How are enzymes used in baby foods
Enzymes Essay; Enzymes used in the Baby Food industry - GCSE Science
- Search
- Join over 1.2 million students every month
- Accelerate your learning by 29%
- Unlimited access from just £6.99 per month
Extracts from this document...
Enzymes used in the 'Baby Food' industry Enzymes allow chemical reactions to be carried out under milder conditions (lower temperature and pressure), thus saving costs. Since most supplements are not substrates for enzymes, the enzymes usually do not interact with them. You should be able to mix most supplements and medicines with enzymes. Enzymes may affect the properties of time-released medications increasing the rate at which they are broken-down, and thus, released. The enzymes which are used in baby food are there because they allow the food to be pre-digested in the baby's stomach. ...read more.
The main two enzymes used in the baby food industry are 'protease' and 'lipases'. A protease enzyme is usually used to break down protein it does this when it breaks peptide bonds by a process called hydrolosis. These bonds are linked together to create an amino acid. The best condition for use of protease is in acidic areas. Finally the proteases occur naturally in all organisms. A lipase is a water-soluble enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of ester bonds in water-insoluble, lipid substrates. ...read more.
A protease in another industry is not used as it creates a higher mortality rate in the medicine industry for HIV/Aids. This enzyme has therefore been made into an alternate structure but with the same properties but not with the same processes. This in turn creates a social factor to be seen when treating the disease so the scientists have made a new type of ingredient called NNRTI to serve the same purpose as the protease enzyme. ?? ?? ?? ?? ...read more.
The above preview is unformatted text
This student written piece of work is one of many that can be found in our GCSE Humans as Organisms section.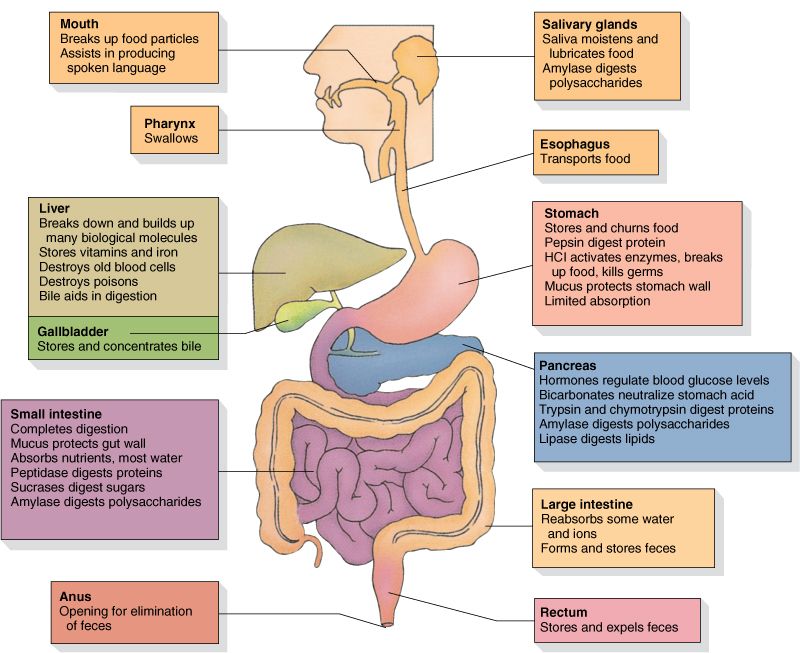
Found what you're looking for?
Here's what a teacher thought of this essay
3 star(s)
***
A few good points but this is otherwise a rather superficial overview of the topic. The author should double check finished work to make sure it reads well and makes sense.
Marked by teacher Adam Roberts 30/07/2013
Not the one? Search for your essay title...
- Join over 1.2 million students every month
- Accelerate your learning by 29%
- Unlimited access from just £6.99 per month
See related essays
-
5 star(s)
protein to boost their immune system * When someone is pregnant they need proteins so that they get passed through to the child. In lactation (breast-feeding) there needs to be extra so that there is enough for the child and you Kwashiorkor Many protein rich foods are expensive.
-
5 star(s)
who fail to develop measles immunity after the first dose. [13] The second dose is given to everyone because it is impossible to distinguish which children have and which have not been immunised by the first vaccination without putting them at risk.

-
4 star(s)
Ventricular pressure continues to rise until eventually the pulmonary and aortic valves are forced open and blood is ejected into the pulmonary artery and aorta'. When the heart rate is increased the amount of time the diastole and systole take place is shortened, so that more blood is pumped out in one minute.
-
3 star(s)
This type of pace maker works on a requirement only bases. These may be used when patients whose sino-arterial node sends out signals too slowly, or the electrical pathway is partly or completely blocked, or the timing of atrial and ventricular contractions is uncoordinated (asynchronous), in this case a double chamber pace maker is used.
-
3 star(s)
doing surgery, that doctor would pass on to the next visited patient a potentially life threatening disease. He insisted that those doctors who worked for him wash their hands in calcium chloride after an operation and before visiting a new patient.
-
Water * Acts a solvent * Absorbs heat (temperature regulation) * Provides a medium for chemical reactions Salt * Maintains the osmotic balance in the body Change in Diet Obesity Kwashiorkor Pregnancy Puberty (Girls) Is excess growth Diet high in fat Leads sudden gain of weight Blockage of blood vessels
-
Respiration may completely stop due to the denaturation of all the enzymes associated with breaking down respiratory substrate. I have used a higher proportion of respiratory substrate in comparison to yeast because in order for the yeast to respire at an optimum rate throughout the experiment there must be excess substrate present.
-
The stronger heart moves more blood with each beat and therefore can do the same amount of work with fewer beats. This means that in my experiment, someone with a higher BMI (of 30, for example) may have a lower resting heart rate than those with a lower BMI.
- Over 160,000 pieces
of student written work - Annotated by
experienced teachers - Ideas and feedback to
improve your own work
Which enzyme is used in making baby foods? | Superminis
Being a parent is a very exciting feeling at first, but it is sometimes hard too. You have to deal with many changes in your everyday routine. Caring can be fun too but it is also a responsible job. Unfortunately for many reasons the mother is not able to breastfeed her child or can’t take care of her child's nutrition. Therefore there is no option other than to formula feed.
You have to deal with many changes in your everyday routine. Caring can be fun too but it is also a responsible job. Unfortunately for many reasons the mother is not able to breastfeed her child or can’t take care of her child's nutrition. Therefore there is no option other than to formula feed.
After birth, the baby is so delicate and is in the underdevelopment stage, therefore the baby's body needs nutrients which promote all-over growth. But like many other parts of the baby, the GI tract is also under development. The GI tract in a baby is responsible for the digestion and absorption of nutrients but it needs extra support. So enzymes play an important role in that. In this article, we will talk about which enzymes are used in making baby food. Before moving to it, we have to understand first what enzymes actually are and their role in the body.
Enzymes and Their Role in the Body?An enzyme is a biological catalyst which speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction in a cell. It is almost a protein which is not destroyed during chemical reactions and is used by the body again and again. A cell has thousands of different enzymes in it and everyone is used for a specific reaction. All living things have enzymes in their bodies which are produced naturally, but they can also be manufactured.
It is almost a protein which is not destroyed during chemical reactions and is used by the body again and again. A cell has thousands of different enzymes in it and everyone is used for a specific reaction. All living things have enzymes in their bodies which are produced naturally, but they can also be manufactured.
The enzyme consists of 1000s of amino acids which are linked in a specific way. The unique shapes are formed due to the fold of enzyme chains. These shapes are responsible for providing the enzyme with the characteristic chemical potential.
The metabolic process of the initial stage depends upon the enzymes which react with a molecule called a substrate. Substrates get converted into other molecules due to enzymes, the other distinct molecule is called products.
Enzymes play an important role in maintaining life processes therefore they are a key element in clinical diagnosis. Except in the class of ribozymes (RNA), the macromolecular components of all enzymes are made up of protein.
Enzymes also play an important role in aiding digestion which is the process of turning the food we eat into energy. There are various enzymes present in our Slavia, pancreas, intestine and stomach which break down fats, protein and carbohydrates and use these nutrients for growth and cell repair.
They also help with:
- Breathing.
- Building muscle.
- Nerve function.
- Ridding our bodies of toxins.
Now you know what important role Enzymes play in our body. Therefore, many baby food companies use enzymes to enhance the flavour, solubility, and digestibility of nutrients in baby foods. They are also added to produce some functional ingredients. Some important enzymes used for baby boys are given below-
Lipase-
Lipase is a water-soluble enzyme which is used in baby foods because it helps your baby break down the food. The breakdown food is easy to digest and the body can easily absorb the important nutrients from it. To fortify baby foods, lipases are used to produce pure concentrates of Functional lipids such as omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and DHA has a unique role in infants' brain and eye development. This Lipase enzyme is also naturally produced in the pancreas but it can also be found in the digestive tracts of newborn babies.
To fortify baby foods, lipases are used to produce pure concentrates of Functional lipids such as omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and DHA has a unique role in infants' brain and eye development. This Lipase enzyme is also naturally produced in the pancreas but it can also be found in the digestive tracts of newborn babies.
Protease
Protein plays a crucial role in adults as well as babies. Protein helps in a child’s growth, maintenance and repair of the body, it also helps to maintain proper balance and pH of body fluids. But babies are not able to digest protein when they eat solid foods therefore the food is treated with protease enzyme. This type of food is easier for a baby's digestive system to digest because it predigests some of the protein. Babies easily get the essential amino acids from food because of the protease enzyme.
Lactase
Lactose is a sugar which is present in milk and other dairy products. Lactose is most important for babies' health and development. 40% of babies' energy comes from lactose which helps babies to absorb calcium and iron. But the baby is not able to break the lactose into simple sugar therefore, lactase enzyme plays an important role in that. If there is a lack of lactase enzyme in the baby's body then lactose can’t be broken down and acts as a great food source for gut bacteria. It also leads to problems like lactose intolerance.
40% of babies' energy comes from lactose which helps babies to absorb calcium and iron. But the baby is not able to break the lactose into simple sugar therefore, lactase enzyme plays an important role in that. If there is a lack of lactase enzyme in the baby's body then lactose can’t be broken down and acts as a great food source for gut bacteria. It also leads to problems like lactose intolerance.
Due to an unhealthy lifestyle, an increase in pollution and other environmental factors, caring for a baby is getting tough day by day. Parents are so much worried about their child's growth and whether he\she is getting proper nutrition or not. But don’t worry, we have mentioned above the important Enzyme which should be there in baby foods. So whenever you visit any shop or market to buy baby foods, always check for these enzymes, whether they are present or not. Time flies too fast, so spend your maximum time with your baby.
Back to Blogs
Ingredients in the production of bread
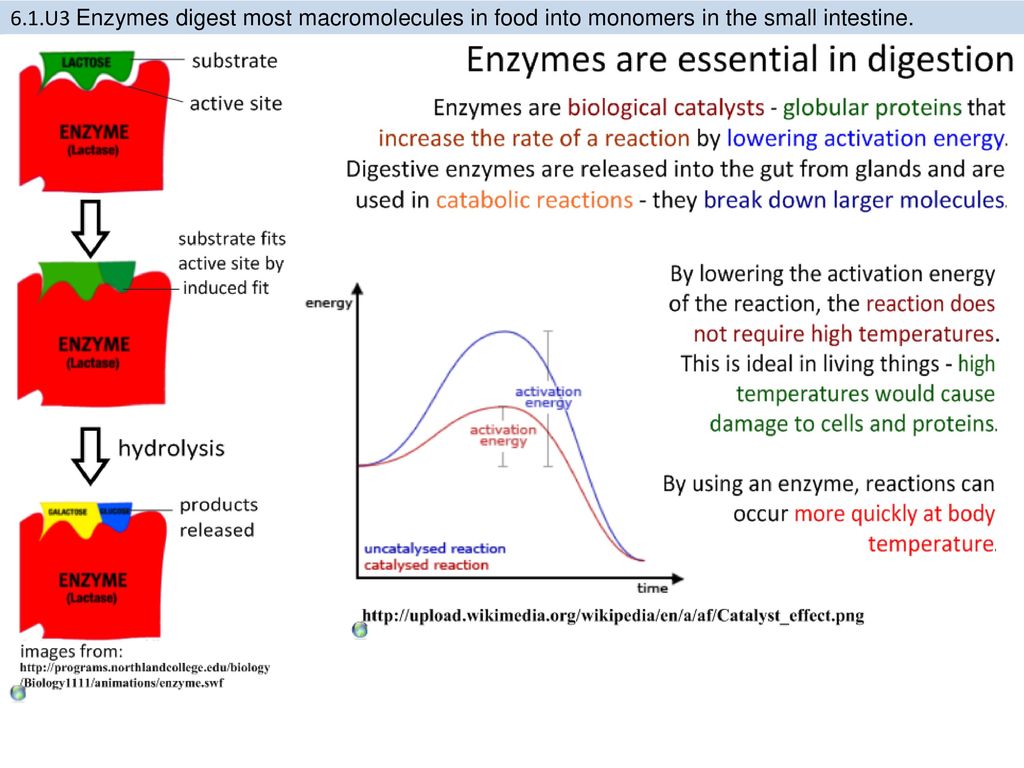
Enzymes (enzymes) are proteins that serve as catalysts (accelerators) of biological reactions. As a rule, they have names that end in "-ase" (lactase, protease, amylase, etc.).
As a rule, they have names that end in "-ase" (lactase, protease, amylase, etc.).
Biological reactions are understood as reactions occurring in living organisms. For example, when we eat, we need to taste it. If there were no enzymes in our bodies, taste qualities would have to be recognized for weeks, and not within an hour. Each enzyme works for a specific type of reaction: for example, lactase works in reactions involving lactose.
Each enzyme has an active site where molecules of a substrate substance are attached to it. The active center of any enzyme has a shape that allows it to interact only with certain types of substances - much like in a puzzle picture, where only certain particles fit together. For different types of enzymes, there are optimal levels of temperature and acidity.
Enzymes in baking
Several reactions take place during the production of bread, accelerated by the action of enzymes. The first of these is the extraction of sugar from starch.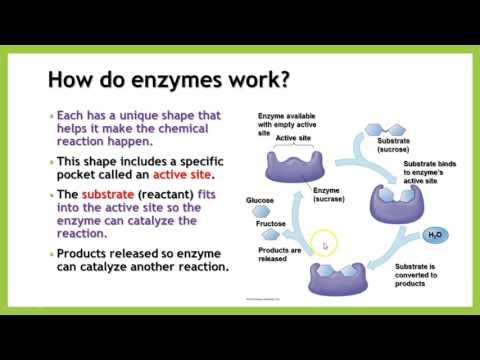 The sugar must then be broken down into a number of simple sugars that can react with the yeast during the fermentation (dough rising) process.
The sugar must then be broken down into a number of simple sugars that can react with the yeast during the fermentation (dough rising) process.
Starch is made up of a large number of glucose particles bound together, but yeast cannot react with starch until it is broken down into its glucose constituents. The breakdown of starch by enzymes can occur in two ways: either by mechanical breakdown or by thickening. At first glance, the breakdown of starch seems to be something like its destruction during the baking process, but it is not. It only means that some particles are destroyed, broken or split in the process of grinding flour. A certain percentage of the presence of split starch in flour is even desirable: if about 6% is destroyed, then everything is within the normal range.
Bread dough requires several enzymes to break down starch into several simple sugars that can react with yeast. This is a complex process involving enzymes such as alpha and beta amylase. The presence of these substances allows you to break down starch and get sugar for yeast fermentation.
Starch can exist in two different forms: straight chain (amylose) or branched chain (amylopectin). Enzymes that break down starch are called amylases. As mentioned above, there are two types of amylase for the breakdown of different types of starch: alpha-amylase and beta-amylase.
Alpha-amylase
The dough should contain some alpha-amylase to break down starch in the form of amylopectin, but if this enzyme is in excess, the starch may completely dissolve.
Alpha-amylase particles can react with starch throughout the chain of molecules and create smaller chains of various lengths. The resulting chains can contain one fragment of the molecule (glucose), two fragments (maltose), or combine into more complex structures called dextrins and consisting of several glucose fragments. As part of the test, beta-amylase can break down dextrins to produce maltose.
Beta-amylase
Grains and flours always contain a certain amount of beta-amylase, an enzyme capable of breaking down amylose into sugar. Beta-amylase comes into contact with amylose chains and breaks them down into maltose molecules, a disaccharide consisting of two glucose particles.
Beta-amylase comes into contact with amylose chains and breaks them down into maltose molecules, a disaccharide consisting of two glucose particles.
With the participation of beta-amylase, the cleavage of amylopectin from one end of the molecule can begin, but this enzyme is not able to break the chain of particles, so the process stops at the moment of association in the chain. However, when starch is broken down by beta-amylase, a mixture of maltose and larger dextrins is formed. Yeast produces an enzyme called maltase, which is capable of breaking down maltose into glucose molecules, followed by fermentation. When the starch is fully processed into simple sugars, other enzymes found in yeast react with them. As a result, alcohol and carbon dioxide are formed: this stage of bread baking is called fermentation. Sugar (sucrose) cannot be formed directly under the influence of an enzyme found in yeast called zymase: before that, another yeast enzyme must break down sucrose into glucose and fructose. Then, under the influence of zymase, these sugars are fermented.
Then, under the influence of zymase, these sugars are fermented.
What is starch?
Starch belongs to a group of chemical compounds known as carbohydrates. They got their name because they contain only three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Pure dry starch is a white powder composed of granules. Wheat flour contains 70-73% starch and 8 to 14.5% protein.
If you look at the flour under a microscope, you can see many cells - structures that resemble bricks in shape. In each cell, a starch granule can be seen surrounded by a layer of glass-like protein. Different types of starch have different structures. Potato starch particles are oval, wheat starch is oval or round, but smaller, corn starch has a rigid structure.
Starch is a complex carbohydrate: it consists of many sugar molecules linked together. There are two main types of it - amylose and amylopectin. Starch is the main carbohydrate found in cereals (wheat, corn, oats, rice, barley), root crops (potatoes, cassava, taro) and legumes (peas, beans). In whole wheat grains, its percentage is 60-70%. It is found in the endosperm, the part of the grain from which white flour is obtained.
In whole wheat grains, its percentage is 60-70%. It is found in the endosperm, the part of the grain from which white flour is obtained.
Starch and starch products are used in the food, brewing, pharmaceutical, and paper industries to create adhesives. In the food industry, starch is used as a thickener, filler, viscous substance or stabilizer in various types of products: soups, custard concentrates, fillings for pies, sausages and other meat products, ice cream, sauces and gravies for dough, for the production of bread and baby food.
Starch in the production of bakery products
When heated, starch interacts with water, its granules absorb water and swell. As a result, the resulting particles burst, and the internal contents of the granules form a thick layer of jelly-like mass: we can see this in the example of a sauce or gravy. This process is called thickening or gelatinization. In the production of bread, less water is used than in the manufacture of sauces, therefore the resulting mass does not thicken completely: the starch granules burst, but most of them do not turn into a homogeneous jelly-like substance and come into contact with each other at the edges.
Starch interacts with gluten during baking. The gluten breaks down and releases water, which is absorbed by the starch particles. The gluten then settles and becomes hard, which is why the loaves of bread don't lose their shape when they are taken out of the oven.
When the dough rises under a microscope, gluten chains can be seen forming in two directions: diagonally downwards and perpendicular to the field of view. Among its particles, granules of starch and yeast can be seen, the latter being the smallest in size.
Starch also serves as a source of “nutrition” for yeast during fermentation. As explained above, alpha- and beta-amylase interact in the process of converting starch into sugar. The resulting sugar feeds the yeast during fermentation, as a result, carbon dioxide is released from them: it is this that “raises” the dough and forms the final bread structure.
Starch, gluten and carbon dioxide from yeast fermentation work together to produce our familiar bread with a crust and bubbly texture.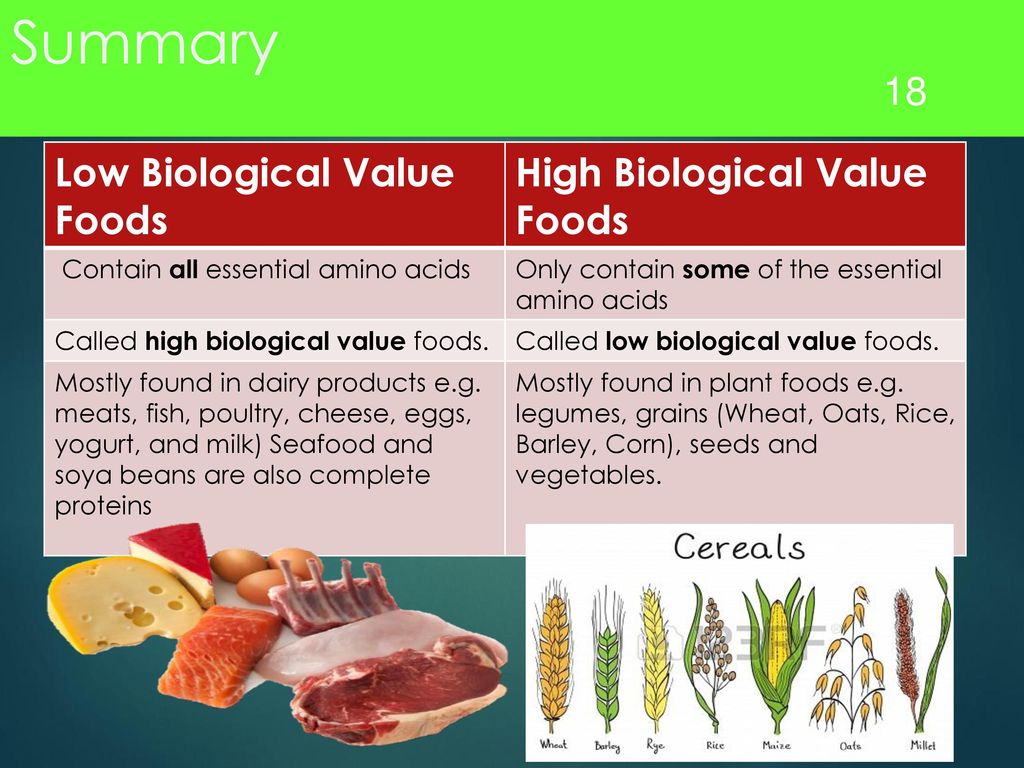 Starch also plays an important role in water retention in some types of baked goods such as cakes. For some types of cakes, chlorinated flour is used. Chlorine compounds slightly change the properties of starch, and therefore the baker can include more sugar and fat (for example, butter) in the recipe. In such cases, soft wheat flour with a reduced protein content is best: a smaller percentage of starch is split, which is why the finished products are more bulky, with a softer crust. In turn, for example, cookies contain a lot of sugar and little liquid (water). These factors slow down the gelatinization of starch, and it does not affect the structure of the already prepared cookies.
Starch also plays an important role in water retention in some types of baked goods such as cakes. For some types of cakes, chlorinated flour is used. Chlorine compounds slightly change the properties of starch, and therefore the baker can include more sugar and fat (for example, butter) in the recipe. In such cases, soft wheat flour with a reduced protein content is best: a smaller percentage of starch is split, which is why the finished products are more bulky, with a softer crust. In turn, for example, cookies contain a lot of sugar and little liquid (water). These factors slow down the gelatinization of starch, and it does not affect the structure of the already prepared cookies.
To refresh the bread, it is warmed up in the oven. The starch granules will re-absorb water, swell, and as a result, the loaf will look fresh.
Source: The Bucking Industry Research Trust (Birt)
Translation: Yanina Krupina
ID "Sphere" 9000
Enterprises on Podkhutskiy.
 experts MAMACO
experts MAMACO
Enterprises on Podkhutskiy.
 experts MAMACO
experts MAMACO Enzymes (or enzymes) are protein catalysts that take part in a chemical reaction and change its speed.
— Alla Anatolyevna, what is the importance of digestive enzymes for newborns?
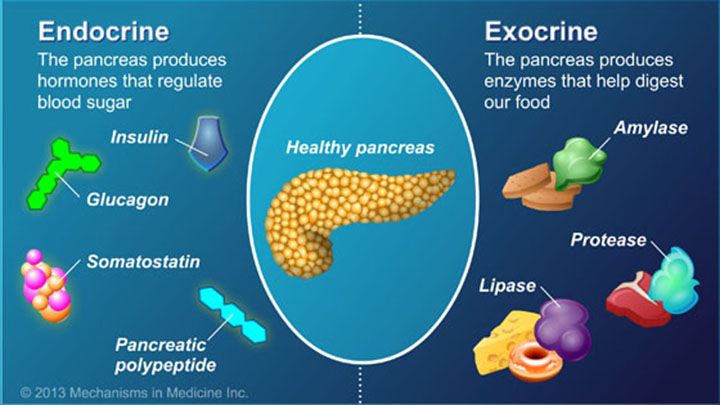
— Enzymes are produced by the pancreas. They are involved in the breakdown of nutrients - proteins, fats, carbohydrates. Enzymes have different structures and functions depending on the reaction in which they are involved. The breakdown of nutrients to the necessary components allows them to be absorbed into the intestines and further participate in the growth and development of a small child.
— What is enzyme deficiency in children?
— Enzyme deficiency, or enzyme deficiency, is a lack of enzymes, which can manifest itself, among other things, in violation of the digestive process. In young children, this is lactase deficiency - a lack of the enzyme lactase, which breaks down the milk sugar (lactose) contained in breast milk, powdered and liquid milk mixtures.
Most infants experience transient (temporary) lactase deficiency in the first three months. At this age, this is the norm, because the pancreas is still immature and its function is reduced, there is a little lack of lactase. The child’s stool is more liquid: we can say that this is how transient lactase deficiency helps to empty the intestines and fights constipation.
If the baby worries moderately, there is no catastrophe, the problem itself will go away with time. This is a difficult period in the life of a child that needs to be experienced.
— Are the causes of enzyme deficiency in a baby explainable?
— Nature invented it so that the body of a newborn is able to absorb not all milk sugar, but only part of it. Milk sugar residues serve as a nutrient substrate for the emerging gut microbiota and promote looser stools.
— What types of enzyme deficiency occur?
- Enzyme deficiency in the gastrointestinal tract can be divided into types depending on the lack of certain enzymes:
- protease - lack of enzymes for the breakdown of proteins;
- lipase - lack of enzymes for the breakdown of fats;
- amylase - lack of enzymes for the breakdown of carbohydrates.

- Despite the fact that the reduced enzymatic activity in children is quite physiological, many parents do not calm down until they pass the tests. How to identify enzyme deficiency in infants?
— A typical medical test for lactose intolerance in an infant is a fecal carbohydrate test that measures the amount of lactose in the stool. In my practice, I do not prescribe such a study, because even lactose found in the feces is the norm for an infant at the age when the pancreas is being trained, its tolerance. And if a child gains weight well, eats well, observes the daily routine, maintains intervals between feedings, he is healthy.
— Alla Anatolyevna, how to treat enzyme deficiency in a newborn in order to alleviate its manifestations?
— Some doctors prescribe enzymes and multienzymes despite the fact that in children of the first months of life, enzyme (lactase) deficiency is not treated. It goes away with time, when the pancreas grows. And adding the enzyme lactase to baby food does not affect the baby's digestion too much. With the baby's expressed anxiety, it is more correct to prescribe an additional examination, look for and treat another cause of problems with the tummy.
And adding the enzyme lactase to baby food does not affect the baby's digestion too much. With the baby's expressed anxiety, it is more correct to prescribe an additional examination, look for and treat another cause of problems with the tummy.
When the child grows up, the pancreas will begin to produce enough enzymes, milk sugar will be completely digested and transient lactase deficiency will go away.
— When are lactose-free milk formulas used that are consonant with the problem?
- The introduction of any mixture is best discussed with your doctor. Lactose is involved in the formation of galactocerebrosides in the brain. This is a necessary component for the growth and full development of the baby. Therefore, lactose-free formula should not be fed for a long time.
Such mixtures can be used in the acute period of intestinal infection, when the functions of the pancreas suffer, for example, after a viral gastroenteritis. During the recovery period, digestion must be supported - therefore, the appointment of a lactose-free nutritional formula is allowed. But only for a few days. When the acute period of intestinal infection passes, the mixture is canceled.
MAMAKO ® Premium formula based on goat's milk is suitable for feeding healthy children up to one year old, including babies with transient lactase deficiency.
— How to introduce complementary foods to a child with an enzyme deficiency?
- The time of introduction of the first complementary foods is 5.5-6 months. At this age, the pancreas is already growing and begins to produce a sufficient amount of enzymes. Therefore, complaints associated with lactase deficiency are already disappearing, and complementary foods are given to such babies as healthy children. With a gradual introduction, these are the same vegetables, cereals, fruit purees, curds.
Enzyme deficiency is a deficiency of enzymes, including those produced by the pancreas and responsible for digestion. They break down nutrients into components that are easily digested in the intestines.