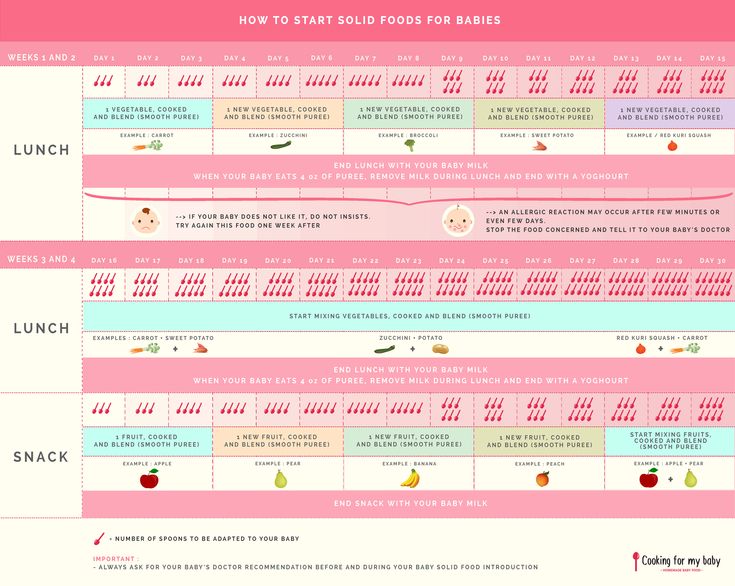
Feeding your baby at 4 months
Feeding Your 4- to 7-Month-Old (for Parents)
Most babies this age are ready to try solid foods. Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Be sure to check with your doctor before giving any solid foods.
Is My Baby Ready to Eat Solid Foods?
How can you tell if your baby is ready for solids? Here are a few hints:
- Does your baby swallow food or push it out of their mouth? Babies have a natural tongue-thrust reflex that pushes food back out. Wait until this reflex disappears (typically when babies are 4–6 months old).
- Can your baby support their own head? To eat solid food, an infant needs good head and neck control and should be able to sit up.
- Is your baby interested in food? Babies who stare, reach and grab, and open their mouths for food are ready to try solid foods.
If your doctor gives the go-ahead but your baby seems frustrated or uninterested in solid foods, try waiting a few days before trying again. Breast milk and formula will still meet nutritional needs as your baby learns to eat solid foods. But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
Do not add cereal or other food to your baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain.
Watch for signs that your child is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your child stop when full. A child who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the breast or the bottle. With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
How Should I Start Feeding My Baby Solid Foods?
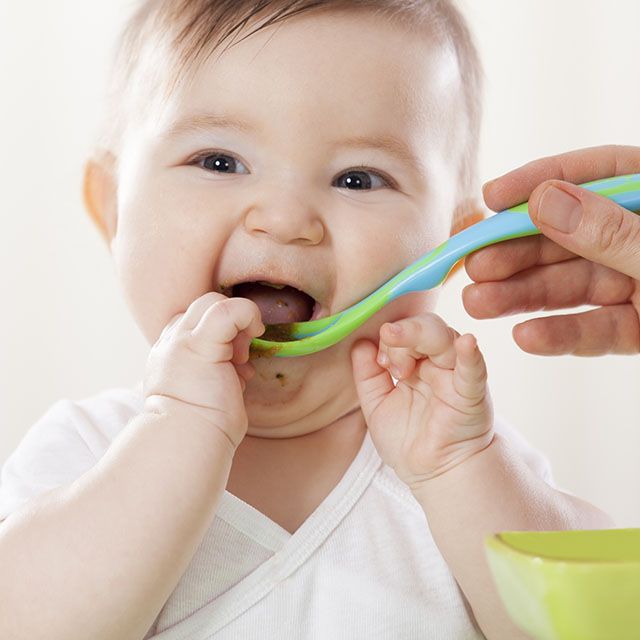
When your baby is ready and the doctor says it’s OK to try solid foods, pick a time of day when your baby is not tired or cranky. You want your baby to be a little hungry, but not so hungry that they’re upset. So you might want to give your baby a little breast milk or formula first.
Have your baby sit supported in your lap or in a high chair with a safety strap.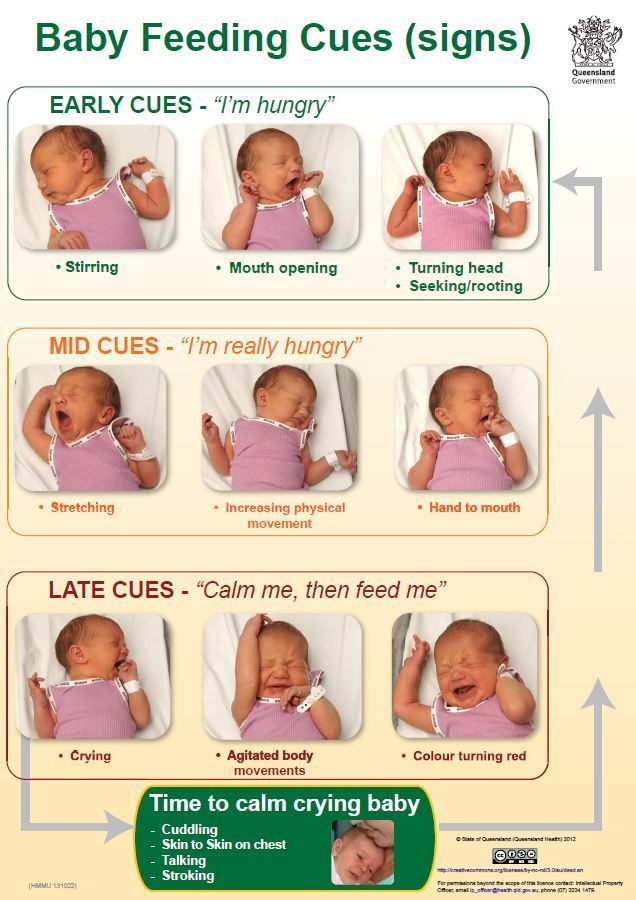
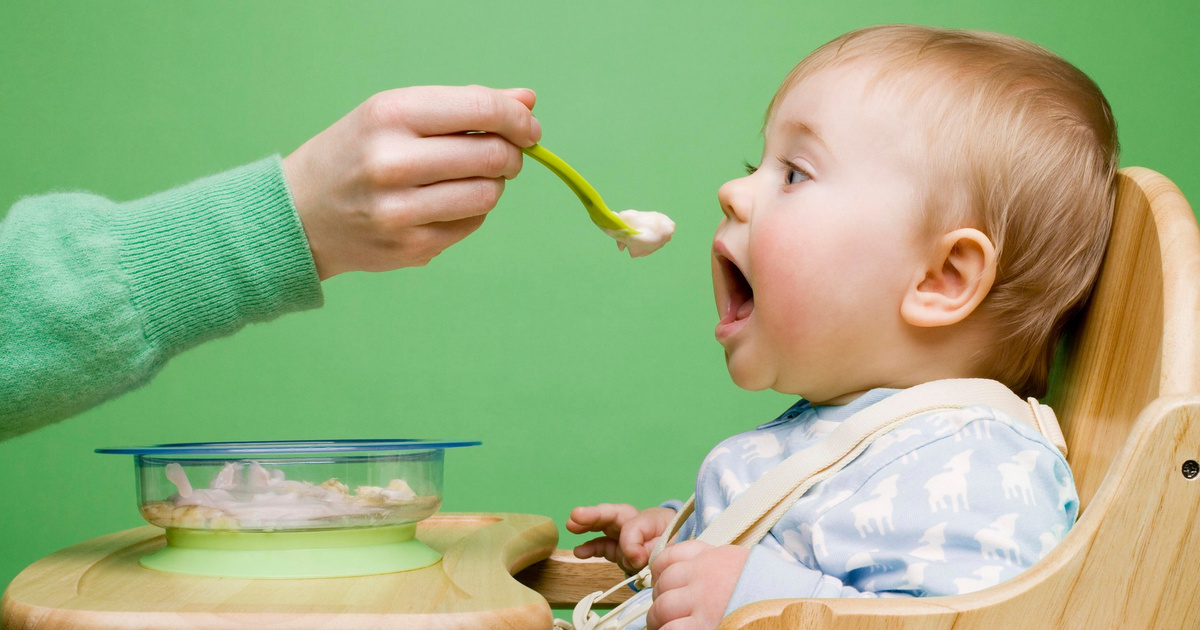
Most babies' first food is iron-fortified infant single-grain cereal mixed with breast milk or formula. Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
When your little one gets the hang of eating cereal off a spoon, it may be time to try single-ingredient puréed meat, vegetables, or fruit. The order in which you give them doesn't matter, but go slow. Offer foods that are high in iron and zinc — such as meat, poultry, eggs, and beans — especially if your baby is breastfeeding. Try one food at a time and wait several days before trying something else new. This will let you identify any foods that your baby may be allergic to.
Which Foods Should I Avoid?
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
Possible signs of food allergy or allergic reactions include:
- rash
- bloating or an increase in gassiness
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Get medical care right away if your baby has a more severe allergic reaction, like hives, drooling, wheezing, or trouble breathing.
If your child has any type of reaction to a food, don't offer that food again until you talk with your doctor.
Babies shouldn't have:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday.
 It can cause botulism in babies.
It can cause botulism in babies. - unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy beverages before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Tips for Feeding Your Baby Solid Foods
With the hectic pace of family life, most parents try commercially prepared baby foods at first. They come in small, convenient containers, and manufacturers must meet strict safety and nutrition guidelines.
If you prepare your own baby foods at home, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Follow the rules for food safety, including washing your hands well and often.
- To preserve the nutrients in your baby's food, cook it in ways that keep the most vitamins and minerals. Try steaming or baking fruits and vegetables instead of boiling, which washes away the nutrients.
- Freeze portions that you aren't going to use right away.

- Whether you buy the baby food or make it yourself, texture and consistency are important. At first, babies should have finely puréed single-ingredient foods. (Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.)
- After your baby is eating individual foods, it's OK to offer a puréed mix of two foods. As babies get older, they will learn to eat a greater variety of tastes and textures.
- If you use prepared baby food in jars, spoon some of the food into a bowl to feed your baby. Do not feed your baby right from the jar — bacteria from the baby's mouth can contaminate the remaining food. If you refrigerate opened jars of baby food, it's best to throw away anything not eaten within a day or two.
- Around 6 months of age is a good time for your baby to try a cup. You might need to try a few cups to find one that works for your child. Use water at first to avoid messy clean-ups. Do not give juice to infants younger than 12 months.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
When Can My Baby Start Eating Solid Foods? (for Parents)
A friend just started giving her 3-month-old applesauce and rice cereal. My son is just 2 weeks younger than hers, and I am wondering if I should be introducing solids soon too. When should I start?
– Taylor
Doctors recommend waiting until a baby is about 6 months old to start solid foods. Starting before 4 months is not recommended.
At about 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — such as iron and zinc — that solid foods provide. It’s also the right time to introduce your infant to new tastes and textures.
Some babies may be ready for solids sooner than 6 months, but don't start until your baby is at least 4 months old.
How do you know it’s the right time to start solid foods? Here are some signs that babies are ready:
- They have good head and neck control and sit up in a high chair.

- They're interested in foods. For example, they may watch others eat, reach for food, and open their mouths when food approaches.
- They don’t push food out of their mouths, which is a natural tongue reflex that disappears when they’re between 4–6 months old.
- They weigh twice their birth weight, or close to it.
Talk to your doctor about the right time to start solid foods.
How Should I Start Solids?
When the time is right, you can start with a single-grain, iron-fortified baby cereal. Start with 1 or 2 tablespoons of cereal mixed with breast milk, formula, or water. Feed your baby with a small baby spoon. Don’t add cereal or other food to a baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain. Let your baby practice eating from a spoon and learn to stop when full.
When your baby gets the hang of eating the first food, introduce others, such as puréed meat, fruits, vegetables, beans, lentils, or yogurt. Try one food at a time and wait a few days before trying something else new to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction.
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you are concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
When starting your baby on solids, avoid:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy drinks before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.

- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Also, do not give fruit juices to infants younger than 12 months old.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: February 2021
sleep, feeding and development of the baby
04/11/2019
108
By 4 months, the biological rhythms of the child are finally formed, and the structure of his sleep becomes the same as in adults. Therefore, the old ways of laying often stop working, the baby may fall asleep longer, wake up more often at night and constantly breastfeed, and the existing daily routine may no longer work. What to do in this case?
Use our tips to improve your child's routine!
4 months
At this age, children still cannot live according to a clear daily schedule, as they still sleep short dreams during the day and are not able to stay awake for a long time. Therefore, the daily routine of four months. is built based on the time of wakefulness, which is no more than 1.5-2 hours between sleeps. At the same time, an infant needs 9-10 hours of sleep per night with awakenings for feeding and 3-4 daytime sleeps with a total duration of about 4-5 hours. That is, the baby will sleep with this schedule 3-4 times a day. The time of evening bedtime will vary and depend on the end of the last day's sleep. To get your baby to bed on time, be alert for signs of fatigue and stay awake for more than 2 hours. So you will prevent overworking the baby, which will improve the quality of his nightly sleep and reduce the number of night awakenings. Morning should start no later than 07:00-07:30 to form the physiological regime of the day.
Therefore, the daily routine of four months. is built based on the time of wakefulness, which is no more than 1.5-2 hours between sleeps. At the same time, an infant needs 9-10 hours of sleep per night with awakenings for feeding and 3-4 daytime sleeps with a total duration of about 4-5 hours. That is, the baby will sleep with this schedule 3-4 times a day. The time of evening bedtime will vary and depend on the end of the last day's sleep. To get your baby to bed on time, be alert for signs of fatigue and stay awake for more than 2 hours. So you will prevent overworking the baby, which will improve the quality of his nightly sleep and reduce the number of night awakenings. Morning should start no later than 07:00-07:30 to form the physiological regime of the day.
What to do if a 4-month-old baby slept well but now has trouble getting to bed:
-
Enter a bedtime ritual if you haven't already done so. In the evening, this can be bathing, light massage, putting on a diaper and clothes for sleep, lullaby and feeding.
 During the day, the ritual can be left the same, only without hygiene procedures. The ritual should be repeated daily and consist of the same actions. It is carried out by one person - either mom or dad.
During the day, the ritual can be left the same, only without hygiene procedures. The ritual should be repeated daily and consist of the same actions. It is carried out by one person - either mom or dad. -
Check that the room has suitable sleeping conditions for a baby: the temperature is no more than 21-23 degrees in winter and no more than 25 degrees in summer, and the air humidity is approximately 40-60%. It is also important to darken the room for all dreams, including daytime, and use white noise.
-
Organize your baby's rest in the crib. The last daytime nap can be done outside in a stroller.
-
Prolong the child's sleep by any means, if the morning and afternoon sleep lasts no more than 30-40 minutes.
-
If nothing helps and the baby still constantly wakes up at night, neither motion sickness, nor the breast, nor the nipple work to prolong sleep, then it is worth teaching the child to fall asleep on his own.
-
Make sure your baby gets enough sleep. Otherwise, overwork will accumulate, which will manifest itself in frequent nocturnal awakenings. This is where following a routine can help.
Check our chart to see if your baby is getting enough sleep
How many feeds does a baby need at night?
At four months old, breast milk or formula is still the main food in his diet.
The diet of the breastfed baby this month will consist of feedings every 3-4 hours. The volume of breast milk drunk at a time will be about 118-210 ml. The duration of feeding may vary.
When formula-fed, the volume of the mixture should be calculated from the recommendations of the pediatrician. This is usually 1/6 of the child's actual body weight. At four months, the baby will eat 800-1000 ml. mixture per day every 3-4 hours during the day.
The baby is becoming more and more interested in the world around him and during feeding he can start to be distracted, not eat enough and make up for hunger at night. Therefore, it is better to feed the baby in a calm environment.
Therefore, it is better to feed the baby in a calm environment.
2-3 feedings are enough at night for a four-month-old baby.
Does the baby wake up at night shortly after feeding and start crying? Instead of refeeding him, try other ways to calm him down, such as petting his tummy and peeing. So the child will not form the habit of falling asleep only with the help of feeding.
Should we start complementary foods at 4 months? WHO (World Health Organization) recommends introducing complementary foods from 6 months. Therefore, before introducing adult food, it is worth consulting with a pediatrician.
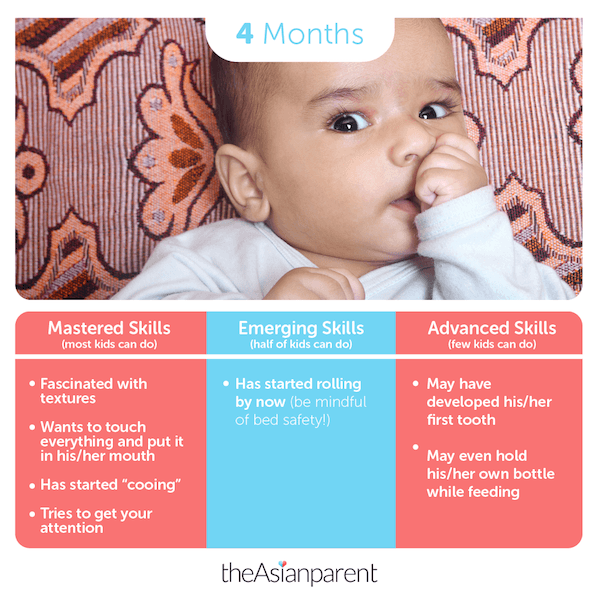
Physical development of a 4-month-old baby
The fourth month is the age when a child already knows a lot and masters new skills.
He is already confidently using both hands at the same time and grasping toys, colorful and shiny objects near him. Soft books, teething rings are a good choice for this age.
For reading, choose large books with different textures inside to develop tactile sensations. Read and sing to your baby every day for a few minutes. This develops the attention and speech of the child. Take a closer look at children's bathing books - their puffy pages are easy to flip through. In addition, they still often squeak, and the pictures in them are bright.⠀
The baby is already holding his head and chest well, being on his stomach and pushing off the surface with his hands. Also, the child can already begin to roll over from his stomach to his back and push with his legs.
The baby sees better, begins to distinguish colors and notice objects in the distance, although he still prefers to look at faces and things near him. During walks in the fresh air, tell the baby about the surrounding objects, point to them and describe them.
From the age of 4 months, the first teeth erupt. If the baby's salivation increased, redness appeared around the mouth, he began to bite, refuse to eat, became moody, his night's sleep worsened, then most likely the child has a new tooth. In the acute period, teething rings, anesthetic gel recommended by the pediatrician, more attention and warmth from the mother's side will help.
If the baby's salivation increased, redness appeared around the mouth, he began to bite, refuse to eat, became moody, his night's sleep worsened, then most likely the child has a new tooth. In the acute period, teething rings, anesthetic gel recommended by the pediatrician, more attention and warmth from the mother's side will help.
Important changes occur in communication with the baby at 4 months. He realizes that his mother is coming to his crying, and begins to use different sounds when communicating with others: oooh .., aah .., aha ... Catch the moment when the child “talks” more than usual and play “echo” with him. He says - you repeat.
Such a game gives the child confidence that his mother listens to him and is happy to talk to him. And, of course, develops the speech of the child. Try it - you'll like it.
Also at this age, finger games will already be useful, for example, "Ladushki", "A horned goat is coming", "Magpie-crow" - they are aimed at developing the child's fine motor skills, which in turn is important for the formation of speech.
If your 4-month-old baby does not sleep well at night, we recommend that you watch the free master class "MY BABY SLEEPS BADLY at NIGHT: 3 SOLUTIONS"
What is the daily routine of your baby at 4 months old?
Like this article? Rate:
Votes: 791
Diet for a 4 year old baby
Your baby is 4 months old now. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
You are still breastfeeding your baby or have had to switch to formula or formula feeding. The child is actively growing, and only with breast milk or infant formula, he can no longer always get all the necessary nutrients. And that means it's time to think about complementary foods.
And that means it's time to think about complementary foods.
The optimal time to start its introduction is between 4 and 6 months, whether the baby is receiving breast milk or formula. This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food. And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc.). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
When is it advisable to introduce complementary foods as early as 4 months, and when can you wait until 5. 5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
The optimal time to start introducing complementary foods to a healthy baby is between 5 and 5.5 months of age.
The World Health Organization recommends that breastfed babies should be introduced to complementary foods from 6 months of age. From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on the big
practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born at term, without malnutrition (because in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows and develops well. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron.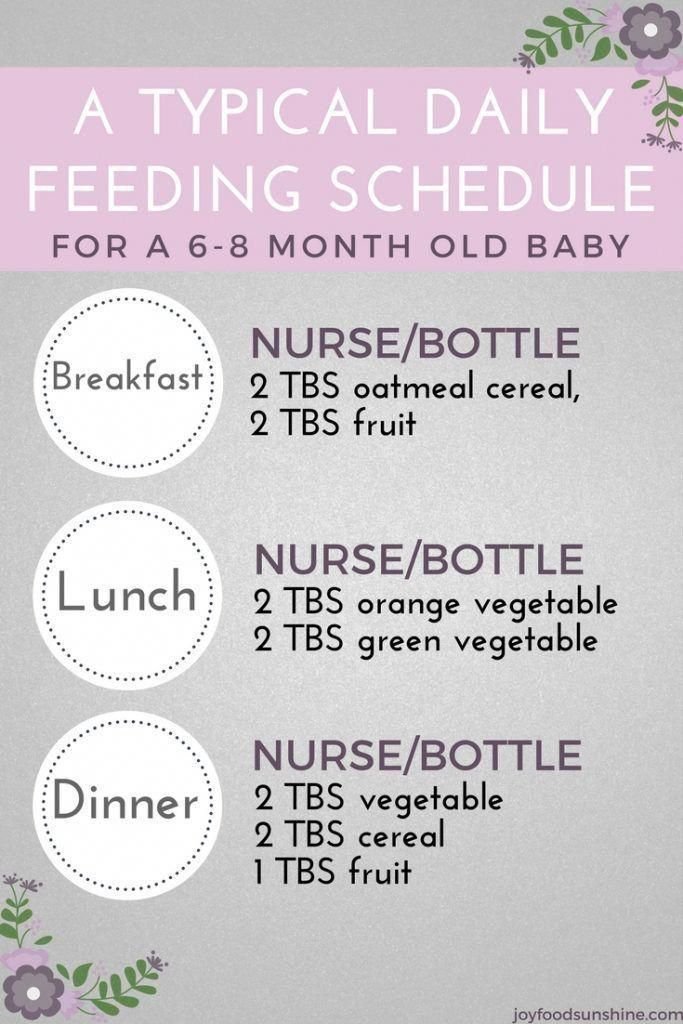 There are other deficits as well.
There are other deficits as well.
The first food product can be vegetable puree or porridge, it is better to give fruit puree to the baby later - after tasty sweet fruits, children usually eat vegetable puree and cereals worse, often refuse them altogether.
Where is the best place to start? In cases where the child has a tendency to constipation or he puts on weight too quickly, preference should be given to vegetables. With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gains - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started introducing complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa.
If the first complementary foods are introduced at 6 months, it must be baby porridge enriched with iron and other minerals and vitamins, the intake of which with breast milk is no longer enough.
Another important complementary food product is mashed meat. It contains iron, which is easily absorbed.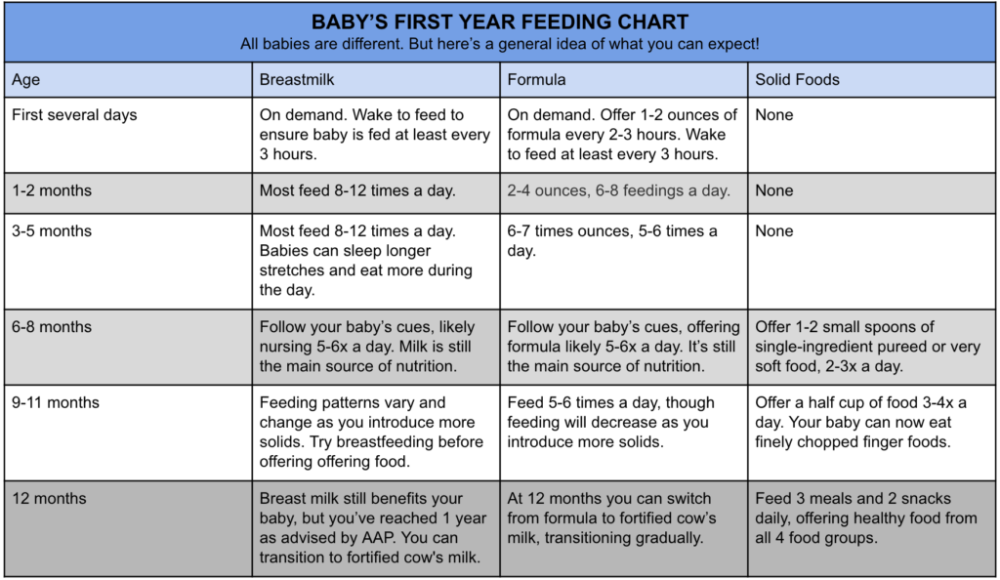 And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them. It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them. It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
But it is better to introduce juices later, when the child already receives the main complementary foods - vegetables, cereals, meat and fruits. After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
Juices should not be given between feedings, but after the child has eaten porridge or vegetables with meat puree, as well as for an afternoon snack. The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to the 5-time feeding regimen.
Complementary feeding rules:
- preference should be given to baby products of industrial production, they are made from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a guaranteed composition and degree of grinding
- Complementary foods should be offered to the baby by spoon at the start of feeding, before breastfeeding (formula feeding)
- the volume of the product increases gradually, starting with ½ - 1 spoon, and in 7 - 10 days we bring it to the age norm, subsequent products within the same group (cereals from other cereals or new vegetables) can be introduced faster, in 5 - 7 days
- start introduction with monocomponent products
- it is undesirable to give a new product in the afternoon, it is important to follow how the child reacts to it
- do not introduce new products in the event of acute illnesses, and before and immediately after prophylactic vaccination (should be abstained for several days)
When introducing a new type of complementary food, first try one product, gradually increasing its amount, and then gradually "dilute" this product with a new one. For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
After the introduction of one vegetable (bringing its volume to the required amount), you can proceed to the intake of porridge, and diversify the vegetable diet later.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up on your plan and continue to offer this vegetable in a small amount - 1-2 spoons daily, you can not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help to form the right taste habits in the baby.
Spoon-feed with patience and care. Forced feeding is unacceptable!
In the diet of healthy children, porridge is usually introduced after vegetables (with the exception of healthy breastfed children, when complementary foods are introduced from 6 months). It is better to start with dairy-free gluten-free cereals - buckwheat, corn, rice. At the same time, it is important to use porridge for baby food of industrial production, which contains a complex of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is already ready for use, you just need to dilute it with breast milk or the mixture that the baby receives.
Children suffering from food allergies are introduced complementary foods at 5-5.5 months. The rules for the introduction of products are the same as for healthy children, in all cases it is introduced slowly and begins with hypoallergenic products. Be sure to take into account individual tolerance. The difference is only in the correction of the diet, taking into account the identified allergens. From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
Diets for different age periods
explain how to make a diet, it is better on several examples that will help to navigate the menu for your child.
From 5 months, the volume of one feeding is on average 200 ml.
Option 1.
I feeding
6 hours
Breast milk or VHI*
200 ml
II feeding
10 hours
Dairy-free porridge**
Supplementation with breast milk or VHI*
150 g
50 ml
III feeding
14 hours
Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Breast milk supplement or VHI*
150 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp
30 ml
IV feeding
18 hours
Fruit puree
Breast milk or VHI*
60 g
140 ml
V feeding
22 hours
Breast milk or VHI*
200 ml
* - Children's dairy mixture (VHI)
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 2.
9010 9010 9010 9010
9000 9000 901
9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 baby 6 months, if complementary foods were introduced from 4 - 5 months:
| I feeding | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
| II feeding | Dairy-free porridge** | 150 g |
| III feeding | Vegetable puree | 150 g |
| IV feeding | Fruit puree | 40 g |
| V feeding | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
* - children's dairy mixture
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 3.
An approximate daily diet for a baby at 6.5 months on breast feeding, if complementary foods began to be administered from 6 months:
| I feeding | Breast milk | |
| II feeding | Dairy-free porridge** | 100 g |
| III feeding | Vegetable puree | 100 g |
| IV feeding | Breast milk |
|
| V feeding | Breast milk |
|
** - diluted with breast milk
Up to 7 months, increase the volume of porridge and vegetable puree to 150 g and introduce fruit puree.