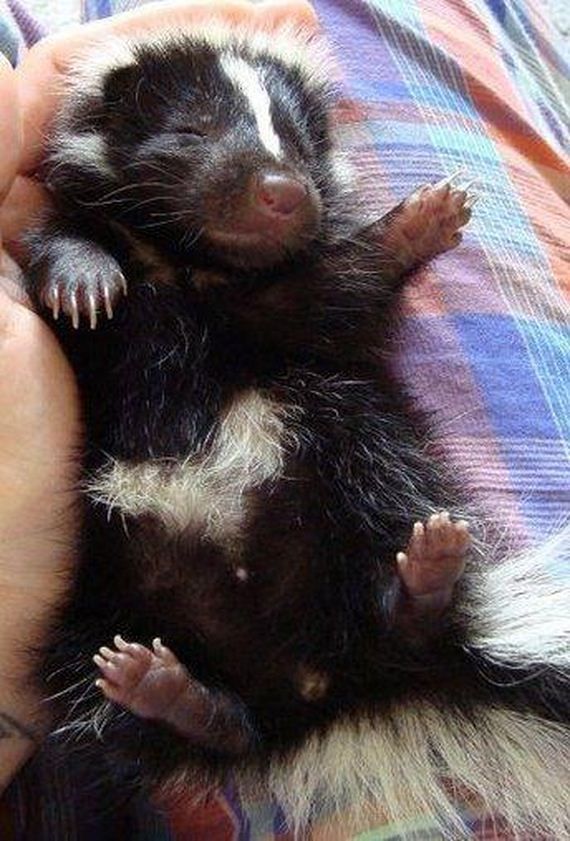
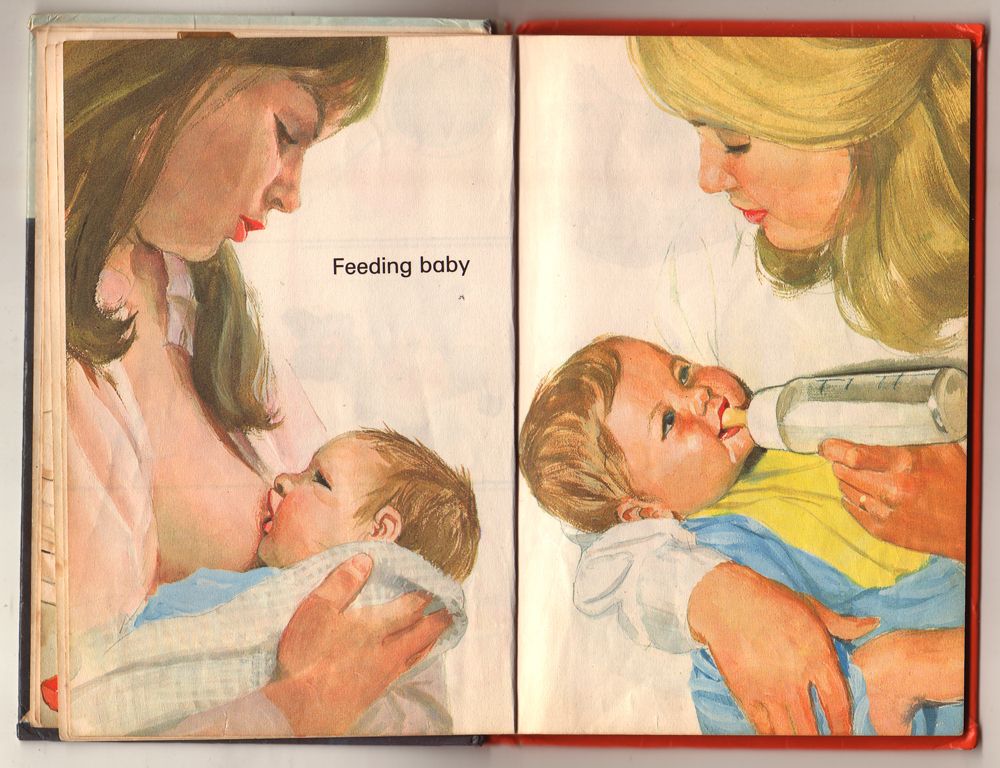
Feeding baby skunks
Skunk Care
CARE FOR ORPHANED SKUNKS
http://www.orphanedwildlifecare.com/skunkcare.htm
|
IS THIS SKUNK TRULY ORPHANED?If the baby skunk is out of its burrow for extended periods of time on its own, it is likely orphaned and worth trying to catch.
RAISING A SINGLE SKUNK: If you determine that
the skunk is orphaned, it will have littermates that also need
help so continue to check the area frequently for up to a week. If no others are found it is vital to the
skunk's proper socialization and release to be raised with other skunks, a
single skunk has little chance of a successful release.
AGING THE SKUNK: In order to properly care for the baby you have found, it is important to know its age. Consult the chart on the back to assess age.
FEEDING: Orphans that have been without their
mother will be suffering from chill and dehydration. They must be thoroughly warmed first, and then offered warmed
rehydration solution. Pedialyte is a
rehydration solution that is available in drug stores- it should be heated to
body temperature and offered every couple hours for the first several
feedings. Feed the baby skunk esbilac
powder, mix only enough for 24hrs and keep it refrigerated. SUPPLEMENTS AFTER WEANING: There are several supplements that are recommended be added to a skunk's diet after it is weaned: Taurine - an amino acid that is available in capsule form from health food stores. Open
capsule and sprinkle granules on skunk's food. Each weaned skunk should get 150 mg. Calcium - 50 mg. elemental calcium per skunk per day - this can be sprinkled on food. It is important as skunks can suffer from metabolic bone disease. Vitamin D - 30 IU Vit D-3 (divide the tablet by 13 if it is a 400 IU tablet). Vitamin D assists in calcium being properly absorbed. If you are not able to get calcium and vitamin D, you can sprinkle bone meal on food for weaned skunks.
HOUSING: Housing requirements will change as the skunk grows and develops, see chart for details.
RELEASE: The skunks will not be ready to be
released until they are 16 weeks old (usually late August or early
September). It is ideal for the skunks
to spend approximately 2 months in their large outdoor cage (4ft x 8ft, made of
1 welded wire mesh). The cage should
also have a bottom made out of welded wire mesh to prevent the skunks from
being able to escape, the cage should set flat on the ground and the bottom can
be covered with some earth.
DISEASE: Skunk kits often carry roundworm and may need to be de-wormed, you can talk to a vet about this. Skunks are susceptible to distemper, you may want to consider having the skunk(s) vaccinated for distemper as well as against rabies. If you are concerned about rabies, you may want to consider having a pre-exposure vaccine for anyone who will be handling the animals-call your vet for further information. Furthermore, with all animals, you should always take precautions to avoid being bitten while you are handling the animal. **In some jurisdictions it is illegal to care for skunks and you should consult your government wildlife agency.
|
|
AGE |
FEEDING
|
STIMULATION |
HOUSING |
SPECIAL CARE |
|
|
Birth 30-35g -nearly naked -fine hair showing black & white pattern -eyes & ears are sealed
|
2 - 2.
5- 6 times per day.
|
-stimulate genital area before and after feeding to induce elimination. -use a q-tip or the tip of your finger dipped in warm water. |
-vital to house baby animals inside a house -cardboard box filled with soft, ravel free blankets and a hot water bottle. -protect from drafts.
|
-when handling the skunk hold its tail between its legs, this way it can not spray. Be gentle and do not startle the skunk and you should not have problems with it spraying. -wrap skunk in a soft towel when removed from box, to protect from drafts. -watch for signs of diarrhea. Stool may turn to a soft, yellow pudding from the formula.
|
|
|
1 week ~50-75g -slightly furred -skin becoming pigmented |
4-6 mls. Formula
5 - 6 times per day
|
-same as above |
-same as above |
-wrap in towel while feeding. |
|
|
2 weeks -weight 125g -fully furred -eyes still closed |
8-10 mls.
4 times per day
|
-same as above |
-same as above
|
-wrap in towel while feeding. -any diarrhea from formula should have cleared up by now. (Call your vet if it still has diarrhea) |
|
|
3 weeks -eyes & ears open |
10-15 mls. Formula
4 times per day
|
-same as above |
-can
be moved into a large pet carrier, continue to provide towels and blankets. |
-wrap in towel while feeding.
|
|
|
4 weeks -weight 340g -attempting to walk on short legs |
15-20 mls. Formula
4 times per day
|
-same as above |
-same as above. -can eliminate artificial heat source
|
-introduce
dry dog kibble (smaller size kibble for small breeds is best), moistened with water, along with a separate dish of drinking
water. Refresh solid foods morning
and night.
* never use either puppy kibble or cat kibble as they are too high in protein and cause metabolic bone disease in skunks. |
|
|
5 weeks -very playful, steadier on legs |
20-25 mls. Formula
3 times per day
|
--skunk should now eliminate on its own. |
- same as above
|
-continue to feed dog kibble (increase as needed), and introduce natural foods, nuts, fruits, cooked meat, vegetables, eggs and occassionally mealworms and crickets. These foods are critical to produce a balanced, healthy diet. *Depending
on teeth development, moistening of kibble can be eliminated. |
|
|
6 weeks
|
25-30 mls. Formula
2 times per day
|
|
-same as above |
-same as above |
|
|
7 weeks -fully weaned
|
30-35 mls. Formula
1-2 times per day
|
|
-
skunks are now ready to live in the large outdoor cage. |
-skunk should require very little formula and should be eating solids consistently. Wean fully during the 7th week. See Supplements outlined under Feeding. |
Should I feed a baby skunk I found?
Need skunk removal in your hometown? We service over 500 USA locations! Click here to hire us in your town and check prices - updated for year 2020.
Baby skunks do look very cute and cuddly with their soft black and white fur, and some finders are tempted to raise them as pets. But raising and feeding a baby skunk is not so easy and straightforward.
In actual fact, that kit is a tiny and fragile animal that needs a lot of care. In fact, it is unlikely to survive if it does not receive adequate care, and so it is safer to hand a baby skunk find over to professional wildlife rehabilitators, rather than give it inexperienced care, albeit well-meaning.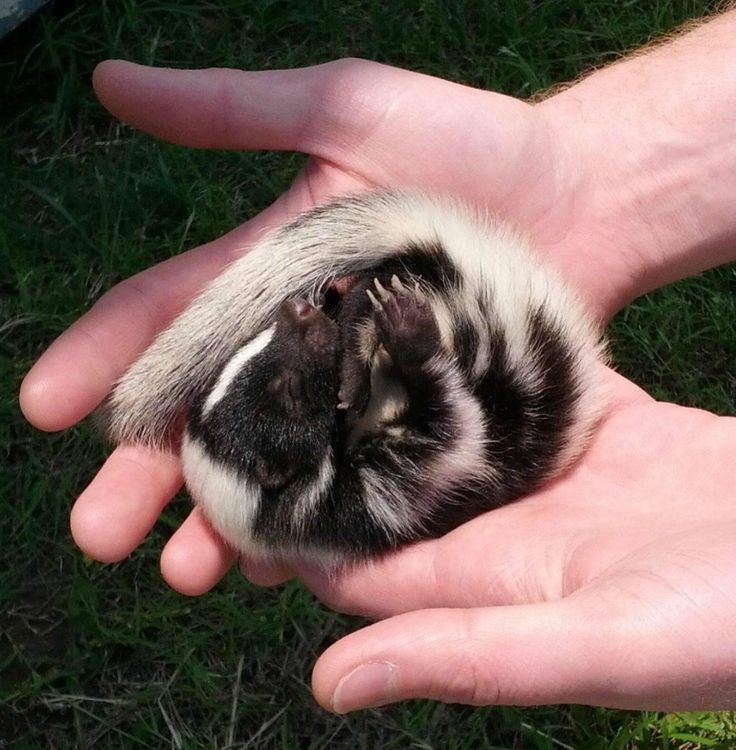 You must also find out what is obtainable in your state or county as regards the care of wild animals.
You must also find out what is obtainable in your state or county as regards the care of wild animals.
If you find a baby skunk, observe to see if it is dehydrated or not. A dehydrated kit should be given warm water wit Nutri-cal orally in the right proportion and with the use of a 1cc syringe.
What should I do if I find an orphaned baby skunk?
What should I do if I find a nest of baby skunks?
Do Baby Or Juvenile Skunks Spray?
It is however, not advisable for you to feed that baby skunk because the food that it needs in not the regular puppy or kitten meals. A baby skunk requires an entirely different meal from a kitten or puppy. Inappropriate meals can result in the animal getting sick and weak with diarrhea.
If you must feed the kit though, note that they are usually well fed with calcium, protein, minerals and vitamins in the right proportions for good growth. If it is not properly fed, a baby skunk may suffer from kidney stone, bone spurs, poor development, bone calcification, and so on. Thus, it is important that these nutrients be given to the baby skunk in the right proportion; it must neither be too much or too small.
Thus, it is important that these nutrients be given to the baby skunk in the right proportion; it must neither be too much or too small.
You can get the correct formula for baby skunk from animal control professional or give a mixture of KMR and warm water. A well fed baby skunk will defecate and urinate with ease and frequently.
After about 3 months of feeding the baby skunk, it should be able to eat on its own. By this time, you may start feeding it with fatty fish, eggs, carrots, sea foods, vegetable oil, yoghurt, cottage cheese, vanilla wafer, chopped mushrooms, peas, corn, squash, nuts, cod liver oil and so on.
Go back to the Skunk Removal page, or learn tips by reading How to get rid of skunks.
Select Your Animal
RaccoonsRaccoon Removal Information & How-To Tips
SquirrelsSquirrel Removal Information & How-To Tips
OpossumOpossum Removal Information & How-To Tips
SkunksSkunk Removal Information & How-To Tips
RatsRat Removal Information & How-To Tips
MiceMouse Removal Information & How-To Tips
MolesMole Removal Information & How-To Tips
GroundhogGroundhog Removal Information & How-To Tips
ArmadillosArmadillo Removal Information & How-To Tips
BeaverBeaver Removal Information & How-To Tips
FoxFox Removal Information & How-To Tips
CoyotesCoyote Removal Information & How-To Tips
BirdsBird Removal Information & How-To Tips
BatsBat Removal Information & How-To Tips
SnakesSnake Removal Information & How-To Tips
DeadDead Animal Removal Information & How-To Tips
OthersOther Wildlife Species Information & How-To Tips
Skunks
Home Mammals Carnivores Skunks
|
Skunks | Our pets | Handbook
Introduction to Skunks
It may seem confusing to many that there are people who voluntarily keep skunks as pets. We've all heard about its odorous anal glands, which secrete a caustic substance from persistent unpleasant smell, that there is unpleasant - very smelly. This substance is the weapon of skunks, and despite this they are kept as pets. It turns out there is nothing strange about this. Skunks are getting very tame, playful and affectionate and usually does not use their fighting arsenal against the owner or his family. Of course, no need to risk scaring or annoying the animal even unintentionally.
Of course, no need to risk scaring or annoying the animal even unintentionally.
Skunks use their weapons only in case of danger, and warning of its possible use by raising the tail and turning back. A disgusting yellowish liquid shoots out in the distance up to 4 meters and accurately hits the enemy, mainly in the eyes, which may cause temporary blindness.
Of course, it is possible to surgically remove the glands, as is done with ferrets. But this is a very painful operation for the animal and difficult for the veterinarian. In many countries, such an operation is only allowed due to medical necessity, otherwise the Protection Act animals prohibits such interference.
1
The skunk is quite a cute animal.
Skunks belong to the skunk family ( Mephitidae ), which includes four genera: pig-nosed / pig-nosed skunks ( Conepatus ), striped skunks ( Mephitis ), spotted skunks ( Spilogale ) and recently added to the skunk family stink badgers ( Mydaus ).
Pig-nosed, white-backed skunk.
Skunks live in South and North America. In the territories Europe, Asia and Australia skunks are not found. And only smelly badgers, until recently belonging to the marten family, and not to skunk family, found on the islands of Indonesia. Skunks don't may be confused with other animals. White streaks or spots on dark back, upturned fluffy tail, they immediately make it clear what it is skunk.
Striped skunk with a rare brown coloration.
All skunks have a thick, rough coat, strong build, short limbs, fluffy tail, powerful claws adapted to dig the ground. Skunks have poor eyesight, but they have an excellent sense of smell and hearing. Spotted skunks are the smallest, weighing from 200 grams to 1 kilograms. The largest pig-nosed / pig-nosed skunks, their weight reaches 9 kilograms. Adult striped skunks weigh between 1. 2 up to 5.3 kilograms. The length of their bodies is 28-40 centimeters, tail 17-30 centimeters (tail can sometimes be longer). males usually slightly larger than females. The variation in weight is due to the fact that skunks lose some weight in winter.
2 up to 5.3 kilograms. The length of their bodies is 28-40 centimeters, tail 17-30 centimeters (tail can sometimes be longer). males usually slightly larger than females. The variation in weight is due to the fact that skunks lose some weight in winter.
In winter, skunks actually go into a shallow hibernation. Their activity at this time is very low, they hardly eat, feed on subcutaneous fat, and sit out in nests. They make nests and shelters in rocky crevices, in earthen burrows that they dig themselves or capture strangers.
Skunks are solitary animals. Only during hibernation of the female can winter several pieces in a nest or with their own, born cubs in spring.
Skunks are omnivorous predators, hunting at dusk or at night. So how much of their diet is insects, and skunks can catch and eat mice, they benefit the agricultural au pair. They can approach human housing, ruining chicken coops, beehives and climbing dustbins. In many American states it is quite normal to tame and keeping skunks in the yards of houses. This tradition is believed to have started from the Indians. In the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century, skunks were hunted for their furs.
This tradition is believed to have started from the Indians. In the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century, skunks were hunted for their furs.
In nature, skunks live 2-3 years, because of the harsh winters and predators are serious tests especially for young animals. In captivity, well cared for, they live up to 5-7 years, often longer.
Home skunk housekeeping and domestication
a breeder who has proven himself on a good side. But before purchase, you need to decide on housing for the animal and who you need a male or female.
How to completely get rid of the specific there is no smell of an unoperated animal in the room perhaps it is better to arrange housing for the skunk in the yard. This quite simply. It is necessary to arrange a lair like a cave or a vast hollow, feeder, put a bowl for drinking water, throw a handful of hay. The territory of the skunk must be fenced off with a low metal mesh in order to he could not go to study the neighbor's plot.
Skunks like to hide in caves of all kinds.
You can keep a skunk in your house/apartment like a cat. Even it is also necessary to accustom to the tray. It is only necessary to provide a lair, otherwise, your sofa or favorite chair can become his sleeping place. A lair in the form of a cave or a hollow should be arranged in a large cage, lined with straw or hay. The skunk can be locked in a cage, so as not to get in the way. But you can't keep it there for long.
Skunk is not fussy and cannot climb high. So whatever above 1.5 meters from the floor is not available for him. And here is everything below should be safe for him and not valuable to you or such that he could not spoil.
Skunks are inquisitive, sociable, friendly and people. They equally need both freedom and contact with people, do not tolerate loud noise and violence. You have to tame them, just like all animals, affection and encouragement with treats.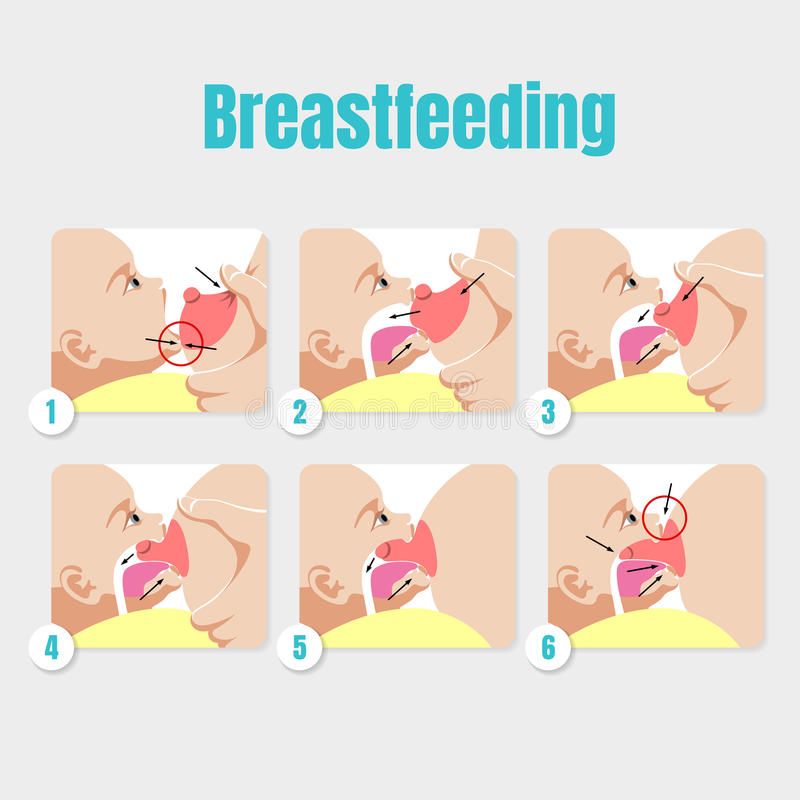 They can even be tamed to harness and leash. You can play with them just like with cats. Skunks don't rodents, and often a plush toy becomes their favorite for a long time remains intact. The domestic skunk gets along easily with children and even makes friends with them.
They can even be tamed to harness and leash. You can play with them just like with cats. Skunks don't rodents, and often a plush toy becomes their favorite for a long time remains intact. The domestic skunk gets along easily with children and even makes friends with them.
You may need to teach your pet to play cat toys and that he sleeps only in his lair. Is not difficult, will require a little of your patience. And make time for your the skunk that lives in the house, that lives in the yard, needs a lot. Living with humans, skunks change their nocturnal lifestyle and become active during the day.
Important information
If you do not want your home (living in house / apartment) the male skunk became a father in the future, it is better than him castrate. An uncastrated male annually in early spring during the rut will look for a female, run, rub against the floor and furniture, and leave bad smell everywhere. A castrated male will not do this. In addition, it will become completely tame and affectionate.
The female behaves a little calmer during the rut. Specialists it is advised to mate the female in the first two ruts. Do not covered in the first two rutting of females may occur undesirable, harmful to health hormonal changes.
This information will help you decide who to choose in as a pet, male or female.
Skunk care
Walking
It is possible even necessary, but it is necessary to ensure that the curious animal does not run away to foreign territory, as he may not return or cause trouble for neighbors, for which you will have to answer.
It is necessary to walk a skunk on a leash (like a dog) in a distance from walking places for other animals (ferrets, cats, dogs) and in a place without garbage and food waste.
Keep in mind that a skunk will start digging when walking.
Washing/bathing
Household skunk should be taught to wash. Stroking and affectionately while talking, start washing your paws in the sink with warm water. When the skunk begins to take this procedure calmly, then, if desired, and opportunities, you can let him swim in a filled bath. Necessary be careful not to get water in your ears. After the skunk shakes off, it can be wiped off with a towel.
When the skunk begins to take this procedure calmly, then, if desired, and opportunities, you can let him swim in a filled bath. Necessary be careful not to get water in your ears. After the skunk shakes off, it can be wiped off with a towel.
Ear cleaning
Skunk gladly allows you to clean his ears. Clean ears with cotton chopsticks for prevention twice a month and after bathing.
Nail clipping
Backyard skunk does not need to have its nails clipped. Living in an apartment it will be necessary not only to cut the claws (just above the pink filling tubular claws), but also grind them with a file. Not sharpened claws the skunk will cling to carpeting, which will be harmful to claws and for coatings. If you cut the claw more than necessary, then may bleed. Treat the wound with a strong solution of potassium permanganate or hydrogen peroxide.
Combing wool
shed. If you don't want winter fur to pollute your home, comb it out with a special comb, as often as possible, until the molt will roll. The rest of the time combing the skunk is not Necessarily.
The rest of the time combing the skunk is not Necessarily.
Foot treatment
It is best to treat soles with sea buckthorn oil. Do it is necessary after washing or when you notice dry skin.
Feeding skunks
Skunks are omnivores. In nature, their diet is diverse. Because of their physiological characteristics, it is more convenient for them to get insects, larvae and earthworms from the ground and forest floor. To this basic diet they add moles, small rodents, bird eggs, lizards, snakes, frogs, salamanders, mushrooms, berries, nuts, roots and leaves of plants, and even sometimes carrion.
Feed skunks at home the way they eat on freedom is difficult, but to provide them with everything necessary for health not difficult.
Skunks are beggars and gluttons, they should not be overfed, and treats best given as a reward or when they are boosted to beg.
Young animals need more food than adults.
Feed skunks 1 to 6 months of age 4 times a day 150-200 grams of feed; aged 6 to 12 months - 3 times a day for 100-150 grams; over the age of 12 months - 2 times a day for 150 grams.

 Esbilac is a puppy milk replacer, which you
should be able to purchase at a vet or pet store. Cow's milk, human baby formulas, and most pet
products (except Esbilac) are not suitable and will likely cause death. Use a 1cc or 5cc oral syringe (try a vet or
pharmacy), warm the formula, and hold the skunk in a towel, firmly, and
covering its eyes. The skunk will suck
very quickly and take too much formula if you are not in total control. If this happens the skunk will sneeze
formula out of its nose Stop feeding, turn upside down, gently rub its
back, and gently wipe the excess formula from its nose. Repeat this for about 5 minutes or until the
sneezing stops and breathing returns to normal. If severe this can cause immediate death or pneumonia on a
long-term basis. This is why bottles
are not suitable to use. To avoid this
from occurring feed in a quiet room, go slowly and watch both the skunk and the
syringe, if air bubbles appear in the syringe, stop feeding and expel the air,
(see chart on back for feeding schedule).
Esbilac is a puppy milk replacer, which you
should be able to purchase at a vet or pet store. Cow's milk, human baby formulas, and most pet
products (except Esbilac) are not suitable and will likely cause death. Use a 1cc or 5cc oral syringe (try a vet or
pharmacy), warm the formula, and hold the skunk in a towel, firmly, and
covering its eyes. The skunk will suck
very quickly and take too much formula if you are not in total control. If this happens the skunk will sneeze
formula out of its nose Stop feeding, turn upside down, gently rub its
back, and gently wipe the excess formula from its nose. Repeat this for about 5 minutes or until the
sneezing stops and breathing returns to normal. If severe this can cause immediate death or pneumonia on a
long-term basis. This is why bottles
are not suitable to use. To avoid this
from occurring feed in a quiet room, go slowly and watch both the skunk and the
syringe, if air bubbles appear in the syringe, stop feeding and expel the air,
(see chart on back for feeding schedule). Once feeding is finished, wash its face well with a damp face cloth, as
formula dries quickly and can cause fur loss.
It is very critical that baby skunks are stimulated to urinate before
and after every feed. The skunk may be
doing it a bit on its own but this may be overflow and if not stimulated the
bladder will rupture. To stimulate a
baby skunk hold it over a garbage container.
Dip either your finger or a Q-tip in warm water and then light feathery
strokes over its genital area will cause the skunk to urinate and/or have a
bowel movement. Once the skunk starts
to pee don't stop as the skunk will then stop.
Once feeding is finished, wash its face well with a damp face cloth, as
formula dries quickly and can cause fur loss.
It is very critical that baby skunks are stimulated to urinate before
and after every feed. The skunk may be
doing it a bit on its own but this may be overflow and if not stimulated the
bladder will rupture. To stimulate a
baby skunk hold it over a garbage container.
Dip either your finger or a Q-tip in warm water and then light feathery
strokes over its genital area will cause the skunk to urinate and/or have a
bowel movement. Once the skunk starts
to pee don't stop as the skunk will then stop.
 per day.
per day. A nesting
box (20 x 15 and 12 high) sits on the floor of the cage. A sand box should also be in the cage that
is used for digging, make sure to change the sand frequently. Do not allow the family pets access to the
skunks, otherwise you are teaching them they have nothing to fear from domestic
cats or dogs, something that could cost them their life in the wild. For release, choose a site well away from roads, with a mixture of
woods, brushy corners, open fields, a water source nearby, and abandoned out
buildings. Before releasing it is
important to investigate the area, if there are neighbours trapping or harming
skunks, they should not be released there.
Also, check the forecast to be sure there will be at least 2-3 days of
dry weather after the skunks are released.
Skunks should be released in late afternoon and transported as far away
from the road as possible. Bring a
supply of dog food so that the skunks can have a food source until they find
their own in the wild.
A nesting
box (20 x 15 and 12 high) sits on the floor of the cage. A sand box should also be in the cage that
is used for digging, make sure to change the sand frequently. Do not allow the family pets access to the
skunks, otherwise you are teaching them they have nothing to fear from domestic
cats or dogs, something that could cost them their life in the wild. For release, choose a site well away from roads, with a mixture of
woods, brushy corners, open fields, a water source nearby, and abandoned out
buildings. Before releasing it is
important to investigate the area, if there are neighbours trapping or harming
skunks, they should not be released there.
Also, check the forecast to be sure there will be at least 2-3 days of
dry weather after the skunks are released.
Skunks should be released in late afternoon and transported as far away
from the road as possible. Bring a
supply of dog food so that the skunks can have a food source until they find
their own in the wild.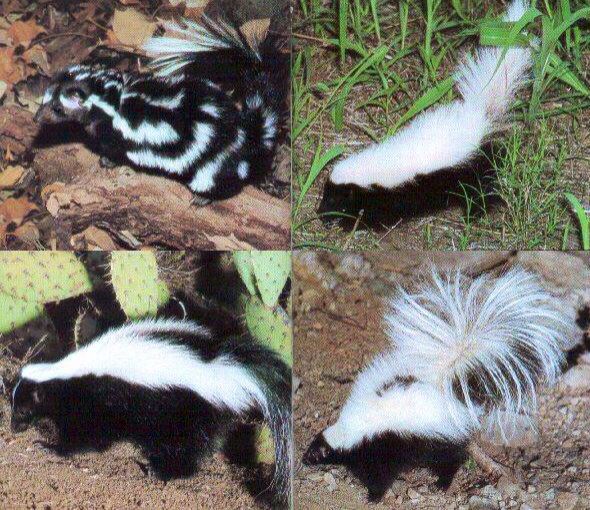
 5 mls Formula
5 mls Formula
 Formula
Formula

 They must have a secure nesting box and a
sand box (change frequently) for digging.
They must have a secure nesting box and a
sand box (change frequently) for digging.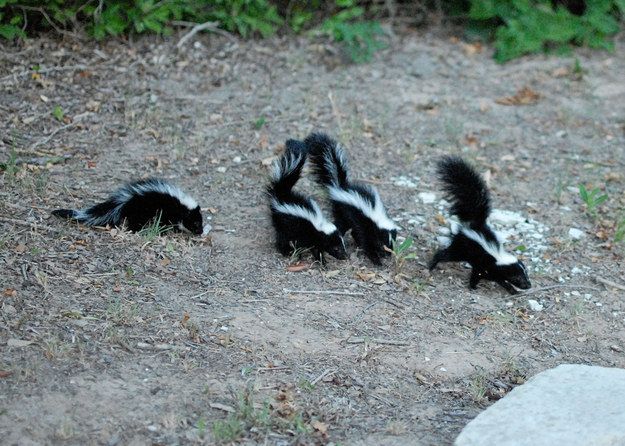
 If this does not help, then he releases a stream of oily, foul-smelling liquid (butyl mercaptan) from his prianal glands located to the right and left of the anus. Both jets merge into one, and are sprayed with fine rain at a distance of up to 4 meters. If it gets into the eyes, the liquid causes temporary blindness. After a while, tears clear the eyes of butyl mercaptan.
If this does not help, then he releases a stream of oily, foul-smelling liquid (butyl mercaptan) from his prianal glands located to the right and left of the anus. Both jets merge into one, and are sprayed with fine rain at a distance of up to 4 meters. If it gets into the eyes, the liquid causes temporary blindness. After a while, tears clear the eyes of butyl mercaptan. 
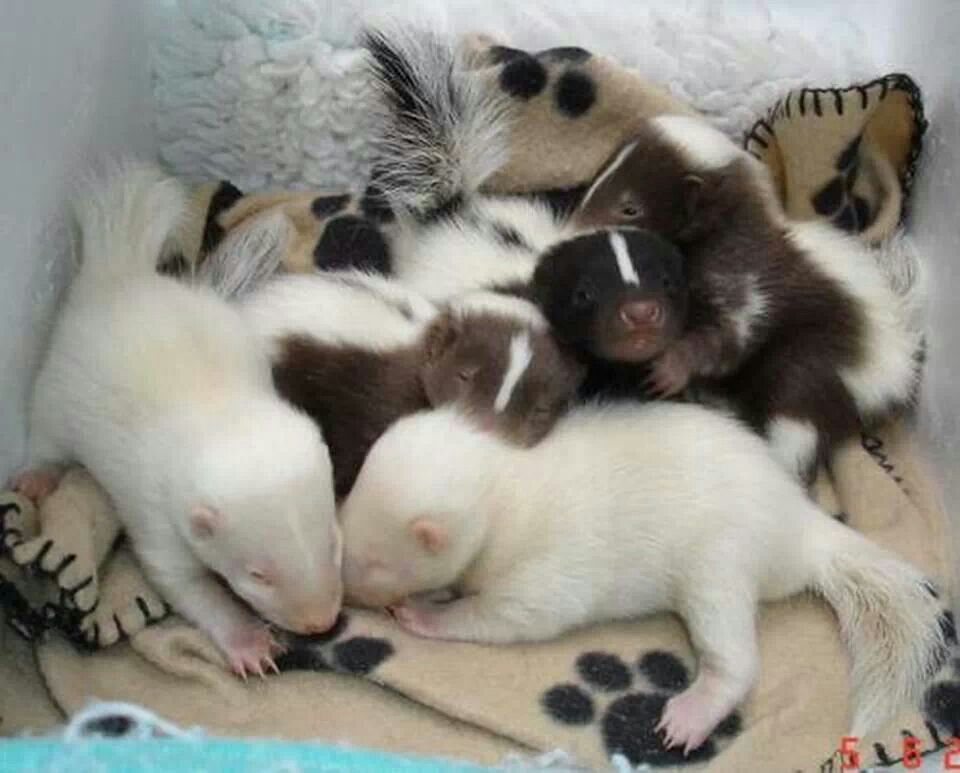 Several animals can even feed next to each other.
Several animals can even feed next to each other.  Avoid dense forests and wetlands. Often settles in the immediate vicinity of a person.
Avoid dense forests and wetlands. Often settles in the immediate vicinity of a person.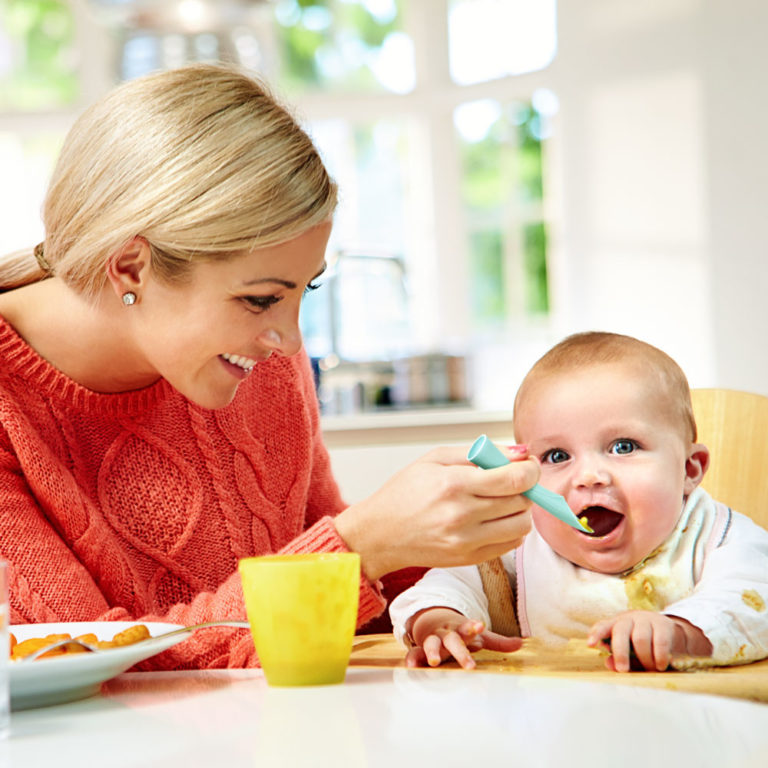  In late April - early May, the female gives birth to 2-5 cubs. Newborn puppies weigh 22.5 g. The eyes open at the age of 32 days, and the ability to shoot the secretion of the anal gland appears on the 40-46th day. Lactation lasts up to 50-54 days.
In late April - early May, the female gives birth to 2-5 cubs. Newborn puppies weigh 22.5 g. The eyes open at the age of 32 days, and the ability to shoot the secretion of the anal gland appears on the 40-46th day. Lactation lasts up to 50-54 days.  Likes to climb the rocks of the canyons. This is an excellent climber, when meeting with the enemy, it climbs trees. For rest, the animal arranges a shelter in the hollows of trees, digs a hole in the ground or occupies the hole of another animal. The warning variegated coloration of the skunk is a good defense against predators. A slow (waddling) gait also indicates the fact of its inedibility.
Likes to climb the rocks of the canyons. This is an excellent climber, when meeting with the enemy, it climbs trees. For rest, the animal arranges a shelter in the hollows of trees, digs a hole in the ground or occupies the hole of another animal. The warning variegated coloration of the skunk is a good defense against predators. A slow (waddling) gait also indicates the fact of its inedibility.  At the age of three months, young people reach adult size.
At the age of three months, young people reach adult size.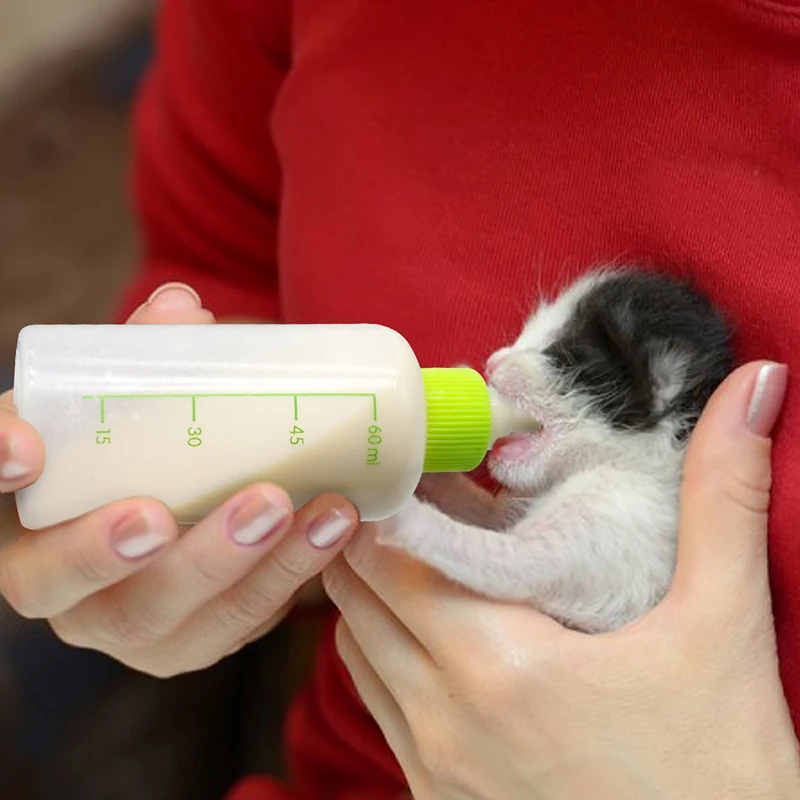 
 Often chooses hollows, which are located at a height of 10 m above the ground. Slick, climbs well. Sometimes several individuals gather in one lair. The anal glands are well developed and use them for defense against enemies.
Often chooses hollows, which are located at a height of 10 m above the ground. Slick, climbs well. Sometimes several individuals gather in one lair. The anal glands are well developed and use them for defense against enemies.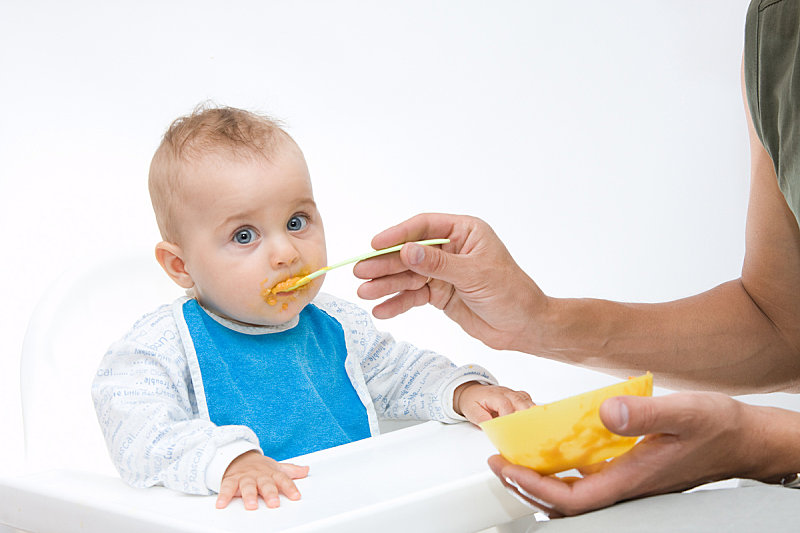 
 1-2.7 kg.
1-2.7 kg.  5 kg.
5 kg.  On cold winter days, the skunk practically does not leave his shelter.
On cold winter days, the skunk practically does not leave his shelter. 
 The hole ends with a nesting chamber, up to 60 cm in diameter, where the animal rests. The entrance to the hole is masked by branches and various vegetation. In the mountainous regions of Borneo, it often uses natural caves for its dwelling. Sometimes a badger occupies burrows dug and abandoned by porcupines. When feeding, the Sunda stink badger uses its snout to find and dig out worms and insects from the soft soil.
The hole ends with a nesting chamber, up to 60 cm in diameter, where the animal rests. The entrance to the hole is masked by branches and various vegetation. In the mountainous regions of Borneo, it often uses natural caves for its dwelling. Sometimes a badger occupies burrows dug and abandoned by porcupines. When feeding, the Sunda stink badger uses its snout to find and dig out worms and insects from the soft soil.  Burrows are not deep (less than a meter). When threatened, the badger most often pretends to be dead. In this state, the animal allows itself to be taken in hand. The other form is defensive, releasing a foul-smelling fluid from the anal glands, like a skunk. Of the sense organs, smell and hearing are best developed, vision is weaker.
Burrows are not deep (less than a meter). When threatened, the badger most often pretends to be dead. In this state, the animal allows itself to be taken in hand. The other form is defensive, releasing a foul-smelling fluid from the anal glands, like a skunk. Of the sense organs, smell and hearing are best developed, vision is weaker. 









