Food with vitamin c for babies
Vitamin C for Babies: Safety, Efficacy, and Dosage
Becoming a parent can be one of the most joyous and challenging experiences of your life.
One of the first lessons every new parent learns is how to make sure your baby is well fed and adequately nourished throughout each stage of their life.
Vitamin C is an important nutrient that’s essential for optimal health across the life cycle.
Many new parents wonder if their infants are getting enough vitamin C and whether a supplement is ever necessary.
This article reviews everything you need to know about vitamin C for babies, including what it is, how much is needed, and how to make sure your baby is getting enough every day.
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble nutrient that plays a critical role in a variety of your baby’s most vital physical functions.
It’s essential for maintaining a healthy immune system, enhancing iron absorption, and producing collagen, the most abundant protein in the human body (1).
Vitamin C is unique to many other nutrients because it also functions as an antioxidant. Antioxidants help protect cells from free radical damage (2).
Free radicals are highly volatile, cell-damaging chemicals that are a byproduct of normal human metabolism. Antioxidants like vitamin C can bind to free radicals, making them unable to harm surrounding tissues (2).
Vitamin C is considered an essential nutrient, which means your baby’s body can’t produce it by itself. Therefore, it must be obtained from the foods they consume each day.
This nutrient can be found in breastmilk, infant formula, and many types of fruits and vegetables.
Vitamin C requirements for infants
Though essential throughout every stage of life, infants need less vitamin C than adults.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends that babies receive the following amount of vitamin C each day (3):
- 0–6 months of age: 40 milligrams (mg)
- 6–12 months: 50 mg
Women who are breastfeeding have increased vitamin C requirements because they’re supplying the baby with vitamin C through their breastmilk.
If you’re breastfeeding, aim to consume 120 mg of vitamin C per day. This is about 60% more than the amount required for women who aren’t breastfeeding (3).
Infant formulas also contain vitamin C. Thus, if your baby is formula fed, they’ll be able to meet their vitamin C needs.
summaryVitamin C is an essential nutrient that supports immunity and collagen production. It also functions as an antioxidant. Babies require 40–50 mg of vitamin C per day, depending on their age.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), infant formula, breastmilk, and food should be the only sources of vitamin C your baby consumes (3).
Supplementing with vitamin C is unnecessary for most healthy babies and could increase their risk of developing symptoms associated with vitamin C toxicity.
Possible side effects associated with overconsumption of vitamin C include kidney stones, nausea, and diarrhea (3).
The U.K.’s National Health Service (NHS) only advises that vitamins and mineral supplements be given to infants 6 months of age or older (4).
Supplementing at 6 months is recommended for infants who aren’t breastfeeding and consume less than 16 ounces (500 mL) of formula per day (4).
If taking a supplement is deemed necessary, the dosage should be determined by your baby’s healthcare provider (4).
When supplementing may be appropriate
If you suspect that your baby isn’t getting enough vitamin C, taking a supplement may be necessary.
Vitamin C deficiencies are rare in developed countries, but babies with neurodevelopmental disorders, digestive dysfunction, or cancer may be at an increased risk of developing them (5).
Severe vitamin C deficiency is the root cause of a serious medical condition known as scurvy.
Symptoms include bleeding gums, bruising, fatigue, loss of appetite, and irritability. If scurvy is left untreated, it can be fatal (1, 5).
You should never attempt to diagnose your baby with a vitamin deficiency on your own.
Be sure to consult with a qualified healthcare provider before adding any supplements to your baby’s diet. They can determine the safest, most appropriate dosage.
They can determine the safest, most appropriate dosage.
summaryVitamin C supplements are generally not recommended for babies. In rare instances, supplements may be required, but dosage should be determined by a qualified healthcare provider.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends beginning to introduce solid foods when your baby is about 6 months old (6).
This is the perfect time to start offering foods that are rich in vitamin C to help your baby continue meeting their nutrient needs as they grow.
At 6 months of age, most babies can meet their daily vitamin C requirements from a combination of food and formula or breastmilk (3).
Here are some examples of baby-friendly foods that are high in vitamin C (7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12):
- Red bell pepper, 1/4 cup (23 grams): 58% of the daily vitamin C recommendation for babies
- Strawberries, 1/4 cup (41 grams): 48% of the daily vitamin C recommendation for babies
- Kiwi, 1/4 cup (44 grams): 82% of the daily vitamin C recommendation for babies
- Tangerines, 1/4 cup (49 grams): 26% of the daily vitamin C recommendation for babies
- Cooked broccoli, 1/4 cup (24 grams): 31% of the daily vitamin C recommendation for babies
- Papaya, 1/4 cup (57 grams): 70% of the daily vitamin C recommendation for babies
Remember that every baby is different and not all of them will be particularly open to trying new foods right away. Be patient with them as they explore all the new flavors and textures that solid foods provide.
Be patient with them as they explore all the new flavors and textures that solid foods provide.
In the meantime, you can rest assured that your baby will get plenty of vitamin C from their formula or breastmilk.
summaryAt 6 months, you can begin introducing foods rich in vitamin C to your baby’s diet. Strawberries, bell peppers, broccoli, and tangerines are all excellent baby-friendly options.
One of the most important parts of caring for a new baby is ensuring they’re provided with adequate nutrition.
Vitamin C is an essential nutrient that plays an important role in immunity, collagen production, and protection from free radical damage.
Breastmilk, infant formula, and whole foods, such as bell pepper, strawberries, and papaya, are the best sources of vitamin C for your baby.
Vitamin C supplements aren’t appropriate for infants unless recommended by a healthcare provider.
If you’re concerned that your baby isn’t getting enough vitamin C, talk to your medical provider before adding any supplements to their routine.
Top 10 Vitamin C Foods for Babies and Kids
Vitamin C is an antioxidant that’s crucial for immunity. Make sure your child gets enough of this nutrient with these Vitamin C Foods for Babies and Kids.
Health Benefits of Vitamin C for Babies and Kids
Top 10 Vitamin C Foods for Babies and Kids
1. Citrus Fruits
2. Bell Peppers
3. Papaya
4. Kiwi Fruit
5. Broccoli
6. Cantaloupe
7. Guava
8. Tomatoes
9. Strawberries
10. Indian Gooseberry
Buy Healthy Nutritious Baby, Toddler food made by our own Doctor Mom !
Ever since COVID-19 began, people have become increasingly concerned about boosting immunity to fend off all kinds of infections. Even if an improved immunity doesn’t actually stop the coronavirus, it can prevent many other common illnesses so that we can avoid hospital crowds during this time. As a way to boost immunity, everyone was researching about one essential nutrient – Vitamin C.
So what is Vitamin C and why is it so important? Vitamin C is also known as ascorbic acid, and it is a water soluble nutrient that is essential for some crucial body functions. While all nutrients are important for kids, Vitamin C has some specific health benefits for children.
Health Benefits of Vitamin C for Babies and Kids
- Vitamin C helps maintain a healthy immune system which can fight off minor infections like the common cold
- Even if we do catch an illness, Vitamin C ensures that it is not severe, by lessening the symptoms and duration
- Vitamin C promotes faster healing and minimizes damage from injuries
- This nutrient is crucial to produce collagen, required for skin, cartilage, tendons, ligaments and bones
- Vitamin C is essential to form blood cells, blood vessels and tissues as well as neurotransmitters
- Vitamin C increases the absorption of iron and calcium from food
- Unlike other Vitamins, Vitamin C is an antioxidant which helps protect against free radical damage
A deficiency of Vitamin C can cause scurvy, an illness that has symptoms like joint pain, bleeding gums and fatigue. In babies and children, Vitamin C deficiency can cause more severe effects like affecting growth and reducing immunity. We all need a certain amount of Vitamin C on a daily basis for optimum health, and these are the recommended amounts:
In babies and children, Vitamin C deficiency can cause more severe effects like affecting growth and reducing immunity. We all need a certain amount of Vitamin C on a daily basis for optimum health, and these are the recommended amounts:
- 0-6 Months – 40 mg
- 6-12 Months – 50 mg
- 1-3 Years – 15 mg
- 4-8 Years – 25 mg
- 9-13 Years – 45 mg
- 14-18 Years (boys) – 75 mg
- 14-18 Years (girls) – 65 mg
During the first six months of life, infants get all their Vitamin C needs through breast milk, which is why the requirement of this Vitamin for pregnant and breastfeeding women is higher. Once the baby starts solids, however, he’ll need to get Vitamin C through food. This is because Vitamin C is an essential nutrient; we cannot make it on our own and need to get it from food.
What’s more, humans cannot store large amounts of Vitamin C in our body, which means we have to constantly include it ion our diet. While Vitamin C is available as a standalone supplement, it is far better to get it from food sources as it is more bio available, i. e. it is more easily absorbed. Here is a list of the top 10 Vitamin C foods for babies and kids to ensure they never run short of this important nutrient.
e. it is more easily absorbed. Here is a list of the top 10 Vitamin C foods for babies and kids to ensure they never run short of this important nutrient.
1. Citrus Fruits
The most obvious choice for Vitamin C foods is citrus fruits, and rightly so! Citrus fruits include oranges, lemons, limes and grapefruits, all of which are rich in Vitamin C. A medium orange provides 70 mg of Vitamin C, while one lemon provides 83 mg an a grapefruit contains 88 mg. In fact, in the 1700s, when British sailors started getting scurvy, they were given lemons as treatment and prevention.
2. Bell Peppers
Bell peppers are a popular ingredient in many cuisines, and we now have a variety of colors available. The sweeter bell peppers are considered to be higher in Vitamin C, like the yellow and red ones. Half a cup of yellow capsicums gives a huge 137 mg of Vitamin C, while green capsicums provide half of it. Besides these, bell peppers are also rich in Vitamins A, B, E and K as well as magnesium, manganese, phosphorous, potassium and folate.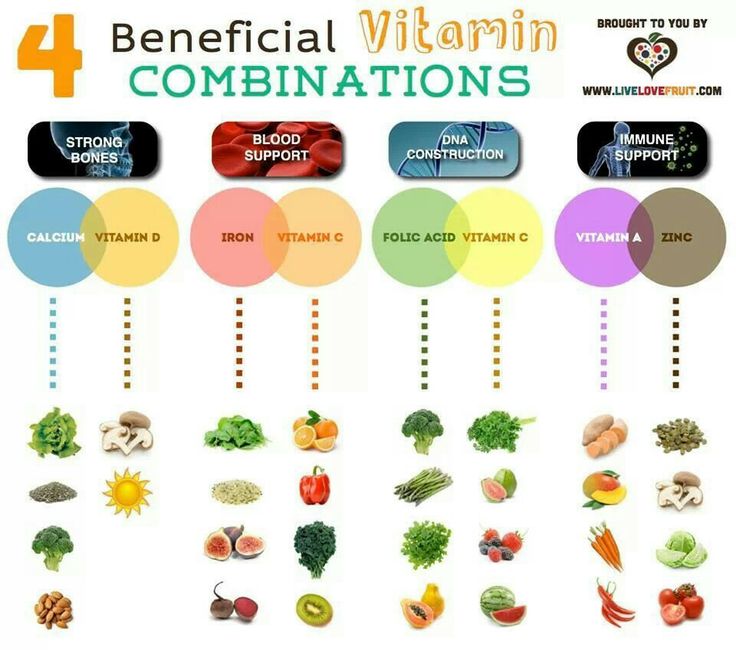
3. Papaya
Papaya is a fruit many of us have growing in our backyards, but little do we realize how nutritionally superior it is! Just one cup of papaya provides 8 mg of Vitamin C, making it an easy way to include this nutrient in our diet. Papaya is also great for digestion and is rich in fiber, magnesium, potassium, carotene, flavonoids and B vitamins. With these, papaya is great to protect against serious illnesses like cancer and Alzheimer’s.
4. Kiwi Fruit
Kiwi fruits are little powerhouses of nutrients, particularly of Vitamin C. One medium sized kiwi contains 71 mg of Vitamin C, along with other nutrients like fiber and antioxidants like flavonoids. Kiwi fruit is generally loved by kids, thanks to its fuzzy exterior and bright insides. Kiwi fruits help reducing blood lots, strokes, cholesterol and also fights against free radical damage.
5. Broccoli
Broccoli is a vegetable that is a constant point of contention between kids and parents. However, parents have a good reason for trying to get kids to eat the tree-like vegetable; just half a cup of broccoli has 51 mg of Vitamin C. This is not all, broccoli is packed with powerful enzymes that have antioxidant function. Broccoli is also rich in fiber that improves digestion and reduces the risk of cancer and heart disease.
However, parents have a good reason for trying to get kids to eat the tree-like vegetable; just half a cup of broccoli has 51 mg of Vitamin C. This is not all, broccoli is packed with powerful enzymes that have antioxidant function. Broccoli is also rich in fiber that improves digestion and reduces the risk of cancer and heart disease.
6. Cantaloupe
Most of us associate muskmelons or cantaloupes with milkshakes – they are a popular summer fruit! Just half a cup of cantaloupes gives 30 mg of Vitamin C, and this fruit is very low in calories as well. It is great for rehydration during summer since it is made up of a good amount of water.
7. Guava
Guavas take us back to our childhood, as we remember plucking guavas and having them with salt and chilli powder. But guavas aren’t just great for a trip down memory lane; just one guava has a whopping 126 mg of Vitamin C, which is 40% more than your daily quota! Eating guava regularly has also shown to reduce blood pressure and cholesterol.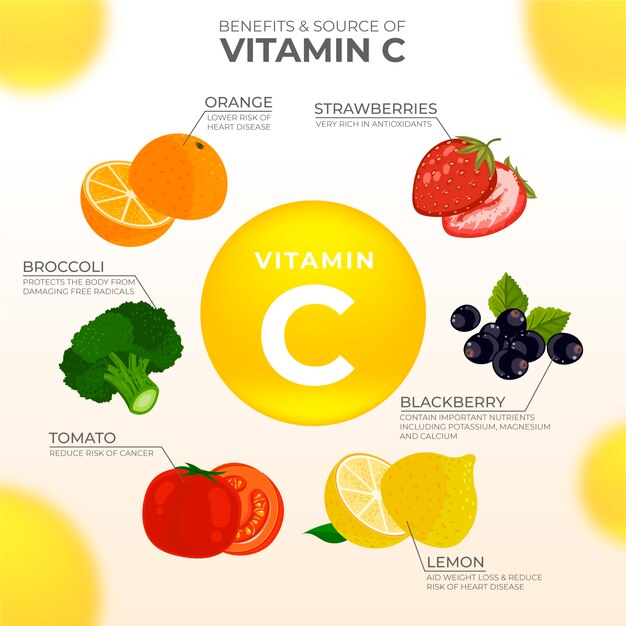
8. Tomatoes
Whether you consider a tomato or a fruit, the fact is that it is an excellent source of Vitamin C. A medium tomato provides 20 mg of Vitamin C, along with other nutrients like folate, potassium, Vitamin K and the important lycopene. Lycopene is an antioxidant that lowers blood cholesterol and improves heart health.
9. Strawberries
We know that berries in general are great for health, but strawberries score extra marks for being rich in Vitamin C. One cup of strawberries contains 89 mg of Vitamin C – nearly an entire day’s worth! That’s not all, strawberries have all the good things we hear about in berries – folate, flavonoids and a load of antioxidants that prevent cancer, dementia and heart disease.
10. Indian Gooseberry
Amla, or the Indian gooseberry is the biggest superstar when it comes to Vitamin C – 100 grams of amla has as much Vitamin C as 20 oranges! Indian gooseberries are great in preventing lifestyle diseases like diabetes, cardiac issues and hypertension. They are also great for improving skin and hair health, vision and for boosting immunity.
They are also great for improving skin and hair health, vision and for boosting immunity.
Most of these foods are best eaten raw, since that is when their Vitamin C stores are at the highest. However, this may not be possible for babies and young kids so it’s okay to cook them lightly. Here are some more tips on feeding your child Vitamin C foods:
- Get fresh produce from a local market. Older fruits and vegetables will have lost some of its Vitamin C.
- Make sure the fruit or vegetable is completely ripe before feeding your baby to get the maximum amount of Vitamin C
- Store the produce in the fridge or in a cold, dark place to ensure the Vitamin C isn’t lost
- Opt for serving the whole fruit or vegetable rather than the juice to get the fiber as well
- When cooking Vitamin C foods, cook them for as short a time as possible, to retain all the nutrients
- Steaming keeps the nutrients intact when compared to boiling
- Serve cooked food as soon as its made to prevent any loss of nutrients
- Avoid using copper pots or adding baking soda while cooking – these can kill the Vitamin C
In some cases, like premature births or severe malnutrition, doctors may prescribe a Vitamin C supplement, but generally speaking we can get all the Vitamin C we require through food. Over consumption of Vitamin C is usually not a problem since it is a water soluble vitamin and is flushed out in urine. However, severe overdoses can cause nausea, diarrhea, gastritis and even kidney stones.
Over consumption of Vitamin C is usually not a problem since it is a water soluble vitamin and is flushed out in urine. However, severe overdoses can cause nausea, diarrhea, gastritis and even kidney stones.
Buy Healthy Nutritious Baby, Toddler food made by our own Doctor Mom !
Shop now!Vitamin C for children: what foods contain what to include in the diet
Adults need vitamins to be vigorous and healthy. Children also need them for active growth and development. Vitamins do not accumulate in the body, are quickly excreted and are practically not synthesized, so they must be ingested daily.
Why do we need vitamin C?
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) plays an enormous role in a growing organism.
The main properties of the Askorbinka:
- contributes to the body's stability to viral and bacterial infections
- participates in the restoration and healing of the body
- helps in blood formation
- retains blood vessels
- .

Important!
A breastfed baby receives vitamin C from breast milk. The content of vitamin C in breast milk depends on the nutrition of a nursing woman.
Formula-fed baby receives it as part of infant formula. When complementary foods are introduced to a child, his vegetables and fruits become an additional source of vitamin C.
Complementary food products and dishes of industrial production are additionally enriched with vitamins.
A little about the dangers of vitamin C deficiency.
Lack of nutrients, including vitamins, changes physical functions and processes at the most basic cellular level: water balance, fermentation functions, nervous and digestive systems, and metabolism are disturbed. This is especially dangerous for an unformed child's body.
The condition of lack of nutrients in the body is called hypovitaminosis. Modern mothers know how dangerous this condition is and make every effort to prevent its development in their child.
A severe form of vitamin deficiency is called avitaminosis. It is characterized by a complete lack of vitamins in the body and causes big problems with the gastrointestinal tract, interferes with the absorption of nutrients. This case already requires the direct intervention of a doctor to draw up a suitable diet.
The main concomitants of vitamin C deficiency in children are frequent colds, increased fatigue and poor appetite, which negatively affects their activity and maturation. The lack of ascorbic acid leads to the fact that the walls of the blood vessels become fragile, as a result of which the gums often bleed in children, and hematomas and bruises appear, which take a long time to pass.
It is worth remembering that there are periods in a child's life when he needs vitamins more than usual - for example, during periods of active growth, illness, and intense exercise. At such a time, an increased intake of vitamin C in the body is especially important, because it is he who is responsible for the body's resistance to various sores and allows the body to develop correctly.
So, what are the signs of vitamin C deficiency in children?
- Loss of appetite;
- Fatigue;
- General weakness of the body; nemia or a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, as well as bruising.
If a child develops these symptoms, the child's diet should be reviewed and the doctor should be consulted.
In addition to hypovitaminosis, there is also such a phenomenon as hypervitaminosis, which occurs when there is an excess content of any vitamin in the body. Most often it is associated with taking medications. An excess of vitamins is no less dangerous than their lack in vitamin deficiency, as it leads to deviations in the development of internal organs, growth retardation, and chronic diseases. Acute hypervitaminosis usually leads to an increase in the body temperature of the child, the appearance of rashes on the skin and other allergic reactions, convulsions.
Therefore, only a doctor can prescribe some vitamin preparations to children, and the task of parents is to ensure proper nutrition, varied and balanced.
How to compensate for the lack of vitamin C? This issue is especially acute during the period of late winter and early spring - the season of colds and flu.
So, here are some practical tips on how to make up for the lack of vitamin C in a child:
- Provide proper, balanced nutrition;
- The child needs more sleep to replenish his strength;
- Walk more often and spend time outdoors;
- Add physical activity, but do not overdo it.
As for nutrition, there are also certain rules:
- The following foods must be added to the child's diet: citrus fruits - lemons, oranges; black currant; rose hip;
- Fruits and vegetables should be consumed fresh or steamed;
- It is better to consume vegetables and fruits, rather than juices from them - fiber is not stored in juices, which directly affects metabolism;
- It is advisable not to exceed the daily norm, because an excess of vitamins is just as dangerous as their lack.

In particular, we should mention the drug restoration of the balance of vitamin C.
For example, there are preparations on the market containing pure vitamin C. However, not all drugs are suitable for consumption by children. For a child, those medicines are suitable, which, in addition to pure ascorbic acid, contain dextrose (glucose), which is completely absorbed by the body and participates in metabolic processes. Such vitamins are prescribed for adults both for preventive and medical purposes; for children, they are prescribed for strictly medicinal purposes.
To summarize
Vitamins play an important role in ensuring the normal growth and development of the child. Vitamin C, in particular, helps the body fight seasonal colds. With an abundance of ascorbic acid, the child grows vigorous, healthy and happy, his body has a great resistance to viruses.
Be friends with vitamins and may your children always be healthy!
20 foods rich in vitamin C per day.

Vitamin C in foods
Vitamin C is a water-soluble trace mineral found in many natural foods. Most of all in vegetables and fruits.
The main feature of the nutrient lies in its powerful antioxidant properties, as it prevents the harmful effects of free radicals and fights oxidative processes. With sufficient intake of vitamin C, there will always be healthy skin and its derivatives, and the immune system will also be strengthened.
Without this trace element it is impossible to imagine the production of collagen, in addition, it helps to strengthen the connective tissue, bone apparatus, take care of the health of small vessels and teeth.
In the human body, the vitamin cannot be produced or accumulated on its own, so it can only be obtained from natural foods.
An average of 90 milligrams of the substance should be taken per day. If there is a shortage or severe deficiency, this is manifested in the following symptoms:
- gums bleed;
- weakens the immune system;
- wounds heal slowly;
- develops anemia and scurvy.

To ensure that your body is always in good shape and filled with the necessary nutrients, you need to include in your diet the best foods fortified with vitamin C. Many people wondered "Where is the most vitamin C", "which fruit has the most vitamin C", "which product has the most vitamin c"? Consider the answers below.
Cockatoo plum
This fruit has the scientific name Terminalia ferdinandiana and is native to Australia. It has a hundred times more nutrient compared to an orange. To date, the plum is the most saturated product in terms of the concentration of vitamin C - 5300 milligrams of the substance per hundred grams of fruit. It is enough to eat one piece to fill the body with 5-30 percent of the daily dosage.
Kakadu plum also contains useful trace elements such as tocopherol, lutein and potassium, which are important for maintaining the health of the organs of vision.
Acerola Cherry
The berries of a plant called Malpighia emarginata contain 1670 milligrams of the substance per hundred grams of product. This allows you to immediately replenish the daily supply for the body.
This allows you to immediately replenish the daily supply for the body.
Cherry extract has been shown to counteract the development of cancerous tumors, protect the body's skin from ultraviolet radiation, and also minimize the damage caused to DNA as a result of malnutrition.
Rose hips
Rose hips are distinguished by their small size, yet sweetness and juiciness. One hundred grams of the product accounts for 650 milligrams of the vitamin, so you can easily satisfy the daily need for this trace element.
The use of wild rose contributes to the activation of collagen synthesis, improves the condition of the skin, regardless of age.
Scientists have found that vitamin C counteracts the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays on the skin, also helps fight wrinkles, eliminates dryness, evens out tone and improves the overall health of the dermis. Also, the nutrient contributes to good wound healing and eliminates inflammatory reactions, in particular, minimizes the risk of dermatitis.
Also, the nutrient contributes to good wound healing and eliminates inflammatory reactions, in particular, minimizes the risk of dermatitis.
Chili Pepper
Green, unripe fruit contains 641 milligrams of vitamin per hundred grams of product. This is 7 times the daily requirement for the body. And in red chili, the concentration is 382 milligrams, while this is still enough to satisfy the body with nutrients.
Peppers also contain a lot of capsaicin, which gives them such a strong pungency. This substance helps to reduce pain and fights inflammation.
Researchers have conducted research and found that 10 grams of chili pepper powder activates fat burning processes in the body.
Guava
Guava is a pink tropical fruit that grows on the South American continent and also in Mexico. One hundred grams of the fruit contains 182 milligrams of vitamin C, which is equal to 2 times the daily requirement for our body. Also, guava is characterized by a high concentration of lycopene, which acts as a natural antioxidant.
One hundred grams of the fruit contains 182 milligrams of vitamin C, which is equal to 2 times the daily requirement for our body. Also, guava is characterized by a high concentration of lycopene, which acts as a natural antioxidant.
In a 6-week study of 45 young, completely healthy people, a 400-gram serving of guava every day in the diet can significantly reduce cholesterol and normalize blood pressure.
Yellow pepper (sweet)
The riper the fruit, the higher the concentration of vitamin C in it. There are 182 milligrams of a useful substance per hundred grams, and this is 2 times the daily requirement for the human body.
Scientists have been able to prove that regular consumption of the vitamin through foods enriched with it improves the functioning of the visual system and provides a preventive effect of cataracts.
In an experiment involving more than 300 women, the group that took more of the nutrient had a 33 percent lower risk of developing an eye disease.
Blackcurrant
One hundred grams of this juicy berry contains 180 milligrams of a useful trace element. Currants have such a dark color due to the high concentration of anthocyanins in it - flavonoids with powerful antioxidant properties.
The combination of vitamin C with these substances provides an effective reduction in the influence of oxidative processes caused not only by the action of free radicals, but also resulting from chronic ailments, including past heart disease, cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
Thyme
This is a popular herb that is widely used in cooking. Compared to an orange, it contains three times more vitamin C. Among all the spices, thyme is characterized by the highest concentration of the nutrient: one hundred grams contains 160 milligrams of a useful micro-substance, and this is half the daily requirement for the human body.
It is recommended to use 1-2 tablespoons of spice every day during cooking to strengthen the immune system and improve your health. This herb helps in the treatment of sore throats and other diseases of the respiratory system, and also activates the production of antibodies that destroy viruses and pathogenic bacteria.
Parsley
One of the best everyday spices that can be found in every housewife's garden. One hundred grams of greens have 125 milligrams of vitamin C. It also contains a considerable amount of non-heme iron. This combination of active trace elements prevents the risk of developing iron deficiency anemia.
Scientists conducted experiments in which people followed a vegetarian diet and received 500 milligrams of the vitamin twice a day during meals. As a result, their iron levels increased by 17 percent, hemoglobin increased by 8 percent, and ferritin levels increased by 12 percent.
Mustard spinach
One hundred grams of this plant contains 130 milligrams of vitamin C - this is almost one and a half daily norm for our body.
Often in the process of cooking and subjecting products to heat treatment, the amount of nutrient in their composition is significantly reduced, but spinach retains its original properties and concentration under any conditions.
This plant also contains potassium, manganese, folate, vitamin A, calcium and fiber.
Cabbage
Raw white cabbage contains 45 milligrams of vitamin C per hundred grams, which is half the daily requirement for a person. It also contains carotenoids, zeaxanthin, lutein, vitamin K.
When cooked, the nutrient content of cabbage is significantly reduced, but it increases the amount of antioxidants that counteract chronic diseases and fight inflammation.
Kiwi
An excellent tropical fruit and a good source of vitamin C - 109 grams contains 109 milligrams (more than the total daily value). Numerous studies have been conducted that have shown that with regular use of the fruit, it is possible to effectively deal with stress, normalize the volume of cholesterol in the blood and strengthen the immune system.
Researchers conducted a study involving a group of 30 people in the age group 20-51. The results of the experiment were such that after 28 days of taking 2-3 kiwi fruit each day, participants experienced an 18 percent reduction in platelet stickiness and a 15 percent reduction in triglyceride levels. This led to the conclusion that the fetus counteracts the risks of blood clots and stroke.
Another study with 14 men diagnosed with vitamin C deficiency found that eating two kiwis daily for a month increased white blood cell activity by 20 percent, and the nutrient content in the blood was restored to normal in 7 days.
Broccoli
This bright green vegetable belongs to the cruciferous family. Half a glass of boiled cabbage contains 51 milligrams of a useful substance, which is equivalent to half the daily rate necessary for the proper functioning of the body.
If you eat broccoli every day, it protects against the risk of cancerous pathologies and heart defects, vascular disorders.
Scientists in a study on a group of 27 men with the status of heavy smokers were able to find that the inclusion of 250 grams of broccoli in the diet helped to reduce the marker of C-reactive protein inflammation by 48 percent after 10 days of the experiment.
Brussels sprouts
One hundred grams of this vegetable contains 100 milligrams of vitamin C. Almost all members of the cruciferous family are fortified with this nutrient, as well as fiber, folate, potassium, and vitamin A.
This complex of nutrients helps to strengthen the bone apparatus, activates collagen synthesis.
In 20218, a large-scale study of the properties of the chemical composition of Brussels sprouts was carried out. It turned out that taking vitamin C prevents hip fractures by 28 percent, and also reduces the risk of osteoporosis by 33 percent.
Lemon
In the 18th century, everyone who worked on large seagoing ships received lemons every day for food. This was necessary so that scurvy did not develop. 100 grams of citrus contains 53 milligrams of vitamin C (slightly more than half of the daily dose).
It is this structural component of the fruit that has strong antioxidant properties. When cutting fruit, the enzyme polyphenol oxidase is released, which oxidizes and causes the surface to darken. If lemon juice is applied to exposed areas, this reaction will slow down and the natural color will last longer.
Lychee
One hundred grams of the product contains 72 milligrams of the nutrient, which is 80 percent of the norm for humans. By eating a whole cup of fruit, you can replenish vitamin reserves by 1.5 doses.
The fruits contain Omega 3 and 6 fatty acids, which are responsible for the proper and full functioning of the brain, heart and blood vessels.
About 196 thousand people took part in a large study conducted by specialists. It was found that taking vitamin C reduces the risk of stroke by 42 percent. With each additional serving of fruits and vegetables listed above, the likelihood of illness is reduced by another 17 percent.
Persimmon
This is a bright and juicy orange fruit, which in its shape is a bit like a tomato. Today, there are many varieties of plants, and the most common is the Japanese fruit. At the same time, the American persimmon is characterized by the highest degree of usefulness and is called Diospyros virginiana. The concentration of vitamin C in its composition is 9 times higher than in Japanese - one hundred grams of the product contains 15 milligrams of the vitamin, or 16 percent of the required norm for a person.
Today, there are many varieties of plants, and the most common is the Japanese fruit. At the same time, the American persimmon is characterized by the highest degree of usefulness and is called Diospyros virginiana. The concentration of vitamin C in its composition is 9 times higher than in Japanese - one hundred grams of the product contains 15 milligrams of the vitamin, or 16 percent of the required norm for a person.
Papaya
One hundred grams of product contains 60 milligrams of trace elements, which is equivalent to 67 percent of the daily value for maintaining body health. Eating this fruit is useful for improving memory, combating the risks of inflammatory reactions in the brain.
According to a study on a group of 20 people with mild Alzheimer's, it turned out that drinking papaya extract for six months can improve health by 40 percent.
Strawberry
Summer berry is rich in flavonoids, folate, manganese and antioxidants. If you eat one hundred grams of strawberries, this will allow you to get 58 milligrams of vitamin C, or almost 64 percent of the daily dosage.
Tests have shown that the antioxidants of the berry actively fight the manifestations of cancer, diabetes, prevent the risk of dementia, heart disease and vascular disease.
An experiment was conducted on a group of 27 people with metabolic syndrome - they were given 450 grams of strawberries every day for food. After 8 weeks, patients had an 11 percent reduction in cholesterol and an 18 percent improvement in vascular health.
Orange
The average fruit contains about 70 milligrams of a nutrient, or 78 percent of the dosage for our body.
The complex use of citrus fruits allows you to fully meet the needs for vitamin C during the day. For example, one hundred grams contains the nutrient:
- grapefruit - 45 milligrams;
- tangerine - 40 milligrams;
- lime - 30 milligrams.
How to get vitamin C regardless of diet
Just click "Select Vitamin C" and you will be able to choose your own Vitamin C in the form of a dietary supplement using convenient filters
If you have not found answers to your questions, and still find it difficult to choose, you can always seek the advice of a pharmacist in the online chat.
|
Conclusion
Vitamin C is an essential microelement in the life of our body and is required by it every day to maintain a full and healthy work.
Its key properties are as follows:
- improvement of the immune system;
- strengthening of connective tissues;
- normalization of the functioning of the heart muscle;
- vascular health support;
- antioxidant.
With a lack of a nutrient in the body, the state of health worsens and biochemical processes are disturbed.
Vitamin C is found not only in citrus fruits, as is commonly believed, but in many other fruits and vegetables. At the same time, in some fruits, the concentration of the substance is quite high.
By including fresh fruits and vegetables in your daily diet, you can meet the body's needs for trace elements, thereby providing a preventive effect and protection against serious diseases.
Resources
C
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminC-HealthProfessional/
3.The Kakadu plum
https://www.agrifutures.com.au/wp-content/uploads/publications/ 14-115.