Food to stop loose motion for babies
When your child has diarrhea: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
Diarrhea is the passage of loose or watery stools. For some children, diarrhea is mild and will go away within a few days. For others, it may last longer. It can make your child lose too much fluid (dehydrated) and feel weak.
The stomach flu is a common cause of diarrhea. Medical treatments, such as antibiotics and some cancer treatments can also cause diarrhea.
This article speaks of diarrhea in children over 1 year of age.
It is easy for a child with diarrhea to lose too much fluid and become dehydrated. Lost fluids need to be replaced. For most children, drinking the kinds of fluids they normally have should be enough.
Some water is OK. But too much water alone, at any age, can be harmful.
Other products, such as Pedialyte and Infalyte, may help keep a child well-hydrated. These products can be bought at the supermarket or pharmacy.
Popsicles and Jell-O can be good sources of fluids, especially if your child is vomiting. You can slowly get large amounts of fluids into children with these products.
You may also give your child watered-down fruit juice or broth.
Do not use medicines to slow down your child's diarrhea without talking to a doctor first. Ask your child's health care provider if using sports drinks is OK.
In many cases, you can continue feeding your child as usual. The diarrhea will normally go away in time, without any changes or treatment. But while children have diarrhea, they should:
- Eat small meals throughout the day instead of 3 big meals.
- Eat some salty foods, such as pretzels and soup.
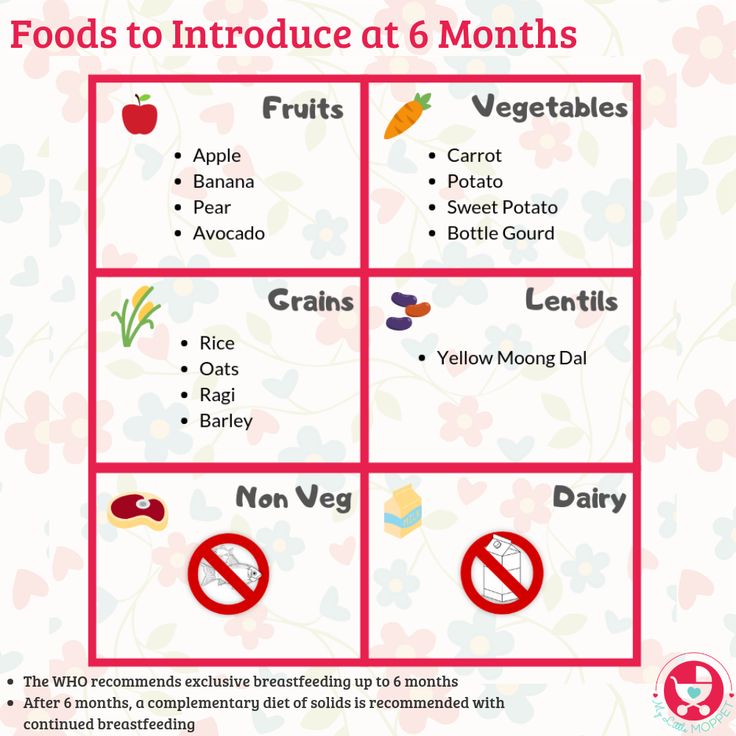
When necessary, changes in the diet may help. No specific diet is recommended. But children often do better with bland foods. Give your child foods such as:
- Baked or broiled beef, pork, chicken, fish, or turkey
- Cooked eggs
- Bananas and other fresh fruits
- Applesauce
- Bread products made from refined, white flour
- Pasta or white rice
- Cereals such as cream of wheat, farina, oatmeal, and cornflakes
- Pancakes and waffles made with white flour
- Cornbread, prepared or served with very little honey or syrup
- Cooked vegetables, such as carrots, green beans, mushrooms, beets, asparagus tips, acorn squash, and peeled zucchini
- Some desserts and snacks, such as Jell-O, popsicles, cakes, cookies, or sherbet
- Baked potatoes
In general, removing seeds and skins from these foods is best.
Use low-fat milk, cheese, or yogurt. If dairy products are making the diarrhea worse or causing gas and bloating, your child may need to stop eating or drinking dairy products for a few days.
Children should be allowed to take their time returning to their normal eating habits. For some children, a return to their regular diet can also bring a return of diarrhea. This is often due to mild problems the gut has while absorbing regular foods.
Children should avoid certain kinds of foods when they have diarrhea, including fried foods, greasy foods, processed or fast foods, pastries, donuts, and sausage.
Avoid giving children apple juice and full-strength fruit juices, as they can loosen stool.
Have your child limit or cut out milk and other dairy products if they are making diarrhea worse or causing gas and bloating.
Your child should avoid fruits and vegetables that can cause gas, such as broccoli, peppers, beans, peas, berries, prunes, chickpeas, green leafy vegetables, and corn.
Your child should also avoid caffeine and carbonated drinks at this time.
When children are ready for regular foods again, try giving them:
- Bananas
- Crackers
- Chicken
- Pasta
- Rice cereal
Call your child's provider if your child has any of these symptoms:
- Much less activity than normal (not sitting up at all or not looking around)
- Sunken eyes
- Dry and sticky mouth
- No tears when crying
- Not urinated for 6 hours
- Blood or mucus in the stool
- Fever that does not go away
- Stomach pain
Easter JS. Pediatric gastrointestinal disorders and dehydration. In: Bakes KM, Buchanan JA, Moreira ME, Byyny R, Pons PT, eds. Emergency Medicine Secrets. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 65.
Kotloff KL. Acute gastroenteritis in children. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 366.
21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 366.
Schiller LR, Sellin JH. Diarrhea. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 16.
Updated by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Browse the Encyclopedia
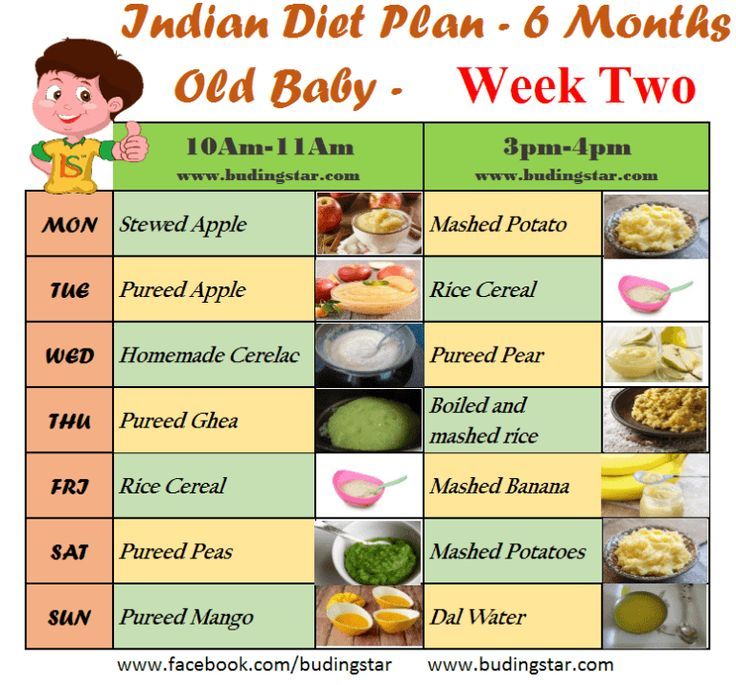
12 Helpful Foods to Give during Loose Motion in Baby & Toddler
The bodily functions in children develop as they grow. Babies and toddlers have a sensitive digestive system, and therefore, they have more chances of suffering from diarrhoea. They may not want to eat or drink anything. But, as a parent, you need to keep your kid hydrated. This article covers the foods you should and shouldn’t feed your child when he has loose motions. Let’s get started then.
Let’s get started then.
Video : Foods to Give and Avoid When a Baby & Toddler Has Diarrhoea
Foods You Should Give When Your Infant/Toddler Has Diarrhoea
The diet for a child with diarrhoea usually includes food items that are not only easy to digest but sometimes, also help resolve the problem.
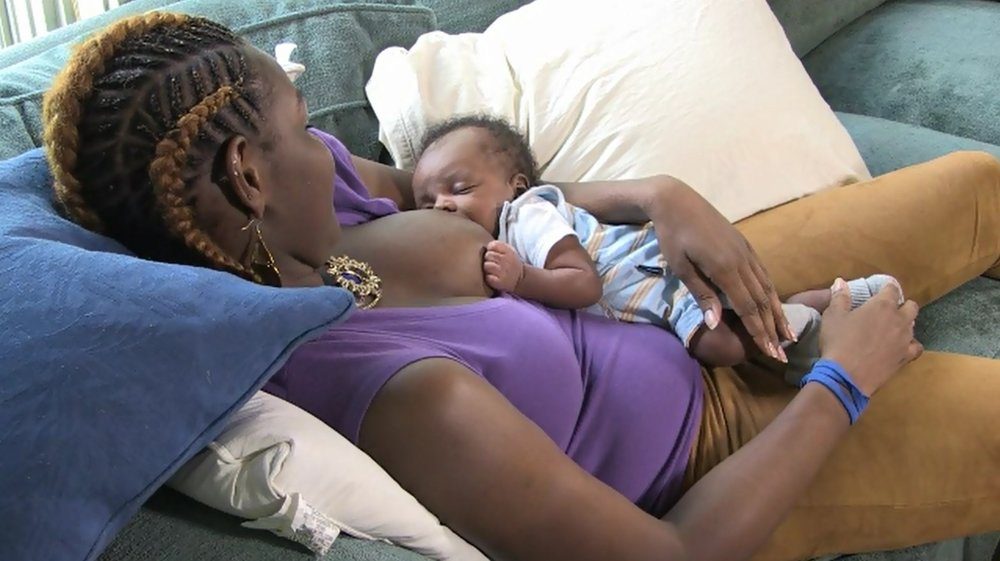
1. Breast Milk (0 Months+)
If your breastfeeding baby soils his diapers often, just stick to breast milk. Breast milk will keep him hydrated and also tackle his bowels.
2. Buttermilk (7 Months+)
Probiotics are very effective in battling diarrhoea. Give foods like curd, buttermilk or lassi yoghurt to your little one.
3. Rice Gruel (6 Months+)
Rice water can help your baby maintain the fluid levels in his body. It also helps to decrease the frequency of stools.
It also helps to decrease the frequency of stools.
4. Ginger
Many mothers and people from the earlier generations swear by the power of ginger in reducing the symptoms of diarrhoea. Usually, this is meant for kids that are slightly older and not young babies. Giving them ginger mixed with some rock salt and jaggery works on providing some relief from diarrhoea and indigestion. You may also try a decocotion or pramathya of carom seeds (ajwain), nagara or ginger (zingiber officinale), pippali (Piper longum), harad (Terminalia chebula), Vacha (Acorus calamus), which is very effective for treating diarrhoea.
5. Nutmeg
Also known as jaiphal in various parts of the country, this is yet another age-old remedy used in various Ayurvedic preparations till date. It is usually prepared by rubbing a small portion of the spice on a stone grinder to get some powder. This powder is then mixed with some water and given to babies. This remedy is an effective one to provide relief or treat diarrhoea in children over 6 months and under 10 years of age.
This remedy is an effective one to provide relief or treat diarrhoea in children over 6 months and under 10 years of age.
6. Lemon Water ( 8 Months+)
There seems to be no ailment that lemon can’t cure. Lemon replenishes the body with the lost fluids. Mix lemon juice with warm water and add some salt to make tasty and healthy lemon water.
7. Cumin Powder
This is a great remedy for improving digestion and stimulating hunger in babies older than 6 months. It can also provide relief from mild gastric pain and indigestion, but may not help control diarrhoea. Roast some cumin powder and fennel seeds in a pan. Boil the roasted spices in some water and let it cool. Feed the water to your child 2 to 3 times a day in small portions depending on your his age.
8. Vegetable Soup (8 Months+)
Babies’ bodies can easily absorb the nutrients from a clear veggie soup. Avoid using spices like pepper and gassy veggies like cauliflower, cabbage, sprouts and spinach during loose motions. You may add a pinch of roasted hing, and jeera powder to improve digestion.
You may add a pinch of roasted hing, and jeera powder to improve digestion.
9. Chicken Soup (9 Months+)
If you wish to try a non-veg soup, clear chicken soup is a great option. It digests easily and is nutritious for children with diarrhoea.
10. Tender Coconut Water (8 Months+)
Dehydration can take a toll on your little one. Coconut water has a lot of natural salts and minerals, along with natural glucose. And the best part is that coconut water works for breastfeeding babies, too!
11.
Sabudana (7 Months+)Khichdi or porridge made from sabudana is quite beneficial for kids during a bout of diarrhoea. Soak the sabudana, cook it, and strain the water. You can add salt or hing for flavour.
12. Baby Bananas (6 Months+)
Bananas help to harden your baby’s stools, thus relieving diarrhoea. Steam and cut the banana into small pieces before offering.
13. Boiled Potatoes (8 Months+)
Food items that have starch can provide nutrition to your baby. Mashed potatoes flavoured with cumin seeds reduce gas as well as work on diarrhoea.
Mashed potatoes flavoured with cumin seeds reduce gas as well as work on diarrhoea.
14. Pomegranate
If your kid has teeth and can chew well, you can feed him pomegranate seeds. Else, it is best to extract pomegranate juice and dilute it with enough water. Giving it to your baby once a day can work towards reducing diarrhoea in babies between 6 months and 5 years of age.
15.
Idli (8 Months+)Yes! Idlis are healthy and easily digestible, as the batter is fermented, but it’s role in controlling diarrhoea is debatable. Crush the idlis properly into small pieces before giving them to the child. Don’t feed chutney along with it.
16.
Moong Dal Soup (6 Months+)Cook a handful of moong dal with a pinch of turmeric powder in water. Then, drain the water and give it to your baby. It can help with stomach pain and diarrhoea.
17. White Bread (1 Year+)
This is yet another preferred food item during diarrhoea. White bread is made of refined flour that acts as a binding agent, and does’t have the fibre that encourages elimination. This bread can be eaten toasted or untoasted. Avoid using spreads, butter, jam, etc. as it will only aggravate the situation.
White bread is made of refined flour that acts as a binding agent, and does’t have the fibre that encourages elimination. This bread can be eaten toasted or untoasted. Avoid using spreads, butter, jam, etc. as it will only aggravate the situation.
18.
Bilva/Bel/Wood Apple SyrupA homemade syrup of bilva (bel/wood apple/Aegle Marmelos) can help control diarrhoea in babies older than 6 months of age. This remedy is useful for adults as well! The syrup can be made by soaking dried wood apples in water overnight, and boiling it in the same water the next day till the water reduces to half the quantity. Then, strain the syrup and let it cool. You may feed the syrup with a spoon to your little one, or dilute it in water to make a sherbet without any sugar.
Another way of making the syrup is to cut wood apples, take out the pulp, and soak it in twice the amount of water, i.e. the pulp to water ratio should be 1:2. When the pulp has soaked enough, mash it properly and sieve it. You can add a pinch of roasted cumin and hing to it. There is no need to mix sugar as its already a little sweet, but if your child has sugar in his diet and you think he could need some, add a small amount to sweeten the syrup.
You can add a pinch of roasted cumin and hing to it. There is no need to mix sugar as its already a little sweet, but if your child has sugar in his diet and you think he could need some, add a small amount to sweeten the syrup.
Foods You Should Avoid
The foods you shouldn’t give your baby/toddler when he has diarrhoea are:
- Dairy products except curd and buttermilk, and yoghurt
- Fruit juices
- Fizzy drinks
- Fruits that start with P (peaches, pears, prunes, plums)
- High fibre foods
- Dry fruits and nuts
- Sweets
- Raw veggies
Diarrhoea can make you quite anxious about your baby. Giving the right foods is the first step to recovery. If your baby’s health doesn’t improve, contact your paediatrician immediately.
Also Read:
Giving Enema for Babies and Kids
Cough Remedies for Kids at Night
Remedies for Stomach Pain in Toddlers
Healthy food - healthy child
Food - our friend or foe?
The choice of food is largely determined by the culture of the society and the country. The food culture is created by traditions over a long period of time, based on the products available in the area, environmental conditions, climate, lifestyle, religion and other related circumstances. Formed culture influences eating habits and behavior. It used to be thought that food culture could be saved, but it turned out to be very easy to destroy it, as evidenced by studies conducted in many parts of the world.
The food culture is created by traditions over a long period of time, based on the products available in the area, environmental conditions, climate, lifestyle, religion and other related circumstances. Formed culture influences eating habits and behavior. It used to be thought that food culture could be saved, but it turned out to be very easy to destroy it, as evidenced by studies conducted in many parts of the world.
Nowadays there is a change in the way people eat: both where they eat, how they cook, and how often they eat. There is also a decrease in physical activity, which leads to the development of nutrition-related diseases. Stir-frying is rapidly replacing healthier cooking methods, and eating habits such as "fast food" and eating out have become very common.
In addition, the way people travel and spend their leisure time has changed. For children, such activities as watching television programs and computer games have become important. The decrease in physical activity is quite noticeable: the use of personal or public transport for transportation significantly exceeds walking. And each of these factors significantly increases obesity.
And each of these factors significantly increases obesity.
Recent studies have shown that a modern physically inactive lifestyle combined with modern dietary principles in an urban environment leads to excessive weight gain, which can lead to an association between stunting, due to insufficient intake of nutrients necessary for a growing body, obesity, hypertension and diabetes.
The incidence of obesity has increased dramatically, which is of great concern. White adipose tissue is not only a depot for storing excess calories as energy, but also an active endocrine organ involved in the regulation of metabolic and immunological processes in the body. In recent years, it has become clear that obesity is associated with low-grade chronic inflammation, which is a unifying factor in the development of many of the complications of obesity. The inflammatory response in obesity occurs in adipose tissue, although other organs such as the liver may also be involved in disease progression.
Therefore, changes in diet and physical activity should be the first steps in the fight against obesity. It is necessary to stop the epidemic of a new disease, which is a combination of obesity and diabetes, for which a new term "diabesity" has even been proposed.
The energy requirement for infants, children and adolescents is the amount of energy needed to balance a desired level of physical activity and support optimal growth and development for long-term health. Evaluation of early nutrition, diet, as well as lifestyle, revealed a clear prevalence of obesity in children who had never been breastfed. Optimal nutrition during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and early development is important not only in terms of immediate outcomes such as fetal or infant weight gain and body composition, but can also have long-term effects on human health, well-being and vitality. in subsequent years. For infants, breast milk is considered the ideal nutrition, with sufficient protein intake to support growth and meet other body needs. The quantity and quality of protein is also important. The need for protein and energy to maintain normal growth is greatest during infancy, after which there is a gradual decrease. After about two years, only a small part of the protein and energy intake is used to support growth, that is, to increase body size; most of it is spent on maintaining and replacing tissues. Chronic malnutrition during infancy and early childhood leads to poor growth, delayed motor skill development, and reduced motor activity, resulting in underfitness. During sports games, these children do not compete in terms of physical development with their peers who receive better nutrition. Thus, the consumption of high quality proteins rich in essential amino acids is recommended, it is important that they are obtained from animal products such as meat, poultry, eggs, dairy products. High consumption of foods and drinks containing fructose can increase the risk of obesity, insulin resistance and, ultimately, type 2 diabetes.
The quantity and quality of protein is also important. The need for protein and energy to maintain normal growth is greatest during infancy, after which there is a gradual decrease. After about two years, only a small part of the protein and energy intake is used to support growth, that is, to increase body size; most of it is spent on maintaining and replacing tissues. Chronic malnutrition during infancy and early childhood leads to poor growth, delayed motor skill development, and reduced motor activity, resulting in underfitness. During sports games, these children do not compete in terms of physical development with their peers who receive better nutrition. Thus, the consumption of high quality proteins rich in essential amino acids is recommended, it is important that they are obtained from animal products such as meat, poultry, eggs, dairy products. High consumption of foods and drinks containing fructose can increase the risk of obesity, insulin resistance and, ultimately, type 2 diabetes. Active consumption of whole grains (in the form of porridge), fruits and vegetables is recommended, taking into account the content of important dietary components in them.
Active consumption of whole grains (in the form of porridge), fruits and vegetables is recommended, taking into account the content of important dietary components in them.
Trans fat is a product of the hydrogenation process of vegetable oils. The use of trans fats extends the shelf life of products, which is in the interest of manufacturers and retailers. This causes great harm to the body, especially growing, resulting in an increase in the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, it is very important to monitor the quality of fats and the amount of sugar and its substitutes in products.
Physical activity does not affect a child's growth and biological maturation, but is an important mechanism for regulating body weight, as well as the functioning of skeletal muscle and bone tissue. According to studies, school-age children need at least one hour of active physical activity daily. Activity should correspond to the level of development, bring joy and be varied.
Energy expenditure for physical activity differs between obese and non-obese children. Data based on questionnaires, registration of changes in heart rate and analysis of time and movement suggest that children and adolescents with obesity are less active, it is more difficult for them to move their body in space, for example, to run, jump. Mechanically, fat is an inert load (dead weight) that needs to be moved. Children and adolescents with obesity are also characterized by a decrease in the fitness of the cardiovascular system. Regular physical activity is important for the development of behavior, it has a significant impact on maintaining health and is one of the ways to prevent diseases.
High weight gain during infancy and during the second year of a child's life is a predictor of an increased risk of overweight and obesity later in life. Thus, it seems reasonable to avoid feeding practices that result in excessive weight gain during early development. Food preferences formed in the first year of life tend to be preserved, but they can change under the influence of parents, siblings, and play partners. School-age children and schoolchildren come into contact more and more with representatives of different social groups, thus getting to know other food preferences. Many children choose not to eat at home, preferring ready-to-eat foods such as fast food and sweets.
School-age children and schoolchildren come into contact more and more with representatives of different social groups, thus getting to know other food preferences. Many children choose not to eat at home, preferring ready-to-eat foods such as fast food and sweets.
The prevalence of the use of products not intended for this age category:
| products | Number of children, % | products |
| 12-23 | 24-35 months | 12-23 months | 24-35 months |

 All adolescents should receive safe food in adequate quantities to promote optimal physical growth, cognitive, social and emotional development. This is very important to remember, as some chronic diseases of adult life begin at this age.
All adolescents should receive safe food in adequate quantities to promote optimal physical growth, cognitive, social and emotional development. This is very important to remember, as some chronic diseases of adult life begin at this age.  Peer opinion tends to conformism, partly this opinion is determined by pressure from the media, aggressive advertising promoting fast food, which in turn leads to regular overeating. The role of parents in shaping the food preferences of a teenager is very important; depending on what the parents themselves eat, their influence can be either positive or negative. Nowadays, many teenagers consume a lot of sweetened drinks, french fries, pizza, hamburgers, while paying little attention to fruits, vegetables, dairy products, lean meats and fish. If dietary iron intake is too low and menstrual blood loss increases, girls can develop iron deficiency anemia, which can limit growth. In addition, the prevalence of obesity is increasing due to a sedentary lifestyle. This disease leads in the future to atherosclerosis, hypertension, metabolic disorders.
Peer opinion tends to conformism, partly this opinion is determined by pressure from the media, aggressive advertising promoting fast food, which in turn leads to regular overeating. The role of parents in shaping the food preferences of a teenager is very important; depending on what the parents themselves eat, their influence can be either positive or negative. Nowadays, many teenagers consume a lot of sweetened drinks, french fries, pizza, hamburgers, while paying little attention to fruits, vegetables, dairy products, lean meats and fish. If dietary iron intake is too low and menstrual blood loss increases, girls can develop iron deficiency anemia, which can limit growth. In addition, the prevalence of obesity is increasing due to a sedentary lifestyle. This disease leads in the future to atherosclerosis, hypertension, metabolic disorders.  Throughout childhood and adolescence, the family must manage exposure to risk factors and prevent diet-related diseases. All possible health risk behaviors that can lead to eating disorders, such as anorexia, bulimia, food addiction, should be prevented, prevented or detected as early as possible. Change in eating behavior and activity should not be forced, this process should be gradual, and the efforts of both the child and parents are important for its success.
Throughout childhood and adolescence, the family must manage exposure to risk factors and prevent diet-related diseases. All possible health risk behaviors that can lead to eating disorders, such as anorexia, bulimia, food addiction, should be prevented, prevented or detected as early as possible. Change in eating behavior and activity should not be forced, this process should be gradual, and the efforts of both the child and parents are important for its success.  Subject to a timely response, the problem can be eliminated with medication.
Subject to a timely response, the problem can be eliminated with medication. 
 The choice of conditioners is wide. Their main function is the removal of inflammation, the removal of pathogenic bacteria. The action is achieved due to the antiseptics contained in the preparations, which suppress the reproduction of bacteria. Rinses also help fight bad breath.
The choice of conditioners is wide. Their main function is the removal of inflammation, the removal of pathogenic bacteria. The action is achieved due to the antiseptics contained in the preparations, which suppress the reproduction of bacteria. Rinses also help fight bad breath.  Not just gum disease, periodontal disease, but also periodontitis, gingivitis. Perhaps the spread of infection in the soft tissues has begun, which, if started, will lead to the need for complex and expensive treatment:
Not just gum disease, periodontal disease, but also periodontitis, gingivitis. Perhaps the spread of infection in the soft tissues has begun, which, if started, will lead to the need for complex and expensive treatment: