Foods that give breastfed babies diarrhea
6 Foods That Cause Diarrhea In Breastfed Baby
https://www.whateatly.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/foods-that-cause-diarrhea-in-breastfed-baby.png
This list of foods that cause diarrhea in breastfed baby is all you'll ever need to answer "what causes diarrhea in breastfed baby" we believe.
Foods that cause diarrhea in breastfed baby is the next topic that we cover in this article.
If you are wondering why we picked this one, it’s because after we’ve written few articles about breastfeeding on our website, we’ve received this email from a mommy asking “what causes diarrhea in breastfed babies?” – and since we were already covering anything-breastfeeding, we thought it’d be good to answer this query as well before we move on to the next topic.
That said, we want to share with you that why one should pay close attention to what she eats: the edibles that are being consumed have a direct effect on your baby as well, not just you.
Whatever that you’re eating or taking in into your stomach will be passed down to your baby from the breastmilk.
If the consumed fluid or food is healthy, your baby will grow and be normal – if, however, the consumed fluid or food is unhealthy, your baby will have to face many different issues, including diarrhea.
That said let’s get started with sharing a list of foods that cause diarrhea in breastfed baby.
Quick Navigation
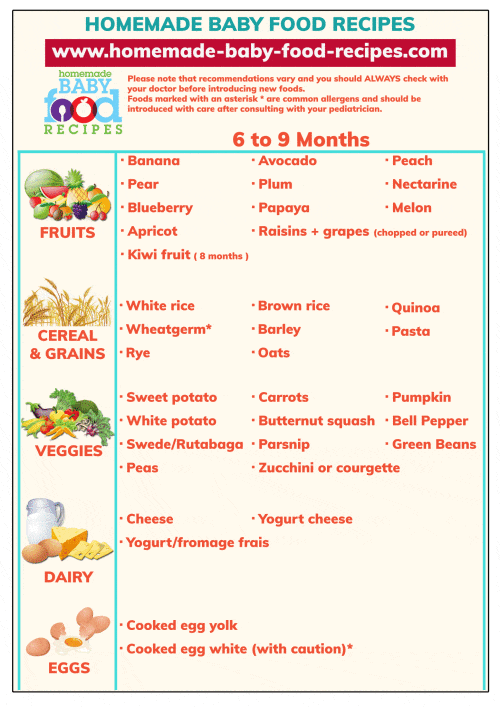
Foods That Cause Diarrhea In Breastfed Baby:
Hey mommy, your question that asked “what causes diarrhea in breastfed babies?” is answered here in this part of the article.
1 – Dairy:
The very first food type you must stop consuming when breastfeeding your baby is a dairy type, or dairy products.
Dairy products have lactose, which in most cases, is hard for babies to digest – their digestive system isn’t as strong as yours and may leave your baby in stomachache or diarrhea.
However, yogurt is okay if you want to add dairy to your diet. Greek yogurt is one of the best ones.
Greek yogurt is one of the best ones.
2 – Greasy foods:
Greasy, fried, or oily foods go hard on the stomach and make digestion slow, even in matured people.
The fact that your baby’s digestive system is only 2/10 powerful and strong than yours is the reason you must stop taking in greasy or oily foods.
3 – Fatty foods:
Foods that have lots of fats are also hard to digest and takes time to be fully dissolved in your system.
Your baby here again isn’t capable of digesting fatty foods.
4 – Raw fruits and vegetables:
If you try to consume edibles raw, the amount of fiber found in them is much more than that of when they are cooked or prepared.
Fiber, in case you don’t know of, can change the speed of how fast your body performs digestion – more the fiber, slower the digestion.
For this very reason, you are not advised to eat raw vegetables and fruits before breastfeeding if you want your baby to be safe from diarrhea and things like it, i. e. stomachache.
e. stomachache.
5 – Spicy foods:
The next very dangerous type of foods you can consume while breastfeeding is a food type that has spices.
Spices can really affect the stomach and digestive tract – only the strongest of systems can fight back the effects of spices on your digestive tract.
As babies have a very weak system, it is strongly advised to keep them away from foods that are spicy.
6 – Whole grains:
Whole grains are not digested easily; they take some time.
This is another food type you must avoid.
However, when your baby is 8-9 months old, you can introduce whole grains to your baby if you want.
Mentioned below are extras included in this article.
Fluids That Cause Diarrhea In Breastfed Baby:
Next comes the list of fluids that you must avoid if you want your baby to be safe from diarrhea.
1 – Tea and coffee:
Tea and coffee have nicotine, which if consumed and passed down to your baby, can leave him disturbed and fussy.
On top of that, the chances of diarrhea due to nicotine are also present and are on the peak.
This is why even smokers aren’t allowed to smoke while breastfeeding.
2 – Alcohol:
Alcohol needs no explanation we believe.
They are not only dangerous for your baby but for your own self as well.
You must put an end to its consumption as soon as possible.
3 – Soda:
Sodas have chemicals that go hard on the stomach, all the time.
Only strongest of systems can survive its effect
Your baby shouldn’t be exposed to sodas yet.
4 – Formulas:
Formulas, like powdered-milk instead of breastmilk, are very dangerous for your baby to consume.
I know this isn’t something you’d want to drink and then pass down to your baby by breastfeeding, but we found some importance of adding this one to this list as well.
You must not make your baby consume formulas for at least a year.
5 – Fruit juices:
Fruits and their juices have sugars which are hard for babies to digest – and these sugars can cause diarrhea and discomfort in return.
Babies younger than 5 months will most likely be affected by fruits and their juices, damaging their immature gastrointestinal systems.
This extensive list of foods that cause diarrhea in breastfed baby is all there is that will answer “what causes diarrhea in breastfed babies?” we believe.
If you think we missed some of the edibles and fluids that aid in the process of digestion, let us know in the comments section.
Conclusions:
A. There are 6 food types you must avoid if you want your baby to be safe from diarrhea.
B. There are 5 fluids that cause diarrhea in breastfed babies as well.
Foods to Eat or Avoid When Breastfeeding
Reviewed by Poonam Sachdev on June 26, 2022
It’s a good source of protein. Some, like salmon and tuna, also give you omega-3s, which your body needs. But what about mercury and other contaminants? You can have cooked seafood twice per week. Each serving can be up to 6 ounces, which is the size of two decks of cards. Choose types that are lower in mercury, such as salmon, tilapia, and trout. Avoid shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish, which have high levels of mercury.
Choose types that are lower in mercury, such as salmon, tilapia, and trout. Avoid shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish, which have high levels of mercury.
Love hot sauce? Most babies can handle it and other fiery foods in your diet. But if your little one is gassy or colicky and gets diarrhea every time you sprinkle red pepper flakes over your pizza, cut back on the heat for a few weeks to see if that helps.
They’re full of flavor. But some herbs may affect how much milk your body makes. For instance, eating a lot of parsley could curb lactation. And too much sage and peppermint may cut your milk supply. For some nursing moms, even peppermint-flavored toothpaste and candies are a problem.
It’s rarely a problem. But see how your baby does. Tell your pediatrician if your tot gets skin problems, has trouble breathing after breastfeeding, or has other symptoms.
As refreshing as your cup of chai or Earl Grey may be, it has some downsides. It’s got caffeine, which can affect your sleep – and your baby’s. It may also make it harder for your body to absorb iron, which you need for energy. If you drink hot or iced tea, try not to sip it when you eat foods that are rich in iron, such as lean meat; dark, leafy greens; and fortified breakfast cereals.
It may also make it harder for your body to absorb iron, which you need for energy. If you drink hot or iced tea, try not to sip it when you eat foods that are rich in iron, such as lean meat; dark, leafy greens; and fortified breakfast cereals.
What if you aren’t allergic, and you want to prevent your baby from developing an allergy? Sorry, but there’s no proof that you can do that by skipping specific foods. Cutting certain foods out of your diet may make the skin condition eczema less likely for your little one. Ask your doctor or pediatrician for advice.
Breastfeeding can make you thirstier than you usually are. If that’s the case, drink a glass of water every time you breastfeed. But no matter how parched you feel, don’t go for regular sodas or fruit drinks, which give you calories without nutrition.
It's best for your baby if you don't have any booze at all. But if you do choose to drink, don’t breastfeed until the alcohol has completely cleared your milk. For 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1. 5 ounces of liquor, wait at least 3 hours. Pumping doesn’t speed that up.
5 ounces of liquor, wait at least 3 hours. Pumping doesn’t speed that up.
Common culprits include beans, broccoli, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts. Bloating, burping, and passing gas are normal. But if your baby is gassy or has colic, avoid these foods for a few weeks to see whether they relieve the symptoms.
Both have caffeine. You’ll also find it in energy drinks and cola. If you’re lost without your latte, limit yourself to 2-3 cups per day of the brewed kind. Or you could switch to decaf.
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
1) Getty
2) Getty
3) Getty
4) Getty
5) Getty
6) Getty, iStock
7) Getty
8) Getty
9) Getty
10) Getty
SOURCES:
Mayo Clinic.
The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
La Leche League.
The American Academy of Pediatrics.
U.S. Department of Agriculture.
© 2022 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. View privacy policy and trust info
Diarrhea in infants - what causes it and how to treat it
- Alla Anatolyevna, please tell us what diarrhea (diarrhea) is in babies.
- Diarrhea is a disease, a functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, which is accompanied by loose stools. There is a Bristol stool scale, according to which diarrhea is considered to be liquid or semi-liquid with hard lumps. Diarrhea is not typical for healthy children.
- What are the symptoms of this problem and how can a mother tell diarrhea from normal stool?
- Diarrhea in young children is quite rare. However, according to the statistics of the World Health Organization, a functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by diarrhea, is in second place among the causes of death in children of the first year of life.
- Loose stools in babies are normal.
A child of the first or second month of life has a more liquid stool than an adult. If a baby has an egg-yolk-like stool and empties his intestines after each feeding, but gains weight well, eats and sleeps, is cheerful and does not cry, then this should not cause concern to the mother.

Important! Diarrhea is not just loose stools. If a child does not gain weight in the first months of life and has frequent watery, frothy or loose stools with mucus or blood, this is a reason to immediately contact your pediatrician.
- Alla Anatolyevna, what can cause diarrhea in a baby?
- For a child of the first months of life, the main cause of diarrhea is food intolerance, for a child of the second half of life and the second year of life - an intestinal infection of a viral nature. But why the baby has diarrhea, in each case, the doctor must decide.
A food allergy in an infant occurs to the food he receives, most often to cow's milk protein. Causes of allergies in infants:
- in a child exclusively breastfed - the use of dairy products by a nursing mother;
- in a bottle-fed child - a reaction to cow's milk formula protein;
- in a child on mixed feeding - more allergic to formula milk, to a lesser extent allergic to mother's milk.

Infection of the baby with intestinal infections occurs through dirty hands and toys (when the child starts to crawl, pick up objects from the floor with his hands, play outside).
Signs of an intestinal infection in a child:
- refusal to eat;
- decreased appetite;
- temperature increase;
- vomiting.
- What does the color of the stool in a breastfed and bottle-fed baby say - what are the norm and dangerous situations?
- Bile pigments are responsible for the color of the stool, which are produced by the liver, accumulate in the gallbladder and are released during nutrition, helping digestion. They stain the baby's stool yellow, green, or olive. Therefore, if the child feels well and gains weight well, and the stool has a greenish-yellow tint, this is the norm for up to a year.
- The baby has yellow diarrhea
If a child of 4, 5 or 6 months has yellow stools and fever, the stools become more frequent and become watery and plentiful, appetite has decreased - these are signs of an intestinal infection.

- Infant has diarrhea with mucus
Mucus in the stool is a product of the goblet cells of the intestine that secrete mucus. Mucus in the stool in a child is a sign of inflammatory colitis of the colon (an indicator of a food allergy or the final stage of an intestinal infection). Mucus in the stool should not be.
- Diarrhea without fever in a child - what can this mean and what should a mother do?
- Do not ignore diarrhea without fever in the baby. This may be a manifestation of pathological conditions. Such as:
- Food allergy - the cause will be determined by the doctor, who will also tell you what to do for mom.
- Antibiotic-associated diarrhea - in children, it occurs during the treatment of an infectious disease, which is associated with the activity of clostridia and their toxins, which is accompanied by diarrhea with blood. Such a serious condition requires a visit to the doctor.

- Gluten intolerance - prolonged diarrhea in celiac disease does not respond to traditional treatment and does not resemble the course of an intestinal infection. The assumption of the presence of such a disease requires additional examination, observation, and at least a consultation with a competent pediatrician and pediatric gastroenterologist.
- Alla Anatolyevna, can diarrhea begin when teething?
- During the teething period, there may be a violation of the stool, but it is not due to the fact that the baby is teething. Teething is a normal, physiological process that occurs in all children. Diarrhea is not a norm, but a pathological disorder of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), which is accompanied by loose stools.
- Diarrhea for complementary foods - what is considered the norm, and what is a problem in such a situation?
- The first complementary foods are introduced to a healthy child in the second half of life. Starting from 6 months, the mother will gradually introduce vegetable purees, cereals, fruit purees and other complementary foods into the baby's menu.
Starting from 6 months, the mother will gradually introduce vegetable purees, cereals, fruit purees and other complementary foods into the baby's menu.
The introduction of complementary foods in a child may be accompanied by a violation of the nature of the stool. But I wouldn't say it's diarrhea. The color of the stool may change in response to the color of the complementary foods, do not worry or worry.
It is necessary to worry and consult a doctor if atopic dermatitis worsens during the introduction of complementary foods, mucus appears in the stool, and skin rashes appear. It is important to determine the cause of the exacerbation (food allergy, intestinal infection, or simply a reaction to complementary foods). Mom needs to remove complementary foods for one or two days, observe the child, and then decide with the doctor what tactics of behavior to choose.
- What medical tests should be done for diarrhea?
- If the child is not gaining weight well, he has diarrhea, stool disorders (mucus, blood in the stool), the doctor should examine him and prescribe studies (and then evaluate their results).
What test should be taken for diarrhea in a child
- Test for dysbacteriosis. But it is worth remembering that there is no such diagnosis as dysbacteriosis, and it makes no sense to treat a child from conditionally pathogenic microorganisms that are in his intestines.
- Coprogram - examination of feces under a microscope. With its help, the doctor draws conclusions about the organoleptic, biochemical and bacterioscopic properties of the stool.
- Intestinal culture - test for intestinal viruses (noroviruses, rotaviruses, bocaviruses) to exclude intestinal infection.
- Complete blood count with leukoformula — to determine the tactics of prescribing antibiotics in severe cases (in the treatment of intestinal infection).
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity - a comprehensive ultrasound examination to determine the causes of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract in a child.

- Should my mother have any tests and when?
- Nursing mothers are often asked to prescribe an analysis for staphylococcus aureus and allergies. If the child is sick, then there is no special point in examining the mother. Staphylococci are opportunistic microbes that live on the skin and in the ducts of the mammary glands of healthy women. They can cause disease under certain conditions.
In 30% of cases, breast milk of healthy women contains staphylococci. Treatment is not required.
There are also no indications for the analysis of breast milk for sterility, because mother's milk should not be sterile. Breast milk contains a microbiota that is specific to this mother and which she will inhabit the baby's intestines.
- Consequences of diarrhea - how to deal with them?
Diarrhea causes a child's body to lose fluid and electrolytes. This leads to dehydration and loss of 10% or more of body weight. This condition can be dangerous, especially for small children and young children. Treatment is carried out in a hospital (infusion therapy or dehydration with a dropper).
This condition can be dangerous, especially for small children and young children. Treatment is carried out in a hospital (infusion therapy or dehydration with a dropper).
In addition, hospital treatment and observation in a hospital environment require serious complications of intestinal infections. If the baby pees little or there is no urination, this can be an alarming sign of hemorrhagic syndrome in infants, which is accompanied by kidney failure.
The indirect consequences of an intestinal infection sometimes include diaper rash (the stool contains digestive enzymes that irritate the skin during diarrhea).
Important! Signs of diarrhea in infants that require an appointment with a doctor during the day:
- Loose stools and no weight gain.
- The appearance of blood in the stool.
- Combination of diarrhea and vomiting.
- Discolored white chair.
- Remedies for diarrhea for children under 1 year old - what does the doctor prescribe, and what can mom use on her own?
- How to treat diarrhea in infants or loose stools in a one-year-old child always depends on the condition of the baby and the opinion of his doctor.
Intestinal infection disappears (1-3 days), stool and appetite are restored, the temperature subsides most often against the background of symptomatic treatment without additional therapeutic measures. The doctor may recommend a diet without milk, coarse fiber, sugar. Enzymes can be prescribed (they are added to food and help digestion), enterosorbents (taken without food and absorb toxic decay products of viruses) or biologics (displace pathogenic viruses from the microbiota and colonize the intestines with good strains).
If we talk about food allergies and diarrhea in infants during breastfeeding, then a dairy-free diet can be recommended to the mother. If diarrhea in a baby occurs during artificial feeding, a special therapeutic milk mixture is selected for the baby. When a child receives nutrition that suits him within a month, he should have a clear positive trend (weight gain, a significant improvement in well-being).
— How to alleviate the condition of a child with diarrhea?
- 10 years ago, for the treatment of diarrhea with an intestinal infection, a water-tea break was prescribed - the child was not fed anything and was given only drink during the day. Now it is believed that such pauses are not needed and the little patient suffers more from hunger than from the manifestation of an intestinal infection.
Now it is believed that such pauses are not needed and the little patient suffers more from hunger than from the manifestation of an intestinal infection.
It is necessary to feed a child with diarrhea in small portions and more fractionally (reduce the interval between meals and reduce the volume of one feeding). No need to give water or supplement the baby. In case of dehydration with children's diarrhea, tea, mineral water, jelly, dried fruit compote are indicated.
A child's stool is an indicator of his health. So do not rush to throw away the diaper and pay attention to its contents. If you suspect diarrhea in a baby, be sure to discuss the situation with a pediatrician, especially if you have a child in the first months of life. Diarrhea is a pathology and a common symptom of an intestinal infection or food allergy in a child under one year old. Mom's care and attention, doctor's advice and appropriate treatment are all that a child needs to cope with diarrhea, be healthy and happy.
* Breast milk is the best food for babies. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of a child's life and continued breastfeeding after complementary foods are introduced until the age of 2 years. Before introducing new products into the baby's diet, you should consult with a specialist. The material is for informational purposes and cannot replace the advice of a healthcare professional. For feeding children from birth. The product is certified.
Diet for diarrhea in a child at 1 year old
When a child is sick, it is always a serious test for a family. Moreover, if the baby has vomiting, frequent loose stools, fever, he refuses to eat. In such cases, parents naturally face the question: what to do?
The first thing to do is to see a doctor. In most cases, this condition is associated with an acute intestinal infection and can lead to serious consequences for the baby. And timely treatment allows you to quickly deal with the problem.
The second significant issue facing the parents of a sick child is the issue of proper nutrition. Unfortunately, you can still find recommendations to stop feeding a child during diarrhea, but this should not be done categorically.
Important!
It has been proven that "water-tea" breaks and starvation diets significantly weaken the protective functions of the child's body and lead to a delay in recovery processes in the intestines. Therefore, at present, most pediatricians insist on the mandatory continuation of the child's nutrition in case of acute intestinal infections, but with the obligatory consideration of the latest achievements in nutrition.
The main principles for managing the nutrition of a child with diarrhea should be:
| Phased | The development of the disease has a staging, each stage must correspond to certain approaches to diet therapy |
| Accounting for the age of the child | Each age should choose its own products and their own schemes for their purpose |
| Accounting for disease severity |
There are three main stages of diet therapy. The first stage corresponds to the acute period of the disease, when the maximum manifestations of the disease are noted (vomiting, loose stools, fever), and the child may refuse his usual diet. During this period, proper nutrition is an integral part of treatment. And the success of treatment largely depends on the correct organization of diet therapy in a child.
The first stage corresponds to the acute period of the disease, when the maximum manifestations of the disease are noted (vomiting, loose stools, fever), and the child may refuse his usual diet. During this period, proper nutrition is an integral part of treatment. And the success of treatment largely depends on the correct organization of diet therapy in a child.
The second stage is the recovery period. There are no longer those manifestations of the disease that were noted in the baby in the acute period, the child has an appetite, he becomes more active, but it must be remembered that any acute intestinal infection leads to significant changes in the child's body. This is a violation of the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, and dysfunction of enzyme systems, bile secretion and other digestive processes. It takes time to restore the correct functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which requires a sparing diet at this stage. Violation of the diet during this period can lead to the formation of a chronic pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
The third stage of diet therapy is aimed at a gradual transition to the usual diet for this baby. Breastfed babies should continue to breastfeed. If the baby is bottle-fed, the doctor will prescribe a formula that matches the baby's condition. In children older than one year, it is necessary to exclude whole milk from the diet, they are also shown the appointment of fermented milk products as a diet therapy, the favorable properties of which are due to a number of positive qualities: the presence of lactic acid gives the product pronounced bactericidal properties and inhibits the growth of pathogenic microflora, the positive effect of these products on intestinal microbiocenosis, the secretory function of the digestive glands and intestinal motility, and they also have immunomodulatory properties.
One of the important components of diet therapy is the use of dairy-free cereals with pro- and synbiotics. Clinical studies have shown that the appointment of this diet therapy contributes to a more rapid relief of the main symptoms of intestinal dysfunction, as well as the restoration of intestinal microflora.
Choose foods for the diet
It is most correct to start with rice porridge, as it has pronounced sorption properties and helps to stop diarrhea. As the child recovers, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge can be included in the diet.
Vegetables and fruits are an important component in the first stage of diet therapy. Preference should be given to products that contain pectin (baked apple, boiled carrots), as they contribute to the sorption of pathogens and their toxins. At the first stage of diet therapy, the use of fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as juices, is not shown.
The second stage - the patient's condition improves, the child becomes active, appetite improves, and in some children it even becomes elevated, which is often perceived by parents as a signal for increased nutrition. It is absolutely impossible to do this, since the child's body has not yet recovered from the disease. During this period, it is necessary to continue eating sour-milk, lactose-free and low-lactose products.