Foods that cause acid reflux in breastfed babies
Acid Reflux in Infants: Causes
Immature lower esophageal sphincter
The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is a ring of muscle at the bottom of baby’s esophagus that opens to allow food into the stomach and closes to keep it there.
This muscle may not be fully matured in your baby, especially if they’re premature. When the LES opens, the contents of the stomach can flow back into the esophagus, causing baby to spit up or vomit. As you can imagine, it can cause discomfort.
This is very common and does not usually cause other symptoms. However, constant regurgitation from acid reflux can sometimes cause damage to the esophageal lining. This is much less common.
If spitting up is accompanied by other symptoms, it may then be called gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD.
Short or narrow esophagus
Refluxed stomach contents have a shorter distance to travel if the esophagus is shorter than normal. And if the esophagus is narrower than normal, the lining might more easily become irritated.
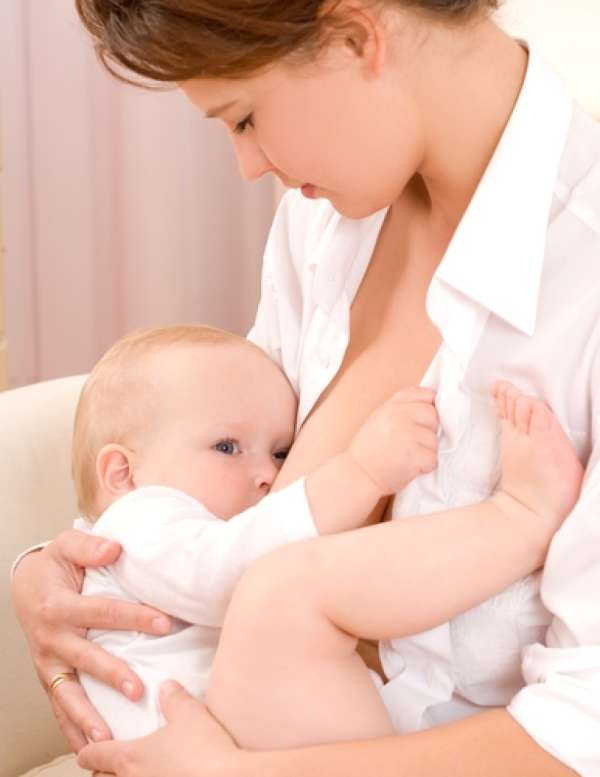
Diet
Changing the foods baby eats may help reduce the chances of acid reflux. And if you breastfeed, making changes to your diet might help your baby.
Some studies have shown that reducing intake of milk and eggs may help, though more research is needed to determine how much this affects the condition.
Certain foods may be causing acid reflux, depending on your infant’s age. For example, citrus fruits and tomato products increase acid production in the stomach.
Foods like chocolate, peppermint, and high fat foods can keep the LES open longer, causing the contents of the stomach to reflux.
Gastroparesis (delayed emptying of the stomach)
Gastroparesis is a disorder that causes the stomach to take longer to empty.
The stomach normally contracts to move food down into the small intestine for digestion. However, stomach muscles don’t work properly if there is damage to the vagus nerve because this nerve controls the movement of food from the stomach through the digestive tract.
In gastroparesis, the stomach contents remain in the stomach longer than they’re supposed to, encouraging reflux. It’s rare in healthy infants.
Hiatal hernia
A hiatal hernia is a condition in which part of the stomach sticks through an opening in the diaphragm. A small hiatal hernia doesn’t cause problems, but a larger one can cause acid reflux and heartburn.
Hiatal hernias are very common, especially in people over the age of 50, but they are rare in infants. However, the causes are unknown.
A hiatal hernia in children is usually congenital (present at birth) and may cause gastric acid to reflux from the stomach into the esophagus.
Position while feeding
Positioning — especially during and after feeding — is a frequently overlooked cause of acid reflux in infants.
A horizontal position makes it easier for the stomach contents to reflux into the esophagus. Simply keeping baby in an upright position while you’re feeding them and for 20 to 30 minutes afterward may reduce acid reflux.
Sleep positioners and wedges, however, are not recommended while feeding or sleeping. These padded risers are intended to keep your baby’s head and body in one position, but are not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration due to the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
Angle of His
The angle at which the base of the esophagus joins the stomach is known as the “angle of His.” Differences in this angle may contribute to acid reflux.
This angle most likely affects the ability of the LES to keep the contents of the stomach from refluxing. If the angle is too sharp or too steep, it may make it difficult to keep the stomach contents down.
Overfeeding
Feeding your little one too much at once can cause acid reflux. Feeding your infant too frequently can also cause acid reflux. It’s more common for bottle-fed babies to overfeed than breastfed infants.
An oversupply of food can put too much pressure on the LES, which will cause your infant to spit up. That unnecessary pressure is taken off the LES and reflux decreases when you feed baby less food more often.
That unnecessary pressure is taken off the LES and reflux decreases when you feed baby less food more often.
However, if your baby spits up often, but is otherwise happy and growing well, you may not need to change your feeding routine at all. Talk with your doctor if you have concerns that you are overfeeding your baby.
Your infant will usually grow out of acid reflux. However, call your child’s doctor immediately if you notice that your child:
- isn’t gaining weight
- has feeding difficulties
- is projectile vomiting
- has blood in their stool
- has pain signs such as arching of the back
- has unusual irritability
- has trouble sleeping
While it isn’t easy to determine the exact cause of acid reflux in infants, lifestyle and diet changes may help eliminate some of the factors.
If the acid reflux doesn’t go away with these changes and your baby has other symptoms, a doctor may want to perform tests to rule out a gastrointestinal disorder or other problems with the esophagus.
A Guide to Foods to Avoid for Acid Reflux While Breastfeeding
"The content below is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition."
Your baby is dealing with acid reflux after breastfeeding and will not stop crying.
Don’t worry, you can help avoid acid reflux episodes like these in the future.
The main way to prevent acid reflux while breastfeeding is to avoid consuming foods that can cause acid reflux.
But what foods cause acid reflux in babies?
In this guide, we will break down all the foods to avoid for acid reflux while breastfeeding and show you how your nutrition can not only prevent acid reflux attacks but benefit your baby’s health even more.
Table of Contents
- How Can a Mother’s Diet Affect a Breastfed Baby?
- What Are Common Signs of Acid Reflux in Breastfed Babies?
- 7 Foods to Avoid When Breastfeeding a Baby With Reflux
- How Can I Soothe Acid Reflux in a Breastfed Baby? 2 Methods to Consider
- Start Treating Your Baby’s Acid Reflux With Holistic Nutrition Today
How Can a Mother’s Diet Affect a Breastfed Baby?
The female body does some miraculous things, and breastfeeding is no exception.
A mother’s diet is directly related to the diet of their breastfeeding baby, as what you eat can impact the nutrition, composition, and even taste of your breast milk.
You may be wondering, how long does it take for ingested foods to influence your breast milk?
The answer? It varies depending on the type of food you ingest.
Let’s take a look at some examples of time it takes for certain foods to influence your breast milk:
- Coffee: 15-60 minutes
- Garlic: 2 hours
- Carrots: 2-3 hours
- Mint 4-6 hours
Some foods that influence your breast milk can affect your baby in different ways. For example, it’s possible for your child to have a food allergy in response to something you ate.
One of the most common reactions linked to a mother’s diet and breastfeeding is acid reflux .
What Are Common Signs of Acid Reflux in Breastfed Babies?
You probably already know that it’s common and normal for infants to spit up after a meal. You’ve cleaned it up dozens of times, likely.
You’ve cleaned it up dozens of times, likely.
This little phenomenon is known as gastroesophageal reflux (GER).
However, frequent vomiting, irritation, and a slew of other symptoms can hint to a more serious problem, known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), commonly known as acid reflux.
Common acid reflux symptoms to look out for include:
- Frequent vomiting and regurgitation
- Persistent coughing or wheezing
- Difficulty eating
- Irritability associated with feeding or following feedings
- Gassiness
7 Foods to Avoid When Breastfeeding a Baby With Reflux
It can seem overwhelming trying to figure out which foods to avoid when breastfeeding a baby with reflux, especially when you have an already fussy baby.
Below, we will discuss what foods cause reflux in breastfed babies. A good rule of thumb is that if certain foods cause acid reflux for you, they could also cause acid reflux for your baby.
#1: Fruit and Fruit Juice
Fruit and fruit juices with high acidity can trigger acid reflux in infants, causing discomfort.
Some acidic fruit and fruit juices you’ll want to avoid consuming are:
- Apples
- Oranges
- Lemons
- Other citrus fruits
#2: Tomatoes and Tomato Sauce
You may be surprised to hear that tomatoes and tomato-based sauces are included in this list of foods to avoid for acid reflux while breastfeeding.
While tomatoes can be an excellent source of vitamin C, which is an essential nutrient for healthy breastfeeding, they are also very acidic— which can lead to a very gassy, uncomfortable, and irritable baby.
#3: Spicy Foods
Have you ever eaten a spicy meal only to get a dose of heartburn afterward? The same can happen to your baby when you breastfeed after eating spicy food.
Spicy foods can irritate the lining of the stomach, which can trigger acid reflux.
#4: Caffeine
While your daily cup of coffee isn’t enough to cause problems for your infant, experts advise breastfeeding mothers to not consume more than 750mL of caffeine per day (the equivalent of 5 cups of coffee).
If your infant takes in too much caffeine from your breast milk, they can experience acid reflux as well as other caffeine stimulation symptoms, such as irritability.
#5: Foods High in Fat
It is best to only consume foods with high fat content in moderation while breastfeeding.
Breastfeeding your baby after consuming foods high in fat can cause the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to stay open longer, which causes the contents of the stomach to reflux.
#6: Seafood with High Mercury Levels
While seafood can be a great source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids that are wonderful building blocks for proper nutrition, some seafood can do more harm than good.
Avoid consuming seafood that is high in mercury. The mercury from these foods can find its way into your breast milk supply. Excessive amounts of mercury in breast milk can have adverse effects on your baby’s developing nervous system.
Some kinds of seafood that are high in mercury include:
- Swordfish
- King mackerel
- Tilefish
#7: Alcohol
No level of alcohol in breastmilk is considered safe for your child to consume.
However, this doesn’t mean that you can’t enjoy a glass of wine every once in a while.
When it comes to breastfeeding and consuming alcohol, you have two options to ensure your child’s safety:
- Pump before consuming alcohol. If you plan on enjoying an alcoholic beverage, you can pump breast milk before drinking alcohol so you have a clean supply to feed your baby later.
- Wait it out. If you drink alcohol, wait for it to completely clear your breast milk before breastfeeding.
 Depending on your body weight, you’ll want to wait at least 2-3 hours after consuming:
Depending on your body weight, you’ll want to wait at least 2-3 hours after consuming: - 12 oz. of 5% beer
- 5 oz. of 11% wine
- 1.5 oz. of 40% liquor
How Can I Soothe Acid Reflux in a Breastfed Baby? 2 Methods to Consider
Neither your heart nor sanity can put up with your baby crying in discomfort for hours due to acid reflux, but it can be difficult to know exactly how to help soothe acid reflux in a breastfed baby or avoid it altogether for that matter.
After all, motherhood doesn’t come with an instruction manual.
There are two ways you can handle acid reflux in babies:
- Treat the symptoms of acid reflux to soothe your baby’s discomfort.
- Treat the root of the cause and avoid acid reflux altogether
#1: Help Baby’s Physical Discomfort
There are a number of ways that you can decrease your baby’s discomfort caused by acid reflux.
If your baby is dealing with acid reflux, you can try to treat their symptoms by:
- Doing smaller, more frequent feeds
- Feeding your baby upright
- Thickening breast milk
- Burping your baby more frequently
Try Smaller, More Frequent Feedings
When your baby’s stomach is too full, they are at greater risk of having acid reflux after feedings.
Feeding your baby more frequently in small amounts can help avoid irritating acid reflux symptoms.
This is because a less-full stomach decreases the amount of pressure put on the lower esophageal sphincter, which is a muscle that prevents food from going back into the esophagus from the stomach.
The lower esophageal sphincter takes about a year to strengthen, which is why babies spit up often.
Feed Your Baby Upright
Feeding your baby in an upright position can help reduce the risk of acid reflux in babies.
Additionally, keeping your baby upright for at least 30 minutes after feeding is also believed to have the same acid reflux prevention effect.
Thicken Breast Milk
With your doctor’s approval, you can thicken your breast milk by adding a small amount of infant rice cereal. Thickening the breast milk can help lessen spit-ups and acid reflux symptoms.
Thickening your breast milk may help reduce the risk of your baby’s stomach contents sloshing up into the esophagus. Always consult your doctor before trying this alternative.
Burp Your Baby More Frequently
It’s important to burp your baby often—both during and after feedings.
Frequently burping your baby can help reduce acid reflux symptoms. Anytime your baby pulls off the nipple during breastfeeding, be sure to give them a little burp.
#2: Acid Reflux in Babies: Mother’s Diet Can Help with Holistic Nutrition
Now that we have discussed how to treat acid reflux symptoms , let’s talk about a better option— preventing acid reflux episodes before they happen.
Holistic nutrition is an excellent tool to help avoid acid reflux in infants caused by breastfeeding.
You may be wondering, “what is holistic nutrition and how is it related to foods to avoid for acid reflux while breastfeeding?”.
Holistic nutrition is based on the idea that your nutrition is related to all aspects of your health.
Holistic nutrition is a lifestyle that involves eating healthy foods that are:
- Whole
- Un-refined
- Un-processed
- Organic
- Locally grown
Let’s talk about how holistic nutrition benefits both the breastfeeding mother and child.
How Does Holistic Nutrition Benefit the Breastfeeding Mother and Baby?
Holistic nutrition focuses on providing your body with nutrient-dense foods that will only have a positive impact on your health.
If your diet is not having a positive impact on your health, chances are that it is not positively impacting the health of your breastfed baby either.
Think about it: if certain foods give you acid reflux, why wouldn’t your baby be susceptible to the same kind of reaction by consuming that food composition through your breast milk?
Holistic nutrition involves eliminating refined and processed foods, which are known to cause acid reflux.
By not consuming these foods or strictly limiting the consumption, you are stopping the problem at the source instead of simply treating symptoms.
However, healthy and whole foods can also be culprits of acid reflux attacks.
If your breastfeeding child is experiencing acid reflux and you are unable to pinpoint what food is causing it, using the elimination diet can help uncover which foods are resulting in episodes of acid reflux in your child.
Start Treating Your Baby’s Acid Reflux With Holistic Nutrition Today
Holistic nutrition goes beyond simply what foods to avoid for acid reflux while breastfeeding.
Not only does holistic nutrition help avoid acid reflux episodes for you and your breastfeeding child, but it provides both of you with the best nutrition possible for optimal health.
Learn more about how holistic nutrition can benefit you and your child today by scheduling a free consultation.
Infant Reflux: Symptoms and Treatment
Search Support IconSearch Keywords
Home ›› What is Reflux in Infants?
Home ›› What is reflux in babies?
↑ Top
Signs and what to do
Post-feed regurgitation is a common occurrence in the first few months of life. This is usually harmless and completely normal, but parents should read about gastroesophageal reflux (GER) and laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) in infants and how long it lasts to give them peace of mind.
We look at signs of reflux in babies, symptoms of different types of reflux, and how to help a child with signs of reflux. If you require further information, always contact your healthcare provider.
If you require further information, always contact your healthcare provider.
What is reflux in babies?
So we know reflux is common, but what causes reflux in babies? Because young children have not yet fully developed the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), that is, the muscle at the bottom of the esophagus that opens and closes to let food into the stomach and keep it there, food can easily pass back up the esophagus.
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux (GER), is a normal reflux that occurs in babies. This type of reflux is considered normal and occurs in 40-65% of babies.
How do I know if my child has acid (gastroesophageal) reflux?
If a baby is spitting up milk after a feed, it is most likely acid reflux. As babies get older, GER usually goes away on its own without any intervention. If a baby has complications beyond just spitting up a small amount of milk (such as feeding difficulties and discomfort), they may have gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).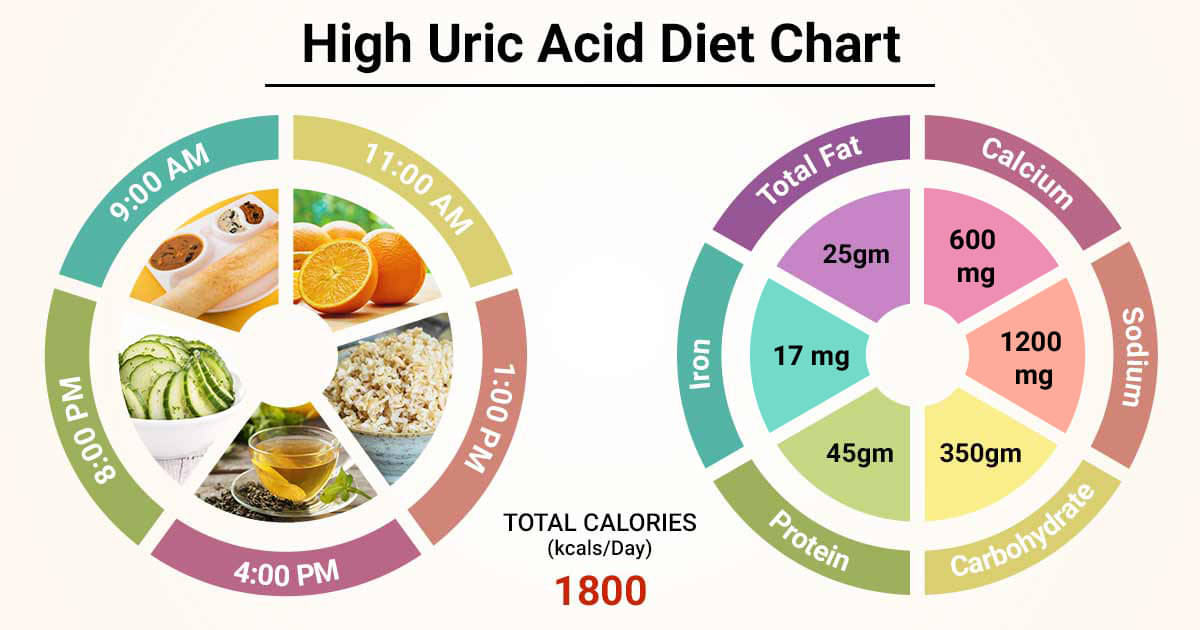
Symptoms of GERD include:
- baby arching during or after feeding;
- crying more than three hours a day for no apparent reason;
- cough;
- gag reflex or difficulty swallowing;
- irritability, restlessness after eating;
- eating little or not eating;
- poor weight gain or loss;
- difficult breathing;
- severe or frequent vomiting.
GERD usually occurs when LES muscles are not toned in time, causing stomach contents to back up into the esophagus.
How do I know if my child has Laryngopharyngeal Reflux?
Another type of reflux, laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR), also called silent reflux, is when the contents of the baby's stomach leak back into the larynx, the back of the nasopharynx. This type of reflux does not always cause external symptoms, which is why it is called "silent". Babies can have GERD and silent reflux at the same time, but their symptoms are somewhat different.
The following are some of the symptoms of laryngopharyngeal reflux:
- breathing problems;
- gag reflex;
- chronic cough;
- swallowing problems;
- hoarseness;
- regurgitation;
- poor weight gain or weight loss.
We have looked at the signs of reflux in infants, now we will move on to the treatment and duration of silent reflux in children, as well as the treatment of GERD.
How to deal with laryngopharyngeal reflux in babies while breastfeeding?
Breastfeeding mothers may need to review their diet if their babies show signs of reflux. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends breastfeeding mothers cut eggs and milk from their diet for two to four weeks to see if their baby's reflux symptoms improve or disappear. It may be worth eliminating acidic foods from your diet.
In most cases, GER and laryngopharyngeal reflux go away on their own. Typically, children outgrow reflux in the first year of life. If a child has persistent symptoms of laryngopharyngeal reflux, parents should consult a doctor. If your baby has severe vomiting, blood in the stool, or any of the symptoms of GERD listed above, parents should contact their pediatrician as soon as possible.
Typically, children outgrow reflux in the first year of life. If a child has persistent symptoms of laryngopharyngeal reflux, parents should consult a doctor. If your baby has severe vomiting, blood in the stool, or any of the symptoms of GERD listed above, parents should contact their pediatrician as soon as possible.
How can I help my child with reflux or GERD?
Reflux symptoms in babies usually go away on their own, but the following tips can help relieve symptoms:
- Thicken food with rice or a special milk thickener.
- Hold the bottle at an angle that fills the nipple completely with milk to reduce the amount of air your baby swallows. This can help prevent colic, gas, and reflux.
- Try the AirFree anti-colic bottle, designed to reduce air swallowing during feeding.
4. Let the baby burp during and after feeding. If the baby is bottle fed, parents can let him burp after every 30-60 ml. If the mother is breastfeeding, she may let the baby burp when changing breasts.
5. Hold baby upright after feeding. As a rule, in order for the milk to remain in the stomach, after feeding the baby, it is necessary to hold it in an upright position for 10-15 minutes. But, if the child has reflux, parents should keep him upright a little longer.
These tips may help relieve symptoms, but they do not replace a doctor's advice.
Parents should not change their infant formula formula without first talking to their healthcare provider.
Don't panic! Reflux is very common in babies during the first three months of life, and most babies outgrow it without any consequences. Although GERD is a slightly more serious condition, there are many treatments, ways to manage it, and help newborns. Feel free to contact your doctor with any questions or concerns you may have.
4 Seattle Children’s Hospital
5 The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases - Treatment for GER & GERD in Infants
Any links to third party websites that may be included on this site are provided solely as a convenience to you. Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain.
Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain.
I understand
You are about to visit a Philips global content page
You are about to visit the Philips USA website.
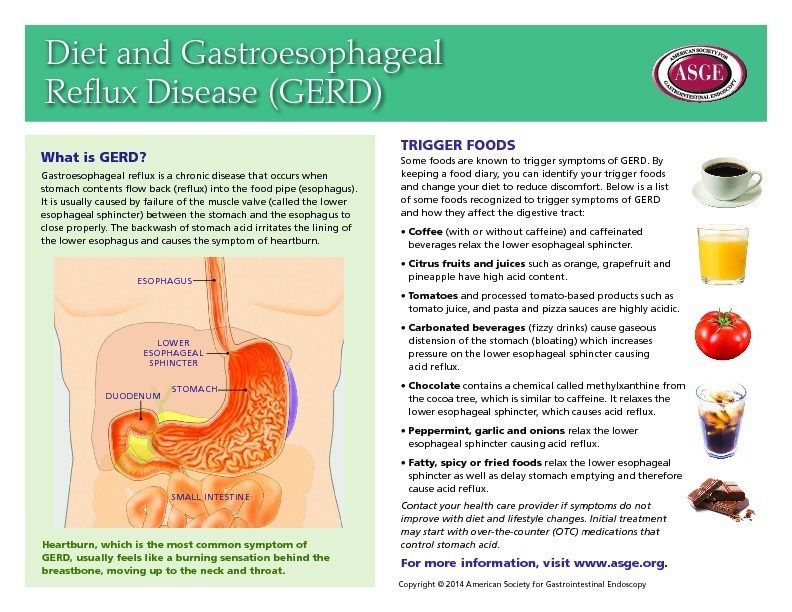
Diet for GERD. What foods to watch out for
Breast baking may have experienced once in your life by eating a lot of food and specific foods and having an unpleasant sensation of burning breasts. However, if you eat several times a week, your breasts will come up, or if your symptoms become severe or you are unable to sleep, you may have gastric floating (GERB). In this case, we recommend that you consult a doctor.
How to treat GERD
Appropriate treatment of gastric float (GERB) begins with an accurate diagnosis after consultation with your doctor. It must be understood that chronic reverse color does not heal naturally. Commercial preparations may relieve symptoms in the short term, but long-term use may cover underlying conditions.
The treatment coat of arms includes doctors recommended by doctors, food and lifestyle improvements. The combination of approach is chosen individually, especially in the case of eating habits, and some people may need trial and error.
Food and lifestyle changes often start with a list of things to avoid. These include foods that can cause or worsen symptoms.
Foods that should be reduced or avoided.
- High product
- caffeine
- chocolate
- bow
- mint
- soda drink
- alcohol
- Citrus and tomato products
In order to make appropriate dietary and lifestyle changes, you need to determine what is best for you. Not all causes and treatments do not affect everyone. Keep in mind that your food is just as important as what you eat. One food that causes reflux when eaten 3-4 hours before bed may be harmless at the start of the day.
Eating right for GERB doesn't always mean giving up all your favorite foods. In many cases, this is enough to change your diet a little.
In many cases, this is enough to change your diet a little.
The "Grb Diet" has not been established, but the following foods may help relieve and avoid symptoms.
Fruits and vegetables
This is a fruit. It would be safer to avoid citrus fruits and juice (orange, grapefruit, lemon, lime). Give priority to banana, melon, apple, pomegranate and pears. Vegetables. Avoid or add fat, such as tomatoes and onions, or reduce or number.
Lean proteins
Eggs. There is a lot of protein. However, those who aren't great with eggs are the protein type, and if they avoid the fatty egg yolk, they can almost always cause symptoms. Soft meat. Fatty and fried foods generally reduce lower esophageal a-sphincter (NP) pressure, delay gastric emptying, and increase the risk of reflux. Choose boiled, dry pan fried or choose low meat.
Complex carbohydrates
Oats, whole grain bread, rice, couscous. All of this is a useful compound supply of sugar. Whole grain foods and brown rice add dietary fiber. Root vegetables such as potatoes.
Root vegetables such as potatoes.
Healthier Fats
Lipids are high in calories and special nutrients but are essential for the diet. Not all fats are the same. In general, it is desirable to avoid or reduce the intake of saturated fatty acids (commonly found in meat and dairy products) and trans fatty acids (found in processed foods, margarine, and fat additives). Replace unsaturated fatty acids taken from plants and fish with the appropriate amount. Below is an example.
- Executive unsaturated fatty acids. Olive, sesame, canola, sunflower, avocado, peanut, peanut, etc. Nuts and seeds
- Unsaturated fatty acid policy. The following oils: safflower, soy, corn, flax, walnuts, soybeans, tofu. Oily fish such as salmon and squares.
Other useful tips
- Chewing gum. Chewing gum (mint or peppermint, which weakens NP, is not allowed) will increase saliva secretion and reduce the amount of acid in the esophagus.
- Please don't drink alcohol.
 All alcohol is well known as a stimulus that weakens NPCs and causes reflux symptoms. However, some people may have a strong symptom to drink one cup while others may resist the appropriate amount. Let's experiment with what suits you.
All alcohol is well known as a stimulus that weakens NPCs and causes reflux symptoms. However, some people may have a strong symptom to drink one cup while others may resist the appropriate amount. Let's experiment with what suits you. - Maintain good posture during and after meals. When drinking, it is recommended to sit down and not lie down for more than 2 hours. Standing or walking after eating promotes the flow of gastric juice in a good direction.
- Please refrain from eating before bed. Digestion increases the amount of stomach acid in the stomach. When you go to bed, stomach material from passing through the esophagus reduces the function of the subcutaneous sphincter. This is a reflux warning sign that large amounts of gastric juice and positioning work together.
- Timing varies, but it is generally said that gerb patients do not eat less than 3-4 hours before bedtime.
The right food for GERB doesn't necessarily throw away all your favorite foods. Simply reviewing your diet will often reduce discomfort for the first time. The goal is to prepare meals around a variety of healthy foods such as vegetables and fruits, low-fat protein sources, composite carbohydrates, and healthy fat.
Simply reviewing your diet will often reduce discomfort for the first time. The goal is to prepare meals around a variety of healthy foods such as vegetables and fruits, low-fat protein sources, composite carbohydrates, and healthy fat.
If you think your gerb symptoms are getting worse with food, try the diary for about a week.
Gastric reflux, or GERB for short, is one of the most common diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Disease Coat of Arms is high in North America (28%), Europe (26%) and the Middle East (33%). Gerb disease in Russia is based on the results of MEGRA studies, and 13.3% of the adult population in Japan experiences the disease.
Gerb is a disease in which the contents of the stomach return to the esophagus, causing unpleasant symptoms for the patient, causing endoscopic signs and complications.
Mechanism of the first fungus
GERD occurs when the contents of the stomach (hydrochloric acid, stomach enzymes, often bile) enter the esophagus and destroy the lining of this organ. Such casts (regurgitation) also usually occur, but they are short-lived and infrequent during the day. GERD increases the number and duration of regurgitation.
Such casts (regurgitation) also usually occur, but they are short-lived and infrequent during the day. GERD increases the number and duration of regurgitation.
What causes throws? Between the esophagus and the stomach is an anatomical barrier, represented by a ring of muscles called the "lower esophageal sphincter". The contraction and relaxation of this sphincter is responsible for the free passage of food and water from the esophagus to the stomach during meals and prevents reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. In GERD, the main cause of reflux is greater and more frequent relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter than in healthy individuals.
One possible cause of frequent relaxation is diaphragmatic hernia, which affects the coordination of the lower esophageal sphincter. Certain medications, foods, and smoking can negatively affect sphincter tone.
Regurgitation of stomach contents into the esophagus causes mucosal damage and is itself symptomatic.
Symptoms of GERD
All manifestations of GERD fall into two categories: esophageal and extraesophageal.
Esophageal symptoms of GERD include:
- heartburn - unpleasant or burning sensation in the chest
- pain behind the sternum when passing food
- Regurgitation of sour or swallowed food (regurgitation).
- dry or bitter mouth
- throat discomfort
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- increased salivation, etc.
Extraesophageal manifestations of GERD include:
- cough
- hoarseness
- sore throat (pharyngitis)
- pain in the ears (otitis media)
- tinnitus (rhinitis)
- Painful or burning tongue (glossitis)
- Damage to tooth enamel (caries), etc.
Because many people experience heartburn and sour vomiting (regurgitation), the diagnosis of GERD is often suspected by the time a doctor complains. However, some patients never experience heartburn in their lives, despite typical changes in the esophageal mucosa. However, there may be other symptoms besides those listed above that can be considered symptoms of GERD.
However, there may be other symptoms besides those listed above that can be considered symptoms of GERD.
Extraesophageal manifestations of GERD often require referral to other specialists, such as an otolaryngologist, pulmonologist, dentist. Causes of vague complaints such as cough, sore throat, and hot tongue may be due to "excessive" regurgitation of stomach contents into the airways, mouth, and pharynx.
Diagnosis of GERD
The typical symptoms of GERD (especially heartburn) allow a provisional diagnosis of GERD to be made without further investigation. However, it is necessary to perform esophagogastroscopy (EGDS) to determine the degree of damage to the esophageal mucosa (no visible changes, erosions, ulcers) and exclude complications (Barrett's esophagus, esophageal stricture, etc.). When performing EGDS, the endoscopist can use additional modes of operation and interpretation methods (chromoscopy, zoom endoscopy (ZOOM), endoscopy in NBI mode).
In an atypical example, EGDS are needed if symptoms other than the chest (such as swallowing, difficulty swallowing, etc. ) are dominant. In some cases, it is possible to detect another disease (cardiac achalasia, eosinophilic esophagitis, systemic skin, esophageal cancer) that the fungus covers.
) are dominant. In some cases, it is possible to detect another disease (cardiac achalasia, eosinophilic esophagitis, systemic skin, esophageal cancer) that the fungus covers.
When EGD is running, the following changes may be detected.
- Esophageal mucosal erosion
- Ulcer defect
- Changes in sputum type
- Esophageal volume
- Stritol (small esophagus)
In the case of 50-70%, it is seen that endoscopy does not change the esophageal mucosa or that the change is minimal swelling, redness (redness) and weakening of the esophageal mucosa. Even with these distinctive symptoms, GERB is not diagnosed with GERB, and there are special terms called "non-relapsing disorders" (NARB).
The absence of erosion does not mean that the disease is easy. As a result, it was found that the weight of the symptoms and the weight of the inflammatory change in the esophagus were not correlated. In other words, patients with NARB experience a difficult time every day, and in patients, the esophagus is largely eroded with only mild symptoms.
If the standard coat of arms treatment is not valid, an additional test is usually required to evaluate the properties of the reflux. In fact, the symptoms alone often cannot accurately judge what is rushing into the esophagus, such as acidic stomach content, bile, or both. In addition, this knowledge is necessary for the selection of effective methods of treatment in difficult cases. For this reason, as a weapon for the gastro-intestinal departments, the PH-meter (every day) and the esophageal PH measurement method (daily) have been added as a gastroenterologist's weapon.
As the name suggests, the daily esophageal p H meter allows you to know the pH vibration in the esophagus per day. As a result, information such as how the environment of this organ changes in a 2 to 4 hour time frame, how much acidity has come out of the stomach, how much of these leaks will last, and symptoms. Can be received.
In contrast to the pH meter, which can only look for acidic suctions, the pH impedance of the esophagus is not only acidic, but also a "non-essential" casting, in which bile mixes with the contents of the stomach, enters the esophagus. I can do it. This is extremely important when choosing the right tactics for the treatment of GERB patients with intractable (resistance to standard treatment).
I can do it. This is extremely important when choosing the right tactics for the treatment of GERB patients with intractable (resistance to standard treatment).
X-Ray barium diagnostic method in the esophagus is still effective. This test, which has been used for decades, allows you to assess the presence or absence of a herniated esophagus at the opening of the esophagus esophagus.
Esophageal pressure tests can assess the amount of esophageal exercise and lower esophageal sphincter members that act as a barrier between the stomach and esophagus.
Finally, a diagnosis of long-term Helicobacter pylori infection is mandatory in patients who must take acid activators (see below). Diagnosis may include measurement of respiratory yeast activity using C13 radiobone urea, antibodies to Helicobacter pylori in the blood, or antigens of the causative agent in feces, subject to appropriate preparation for testing. Note that GERD is not caused by Helicobacter pylori infection and the presence or absence of this infection does not affect the course of the esophagus. However, prolonged use by infected people of drugs that suppress stomach acid can lead to the spread of Helicobacter pylori infection. As a result, bacteria colonize not only the productive part of the stomach, but also other areas, increasing the risk of atrophy and subsequent precancerous disease.
However, prolonged use by infected people of drugs that suppress stomach acid can lead to the spread of Helicobacter pylori infection. As a result, bacteria colonize not only the productive part of the stomach, but also other areas, increasing the risk of atrophy and subsequent precancerous disease.
Complications of GERD
Complications of GERD include esophageal stricture, esophageal bleeding, Barrett's esophagus, and esophageal cancer (adenocarcinoma).
Esophageal stricture - narrowing of the organ passage as a result of intense inflammation lasting for a long period of time. After healing of the ulcer, a scar and stenosis form on the site. As a result, the passage of food and liquid from the esophagus to the stomach can be difficult. The frequency of this complication according to various literary sources is 7-23%.
Bleeding from the esophagus may occur in the presence of ulcerative lesions of the esophageal mucosa, which occurs in 2% of patients. It occurs in large numbers, goes undiagnosed, and can be life-threatening. Therefore, in the treatment of a very important step is to achieve a complete cure for erosion and ulcers of the esophagus.
Therefore, in the treatment of a very important step is to achieve a complete cure for erosion and ulcers of the esophagus.
Barrett's esophagus is a complication of GERD in which normal cells of the lining of the esophagus are replaced by cells characteristic of the small and large intestine. Barrett's esophagus is a precancerous disease that increases the risk of developing esophageal cancer by 50 times.
Esophageal cancer is a complication of long-term GERD, most commonly (95%) resulting from Barrett's esophagus.
Answering Gelba
1. Non-therapeutic treatment of GERD.
Non-drug therapy includes lifestyle modification and dietary therapy.
Weight loss is an important event in preventing GERD recurrence and increasing the effectiveness of treatment. Obese individuals are 1.5-2 times more likely to develop symptoms of the disease and erosive esophagitis according to FGDS. The risk of developing adenocarcinoma (cancer) of the esophagus in people with obesity is 2. 5 times higher than in people with normal weight. Recent studies have shown that not only obesity, but also overweight (body mass index 25-29.9 kg/m2) is a negative factor in GERD. A 2 kg/m2 reduction in body mass index further reduces GERD symptoms.
5 times higher than in people with normal weight. Recent studies have shown that not only obesity, but also overweight (body mass index 25-29.9 kg/m2) is a negative factor in GERD. A 2 kg/m2 reduction in body mass index further reduces GERD symptoms.
Because smoking is associated with the risk of developing symptoms of GERD and Barrett's esophagus, smoking cessation is an important step in lifestyle changes.
Diet therapy recommends changing the content and nature of nutrition, adjusting eating habits.
- Changes in GERB strength.
- Avoid long breaks between meals and eat regularly. This way you can prevent overeating due to severe hunger. If you eat too much, the pressure in your stomach increases, making reflux and symptoms more likely.
- 1-2 hours after eating, do not sleep, do not bend your hips, do not work on a slope. Immediately after eating, an inverted posture will cause the contents of the stomach to enter the esophagus, which is more likely to remove the food from the stomach.

- The last meal should be done two to three hours before bedtime.
- Eliminates wear with a narrow band.
- It limits exercises that increase the pressure of the internal cavity (for example, exercises to train the abdominal muscles).
- Raise your head 15-20 cm in bed and sleep.
-Resolution of eating habits in the coat of arms.
- Limit or reject drinks containing gas (sugary soft drinks, sparkling mineral water). The gas contained in the drink can cause gerb symptoms and worsen.
- Foods that relax the lower esophageal sphincter: citrus fruits, tomatoes (especially tomato paste and ketchup), mint, chocolate, coffee, caffeine.
- By limiting excessive intake, it is possible to maintain a longer Laparus pressure without being discharged from the stomach for a long time.
2. GERB treatment treatment
Coat treatments have several groups.
- A drug that suppresses acidic foods in the stomach (h3-hydraulic blocker, proton pump inhibitor).

- Foods that regulate motor function in the upper gastrointestinal tract promote the release of food from the stomach.
- Symptomatic drug (acid control agent t-control, algin acid, etc.) - laying with hydrochloric acid in the stomach and reduces the amount of acid in the esophagus.
- Bile acid preparation is used for mixed backflow, reducing bile aggression in the esophagus.
3. Surgical treatment.
Surgical treatment Herb is usually recommended for intractable (resistance to pharmacotherapy), the existence of complications and the combination of hernias in Chinese medicine. The most famous of the surgical methods are burials performed with laparoscopes.
In recent years, the effectiveness of new technologies has been actively studied, and in particular the placement of a magnetic sphincter muscle implant that electrically stimulates the lower esophageal sphincter.
Gel prognosis
Germ is a disease that is easy to recur, but the prognosis is usually good, and with timely appropriate treatment, more than 90% of patients achieve good control during the process.
FAQ
Can Barrett's esophagus be treated?
By providing appropriate basic treatment and supporting therapy and advocating dietary and lifestyle recommendations for a long time, it is possible to reduce the influence of organs and reverse the mucosal membrane of these organs.
Is it harmful to take a proton pump inhibitor for a long time (several months, several years)?
We provide long-term supportive care based on successful treatment.
What should I do for breast burn torture during pregnancy?
The presence or absence of a breast during pregnancy is not transferred to the coat of arms. Abnormal acid casting, which is chest heartburn, is a multiple factor in pregnancy (increased internal cavity pressure and due to fetal growth, remodeled hormone, etc.). In some cases, this period can be tolerated, or if you are advised by a doctor, you can start taking safe alginic acid preparations during pregnancy and prescribe a proton pump inhibitor approved during pregnancy in the third semester. 。
。
Should I always follow recommendations to change my lifestyle?
Lifestyle advice should always be followed to reduce the risk of relapse.
Is frequent tooth decay an effect of the first coat of arms?
Yes, there is, of course, petit's tooth mask. To do this, it is necessary to check the test method using the device and jointly process the dentist and the digestive doctor.
Treatment history
HISTORY 1
Patient K (25 years old) mainly visited Laura, an expert on the clinic, mainly suffering from dry cough and constant sore throat at night. In the test, the hypothesis was that acid was thrown as the cause of the cough (gastric reflux mask). The patient was referred to the clinic's expert, a digestive physician.
The diagnosis was confirmed by endoscopy. The patient was scheduled to provide dietary guidance and lifestyle improvements, help control casting and pathological acid treatments, and prescribe treatment along with otolaryngology. As a result of a comprehensive treatment designed individually, vague complaints were no longer available. Continue to support treatment and follow-up by GI physician and Laura.
As a result of a comprehensive treatment designed individually, vague complaints were no longer available. Continue to support treatment and follow-up by GI physician and Laura.
Case history 2
A 5 to 6-year-old patient was not consulted for coronary artery disease and angina pectoris. Recently it has been noted that the back of the sternum has become hot in connection with diet, regardless of physical and mental stress. The patient underwent a comprehensive examination to rule out progression of cardiovascular disease. The patient was sent to the gastrointestinal department to clarify the properties of rally pain without negative evidence. After an appropriate drug, endoscopy of the esophagus, stomach, and 12th intestinal tract has been proven to be due to stimulation of the esophagus by sucking (cast) hydrochloric acid from the stomach. This patient was prescribed a complex treatment, which agreed with the gastrointestinal and cardiological doctors. Currently, he has no vague complaints and continues to observe and treat experts at the clinic.
Gastric float (GER) is also called acid reflux, which is a common problem that causes heartburn.
Many people regularly experience breasts (or the reverse color of acid in the mouth), but they usually do not worry. This sensation is not the most fun, but it usually heals quickly. There are not many of them, but after a big meal or a spicy and sour dish, it can damage the lower part of the chest, which is reflux.
In the case of GER, a reverse color occurs after each meal, resulting in remarkable discomfort. After eating, GER people feel their chest, throat, and neck become hot. There are many adults, but children, youth and infants can have stomach fluid.
What is gastroesophageal reflux disease?
GERD is an abbreviation for acid reflux that occurs more than twice a week. This is a more serious disease than Ger. Doctors usually treat them with drug therapy. Leave Gerd behind because the backflow of stomach acid destroys the tissue that covers the esophagus, causing inflammation and pain. In the case of adults, leaving GERD untreated for a long time can lead to permanent damage to the esophagus and sometimes cancer.
In the case of adults, leaving GERD untreated for a long time can lead to permanent damage to the esophagus and sometimes cancer.
What are the signs and symptoms of GERD?
Gerd often experiences chest burns with sensation of burning chest and stomach. This lasts up to several hours. Many people find that their chest is on fire after eating.
"Reflux", in which foods containing stomach acids and reflux of moisture in the throat and mouth are also signs of GERD. However, as in the realm of heartburn, everyone is always hungry.
Other symptoms of GERD include:
- Sore throat, weak voice
- sour
- Mouth insertion
- When your throat hurts, especially when your mouth is noisy, or when your mouth hurts
- Feeling that the throat is stuffed up
- Graceful
- Dry cough
- bad breath
GERD occurs when the acid content in the stomach flows back into the esophagus. This is the tube that carries food and liquid from the mouth to the stomach. The stomach is separated by a small muscle (esophageal sphincter). This muscle opens to allow food and liquid to enter the stomach, preventing food and liquid from returning back to the esophagus. GERD and GERD are caused by the fact that the muscles are relaxed or not closed after food is swallowed. This happens for various reasons.
The stomach is separated by a small muscle (esophageal sphincter). This muscle opens to allow food and liquid to enter the stomach, preventing food and liquid from returning back to the esophagus. GERD and GERD are caused by the fact that the muscles are relaxed or not closed after food is swallowed. This happens for various reasons.
- Depending on the person, the muscles may be too weak and may not contract as expected.
- In addition, stomach contents cannot be returned to the esophagus because the sphincter is fast enough or at the right time.
- If you eat too much, your stomach may grow and your muscles may not close enough.
Nobody knows exactly why he gets GERD. Doctors have noted that certain factors, such as obesity, alcohol use, and pregnancy, can worsen GERD.
Certain foods and medications can also make GERD symptoms worse.
For example, this causes reflux s-esophagitis.
- Citrus
- chocolate
- Caffeinated drinks or caffeinated products
- Caffeine / coffee n-containing food
- Garlic, onion
- Mint flavor
- Sharp things
- Tomato products such as spaghetti sauce, chili and pizza.

How is GERD diagnosed?
If you have symptoms of GERD, such as heartburn, for a period of time, you should see your doctor. Doctors may ask questions about physical tests and symptoms, and sometimes do additional tests to diagnose GERD and rule out other possible problems.
- A special x-ray called a barium swallow x-ray can help doctors judge whether fluid is properly discharged into the esophagus. In addition, you can see if the esophagus is inflamed and there are other abnormalities in the esophagus and stomach, and alleviate the reverse color. In the test, you have to drink a special solution (a liquid similar to barium) and detect the liquid using x-Ray.
- Upper endoscopy can be used to examine the esophagus, stomach, and part of the small intestine using a small camera. During this test, your doctor may give you medication to help you relax or have you jump up and down to numb your throat to make the test more comfortable. Most patients are under anesthesia and are "asleep" when the endoscopy is performed.
 A thin, flexible plastic tube called an endoscope is then passed down the neck into the esophagus and stomach. A small camera built into the endoscope is used to check the lining of the esophagus and stomach for abnormalities. During an endoscopy, the doctor may use small forceps to take a piece of tissue for a biopsy. A biopsy can help detect lesions caused by acid reflux or infection and rule out other problems.
A thin, flexible plastic tube called an endoscope is then passed down the neck into the esophagus and stomach. A small camera built into the endoscope is used to check the lining of the esophagus and stomach for abnormalities. During an endoscopy, the doctor may use small forceps to take a piece of tissue for a biopsy. A biopsy can help detect lesions caused by acid reflux or infection and rule out other problems. - In another type of yeast, called the 24-hour impedance test, the doctor inserts a small tube through the nose and down the esophagus until the tip is just above the opening in the stomach. Leave the phone on for 24 hours. This tube is attached to a device that monitors the level of acid in the esophagus as people go about their normal daily activities. Also monitor the number of episodes of acid reflux and non-obstructive reflux. This test is useful for diagnosing people with GERD symptoms but no esophageal involvement. It can also determine if reflux is causing respiratory symptoms such as choking or coughing.

How is GERD treated?
It all depends on the severity of your symptoms. For some people, treatment may require lifestyle changes, such as diet and alcohol consumption. Also, some people need medication. Very rarely, if GERD is particularly severe, a doctor may recommend surgery.
These lifestyle changes can help relieve or prevent symptoms of GERD.
- Refusal of alcohol, smoking
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse, smoking and tobacco cessation, alcohol and tobacco cessation, overweight weight loss, etc.
- eat in small portions
- choose casual clothes
- Refusal of carbonated drinks
- Avoid foods that cause reflux.
- Also effective is bipedalism, refraining from eating for 3 hours after eating and 2-3 hours before bedtime.
- Your doctor may also recommend raising the head of your bed 30 to 40 cm. But before you start repairing your bedroom headboard, talk to your doctor about the situation that is most comfortable for you.

Your doctor may also recommend various medicines to help relieve your symptoms. OTC antacids neutralize stomach acid and are effective for mild symptoms. Other drugs, called h3 blockers, are available over-the-counter and by prescription. It works by inhibiting gastric acid secretion.
If your doctor thinks you should take it, he or she will recommend or write you a prescription for a certain over-the-counter drug. The most powerful prescription drugs, called proton pump inhibitors, also reduce the amount of acid produced by the stomach. There are some that are sold without a prescription. Doctors prescribe it to people with a more severe and persistent course. Drugs belonging to the prokinetic class can be used to strengthen the muscles of the lower esophageal sphincter and speed up gastric emptying, which reduces the frequency of reflux.
Some doctors recommend using medicines together to suppress various symptoms. For example, if you have breasts after eating, you can take both acid control and h3 blockers. Acid control agents maintain stomach acid and the h3 inhibitor works to produce acid. By the time acid control is no longer effective, the h3 blocker stops acid production.
Acid control agents maintain stomach acid and the h3 inhibitor works to produce acid. By the time acid control is no longer effective, the h3 blocker stops acid production.
Surgery is an extreme treatment for people with coat of arms. The typical surgical treatment of the Coat of Arms is called a specialist. During the operation, the doctor will thicken the sphincter of the esophagus, wrap it around the stomach so that there is no casting. Funding is used across a wide range of ages and is also used for children with a severe outlook.
Living with GERD
The key to living with GER B is not to ignore the symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can reduce or stop unpleasant symptoms. However, if you don't treat it, GERB can cause permanent damage to the esophagus.
The main complications of GERB are called Barrett's esophagus. In this condition, the cells in the esophagus are changed and the stomach acid has been disturbed for a long time, causing arrhythmias. Eventually, the swelling of the esophagus becomes stronger.
Eventually, the swelling of the esophagus becomes stronger.
I think one of the easiest ways to coexist with GERB is to avoid symptoms. Some people need to limit the use of certain products. You may also need to give up completely. It all depends on your personal symptoms.
First of all, it can be difficult to give up carbonated drinks and your favorite foods. However, after a while, many people feel better and cannot return to the unpleasant meal.
If you are in good health and have initial symptoms of reflux disease, register your doctor.
There is a condition called "esophagitis" that causes inflammation in the lining of the esophagus. The back of the chest is accompanied by discomfort, burning and pain. Pathological opening of the heart hole (sphincter) causes the contents of the stomach to enter the esophagus. According to a study by the World Health Organization, about 50% of the population of developed countries suffer from this disease. Literally 30% seek help from a medical institution and receive special treatments less than 4% in accordance with the recommendations.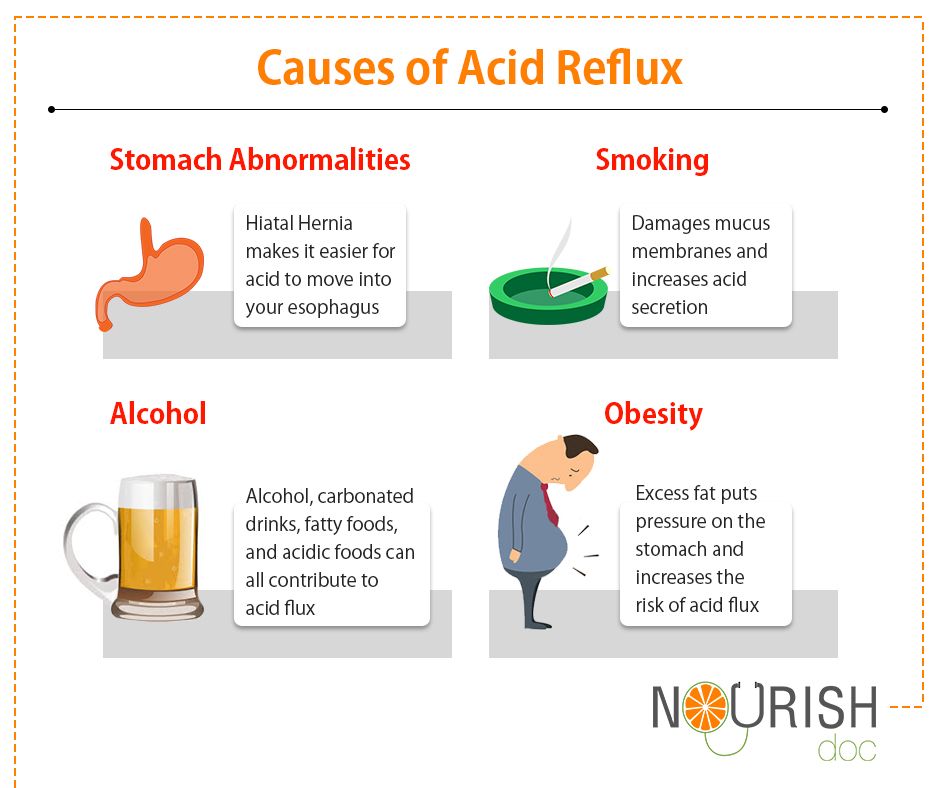
Disease information
According to epidemiological studies, about 23.6% of the adult population suffers from gastro-intestinal reflux. Characteristic is that it is chronic and easy to repeat. The search for the contents of the stomach in the lower part of the esophagus naturally occurs. Inflammation occurs at the site of contact with the mucous membrane, causing discomfort and poor physical condition. In the medical field, the official name is Reflux Gastronomy (GERB).
Manifestation of symptoms and signs
The coat of arms has many symptoms and signs depending on the stage of the disease.
- Breast burn (most common symptoms).
- Pain in the chest near the heart
- The most common symptoms are stiffness and swallowing of the throat.
- Often cough, causing inflammation of the airways.
- Weight Loss
- Hoarse voice.
- I have a light sleep.
- I have nausea and stomach pain.
- Bloating.
- Vom
Only doctors can diagnose accurately. Please do not delay consultations - Phone: +7 (495) 775-73-60
Causes of the disease
Esophagitis is caused by various factors that are associated with a hectic lifestyle. In this regard, unsuitable diets with high fat and frequent consumption of carbonated drinks are distinguished. Cause list:
- Intestinal peristalsis
- I have diabetes.
- metabolic syndrome
- Infection (Candida fungi, herpes simplex virus, site megalovirus).
- Esophageal mouth diaphragm hernia.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Take some drug group.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
GERD types, manifestations and complications
The medical classification is divided into two types: acute esophagitis and chronic esophagitis. It depends on the type of inflammation process. The walls of the esophagus are exposed during the acute phase and the mucosa is exposed for six months during the chronic period. Reflux esophagitis is caused by disturbed eating habits, exposure to chemicals, and a wide range of infections. During the acute phase, there is an increase in body temperature, general malaise and discomfort at the entrance to the esodial. Patients may have saliva, abuse, and pain during an attack. Alcohol addiction, spicy food and rough food make inflammation. Enter a chronic period. If you don't treat, the esophagus will change and scars will form.
Reflux esophagitis is caused by disturbed eating habits, exposure to chemicals, and a wide range of infections. During the acute phase, there is an increase in body temperature, general malaise and discomfort at the entrance to the esodial. Patients may have saliva, abuse, and pain during an attack. Alcohol addiction, spicy food and rough food make inflammation. Enter a chronic period. If you don't treat, the esophagus will change and scars will form.
Treatment information
Treating submitted candidates is a great point to know when symptoms or poor physical condition appear. By early diagnosis and treatment, you can reduce pain and discomfort and present them with a stable remission.
How Diagnosis is Made
Digestive medicine has several methods of making an objective diagnosis to judge the patient's condition and the degree of esophageal disorders. Esophagitis can cause a strong symptom that triggers a consultation. Diagnosis and treatment are performed by the gastrointestinal departments. The patient test is performed with the following.
The patient test is performed with the following.
- Collect happiness anesthesia and illness.
- X-ray contrast agent (with barium).
- Endoscopic gastric chamber
- PH metal and manometry.
- Laboratory testing of gastric fluid
Methods of treating the disease
In the case of esophagitis, treatment is prescribed taking into account the condition and condition of the patient. The most important condition is to change the lifestyle and plan to reduce the amount of acids in the esophagus. Includes processing device.
- I take medicine to suppress stomach acid.
- If there is an infection, antibiotic treatment is given.
- Continue diet.
- Surgery for complex diseases.
What is reflux esophagitis diet
The reflux esophagitis diet can help maintain normal weight and increase stomach acid. Patients need to maintain a meal schedule of 4-5 times a day. Flash should be smaller. It is recommended that carbonated drinks, coffee, chocolate, citrus fruits and strong tea be excluded from meals. It is important not to create a reason for increasing internal pressure. To do this, it is better to stop tight belts and tight clothes without having a heavy one (8-10 kg or more). The place to sleep is positioned so that the head and neck are higher than the height of the abdomen. This prevents the stomach from passing into the esophagus during rest.
It is recommended that carbonated drinks, coffee, chocolate, citrus fruits and strong tea be excluded from meals. It is important not to create a reason for increasing internal pressure. To do this, it is better to stop tight belts and tight clothes without having a heavy one (8-10 kg or more). The place to sleep is positioned so that the head and neck are higher than the height of the abdomen. This prevents the stomach from passing into the esophagus during rest.
Answers to frequently asked questions
How to cure esophagitis?
Esophagitis is treated according to the degree of expression of the disease and the inflammation of the esophagus. Medicine is prescribed during the acute phase, but it is recommended to protect the principle of dietary supplementation. Surgery may be indicated if difficult cases or reflux s-esophagitis progress.
Esophagus What is this disease?
Reflux Esophagitis s is a non-infectious disease that causes inflammation of the esophagus because the back content of the stomach contents cannot be controlled. GERD is one of the diseases commonly found in digestive medicine.
GERD is one of the diseases commonly found in digestive medicine.
How to treat reflux esophagitis?
90% of patients have a good recovery prognosis. Treatment is prescribed by a doctor after a diagnosis and clinical examination. In most cases, medical treatment is required. The drug is prescribed to reduce the acidity of gastric juice and eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
Share information with friends
Current problem
For most people, heartburn occurs occasionally. In developed countries, about 20% of the population is tested at least once a month.
However, for the 6% of people with chronic breasts, called gastric floaters (GERD), no treatment (unproductive treatment) can cause various health complications. People with esophageal mucosa and acid reflux often do not notice the harm of GERD until the disease progresses.
If your heartburn is frequent or long-lasting (occurs about twice a week), talk to your doctor. Here are nine reasons you shouldn't ignore acid reflux symptoms.
Here are nine reasons you shouldn't ignore acid reflux symptoms.
1. Development of inflammation in the esophagus (esophagitis)
In the reverse flow of acid, food, acid and digestive juices are thrown into the esophagus. As a result, the lining of the esophagus is stimulated from within and swollen. This is esophagitis. If you only see in the esophagus, the mucosal inflammation may only progress for a few weeks. As a result, there may be a feeling of inconsistency or pain along the midline of the abdominal wall, "under the gastric opening", as well as the left and right side that converges with the sternum. With this inflammation, the esophagus is more likely to fall into more dangerous conditions, such as being startled.
2. Esophageal stricture
If esophagitis persists for a long time, scar tissue may form and the esophagus may become narrowed. This stenosis can make it difficult to pass and swallow food, blockage at the level of scar tissue, which can cause pain.
Large food may be clogged and may need to be removed by endoscopic intervention in this condition. And because of the stenosis, sedation can often occur during meals. As a result, patients refuse to eat and lose weight dramatically.
Stenosis is treated by dilating or dilating the esophagus (whine or dial). These treatments can be performed repeatedly to get an impact on the stenosis. However, taking a gastric acid secretion inhibitor (proton pump inhibitor, PPI, h3 inhibitor) may prevent future recurrence of the esophagus.
3. Throat and voice problems
The main symptoms of acid reflux are chest burns, but not everyone feels and expresses it. There may also be other symptoms that are difficult to diagnose. Doctors call such cases "dambar flow" or asymptomatic reflux. Even if there is no chest in the textbook, as the textbook says, there may be some problems that occur in parts other than the esophagus, such as hoarseness, voice changes, pain in the pharyngeal region, and chronic cough. There is a sensation of lumps and hairs in the throat and you should always cough and cough.
There is a sensation of lumps and hairs in the throat and you should always cough and cough.
4. Breathing problems
Coat of arms can worsen the progress of bronchial asthma and pneumonia when stomach acid in the esophagus in the esophagus reflux into the esophagus. Even if there is no problem with the lung coat of arms, it may cause shortness of breath or shortness of breath. And the treatment in this state is an e-sword with a double substance. Garb therapy, such as proton pump inhibitors, can actually increase the risk of pneumonia. (This promotes the spread of bacteria and suppresses coughs caused to clear the lungs).
Have your doctor check your lung function when treating reflux.
5. Tooth Decay
When stomach acids and digestive juices enter the mouth from the esophagus, it feels sour, and when this is common, tooth enamel becomes damaged and is more likely to become tooth decay.
6. Ulcers of the esophagus
Acid organization in gastric acid. The membrane of the esophagus, causing injury and ulcers. Esophageal ulcers are different from gastric ulcers caused by bacteria. Those who have love or an ulcer may vomit blood. It can also vomit blood. It seems that the blood can be mixed in the stool. The blood looks like red, cherry brown particles. In stool, blood from the esophagus and stomach usually becomes black and bad flash, color, color and oil, sticky, slippery, slippery and bad flash.
The membrane of the esophagus, causing injury and ulcers. Esophageal ulcers are different from gastric ulcers caused by bacteria. Those who have love or an ulcer may vomit blood. It can also vomit blood. It seems that the blood can be mixed in the stool. The blood looks like red, cherry brown particles. In stool, blood from the esophagus and stomach usually becomes black and bad flash, color, color and oil, sticky, slippery, slippery and bad flash.
If you have these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately. Endoscopy can find esophageal ulcers. It is also possible to lose it with an acid blocker or acid smoke.
7. Barrett's esophagus
If left untreated for many years, stable acid reflux can form cellular changes and a trigger condition called bullet esophagus can occur. This symptom has no specific symptoms except for backflow symptoms. Doctors can be diagnosed by endoscopy.
If you have a long period of time or more over a long period of time, if the symptoms of acid reflux are worse, if you find a new symptom that you did not have, all this should be checked or endoscopy.