapes, raw carrots, raisins, as they are easy to choke on.
Offer new food in the morning. And in the evening you can have the dishes familiar to the child.
A table with an example of what a daily menu for an 8-month-old baby might look like (suitable for both breastfeeding and IV):
Remember that this is just one example of nutrition at this age.
When introducing new products and monitoring the nutrition of an eight-month-old baby, be guided by the baby and his taste preferences.