Foods to stop diarrhea for babies
When your child has diarrhea: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
Diarrhea is the passage of loose or watery stools. For some children, diarrhea is mild and will go away within a few days. For others, it may last longer. It can make your child lose too much fluid (dehydrated) and feel weak.
The stomach flu is a common cause of diarrhea. Medical treatments, such as antibiotics and some cancer treatments can also cause diarrhea.
This article speaks of diarrhea in children over 1 year of age.
It is easy for a child with diarrhea to lose too much fluid and become dehydrated. Lost fluids need to be replaced. For most children, drinking the kinds of fluids they normally have should be enough.
Some water is OK. But too much water alone, at any age, can be harmful.
Other products, such as Pedialyte and Infalyte, may help keep a child well-hydrated. These products can be bought at the supermarket or pharmacy.
Popsicles and Jell-O can be good sources of fluids, especially if your child is vomiting. You can slowly get large amounts of fluids into children with these products.
You may also give your child watered-down fruit juice or broth.
Do not use medicines to slow down your child's diarrhea without talking to a doctor first. Ask your child's health care provider if using sports drinks is OK.
In many cases, you can continue feeding your child as usual. The diarrhea will normally go away in time, without any changes or treatment. But while children have diarrhea, they should:
- Eat small meals throughout the day instead of 3 big meals.
- Eat some salty foods, such as pretzels and soup.
When necessary, changes in the diet may help. No specific diet is recommended. But children often do better with bland foods. Give your child foods such as:
- Baked or broiled beef, pork, chicken, fish, or turkey
- Cooked eggs
- Bananas and other fresh fruits
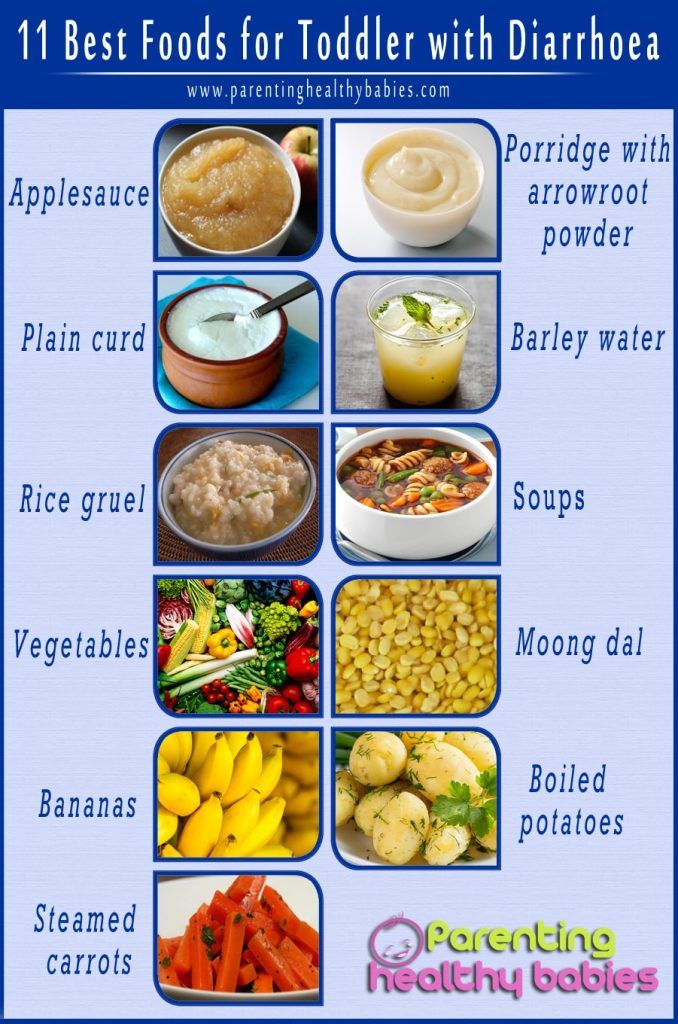
- Applesauce
- Bread products made from refined, white flour
- Pasta or white rice
- Cereals such as cream of wheat, farina, oatmeal, and cornflakes
- Pancakes and waffles made with white flour
- Cornbread, prepared or served with very little honey or syrup
- Cooked vegetables, such as carrots, green beans, mushrooms, beets, asparagus tips, acorn squash, and peeled zucchini
- Some desserts and snacks, such as Jell-O, popsicles, cakes, cookies, or sherbet
- Baked potatoes
In general, removing seeds and skins from these foods is best.
Use low-fat milk, cheese, or yogurt. If dairy products are making the diarrhea worse or causing gas and bloating, your child may need to stop eating or drinking dairy products for a few days.
Children should be allowed to take their time returning to their normal eating habits. For some children, a return to their regular diet can also bring a return of diarrhea. This is often due to mild problems the gut has while absorbing regular foods.
Children should avoid certain kinds of foods when they have diarrhea, including fried foods, greasy foods, processed or fast foods, pastries, donuts, and sausage.
Avoid giving children apple juice and full-strength fruit juices, as they can loosen stool.
Have your child limit or cut out milk and other dairy products if they are making diarrhea worse or causing gas and bloating.
Your child should avoid fruits and vegetables that can cause gas, such as broccoli, peppers, beans, peas, berries, prunes, chickpeas, green leafy vegetables, and corn.
Your child should also avoid caffeine and carbonated drinks at this time.
When children are ready for regular foods again, try giving them:
- Bananas
- Crackers
- Chicken
- Pasta
- Rice cereal
Call your child's provider if your child has any of these symptoms:
- Much less activity than normal (not sitting up at all or not looking around)
- Sunken eyes
- Dry and sticky mouth
- No tears when crying
- Not urinated for 6 hours
- Blood or mucus in the stool
- Fever that does not go away
- Stomach pain
Easter JS. Pediatric gastrointestinal disorders and dehydration. In: Bakes KM, Buchanan JA, Moreira ME, Byyny R, Pons PT, eds. Emergency Medicine Secrets. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 65.
Kotloff KL. Acute gastroenteritis in children. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 366.
21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 366.
Schiller LR, Sellin JH. Diarrhea. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 16.
Updated by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Browse the Encyclopedia
Diarrhea in infants: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
URL of this page: //medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002118.htm
To use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript.
Children who have diarrhea may have less energy, dry eyes, or a dry, sticky mouth. They may also not wet their diaper as often as usual.
Give your child fluids for the first 4 to 6 hours. At first, try 1 ounce (2 tablespoons or 30 milliliters) of fluid every 30 to 60 minutes. You can use:
- An over-the-counter drink, such as Pedialyte or Infalyte -- do not water down these drinks
- Pedialyte frozen fruit pops
If you are nursing, keep breastfeeding your infant. If you are using formula, use it at one half strength for 2 to 3 feedings after the diarrhea starts. Then begin regular formula feedings again.
If your child throws up, give only a little bit of fluid at a time. You can start with as little as 1 teaspoon (5 ml) of fluid every 10 to 15 minutes.
When your child is ready for regular foods, try:
- Bananas
- Chicken
- Crackers
- Pasta
- Rice cereal
Avoid:
- Apple juice
- Dairy
- Fried foods
- Full-strength fruit juice
The BRAT diet was recommended by some health care providers in the past. There is not a lot of evidence that it is better than a standard diet for upset stomach, but it probably can't hurt.
There is not a lot of evidence that it is better than a standard diet for upset stomach, but it probably can't hurt.
BRAT stands for the different foods that make up the diet:
- Bananas
- Rice cereal
- Applesauce
- Toast
Bananas and other solid foods are most often not recommended for a child who is actively vomiting.
WHEN TO CONTACT THE HEALTH CARE PROVIDER
Contact your child's provider if your child has any of these symptoms:
- Blood or mucus in the stool
- Dry and sticky mouth
- Fever that does not go away
- Much less activity than normal (is not sitting up at all or looking around)
- No tears when crying
- No urination for 6 hours
- Stomach pain
- Vomiting
When your infant has diarrhea; When your baby has diarrhea; BRAT diet; Diarrhea in children
- Bananas and nausea
Kotloff KL. Acute gastroenteritis in children. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds.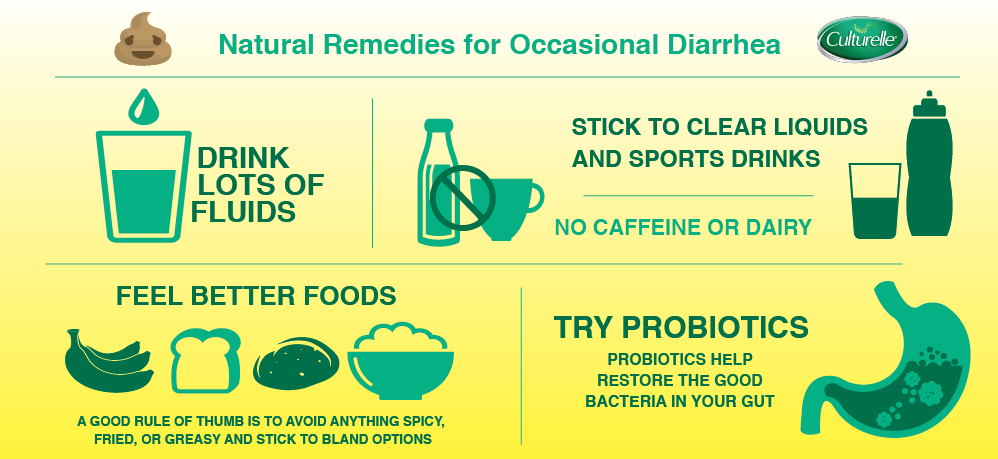 Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 366.
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 366.
Larson-Nath C, Gurram B, Chelimsky G. Disorders of digestion in the neonate. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, Walsh MC, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 83.
Nguyen T, Akhtar S. Gastroenteritis. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 84.
Updated by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Foods to eat and not to eat with diarrhea
A person's diet is critical if they are experiencing diarrhea. Some foods can help relieve this symptom, while others can make it worse.
What to eat and drink
To relieve diarrhea, it is recommended to eat soft, simple foods that are easy to digest, which will help absorb excess water from the stool. Among them it is worth noting: oatmeal, rice porridge, bananas, plain white rice, bread or toast, boiled potatoes. These foods may be especially helpful on the first day of diarrhea treatment. Frequent consumption of such food in small quantities throughout the day will help improve the functions of the digestive system.
Probiotic foods such as yogurt and kefir may help in some cases, but can sometimes further irritate the digestive system.
Fluids are vital to recovery. Persons with diarrhea should drink plenty of water, during the day it is necessary to drink an additional cup of water after each bowel movement. A large intake of fluid helps prevent dehydration and remove toxins from the body. However, in addition to water, the body also loses minerals and electrolytes. To replenish them, it is recommended to use soup-broth, electrolyte water, sports drinks.
To replenish them, it is recommended to use soup-broth, electrolyte water, sports drinks.
Foods and drinks to avoid
Many foods can aggravate irritation of the digestive system and increase the severity of diarrhea. These include: spicy foods, fried foods, sweets and foods with artificial sweeteners, foods high in fiber, onions and garlic, raw vegetables, foods that lead to gas formation in the intestines (cabbage, broccoli and cauliflower), citrus fruits, fatty meat, including pork and veal, dairy products. You should also avoid carbonated drinks, those containing caffeine, alcohol.
In addition to diet, over-the-counter medications can help manage diarrhea. Persons with diarrhea should also be provided with sufficient rest, as stressful situations can worsen the situation. Physical activity can lead to a higher risk of dehydration and should be limited.
Hospitalization is required if there is blood or mucus in the stool accompanied by fever. In severe cases of diarrhea, hospitalization and intravenous electrolytes may also be required. Diarrhea in children requires special attention. If your child shows any signs of dehydration, seek immediate medical attention. Symptoms include: dry mouth, weight loss, crying without tears.
In severe cases of diarrhea, hospitalization and intravenous electrolytes may also be required. Diarrhea in children requires special attention. If your child shows any signs of dehydration, seek immediate medical attention. Symptoms include: dry mouth, weight loss, crying without tears.
Many cases of diarrhea last only a few days and are well controlled by home treatments. A simple diet, increased fluid intake, and use of over-the-counter medications as needed can help relieve symptoms quickly. In cases where the body does not respond to these procedures, you should consult a doctor after 2-3 days.
According to www.medicalnewstoday.com
What can you eat with diarrhea in a child and an adult | Diet for diarrhea
Co-author, editor and medical expert - Klimovich Elina Valerievna.
Views: 2 835 310
Last update date: 26.10.2022
Average reading time: 4 minutes
Content
What can be eaten with diarrhea?
What to drink with diarrhea?
What should I avoid if I have diarrhea?
What is diarrhea and how to treat it
It is very important to adjust the diet and diet in case of bowel disorder in such a way as to help the body cope with the problem as efficiently as possible. If you do not know what to eat with diarrhea, use our recommendations.
If you do not know what to eat with diarrhea, use our recommendations.
Back to Contents
What Can You Eat When You Have Diarrhea?
- Diet for diarrhea should include foods high in pectin: applesauce, bananas, yogurt. Pectin - water-soluble fiber - helps to cope with indigestion.
- Pay attention to foods rich in potassium - fruit juices, jacket potatoes, bananas. When the intestines are upset, the body actively loses potassium and its restoration is necessary.
- Don't forget to add salt to your meals. Meals should include salty soups, broths, crackers, etc., which will help retain water in the body and stay hydrated.
- Get enough protein. With an upset stomach, you can eat lightly fried beef, turkey, chicken, or hard-boiled eggs to avoid fatigue and fatigue.
- Eat hot processed vegetables and fruits. Some raw vegetables and fruits can make diarrhea worse. When dieting, try a simple soup with asparagus, carrots, beets, zucchini, mushrooms or celery, mashed potatoes or jacket potatoes.

Top of page
What to drink with diarrhea?
Drink at least a glass of fluid after each bout of diarrhea to prevent dehydration. In case of intestinal upset, drink water, weak tea, apple juice, low-fat broth. A liquid diarrhea diet does not burden the digestive tract with heavy work and helps prevent irritation.
Top of page
What should I avoid if I have diarrhea?
- Avoid caffeinated drinks and foods that are very hot or cold. It will irritate the gastrointestinal tract.
- Avoid fatty, fried and heavy foods during the diet. Such a diet will only exacerbate intestinal upset.
- Avoid foods that cause gas in the intestines - chewing gum, carbonated drinks. They irritate the digestive tract.
- Limit milk and dairy products. They can be hard to digest.
- Avoid nuts, raw fruits and vegetables, bran and whole grain bread in your diet. They irritate the digestive tract.
Try not to smoke or drink alcohol.