Food for 4months baby
Top 10 Ideas For 4 Month Baby Food
Some fruits and boiled vegetables may be given to your baby to fulfill their needs.
Image : Shutterstock
Finding suitable food ideas for your four months old baby may be confusing as this is probably the first time they are being introduced to solid food.
As babies turn four months, they become more active and playful. In addition, they start to exhibit more interest in their surroundings. Their stomachs also grow bigger and are ready for more food. Moreover, they seem less interested in milk and are ready to explore new food varieties.
If you recognize these signs in your baby, it is an indication that they have reached the developmental milestone where you may introduce them to solid foods.
Read the post to find whether your baby is ready for solids and to discover some interesting food ideas for them.
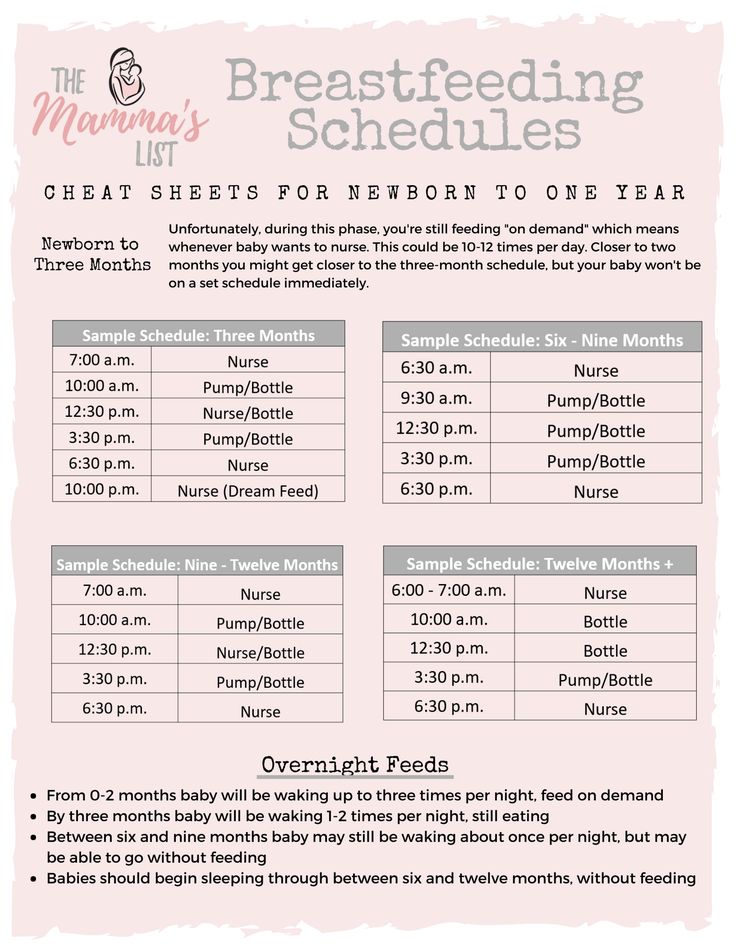
Is Your Baby Ready For Solids?
Your baby must have lost the ‘tongue thrust reflex’ by the time he is four months of age. Thrust reflex prevents the infants from choking. It also causes them to push the food out of their mouths. The World Health Organization recommends that we start solids at six months but solids may be introduced at four months. If your baby seems unsatisfied after milk feeds, can hold their head up without any support, can sit without support, wakes up more frequently at night to feed, follows your food with their eyes when you eat, then probably it is the time to introduce him to solid foods. See if your baby is interested in the food or not. If your child stares and grabs your food at dinnertime, then he is ready for some variety. The baby should be able to sit well without any support. Your child needs a good neck control to eat solid foods. It will enable him to swallow his food efficiently. The 4 months baby food should consist of solids.
Top 10 Ideas:
Here are the top 10 ideas for 4 month baby food old as he begins his journey into solid foods.
1.
 Baby Cereal:
Baby Cereal:Baby cereal is the most recommended first food for infants. Prepare the cereal with formula or breast milk. It will give the cereal a texture and taste that he is already familiar with. Cereal is also one of the least allergenic foods, making it suitable for babies of 4 months. Give gluten-free cereal, particularly if you have a family history of Celiac diseases or allergies. Wheat, barley and rye cereal may be unsuitable for babies as they contain gluten. Rice and oatmeal are the least allergenic varieties of cereal.
2. Avocado:
Image: Shutterstock
If you want to serve a complete and delicious meal for your baby, then you can serve him avocado. Slice an avocado and spoon out the flesh. Mash it with a fork or puree in a food processor. Add breast milk or formula milk to make it more ‘soupy’.
3. Banana:
Bananas are considered one of the nature’s most perfect foods. Babies love them for their natural sweetness. Also, banana is rich in fiber, so it will keep the things moving through your tot’s digestive system.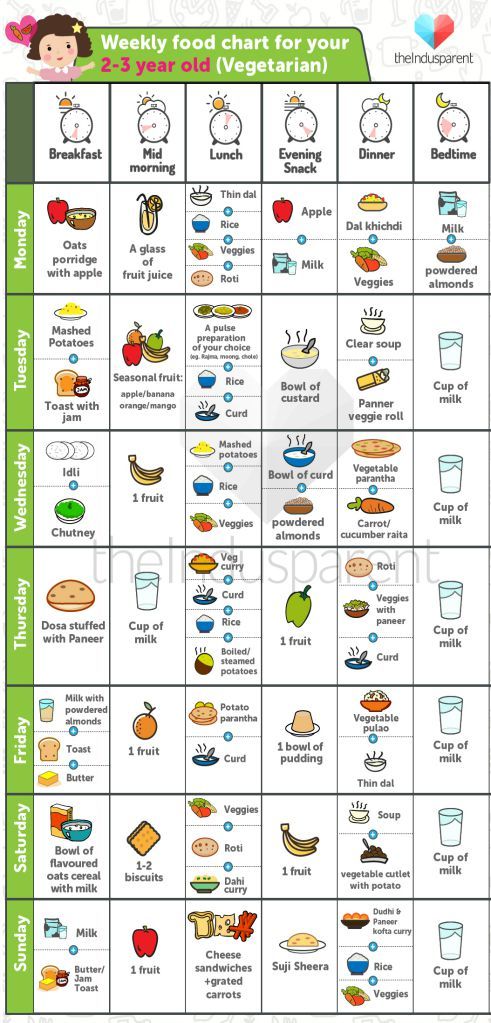 Remove the skin of the banana and puree the flesh. You can also thin it with a little formula milk or breast milk. The food for 4 months baby is tasty with this all round nutritious fruit.
Remove the skin of the banana and puree the flesh. You can also thin it with a little formula milk or breast milk. The food for 4 months baby is tasty with this all round nutritious fruit.
4. Butternut Squash:
Image: Shutterstock
Butternut squash has a pleasing texture, making it ideal for a baby’s palate. Baked butternut squash will make a great food for your little one. All you need to do is pierce the butternut squash and bake for an hour at 375 degrees. Cut it lengthwise and then scoop out the fibers and seeds. Then spoon out the flesh and mash with a fork or masher.
5. Sweet Potato:
Sweet potato is a popular first food for babies. It is easier to digest and does not cause constipation in children. Cut the sweet potato and simmer in a little water until tender. Transfer to a food processor and puree, adding a little water or breast milk.
6. Carrots:
Image: Shutterstock
Carrot is another great choice for baby food.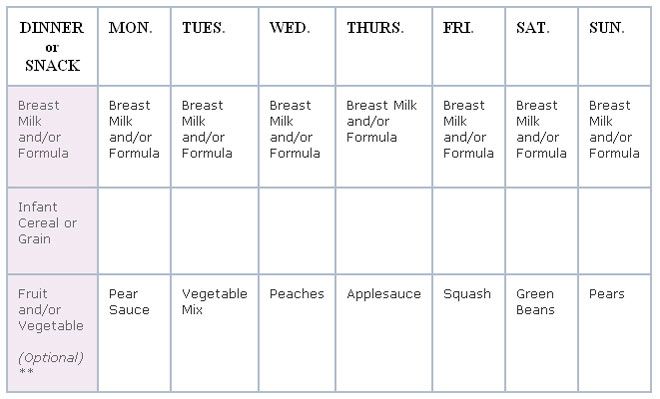 Cut the carrots into sticks and bake for over 20 to 30 minutes at 375 degrees Fahrenheit. The food for 4 month old baby is healthy with carrots.
Cut the carrots into sticks and bake for over 20 to 30 minutes at 375 degrees Fahrenheit. The food for 4 month old baby is healthy with carrots.
7. Apple:
With your doctor’s consent, you can serve cooked apples to your baby. Dice the apple and simmer or steam until tender. Cooking apple until it is just tender will ensure that all the nutrients are preserved. Transfer to a blender or food processor and blend until smooth. The 4 month old baby food is extremely nutritious with this addition.
8. Pear:
Image: Shutterstock
Pears are one of the safest foods to give as a first food. The allergic reactions to pear are rare. Also, they have a low acidity level, which makes them gentle on the tiny tummies. Puree steamed pear and add to the baby’s cereal.
9. Milk:
At this stage, breast milk will provide total nutrition to your baby. Don’t even think of replacing breast milk or formula until 12 months of age. It can cause serious health implications. Also, never give your child low-fat or skim milk products until he is 2 years old. The 4 months old baby food is extremely delicious with milk.
Also, never give your child low-fat or skim milk products until he is 2 years old. The 4 months old baby food is extremely delicious with milk.
10. Peas:
Image: Shutterstock
Fiber filled peas will make an ideal first veggie for babies. Steam the peas for 6 minutes and puree in a food processor, adding the cooking liquid. Strain using a sieve to discard the solids. Pea puree may thicken after it is refrigerated. So stir in a small amount of water, formula or breast milk while heating.
Tips:
- A baby’s tummy is the size of his fist. Do not expect your baby to finish a meal. He probably will eat just ½ of a tablespoon portion of what you serve to him.
- Serve a food to baby for four days at a stretch. It will help you learn the signs of intolerance and allergy. Follow this process until your baby has tried a variety of foods.
- Always serve cooked veggies to your baby so that he can chew it easily. Cooking breaks down the cell wall, making the food easier to digest by the baby.

- Place the spoon near your baby’s lips and let him taste and smell. Don’t be surprised if your tot rejects the first spoon. Wait for a few minutes and try again.
- Do not add any salt or pepper to the baby food.
- As your baby gets used to solid food, make the puree less runny. You can mash the food instead of pureeing it.
1. What if a baby refuses their first solid food?
A baby might refuse solid food if they are full, unwell, or irritable. Hence, try feeding them when they are hungry. Check the consistency of the solid food and make it baby-compatible. Foods that are too hot or too cold might also be refused. Try a variety of foods initially to see the taste they prefer the most. If your baby still refuses to eat solid foods, consult a pediatrician.
2. Can I give my four-month-old orange juice?
Juices may seem easy to introduce babies to the taste of fruits. However, the American Academy of Pediatrics advises not to give babies juices until one year unless recommended by a pediatrician (1).
3. How do I keep baby foods safe?
Always feed your baby fresh, home-cooked food. Wash the ingredients properly in clean tap water. If you are preparing baby food in bulk, freeze the food immediately in a tightly sealed container. Label the container with the date of preparation and time. Only take out the required amount of food from the container when feeding a baby (2). Always check the quality of the food before feeding it to a baby.
If you are looking for food ideas for your 4-month-old baby, begin by offering easily digestible foods such as bananas, sweet potatoes, and cereals. At four months, your tiny tot may be interested in eating foods other than milk. Though most babies are fed various solid foods after six months, you may introduce mashed forms of foods after they cross the four-month mark. Nevertheless, do not rush into introducing foods to your baby. Also, remember that all babies do not react to new foods alike. Hence, if you notice that your baby is not interested in certain foods, give them some time or try feeding other varieties.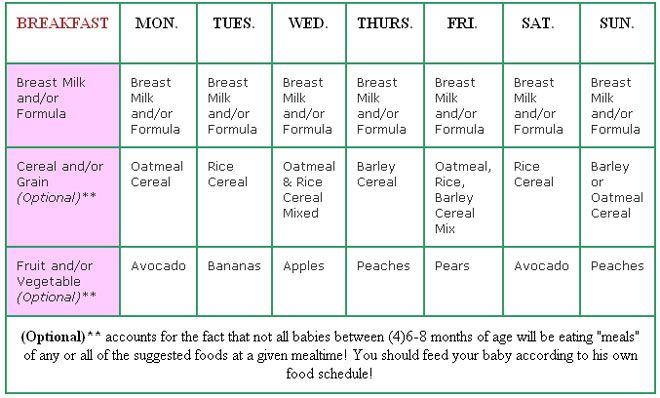
Key Pointers
- 4-month-old babies can consume the puree of avocado, banana, and carrots.
- To identify food intolerance issues while introducing solids, serve one food for three to four days instead of feeding mixed foods.
- Avoid adding spices or salt to baby food.
References:
MomJunction's articles are written after analyzing the research works of expert authors and institutions. Our references consist of resources established by authorities in their respective fields. You can learn more about the authenticity of the information we present in our editorial policy.
- Weighing in on fruit juice: AAP now says no juice before 1.
https://publications.aap.org/aapnews/news/14804 - How to make homemade baby food?
https://www.eatright.org/food/planning-and-prep/snack-and-meal-ideas/how-to-make-homemade-baby-food#
The following two tabs change content below.
- Reviewer
- Author
Jessica Albert is a passionate writer who seeks to connect with her readers through wit and charm. Her work aims to invoke curiosity and keep the readers engaged through and through. She has prior experience working with magazines and e-commerce establishments as a content marketer and editor. Being a mother herself, she puts all her knowledge into creating content about... more
Moloko Mehlape is a registered dietitian in private practice with special interest in nutrition education, sports nutrition, weight and chronic disease management. She is a philanthropist passionate about making a positive impact in public health through nutrition. Dt. Mehlape has completed extensive formal education and training, and holds qualifications BSc Dietetics (Hons) - Medunsa, MSc Dietetics from the University of... more
Is It Safe To Eat Lotus Seeds (Makhana)..
Is It Safe To Eat Lotus Seeds (Makhana)..
Dry Fruits During Pregnancy: Benefits,.
 .
.Dry Fruits During Pregnancy: Benefits,..
Spinach For Babies: Right Age, Benefits..
Spinach For Babies: Right Age, Benefits..
Cinnamon For Babies: Safety, Benefits..
Cinnamon For Babies: Safety, Benefits..
Is It Safe To Consume Cinnamon During..
Is It Safe To Consume Cinnamon During..
Top 10 Food Ideas For Your 16 Months..
Top 10 Food Ideas For Your 16 Months..
4 Possible Health Benefits Of..
4 Possible Health Benefits Of..
ORS for Babies: Dosage, Benefits And..
ORS for Babies: Dosage, Benefits And..
13 Excellent Benefits Of Avocados..
13 Excellent Benefits Of Avocados..
Age-by-age guide to feeding your toddler
- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
Your growing toddler can enjoy a wide range of foods.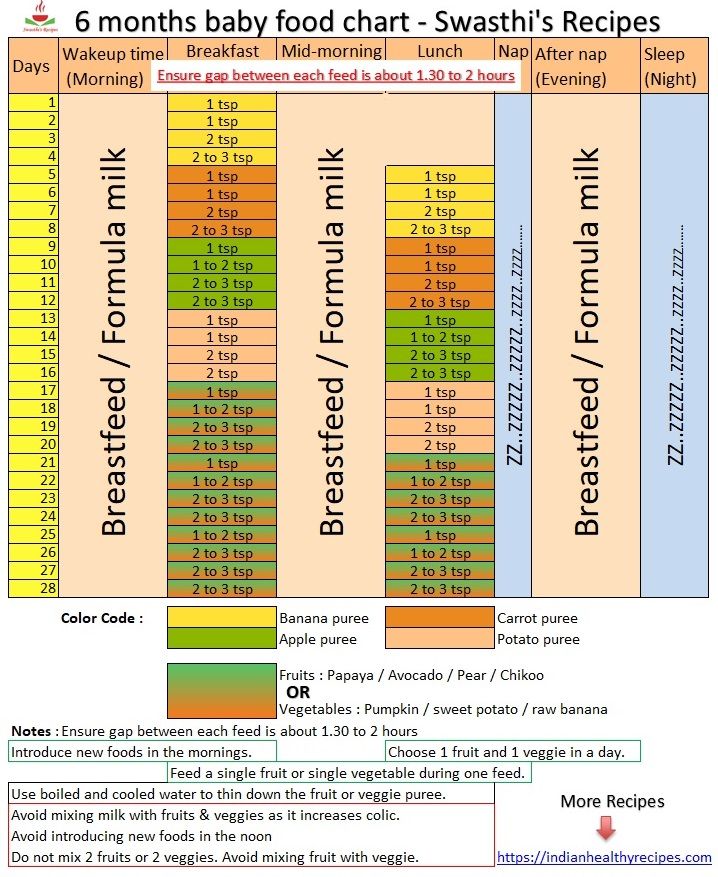 Expect your little one to have about 2 cups of milk or yogurt, 3 ounces of whole grains, 1 cup each of fruit and vegetables, and 2 ounces of protein a day. Help your toddler eat well by offering healthy foods including dairy products, iron-fortified cereals, whole grains, fruit, vegetables, and protein. Limit added sugars and watch out for choking hazards. It's fine to give your toddler a vegan or vegetarian diet as long as you make sure to include enough essential nutrients.
Expect your little one to have about 2 cups of milk or yogurt, 3 ounces of whole grains, 1 cup each of fruit and vegetables, and 2 ounces of protein a day. Help your toddler eat well by offering healthy foods including dairy products, iron-fortified cereals, whole grains, fruit, vegetables, and protein. Limit added sugars and watch out for choking hazards. It's fine to give your toddler a vegan or vegetarian diet as long as you make sure to include enough essential nutrients.
Photo credit: Thinkstock
Use this guide to find out what and how much to feed your toddler. Don't worry if your child eats more or less than the amounts suggested – they're meant as general guidelines.
Your toddler may actually seem to eat less than before, and that's perfectly normal at this stage. If you wonder whether your child is getting enough calories, follow this guideline: The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children get about 40 calories a day for every inch of height.
(See our article about what to feed children younger 12 months. )
)
What to feed a 1-year-old
Developmental milestones
- Can use a spoon (though proficiency will take a while!)
What to feed
- Whole milk
- Other dairy products (soft pasteurized cheese, full-fat yogurt and cottage cheese)
- Iron-fortified cereals (oats, barley, wheat, mixed cereals)
- Other grains (whole wheat bread, pasta, rice)
- Fruits (melon, papaya, apricot, grapefruit)
- Vegetables (broccoli and cauliflower "trees," cooked until soft)
- Protein (eggs, beans, thinly spread peanut butter, small pieces of meat, poultry, boneless fish, or tofu)
- Honey
How much per day
- 2 cups milk, or 2 cups yogurt, or 1 1/2 to 2 ounces cheese
- 3 ounces grains, at least half whole grains (1 ounce = 1 cup cold cereal, 1/2 cup pasta or rice, one slice of bread)
- 1 cup fruit (fresh, frozen, or canned. Cut fresh fruits into very small pieces.
 )
) - 1 cup vegetables (a variety cut in small pieces and cooked well)
- 2 ounces protein (1 ounce = one slice of sandwich meat, about 1/3 of a chicken breast, 1/4 can of tuna, 1/4 cup cooked dry beans, or one egg)
Feeding tips
- Experts used to say you shouldn't give a young child eggs, fish, or peanut products because the child might develop a food allergy. But the latest research from the American Academy of Pediatrics found no evidence to support this claim. Talk to your child's doctor if you have a family history of food allergies.
- Limit added sugars. Toddlers' added-sugar intake should be no more than 10 percent of their total daily calories. Keep in mind that these sugars and syrups creep into common foods toddlers love, from breakfast bars to mac n' cheese to flavored drinks. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and try to steer clear of foods that list 1 gram or more of "Added Sugars."
- Choking is still a danger.
 Learn more about which foods pose the greatest hazard.
Learn more about which foods pose the greatest hazard.
What to feed a 2-year-old
Developmental milestones
- Self-feeding
- Eagerness to make own food choices
What to feed
- Low-fat milk (It's okay to switch to low-fat or nonfat milk once your child is older than 2, but check with your child's doctor if you have questions.)
- Other dairy products (diced or grated cheese, low-fat yogurt, cottage cheese, pudding)
- Iron-fortified cereals (oats, barley, wheat, mixed cereals)
- Other grains (whole wheat bread and crackers, bagel pieces, pretzels, ready-to-eat cereal, pasta, rice)
- Fruits (sliced fresh or canned)
- Dried fruit, soaked until soft to prevent choking (apples, apricots, peaches, pears, dates, pitted prunes)
- Vegetables (a variety cut in small pieces and cooked well)
- Protein (eggs, beans, thinly spread peanut butter, small pieces of meat, poultry, boneless fish, or tofu)
- Combo foods like macaroni and cheese, casseroles
How much per day
- 2 cups milk, or 2 cups yogurt, or 1 1/2 to 2 ounces cheese
- 3 ounces grains, at least half whole grains (1 ounce = one slice of bread, 1 cup ready-to-eat cereal, or 1/2 cup of cooked rice, cooked whole wheat pasta, or cooked oatmeal)
- 1 cup fruit (fresh, frozen, canned, or dried.
 Cut fresh fruits into very small pieces.)
Cut fresh fruits into very small pieces.) - 1 cup vegetables (a variety cut in small pieces and cooked well)
- 2 ounces protein (1 ounce = 1/4 cup cooked dry beans or peas, one egg, 1 ounce of meat, poultry, or fish)
Feeding tips
- Experts used to say you shouldn't give a young child eggs, fish, or peanut products because the child might develop a food allergy. But the latest research from the American Academy of Pediatrics found no evidence to support this claim. Talk to your child's doctor if you have a family history of food allergies.
- Limit added sugars. Toddlers' added-sugar intake should be no more than 10 percent of their total daily calories. Keep in mind that these sugars and syrups creep into common foods toddlers love, from breakfast bars to mac n' cheese to flavored drinks. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and try to steer clear of foods that list 1 gram or more of "Added Sugars."
- At this age, children can have strong opinions about food.
 Let your child have a say in what to eat, while you provide the balance, boundaries, and encouragement to make healthy choices.
Let your child have a say in what to eat, while you provide the balance, boundaries, and encouragement to make healthy choices. - Choking is still a danger. Learn more about which foods pose the greatest hazard.
What if we're vegetarians?
If you're a vegan or vegetarian, you can still provide your infant or toddler with everything she needs. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and American Academy of Pediatrics agree that well-planned vegetarian and vegan diets are fine for infants and toddlers. Just pay attention to make sure your child gets plenty of the following nutrients:
- Vitamin B12: Vegetarians can get this nutrient from milk products and eggs. Vegans can use fortified soy beverages, cereals, and meat substitutes.
- Vitamin D: Breastfed babies should get an additional 400 IU per day from fortified cow's milk or soy milk.
- Calcium: Vegan babies may need calcium-fortified foods, beverages, or supplements.
 Check with your doctor or a dietitian.
Check with your doctor or a dietitian. - Zinc: This important nutrient helps the immune system and can be found in beans, fortified cereal, milk, and wheat germ.
- Iron: You can find this mineral in iron-fortified cereal or supplements. Serve with foods high in vitamin C – like oranges, tomatoes, and strawberries – to improve iron absorption.
- Protein: Vegetarians can get added protein from yogurt and eggs. Vegans can get plant proteins from beans, cereals, and fortified soy milk.
- Fiber: Good sources of fiber include whole grain breads, fortified cereals and pastas, and high-fat plant foods like sunflower butter and avocados.
Sources
BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies.
We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies.
AAP. 2016. Serving Sizes for Toddlers. American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/toddler/nutrition/Pages/Serving-Sizes-for-Toddlers.aspx [Accessed April 2021]
AAP. 2017. Feeding and Nutrition Tips: Your 2-Year-Old. American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/toddler/nutrition/Pages/Feeding-and-Nutrition-Your-Two-Year-Old.aspx [Accessed April 2021]
USDA. MyPlate. U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://www.myplate.gov/life-stages/toddlers [Accessed April 2021]
USDA and DHHS. 2020. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025. 9th Edition. U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://DietaryGuidelines.gov [Accessed April 2021]
Karisa Ding
Karisa Ding is a freelance health writer and editor with expertise in preconception, pregnancy, and parenting content. A mother of two, Ding finds great joy in supporting new and expectant parents by providing information they need for the life-changing journey ahead. Ding lives in San Francisco with her family.
A mother of two, Ding finds great joy in supporting new and expectant parents by providing information they need for the life-changing journey ahead. Ding lives in San Francisco with her family.
Complementary foods at 4 months | Useful tips from the Tyoma brand
It is well known that the ideal time to introduce complementary foods is between 4 and 6 months of age. The presence of a child's teeth or the ability to sit are not signs of a child's readiness for complementary foods. It is important that the baby does not have a reflex of pushing the spoon with his tongue, and he can swallow food thicker than breast milk or formula well.
The pediatrician will help determine the exact start date for complementary foods, and in most cases this is the golden mean of 5-5.5 months. But there are situations when complementary foods need to be started from 4 months, including even a child who is exclusively breastfed.
In what cases are complementary foods introduced from 4 months?
- The child is not gaining weight well or is lagging behind in physical development.
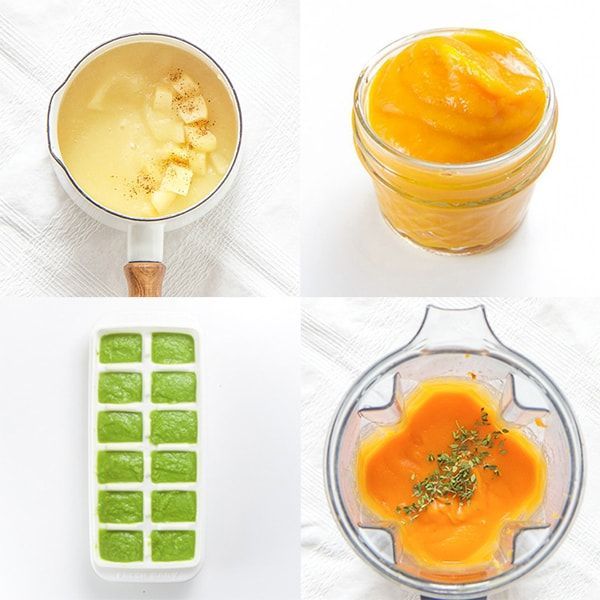

- The child has functional digestive disorders (regurgitation, constipation).
- The mother has little breast milk or it is poorly absorbed.
- The child has a reduced appetite or is not digesting formula well.
- The child has signs of iron deficiency (anemia).
- The child has a pronounced food interest: he watches with interest the food of adults, reaches for food.
- The child stopped eating formula and began to demand food more often.
How to start complementary foods at 4 months?
The first product of complementary foods, regardless of the age and type of feeding of the baby (breast or artificial), should be energy-intensive foods: either porridge or vegetable puree. Porridge can be chosen first if the child has loose or unstable stools, and also if the child is underweight. After 4-5 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge, butter can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of porridge in 150 g)
Mashed vegetables can be the first meal of the day if a child is prone to constipation, when it is better to choose zucchini, which can have a mild laxative effect on the child's stool. Starting from the 4-5th day of the introduction of vegetable puree, vegetable oil can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of vegetables in 150 g).
Starting from the 4-5th day of the introduction of vegetable puree, vegetable oil can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of vegetables in 150 g).
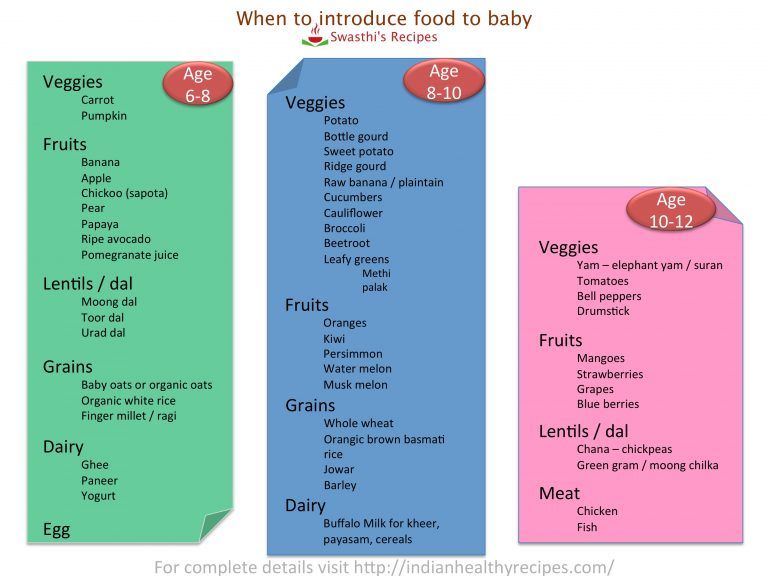
What foods can be introduced into the diet of a child at 4 months?
Kashi
Of the first cereals, it is better to give preference to buckwheat or rice. They must be dairy-free and can be diluted with water or breast milk, or the mixture that the baby eats. Later, you can introduce corn and oatmeal.
Vegetables
The first vegetable puree can be zucchini, broccoli, or cauliflower.
Fruit
The third type of complementary food can be fruit puree from apples or pears. Later, you can introduce mashed banana or apricot. At first, fruit puree can not be given to the child separately, but it is better to mix it with cereal or vegetables so that the child does not begin to prefer the sweet taste of fruits. When the amount of fruit puree reaches 50 g or more, it can also be given separately, for example, after the child has eaten porridge or for an afternoon snack.
Juices
Juices should not be the first feeding, in addition, they can not be introduced into the baby's first year of life at all, given their sweet taste and low nutritional value.
Can you make your own first meal?
You can prepare the first complementary foods yourself, but it is safer to use hypoallergenic monocomponent cereals or commercially produced purees prepared to high quality standards for baby food. In addition, it is important to consider that industrially produced baby cereals are often fortified with vitamins and minerals, which makes them especially useful for the first feeding.
How to start the introduction of a new product?
Complementary foods are introduced before breastfeeding or formula. The introduction of a new product should be gradual. But how is it?
- On day 1, give your baby 1 tsp. complementary foods before breastfeeding or formula
- On day 2 - 3 tsp.
 (15 g)
(15 g) - On day 3 - 6 tsp. (30 g)
- Day 4 - 50 g
- Day 5 - 70 g
- Day 7 - 100 g
- For 8-10 days - bring to 150 g.
Please note that if complementary foods are introduced from 4 months, then the introduction of 1 new product may take longer than the introduction of complementary foods from 5 or 6 months, namely up to 10 days or more, depending on the reaction of the baby.
Important!
If on the 8-10th day of the introduction of a new product, the baby still cannot eat 100-150 ml of porridge or puree at once, then this amount can be divided into 2 or even 3 doses, for example, give 50 ml of porridge in the morning, 50 ml in the afternoon and 50 ml in the evening. Why do this? So that the child gradually gets used not only to the new product, but also to its quantity. In the future, you need to try to gradually increase the one-time amount of the product to the age volume.
Questions and answers
Will the amount of breast milk decrease if we start introducing complementary foods from 4 months?
Of course, with the introduction of complementary foods, breast milk will be produced less, but only by the amount of complementary foods introduced. As long as you breastfeed your baby on demand and attach him to the breast every time after giving complementary foods, as well as maintaining nightly breastfeeds, you will maintain long-term successful breastfeeding.
Dear parents, remember that the introduction of complementary foods is a creative process that requires an individual approach and attention to the needs of the child. The proposed complementary feeding schemes in terms of time and quantity of introduced products are advisory in nature and do not imply their forced introduction.
Diet for a 4 year old baby
Your baby is already 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
You are still breastfeeding your baby or have had to switch to formula or formula feeding. The child is actively growing, and only with breast milk or infant formula, he can no longer always get all the necessary nutrients. And that means it's time to think about complementary foods.
The optimal time to start its introduction is between 4 and 6 months, whether the baby is receiving breast milk or formula. This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food. And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc.). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed.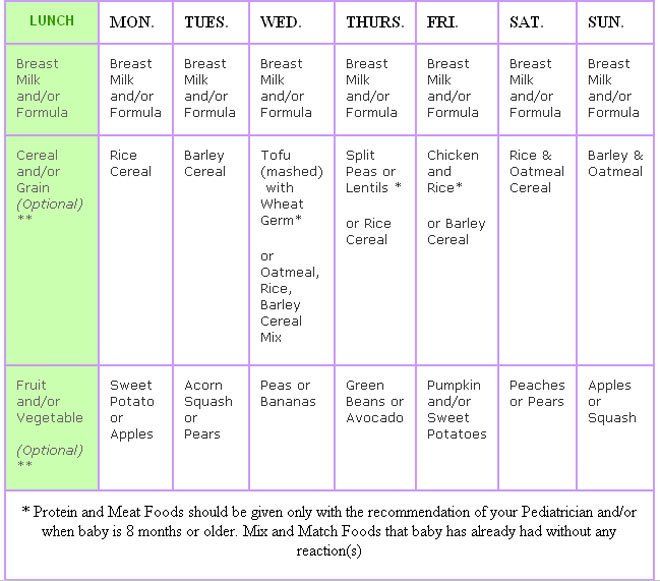 It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
When is it advisable to introduce complementary foods as early as 4 months, and when can you wait until 5.5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
The optimal time to start introducing complementary foods to a healthy baby is between 5 and 5.5 months of age.
The World Health Organization recommends that breastfed babies should be introduced to complementary foods from 6 months of age. From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on the big
practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born at term, without malnutrition (because in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows and develops well. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
The first food product can be vegetable puree or porridge, it is better to give fruit puree to the baby later - after tasty sweet fruits, children usually eat vegetable puree and cereals worse, often refuse them altogether.
Where is the best place to start? In cases where the child has a tendency to constipation or he puts on weight too quickly, preference should be given to vegetables. With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gain - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started the introduction of complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa.
If the first complementary foods are introduced at 6 months, it must be baby porridge enriched with iron and other minerals and vitamins, the intake of which with breast milk is no longer enough.
Another important complementary food product is mashed meat. It contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them. It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
But it is better to introduce juices later, when the child already receives the main complementary foods - vegetables, cereals, meat and fruits. After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
Juices should not be given between feedings, but after the child has eaten porridge or vegetables with meat puree, as well as for an afternoon snack. The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.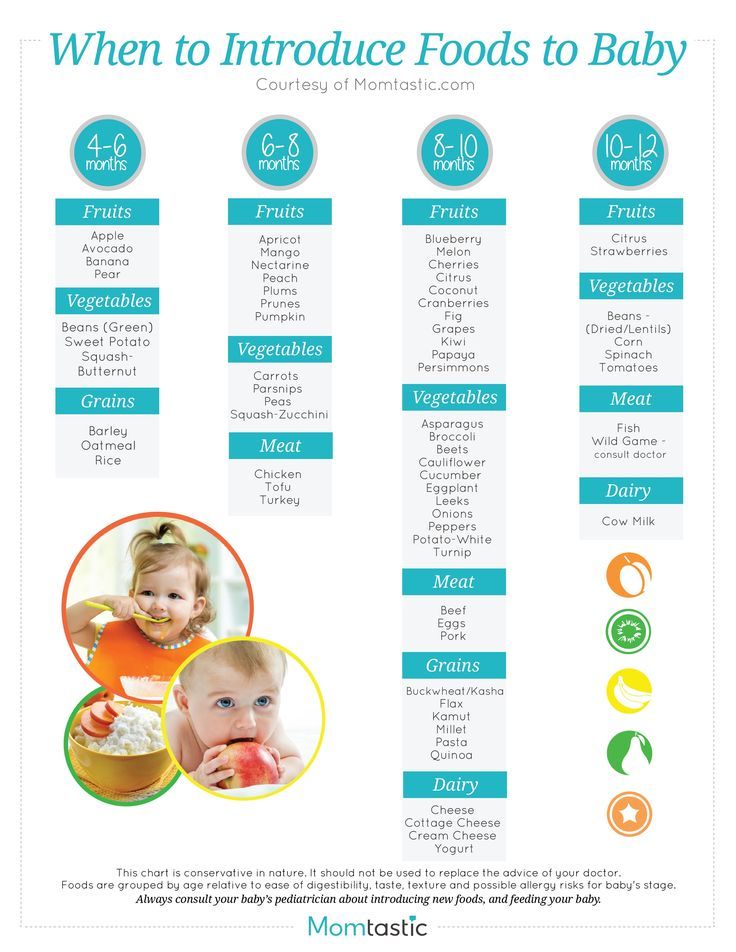
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to the 5-time feeding regimen.
Complementary feeding rules:
- Preference should be given to baby products of industrial production, they are made from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a guaranteed composition and degree of grinding
- Complementary foods should be offered to the baby by spoon at the start of feeding, before breastfeeding (formula feeding)
- the volume of the product increases gradually, starting with ½ - 1 spoon, and in 7 - 10 days we bring it to the age norm, subsequent products within the same group (cereals from other cereals or new vegetables) can be introduced faster, in 5 - 7 days
- start introduction with monocomponent products
- it is undesirable to give a new product in the afternoon, it is important to follow how the child reacts to it
- new products are not introduced in the event of acute illnesses, as well as before and immediately after prophylactic vaccination (should be abstained for several days)
When introducing a new type of complementary food, first try one product, gradually increasing its amount, and then gradually "dilute" this product with a new one. For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
After the introduction of one vegetable (bringing its volume to the required amount), you can proceed to the intake of porridge, and diversify the vegetable diet later.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up on your plan and continue to offer this vegetable in a small amount - 1-2 spoons daily, you can not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help to form the right taste habits in the baby.
Spoon-feed with patience and care. Forced feeding is unacceptable!
In the diet of healthy children, porridge is usually introduced after vegetables (with the exception of healthy breastfed children, when complementary foods are introduced from 6 months). It is better to start with dairy-free gluten-free cereals - buckwheat, corn, rice. At the same time, it is important to use porridge for baby food of industrial production, which contains a complex of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is already ready for use, you just need to dilute it with breast milk or the mixture that the baby receives.
Children suffering from food allergies are introduced complementary foods at 5-5.5 months. The rules for the introduction of products are the same as for healthy children, in all cases it is introduced slowly and begins with hypoallergenic products. Be sure to take into account individual tolerance. The difference is only in the correction of the diet, taking into account the identified allergens.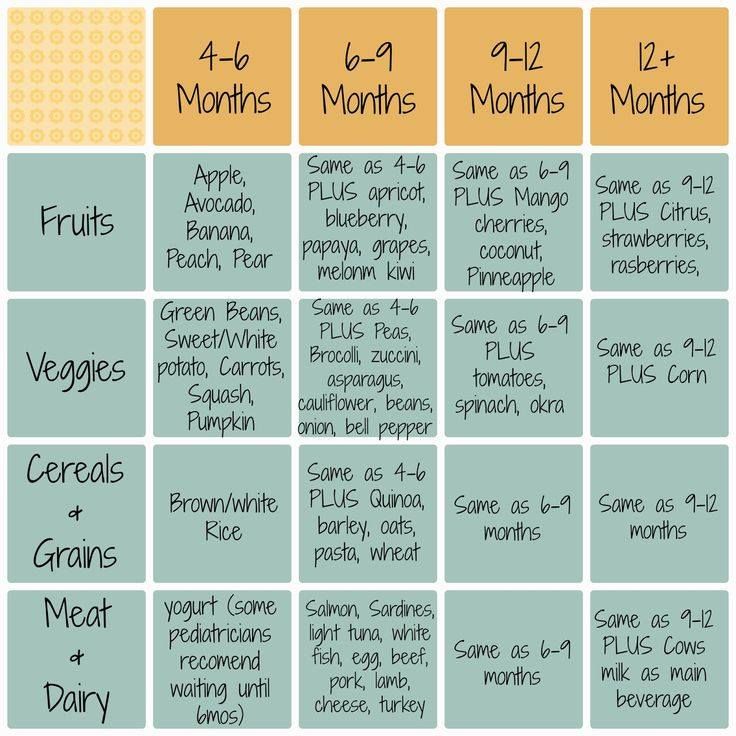 From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
Diets for different age periods
explain how to make a diet, it is better on several examples that will help to navigate the menu for your child.
From 5 months, the volume of one feeding is on average 200 ml.
Option 1
I feeding
6 hours
Breast milk or VHI*
200 ml
II feeding
10 hours
Dairy-free porridge**
Supplementation with breast milk or VHI*
150 g
50 ml
III feeding
14 hours
Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Supplemental breast milk or VHI*
150 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp
30 ml
IV feeding
18 hours
Fruit puree
Breast milk or VHI*
60 g
140 ml
V feeding
22 hours
Breast milk or VHI*
200 ml
* - Children's dairy mixture (VHI)
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 2.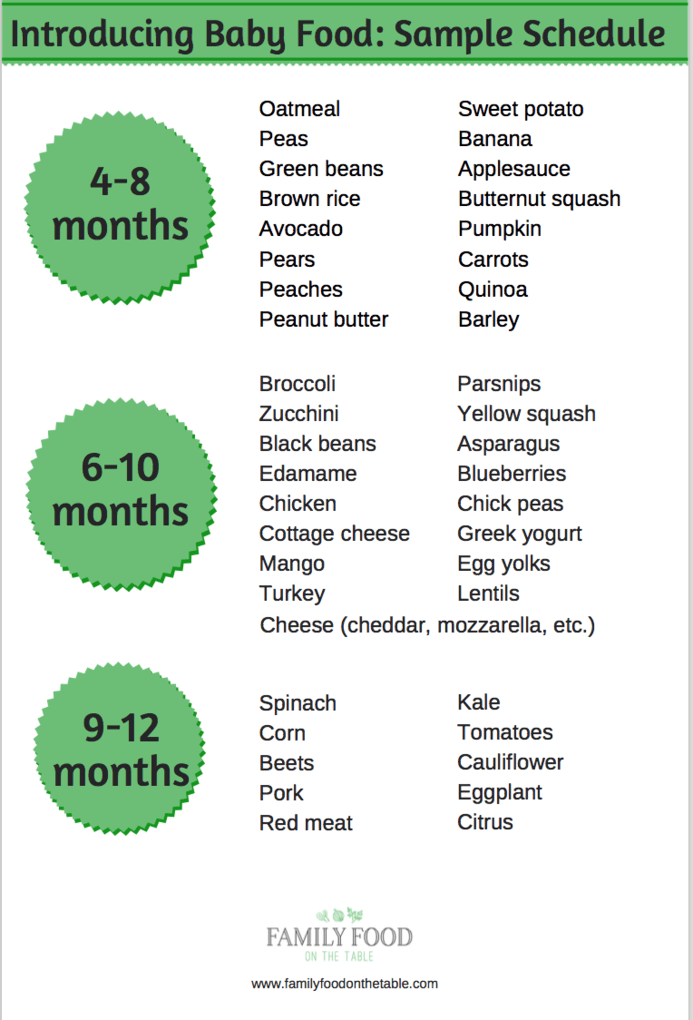
9000
9000 9000 9000 9000 9000
002
Another diet option for a 6-month-old baby, if complementary foods were introduced from 4-5 months:| I feeding | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
| II feeding | Dairy-free porridge** | 150 g |
| III feeding | Vegetable puree | 150 g |
| IV feeding | Fruit puree | 40 g |
| V feeding | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
* - infant formula
** - diluted with breast milk or VMS
Option 3.