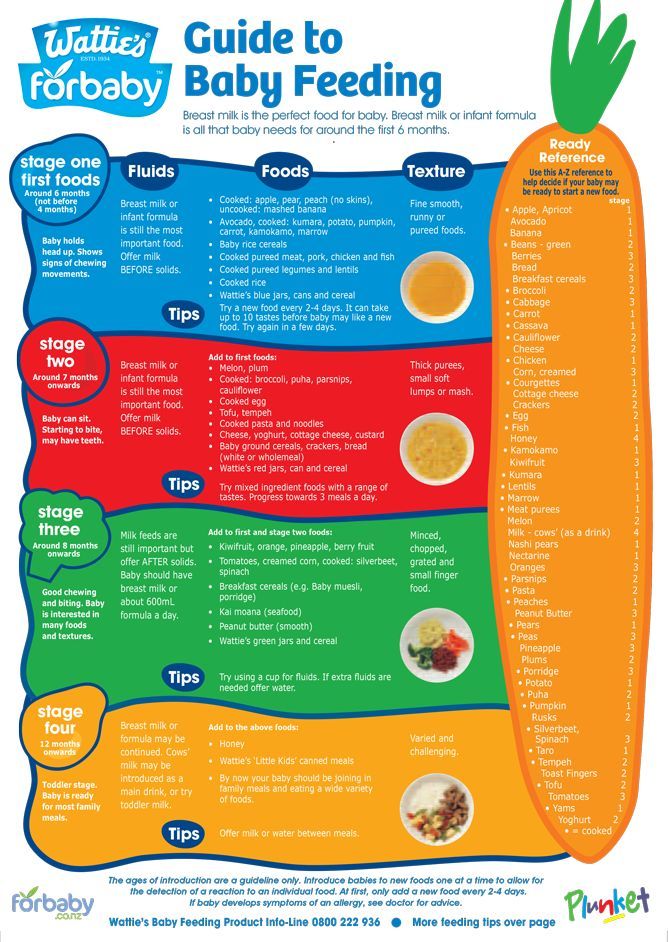
Feeding baby bunny milk
Caring for Newborn Baby Rabbits
IF THESE ARE WILD BABIES
It’s that time of year again. Wild babies everywhere. But are they at risk?
Wild rabbits hide their nests in plain view, often in the middle of your yard, bushes, etc. If you find a nest that has been disturbed, do the best you can to restore it and leave the babies in there. If a dog discovers the nest, do your best to restore it (with grass, leaves, whatever mama has used), make sure the kits are in there, and find a way to keep the dog(s) away from the nest. Mama will return for her babies and taking them away will seriously decrease their chance of survival. If you do not see the mama—DON’T WORRY—they only nurse their babies a few minutes a day, then they stay away so as to not draw predators to the nest.
If a kit is injured or an animal brings you an injured baby, if you have no choice but to help a baby, please do not try to care or it yourself—-get it to a rabbit vet or a wildlife rehabilitator
- Local wildlife rehabilitator: https://www.
nwrawildlife.org
- List of rabbit vets: http://rabbit.org/vet-listings/
The best thing you can do for wild babies is to leave them alone (restored to the nest) or, if injured, get them to a rabbit vet or wildlife rehabilitator.
DOMESTIC/PET RABBITS
WHERE TO PUT THE BABIES
Make the babies a soft nest area in a box with clean towels. We like to put one folded towel on the bottom and another bunched on top of that, so the babies can snuggle into it. You can also purchase soft nesting wool from a pet store and put that on top of the towel. You can also take whatever nesting material they were in and put it in the box as well. Cover the box almost entirely with a light towel, making sure that there will be enough air so the babies do not suffocate. Leaving about a one inch gap at the top is usually sufficient. Keep the babies in an out-of-the way, QUIET area, such as an adult’s bedroom. If the room temperature is between 68-72 degrees you will not need to provide extra heat, but if it’s cooler than that you will need to provide extra warmth. Use a heating pad set on low and slip it under one half only of the box. We do it this way so that the babies can move to a cooler area if it gets too warm. DO NOT put babies directly on heating pad, as babies can burn themselves very badly.
Use a heating pad set on low and slip it under one half only of the box. We do it this way so that the babies can move to a cooler area if it gets too warm. DO NOT put babies directly on heating pad, as babies can burn themselves very badly.
If the babies were with their mamma, but she is not caring for them (and you are sure she is ignoring them) you may need to separate her from them so they will not get hurt. Rabbit milk is very caloric and the kittens (baby rabbits) only nurse for a few minutes a day, so if you think that she is not caring for them based only on the fact you don’t see them feed…think again. If you do think they are being neglected, you can check: Are they cold? Are they making crying sounds for more than a few minutes before (or at) feeding time? Are they blue? Is the skin shriveled? Check for dehydration: gently pinch together the skin at the nape of the neck. If it sticks together or stays in a tent, they are dehydrated. A healthy kit has a round belly, is warm, gains weight on a daily basis, and snuggles with its litter mates. If they are dehydrated, cold, losing weight or becoming injured, of course, something must be done
A healthy kit has a round belly, is warm, gains weight on a daily basis, and snuggles with its litter mates. If they are dehydrated, cold, losing weight or becoming injured, of course, something must be done
WHAT TO FEED THE BABIES
Baby rabbits should be fed Kitten Milk Replacer (KMR) or goat milk, which you can buy at pet stores, or sometimes even a local veterinarian’s office. Because rabbit milk is the most caloric of all mammals, we add in one tablespoon of 100% heavy whipping cream (no sugar) to each can of KMR. Most kits will not nurse from the baby animal bottles you can buy at stores. Instead, use a sterile oral syringe, which can be purchased at most pharmacies. A better alternative are these nipples, which come the a syringe, but you may not be able to find them locally/right away (link).
It is best to feed baby rabbits no more than twice a day, but sometimes it takes more feedings to get an adequate amount into them, especially at first.
How much to feed varies greatly on what breed of rabbit you are feeding, and how big the kit is, but here is a basic guideline for the daily amount to feed a domestic rabbit who will be approximately 5-6 pounds as an adult (average rabbit size). You can increase the amounts as needed for larger breeds.
To help the kits maintain healthy gut bacteria, go to your local health food store (and get a bottle of ACIDOPHILUS. Ask for the capsules that have the “grainy stuff” inside (they are easier to mix than the “powdery stuff”) and add a bit to the formula at each feeding.
ALL amounts below should be divided into two feedings per day.
- Newborn – 1 week
- 4-5 cc formula
- 1-2 weeks
- 10-15 cc formula
- 2-3 weeks
- 15-30 cc formula
- 3-6 weeks, until weaned
- 30 cc formula
HOW DO I DO THIS?
Baby rabbits feed from their mothers while lying on their backs. You may loosely wrap baby in a soft face cloth or hand towel and lay it on your lap or in the crook of your arm. If bunny will NOT eat this way, of course, do the best you can. It is ABSOLUTELY CRUCIAL to let the baby eat at it’s own pace—especially if it is not suckling from the syringe willingly. If you squirt the liquid in too quickly you can aspirate (get liquid in) the lungs and the rabbit will suffocate.
You may loosely wrap baby in a soft face cloth or hand towel and lay it on your lap or in the crook of your arm. If bunny will NOT eat this way, of course, do the best you can. It is ABSOLUTELY CRUCIAL to let the baby eat at it’s own pace—especially if it is not suckling from the syringe willingly. If you squirt the liquid in too quickly you can aspirate (get liquid in) the lungs and the rabbit will suffocate.
Until their eyes open (10 days): After each feeding it is important to make the bunny defecate and urinate to keep the intestinal tract and urinary system running smoothly. Use a soft cloth or a cotton ball moistened with warm water and gently stroke the genital area until the bunny starts producing stool and urine. Keep stroking until the bunny stops. You are replicating the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom. The stool will be soft and may be varying shades of green and yellow. If the urine is brown and gritty, the buns are not adequately hydrated and you need to get them to a rabbit vet ASAP—-it is an emergency. Be sure to clean baby’s mouth with a damp cloth or paper towel, so that no milk dries in the hair.
If the urine is brown and gritty, the buns are not adequately hydrated and you need to get them to a rabbit vet ASAP—-it is an emergency. Be sure to clean baby’s mouth with a damp cloth or paper towel, so that no milk dries in the hair.
Baby rabbit eyes open at about 10 days of age. You may start introducing them to hay and pellets at this point, but no veggies or fruits yet. Just leave some timothy or orchard and alfalfa hay and pellets in a corner of the box where the babies can easily get to them. Make sure it the pellets are plain, high fiber and fresh, with no added goodies such as dried banana chips or seeds. Don’t ever leave a deep water dish in which a baby could drown; instead, use something shallow and rinse and fill it frequently.
If you have any questions, please contact us.
How to Feed a Baby Rabbit (And What to Feed Them)
Has your rabbit mother recently given birth? Or maybe you’ve found a baby rabbit that was separated from its mother? Either way, your mind may be turning towards what you need to do to make sure that these baby rabbits are happy, healthy, and well-fed.
In this guide, you’ll find what you need to know to determine if you really do need to feed a baby rabbit, as well as a list of equipment and step-by-step walkthrough for how to feed.
How Do I Know If I Need to Feed a Baby Rabbit?
Did you know that rabbit mothers feed their babies only once or twice per day? Or that, outside of these feeding times, they mostly leave their young completely alone?
Unlike many other mammals, rabbit mothers do not stick extremely close to their babies, sometimes even right after they’re born. Because rabbits are prey animals, their instincts tend to make them wary of staying near anything that a predator might target — including their own children.
In most cases where the rabbit mother is still present, you’ll not have to intervene and help feed her babies. Only if the babies are showing clear signs of distress, such as wandering around their nests and crying, will you maybe have to help feed them.
However, in the unlikely and unfortunate circumstance that the mother rabbit is dead, missing, or completely ignoring her newborns, you’ll need to take action and begin feeding them right away! For the next three weeks, you’ll be their most vital source of nutrition and care.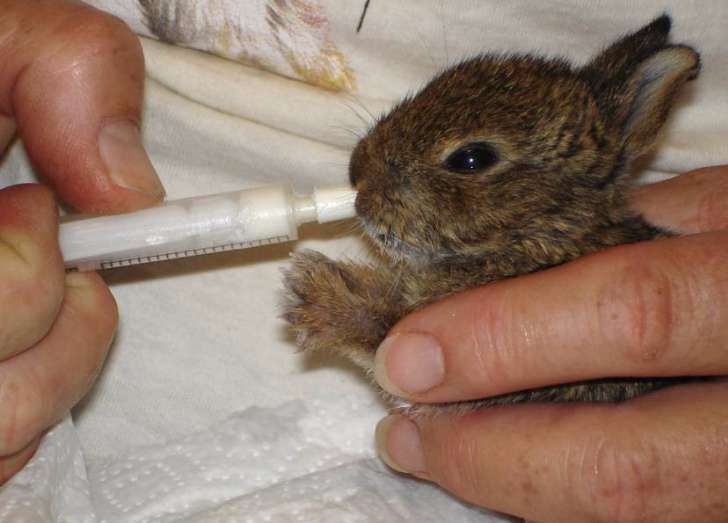
The Right Supplies and Best Food for Baby Rabbits
When you are called upon to feed one or more baby rabbits, you’ll need to gather some special supplies to make sure that you’re feeding them in the safest and most nutritious way possible. Before mixing your formula recipe, make sure you have both a Sterilizing steam bag, such as the ones used by breastfeeding human mothers, and Nursing bottles and nipples, often available in package sets.
Then, you’ll need to mix your baby formula from this recipe, courtesy of Doctor Dana Krempels of the University of Miami Biology Department:
- ½ cup fresh, whole goat milk (available at most health food stores)
- ½ cup Kitten Milk Replacer
- 1 tablespoon freeze-dried colostrum
- ½ teaspoon heavy cream
Be sure to mix this in advance so the colostrum has time to fully dissolve into the formula. The combination of nutrients in this formula most closely resembles rabbit mothers’ milk, making it an almost-perfect match for feeding orphaned babies.
Step-by-Step: How to Feed a Baby Rabbit
Image by auenleben from PixabayFeeding baby rabbits takes special care and attention, so as not to overwhelm their sensitive immune and digestive systems. Follow these steps to the letter:
- Thoroughly wash your hands with warm, soapy water.
- Follow the instructions that come with the steam bags to sterilize and disinfect the bottle and nipples.
- Fill the bottle with formula, then warm it to body temperature.
- Sit on the floor, and spread out plenty of cushioning under where you’ll feed the rabbits.
- Hold the baby horizontally in your non-dominant hand, and gently place the nipple of the bottle to its lips.
- Sometimes, the baby will resist being bottle-fed; in this case, wet their lips with a drop of formula, and be persistent.
- DO NOT try to force formula out of the bottle! The last thing you want is to overfill the baby’s mouth, causing it to breathe in the formula.

That’s it! Over time, the babies will acclimate to your feedings and not put up a fuss. For the first three weeks of their lives, they’ll be relying solely on formula for their nutrition.
From 3 to 6 weeks, you’ll notice them starting to try out solid foods. This will form the foundation for weaning them off of the bottle, but they’ll still need the nutrients provided by formula up until about 8 weeks of age — at which point you can safely stop feeding them. A fantastic way to make this transition is with a food designed for young rabbits, such as this one from Oxbow.
Final Thoughts on Feeding Baby Rabbits
When you’re called upon to feed a baby rabbit due to conditions outside of the mother’s control, it’s a big responsibility. With the help of this guide and the proper equipment, you can give your baby rabbits the best chance at a long and healthy life in your home! As always, if you’re unclear on anything you’ve read here, it’s best to contact your local veterinarian for personalized help.
Featured Image: Motortion Films, Shutterstock
What to do and how to feed baby rabbits without a female rabbit, artificial feeding of baby rabbits without a mother
Many rabbit breeders face the problem of a female refusing or being unable to feed her offspring. Babies are simply left to fend for themselves. If this happened to you, don't despair. After all, animals can be raised to their feet with the help of artificial nutrition. How to feed rabbits without a rabbit, find out with us.
Contents
- 1 Is it possible?
- 2 Nutrition Rules
- 2.1 Milk
- 2.2 Kozie milk
- 2.3 Herbal granules
- 2.4 Artificial mixtures
- 3 Power of Orphans at a different age 9000 3.3 At the age of 17-30 days
- 3.4 When to switch to an adult diet?
- 4.1 Similar items
Is it possible?
Of course, it is quite possible to organize the feeding of rabbits left without a mother by yourself. The organization will take you some time, you will need syringes, nipples, mixtures or milk directly, but the result will please. Often, rabbits fed with milk and milk mixtures grow up even stronger than those that were next to their mother. But why kids remain orphans, you can find out from our previous article.
The organization will take you some time, you will need syringes, nipples, mixtures or milk directly, but the result will please. Often, rabbits fed with milk and milk mixtures grow up even stronger than those that were next to their mother. But why kids remain orphans, you can find out from our previous article.
In addition to feeding rabbits by a person, you can use another method - to plant babies with another nursing mother. With the right approach, she will take care of the orphans as if they were her own. But in this case, you should carefully select the female, because not everyone will agree to feed "foreign" children. If you don’t have any other nursing rabbits on the farm, except for the one that left her cubs, do not be alarmed.
Nutrition Rules
As you know, for any newborn babies, including rabbits, feeding with mother's milk is best. There are other options, but only this product is suitable for the smallest rabbits. Next - more about the products that can be used to feed rabbits.
Cow's milk
The first product that all livestock breeders turn to is cow's milk. Feeding pure cow product is not suitable for rabbits - it is too different from mother's milk. If you intend to feed newborn rabbits with cow's milk, dilute it in equal proportions with regular condensed milk. This increases fat content and nutritional value. From the first days, you need to do 5 feedings, giving the fluffies 1 ml of such mixed milk per dose, and then, as they grow older, gradually increase the portions.
Goat milk
If you do not consider cow's milk as an acceptable option, you can choose goat's milk. It is no less beneficial for little rabbits than that produced by the mother, and it does not need to be mixed with other types of foods. Some farmers give Acidophilus in a mixture with goat's milk, but it is better to check its dosage with a veterinarian. Goat milk is given to rabbits from birth, 2 ml twice a day. From the beginning of the second week of life - 5 ml twice a day.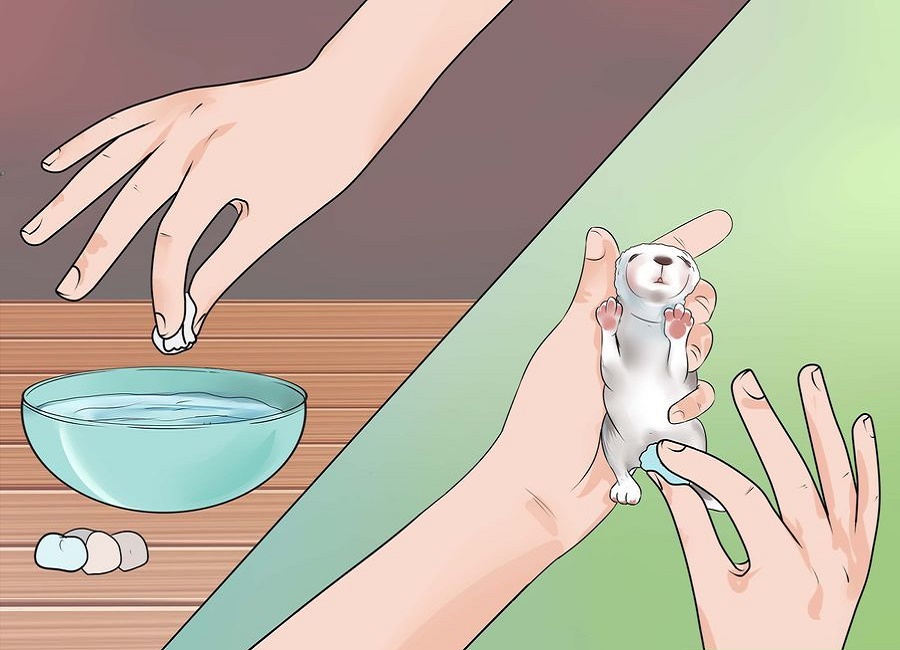
Herbal granules
Feeding orphans in the first weeks should be only dairy. You can make a combination of herbal granules with milk only from 3 weeks or from the 1st month of life, if the babies are developing well. Newborn rabbits should not be given such a nutritional supplement, otherwise they will have stagnation in the intestines! The amount of herbal granules after 30-40 days of life is calculated by the amount of weight (about 3% of the total weight of the animal). Each serving must be weighed, as pellets from different manufacturers weigh differently.
Artificial mixtures
Formula-fed formula-fed rabbits are a good option as they are nutritious and digestible. You need to make such a milk "porridge" by diluting the mixture more concentrated than indicated in the instructions. Feeding mixtures in the first week of life of rabbits should be built according to the schedule.
If the babies are gaining weight well, well-fed, they do not have indigestion, it will be noticeable immediately. From the 1st day of life to the 7th, the mixture is given 5 ml 3 r / day, from 7 to 25 days - twice a day, 20 ml each, increasing by the end of the month each meal to 60 ml.
From the 1st day of life to the 7th, the mixture is given 5 ml 3 r / day, from 7 to 25 days - twice a day, 20 ml each, increasing by the end of the month each meal to 60 ml.
Experienced livestock breeders are advised to leave rabbits in cages with various special feeds and finely chopped vegetables from the age of 17 days, because it is at this age that their teeth change. The replacement of teeth stops at the age of 45 days, the animals finally stop eating milk and milk formulas. Also, rabbits are weaned from their mother if they are suckling.
Important! Rabbits have a well-developed instinct to imitate their relatives. From 14 days of life to 30, you can offer them finely grated carrots, a small amount of dry rabbit food, greens.
Feeding orphans at different ages
We figured out that small rabbits may even need to be fed milk, as well as powdered milk mixtures similar to mother's milk. Herbal granules up to a certain age must be said "no". How exactly to feed your newborn pets from the moment they are born? And when should you switch to a more adult diet so that the transition is natural? Let's find out more about this.
How exactly to feed your newborn pets from the moment they are born? And when should you switch to a more adult diet so that the transition is natural? Let's find out more about this.
Newborns
A newly born or day old rabbit is fed with milk or formula. On the first day, we give food literally drop by drop, making sure that the rabbit's tummy does not overflow. Little fluffies still do not have an understanding of how much liquid they need to suck out, they will drink how much you give.
From the first to the fifth day of life, we feed 4-5 times a day, 1 ml of milk or formula. By the 5-6th day of life, if the animal gains weight well, defecates regularly and grows, its weight should exactly double. The weight of a newborn rabbit on average ranges from 40 to 80 grams.
Nutrient liquids should not be heated above 37 degrees. It is better to drink milk through a pipette or through a syringe without a needle. All manipulations must be carried out with clean hands, done in clean dishes.
5-14 days old
If you are successful in feeding milk to newborn rabbits, by 5 days of age, the babies will double their birth weight. From five days, pets are watered not 5, but 3 times a day, giving 25-30 grams of mixture or milk. This continues for about 14 days. By the end of the second week, the rabbits are already noticeably gaining weight, and they can be transferred to a two-time diet. The weight of such an animal during this period reaches 260 grams.
17-30 days old
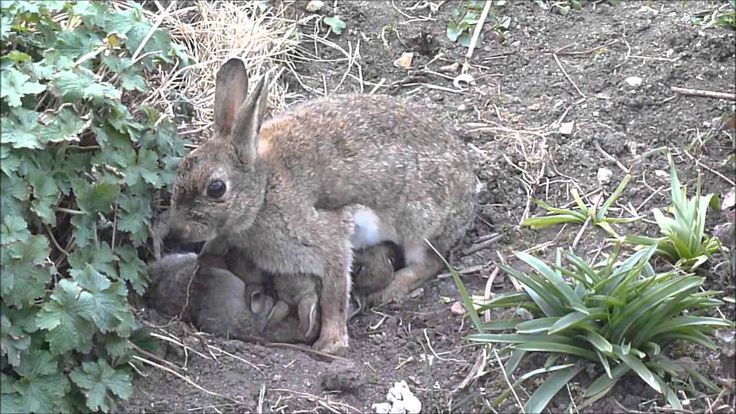
Feeding rabbits at the age of one month is much easier than newborns. By the month the animal gets stronger, weighs about 500 grams, and sometimes more. From 17 days of age to 30 days from birth, most of the milk teeth are replaced by molars in pets. If the animal is healthy, it is actively interested in new food: vegetables, grass, it can eat hay, dry oatmeal, a mash of milk porridge. The diet at the age of one month is two times a day, many breeders exclude milk and mixtures after a 30-day milestone.
When to switch to an adult diet?
Rabbits can and should be introduced to an adult diet from 30-45 days, similar to the period when they are weaned from their mother. Dairy feeding at this time is a controversial issue. Some people advise not to remove milk, but if your babies are large and healthy, feel free to remove this product. The adult diet is very diverse, these are root crops, vegetables, fresh green grass, hay, special rabbit feed, oats. After a dry meal, you can give wet food, root vegetables or vegetables.
Why is it necessary to moisten food and mix dry and wet foods? Dry food irritates the rabbit's respiratory tract, especially during growth.
Video "How to feed a rabbit with a syringe"
Informative video about how rabbits eat from a syringe. The babies in the video are 3 weeks old.
milk replacers, supplements, newborn care
Sometimes it happens that young rabbits, as soon as they are born, are left without mother's milk and care. Then these worries fall on the shoulders of a person. Feeding rabbits without a rabbit is a serious and responsible matter, because the life of babies depends on the speed of decision-making and subsequent actions.
Then these worries fall on the shoulders of a person. Feeding rabbits without a rabbit is a serious and responsible matter, because the life of babies depends on the speed of decision-making and subsequent actions.
Why are baby rabbits left without mother's milk and care? What is the danger?
The decision in favor of artificial feeding is made by the farmer for one of the following reasons:
- as soon as she has calved, the female refuses the young rabbits and abandons them;
- the female rabbit has no milk or has developed mastitis;
- the female is in a very serious condition after birth or she has died;
- other nurse does not accept babies.
It is especially dangerous for rabbits when the female dies without having time to feed them with valuable colostrum for the first time. It contains antibodies necessary for babies, which contribute to the development of their own immunity.
Human care and care will not replace mother's cubs, and incorrect actions on the part of breeders increase the mortality rate.
Ornamental rabbits are less likely to survive, and meat breeds, even on artificial feeding, grow into healthy strong individuals.
What to try before artificial feeding?
The purpose of artificial feeding is not only to ensure the satiety of rabbits, but comprehensive care for offspring. Before you begin your duties, try the following alternatives:
- Find a litter nurse. This course of events is possible if the breeder has several queens. You can’t just plant baby rabbits with another lactating female. There is practically no chance that she will accept someone else's offspring.
Therefore, remove the rabbit for half an hour in another cage, and wipe the babies with fluff and straw from her dwelling. The nurse will return to the cage and will probably take on new wards. - Awaken the parental instinct. Most often, it is after the first birth that a mother does not want to feed her babies. Try to solve this problem by simply holding the rabbit during several feedings.

With a favorable outcome, feeding on mother's milk, the rabbits will quickly get stronger and begin to gain weight. But it happens that these tips do not help.
How to properly feed baby rabbits for the first 30 days?
Baby rabbits are born completely blind, without wool. The first fluff on the body begins to grow on the 6th day, and the opening of the eyes occurs on the 10th day. Newborns weigh 60-90 g, but with comprehensive care and good nutrition, they quickly gain weight and grow.
A farmer should prepare for artificial feeding of offspring - master the skills of care and purchase equipment.
Tools
Baby rabbits require teats and containers.
Buy Animal Feeding Kit from the shop. It includes a special syringe with rubber nozzles of various shapes and sizes. Such a set is sold in the form of a bottle with several special nipples.
You can also use improvised means:
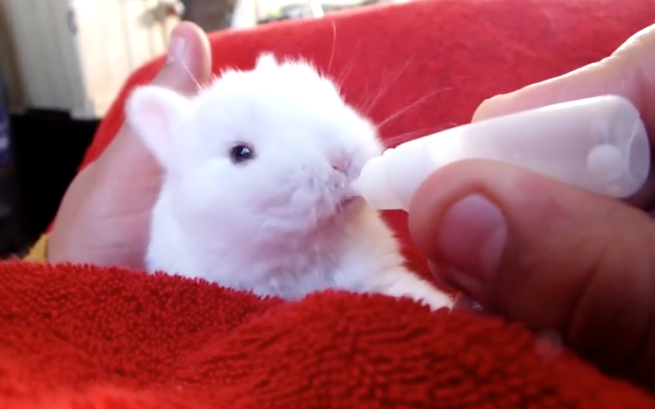
- Use the syringe and the rubber pipette tip for feeding, making a few small holes in it.

- eye drop bottle is suitable for the procedure. For convenience, use it together with a pipette tip.
- Small baby bottle is useful for older animals.
The process of artificial feeding should be as close as possible to natural.
Before opening their eyes, the reaction of rabbits to teat substitutes is weak. When pouring milk into the mouth, be careful and do not rush, otherwise the rabbit may choke or choke.
Milk replacers
Newborn baby rabbits require good nutrition. Rabbit milk substitutes include:
- Goat milk. The best option for artificial feeding of rabbits. There is no need to dilute or add anything, because the composition is similar to rabbit milk, only slightly inferior to it in fat content.
- Cow's milk. The most affordable and common option for replacing rabbit milk. In its pure form, it cannot be fed to babies, because it lacks carbohydrates in its composition.
 Mix cow's milk with condensed milk in a ratio of 3:1. Heat the mixture for 40-60 minutes. at a temperature of 70. Before feeding, cool to 37 degrees.
Mix cow's milk with condensed milk in a ratio of 3:1. Heat the mixture for 40-60 minutes. at a temperature of 70. Before feeding, cool to 37 degrees. - Special blends. Sold in pet stores and veterinary pharmacies in a large assortment. Buy milk substitutes designed for rabbits or dogs. In a pinch, suitable food for cats. In terms of components, their composition is as similar as possible to rabbit milk.
- Infant formula . Such food is suitable for rabbits if it contains a minimum of sugar and additives.
In the presented video you can see the principle of artificial feeding of rabbits:
Thus, the most suitable food for newborn rabbits is special dry mixes, and cow's milk is the least preferred option.
Feeding procedure
During the procedure, hold the animals upright, firmly, but without crushing. At first, rabbits may not respond to simulated nipples. Be patient.
Gently moisten your baby's mouth with milk, he will lick it off himself. Repeat several times. This will stimulate the sucking reflex.
During the feeding procedure, be careful not to get liquid into the animal's respiratory tract. This is fraught with the death of the rabbit.
Make sure that the tummy does not overflow, because babies themselves can not yet determine the level of their satiety. Overeating causes indigestion and related problems.
Feeding liquid should be 37 degrees. Store milk for up to 3 days in the refrigerator, and always use freshly prepared formula for feeding.
Adjust the diet according to the needs of the cubs. Well-fed babies sleep quietly, and hungry babies squeak and actively look for a source of food.
Dosage and frequency
The amount of mixture and the frequency of feeding directly depend on the age of the rabbits.
The female feeds the young rabbits 1-3 times a day. Her milk is very nutritious, so many feeding sessions are enough for rabbits for proper development, growth and weight gain.
But none of the mixtures can replace the milk of a rabbit, so bottle-fed babies are fed up to 6 times a day.
In the first 2 days, the rabbits need a few drops of food per dose, even 1 ml of the mixture is an overabundance for them.
Gradually, the amount of milk needed for the development of the cubs increases, and the number of feedings decreases.
Artificial feeding by age
Organizing artificial feeding is a responsible business. You need to be extremely careful when choosing a diet for rabbits, depending on their age and physical health. After all, errors in the quantity and quality of the diet adversely affect the cubs.
From birth to 5 days
A newborn rabbit needs 1 drop of nutrient fluid. For the first day they feed 5-6 times. Since babies have not yet learned to swallow on their own, care must be taken.
Since babies have not yet learned to swallow on their own, care must be taken.
On the second day, 4-5 meals are enough. On the 5th day - 4 feedings. The daily norm of milk is 5-6 ml. By the end of this period, rabbits with normal development double their weight.
From 6 to 14 days
Animals grow up and the amount of nutrient mixture per feeding increases. They drink 7-10 ml of milk per day. The number of feedings remains the same, or decreases to 3. The weight of the rabbits reaches 250 g.
From the 15th to the 30th day
From the 15th day the animals are transferred to two meals a day. In the first 2-3 days, observe the behavior of the young and, if signs of hunger are present, supplement them with a small amount of formula in the 3rd feeding.
The amount of the mixture per day by the end of the month reaches 60 ml. While this is their main food. Weaning from the nipple should be on the 20-25th day.
The readiness for the introduction of complementary foods is determined by the condition of the teeth. If the molars have replaced the milk teeth, then solid food can be gradually introduced and taught to drink from a saucer.
If the molars have replaced the milk teeth, then solid food can be gradually introduced and taught to drink from a saucer.
Weight of animals by the end of the period reaches approximately 500 g.
Starting from the third week, put small piles of dry grass in the cage - this will prepare the rabbits for solid food.
At this time, it is important to monitor the change in the baby's stool. Remove hay from the diet immediately if diarrhea occurs. If adaptation to new food goes without problems, then add a small amount of compound feed, grass, carrots.
From the 31st day, if there is no shortage in weight, the rabbits are gradually removed from the diet of milk. When the offspring are 45 days old, their diet completely switches to an adult.
Vitamin A and Vitamin D
In nature, baby rabbits get their vitamins and minerals from their mother's milk and then from a varied adult diet. Artificially fed individuals need more vitamin supplements.
Artificially fed individuals need more vitamin supplements.
If the body lacks vitamin A , then rabbits suffer from a runny nose and dry eyes. This vitamin is responsible for the desire to reproduce and have healthy offspring, as well as the healthy functioning of the nervous system. Its sources are: beet tops, carrots, cabbage leaves, young grass, etc.
Vitamin D is responsible for bone formation. With its lack, growth retardation and various deformities of the limbs and spine are possible. Vitamin D is produced by the body itself under the influence of sunlight. This will help bone meal, fish oil, milk. Feed food in places where the sun's rays do not have access, because under their influence vitamin D is destroyed.
Oatmeal and oat sprouts
Oats are a fundamental cereal in rabbit nutrition, containing a storehouse of vitamins and microelements. Its calorie content is 336 kcal/100 g. It can take up to 50% of the total mass of feed. Rabbits on such feed gain weight well, but oats do not cause obesity.
Rabbits on such feed gain weight well, but oats do not cause obesity.
This cereal is introduced into the diet of rabbits as soon as they begin to feed on their own. First, they are fed with oatmeal or crushed grain, and later they switch to feeding with whole grains.
Animals eat such food with pleasure up to 5 times a day, and adults - 3 times a day.
Oat seedlings have a good effect on the reproductive system of rabbits. For mating, it is introduced into the diet of both males and rabbits. Oats help lactating females recover after birth and stimulate the production of nutritious milk.
Useful substances, which are rich in sprouted oats, have a beneficial effect on the gastrointestinal tract of animals. Appetite increases, fur becomes beautiful and shiny, body weight grows.
Be sure to include a drinker in the cage if the rabbits diet is dominated by dry cereal food.
Bone meal and chalk
Bone meal is a powder from the bones of animals and birds, the most valuable source of calcium, phosphorus, fluorine, zinc, iron, protein and other micro and macro elements.
By introducing it into complementary foods, the likelihood of diseases associated with the musculoskeletal system in rabbits is significantly reduced. Thanks to proteins, the muscle mass of animals grows faster.
The doses indicated on the packaging of bone meal must be strictly observed. An overdose is even more dangerous than the problems associated with the lack of this bait:
- The stomach of rabbits becomes clogged with a jelly-like mass, because of which the animals often die.
- Females become aggressive, lose the ability to reproduce.
- There are cases of cannibalism among individuals.
If the beginnings of these problems appear, reduce portions or remove flour from the diet.
Chalk is a safe mineral supplement providing calcium to the body. It can be used in powder form, in lump form and in mineral briquettes. Chalk is useful for the prevention of diseases of bone tissue.
Branches and acorns
Branches of trees and shrubs are used not only as food.![]() Some are useful for the prevention of ailments.
Some are useful for the prevention of ailments.
So, for example, walnut branches remove parasites from the body, linden and willow - work as an anesthetic, birch - as a diuretic. Give them to rabbits infrequently, as needed.
Trees and shrubs whose branches can be used as permanent feeding include: .
Trees whose branches can be given to rabbits occasionally :
- Pear, rowan, oak, chestnut.
- Pine, juniper.
Do not use branches of bird cherry, lilac, elder, rosemary in the diet.
Another nutritious food for rabbits is acorns. You can feed them both green and dry. The norm of acorns per day for an adult is 50 g.
Introduce them into the diet gradually - first in the form of flour, as an additive to the main grain feed, and then as an independent complementary food. Rabbits love to chew on them.
For more information, read our article on how, when and what to feed rabbits.

Edible salt
Table salt is used not only as a seasoning. Chlorine ions contribute to the production of hydrochloric acid in the composition of gastric juice, and sodium ions are responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses.
Rabbits gnaw on the wooden partitions in the cage due to salt deficiency. This indicates such problems:
- violation of metabolic processes;
- decrease in offspring productivity, increase in the number of miscarriages;
- slow growth of newborn animals;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- water-salt imbalance and diseases associated with blood formation.
Edible salt is usually given in combination with chalk. For this, mineral briquettes are prepared. The following components are required:
- 500 g feed chalk;
- 500 g red clay flour;
- 300 g ground hardwood charcoal flour;
- 5 st. l. salt;
- 3 tbsp.
 l. fodder sulfur.
l. fodder sulfur.
Mix ingredients with water until a thick dough is obtained. From it, fashion shapes the size of a matchbox. String them on the wire. Dry first in the shade and then in the sun. Fire it like clay in a kiln.
Place one in each rabbit cage. They themselves will learn to gnaw a briquette in the amount that their body requires.
Acidophilus
Rabbits are not very healthy, the gastrointestinal tract is their weak point. Gastrointestinal stasis is often found in these animals, when the stomach stops working and the individual dies.
Acidophilus is a complex of useful lactobacilli. It helps digest food in the large intestine and protects against harmful bacteria that can lead to bloating, diarrhea, and other problems.
This drug will also help when taking antibiotics, when the entire intestinal microflora is destroyed.
Caecotrophs are the primary feces of the rabbit. It has an oblong shape, often reminiscent of a bunch of grapes due to sticky spools. The color varies from light green to black. The smell is unpleasant, sour.
The color varies from light green to black. The smell is unpleasant, sour.
This feces is formed in a special compartment of the caecum, which is found only in lagomorphs. Therefore, do not confuse caecotrophs with ordinary feces.
Usually rabbits eat caecotrophs from the age of 20 days as soon as they leave the body. In this way, they re-absorb vitamins and minerals. Without this, the animals would suffer from beriberi.
If there are too many caecotrophs, the animal does not eat them, then you are overfeeding the rabbit with cereals. Remove grains from the diet for a couple of days, leaving water, branches and hay.
The second reason may be worms. Get rid of the parasites and everything will be back to normal.
Artificial feeding of rabbits has its positive and negative aspects.
Benefits include:
- Getting used to milk substitutes, rabbits are undemanding to eat.
- Good appetite leads to weight gain and growth of individuals.

- The diet is adjusted to the person and his capabilities.
Disadvantages of artificial feeding:
- Nutritional value, composition of vitamins and minerals in substitutes is much lower than in natural rabbit milk.
- Inability to transfer antibodies, which means weakened immunity of the offspring.
- Difficulty in nipple training.
- Baby rabbit may be injured while feeding.
- The constant presence of a person next to the kids for care and attention.
Baby rabbit care
The earlier the baby rabbits were left without a queen, the more complex care they need. The conditions of detention and the feeding regime require a great responsibility and dedication from a person.
Lighting and heat
Newborn rabbits require special care, attention should be paid to lighting and heat when rearing babies.
There must be a place in the cage where the sun's rays do not reach. Direct solar radiation is dangerous for animals. Daytime lighting should be dimmed, and it is recommended to turn off the lights at night.
Daytime lighting should be dimmed, and it is recommended to turn off the lights at night.
Keep the rabbits warm. To do this, build a nest from the fluff of adult rabbits or put a heating pad in the cage. The optimum temperature is considered to be when a person’s hand is comfortable, and not hot.
Hygiene
Cleanliness in the care of rabbits is essential, because without immunity they are more susceptible to germs and bacteria.
Boil utensils and teats before use. Prepare the mixture before feeding, according to the instructions. Store milk in the refrigerator for up to 3 days.
Before feeding, wash your hands with fragrance-free soap and dry with a towel. After feeding, clean the babies from the remnants of food and bowel movements.
Belly massage
Bowel and bladder emptying requires special attention, because babies do not know how to cope with it.
Before feeding, the female licks the baby rabbit, pressing on the stomach with her tongue, moving from the navel to the hind legs. Thus, it causes the intestines and bladder to empty.
Thus, it causes the intestines and bladder to empty.
A person who substitutes a mother for rabbits should not forget about this procedure. Otherwise, the bladder will burst.
Before each feeding, massage the baby's belly with a damp soft cloth or piece of cotton wool.
This manipulation is completed when the offspring are more than 14 days old.
In healthy rabbits, the belly is elastic and slightly convex. If it is sunken, then this is a sign of gastrointestinal problems.
In the video below, the breeder demonstrates how to massage the belly of a rabbit before feeding:
Caring for orphaned rabbits requires a lot of strength, skills and patience from a person.