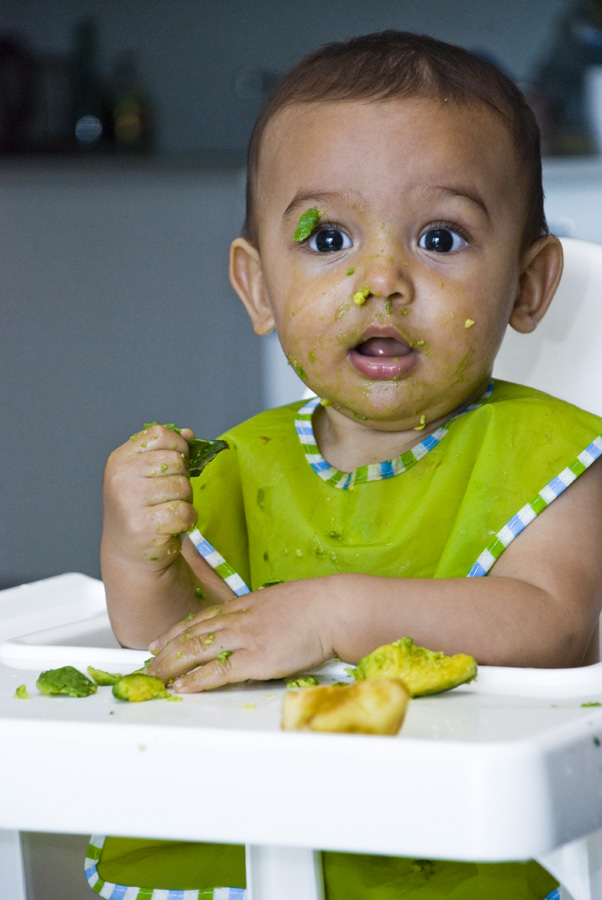
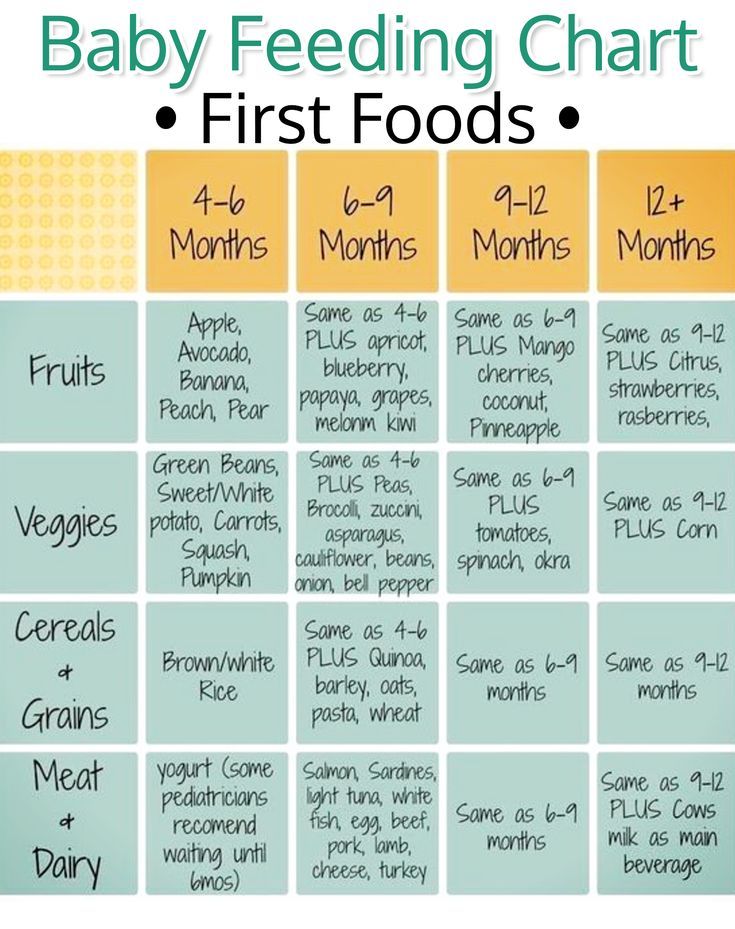
Great first finger foods for baby
Best Early Finger Foods for Baby (With Tips, Visuals, and Recipes)
Use this list of safe, nutritious, and easy to eat finger foods for baby to help you know exactly what (and how) to offer at meals and snacks. Plus, find the best first finger foods, troubleshooting tips, and visuals of foods broken down by food group to keep things easy!
Finger Foods for Baby
After baby starts solids and is ready to move onto finger foods, you may feel a little confused by exactly what to serve and how to serve it. Which is totally normal because it can be scary to let baby feed themselves this way and we may not have any experience doing this—or we may have totally forgotten from our last kiddo!
This list of finger foods for baby will cover some great first finger foods to start with, then set you up with plenty of healthy options from each food group.
TIP: Find more info on starting solids here and the best foods to start with if doing baby led weaning or purees with baby.
Healthy Baby Food
I love sharing these ideas for baby food since they are easy to prepare and serve and because I know how hard it can be to continue to come up with flavorful and healthy meals and snacks for our little ones. Let me tell you, I’m on my third kiddo and it can be such a challenge to feed him during the chaos of parenting the rest of my crew! These foods are wholesome and nutritious—perfect for your baby.
TIP: I’m a big fan of SpoonfulONE, a company that offers the most complete way to introduce food allergens to our kids. They make mix-ins, puffs, and crackers that are yummy and easy for babies and toddlers to eat. Learn more about their pediatrician-approved baby foods here. (sponsored link)
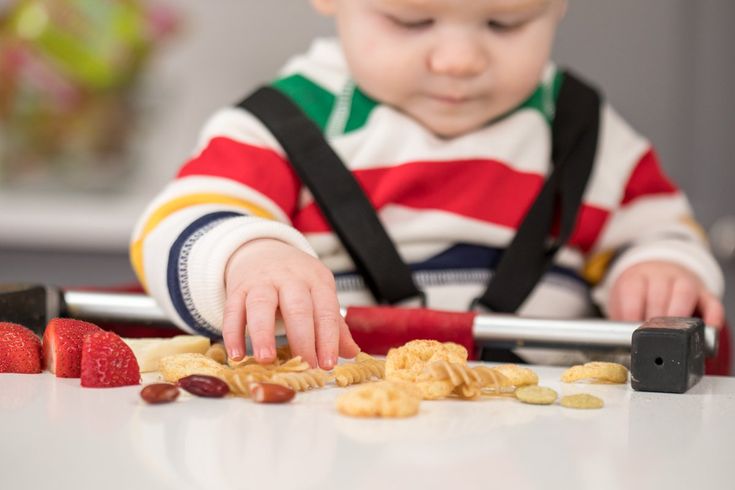
Best First Finger Foods
When baby is around 9 months, you’ll notice that they’re able to pick up smaller pieces of food with two fingers. This is known as the “pincer grasp” and is a sign that they’re ready to start finger foods. To be clear, when I say “finger foods” I mean small pieces of food that a baby (or toddler) can feed themselves.
To be clear, when I say “finger foods” I mean small pieces of food that a baby (or toddler) can feed themselves.
Here are some of my favorite ones to start with that are all super soft, safe to eat, and easy to pick up.
- Scrambled egg, broken up into small pieces
- Roasted sweet potato mashed and broken up into small pieces
- Fresh raspberries, broken up into smaller pieces
- Oatmeal, cooked according to package directions and allowed to cool
- Tofu, diced and sauteed lightly or steamed
- Ground beef, chicken, or turkey, broken up into small pieces or lightly mashed meatballs
- Shredded cheese or crumbled goat cheese
- Mashed sweet potato, in little pieces
- Peanut butter puffs
TIP: You can serve the tofu, ground meat, or meatballs in veggie puree from a pouch or a simple marinara sauce for extra moisture and flavor. Learn more about how and why to introduce peanut butter.
Finger Foods for Baby: Fruits and Veggies
Some of my favorite early fruits and veggies to serve babies are:
- Mashed roasted sweet potato, broken up into small pieces
- Warmed frozen peas, slightly mashed if desired
- Roasted Zucchini
- Diced Roasted Sweet Potato or Butternut Squash
- Fresh blueberries, cut in half or quarters
- Fresh raspberries, broken into small pieces
- Banana, broken into small segments (they are less slippery this way versus slicing them)
- Avocado, diced and mashed slightly (be sure it’s ripe and very soft)
TIP: A good rule of thumb is to serve pieces of food that are about the size of a pea to start and soft enough that they are easy to squish between your fingers. This will be easy for baby to pick up and eat and will also reduce chances of choking.
This will be easy for baby to pick up and eat and will also reduce chances of choking.
Finger Food Ideas: Carbohydrates
Offering complex carbohydrates can provide fiber, a variety of textures, B vitamins, and more. Try these with your baby.
- Spinach pancakes (moisten with applesauce or plain yogurt if needed; this recipe is particularly moist and great for babies)
- Oatmeal, cooked according to package directions and allowed to cool
- Baby Puffs
- Peanut Butter Puffs
- Rice (it’s easiest if it’s in little clumps so baby can pick it up; this Coconut Rice or this Cheesy Rice are both good options)
- Baby Banana Muffin
- O cereal (soften in nondairy unsweetened milk or yogurt as needed)
- Baked Oatmeal, diced
Finger Food Ideas: Proteins
Offering proteins will continue to expose baby to a range of nutrients. These are my go-tos for babies newer to finger foods—and toddlers too.
- Shredded cheese (thicker cuts are a little easier to pick up)
- Tofu, diced and sauteed lightly or steamed
- Flaked cooked wild salmon
- Lightly mashed meatballs
- Shredded chicken, cut up finely (we love this Butter Chicken to share with baby)
- Ground beef, turkey, or chicken, broken into smaller pieces
- Lightly mashed beans
- Scrambled eggs, broken up into small pieces
- Diced egg muffins
I’d love to hear any questions you may have, or if you have foods that your babies enjoy that I didn’t include here.
 Chime in below in the comments!
Chime in below in the comments!Prep Time 5 minutes
Cook Time 5 minutes
Total Time 10 minutes
Author Amy Palanjian
Cuisine American
Course Baby Food
Calories 124kcal
Servings 1
First Finger Foods (choose 1-3 per meal)
- ▢ 1 Scrambled egg (broken up into small pieces)
- ▢ 1/4 cup Roasted sweet potato, mashed and broken up into small pieces
- ▢ 1/4 cup Fresh raspberries (broken up into smaller pieces)
- ▢ 1/4 cup Oatmeal (cooked according to package directions and allowed to cool)
- ▢ 2 tbsp Tofu (diced and sauteed lightly or steamed)
- ▢ 2 tbsp ground beef, chicken, or turkey, broken up into small pieces or lightly mashed meatballs
- ▢ 2 tbsp shredded cheese or crumbled goat cheese
- ▢ 1/4 cup Mashed sweet potato (broken into little pieces)
- ▢ 1/4 cup Peanut butter puffs
Fruits and Veggies
- ▢ 1/4 cup mashed roasted sweet potato (broken up into small pieces)
- ▢ 1/4 cup warmed frozen peas
- ▢ 1/4 cup Roasted Zucchini
- ▢ 1/4 cup diced Roasted Sweet Potato or Butternut Squash
- ▢ 1/4 cup blueberries (cut in half or quarters)
- ▢ 1/4 cup raspberries (broken into small pieces)
- ▢ 1/4 cup banana slices (broken into small segments—they are less slippery this way versus slicing them)
- ▢ 2 tbsp avocado (diced and mashed slightly—be sure it's ripe and very soft)
Whole Grains and Carbohydrates
- ▢ 1 Spinach pancakes (moisten with applesauce or plain yogurt if needed; this recipe is particularly moist and great for babies)
- ▢ 1/4 cup Oatmeal (cooked according to package directions and allowed to cool)
- ▢ 1/4 cup Baby Puffs
- ▢ 1/4 cup Peanut Butter Puffs
- ▢ 1/4 cup fully cooked rice (it's easiest if it's in little clumps so baby can pick it up; this Coconut Rice or this Cheesy Rice are both good options)
- ▢ 1 Baby Banana Muffin
- ▢ 1/4 cup O cereal (soften in nondairy unsweetened milk or yogurt as needed)
- ▢ 1/4 cup Baked Oatmeal (diced or regular oatmeal broken into little pieces)
Dairy
- ▢ 2 tbsp Shredded cheese (such as mozzarella)
- ▢ 2 tbsp Tofu (diced and sauteed lightly or steamed)
- ▢ 2 tbsp flaked cooked wild salmon
- ▢ 1 lightly mashed meatballs
- ▢ 2 tbsp finely shredded chicken (we love this Butter Chicken to share with baby)
- ▢ 2 tbsp ground beef, turkey, or chicken (broken into smaller pieces)
- ▢ 2 tbsp lightly mashed beans
- ▢ 1 Scrambled egg (broken up into small pieces)
- ▢ 1 Diced Egg muffins
For each meal or snack, choose 2-3 foods from a mix of food groups.
 Aim to include some fat in most meals and protein in many too.
Aim to include some fat in most meals and protein in many too.Prepare the food, cutting into small pieces and/or mashing as needed to make the food easy to eat.
Start with small portions and allow more as baby indicates according to their hunger.
- Store leftovers in an airtight container for 3-5 days in the fridge.
- Many foods you cook for your family will work as baby finger foods—just be sure they are easy to squish between your fingers and the pieces are small and easy to chew.
- Babies very normally make a lot of faces when they eat, so don't assume they don't like something just because they scrunch their nose!
- Flavors and textures can take time to learn to eat, so continue offering foods in small portions even if baby hasn't liked them in the past—and make sure they taste good to you!
Calories: 124kcal, Carbohydrates: 14g, Protein: 7g, Fat: 4g, Saturated Fat: 1g, Polyunsaturated Fat: 1g, Monounsaturated Fat: 2g, Trans Fat: 1g, Cholesterol: 164mg, Sodium: 81mg, Potassium: 344mg, Fiber: 4g, Sugar: 5g, Vitamin A: 9857IU, Vitamin C: 18mg, Calcium: 51mg, Iron: 1mg
Tried this recipe?Rate in the comments and tag @yummytoddlerfood on IG!
Easy, Healthy, Perfect for Kids and Babies!
These sweet Banana Spinach Pancakes are a favorite when you’re looking to boost nutrition in a favorite breakfast option. Or to have a little fun at the breakfast table by serving up a colorful meal.
Or to have a little fun at the breakfast table by serving up a colorful meal.
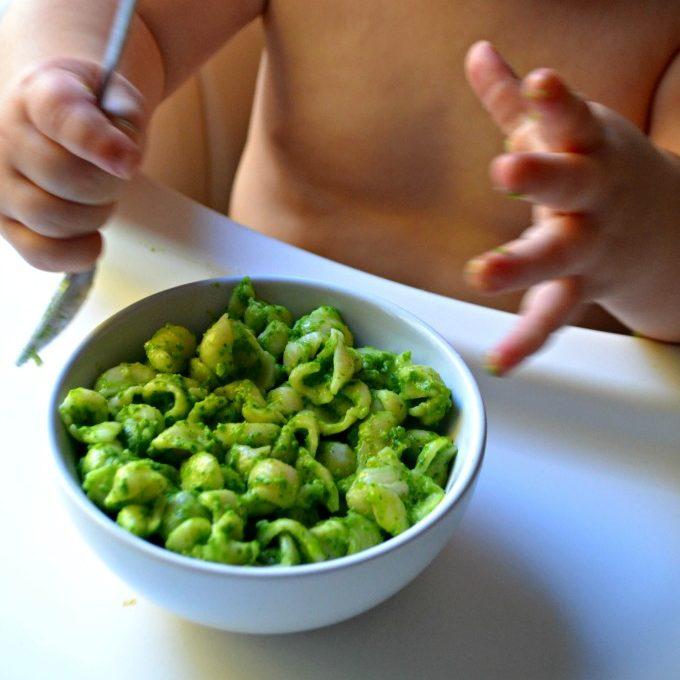
Spinach Pancakes
I never thought that my older daughter would be such a fan of green pancakes, but just when you think you know your kiddo, they go and surprise you! It turns out that she’ll eat pretty much anything in pancake form. This (and Spinach Pesto and my Spinach Muffins) are by far her preferred ways to get her greens.
I love how these are both easy to make and they’re so easy for the kids to enjoy.
The beauty of this kids pancake recipe is that it comes together in the blender so you don’t have to dirty a sink full of dishes to make it happen.
And it includes two bananas and small pile of spinach, so everyone will get a nice amount of vitamins and minerals to start the day.
TIP: The flavor is sweet, so despite the color, they taste like healthy banana pancakes.
Ingredients You Need
To make this simple pancake recipe you’ll need:
- Very ripe bananas: Those with brown spots will have the best flavor
- Eggs
- Buckwheat flour or whole wheat flour
- Milk: Dairy or nondairy
- Baby spinach: You can use fresh spinach or spinach that you’ve frozen
- Ground flaxseed
- Baking powder
- Cinnamon
- Vanilla extract,
- Oil or butter for cooking
Ingredient Substitutions
Both whole wheat and buckwheat flour work well in this recipe, though the pancakes cook through more easily with buckwheat. Look for it in the natural flours section of your supermarket. It’s widely available and very nutritious. For tips on using whole wheat flour, see the Notes section at the bottom of the recipe as you’ll want to reduce the milk amount slightly.
Look for it in the natural flours section of your supermarket. It’s widely available and very nutritious. For tips on using whole wheat flour, see the Notes section at the bottom of the recipe as you’ll want to reduce the milk amount slightly.
Use an egg replacer like the one from Bob’s Red Mill to make these egg-free.
Use buckwheat flour to make these gluten-free.
Use nondairy milk to make these without dairy.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Here’s a look at how to make these healthy pancakes. Scroll down to the bottom of this post for the full information.
- Add all ingredients to a blender except the flour.
- Blend, starting on low and working up to high. You want the spinach to be very well incorporated.
- Stir or pulse in the flour. Avoid over-blending but do make sure to get all of the flour blended in.
- Cook as you would any other pancakes and serve warm.
TIP: I like to cook these in a nonstick skillet or griddle since they are easiest to flip. Cast iron also works if well greased.
Cast iron also works if well greased.
Gluten-Free Spinach Pancakes
Yes! Buckwheat flour is naturally gluten-free and it works well in this recipe.
Dairy-Free Spinach Pancakes
To make these dairy-free, simply use nondairy plain unsweetened milk instead of dairy milk and cook with neutral oil.
Easy Baby Pancakes
Due to the very soft texture of these pancakes, they tend to be much easier for babies to eat than traditional ones. And since they are packed with nutrients, this is a favorite pancake recipe to make for baby led weaning and once a baby is starting to eat finger foods.
TIP: Find my favorite early finger foods for babies here.
Serving Suggestions
Maple syrup and butter of course, or nut butter, yogurt, applesauce, chopped fruit, or jam are all good options. When my middle kiddo was a baby, she ate them plain!
TIP: We like to have ours with a fruit salad rainbow (without the pot of gold at the end, unfortunately!) for St.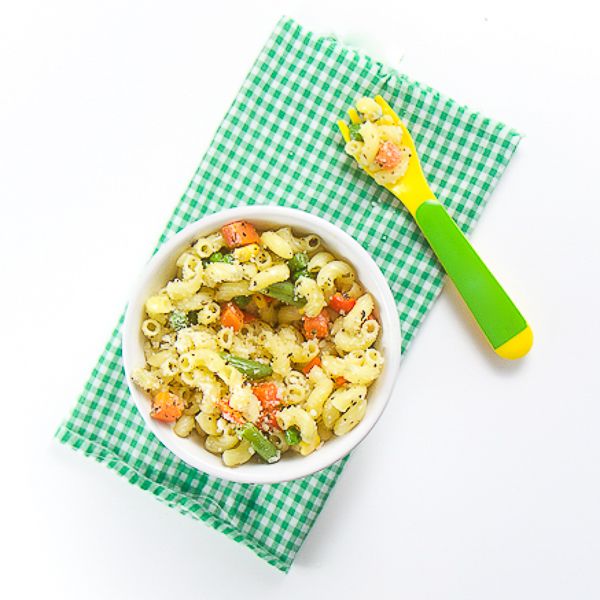 Patrick’s Day, but that part is of course optional.
Patrick’s Day, but that part is of course optional.
How to Store
These store really well if you let any leftovers cool and store in an airtight container or zip top freezer bags. You can store leftovers in an airtight container in the fridge for 3-5 days or in a freezer safe container or bag for up to 3 months. Warm in 15 second increments in the microwave to serve.
Tips for Making the Best Spinach Pancakes
- You can store a bag of baby spinach in the freezer to use in smoothies and pancakes. Freezing it maintains the nutrients but it knocks out any “green” flavor which is handy! It’s also nice that you don’t have to worry about it going bad before you can use it up.
- Be sure to blend the batter very smooth to get the greens very well processed.
- You can sub in whole wheat flour for the buckwheat, but you’ll want to reduce the milk by ¼ cup.
- If the bottoms start to brown too much before they are set, lower the heat to medium-low.
- Look for buckwheat in the natural flours section of your supermarket.
 It’s widely available and very nutritious.
It’s widely available and very nutritious. - If making for a baby who’s not yet consuming cow’s milk, you can use unsweetened nondairy milk.
- I prefer to use a nonstick skillet or griddle for this recipe, though cast iron works too.
- You may also like Spinach Banana Muffins, 2-Ingredient Pancakes, Banana Oatmeal Pancakes, and Yogurt Pancakes.
I’d love to hear what you think of this recipe so please comment below with feedback!
This post was first published March 2018.
Prep Time 5 minutes
Cook Time 15 minutes
Total Time 20 minutes
Author Amy Palanjian
Cuisine American
Course Breakfast
Calories 237kcal
Servings 4
- ▢ 2 small very ripe bananas (about 1 cup tightly packed sliced banans)
- ▢ 2 large eggs
- ▢ 1 cup buckwheat flour or whole wheat (See Notes at the bottom if using whole wheat)
- ▢ 1 cup milk
- ▢ 2 cups lightly packed baby spinach
- ▢ 1 tablespoon ground flaxseed
- ▢ 1 1/2 teaspoons baking powder
- ▢ 1 teaspoon cinnamon
- ▢ 1 teaspoon vanilla extract
- ▢ Coconut oil for cooking (or canola oil or butter)
Add all ingredients to a blender except the flour.

Blend on high until very well combined, about 20-30 seconds, or until you no longer see any noticeable flecks of spinach.
Stir or pulse in the flour and thoroughly combine without over-mixing.
Warm a nonstick or cast iron skillet or griddle over medium heat and coat with oil or butter. Pour small rounds of batter onto the hot surface—the batter should spread fairly thinly on its own—and let cook until bubbles form on the surface and the surface is mostly set, about 3-4 minutes.
Flip and cook for an additional 3 minutes, or until fully cooked.
Continue to prepare the rest of the batter, keeping the finished pancakes warm in a 275 degree oven if desired.
Serve warm with fruit, maple syrup, or another favorite dip.
Green Pan Non-Stick Pan
Vitamix Blender
Spatula
- To store, let cool fully and keep in an airtight container in the fridge for up to 3 days.
 Warm slightly before serving. Or, store in a zip top freezer bag for up to 3 months and warm through to serve.
Warm slightly before serving. Or, store in a zip top freezer bag for up to 3 months and warm through to serve. - Whole-wheat flour: You can sub in whole wheat flour for the buckwheat. Just reduce the milk to ¾ cup.
- You can use baby kale in this recipe if you prefer.
- You can store a bag of baby spinach in the freezer to use in smoothies and pancakes. Freezing it maintains the nutrients but it knocks out any “green” flavor which is handy! It’s also nice that you don’t have to worry about it going bad before you can use it up.
- Be sure to blend the batter very smooth to get the greens very well processed.
- If the bottoms start to brown too much before they are set, lower the heat to medium-low.
- Look for buckwheat in the natural flours section of your supermarket. It’s widely available and very nutritious.
- If making for a baby who’s not yet consuming cow’s milk, you can use unsweetened nondairy milk.
- I prefer to use a nonstick skillet or griddle for this recipe, though cast iron works too.
Calories: 237kcal, Carbohydrates: 40g, Protein: 9g, Fat: 6g, Saturated Fat: 2g, Polyunsaturated Fat: 1g, Monounsaturated Fat: 2g, Cholesterol: 104mg, Sodium: 206mg, Potassium: 577mg, Fiber: 6g, Sugar: 11g, Vitamin A: 1674IU, Vitamin C: 9mg, Calcium: 208mg, Iron: 2mg
Tried this recipe?Rate in the comments and tag @yummytoddlerfood on IG!
what products are possible, features of complementary foods
It is no secret that young and not very experienced mothers receive information on the nutrition of an infant, including recommendations on how to introduce the first complementary foods, mainly from two sources: grandmother's stories and from the Internet. Unfortunately, both of these respected sources of information may voluntarily or not voluntarily, but be very mistaken, since grandmothers grew up in a more prosperous time in terms of environmental conditions, and the Internet is littered with various articles that are rarely written by professionals, moreover, they rely either on explicit outdated guides on baby food, or frankly on unverified information.
In this article, I will try to combine the latest scientific data and recommendations on how to introduce the first complementary foods with many years of observations from the experience of a practical pediatrician and an allergist-immunologist.
At what age is it time to introduce the first complementary foods
According to the recommendations of the Research Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, the first complementary foods can be introduced from 4.5 - 5 months, regardless of the type of feeding. This is "average". In practice, the choice of when to start introducing complementary foods still depends on the individual characteristics of the child. For example, for a child with widespread atopic dermatitis (diathesis), we will not introduce complementary foods until at least acute skin symptoms, such as cracks, weeping or secondary eczema, have steadily disappeared. Increased dryness and flaking of the skin, of course, require constant application of moisturizers to the skin, but in no case are they a contraindication to the start of the introduction of the first complementary foods.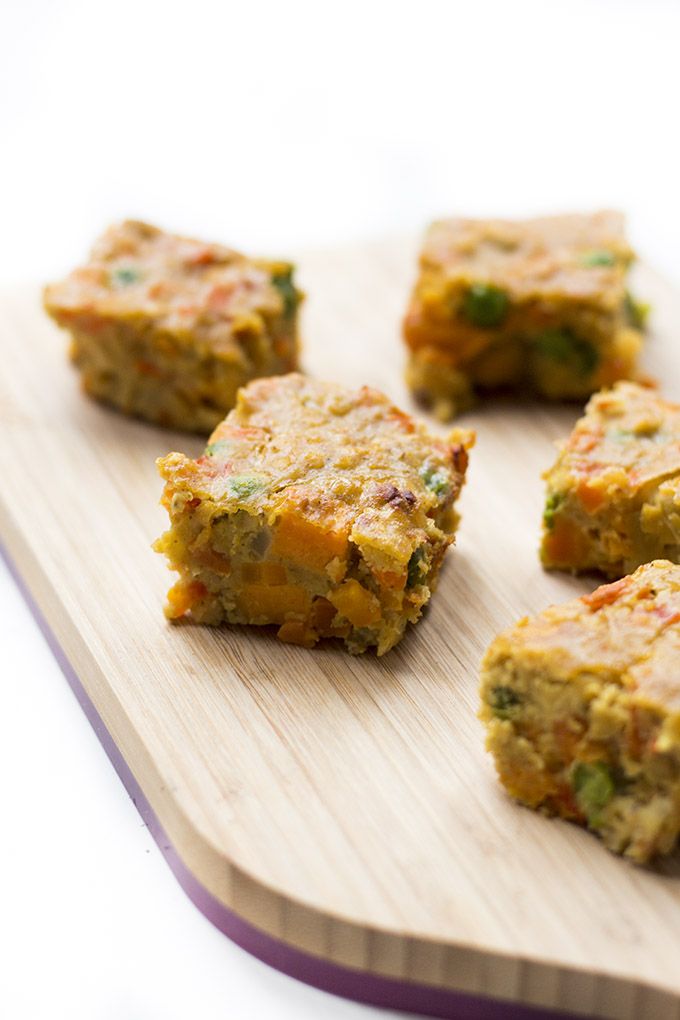
Another important point when choosing the time to start introducing complementary foods is the dynamics of the child's weight gain. The more intensively the child gains in height and weight, the sooner he may need additional calories, since the energy value of breast milk or artificial formula alone will most likely not be enough for a child who grows faster than his peers by 4 - 5 months. We must not forget that natural products contain a fairly large range of minerals and vitamins, and a mother’s body, alas, cannot be an eternal and bottomless source of useful nutrients, somewhere something will gradually begin to be missed.
In addition, the nature of lactation in the mother has a great influence on the timing of the introduction of complementary foods. If a nursing mother begins to feel a lack of milk, I would prefer to first give her advice on stimulating lactation, and at the same time begin to introduce complementary foods. It will be better than introducing an artificial mixture. But I repeat that the earliest start date for the introduction of the first complementary foods is the age of 4 months, before the child's body is not yet ready, the risk of developing allergies is also high.
But I repeat that the earliest start date for the introduction of the first complementary foods is the age of 4 months, before the child's body is not yet ready, the risk of developing allergies is also high.
So, we agree with you that the first complementary foods can be introduced no earlier than 4 months of a child's life.
First complementary foods: Which foods to choose?
The first complementary foods, as a rule, should consist of vegetable or fruit purees, but in no case juices. Still, juices, even for children, are highly filtered, mainly contain a large amount of organic acids and “light” carbohydrates (that is, sugar, to make it clear to everyone). I will not waste time explaining why juices are harmful to an infant, but I will describe a clinical case from practice.
Parents with an 8-month-old girl came to the reception. Somewhere from 5 months she practically did not gain weight, although before that all indicators were normal. In the analyzes, apart from visible signs of iron deficiency, slightly reduced hemoglobin, no pathology was also detected. The main complaint: "does not eat anything." And when I began to find out what she still eats, it turned out that the child drinks half a liter of juice every day. But porridge or cottage cheese, or mashed potatoes cannot be forced together, they spit everything out. I don't like the taste. And so - for three months. The child, of course, became very nervous, yelling at night, demanding juice.
The main complaint: "does not eat anything." And when I began to find out what she still eats, it turned out that the child drinks half a liter of juice every day. But porridge or cottage cheese, or mashed potatoes cannot be forced together, they spit everything out. I don't like the taste. And so - for three months. The child, of course, became very nervous, yelling at night, demanding juice.
So draw your own conclusions and be careful.
For the first feeding, this is now recognized by everyone, the best dishes are vegetable purees from green varieties of vegetables: zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli. The first complementary foods are introduced, starting with half a teaspoon, in the morning for three days, then gradually increase the amount of the product to 40-50 grams per week. Supplemented with breast milk or formula.
For problems with stools, constipation, it’s good to start introducing prune puree, green apple, you can try pumpkin, even apricot puree, but in no case start with carrots. Beta-carotenoids, which are abundant in carrots, are generally poorly absorbed and can cause allergies in a child.
Beta-carotenoids, which are abundant in carrots, are generally poorly absorbed and can cause allergies in a child.
Second food. Porridge or meat?
Even 5 - 6 years ago, we taught students at the medical institute that from 5 - 5.5 months old, an infant should begin to give cereal porridge for complementary foods. This is rice, buckwheat, corn. The first week you can cook 5% porridge: 5 grams of ground cereal per 100 ml of water. Then the porridges are cooked already denser: 10 grams of cereal per 100 ml of water. But now, basically everyone uses instant (soluble) cereals, which are diluted with water according to the instructions on the package. In addition, ready-to-eat liquid cereals are on sale: for example, Bellakt, Frutonyanya, etc.
Why meat? You ask. According to modern recommendations (they really began to change quite often), but in this case I support: if a child has a pronounced decrease in hemoglobin in the blood below 100 g / l by the age of 5 months, it makes sense to start introducing fruit or vegetable purees as a second types of complementary foods - meat purees as a source of the most well-absorbed heme iron. You need to choose from varieties such as turkey, rabbit, lamb. Beef and veal can only be offered to children who did not have red cheeks and diathesis.
You need to choose from varieties such as turkey, rabbit, lamb. Beef and veal can only be offered to children who did not have red cheeks and diathesis.
In the absence of problems with low hemoglobin, feel free to introduce porridge as the second meal of complementary foods, especially if the child is small and does not gain weight very well. In this case, we can recommend breeding cereals with the addition of breast milk or a mixture (Nan, Nutrilon, Celia, Nanny). With mixtures based on goat's milk, parents of children with a predisposition to allergies should be very careful. Goat milk formulas are not the best choice for babies who are allergic or intolerant to cow's milk protein, whatever the internet says. Believe me, there are serious scientific articles by foreign authors, which provided data on a very high frequency of cross-allergy between cow and goat milk proteins in children who were transferred to goat milk mixtures. And I saw it myself in my practice, when a child with dermatitis was transferred to a mixture of goat's milk, there was a clear improvement for a month or two, and then all over again and with a doubled degree of allergic skin damage.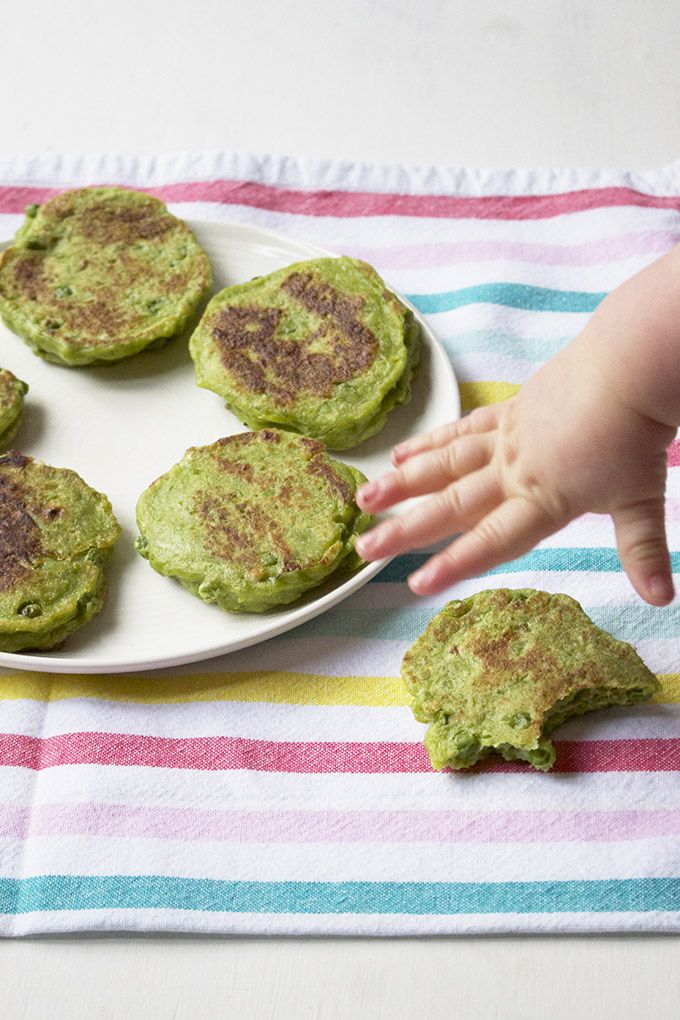
Introduction to fermented milk products
This is the most difficult question. I am sure that most of our grandparents demand that their stupid parents start drinking milk and kefir as soon as possible. In a number of cases, children really start to absorb sour-milk products quite well after 6 months, but before this age I am very careful even with sour-milk Agusha, and even introducing milk or kefir before 6 months is a bad form, believe me, and can lead to very bad consequences for the child. I understand the Western European medical community, which has recently banned its pediatricians from recommending fermented milk products for complementary foods for children under 3 years of age, just imagine!
They (the Europeans) need to do something with their artificial milk mixtures. Even 20 years ago, we did not know other mixtures after the "two", that is, the second formula for children from 6 to 12 months. Then there were formulas for children from 1 to 2 years old, then from 2 to 3 years old, and now there are already mixtures for children up to 4 years old, and I think if this goes on, then until the age of sixteen there will be their own milk substitutes. Dismiss me, I don't think this approach is correct. But the fact is that our grandparents had much better genetics than the generation of our children, alas. In the context of the growth of medical capabilities, genetically determined diseases are also growing, and in this case, intolerance to cow's milk protein, and with every 10 years there are more and more such people among us. But if a child really suffers from an allergy to cow's milk protein or is severely deficient in enzymes, then he will carry this peculiarity through his whole life, and most likely he will not drink milk or kefir himself, and there is no need to force him if he himself won't want to!
Dismiss me, I don't think this approach is correct. But the fact is that our grandparents had much better genetics than the generation of our children, alas. In the context of the growth of medical capabilities, genetically determined diseases are also growing, and in this case, intolerance to cow's milk protein, and with every 10 years there are more and more such people among us. But if a child really suffers from an allergy to cow's milk protein or is severely deficient in enzymes, then he will carry this peculiarity through his whole life, and most likely he will not drink milk or kefir himself, and there is no need to force him if he himself won't want to!
But you are lucky with genetics, and no one in the family has ever had an allergy (which is hard to imagine nowadays), and most importantly, if your child has always had perfectly clean skin, then the first of the dairy products - cottage cheese, you will begin to offer your child with 7 months, kefir - from 10 months.:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/2715426/original/084314100_1548738668-adorable-baby-baker-35666.jpg) Milk - after a year. It will be better this way.
Milk - after a year. It will be better this way.
But if your family does not have a very close and joyful relationship with milk, then it is better to postpone even the introduction of kefir and yogurt into complementary foods for a child until the age of 18 months.
Fish day and first meal
Fish is a very healthy product, rich in vitamins and antioxidants, but it must also be introduced carefully. I advise you to start introducing the first fish food at about 7-8 months. It is better to start with species such as cod, hake, haddock. The rules are the same: the first three days on the "gram," then slowly add. If there are no problems in a week or two, you can try such delicacies as tuna or salmon, of course, canned children, if you can find it. It is better not to mess with trout and salmon in the first year of life, this fish is all stuffed with dyes and antibiotics.
No matter how hard I tried, the article about the first complementary foods turned out to be long. Thank you for reading to the end, I hope it will be useful. If you have questions about the introduction of complementary foods, you can write your appeals on our website in the question to a specialist section. A short answer can be obtained on the Internet, but in order to make a diagnosis and give a detailed consultation, of course, you need to come to a face-to-face appointment with a pediatrician and a pediatric allergist.
Thank you for reading to the end, I hope it will be useful. If you have questions about the introduction of complementary foods, you can write your appeals on our website in the question to a specialist section. A short answer can be obtained on the Internet, but in order to make a diagnosis and give a detailed consultation, of course, you need to come to a face-to-face appointment with a pediatrician and a pediatric allergist.
Baby's first complementary foods at 4-6 months - where to start with porridge or vegetable puree? Principles, schemes for the introduction of complementary foods
At what age and when should complementary foods be started? What do you think? At 4 months, at 5, 6 months , later? And where to start, what to give preference to: cereals or vegetable puree? Or maybe first give tasty and healthy fruits?
We have already made a whole series of video lectures on complementary foods for children, by months and products, but we are faced with the fact that many parents ask what is the best way to start complementary foods and at what age it is advisable to introduce it.
Especially a lot of questions and uncertainties, oddly enough, parents, whose children are breastfeeding . You quite often confuse the two concepts until what age it is advisable to breastfeed and at what age it is worth introducing complementary foods.
Valid according to all recommendations, breastfeeding is necessary for a baby at least up to 6 months , and if possible longer. But this does not mean at all that a child at 5 or 6 months does not need complementary foods that will not allow the development of deficient conditions in a child, for example iron deficiency . Modern principles of introducing complementary foods to children are a kind of fusion of practical experience and the latest scientific developments. They are based on the recommendations of the European Association of Pediatric Gastroenterologists, Hepatologists and Nutritionists " ESPGHAN " 2017, the American Academy of Pediatrics " AAP " and national recommendations of relevant ministries and associations.
According to European recommendations, which also apply to our countries, the first complementary foods should be started:
That is optimal, Complementary foods should be introduced within 5-6 months life. There is no specific, clear, unambiguous age at which complementary foods should be introduced. You have a certain corridor - 2 months and you and your pediatrician must decide when to start complementary foods, focusing on how the child develops, how he gains weight, whether he has signs of readiness for complementary foods, which we have already talked about in previous our videos, what hemoglobin is, and even if you have enough milk if the baby is breastfed. At the same time, there is a kind of paradoxical situation, despite the fact that breast milk is the best food for babies ,
Quite often, scientists recommend breastfeeding children to introduce complementary foods a little earlier including iron, and in breast milk for a child aged 5-6 months, it may already be a little lacking.
At the same time, there are no separate recommendations for introduction of complementary foods for breastfed or formula-fed children, approaches in these cases are the same . Thus, I hope that we have understood when to introduce complementary foods to healthy full-term babies who do not have serious diseases. Timely introduction of complementary foods contributes to the optimal development of all systems and organs of the child, physical parameters, psychomotor development, and the activity of the nervous system. The period of introduction of complementary foods, on the one hand, is very important for the growth and development of the child, on the other hand, it is a kind of stage in the transition of the child from breastfeeding to food from the general table.
First complementary foods - where to start?
- If the child develops normally , has a good or even excessive weight gain, it is better to start with one-component vegetable puree .

- If the child is not gaining weight well enough, then gluten-free cereals are better: rice, buckwheat, corn
- Not recommended
The child is very smart and if he tries sweet fruit puree, he can refuse relatively tasteless vegetable foods and cereals for a long time, and you may have difficulty introducing these healthy dishes.
Which is better factory-made or homemade?
Quite often we are asked what is better to give: ready-made vegetable purees and cereals, that is, factory-made, or making them yourself at home. It's up to you to decide. I often recommend industrial products from European manufacturers to my patients, because I am confident in the very strict quality control of baby food in Europe, but if you are confident in the products and water that you have at home, you can do everything yourself.
What is useful in vegetable supplements and what is the best way to prepare it?
Vegetable puree - for the first feeding can be prepared from cauliflower, zucchini, pumpkin, broccoli and vitamins and microelements! Fiber helps move food through the digestive tract and promote beneficial microflora in the gut. Pectins absorb and remove toxins from the baby's body. Vegetables have a positive effect on the acid-base balance of the body, creating conditions for the proper functioning of all organs and systems.
Cauliflower - is a source of fiber, protein, minerals and various vitamins, it contains a lot of magnesium, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, calcium, iron.
Iron it contains twice as much as green peas, peppers and lettuce. Cauliflower protein is easily digestible and its content is quite significant. The cauliflower protein contains methionine . It is one of the essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the human body. Other essential amino acids are also present in a small amount: arginine, tryptophan.
It is one of the essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the human body. Other essential amino acids are also present in a small amount: arginine, tryptophan.
Zucchini - rich in vitamins and microelements. It contains potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium, vitamins, folic acid. The latter plays an important role in the processes of hematopoiesis. Zucchini is rich in trace elements that are necessary for the formation of nervous tissue, normal metabolism, and the formation of hemoglobin.
Broccoli is a very healthy vegetable that is a type of cauliflower. Pleasant soft taste and good digestibility of the product, the unique composition has a positive effect on the health of children. Eat unopened cabbage inflorescences.
This is also a low-allergenic vegetable rich in protein, fiber, vitamins, calcium, iron, trace elements and even phytoncides. The content of calcium and magnesium in broccoli is enough to balance the work of the nervous system, ensure the normal regulation of the child's sleep cycle, good resistance to stress. When eating this vegetable, the child becomes calmer, less excited and naughty. In addition, broccoli is the leader in content choline and methionine which the child needs.
When eating this vegetable, the child becomes calmer, less excited and naughty. In addition, broccoli is the leader in content choline and methionine which the child needs.
Pumpkin - the largest vegetable on Earth. It is one of the ten most useful vegetables in the diet of children, contains a large amount of healthy proteins, fiber and vitamins, iron, potassium, magnesium and trace elements, which are indispensable for children's nutrition, as they strengthen the immune system and help fight inflammation, have a positive effect on the nervous system .
Vitamins and microelements contained in pumpkin help the child grow, provide healthy sleep, are responsible for the condition of the skin and eyes, improve metabolic processes, and accelerate the removal of harmful substances from the child's body. Due to its beneficial qualities, pumpkin can be one of the first types of complementary foods for a baby. All vegetable purees have a specific vegetable smell, this is absolutely normal.
All vegetable purees have a specific vegetable smell, this is absolutely normal.
Scheme for the introduction of vegetables in baby food
You need to introduce vegetables into the child's menu gradually. Each new vegetable should be started as a single-component puree in the amount of ½ teaspoon , preferably at breakfast, so you can track the manifestations of a food allergy or intolerance reaction to the product. If all is well, then the next day offer him a teaspoon .
So, gradually, you need to bring the portion to the age norm. Serving of vegetable puree per day for a child 6 months old - is about 100 grams, at this age you can start adding vegetable oil to vegetable puree : unrefined olive or sunflower (start with 3-4 drops and gradually bring to 1 teaspoon ), the rest of the portion is replenished with breast milk or formula. A serving of vegetable puree is 200 grams per year. The next vegetable product can be introduced no earlier than 4-5 days later, when the child gets used to the one he is already eating. In the future, you can make mashed potatoes from several vegetables. But don't be too hasty. If the child has a rash on the skin, diarrhea or constipation, then you need to temporarily remove the product from the diet, and after a while try again. If an undesirable reaction occurs again, it is better to exclude such a product from the child's diet for 6 months and consult a pediatrician.
A serving of vegetable puree is 200 grams per year. The next vegetable product can be introduced no earlier than 4-5 days later, when the child gets used to the one he is already eating. In the future, you can make mashed potatoes from several vegetables. But don't be too hasty. If the child has a rash on the skin, diarrhea or constipation, then you need to temporarily remove the product from the diet, and after a while try again. If an undesirable reaction occurs again, it is better to exclude such a product from the child's diet for 6 months and consult a pediatrician.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, did not like broccoli, do not refuse what was planned and continue to offer it in small quantities - 1-2 spoons a day, you can even not just once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste.
This will diversify the diet, help the child form the right taste habits. Porridges, as a rule, are the second complementary food after vegetable puree.
How and when to introduce porridge as the first complementary food?
If your child is not gaining weight very well, then complementary foods can be started with the introduction of cereals. It is important to start by choosing one-component, low-allergenic cereals , which do not contain gluten: these are buckwheat, rice, corn porridges .
gluten-containing cereals include: wheat, oats, rye, barley, millet.
According to modern data , the period of introduction of gluten into the child's diet is not of fundamental importance, but the latest recommendations draw attention to the fact that the amount of gluten in the diet of a baby up to a year old should not be large. Therefore, semolina and oatmeal porridge is better to add to other porridge in a limited amount , and not to give a whole separate portion of such porridge. If your child hasn't tried porridge yet, start with a dairy-free, gluten-free, one-ingredient buckwheat or rice porridge. Please note that completely eliminating cereals containing gluten from the child's diet is also a bad idea, the child should familiarize himself with such cereals before 8 months of age.
If your child hasn't tried porridge yet, start with a dairy-free, gluten-free, one-ingredient buckwheat or rice porridge. Please note that completely eliminating cereals containing gluten from the child's diet is also a bad idea, the child should familiarize himself with such cereals before 8 months of age.
Rice - very useful for growing baby. It has a low content of vegetable proteins, so it is easily digestible and is especially useful for children with loose stools . Rice has a high nutritional value and protects the baby's delicate intestines to a certain extent thanks to its enveloping effect . This is a hearty and nutritious dish with a good content of carbohydrates and proteins, potassium and magnesium, calcium and phosphorus, beneficial amino acids and vitamins. It covers energy costs, energizes and gives strength. But rice is not recommended for overweight children and those who suffer from severe constipation.
Gluten-free buckwheat porridge - very nutritious and rich in iron, fiber, rich in various vitamins and microelements. This is a very good option for to introduce a child to adult food . All porridges can be prepared with water, breast milk, milk formula, which your child is used to. It is not recommended to give ordinary cow's milk to a child under one year old and use it to make cereals. No need to add salt and sugar.
If a child already eats porridge from 5 months - then at 6 months you can offer a more complex porridge, for example: rice porridge with apricot or raspberries, rice porridge with banana
is very successful
combination both in taste and properties) or even more complex porridge - corn-rice with banana .
Subsequently, apple, banana, pear, plum and prunes, apricot and dried apricots, broccoli, carrots, berries can be added to the porridge, provided that the child is not allergic to them.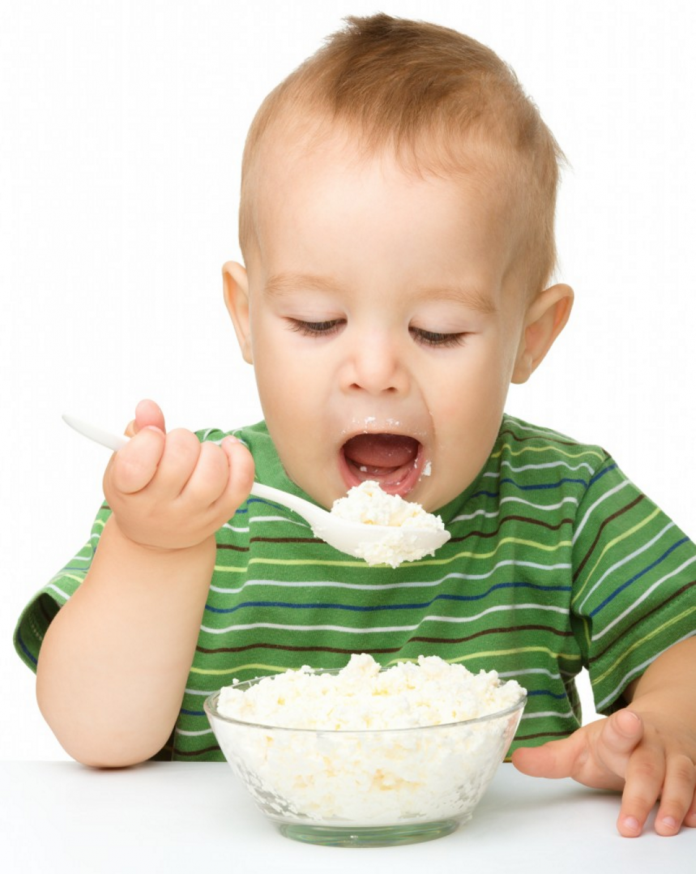
Rules for the introduction of cereals as complementary foods for the baby
The same as for vegetable puree. To make it easier for the child to get used to the new product and its consistency, first prepare 5% porridge: 5 g of cereal per 100 g of water if you make it yourself. Porridge is usually cooked with water, but can be made with breast milk, infant formula. First, give the baby one teaspoon of porridge, then during 7-10 days bring the volume of porridge of the same percentage to the full volume of feeding, for example 150 g.
there are no skin rashes, the child has normal stools - they switch to the gradual introduction of porridge of the same cereal, but already 10% concentration: 10 g of cereal per 100 g of water . Full introduction of 10% porridge to the baby is also carried out for 7-8 days . The third week falls on the complete addiction of the child to a new dish. Only after that you can introduce a new cereal in the form of 10% porridge or the next complementary foods. Porridge should be given from a spoon, preferably in the morning, for breakfast . After porridge, at the stage of its introduction, the child should be offered breast or milk formula.
Only after that you can introduce a new cereal in the form of 10% porridge or the next complementary foods. Porridge should be given from a spoon, preferably in the morning, for breakfast . After porridge, at the stage of its introduction, the child should be offered breast or milk formula.
When artificially fed - the volume of the mixture after a portion of porridge should be such that together with porridge it is 200 ml for five feedings. In the future, the volume of a serving of porridge gradually increases, amounting to 160-170 ml at 7-8 months, 170-180 ml at 8-9 months, and up to 200 ml after 9 months (there is a complete replacement of one feeding of the child with complementary foods.
Cereal schedule
- day - 1 teaspoon 5 g
- day - 2 teaspoons 10 g
- day - 3 teaspoons 15 g
- day - 4 teaspoons 20 g
- day - 50 ml 50 g
- day - 100 ml 100 g
- day - 150 ml 150 g
General rules for the introduction of first complementary foods
Concluding our meeting, I would like to dwell on the general rules for the introduction of complementary foods to children in the first year of life, 10 tips from the professor:
- It is better to introduce the first complementary foods in the morning 9-11 am
- Do not add sugar or salt .

- When the child is calm and not tired.
- Start with 0.5-2 teaspoons . If the child refuses, do not insist.
- If there is no rash, skin changes, stool changes, double the dose the next day. Gradually, in 7-10 days bring the first complementary foods of the child to the age norm : 100-200 g
- If there is allergic reaction - refuse for 3 days
- Each subsequent new complementary food must be one-piece
- A dish of mixed foods give when the child has already become familiar with all foods separately.
- It is not advisable to introduce new products 3 days before and after vaccinations.
- Start giving your baby at ode when you start feeding.