Feeding baby first cereal
How to Get Started – The Baby's Brew
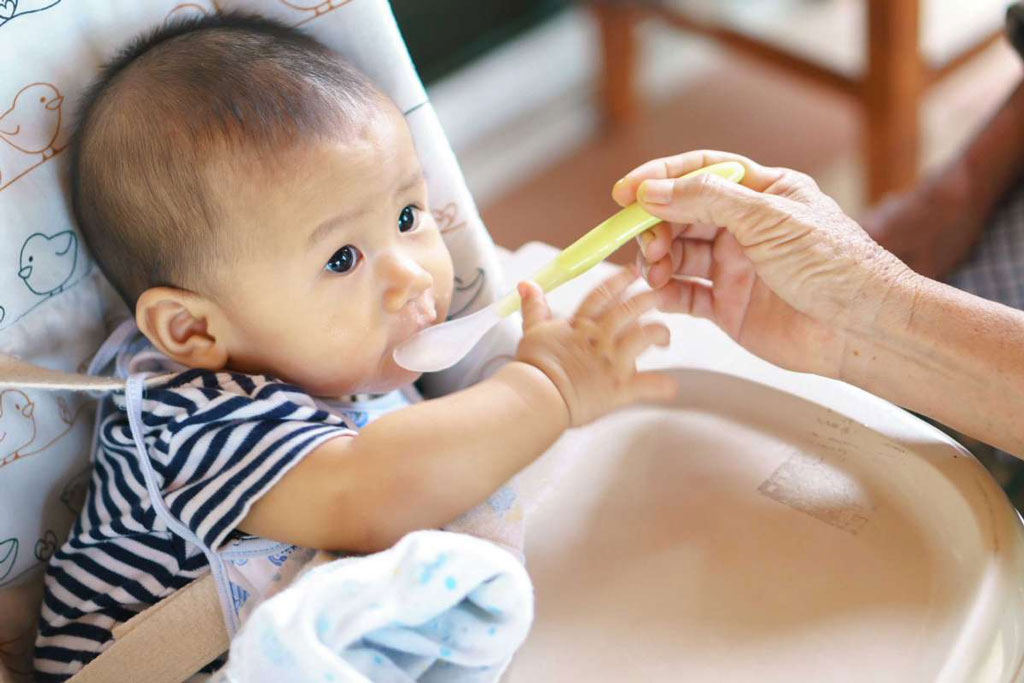
I will always remember feeding each of my babies their first foods. After months of only breastfeeding and bottles, my husband and I couldn’t wait to introduce the next milestone to each of our babies. But with the first baby at least, there was also apprehension. Our pediatrician had recommended we start with a single-grain baby cereal such as rice cereal, but I didn’t know which one to get and I wanted to make sure I fed my baby the right way!
So to get you started off on the right food with baby feeding 101, I’ve put together this guide to giving your baby cereal for the first time. And it will only get more exciting as you introduce other foods to your little one.
Choosing a First Baby CerealBefore you actually feed your baby, you have to choose what you want to give them from the array of cereals and other options available.
Most parents reach for the rice cereal to give their baby as their first food. I know I did as a new mom! It’s an easy choice and one that doctors suggest due to its benefits. It's easy to such as its digest, won’t trigger an allergic reaction and is tolerated well by babies who’ve only been fed breastmilk or formula. It’s also iron-fortified, which babies need as their iron stores start to deplete around 6 months of age.
Though rice cereal has traditionally been suggested as the best first food for your baby, even many doctors may still give this recommendation, it has gotten a bit of a bad rap in recent years due to the arsenic that’s found in rice - causing parents to look at other options. (This article from Healthy Children explains how you can ensure rice cereal can be used in a healthy diet for your baby.)
If you do choose rice cereal, you’ll want to start introducing other solids to your baby shortly so that’s not all that they are getting, as recommended by the FDA.
Fortunately, if you want to skip the rice cereal completely, you can! There is no need to feel like this is the only first food for your baby. Many experts share that any iron-fortified single-grain baby cereal is a great choice, such as baby oatmeal or barley. You can even start with other pureed foods which we discuss later on in this article.
When to Start Feeding Your Baby CerealSeveral years ago the recommendation was that parents could feed their babies at four months if they showed readiness signs. But medical advice evolves and this is a guideline that medical experts have changed to give babies the healthiest start possible.
It’s now suggested that it’s best to wait til closer to your baby’s ½ birthday to introduce solids, especially if he is breastfed. There’s really no reason to rush it!
But it’s not just age you want to pay attention to as we know that all babies develop at different rates.
Here are signs to look for that will let you know your baby is ready for solid foods:
- able to sit up supported in a high chair
- has proper head control
- no more tongue thrust
- eager to take a spoon
- are interested in the food that you are eating
If your baby isn’t yet showing these signs, you’ll want to wait a bit longer before starting baby cereal or other solid foods. No need to worry - all babies are ready in their own time! Your baby will continue to get the nutrition they need from their breastmilk or formula so you don’t need to be concerned that they are missing out on important nutrients. If you do have concerns, it’s always best to talk to your pediatrician.
Can you give your baby cereal in a bottle?Even though your well-meaning grandma may suggest that you mix cereal into your baby’s bottle to help fill them up so they can sleep better, this practice is actually not safe according to the CDC.![]() In fact, they share that it won’t help your baby sleep better anyway. This practice puts your baby at risk for choking or overfeeding and also may encourage parents to start solid foods long before they are ready.
In fact, they share that it won’t help your baby sleep better anyway. This practice puts your baby at risk for choking or overfeeding and also may encourage parents to start solid foods long before they are ready.
Instead, follow the guideline to not feed your baby solid foods until he or she is at least 5-6 months in age and watch for the other readiness signs mentioned above. At this point you can feed your baby with a spoon and introduce finger foods as they are ready.
RELATED: Starting Solid Foods With Your Baby
How to Introduce Cereal to Your BabyBreastmilk and formula will continue to be your baby’s primary source of nutrition until the age of one, but cereal is a great way to get them started with supplemental nutrition and transition them to solid foods. So how do you go about it?
Here are the steps to follow to give your baby her first single-grain cereal:
- Make sure they meet the recommended readiness signs. This will not only make for a safe feeding experience for your little guy or gal, but it will also be a lot more enjoyable for you.

- Plan to feed your little one after they’ve had a full feeding of breastmilk or formula. This way their tummy will mostly be full which means they’ll likely be happy to try a little cereal. (If you try to introduce solids to a hungry baby they will most likely be uncooperative!) Initially you’ll only feed your baby once per day, and it’s up to you when you want that time to be. We recommend choosing a time that your baby is usually in good spirits!
- Follow the directions on the label of your chosen baby cereal. You don’t need much to start! 1 tablespoon of cereal mixed with breastmilk or formula until it’s a runny consistency will be plenty for those first couple of feedings. If your baby is used to drinking warm milk or formula, you’ll want to use that same temperature of milk to mix with your baby’s food. (This is why we love the Baby’s Brew portable bottle warmer...you can choose your baby’s milk temperature with the push of a button!)
- Be sure your baby is sitting upright.
 Ideally this would be in a highchair, but they could also be sitting on your lap. You’ll want them to be wearing a bib as a lot your little one’s food won’t make it into their mouth initially.
Ideally this would be in a highchair, but they could also be sitting on your lap. You’ll want them to be wearing a bib as a lot your little one’s food won’t make it into their mouth initially. - Use an infant spoon to feed your baby. Do your best to get the spoon into their open mouth, but just know it’s going to be a bit messy at first as they get the hang of what’s going on. It won’t be long before they are opening wide at mealtime!
- Watch for cues from your baby that show that they are full (or are just are no longer interested). If your baby turns their head, is fussy or won’t open their mouth to eat, it’s time to be “all done!”
And that’s it! You can do another feeding the next day (or you can just do every other day) with the same type of cereal. Be sure to wait three - five days before introducing another food so you can keep an eye out for any allergic reactions. This is the recommendation given by the CDC.
After a couple weeks to a month of successfully feeding your baby once per day you can move to twice per day.
Some parents choose to start with a different food or may take baby cereal out of their little one’s diet altogether. Starting with other pureed foods instead is totally fine and may even work better for some babies. WebMD shares that both pureed vegetables or fruits are good starter foods and that there’s no rule saying that baby cereals must be first.
Some great first foods, if you want to skip the cereal route, include:
- Avocados
- Bananas
- Blended Red Meat (great source of iron)
- Squash
- Sweet Potatoes
- Pears
Just remember that these all need to be pureed and made into a runny consistency that’s easy for your baby to eat. Mixing with your baby’s warmed breastmilk or formula will help to bring this to a consistency that your baby can manage. You’ll also want to avoid giving your baby any of the top allergen foods such as the ones listed here unless you’ve been given different advice from your doctor. These are best introduced when your baby gets a little older.
These are best introduced when your baby gets a little older.
Still not sure which food to start with? It can be a bit overwhelming! This is a great conversation to have with your doctor before your baby turns 6 months and they can help guide you on what would be the best option. Whatever you choose, it is sure to be an exciting time for your family as your little guy or gal begins his journey of eating "real" food!
Feeding Your 4- to 7-Month-Old (for Parents)
Most babies this age are ready to try solid foods. Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Be sure to check with your doctor before giving any solid foods.
Is My Baby Ready to Eat Solid Foods?
How can you tell if your baby is ready for solids? Here are a few hints:
- Does your baby swallow food or push it out of their mouth? Babies have a natural tongue-thrust reflex that pushes food back out.
 Wait until this reflex disappears (typically when babies are 4–6 months old).
Wait until this reflex disappears (typically when babies are 4–6 months old). - Can your baby support their own head? To eat solid food, an infant needs good head and neck control and should be able to sit up.
- Is your baby interested in food? Babies who stare, reach and grab, and open their mouths for food are ready to try solid foods.
If your doctor gives the go-ahead but your baby seems frustrated or uninterested in solid foods, try waiting a few days before trying again. Breast milk and formula will still meet nutritional needs as your baby learns to eat solid foods. But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
Do not add cereal or other food to your baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain.
Watch for signs that your child is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your child stop when full. A child who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the breast or the bottle. With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
How Should I Start Feeding My Baby Solid Foods?
When your baby is ready and the doctor says it’s OK to try solid foods, pick a time of day when your baby is not tired or cranky. You want your baby to be a little hungry, but not so hungry that they’re upset. So you might want to give your baby a little breast milk or formula first.
Have your baby sit supported in your lap or in a high chair with a safety strap.
Most babies' first food is iron-fortified infant single-grain cereal mixed with breast milk or formula. Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
When your little one gets the hang of eating cereal off a spoon, it may be time to try single-ingredient puréed meat, vegetables, or fruit. The order in which you give them doesn't matter, but go slow. Offer foods that are high in iron and zinc — such as meat, poultry, eggs, and beans — especially if your baby is breastfeeding. Try one food at a time and wait several days before trying something else new. This will let you identify any foods that your baby may be allergic to.
The order in which you give them doesn't matter, but go slow. Offer foods that are high in iron and zinc — such as meat, poultry, eggs, and beans — especially if your baby is breastfeeding. Try one food at a time and wait several days before trying something else new. This will let you identify any foods that your baby may be allergic to.
Which Foods Should I Avoid?
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
Possible signs of food allergy or allergic reactions include:
- rash
- bloating or an increase in gassiness
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Get medical care right away if your baby has a more severe allergic reaction, like hives, drooling, wheezing, or trouble breathing.
If your child has any type of reaction to a food, don't offer that food again until you talk with your doctor.
Babies shouldn't have:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy beverages before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Tips for Feeding Your Baby Solid Foods
With the hectic pace of family life, most parents try commercially prepared baby foods at first. They come in small, convenient containers, and manufacturers must meet strict safety and nutrition guidelines.
If you prepare your own baby foods at home, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Follow the rules for food safety, including washing your hands well and often.

- To preserve the nutrients in your baby's food, cook it in ways that keep the most vitamins and minerals. Try steaming or baking fruits and vegetables instead of boiling, which washes away the nutrients.
- Freeze portions that you aren't going to use right away.
- Whether you buy the baby food or make it yourself, texture and consistency are important. At first, babies should have finely puréed single-ingredient foods. (Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.)
- After your baby is eating individual foods, it's OK to offer a puréed mix of two foods. As babies get older, they will learn to eat a greater variety of tastes and textures.
- If you use prepared baby food in jars, spoon some of the food into a bowl to feed your baby. Do not feed your baby right from the jar — bacteria from the baby's mouth can contaminate the remaining food. If you refrigerate opened jars of baby food, it's best to throw away anything not eaten within a day or two.
- Around 6 months of age is a good time for your baby to try a cup. You might need to try a few cups to find one that works for your child. Use water at first to avoid messy clean-ups. Do not give juice to infants younger than 12 months.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
What kind of porridge to choose for the first feeding | How to introduce porridge: how to cook, properly breed porridge for the first feeding
Your baby is growing up, getting stronger, gaining weight, and now there comes a moment when feeding only breast milk or formula is not enough for the full development of the crumbs. It's time to introduce complementary foods into your baby's diet. The question arises - where to start? Your pediatrician should answer it.
Today we’ll talk about how to properly introduce complementary foods with cereals. Let's talk about how to breed porridge, which one is better to choose for the first feeding, and how homemade porridge differs from store-bought.
Let's talk about how to breed porridge, which one is better to choose for the first feeding, and how homemade porridge differs from store-bought.
Cereals for children up to one year old
Porridge contains all the necessary set of trace elements, is perfectly absorbed, and has a beneficial effect on the digestive system.
Usually, cereals begin to be introduced into the diet of a baby at the age of six months. If the child is bottle-fed, it is permissible to start earlier, at 4-5 months. These are only approximate dates, in fact, everything is individual. It is necessary to take into account the pace of development of the child, his readiness for adult food and the tendency to allergic reactions.
Complementary foods with cereals are recommended for children who are not gaining weight well. Most likely, the baby simply does not have enough calories. In any case, before starting complementary foods, a pediatrician should be consulted. He will help you choose porridge, tell you in what quantities and how often to feed her child.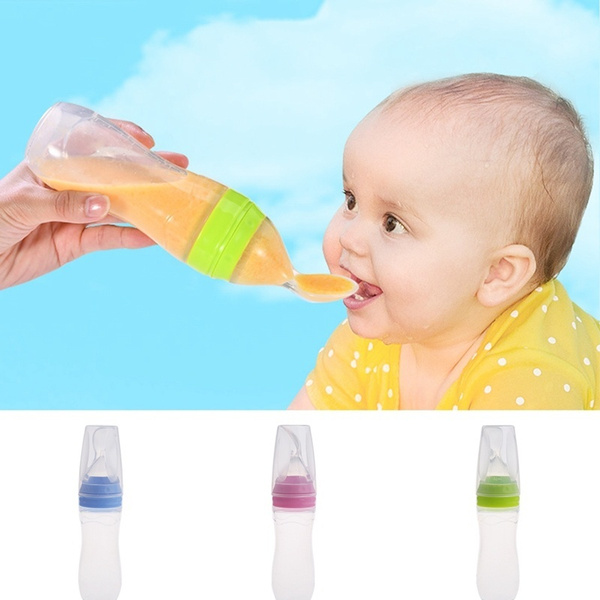
It is important that the first porridge be:
- Industrial production . Not only because the raw materials are sterilized and undergo rigorous quality control. But also because at home it is difficult to achieve such a degree of grinding cereals, as cereal manufacturers do. For example, Materna porridges consist of delicate cereal flakes, which form an absolutely homogeneous mass when brewed. If desired, they can be diluted to a thick mixture and offered to the baby to drink from a bottle.
- Single component . To track down the cause of an allergic reaction if it occurs.
Dairy or non-dairy: with which cereals does the first weaning start
Pediatricians recommend starting complementary foods with dairy-free gluten-free cereals. Gluten is a fairly heavy vegetable protein for digestion by a child's body. Its use can lead to allergies. Dairy-free cereals can be diluted with breast milk or your own milk formula to make them more nutritious and taste more familiar to the baby.
The first gluten-free cereals include: corn, rice and buckwheat.
How to switch from dairy-free to milk porridge
If no allergic reactions occur within 4-7 weeks from the start of complementary foods and dairy-free cereals are well absorbed, you can start offering milk cereals for children up to a year old to the baby, their energy value is much higher.
How to properly organize feeding with cereals
For the first acquaintance, you need to cook a five percent porridge, which means that for five grams of dry porridge there should be 100 mg of water. The resulting consistency will be ideal for a child who is not yet able to chew and swallow thick food.
The best time to feed is the morning meal. So you will have time to track the baby's reaction to a new product: if there are any allergies or stool disorders.
For feeding, a baby spoon made of safe material for the baby's delicate gums or a regular teaspoon is used.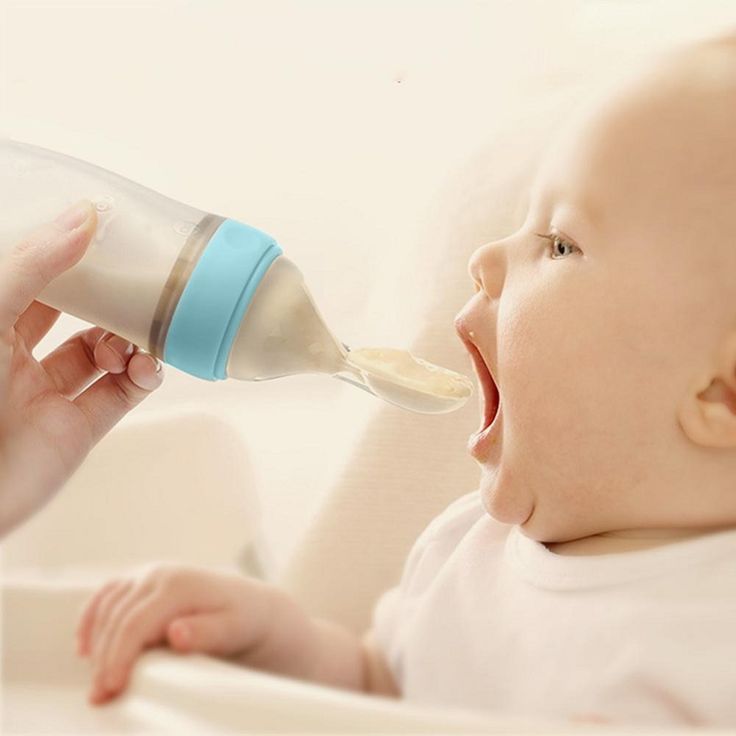
As a first test, it is enough to give the child about half a tablespoon of liquid porridge. The kid should try out a new product, get used to the change in texture and taste.
Make sure the porridge is not too cold or hot, and does not contain lumps.
After porridge feeding, feed your baby his usual food - breast milk or formula.
Increase the volume of a serving of porridge only when you are sure that the baby eats it with pleasure, and he does not experience unwanted reactions.
Every day, increase the amount of porridge per spoon until the serving is 150 g for a six-month-old baby, 160-170 g for a child aged 7-8 months and 170-180 g for an age of 8-9months. Closer to the year, the serving volume will be about 200 g. And the five percent porridge is replaced by a thicker, ten percent one.
We remind you that these are only general recommendations, and the development of each child is individual and the dosage may differ from that described above.![]() It is important not to change cereals at the beginning of complementary foods, your baby should get used to one cereal, and only after a successful debut, you can offer the next one - not earlier than in two weeks.
It is important not to change cereals at the beginning of complementary foods, your baby should get used to one cereal, and only after a successful debut, you can offer the next one - not earlier than in two weeks.
If you start experimenting ahead of time and give your child a different porridge every day, in case of an allergy, it will be very difficult for you to understand what exactly the child's body reacted to.
The child does not eat porridge
Toddlers refuse porridge for various reasons.
- Don't like the taste or texture.
It happens that children who started complementary foods with fruits and vegetables do not eat porridge, because their taste is very different and not so bright. Try adding an already familiar apple or broccoli to a new porridge. In addition, a child may not like the taste of some cereal today, but in a couple of weeks he will eat it with pleasure. Set this mess aside for a while and try again later.
- The porridge is too hot or too cold.
Check food temperature on the inside of your wrist. If you do not feel cold or hot, then the temperature is optimal. - The child is not yet hungry. Set the plate aside for half an hour and then try again.
The main advice to parents is not to despair, and offer the same porridge many times in different combinations.
What kind of porridge to introduce first into complementary foods
Be sure to ask your pediatrician for advice on which cereal to give your baby first. After all, all kids are different.
The main types of cereals recommended for consistent introduction into the child's diet:
- Buckwheat porridge . It is considered indispensable in the diet of the child. Contains vitamins B1 and B2, iron, magnesium, protein.
- Rice porridge . Contrary to the common misconception of many parents, baby rice porridge will not cause constipation because it does not contain crushed rice.
 For the manufacture of these cereals, rice flour is used, which has a beneficial effect on the digestion of the child and is rich in healthy dietary fiber.
For the manufacture of these cereals, rice flour is used, which has a beneficial effect on the digestion of the child and is rich in healthy dietary fiber. - Corn porridge . Such porridge is a leader among other cereals in terms of the content of potassium in its composition. Also contains a large amount of protein, iron and fiber.
- Oatmeal . No other cereal compares to oatmeal in terms of fat and fiber content. In addition, oatmeal is rich in vegetable protein and calcium, iron, magnesium, vitamins B1, B2, PP. Oatmeal is introduced last of all the described cereals, because it is very rare, but there is an allergy.
The Materna product line includes dairy-free and milk porridges for children from 6 months. All cereals do not contain salt and sugar and are made from cereals and fruits grown in Israel specifically for baby food.
Porridge for the first feeding - NCCH
Porridge is one of the most useful and important foods in the diet of a child in the first year of life. It is porridge that is most often recommended for introduction as the first complementary food, as it is a rich source of healthy carbohydrates, vegetable proteins, fats and dietary fiber.
It is porridge that is most often recommended for introduction as the first complementary food, as it is a rich source of healthy carbohydrates, vegetable proteins, fats and dietary fiber.
As you know, complementary foods can be introduced in the interval from 4 to 6 months, depending on the individual needs of the child, respectively, and porridge as the first complementary foods can be prescribed both from 4 and 6 months, or in this interval [1 , 2].
Start complementary foods with porridge, usually if the child is underweight or has a tendency to loose stools. But even here everything is not so clear.
Kasha porridge - strife, so their value and safety in the nutrition of a child is determined by many points.
There are different types of porridge.
Depending on the production, children's cereals are divided into industrial and homemade.
Industrial porridges include:
- Instant porridges
These porridges do not need to be boiled. They come in dairy and non-dairy .
They come in dairy and non-dairy .
Milk porridges are diluted with warm boiled water before use.
Dairy-free porridge can be diluted with either expressed breast milk or the formula that the baby eats before use. You need to start complementary foods with dairy-free porridge, since cow or goat milk proteins contained in milk porridges can be strong allergens for a child of the first year of life.
- Cereals, ready to eat. Usually these are milk porridges. They are comfortable on the road or for a walk. Before use, they can simply be warmed to room temperature.
- Cereals enriched and unenriched . What does it mean?
Vitamins and minerals necessary for the growth and development of
children are often added to industrial cereals, including iron, the reserves of which are significantly reduced by the age of 4-6 months. Such cereals are called enriched and they are best suited for the first feeding.
Non-enriched cereals consist only of cereal flour.
- Mono-component and multi-component cereals.
If the porridge consists of flour of only one type of grain - it is a monocomponent porridge, if the porridge contains flour of several types of grain crops - this is a multicomponent porridge (may contain up to 2, 4 or more cereals). Complementary foods should be started with monocomponent porridge, so that if a child develops an allergic reaction, it would be easier to identify a possible allergen.
Also, cereals are divided into gluten-containing and gluten-free.
Gluten-containing cereals are cereals made from wheat, rye, spelled, barley, oats. In extremely rare cases, gluten is not absorbed by the body, and then we are talking about a serious disease called celiac disease, in which these cereals are excluded from the child's diet. But just in case, you don't have to do that. The vast majority of children tolerate gluten-containing cereals well, although in some cases allergic reactions can develop on gluten, so it is better to start complementary foods with gluten-free cereals (rice, buckwheat, corn).
Which cereals are better: industrial or home-made?
An important advantage of commercially produced cereals is that they are produced from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a stable, guaranteed composition, the required degree of grinding, and also that they contain vitamins and minerals necessary for a child of the first year of life, the deficiency of which widespread and dangerous to the health of the child. The amount of vitamins introduced into industrial cereals is calculated by the manufacturer, taking into account their losses during industrial production and storage.
In home-made cereals, the content of vitamins and minerals is much lower, in addition, it decreases even more during the cooking process. "Homemade" cereals, of course, can also be used in the nutrition of a child in the first year of life, but it is better not as a first complementary food, but a little later - after 8-9 months.
So, the ideal porridge for the first feeding is industrial porridge, soluble, dairy-free, monocomponent, gluten-free, enriched, sugar-free.
When is the best time to give porridge?
Porridge is best offered to your baby for breakfast. From 8-9 months, porridge can also be offered for dinner, as a main course or as a side dish (for vegetables, meat).
What is the best way to give the first porridge for complementary foods: from a spoon or from a bottle?
Ideally, like any complementary food, it is better to give porridge to a child only from a spoon. At first, it can be a more liquid consistency, and later, when the child gets used to it, the porridge can be made thicker. An exception may be babies with special needs (for example, premature babies), when it is difficult for them to eat food from a spoon, and then the porridge is poured into a bottle.
How to enter the first porridge correctly?
The introduction of the first porridge should be gradual, but how?
on day 1, give the baby 1 tsp.











