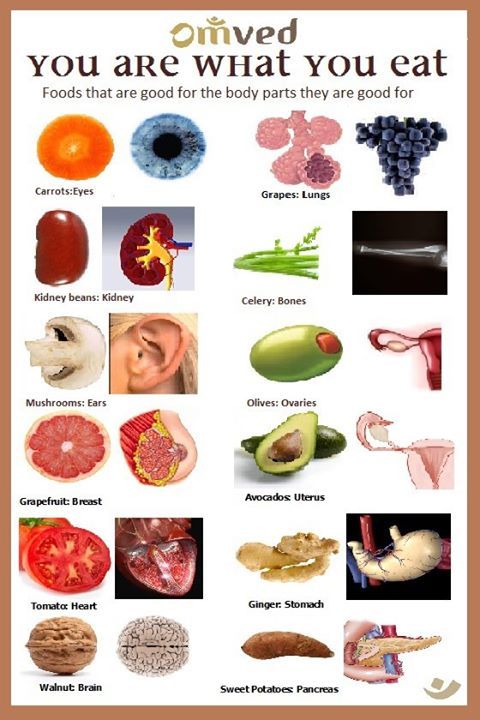
Foods that help babies lungs develop
Fetal lung development: Practice breathing, steroids for lung development, and more
Your baby's lungs are fully developed at 36 weeks, or 9 months pregnant. The lung development process starts at just 3 weeks gestation and continues through each trimester. Babies at risk of preterm birth can greatly benefit from steroids at 24 to 33 weeks to speed up lung development. To support your baby's lung development in the womb, be sure to take prenatal vitamins, eat a well-balanced diet, and contact your healthcare provider right away if you notice any signs of preterm labor.
Baby lung development in the womb
During pregnancy, your baby gets oxygen from your bloodstream through the placenta. So, although babies don't need lungs until they're born and take their first breath, their respiratory system has been developing all along in preparation.
The process starts at just 6 weeks of pregnancy when the lower respiratory tract begins to develop.
At this point, a small pouch of tissue called the lung bud is created from the front wall of the tube that will become your baby's esophagus. Over the next week, this single bud will split into two separate buds (one for each lung), and the windpipe will start to form between them.
At the end of 6 weeks, the lung buds start branching internally to create the system of tubes (bronchi) that connect with the windpipe in a respiratory "tree." At first, two bronchi form and connect to each lung. As the weeks go by, smaller branches form off these main bronchi, and the branches get smaller and smaller as more are added.
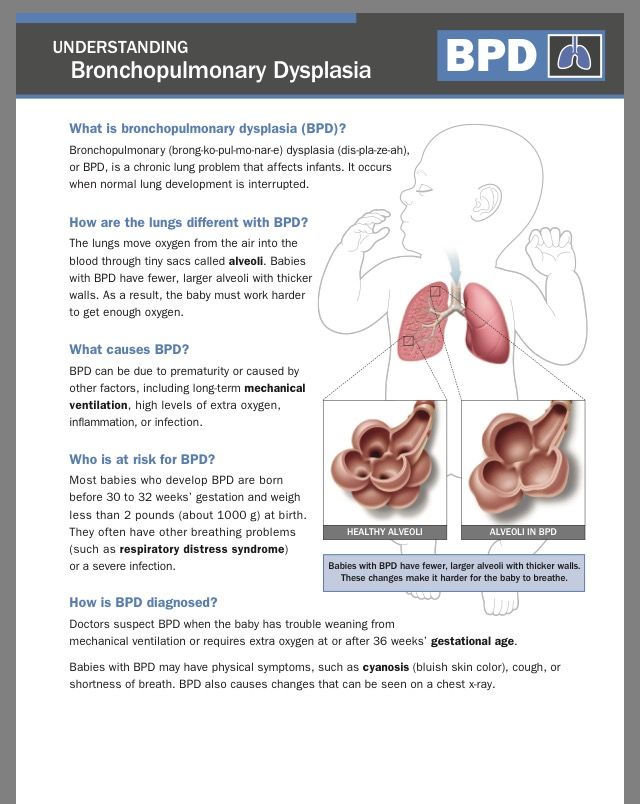
At about 18 weeks, the smallest tubes (bronchioles) start to develop at the tips of the branches. At the end of these tiny tubes, respiratory sacs that eventually form the alveoli begin to appear.
By the time your baby is born, these sacs will become enmeshed with tiny blood vessels. This allows oxygen and carbon dioxide to flow in and out of the bloodstream in the process known as "gas exchange." This allows oxygenated blood to circulate to all of the body's organs and tissues through the arteries, while carbon dioxide is ferried back to the lung through the veins.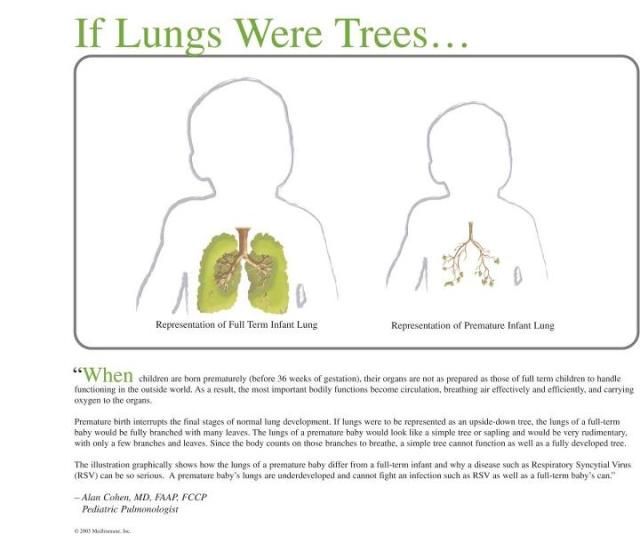
From 24 weeks of pregnancy on (until your child is about 8 years old) these respiratory sacs grow and multiply, adding more surface area for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Starting at 24 weeks, they start making a substance called surfactant, which coats the alveoli and keeps them inflated when there's not a lot of air in the lungs (when exhaling, for example). However, adequate surfactant production is not until about 35 weeks, so infants born at that time have a much higher likelihood of independent breathing and survival than those born at 24 weeks.
What is practice breathing?
Even though your baby won't breathe on their own until birth, they begin taking practice "breaths" as early as 10 weeks by inhaling and exhaling small amounts of amniotic fluid. This process is essential for lung development and helps your baby prepare for life outside the uterus.
When do babies start breathing on their own?
By 28 weeks of pregnancy, gas exchange in your baby's tiny lungs may be possible, although the alveoli are not yet fully formed. There's also still not a lot of surfactant to support the baby breathing on their own.
There's also still not a lot of surfactant to support the baby breathing on their own.
By 35 weeks of pregnancy, there may be enough surfactant to support lung function outside the uterus, though often a baby will still need some extra help breathing and oxygenating. Transitioning from receiving oxygen through the placenta to receiving oxygen through the lungs is one of the biggest shifts your baby will experience after delivery!
Many babies that are born early need some extra monitoring and support. For some babies, this may mean just a few hours in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), a special part of the hospital that treats babies who need extra care after birth. For babies born very premature, this may mean longer time in the NICU, surfactant therapy, and longer-term respiratory problems. Each baby is different, and the intensity of support depends on how early they are.
At 36 weeks, baby's lungs are fully formed, and by 40 weeks, your baby has about 150 million alveoli in their lungs, ready to take over the job of breathing on their own once they're born.
So how does your baby know to take their first breath? It's most likely a reflex response to touch and being exposed to air for the first time. When your baby inhales for the first time – within about 10 seconds after delivery – their lungs expand, and any fluid remaining in the alveoli is replaced with air. The alveoli then start the life-sustaining process of gas exchange.
When do babies need steroids for lung development?
Steroids are typically recommended for lung development for women who are 23 weeks to 34 weeks pregnant and at risk of preterm delivery within seven days. Healthcare providers might also recommend steroids for women who are 34 to 36 weeks pregnant, if they have not had a previous course of steroids and are medically eligible.
Steroids are one of the most important therapies available to improve lung development and a newborn's outcome for those babies who are at risk of being born preterm. Steroids used between 23 and 34 weeks of pregnancy can greatly speed up lung development, giving baby a much better chance of survival. This is because the steroids help the baby to produce more surfactant.
This is because the steroids help the baby to produce more surfactant.
Steroid treatment is typically given as two intramuscular injections, 24 hours apart. In addition to helping lung development, steroids also help other organs develop in preterm babies. Other benefits of steroid use include a lower risk of bleeding in the brain and a lower risk of a serious bowel condition called necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC).
How to support your baby's developing lungs
Eating a well-balanced diet and taking prenatal vitamins during pregnancy will help your baby's lungs develop normally. Researchers have found that the most important nutrients for baby's prenatal lung development are vitamins A, D, and E, selenium, and the omega-3 fatty acid DHA.
Beef, eggs, fish, sweet potatoes, carrots, spinach, and mango are all excellent sources of vitamin A. For vitamin D, choose fortified milk and cereals and fatty fish like salmon. Leafy green vegetables, whole grains, and nuts have plenty of vitamin E, while seafood and walnuts are also good sources of selenium.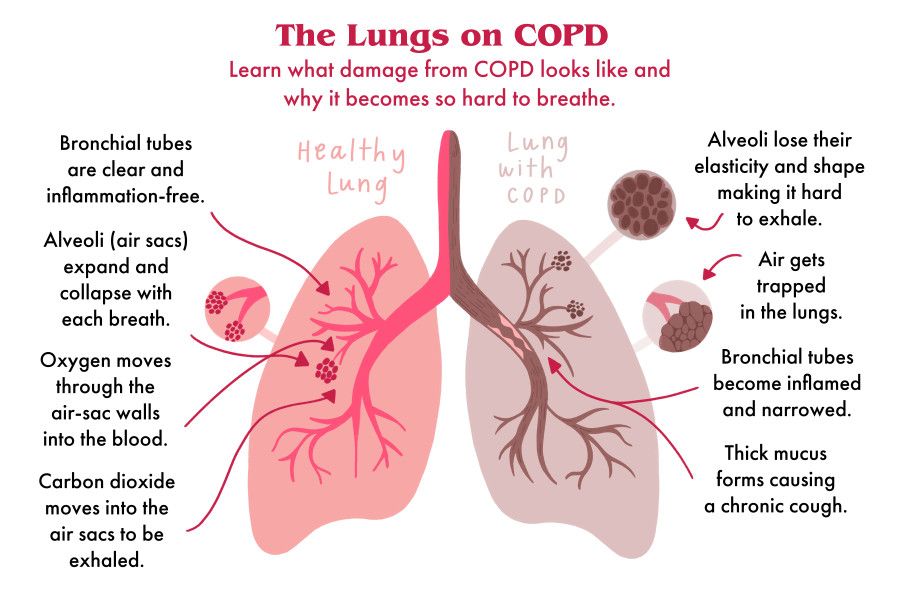 Fish is the best source of omega-3 fatty acids, too. Be sure to avoid high-mercury fish like swordfish and follow current guidelines for safe fish consumption during pregnancy.
Fish is the best source of omega-3 fatty acids, too. Be sure to avoid high-mercury fish like swordfish and follow current guidelines for safe fish consumption during pregnancy.
Preterm birth is the greatest threat to the development of your baby's lungs, so call your healthcare provider right away if you notice any of the following signs of preterm labor:
- More vaginal discharge than usual
- A change in the type of discharge – like if you're leaking watery fluid or if your discharge becomes watery, mucusy, or bloody (even if it's pink or just tinged with blood)
- Any vaginal bleeding or spotting
- Abdominal pain that feels like menstrual cramps, or having more than four contractions in one hour (even if they don't hurt)
- Increased pressure in your pelvic area (a feeling that your baby is pushing down)
- Low back pain, especially if it's dull or rhythmic, or you didn't previously have back pain
These symptoms can be confusing because some (such as pelvic pressure or low back pain) are common during pregnancy, and sporadic early contractions may be Braxton Hicks contractions.
But it's always best to be cautious, so call your provider right away if you have any unusual symptoms at any time during your pregnancy.
Key milestones in fetal lung development
| Weeks pregnant | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 6 weeks | Respiratory tract begins to develop. |
| 7 weeks | Lung bud develops. |
| 8 weeks | Bronchi (air tubes) start to form in the lungs. |
| 18 weeks | Bronchioles and respiratory sacs begin to develop. |
| 24 weeks | Respiratory sacs begin making surfactant. |
| 35 weeks | There may be enough surfactant to support lung function. |
| 36 weeks | Baby's lungs are fully formed. |
| 40 weeks | There are now 150 million alveoli in the lungs, and another 150 million will form during childhood. |
Learn more:
Slideshow: Fetal development, week by week
advertisement | page continues below
7 Healthy Foods To Eat During Pregnancy
What you eat during pregnancy will reflect on your baby's health, either at birth or later
Highlights
- Vitamin C supplements can reduce the babys risk of developing a wheeze
- Greek yogurt is very beneficial for pregnant women
- Choline in eggs is beneficial for the baby's brain development
Smoking during pregnancy can have a number of negative effects on the baby's health. However, some women still continue to smoke during pregnancy. While the negative effects of smoking are inevitable, there are some ways of mitigating the ill-effects of smoking on the baby's lungs. A new study says that consumption of vitamin C supplements can reduce the baby's risk of developing a wheeze. Wheezing is a condition characterized by a whistle-like sound due to an obstruction in the respiratory tract. The results showed an improvement in the lung function of the babies, three months of age, born to women who consumed vitamin C supplements instead of a placebo. However, researchers still focus on the need to get women to quit smoking during pregnancy. And for those women who simply can't quit smoking, vitamin C supplementation can be a helpful way to get their kids to breathe better.
However, some women still continue to smoke during pregnancy. While the negative effects of smoking are inevitable, there are some ways of mitigating the ill-effects of smoking on the baby's lungs. A new study says that consumption of vitamin C supplements can reduce the baby's risk of developing a wheeze. Wheezing is a condition characterized by a whistle-like sound due to an obstruction in the respiratory tract. The results showed an improvement in the lung function of the babies, three months of age, born to women who consumed vitamin C supplements instead of a placebo. However, researchers still focus on the need to get women to quit smoking during pregnancy. And for those women who simply can't quit smoking, vitamin C supplementation can be a helpful way to get their kids to breathe better.
Your diet during pregnancy plays a very crucial role in terms of your health and your baby's health too. What you eat will reflect on your baby's health, either at birth or later in life.
Promoted
Listen to the latest songs, only on JioSaavn.com
Also read: Planning To Get Pregnant? You Must Have These 5 Nutrients
1. Dairy products
Pregnancy is when the body needs more protein and calcium than usual. This is to meet the needs of the fetus. One of the best sources of protein and calcium is dairy products. It is also a rich source of magnesium, zinc and phosphorus. Greek yogurt is very beneficial for pregnant women. It contains more calcium than any other dairy product and is a rich source of healthy bacteria as well. Greek yogurt can also be consumed by some lactose intolerant women.
Healthy pregnancy foods: Greek yogurt is very beneficial for pregnant women
Photo Credit: iStock
2. Sweet potato
Sweet potatoes are a rich source of beta-carotene, a healthy compound which turns into vitamin A in the human body. This nutrient is essential for growth which is very essential for the fetus. Pregnant women are required to increase their vitamin A intake by 10-40% for optimum growth of the baby. Sweet potatoes boosts digestive health and prevent blood sugar spikes as well.
This nutrient is essential for growth which is very essential for the fetus. Pregnant women are required to increase their vitamin A intake by 10-40% for optimum growth of the baby. Sweet potatoes boosts digestive health and prevent blood sugar spikes as well.
Healthy pregnancy foods: Sweet potatoes are also rich in fiber which induces a sense of fullness
Also read: 7 Foods You Must Avoid During Pregnancy
3. Salmon
Salmon is a rich source of vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acids. These nutrients are very important for pregnant women because they promote brain and eye development of the fetus. Sadly, most women fail to get enough omega 3 fatty acids in their diet. 2-3 servings of seafood should suffice for pregnant women. However, they must be careful about the mercury content in seafood, it can be harmful for the baby.
Vitamin C for pregnant mothers: Salmon promotes brain and eye development of the fetus
4. Eggs
Eggs
Eggs are extremely healthy because they contain a small amount of every nutrient you need. They are one of the best sources of protein and healthy fats. Eggs are a rich source of fiber as well. Choline in eggs is beneficial for the baby because it promotes brain development. Low choline intake during pregnancy may have a negative impact on the baby's brain function.
Healthy pregnancy foods: Choline in eggs is beneficial for the baby because it promotes brain development
Photo Credit: iStock
Also read: 7 Useful Pregnancy Tips For A Vaginal/Normal Delivery
5. Dark leafy greens
Green leafy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, kale and asparagus contain all the essential nutrients required by a pregnant woman's body. They are rich in vitamin C, K, A, calcium, iron, folate and potassium. They are rich in fiber as well which keeps the digestive system in check. Constipation is a common problem in pregnant women and can be treated with green leafy vegetables.
Constipation is a common problem in pregnant women and can be treated with green leafy vegetables.
Healthy pregnancy foods: Green leafy vegetables can be very beneficial for pregnant women
Photo Credit: iStock
Also read: Do You Really Need Ghee During Pregnancy?
6. Berries
Berries are a rich source of vitamin C, fiber, water and antioxidants like flavonoids. Vitamin C in berries promotes better absorption of iron in the body. They have a low-glycemic index as well which prevents blood sugar spikes. Berries can be a healthy snack for pregnant women because of the high nutritional content and lesser calories.
Vitamin C for pregnant mothers: Berries can be a healthy snack for pregnant women
7. Whole grains, flour
Fortified whole grains and cereals which contain calcium and folic acid are beneficial for pregnant women. Whole wheat bread, whole wheat pasta and brown rice are some of the healthy food options for pregnant women.
Whole wheat bread, whole wheat pasta and brown rice are some of the healthy food options for pregnant women.
Also read: Pregnant? Top 5 Must Haves
Healthy pregnancy foods: Brown rice is one of the healthiest grains for pregnant women
Photo Credit: iStock
Disclaimer: This content including advice provides generic information only. It is in no way a substitute for qualified medical opinion. Always consult a specialist or your own doctor for more information. NDTV does not claim responsibility for this information.
Your baby was born prematurely | Regional Perinatal Center
Premature babies
If your baby is born too early, the joy of having a baby can be overshadowed by health concerns and thoughts about the possible consequences.
Instead of returning home with the baby, holding him and caressing him, you will have to stay in the department, learn to cope with the fear of touching the baby, realize the need for treatment and various manipulations, get used to the complex equipment that surrounds him. nine0005
nine0005
In this situation, not only your baby needs help, you need it too! The best assistants are your loved ones, their love and care, as well as professional advice and recommendations from doctors and psychologists. This section of articles will help you improve your knowledge of preterm infant care, development and nutrition.
Your help for the baby
Previously, parents were often not allowed into the neonatal unit and, especially, into the intensive care unit because of the fear of infection of the baby, but now the contact of the parent with the child is recognized as desirable and is prohibited only in exceptional cases (for example, if parents have acute infections)
Close communication between you and your baby is very important from the first days of his life. Even very immature premature babies recognize the voices and feel the touch of their parents.
The newborn needs this contact. Studies have shown that it greatly contributes to the faster adaptation of an immature child to new conditions and the stabilization of his condition. The baby's resistance to therapy increases, he absorbs large amounts of food and quickly begins to suck on his own. Contact with the child is important for parents. Taking part in the care of the baby, they feel their involvement in what is happening and quickly get used to a new role, especially when they see how he reacts to their presence. nine0005
The baby's resistance to therapy increases, he absorbs large amounts of food and quickly begins to suck on his own. Contact with the child is important for parents. Taking part in the care of the baby, they feel their involvement in what is happening and quickly get used to a new role, especially when they see how he reacts to their presence. nine0005
By constantly and attentively observing the baby, parents can notice the smallest changes in his condition before others. In addition, communication in the hospital is a good practice that will undoubtedly come in handy after discharge. For parents, early physical contact with the baby is very valuable, because it allows them to feel him, despite the incubator and other obstacles, and show him their love.
Treatment in the neonatal intensive care unit requires parents to have full confidence in all medical staff. nine0005
Nursing premature babies in the hospital
Many premature babies cannot breathe, suckle and regulate their body temperature sufficiently after birth. Only in the last weeks of pregnancy is the maturation of the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, brain, which regulates and coordinates the work of all organs and systems.
Only in the last weeks of pregnancy is the maturation of the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, brain, which regulates and coordinates the work of all organs and systems.
Fluid loss due to the immaturity of the skin of premature babies and the insufficiency of thermoregulation processes require constant attention. Modern approaches focused on nursing premature babies help to cope with these problems. nine0005
Heat regulation incubator
Premature babies are very susceptible to temperature fluctuations. At the same time, clothing can interfere with the monitoring of the baby's condition and its treatment. That is why an incubator is used to provide the conditions necessary for premature babies. It maintains a certain temperature and humidity, which change as the child grows. When the body weight of a premature infant reaches 1500-1700 g, he can be transferred to a heated bed, and after reaching a weight of 2000, most premature babies can do without this support. There are no strict rules here: when nursing children with low body weight, doctors are guided by the severity of the condition of each premature baby and its degree of maturity. nine0005
There are no strict rules here: when nursing children with low body weight, doctors are guided by the severity of the condition of each premature baby and its degree of maturity. nine0005
In incubators, very young premature babies are placed in special "nests" - soft hemispheres in which the baby feels comfortable and assumes a position close to intrauterine. It must be protected from bright lights and loud noises. For this purpose, special screens and coatings are used.
Critical treatments during the first days of life of premature babies with low and very low birth weight:
Use of an incubator or heated bed. nine0005
Oxygen supply for respiratory support.
If necessary, artificial ventilation of the lungs or breathing using the CPAP system.
Intravenous administration of various drugs and fluids.
Carrying out parenteral nutrition with solutions of amino acids, glucose and fat emulsions.
Don't worry: not all premature babies need such extensive treatment!
Mechanical ventilation and CPAP for respiratory support
When it comes to nursing, oxygen supply is of the utmost importance for premature babies. In a child born before the 34-35th week of pregnancy, the ability of the lungs to work independently is not yet sufficiently developed. The use of a constant flow of air with oxygen, which maintains a positive airway pressure (CPAP), leads to an increase in blood oxygen saturation.
In a child born before the 34-35th week of pregnancy, the ability of the lungs to work independently is not yet sufficiently developed. The use of a constant flow of air with oxygen, which maintains a positive airway pressure (CPAP), leads to an increase in blood oxygen saturation.
This new method made it possible for the majority of even very immature children to do without mechanical ventilation. The need for intubation of children has disappeared: during treatment with CPAP, oxygen is supplied through short tubes - cannulas that are inserted into the nasal passages. CPAP or mechanical ventilation is continued until the lungs can function at full capacity on their own. nine0005
In order for the lungs to expand and remain in such a state in the future, a surfactant is needed - a substance that lines the alveoli from the inside and reduces surface tension. Surfactant is produced in sufficient quantities starting from the 34-35th week of pregnancy. Basically, it is by this time that the formation of the lungs is completed. If the baby was born earlier, modern technologies allow the introduction of surfactant into the lungs of premature babies immediately after their birth.
If the baby was born earlier, modern technologies allow the introduction of surfactant into the lungs of premature babies immediately after their birth.
Parenteral nutrition - administering nutrient solutions by vein
Premature babies, especially those born weighing less than 1500 g, are not able to get and absorb enough nutrients, even when fed through a tube. For the rapid growth of the baby, a large amount of nutrition is needed, and the size of the stomach is still very small, and the activity of digestive enzymes is also reduced. Therefore, such children are given parenteral nutrition.
Special nutrients are injected into a vein using infusion pumps that deliver solutions slowly at a predetermined rate. In this case, amino acids necessary for building proteins, fat emulsions and glucose, which are sources of energy, are used. These substances are also used for the synthesis of a number of hormones, enzymes and other biologically active substances. Additionally, minerals and vitamins are introduced. nine0005
Additionally, minerals and vitamins are introduced. nine0005
Gradually, the volume of enteral nutrition increases, and parenteral nutrition decreases until it is completely canceled.
Premature infants with gastrointestinal disease require parenteral nutrition for a longer period of time.
By the time your grown baby is discharged from the hospital, everything should be well prepared at home. And this applies not only to the environment, clothes and means of caring for the child.
All family members must be ready to receive the baby. Of course, the main care will fall on the shoulders of the parents. Although you have already gained some experience in the hospital, it is important to feel the support of others, especially in the early days.
Older children can also help. The discharge of your baby is a great joy that you want to share with all your relatives.
While you are getting used to your new role, it is important that nothing distracts you from communicating with your child. Now all the care and responsibility for the baby lies entirely with you. Everything you need to take care of him should be at hand. nine0005
Now all the care and responsibility for the baby lies entirely with you. Everything you need to take care of him should be at hand. nine0005
Preparing for discharge from the hospital
Before discharge, you must make sure that:
- Prepared the crib, bath for bathing and a place for changing clothes, preferably a changing table. A crib should be placed in the parents' bedroom, the child should not be left alone even at night. A stroller is also required. you have baby milk that was recommended by the doctor before discharge (if the child is on mixed or artificial feeding). As a rule, this is a specialized medical product. You need a certain number of small bottles and teats of the appropriate size, as well as a sterilizer. All premature babies will need pacifiers. nine0126
- You have fully mastered breastfeeding or bottle feeding.
- If your baby is not suckling all the required amount of milk from the breast and is supplementing from a bottle, you have purchased a breast pump that you have learned to use; you may also need it if you have a lot of breast milk.
- You have asked your doctor how often your child's weight should be monitored.
- If your baby still needs medication, you have the required amount at home. And you know exactly how and when to give them to your child. nine0126
- You know which warning signs to look out for.
- After the baby is discharged, a pediatrician and a neonatologist will look after the baby, to whom you will give the discharge summary from the hospital.
- You know how the hospital from which your child is being discharged will provide follow-up care after discharge.
- You know which specialists and how often should examine your baby (oculist, neuropathologist, etc.). nine0126
- All the emergency phone numbers you need are at your fingertips.
When can a child go home
This question is very difficult to answer because all children are different. The stay in the hospital can last from 6 days to 6 months, depending on the degree of prematurity of the child, the severity of his condition, as well as the presence of certain complications.
Of course, all parents look forward to the moment when the baby can be brought home. Long-term nursing of a premature baby is often a difficult test for you. But we must not forget that safety comes first, and the baby can be discharged home only when the doctors are confident in the stability of his condition. It is certainly in your interest as well. nine0005
The rate of increase in body weight and length
Weight gain is the main indicator of the growth of the baby and the adequacy of the treatment. The weight of the child, especially in the first days and weeks of life, is influenced by a number of factors: the presence of milk in the stomach (immediately after feeding), the time of bowel movement, the degree of filling of the bladder, the presence of edema. Therefore, if an edematous child does not gain weight for several days, and perhaps even loses it, do not worry. It should be remembered that children grow unevenly and periods of high weight gain alternate with lower ones. It is better to focus not on weight gain per day, but on the dynamics of this indicator over several days or a week. nine0005
It is better to focus not on weight gain per day, but on the dynamics of this indicator over several days or a week. nine0005
It is currently accepted that in the interval corresponding to 28-34 weeks of pregnancy, the normal weight gain of the child is 16-20 g/kg per day. Then it is reduced to 15 g/kg.
It is also important to take into account the rate of increase in body length. With malnutrition, at first the child gains less weight (or even loses it), and with a more pronounced deficiency of nutrients, his growth is also disturbed.
The weight must not only increase at a certain rate, but must also correspond to the length of the baby. An important parameter characterizing the development of the baby is an increase in the circumference of the head. The brain most actively increases in size during the first 12–18 months of life. But an excessively rapid increase in head circumference, as well as a slowdown in its increase, indicate neurological disorders. nine0005
A premature baby can be discharged from the hospital if:
- he is able to independently maintain the required body temperature;
- does not need breathing support and constant monitoring of the work of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems;
- can suck out the required amount of nutrition on its own;
- does not need round-the-clock monitoring and frequent determination of biochemical or other indicators; nine0126
- supportive care can be provided at home;
- he will be under the supervision of a local pediatrician and neonatologist at the place of residence.

The decision to discharge home is made for each patient individually. In addition to the state of health of the baby, the degree of preparedness of parents, their ability to provide high-level care for a premature baby is also taken into account.
Feeding a premature baby after discharge
Breastfeeding is the ideal way to feed premature babies.
However, if the baby was born much prematurely and his birth weight did not exceed 1800-2000 g, his high nutritional requirements cannot be met by breastfeeding. The growth rate will be insufficient. Moreover, over time, the content of many nutrients, including protein, in milk decreases. And it is the main material for building organs, and primarily brain tissue. Therefore, proteins must be supplied to the body of a premature infant in the optimal amount. nine0005
In addition, premature babies have a significantly increased need for calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for bone formation.
In order for the baby's nutrition to be complete even after being discharged from the hospital, special additives - "enrichers" are introduced into breast milk in a certain amount, already less than in the hospital. They make up for the lack of protein in it, as well as some vitamins and minerals. As a result, the child receives them in the optimal amount. The duration of their use will be determined by your doctor. If there is not enough milk or it does not exist at all, children born prematurely should be transferred to artificial feeding. Complementary feeding of premature babies is carried out with special children's dairy products designed for children with low birth weight. This baby milk is ideally suited to both the ability of immature children to digest and assimilate nutrients, and their needs. nine0005
Premature infant milk contains more protein, fat and carbohydrates than term infant milk, resulting in a higher calorie content. In specialized baby milk, the concentration of many minerals is higher, especially iron, zinc, calcium, phosphorus, as well as vitamins, including vitamin D. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids of the Omega-3 and Omega-6 classes are introduced into such products, which are necessary for proper development of the brain and organ of vision, as well as nucleotides that contribute to the optimal development of immunity. However, when the child reaches a certain weight (2000-2500 g), you should gradually switch to feeding with standard baby milk, but not completely. Specialized baby milk can be present in the diet of a premature baby for several months. This time, as well as the volume of the product, will be determined by the doctor. He will answer all your questions about how to feed your baby. nine0005
Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids of the Omega-3 and Omega-6 classes are introduced into such products, which are necessary for proper development of the brain and organ of vision, as well as nucleotides that contribute to the optimal development of immunity. However, when the child reaches a certain weight (2000-2500 g), you should gradually switch to feeding with standard baby milk, but not completely. Specialized baby milk can be present in the diet of a premature baby for several months. This time, as well as the volume of the product, will be determined by the doctor. He will answer all your questions about how to feed your baby. nine0005
At present, specialized children's dairy products have been developed and are being used to feed premature babies after discharge from the hospital. In its composition, it occupies an intermediate position between a specialized product for premature babies and regular baby milk. Your baby will be transferred to such baby milk while still in the hospital. You will continue to give it to your child at home, and the doctor, watching him, will tell you when it will be possible to switch to regular standard baby milk. If the baby was born with a very low body weight or is not gaining weight well, special baby milk can be used for a long time - up to 4 months, 6 or even 9months. The beneficial effect of such children's dairy products on the growth and development of the child has been proven in scientific studies.
You will continue to give it to your child at home, and the doctor, watching him, will tell you when it will be possible to switch to regular standard baby milk. If the baby was born with a very low body weight or is not gaining weight well, special baby milk can be used for a long time - up to 4 months, 6 or even 9months. The beneficial effect of such children's dairy products on the growth and development of the child has been proven in scientific studies.
Feeding needs for premature babies
Higher caloric intake because they need to gain weight faster than term babies.
More protein as premature babies grow faster.
More calcium and phosphorus for bone building.
More trace elements and vitamins for growth and development. nine0005
A premature baby grows faster than a term baby. Nutrition for such children is calculated taking into account body weight at birth, the age of the baby and its growth rate. As a rule, the calorie content of the daily diet is about 120-130 calories per 1 kg of body weight.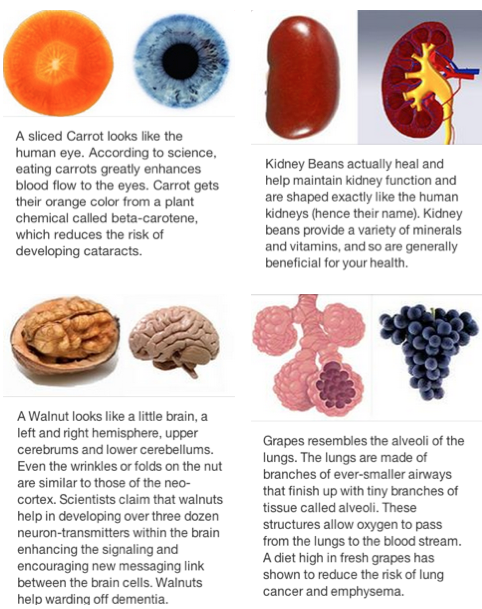
It is very important that your baby continues to gain weight quickly and grow in length after discharge. To do this, feeding premature babies must be carried out using a specialized fortified diet prescribed by a doctor. nine0005
How to restore lungs after coronavirus
Do lungs recover after COVID-19? Yes. But you need not to miss the terms of rehabilitation and take seriously the recommendations of the doctor.
The new coronavirus infection caused by SARS-CoV-2 is not well understood, but it is clear that it harms all human organs and tissues. The virus enters the body through the mucous membranes of the nose, eyes, and pharynx. The first symptoms appear on the 2-14th day. Usually this is a temperature increase above 37.5 degrees Celsius, runny nose, loss of smell, dry cough, loose stools, weakness and headache. On the 6-10th day from the moment the first symptoms appear, shortness of breath, chest pain, increased coughing may begin to bother. These are alarming symptoms that speak of lung damage and require additional examination: computed tomography of the lungs, measurement of blood oxygen saturation (saturation). nine0005
These are alarming symptoms that speak of lung damage and require additional examination: computed tomography of the lungs, measurement of blood oxygen saturation (saturation). nine0005
Lungs after COVID-19
Entering the human body through the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, SARS-CoV-2 causes a powerful inflammatory response. Immune cells are activated, a huge amount of inflammatory substances (inflammatory cytokines) is produced. The intensity of this reaction is most likely genetically determined. It is the intensity of the inflammatory reaction that determines the severity of damage to the lung tissue according to research data. In the lung tissue, a lesion in COVID-19due to both the defeat of the alveoli themselves (in which gas exchange occurs and the blood is saturated with oxygen from the air) by our own immune cells and the defeat of the pulmonary vessels that braid the alveoli. The degree of damage to the lungs can be determined using CT (computed tomography).
Table 1. Lung Injury in COVID-19
| No. | Percentage of lung tissue damage nine0005 | Manifestations | Hospitalization |
| 1. | 15 | Part of the lung is damaged. Slight difficulty in breathing. | Not shown. nine0005 |
| 2. | 25 | Half of one lung is affected. There is difficulty in breathing, but the person copes with the situation. | Treatment at home is possible. |
| 3. nine0250 | 50 | One lung is out of breath. Noticeable shortness of breath. Requires active treatment. | The decision on hospitalization is made by the doctor. |
| four. | 75 | nine0002 Only half of one lung breathes. Severe respiratory failure. | shown. |
Lungs after COVID-19 may lose elasticity. The affected areas of the lung tissue are replaced by connective (scar) tissue, fibrosis occurs. Due to fibrotic changes in the lungs, the gas exchange function of the lung tissue suffers. There is no more inflammation, but respiratory failure persists. If you do not take action already during the disease itself, pathological changes in the lungs can remain for life. The person will be concerned about: nine0005
- shortness of breath, aggravated by physical exertion;
- frequent dizziness;
- dry cough;
- chest pain;
- growing weakness;
- decrease in performance.
Sometimes the weakness is so pronounced that the ability to self-service is lost.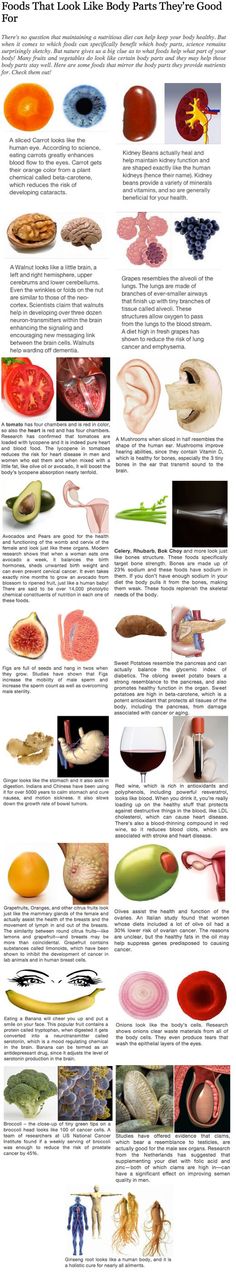 To avoid these serious complications, it is necessary to carry out rehabilitation measures - rehabilitation. nine0005
To avoid these serious complications, it is necessary to carry out rehabilitation measures - rehabilitation. nine0005
Principles of Lung Rehabilitation after COVID-19
Rehabilitation begins 20-25 days after the onset of the disease, sometimes even in the hospital. As soon as the acute process has ended, the body temperature has returned to normal, an examination is carried out. It is clarified whether there is a violation of the function of the kidneys, heart, blood vessels, and other organs. The recovery program for the lungs after COVID-19 is developed individually. Taken into account:
- the severity of the coronavirus infection; nine0126
- the nature of viral pneumonia, the degree of lung damage;
- floor;
- the weight;
- age;
- related diseases.
The duration of rehabilitation is from 2 weeks to a year. It can go continuously or in courses of 10-14 days with breaks of 5-7 days. With minimal changes, respiratory gymnastics, physiotherapy exercises, inhalations, massage, physiotherapy are prescribed. Diet and diet play an important role. nine0005
With minimal changes, respiratory gymnastics, physiotherapy exercises, inhalations, massage, physiotherapy are prescribed. Diet and diet play an important role. nine0005
General recommendations for post-COVID-19 lung rehabilitation
-
Compliance with the regime of the day, a full eight-hour sleep
-
Moderate physical activity (10,000 steps per day - walks in the park, forest in dry and warm weather). On a cold, windy or rainy day, it's best to stay at home. For a walk, dress according to the weather, shoes should be comfortable.
- nine0002 Breathing exercises
-
Daily wet cleaning and airing in the room.
-
Refusal to visit the bath, sauna. Do not take hot baths.
-
Prohibition of drinking alcohol, smoking.
COVID-19 Lung Recovery Nutrition
A full-fledged diet is recommended 5-6 times a day, in small portions. nine0005
nine0005
Table 2. Required Power Supplies
| No. | Component | Product examples |
| 1. | Easily digestible protein | nine0247 |
| 2. | Healthy fats | Sea fish, nuts, vegetable oils. |
| 3. | Alimentary fiber nine0005 | Cereals, fresh vegetables and fruits. |
| four. | Slow carbs | Cereals, vegetables. |
| five. | Probiotics nine0005 | Sour-milk drinks, sauerkraut. |
| 6. | Iron | Parsley, beef liver, buckwheat. |
It is necessary to drink 1.5-2 liters of water per day. Ordinary drinking water, fruit drinks, unsweetened compotes, rosehip broth are suitable. nine0005
Banned: "fast" carbohydrates - cakes, sweets, buns, fatty, spicy, spicy foods, meat delicacies.
Breathing exercises for lung recovery after COVID-19
Breathing exercises stimulate blood circulation, train the respiratory muscles, increase the elasticity of the lung tissue, and improve bronchial drainage. You need to perform gymnastics in a clean, ventilated area. Start with 30 seconds, gradually increase to a quarter of an hour. Overwork should be avoided. If you feel dizzy, take a break. nine0005
Preparatory exercises
-
In the supine position, take a slow breath for 3-4 seconds, then the same slow exhalation - for 5-6 seconds.
-
Diaphragmatic breathing, when the stomach "inflates" on inspiration.
-
Slowly inhale air, slowly exhale through a tube into a glass of water, relax. Repeat 2-3 times, gradually increase to 10 times. nine0005
Initial exercises
-
Sit on a chair, press your back against the back of the chair, put your hands down. As you inhale, slowly raise your arms forward and then up. As you exhale, return to the starting position.
-
The same exercise, only raise your arms up through the sides.
-
Stand up, put your fingers on your shoulders. While inhaling, slowly spread your arms to the sides. Exhaling through your mouth, return to the starting position. nine0005
Basic Exercises
The gymnastics of Strelnikova A.N. has proven itself well. It is difficult to master it on your own. It is necessary that the movement was shown by a person who owns the technique. Instead of this breathing exercise, the doctor may recommend another one.
Physical exercise for the treatment of lungs after COVID-19
Exercise therapy strengthens muscles weakened by the disease, stimulates blood circulation, and normalizes the nervous system. Gymnastics is performed after breathing training, at a slow pace. Next you need to put a chair, hold your hand on its back to control balance. The first part of each exercise is performed on the inhale, the second on the exhale. nine0005
Sample list of exercises
-
Rise on toes, stand on a full foot.
-
Bend the leg at the knee, lifting it up, lower it. Then the second leg.
-
Take the leg back, return to the place. Same with the other leg.
-
Circular movements of the shoulders forward, then back. nine0005
-
Take the right hand back, return to the starting position, then the left.
-
Put your hands on your belt. Turn your body to the right, then to the left.

-
Lean forward 20-30 degrees, straighten up.
-
Lean to the right, straighten up, then to the left.
nine0126
Inhalations for the treatment of lungs after COVID-19
Prescribed by a doctor if indicated. Inhalations are carried out through a nebulizer device. For inhalation, ready-made moisturizing preparations based on saline and expectorants are used. If necessary, bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Therapeutic massage for lung rehabilitation
Therapeutic massage performed by a specialist improves blood circulation in the lungs, eliminates congestion, speeds up metabolism, and promotes rapid recovery of the lungs. In addition, it relieves muscle and nervous tension, helps to cope with fatigue, improves mood and performance. Percussion massage gives a good effect. nine0005
Do the lungs recover after COVID-19 with manual therapy?
The manual therapist uses special techniques of influence: squeezing, traction, stretching.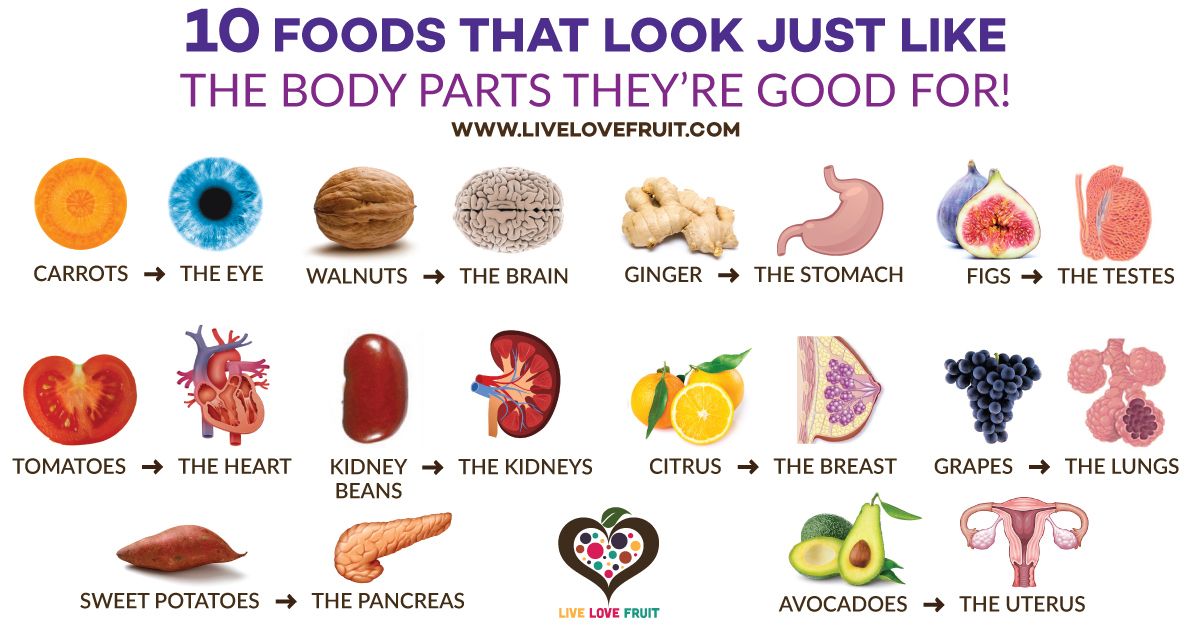 Costovertebral joints become more mobile, the diaphragm works better. As a result, the chest becomes more elastic, the volume of the lungs increases, sputum discharge improves, and oxygen supply is restored.
Costovertebral joints become more mobile, the diaphragm works better. As a result, the chest becomes more elastic, the volume of the lungs increases, sputum discharge improves, and oxygen supply is restored.
Physiotherapy after coronavirus
Table 3. Popular Physiotherapy Treatments
| No. | Name | Action |
| 1. | SMT therapy | nine0247 |
| 2. | Laser therapy | Improves blood circulation, has a resolving and anti-inflammatory effect. |
| 3. nine0005 | Polychromatic polarized light | Accelerates the resorption of infiltrate, improves bronchial patency. |
| four. | Magnetotherapy | Eliminates inflammation, swelling, pain. nine0005 |
| five. | Ultrasound Therapy | Removes phlegm, prevents the development of fibrosis. |
Fibrosis as a consequence of the lungs after COVID-19
Signs of pneumofibrosis on CT (computed tomography) indicate that part of the lung tissue is replaced by scar tissue. Fibrosis does not develop in a few days. This usually takes up to 6 months. Fortunately, fatal pulmonary fibrosis with the development of severe respiratory failure is not common, and in most people who have had a coronavirus infection, the changes in the lungs that remain will not affect their health. In most cases, the control study shows a clear positive trend. Signs of fibrosis decrease or disappear. Normal lung tissue is restored. nine0005
nine0005
Therefore, it is so important to consult a doctor in time and start the correct treatment for COVID-19, which will help to avoid serious complications and reduce the rehabilitation time after SARS-CoV-2 damage to the lungs.
If fibrosis has indeed formed, it is irreversible. In this case, doctors try to create optimal conditions for the work of the remaining lung tissue. Often this can be done, since the compensatory capabilities of the respiratory system are great. But simple methods are not enough for this. We have to connect serious therapy, including drugs and respiratory support. nine0005
Restore your health in one of the best clinics in Moscow
The Family Doctor knows exactly how to restore the lungs after a coronavirus infection. We have developed several rehabilitation programs after COVID-19. In the shortest possible time, you will undergo a full examination, you will know exactly how to restore your lungs after COVID-19.