Food restrictions for babies
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
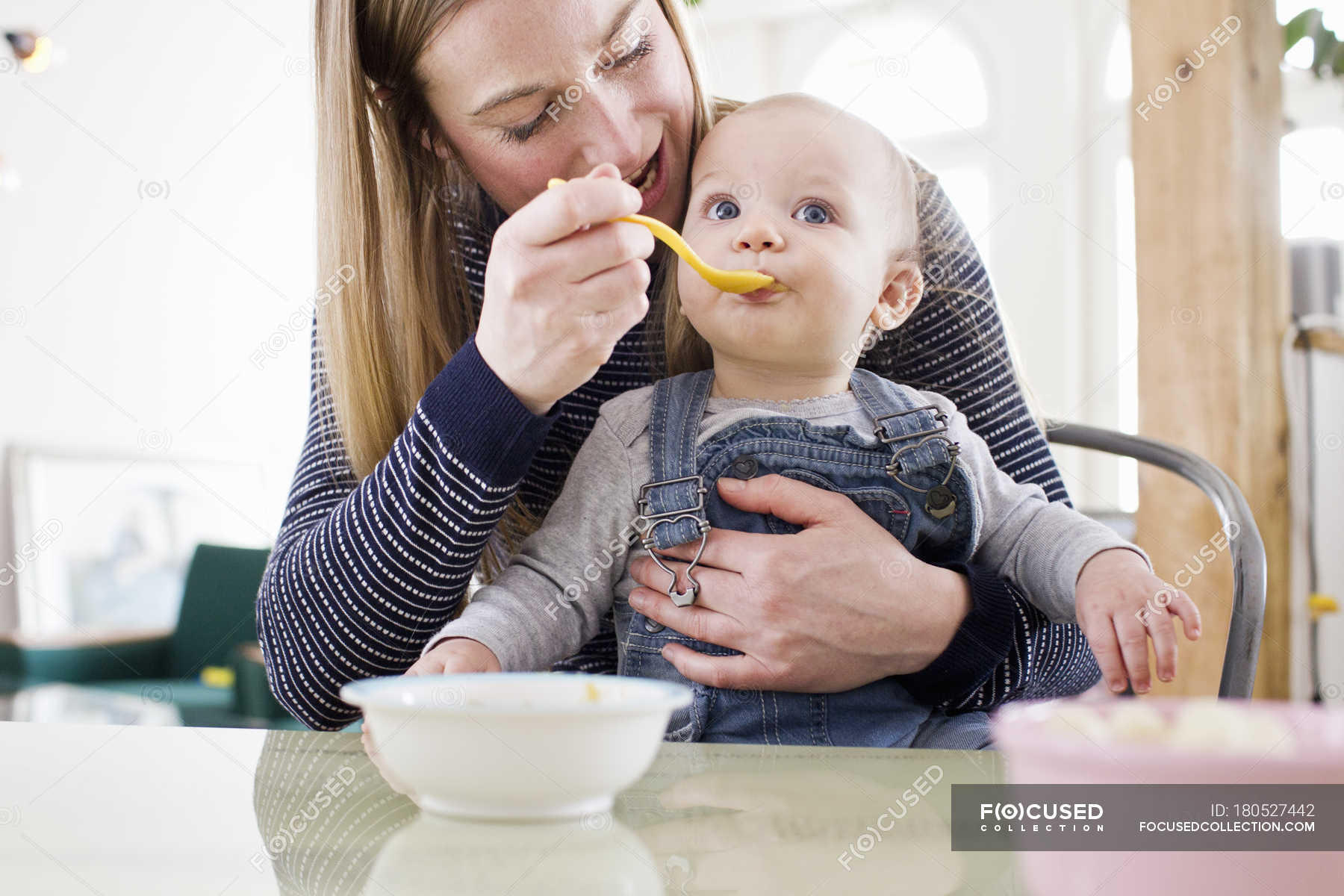
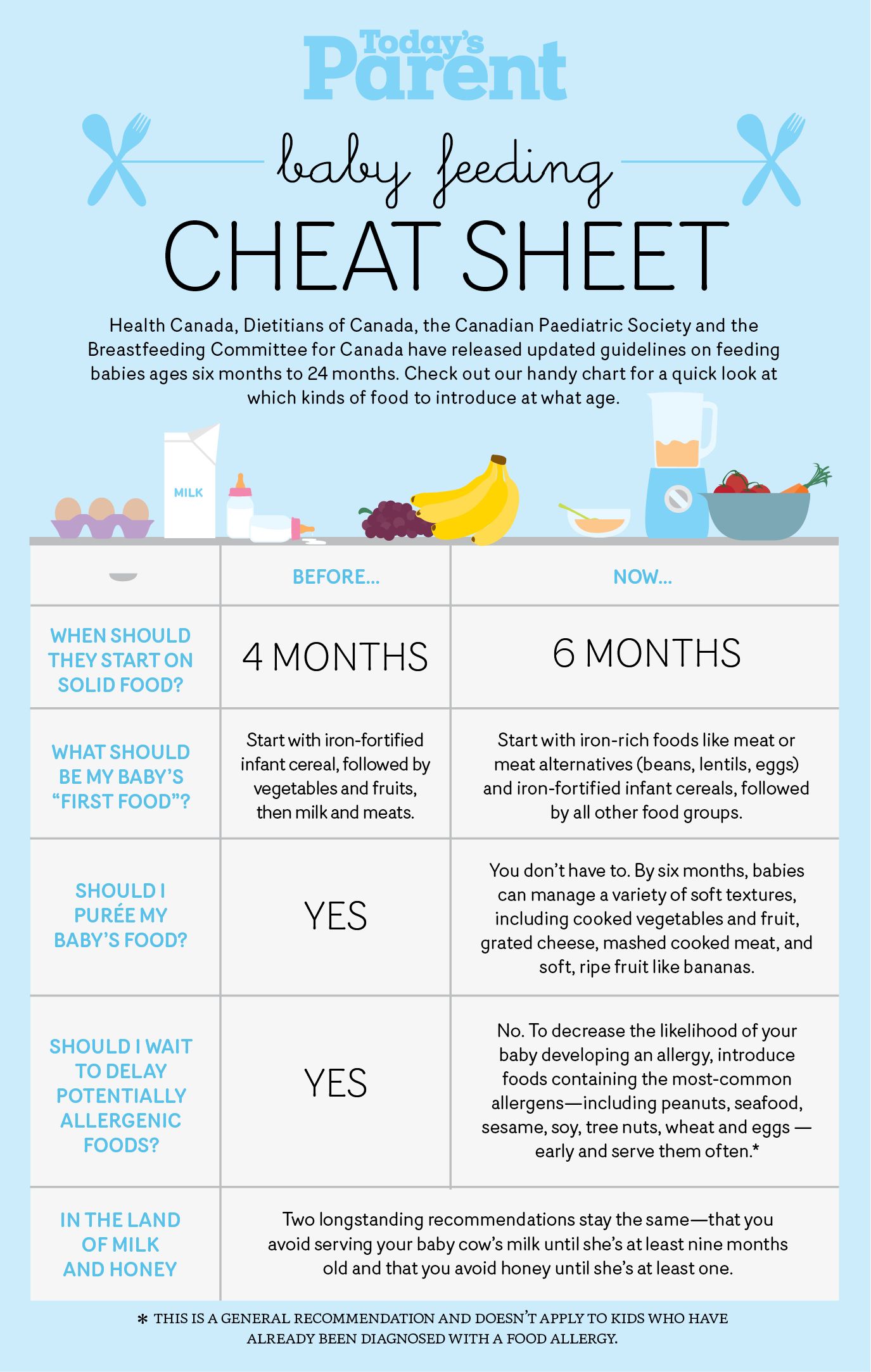
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Helpful Resources | Nutrition | CDC
If you would like more information on topics related to feeding your baby or toddler, here are some resources:
General
CDC’s Infant and Toddler Nutrition microsite syndication
CDC offers a free Web Content Syndication service that gives public health partners the opportunity to syndicate CDC content directly to their sites without having to monitor or copy updates. To search the CDC infant and toddler nutrition website available for syndication as well as other resources you can share, visit the CDC Public Health Media Library and browse or search for “infant and toddler nutrition”. Learn more about content syndication and how to add CDC syndicated content on your site.
To search the CDC infant and toddler nutrition website available for syndication as well as other resources you can share, visit the CDC Public Health Media Library and browse or search for “infant and toddler nutrition”. Learn more about content syndication and how to add CDC syndicated content on your site.
CDC’s Child and Teen Resources
This collection of resources provides parents and caregivers, health care providers, and partners with tools and information to help children and teens maintain a healthy weight and prevent obesity.
CDC’s Child Development Positive Parenting Tips (Infants)
This CDC website provides information about infants’ development, as well as tips for positive parenting and promoting the safety and health of infants.
CDC’s Learn the Signs. Act Early.
This website includes tools to track children’s milestones and resources about children’s development.
CDC’s Parent Information
This CDC website provides resources and information on pregnancy, infants and toddlers, children, and teens. Learn how to handle common parenting challenges through interactive activities, videos, and more. Healthcare professionals and researchers can also find information on children’s health and safety.
Learn how to handle common parenting challenges through interactive activities, videos, and more. Healthcare professionals and researchers can also find information on children’s health and safety.
CDC’s Division of Oral Health
Tooth decay (cavities) is one of the most common chronic diseases of childhood in the United States. Untreated tooth decay can cause pain and infections that may lead to problems with eating, speaking, playing, and learning. CDC’s Division of Oral Health provides information on what parents and caregivers can do to ensure good oral health for your child.
Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020–2025 pdf icon[PDF-30.6MB]external icon
These guidelines provide science-based advice for Americans on what to eat and drink to promote health, reduce chronic disease, and meet nutrient needs. The 2020–2025 edition provides recommendations for all life stages, including infants and toddlers.
Feeding Guidelines for Infants and Young Toddlers: A Responsive Parenting Approachexternal icon
This report presents recommendations for promoting healthy nutrition and feeding patterns for infants and toddlers from birth to 24 months, with an emphasis on dietary quality, portion sizes, and mealtime environment.
Healthy Childrenexternal icon
This website was developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics for parents. It features thousands of articles in English and Spanish on children’s health and safety, as well as interactive tools.
United States Department of Agriculture Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC)external icon
The WIC Program provides support to low-income pregnant, postpartum, and breastfeeding women, babies, and children up to age 5. WIC provides nutritious foods, information on healthy eating, breastfeeding promotion and support, and referrals to health care.
United States Department of Agriculture Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)external icon
SNAP provides benefits to low-income individuals and families and provides economic benefits to communities.
Feeding and Beverage Recommendationsexternal icon
Healthy Eating Research, a national program of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, offers science-based recommendations for parents and caregivers. Tips are available for feeding children from birth through 24 monthsexternal icon and beverages for children from birth through 5 yearsexternal icon. Tips for older children are also available.
Tips are available for feeding children from birth through 24 monthsexternal icon and beverages for children from birth through 5 yearsexternal icon. Tips for older children are also available.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Advice About Eating Fishexternal icon
The U.S. FDA and EPA provide advice regarding eating fish. This advice can help people make informed choices when it comes to the types of fish that are nutritious and safe to eat. It is especially important for those who might become pregnant, who are pregnant, or who are breastfeeding, as well as for parents and caregivers who are feeding children. This advice supports the recommendations of the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
Top of Page
Breastfeeding
CDC’s Breastfeeding Information
CDC’s Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity (DNPAO) is committed to increasing breastfeeding rates throughout the United States. CDC provides information for public health professionals and others to help support breastfeeding mothers, such as managing breastfeeding during various maternal and infant illnesses and conditions, any precautions for vaccines during breastfeeding, and recommendations for proper storage and handling of expressed human milk.
CDC provides information for public health professionals and others to help support breastfeeding mothers, such as managing breastfeeding during various maternal and infant illnesses and conditions, any precautions for vaccines during breastfeeding, and recommendations for proper storage and handling of expressed human milk.
International Lactation Consultant Association (ILCA)external icon
ILCA is the member association for professionals who care for breastfeeding families. ILCA’s “Find a Lactation Consultant Directory” can help you find a lactation consultant to get the breastfeeding support you need.
United States Lactation Consultant Association (USLCA)external icon
USLCA is a professional association for International Board Certified Lactation Consultants (IBCLCs) and other health care professionals who care for breastfeeding families. USLCA’s “Find an IBCLC” can help you find a lactation consultant to get the breastfeeding support you need.
WIC, the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children—Breastfeeding Support external icon
The United States Department of Agriculture Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) Breastfeeding Support website includes resources for expectant and current mothers about breastfeeding, overcoming common challenges, and thriving to make breastfeeding work for their families.
La Leche League USAexternal icon
La Leche League USA helps mothers to breastfeed through mother-to-mother support, encouragement, information, and education and promotes a better understanding of breastfeeding as an important element in the healthy development of the baby and mother.
Office on Women’s Healthexternal icon
The Office on Women’s Health’s vision is for all women and girls to achieve the best possible health outcomes. They provide information on breastfeeding to help women make infant feeding decisions and to guide mothers through the breastfeeding process.
Top of Page
Infant Formula
Questions & Answers for Consumers Concerning Infant Formulaexternal icon
The U.S. Food & Drug Administration regulates infant formula and has a list of questions and answers about infant formula.
Infant Formula Do’s and Don’tsexternal icon
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration provides information on infant formula preparation and storage, as well as other tips on how to keep infant formula safe.
Top of Page
Food Safety
Food Safety Concerns for Children Under Fiveexternal icon
Food safety is particularly important for young children. Foodsafety.gov provides information on safely preparing food for your child.
Top of Page
Meal Time
Fruits & Veggies—Have a Plant Movementexternal icon
A resource designed to help spread the word about the health benefits of adding more fruits and veggies to your diet.
USDA MyPlate Kitchenexternal icon
This online tool features a large collection of recipes and resources to support building healthy and budget-friendly meals. Site features include:
- Extensive search filters on cuisine, cooking equipment, nutrition content, and more.
- Detailed nutrition information.
- Cookbooks to browse and download or build your own.
- Recipe star ratings, review comments, and sharing on social networks.
Video Series on How to Introduce Solid Foods
1,000 Days has developed helpful videos about introducing solid foods to your baby.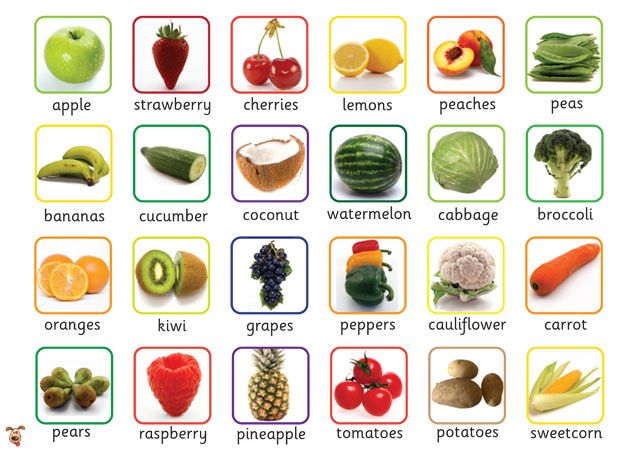 Topics include:
Topics include:
- Is your baby ready to start eating foods?
- What is a good first food for your baby?
- What to expect when introducing first foods
- How much should I feed my baby?
- How to win at mealtimeexternal icon
- What foods should my baby avoid?
- What should your baby eat in the first year?
Top of Page
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamin and Mineral Fact Sheetsexternal icon
The National Institutes of Health’s Office of Dietary Supplements has fact sheets for consumers and health professionals about vitamins, minerals, and dietary supplements.
Top of Page
Prohibited foods for children
List of prohibited foods for children.
Feeding a child with illness
What foods should not be eaten by children with various illnesses?
Anxious mood of parents is often associated with the problem of poor appetite of their own child. Moms and dads are worried about what to feed the child so that he eats with appetite and, God forbid, does not lose weight. But most of the problems arise with feeding the baby, when he has health problems and there are severe dietary restrictions. What kind of food should not be eaten by children with this or that disease?
Moms and dads are worried about what to feed the child so that he eats with appetite and, God forbid, does not lose weight. But most of the problems arise with feeding the baby, when he has health problems and there are severe dietary restrictions. What kind of food should not be eaten by children with this or that disease?
Prohibited foods for children
The small organism grows rapidly and requires proper and balanced nutrition for its development. Carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, macro- and microelements are necessary substances for the normal physiological development of muscle and bone tissue, the brain, the proper formation of internal organs: the heart, kidneys, lungs, spleen, liver.
Proper nutrition of a child in the first years of life determines his subsequent health and the possibility of self-realization in adulthood. Therefore, it is important to lay the foundation for proper nutrition from an early age in order to avoid health problems in the future.
What should not be eaten by children under one year old?
Most pediatricians have come to the conclusion that breastfed babies should not receive whole cow's and goat's milk in any form. If a child is deprived of the opportunity to receive mother's milk, then such children are recommended adapted milk formulas for breast milk.
Cow's and goat's milk
Cow's milk is considered heavy food for the baby. It contains a large amount of proteins, fats, mineral salts. The kidneys of the child begin to work with great effort, which leads to their overload. The liquid is excreted in a larger amount than necessary according to the physiological norm, which leads to the thirst of the baby. He receives a new portion of milk, so a "closed ring" is created.
Cow's milk does not contain enough iron for a growing baby. Goat's milk contains less vitamin A than cow's milk, although in other respects it is closest to mother's milk.
The use of cow's milk in the early period of life can lead to the development of diabetes, iron deficiency anemia, and allergic diseases.
In addition, babies under two years of age have not yet formed enzymes that can break down the nutritional components of cow's milk. As a rule, cow's milk is not completely absorbed by the child's body.
IMPORTANT: It is not recommended to give yogurt to children under one year old, as it has a high acidity and contains alcohol.
What should children under 3 not eat?
Sugar and salt
Salt and sugar should not be given to children, at least as long as they can be dispensed with. And it is best not to give these products until the age of three. Since the addition of salt and sugar is considered traditional in cooking, the baby will sooner or later get acquainted with the taste of salted and sweet food in kindergarten or school.
IMPORTANT: As shown by Roskontrol: many children's fermented milk products contain a high percentage of sugar. Therefore, babies should be given unsweetened and not very acidic natural fermented milk products with a short shelf life.
Semolina
Gone are the days when semolina was considered an indispensable product for baby food. It turns out that semolina contains gliadin, one of the components of gluten that makes it difficult for children's intestines to work. Fitin - another ingredient in semolina, inhibits the absorption of vitamin D and calcium.
Semolina gluten can cause allergic manifestations in a child in the form of red itchy spots. Excessive feeding of semolina often leads to overweight children, which is difficult to get rid of later.
Juice or puree?
Many pediatricians differ in their opinion: is it possible to give children juices of industrial production and their own preparation? Some allow giving juice to babies, other doctors do not recommend drinking juice for babies up to a year and a half, but insist on the use of fruit and vegetable purees. Their motivation is based on the fact that such food is rich in plant fiber and has a beneficial effect on the baby's intestines.
What should children 4-5 years old not eat?
Babies at the age of 4-5 years old parents often transfer to adult food.
IMPORTANT: Dairy and sour-milk products made according to general production standards, and not according to special baby food technology, are of particular danger to children.
Honey
Honey is a useful natural product containing many biologically active components, macro- and microelements, and vitamins. But this bee product can cause allergic manifestations. In early childhood, it is better to give up honey and carefully introduce it into baby food later.
Sausages and frankfurters
Sausages and frankfurters are allowed to be given to children after the age of three, prepared according to a special technology for baby food. Labels on such products are usually provided with inscriptions from what age this product can be consumed. There will be no great harm to the health of the child if he eats baby sausages no more than once every two weeks.
IMPORTANT: Roskontrol does not recommend giving young children sausage products intended for adult nutrition. These products contain many ingredients that are harmful to the child's body: preservatives, flavor enhancers, phosphates, nitrites and other harmful substances.
Chocolate
Sweet treats should not be given to babies for a number of reasons:
chocolate contains sugar
cocoa powder can provoke allergies
cocoa butter is difficult to digest in the gastrointestinal tract9 of a child
2 seafood and caviar red caviar is a healthy food product containing a lot of complete protein and other useful components. But this is not food for younger children. Sea food ingredients are very allergenic, besides, seafood products and red caviar are processed with many preservatives and have a strong salty taste, which is unacceptable in baby food.
Strawberries, citrus fruits and other exotic fruits
Beautiful and tasty exotic fruits and fruits: kiwi, avocado, citrus fruits, pineapple, can cause severe allergic skin manifestations not only in babies, but also in older children.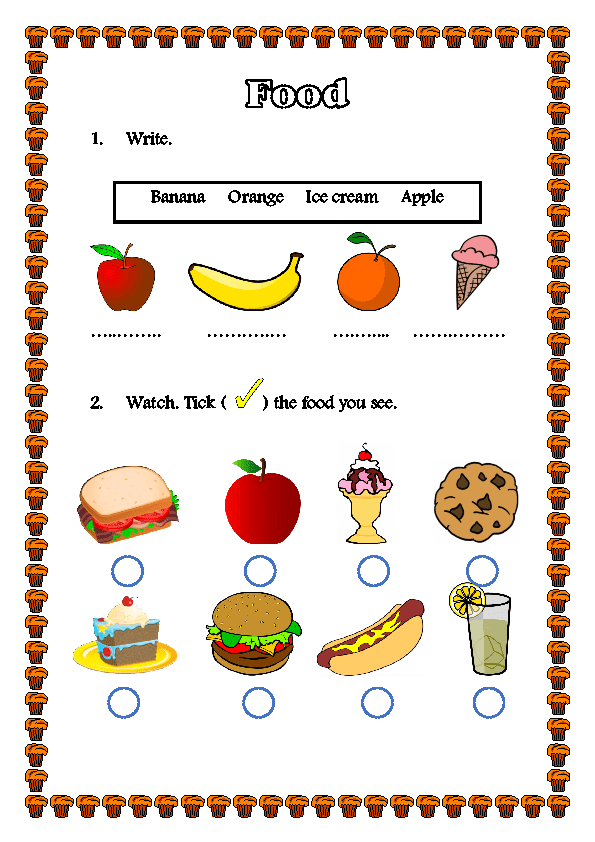 Strawberries, wild strawberries, raspberries also contain allergens, it is better not to give them to children, especially those who are prone to allergic reactions.
Strawberries, wild strawberries, raspberries also contain allergens, it is better not to give them to children, especially those who are prone to allergic reactions.
What is strictly prohibited for children to eat?
There are forbidden foods for babies in their first years of life:
whole milk
honey
mushrooms
Nuts
Black and green tea
Coffee
Chocolate
Fastfood
In the industrial production of children's food, there is a list of products unacceptable for children:
9000 with a concentration of more than 0.2%apricot kernels
sweeteners (except those special for dietary and baby food)
artificial flavors
benzoic and sorbic acids (they are used as preservatives)
hot and hot spices: pepper, mustard, horseradish
red meat, fish and poultry after refreezing
trans fats and hydrogenated oils
juice concentrates
food additives (various E additives not allowed in Russia for the production of baby food)
Prohibited products for children with various diseases
Childhood diseases are a test not only for the child's body, but also for parents. Only by the joint efforts of a doctor and loving moms and dads can the child’s recovery be accelerated, and these are: drug treatment, proper regimen and hygiene, good nutrition, excluding certain foods from the diet for various diseases.
Only by the joint efforts of a doctor and loving moms and dads can the child’s recovery be accelerated, and these are: drug treatment, proper regimen and hygiene, good nutrition, excluding certain foods from the diet for various diseases.
What should not be eaten in children with lactose?
Lactase deficiency is associated with the absence or insufficient amount of an enzyme that can break down milk sugar - lactose, which enters the body with dairy products.
In this disease, children experience disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: diarrhea or constipation, weight loss, fetid frothy stools, regurgitation, vomiting, colic, bloating.
If lactose intolerance is suspected, babies are placed on a lactose-free or low-lactose diet. After the diagnosis and treatment of the disease that caused lactase deficiency, the child undergoes control tests. With positive dynamics, the doctor may give permission for the gradual introduction of fermented milk products into the diet.
IMPORTANT: Lactose is not only found in milk and dairy products, it is used in the production of medicines, margarine, candy, bread, ham and sausages. Before buying certain products, you should carefully read their composition on the label.
What should not be eaten by children with angina?
Angina is a disease caused by viruses and bacteria. It is characterized by severe sore throat and high fever. During illness, the child's appetite is usually absent and this worries parents very much.
During an acute illness, do not force-feed your baby. Lack of appetite is a protective reaction of the body to the disease. After a few days, the child will begin to recover and the desire to eat will appear again.
Children with angina should not be given solid food. Food should be well ground, preferably to a puree state. Sour drinks, hot and cold dishes are contraindicated for an inflamed throat. Food should be warm and good tasting.
What should children not eat if they have allergies?
Allergic manifestations in children are caused by many reasons: food intolerance, drug intolerance, allergy to dust, animal dander, plant pollen, etc. During allergic manifestations, it is very important to adhere to the right diet and completely eliminate the products that provoke the appearance of allergies.
Allergic products
cow's milk
chicken eggs
bakery and pasta products containing gluten
honey
chocolate
citrus fruits
red berries: strawberries, wild strawberries, raspberries
chicken meat
seafood and some types of fish
Chickenpox is an infectious viral disease that affects almost all children attending preschool or school institutions. The acute period of the disease is associated with a rise in temperature, headache, itchy skin rashes in the form of fluid-filled vesicles.
To help your child cope with the disease and move to the recovery stage faster, you need to follow the right diet, consisting of healthy and complete foods. During illness, food should be excluded, which is difficult for the child's body to digest and can cause a number of complications from the gastrointestinal tract.
During illness, food should be excluded, which is difficult for the child's body to digest and can cause a number of complications from the gastrointestinal tract.
It is not recommended to feed a sick child with fatty, spicy, salty, sour and fried foods. Food should be balanced, light, soft, warm. Too hot and cold food is contraindicated for the child.
Foods to avoid during chicken pox:
milk
garlic
ginger
citrus fruits
red meat
Dysbacteriosis is a disease associated with disturbances in the normal intestinal microflora of the body. An imbalance between “beneficial bacteria” and pathogenic bacteria causes improper bowel function.
The child is concerned about:
intestinal motility disorder (constipation or diarrhea)
abdominal pain
vomiting
Bloating
Apathy and lethargy
Lack of appetite
causes of dysbiosis in children are different:
consequences of antibiotic therapy
9000 with dysbacteriosis and the exclusion of unacceptable products contribute to the rapid recovery of the baby.
Foods to avoid in dysbacteriosis:
sour berries and fruits (cherries, sour apples, cranberries, pomegranates, tangerines)
raw vegetables and fruits
products that cause fermentation in the intestines (grapes, cabbage, legumes, carbonated drinks)
sweets
canned food
smoked meats
fast food dishes
What should not be eaten when a child has colic?
Colic often accompanies the little man in the first months of life. The baby is born with a sterile intestine and an immature gastrointestinal tract. In the body of a child, there are still not enough enzymes that can fully break down food. That is why a nursing mother should pay great attention to her nutrition.
Products that should not be included in the diet of a nursing mother
whole milk
cabbage
SAMS WATER
store vegetables and fruit juices
Sweets and SDOBA
Chocolate
Freight
Bob
to prevent colic baby, the diet of a nursing mother should consist of steamed, boiled or baked foods. Preference should be given to vegetables and fruits with a green color. With further maturation of the child and the disappearance of colic, the choice of food products can be expanded, based on the recommendations of the doctor.
Preference should be given to vegetables and fruits with a green color. With further maturation of the child and the disappearance of colic, the choice of food products can be expanded, based on the recommendations of the doctor.
What should not be eaten if a child has diarrhea?
Diarrhea in a child can be caused by various reasons. These include poisoning, viral and infectious diseases, teething, gastrointestinal diseases, etc. But whatever the appearance of a digestive tract disorder is associated with, the key to a successful recovery of the body is properly prescribed nutrition for the disease
breastfeeding should not stop breastfeeding. Pediatricians recommend increasing the number of feedings, but reducing the dose of milk to avoid overfeeding and reduce the load on the baby's gastrointestinal tract
Formula-fed babies should be fed in the same way. That is, reduce the dose of formula for one feeding, but increase the frequency of feedings. In this case, it is recommended to use adapted fermented milk and low-lactate mixtures
In this case, it is recommended to use adapted fermented milk and low-lactate mixtures
For older children who have switched to "adult food", a special diet should also be developed by a doctor. At the same time, food must be prepared according to certain rules.
Food products that are difficult to digest and cause fermentation processes in the intestines should be discarded. Food is recommended to boil, bake, steam. Food products should be crushed with a blender or rubbed through a sieve. You can not eat fatty foods. Kashi (rice, oatmeal, buckwheat) should be boiled in water without adding milk.
Products prohibited by children
Fresh vegetables, fruits and berries
Fatty meat
Fresh bread
Assed products
Concentrated meat broth
What can not be eaten under the REMODISUS?
Rotavirus infection is called "intestinal flu". The disease is transmitted by viruses through food, especially dairy products. Babies from 6 months to 2 years of age are most often infected with a viral infection.
Babies from 6 months to 2 years of age are most often infected with a viral infection.
Intoxication of the child's body leads to fever, intestinal colic, liquid diarrhea, dehydration.
IMPORTANT: Young children become dehydrated very quickly. With intestinal flu, a loss of 10% of fluid can seriously affect the health of the baby, and in some cases even lead to death.
If the child is sick with rotavirus infection and refuses to eat, do not insist and force-feed the baby. But you need to drink the child often in small portions of water every half hour. This is an important and strict requirement that must be met in order to avoid fluid loss.
For intestinal flu in children, follow the recommendations:
In the acute period of infection, accompanied by high fever and vomiting, it is better not to feed the child, but to give him saline rehydration solutions and drinking water
water between feedings
Formula-fed babies should switch to lactose-free formulas during the period of illness, in consultation with the pediatrician.
Eliminate from the diet foods that irritate the intestines: fried, salty, canned foods, foods containing coarse fiber
Feed the child often in small portions cook boiled dairy-free cereals, weak meat and vegetable broths, give mashed fruits and vegetables, fermented milk products
IMPORTANT: Until the stool normalizes, the following should be excluded from the child's diet: whole milk, juices, fresh fruits and vegetables
What can not be eaten with stomatitis in children?
Stomatitis is a disease associated with inflammation of the oral mucosa. The disease causes the child suffering in the form of pain, high fever, inability to eat due to sores in the oral cavity. It is extremely difficult to feed a child with such a disease. This circumstance worries parents a lot.
Nutrition recommendations for a child with stomatitis
Do not feed your child with spicy, sour and salty foods that can irritate the oral mucosa
The temperature of food should be warm, comfortable for consumption. Hot and cold foods are not suitable for feeding a child
Hot and cold foods are not suitable for feeding a child
Cocoa, chocolate are excluded from the menu, sweet foods are limited as much as possible
Solid texture of food is not suitable for eating. Food should be in the form of purees, soups, liquid cereals
It is not recommended to eat dry bread and coarse-ground bakery products
Tomatoes, sour berries and fruits, citrus fruits are excluded from the diet.
Garlic, onion, radish, spices that irritate the oral mucosa are not allowed in the diet.
What not to eat when a child has a temperature. Lack of appetite and unwillingness to eat in the early days of illness is normal. You can not force the child to eat at this time.
At high temperatures, it is preferable for children to drink plenty of water in the form of sweetened teas, fruit drinks, compotes with dried fruits, jelly. Such drinks are rich in vitamins, which a sick child really needs.
IMPORTANT: At a high temperature, all dairy products should be excluded from the child's diet: whole milk, cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, cheese. It is not recommended to use cereals cooked in milk.
It is not recommended to use cereals cooked in milk.
Milk protein (casein) is practically indigestible at high temperatures. Products containing milk in the baby's stomach churn into a rubbery mass. When the temperature drops, there is a high risk of acetonemic syndrome, which manifests itself in the form of vomiting.
What not to eat after mantoux for a child
The Mantoux test is performed to diagnose tuberculosis in children. The examination is carried out by intradermal injection of tuberculin, which is a collection of filtrates of mycobacteria that died during heating.
Tuberculin is a strong allergen that can cause an allergic reaction in allergic children.
IMPORTANT: In order not to distort the child's true reaction to the Mantoux test, foods that can cause an allergic reaction should be excluded from his diet.
Allergen products that are not allowed before and after the Mantoux test:
cow's milk
fish
seafood (shrimps, lobsters, crayfish, oysters)
red caviar
eggs and broth3
chocolate
nuts
citrus and exotic fruits (pineapples, persimmons, mangoes)
fruits and berries with a predominance of red and bright orange pigment (strawberries, raspberries, red apples, apricots)
canned food
sweets
industrial food products with food additives (chips, crackers)
fast food
What should not be eaten by a child with constipation?
Due to the imperfection of the child's gastrointestinal tract, malnutrition, insufficient water intake and many other factors, children may develop constipation from time to time.
Thick and hard stools with pain, difficulty in defecation - all these signs of poor intestinal motility cause great suffering to babies.
Children's doctors are engaged in finding out the causes of constipation and treating this ailment. Often constipation occurs when the child is not eating properly and early transition to "adult food".
Products that are excluded from the nutrition for constipation
Fresh white bread and baking
pasta
semolina
mucous membranes
jelly
strong tea, coffee
90,000 problems with nutrition with nutrition of nutrition with nutrition. child - food restrictions: ru_psiholog — LiveJournal ?- children
- food
My daughter is almost five years old.
I would like to teach my daughter to eat right, or at least not make it a habit to eat high-calorie foods every day... turns out..So, my basic rule:
1. we don’t eat outside, we walk around because our hands are dirty (actually because it’s impossible to eat something non-caloric on the street, even if it’s possible, how can I explain to my daughter why on the street we can eat an apple, but not ice cream or a hamburger, I can’t say that I consider her predisposed to be overweight, I will never tell her about it!!!)
2. we eat sweets only on weekends, I tell my daughter : choose - ice cream or chupachups or something else. I explain this to her by the fact that it is often harmful to eat sweets, your teeth will hurt, but once a week you can (of course, I limit sweets not because of my teeth, but because if I somehow buy her sweets during the week she will ask him every day and how will I then refuse her what she used to allow, she will not understand me ... but the rule is that only on the weekend)Usually everything is fine with us, but this year I'm taking my daughter to dances, and I agreed to take my daughter's girlfriend, as her mother doesn't have time to get home from work.
 but this mother comes for her at the end of the lesson, pulls out pies,
but this mother comes for her at the end of the lesson, pulls out pies,
my daughter communicates closely with this girlfriend, and of course, she also wants these delicious pies,
And now my problems begin .....
a pie is not sweet, that is, it does not fit the category, but it can be a sausage in a dough, it can be a sweet cheesecake. But my daughter had dinner already in the kindergarten before the dance. it's only been 1.5 hours. We don't die of hunger, we can walk home. Previously, without this girlfriend, we always got home normally, didn’t demand food immediately, but ate dinner at home (that year, unlike this year, we didn’t have time to dine in the kindergarten, and sometimes I made my daughter a non-calorie cottage cheese cake), after dancing we even walked around without asking for food. that is, the food was sufficient. And now my daughter does not want to eat, she just wants something tasty, what her friend eats.My parents never forbade me anything, I didn't grow up fat.
 ....
.... What should I do, how can I restrict and pretend that I didn't restrict, suddenly, my daughter starts having problems because of this?
Maybe I made it up, and there is no problem, maybe I need to allow her these pies twice a week (but then I feel bad, because all the other days of the week my grandmother - I leave my daughter to her, while at work in the evening she cooks pasta for her since she wants nothing but pasta).
But if I smash all this, won't it become a bad habit, won't it turn into a fat person (my husband is very fat)?
I don't know who to ask for advice....
Tags: easy children
Subscribe
-
Unbearable guilt For almost a week now I have not found a place for myself, it comes to hysteria. I work in a bridal salon located in a cottage, behind the house there is…
-
I regret my talkativeness
Good afternoon everyone! I am here again for help.

-