Feeding pattern of newborn baby
Feeding patterns and diet - babies and infants Information | Mount Sinai
Babies and infants - feeding; Diet - age appropriate - babies and infants; Breastfeeding - babies and infants; Formula feeding - babies and infants
Recommendations
During the first 6 months of life, your baby needs only breast milk or formula for proper nutrition.
- Your baby will digest breast milk more quickly than formula. So if you breastfeed, your newborn may need to nurse 8 to 12 times per day, or every 2 to 3 hours.
- Be sure you empty your breasts regularly by feeding or using a breast pump. This will prevent them from becoming overly full and achy. It will also allow you to continue producing milk.
- If you feed your baby formula, your baby will eat about 6 to 8 times per day, or every 2 to 4 hours. Start your newborn with 1 to 2 ounces (30 to 60 mL) at every feeding and gradually increase the feedings.
- Feed your baby when they seem hungry. Signs include smacking lips, making suckling movements, and rooting (moving their head around to find your breast).
- Do not wait until your baby cries to feed them. This means they are very hungry.
- Your baby should not sleep more than 4 hours at night without feeding (4 to 5 hours if you are feeding formula). It is OK to wake them up to feed them.
- If you are breastfeeding exclusively, ask your pediatrician if you need to give your baby supplemental vitamin D drops.
You can tell your baby is getting enough to eat if:
- Your baby has several wet or dirty diapers for the first few days.
- Once your milk comes in, your baby should have at least 6 wet diapers and 3 or more dirty diapers a day.
- You can see milk leaking or dripping while nursing.
- Your baby starts to gain weight; about 4 to 5 days after birth.
If you are concerned your baby is not eating enough, talk with your pediatrician.
You should also know:
- Never give honey to your infant. It may contain bacteria that can cause botulism, a rare but serious illness.
- Do not give your baby cow's milk until age 1 year. Babies under age 1 have a difficult time digesting cow's milk.
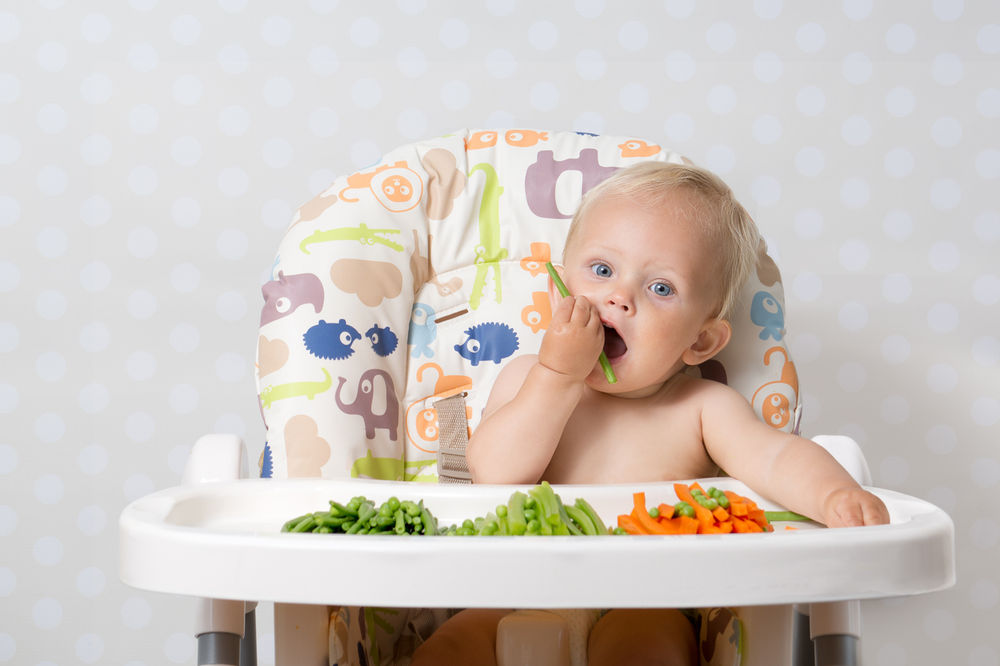
- Do not feed your baby any solid food until 4 to 6 months old. Your baby will not be able to digest it and may choke.
- Never put your child to bed with a bottle. This can cause tooth decay. If your baby wants to suck, give them a pacifier.
There are several ways you can tell that your infant is ready to eat solid foods:
- Your baby's birth weight has doubled.
- Your baby can control their head and neck movements.
- Your baby can sit up with some support.
- Your baby can show you they are full by turning their head away or by not opening their mouth.
- Your baby begins showing interest in food when others are eating.
When to Call the Doctor
Call the health care provider if you are concerned because your baby:
- Is not eating enough
- Is eating too much
- Is gaining too much or too little weight
- Has an allergic reaction to food
American Academy of Pediatrics, Section on Breastfeeding; Johnston M, Landers S, Noble L, Szucs K, Viehmann L. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e827-e841. PMID: 22371471 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22371471/.
Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e827-e841. PMID: 22371471 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22371471/.
HealthyChildren.org website. How often and how much should your baby eat? www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/feeding-nutrition/Pages/How-Often-and-How-Much-Should-Your-Baby-Eat.aspx. Updated October 29, 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021.
Parks EP, Shaikhkhalil A, Sainath NN, Mitchell JA, Brownell JN, Stallings VA. Feeding healthy infants, children, and adolescents. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 56.
Last reviewed on: 8/10/2021
Reviewed by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Feeding Patterns | Baby Behavior
Home / Baby Behavior / Feeding Patterns
Content begins hereFirst Feedings
Your newborn baby is growing quickly, and that means she needs to eat often. Follow your baby’s lead. It is normal and healthy for your baby to eat 8-12 times in a 24-hour period. That’s about once every 2-3 hours!
Follow your baby’s lead. It is normal and healthy for your baby to eat 8-12 times in a 24-hour period. That’s about once every 2-3 hours!
In these early days, each breastfeeding session might last 25-40 minutes, but this can vary based on how hungry or sleepy your baby is. It is important to remember that, in addition to food, babies get their hydration, comfort and snuggle time while at the breast.
Offer Both Breasts
Feed your baby on the fuller breast first until she naturally comes off or falls asleep, then try to burp her and offer the other breast. Breastfed babies often don’t burp, but it never hurts to try. Sitting your baby up to burp can also help wake her up, which may help her eat more actively on the second breast.
Cramps While Breastfeeding
In the days after delivery, you may feel uterine cramping when you breastfeed. This is completely normal and can last for several days or weeks. Cramps are a sign that your uterus is contracting and shrinking to its pre-pregnancy size. If you have any concerns, reach out to your healthcare provider.
If you have any concerns, reach out to your healthcare provider.
Cluster Feeding
Your baby may have a period of time during the day when she wants to nurse more often—sometimes every hour. This “cluster feeding” tends to happen in the evenings for the first 4-6 weeks of a baby’s life. As long as your baby is cluster feeding only during one part of the day, you can be sure that all is well and she is healthy.
Follow your baby’s lead, and offer her the breast whenever she is showing hunger cues. Cluster feeding helps your baby get what she needs and also boosts your milk supply. Talk with a lactation consultant or your pediatrician if your baby is cluster feeding for more than one stretch during the day or if you have any concerns about her feeding pattern.
Growth Spurts
As your baby grows and her body changes, her feeding patterns will likely change, too. You may hear these periods called “growth spurts,” and they are a normal part of a baby’s development. During these times, your baby may spend 1-2 days nursing more often and for longer sessions. Some babies may be also be more fussy during this time. You can learn about calming your crying baby here.
During these times, your baby may spend 1-2 days nursing more often and for longer sessions. Some babies may be also be more fussy during this time. You can learn about calming your crying baby here.
Growth spurts are not always predictable, but they often happen around 1-3 weeks, around 4-6 weeks, at 3 months, and again at 6 months. As your baby grows, she’ll need to eat more, and these increased feedings help build your milk supply. If you feel your baby isn’t getting enough to eat, talk to your pediatrician and a lactation consultant.
Introducing a Bottle
Most lactation consultants recommend that you wait to offer a bottle until your baby is around 4 weeks old and breastfeeding is well established. Many families find it helpful to have someone other than mom, such as dad, grandma or another caregiver offer the first bottle. Learn how to help your baby move between the bottle and breast by downloading Bottle-Feeding Your Breastfed Baby: A Guide for Success.
Solid Foods
Breastmilk provides complete nutrition for the first 6 months. Once your baby is able to sit up on her own, has good control of her head and neck and begins to show interest in food, you can start offering solid foods.
Once your baby is able to sit up on her own, has good control of her head and neck and begins to show interest in food, you can start offering solid foods.
Great options for first foods are pureed or soft meats, fruits and vegetables. Breastmilk and formula will still provide the bulk of nutrition for your baby’s first year. Visit the Solid Foods page to learn more about introducing solids.
Weaning
Breastfeeding is recommended for the first year of your baby’s life and can continue for as long as you both wish. When you are ready to wean, do it slowly over time. Choose the breastfeeding or pumping session you or your baby like the least and remove it from your day. Give your body 3-5 days to adjust before removing the next feeding session.
This slow and steady approach to weaning helps your body and your baby transition more smoothly away from breastfeeding. Talk to your pediatrician about how to replace your breastmilk with formula or cow’s milk. (Cow’s milk is only recommended for babies 1 year of age or older. )
)
Related Articles
Breastfeeding norms for newborns
When a child is born in a family, parents have many questions about the proper care of the baby. One of the most frequently asked questions is related to breastfeeding norms.
Dry initial milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 1 NutriValio for feeding children from birth to 6 months More
Follow-up dry milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 2 NutriValio for feeding children from 6 to 12 months Read more
Dry milk drink "Baby milk" Valio Baby 3 NutriValio for feeding children over 12 months Read more
Starting from the first feeding and in the first days of life, the child receives colostrum. It is very nutritious. The newborn eats little, but remains full. The volume of the stomach in babies in the first days of life does not exceed 10 ml. In one day, a baby eats about 100 ml of breast milk. This volume is increasing every day. For a baby older than 10 days, it is very easy to calculate the feeding rate. To do this, you need to multiply the number of days lived by 10. The amount of food eaten per day should be 1/5 of the baby's body weight. nine0003
The newborn eats little, but remains full. The volume of the stomach in babies in the first days of life does not exceed 10 ml. In one day, a baby eats about 100 ml of breast milk. This volume is increasing every day. For a baby older than 10 days, it is very easy to calculate the feeding rate. To do this, you need to multiply the number of days lived by 10. The amount of food eaten per day should be 1/5 of the baby's body weight. nine0003
To determine the rate of feeding children from the first month of life to a year, experts have developed the following table for calculating the volume of feeding:
You can also determine the correct amount of food for feeding a baby, focusing on the age, weight, behavior and development of the child.
At present, the so-called free-feeding regimen is recommended, i.e., to give the child a breast not according to the schedule, but at his first request, including at night. This allows the baby to take full advantage of the first milk - colostrum, which is characterized by a high concentration of antimicrobial factors, which prevents the possibility of infection of the newborn. Colostrum, which contains a high percentage of protein and minerals, even in small quantities satisfies the nutritional needs of the child. In addition, the entry of colostrum into the child's digestive tract ensures a faster "maturation" of the intestinal mucosa. A mother can learn to correctly identify the "hungry" cry of her child: at the same time, he turns his head in search of the mother's breast, smacks his lips, cries loudly, insistently. Usually, with a free-feeding regimen, a newborn baby receives breasts up to 10-12 times a day. on, initiating the secretion and release of milk. It has been shown that with free feeding, the volume of milk is 1.5 times higher than with hourly feeding. Subsequently, as the child grows, he usually develops his own feeding regimen by 2-3 months - from 6 to 8 times a day and, as a rule, without a night break. Observations show that with this feeding regime, children are distinguished by calm behavior, good mood, sleep soundly, give normal weight gain, and mothers produce more breast milk and the ability to secrete it lasts longer.
Colostrum, which contains a high percentage of protein and minerals, even in small quantities satisfies the nutritional needs of the child. In addition, the entry of colostrum into the child's digestive tract ensures a faster "maturation" of the intestinal mucosa. A mother can learn to correctly identify the "hungry" cry of her child: at the same time, he turns his head in search of the mother's breast, smacks his lips, cries loudly, insistently. Usually, with a free-feeding regimen, a newborn baby receives breasts up to 10-12 times a day. on, initiating the secretion and release of milk. It has been shown that with free feeding, the volume of milk is 1.5 times higher than with hourly feeding. Subsequently, as the child grows, he usually develops his own feeding regimen by 2-3 months - from 6 to 8 times a day and, as a rule, without a night break. Observations show that with this feeding regime, children are distinguished by calm behavior, good mood, sleep soundly, give normal weight gain, and mothers produce more breast milk and the ability to secrete it lasts longer. nine0003
nine0003
How can you tell if your baby is getting enough milk?
There is a so-called "wet diaper test". If the baby receives the necessary daily nutritional intake, he pees an average of 16-18 times. At the same time, 6-8 or more richly filled diapers are usually spent per day.
You can also determine if a child is getting enough nutrition by observing how much weight he gains each month. Infants from 2 to 13 weeks of age should gain between 170 and 200 grams per week. nine0003
Keep track of whether the baby grows out of the clothes he wears and out of diapers. If the baby eats properly, then on the 10-14th day of life, he returns to his original weight at birth. Babies who get enough food also sleep well and look cheerful and cheerful.
#PROMO_BLOCK#
Learn more about proper breastfeeding and check out our blog for tips.
nine00343.1 39
Power supplyShare:
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk. However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
Read
Author: Ivargizova Oksana
How to choose milk formula for a baby
Breast milk is the best food for a newborn baby. It contains all the necessary nutritional components that fully meet the needs of the child and are necessary for his healthy and harmonious development. nine0003
Read
Show all
IV newborn diet, how to feed your baby with formula from a bottle
The desire for a child to grow up strong and healthy is natural for mothers. And the health of a newborn begins with proper nutrition. Mother's milk has always been considered the best option for feeding - the most healthy and nutritious food for infants. However, in some cases, breastfeeding is not possible. And then mixtures come to the aid of mothers. nine0003
And then mixtures come to the aid of mothers. nine0003
Content: Hide
- In what cases is the transition to artificial feeding
- How to choose a mixture
- Basic feeding rules
- The main errors for artificial feeding
in which transitions are required for which transitions are required. feeding
Medical contraindications to breastfeeding. There are a number of diseases in which breast milk is prohibited. On the mother's side, these are HIV, an open form of tuberculosis, dangerous infections, and a serious state of health. On the part of the child, these are leucinosis, galactosemia, and individual food intolerance. It is not necessary to take tests after hearing the terrible names of diseases. All newborns are checked in maternity hospitals for their presence. But allergies are not so easy to identify. Many newborns have skin rashes and redness, which may be due to a reaction to an aggressive environment. Only a strict diet for the mother can help here, so that her milk does not contain allergens, monitoring the baby and consulting a doctor. nine0003
nine0003
Lack of lactation or its complete cessation. This is the second objective reason for transferring a child from breast milk to formula. Lactation does not always come in the right amount and it can be increased. It happens that milk disappears a few days after the birth of the crumbs. This often depends on the individual characteristics of the mother's body. So that the child does not starve, he is first transferred to mixed, and then completely to artificial feeding.
Insufficient nutritional value of mother's milk. Usually this problem can be solved without resorting to the transition to IoT, but this is not always possible. A woman may have a lot of milk, but it will be like water in both color and consistency. In such cases, doctors give advice to the mother on nutrition in order to increase the fat content of milk and its usefulness. If the milk remains watery, the child stops eating, cries of hunger, loses weight. The only way out in this situation is the transition to the mixture. nine0003
nine0003
Impossibility of regular feeding. Children who, for a number of reasons, are separated from their mother for long periods of time are transferred to artificial feeding: the woman is in a hospital, going to work or study, business trips, etc. If the break in breastfeeding is one-time, then restoring lactation and breastfeeding is still possible . However, more often in such cases, breastfeeding has to be abandoned.
Mother's personal wish. Unfortunately, there are cases when a woman, having every opportunity to breastfeed her baby, refuses to breastfeed for various subjective reasons. In this case, lactation is interrupted, and the baby is transferred to the mixture. nine0003
Read also: Newborn weight gain by month
How to choose a formula
If you are going to transfer your baby to artificial feeding, then the first thing you will encounter will be the choice of nutrition. Today there are a large number of different mixtures: adapted and non-adapted, dairy and sour-milk, dry and liquid. There are mixtures against regurgitation, hypoallergenic, for premature babies, etc. How to choose the optimal replacement for mother's milk from such a variety? nine0003
There are mixtures against regurgitation, hypoallergenic, for premature babies, etc. How to choose the optimal replacement for mother's milk from such a variety? nine0003
- Make your choice only after consulting a pediatrician. The doctor will examine the baby and give all the necessary recommendations.
- Monitor your child. When adapting to a new diet, the child may have small rashes, but they disappear if the body begins to absorb the mixture normally. The baby eats with appetite, he has a normal stool and no colic. Otherwise, the mixture must be changed.
- If there is a need to replace the mixture with a thicker one (anti-spitting), choose the same brand of food that was previously used. nine0070
- Consider the age of the baby. All mixtures have a gradation by months of life.
- Prefer adapted formulas, they are usually easier to digest
Basic rules for artificial feeding save you a lot of problems.
1. Choose proven blends. This applies not only to the choice of brand, but also to the packaging itself. Look at its integrity, check the expiration date. nine0003
This applies not only to the choice of brand, but also to the packaging itself. Look at its integrity, check the expiration date. nine0003
2. Observe the storage conditions for opened packaging at home (in a dry and cool place, but in no case in the refrigerator, the mixture must not become damp). Remember that the open mixture is stored for three weeks. After this period, it can no longer be used.
3. Strictly follow the instructions when preparing meals. It is indicated on the packaging. Water for the preparation of the mixture must be purified and boiled. The optimal temperature for preparing the mixture is 36–37 °C. You can cook food right in the bottle. This is quite convenient, since baby bottles have a volume scale that makes it easier to calculate the right amount of scoops. The mixture must be stirred until completely dissolved, and then cooled to an acceptable temperature so that the baby can drink without burning himself. You can check if the milk is hot by dropping it on your wrist - there the skin is most tender and sensitive. If the temperature is almost not felt, then the mixture can be given to the child. nine0003
If the temperature is almost not felt, then the mixture can be given to the child. nine0003
4. Sterilize baby dishes. Baby bottles and nipples should be thoroughly rinsed using a special brush so that no food residue remains. You can use children's dishwashing detergents. Do not wash bottles with common cleaning products that you are used to using, no matter how good they are. After washing, be sure to place the dishes in boiling water. This helps to kill harmful bacteria. It is recommended to sterilize children's dishes during the entire first year of a baby's life. Then you can limit yourself to just a thorough wash. nine0003
5. Hold the bottle in a semi-vertical position when feeding. The milk should completely fill the nipple. This prevents the child from swallowing air. After feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in a column for several minutes to avoid spitting up.
6. Monitor the amount of formula consumed and the feeding schedule. Maintaining a balance is extremely important for the healthy and full development of the baby. nine0003
nine0003
- Calculate the amount of formula to be prepared based on the baby's weight. It is body weight, and not the age of the crumbs, that is the main indicator when calculating the daily nutritional intake. You can find out the required volume of the mixture for feeding either at a pediatrician’s appointment, or on your own (it is recommended to use Maslov’s caloric method when calculating).
- Observe the breaks between feedings. During the day they should be 3.5 hours, at night - 6. Try not to break the schedule.
- Give your child water. Supplementation with water is a necessity for artificial feeding. Water should be given somewhere in the middle of the interval between feedings or 10-15 minutes after it. Avoid supplementation before meals. nine0070
Major mistakes in artificial feeding
Overfeeding. The desire to feed the child is understandable, but in the case of mixtures, feeding must be approached strictly. On artificial feeding, the child is normally gaining weight very well. Excess body weight is an additional burden on the body and health problems. Even an adult can find it difficult to cope with problems from being overweight. What to say about the tiny weak body of a newborn? Follow the diet and control the daily milk intake. Fortunately, you can always see how much the child ate. nine0003
Excess body weight is an additional burden on the body and health problems. Even an adult can find it difficult to cope with problems from being overweight. What to say about the tiny weak body of a newborn? Follow the diet and control the daily milk intake. Fortunately, you can always see how much the child ate. nine0003
Unreasonable mixture change. If the child eats the current mixture well, then it is not necessary to change it. The baby will have to go through a difficult period of adaptation again, and it’s not a fact that his body will accept new food just as well.
Use of old mix. The child's food must be fresh. If the child has not finished eating, then literally after half an hour the milk can only be poured out. Milk mixtures are an excellent environment for the life of pathogenic bacteria.
Pet milk feeding. Do you think this is a more natural option than artificial mixtures? This is an erroneous opinion. For a child under one year old, cow or goat milk, even boiled, is strictly prohibited.