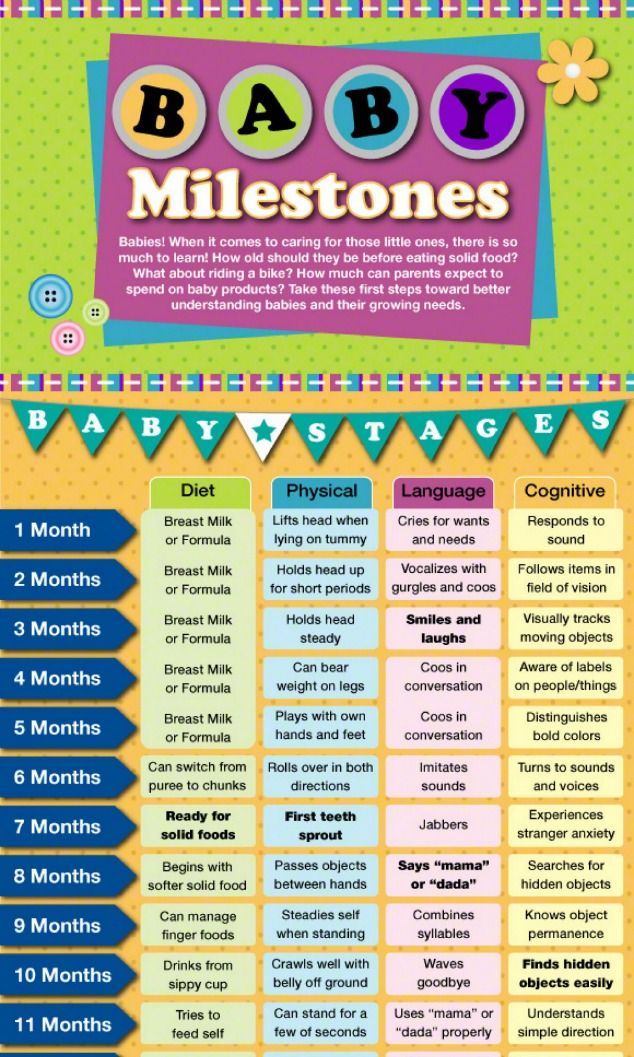
How do i know if my baby is ready for solid food
Introducing solids: why, when, what & how
Solid foods: why babies need them
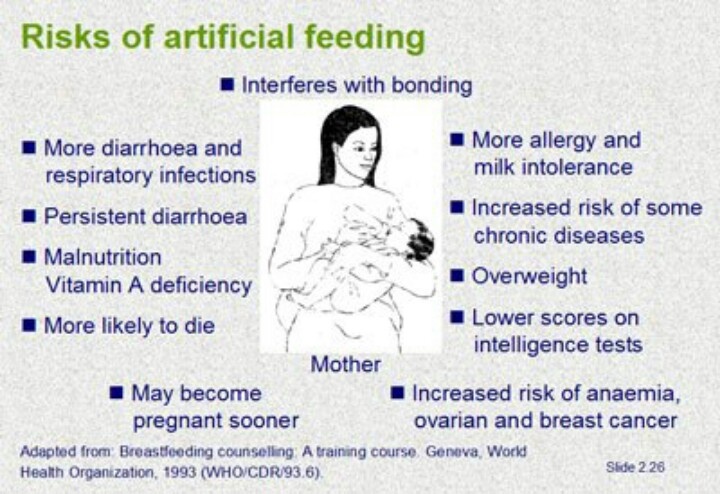
As babies get older, they need solid food to get enough nutrients for growth and development. These essential nutrients include iron, zinc and others.
For the first 6 months of life, babies use iron stored in their bodies from when they were in the womb. They also get some iron from breastmilk and/or infant formula. But babies’ iron stores go down as they grow. By around 6 months, babies need to start having solid food.
Introducing solids is also important for helping babies learn to eat, giving them experience of new tastes and textures from a range of foods. It develops their teeth and jaws, and it builds other skills that they’ll need later for language development.
Signs that it’s time to introduce solids
Signs your baby is ready for solids include when your baby:
- has good head and neck control and can sit upright when supported
- shows an interest in food – for example, they look at what’s on your plate
- reaches out for your food
- opens their mouth when you offer them food on a spoon.
Most babies start to show these signs by around 6 months, although this can vary.
It’s recommended not to introduce solids before 4 months.
If your baby is nearing 7 months of age and hasn’t started solids, you might like to get some advice from your child and family health nurse or GP.
The best times of day to introduce solids
When you’re first introducing solids, it’s good to offer solids when you and your baby are both happy and relaxed.
This is often after a feed of breastmilk or formula. Babies will still have room in their tummies for a taste of new foods after a feed of breastmilk or formula. But if they’re really hungry before a feed, they just want the breastmilk or formula that they know satisfies their hunger.
As time passes, you’ll learn when your baby is hungry or full, not interested or tired.
Signs of hunger include your baby:
- getting excited when they see you getting their food ready
- leaning towards you while they’re sitting in the highchair
- opening their mouth as you’re about to feed them.

Signs your baby is no longer interested include:
- turning their head away
- losing interest or getting distracted
- pushing the spoon away
- clamping their mouth shut.
Your baby’s appetite can vary from day to day.
How much food to offer when introducing solids
When you’re first introducing solids, try offering 1-2 teaspoons of food once a day. At first, your baby might have only a small taste and probably won’t swallow much.
As your baby grows, you can increase the amount according to your baby’s appetite and signs.
By 12 months, your baby should be eating around 3 small meals a day, plus breastmilk or infant formula.
The right textures for first foods
When your baby is ready for solids, first foods might be smooth or finely mashed, depending on what baby likes. Over the next weeks and months, your baby can move on to roughly mashed or minced foods and then chopped foods.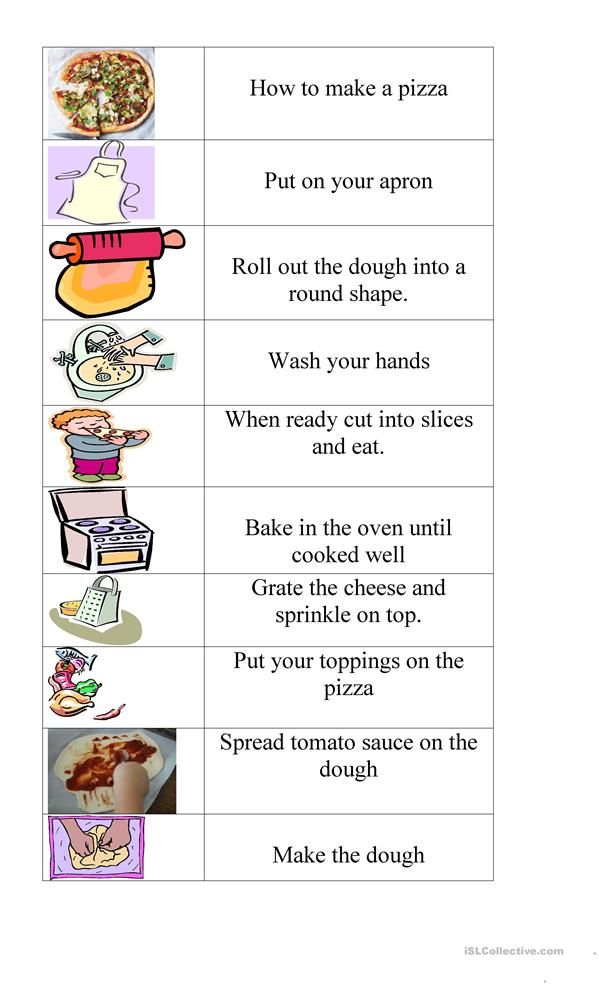 All foods should be very soft.
All foods should be very soft.
Your baby needs a variety of food textures. This helps your baby learn how to chew, and chewing helps with speech development and self-feeding. It also helps to prevent feeding difficulties as your baby develops. Babies can chew even before they get their first teeth.
By the time your baby is 12 months old, they should be eating the same foods that the rest of the family is eating. But you might still need to chop some foods into smaller pieces and cook vegetables until they’re soft.
To prevent choking, always supervise babies and young children while they’re eating solid food. Avoid nuts, take special care with pieces of meat and check fish for small bones, because these are choking hazards. And if your baby can move around, make sure baby is sitting down while they’re eating. If you sit with your baby while they’re eating, baby is less likely to move around.
Types of food to offer when introducing solids
All new foods are exciting for your baby.
The key is to include iron-rich foods of the right texture in your baby’s first foods. Iron-rich foods include:
- iron-fortified infant cereal
- minced meat, poultry and fish
- cooked tofu and legumes
- mashed, cooked egg (avoid raw or runny egg).
To these iron-rich foods, you can add other healthy foods of the right texture like:
- vegetables – for example, cooked potato, pumpkin, sweet potato, carrot, broccoli or spinach
- fruit – for example, banana, apple, pear, melon or avocado
- grains – for example, oats, bread, rice and pasta
- dairy foods – for example, yoghurt and full-fat cheese.
You can introduce any number of new foods at a time and in any order. When you offer your baby a variety of foods, they can try plenty of new tastes and get a range of nutrients.
Read our tips for introducing solid foods to learn how to get your baby interested in new foods and manage mealtime mess and play.
Breastmilk and infant formula while introducing solids
You should keep breastfeeding or using infant formula until at least 12 months.
When you start introducing solids, breastmilk or infant formula should still be the main source of your baby’s nutrition. Over the next few months, your baby will start having more solids and less milk or formula. The rate that this happens will vary.
By around 9 months, babies have generally developed enough chewing and swallowing skills to move from having milk before solids to having milk after solids.
Here are some signs that your baby is getting enough nutrition from both solids and breastmilk or formula during this time. Your baby:
- has plenty of wet nappies – at least 6-8 wet cloth nappies or 5 very wet disposables in 24 hours
- is alert and mostly happy after and between feeds
- is gaining weight at about the right rate – your child and family health nurse will weigh your baby at your regular check-ups.

From 12 months onwards, solids should be the main source of your baby’s nutrition. Your baby doesn’t need infant formula after 12 months, but you can keep breastfeeding for as long as you and your baby like.
If solid food replaces breastmilk and/or infant formula too quickly, babies can miss out on important nutrition. If you have any concerns about your baby’s feeds or weight, talk to your midwife, child and family health nurse, lactation consultant or GP.
Introducing water
Once your baby has reached 6 months, you can start to offer baby cooled, boiled water in a cup at mealtimes and at other times during the day. This is so your baby can practise drinking from a cup, but baby still doesn’t really need fluids other than breastmilk or formula at this age.
Once your baby has reached 12 months, you can offer fresh tap water without boiling it.
Foods and drinks to avoid while introducing solids
There are some foods to avoid until your baby is a certain age:
- Honey until 12 months – this is to avoid the risk of infant botulism.

- Raw or runny eggs and foods containing raw eggs like home-made mayonnaise until 12 months – bacteria in raw eggs can be harmful to babies.
- Reduced-fat dairy until 2 years – babies need full-fat dairy for growth.
- Whole nuts and similar hard foods until 3 years – these are choking hazards.
There are some drinks to avoid until your baby is a certain age:
- pasteurised full-fat cow’s milk as a main drink until 12 months
- dairy alternatives like soy, goat’s, sheep’s, rice, oat, almond and coconut milk until 2 years, unless your GP or child and family health nurse has recommended these for a particular reason
- unpasteurised milks at all ages
- tea, coffee or sugar-sweetened drinks at all ages
- fruit juice – this should be limited at all ages (whole fruits are better because they have fibre and help babies develop chewing and feeding skills).
Your baby doesn’t need added salt or sugar. Processed or packaged foods with high levels of fat, sugar and/or salt aren’t good for babies and children. These foods include cakes, biscuits, chips and fried foods.
Processed or packaged foods with high levels of fat, sugar and/or salt aren’t good for babies and children. These foods include cakes, biscuits, chips and fried foods.
Food allergy and introducing solids
Introducing allergenic foods early can reduce the risk of your child developing food allergy. Allergenic foods are foods that might cause allergies.
All babies, including babies with a high allergy risk, should try solid foods that might cause allergies from around 6 months of age. These foods include well-cooked egg, peanut butter and other nut butters, wheat (from wheat-based breads, cereals and pasta) and cow’s milk (but not as a main drink).
Once you’ve introduced an allergenic food, it’s a good idea to regularly include it in your baby’s diet.
It’s a good idea to get advice from your GP, child and family health nurse, dietitian, paediatrician or allergy and immunology specialist for the following reasons:
- Your baby already has a food allergy.
- Your baby has severe eczema.
- Your family has a history of food allergy and you’re concerned about starting solids.
- You’re worried about reactions to foods.
Is baby ready for solid foods? (Developmental signs of readiness) • KellyMom.com
What do the experts say?
Health experts and breastfeeding experts agree that it’s best to wait until your baby is around six months old before offering solid foods. The American Academy of Pediatrics, the World Health Organization, and many other health organizations recommend that babies be exclusively breastfed (no cereal, juice or other foods) for the first 6 months of life. I’m not going into the many health benefits of delaying solids here; see When Should Baby Start Solids? for more information.
Developmental signs that baby is ready for solids
Solids readiness depends on both the maturity of baby’s digestive tract and baby’s developmental readiness for solids. Although the maturity of baby’s digestive system is not something that we can readily observe, research indicates that 6 months appears to be ideal for avoiding increased illness and other health risks of too-early solids. After this point, different babies are ready for solids at different times — developmental readiness for solids cannot be determined using a calendar. Most babies are developmentally ready for solids somewhere between 6 and 8 months.
After this point, different babies are ready for solids at different times — developmental readiness for solids cannot be determined using a calendar. Most babies are developmentally ready for solids somewhere between 6 and 8 months.
.
Signs that indicate baby is developmentally ready for solids include:
- Baby can sit up well without support.
- Baby has lost the tongue-thrust reflex and does not automatically push solids out of his mouth with his tongue.
- Baby is ready and willing to chew.
- Baby is developing a “pincer” grasp, where he picks up food or other objects between thumb and forefinger. Using the fingers and scraping the food into the palm of the hand (palmar grasp) does not substitute for pincer grasp development.
- Baby is eager to participate in mealtime and may try to grab food and put it in his mouth.
We often state that a sign of solids readiness is when baby exhibits a long-term increased demand to breastfeed (sometime around 6 months or later) that is unrelated to illness, teething pain, a change in routine or a growth spurt. However, it can be hard to judge whether baby’s increased breastfeeding is related to readiness for solids. Many 6-month-old babies are teething, growth spurting, beginning to experience separation anxiety, and experiencing many other developmental changes that can lead to increased breastfeeding – sometimes all at once! Make sure you look at all the signs of solids readiness as a whole, because increased breastfeeding alone is not likely to be an accurate guide to baby’s readiness.
However, it can be hard to judge whether baby’s increased breastfeeding is related to readiness for solids. Many 6-month-old babies are teething, growth spurting, beginning to experience separation anxiety, and experiencing many other developmental changes that can lead to increased breastfeeding – sometimes all at once! Make sure you look at all the signs of solids readiness as a whole, because increased breastfeeding alone is not likely to be an accurate guide to baby’s readiness.
More on developmental readiness…
In April 2001, a literature review “of the developmental readiness of normal full term infants to progress from exclusive breastfeeding to the introduction of complementary foods” was jointly published by Wellstart International and the LINKAGES Project. Per the authors, “The review does not focus on health outcomes associated with discontinuing exclusive breastfeeding at a particular age but rather on the biologic/developmental readiness for this complex experience. Four processes or functions were selected for inclusion: gastrointestinal, immunologic, oral motor and the maternal reproductive processes that relate to the continuation of lactation and the provision of breastmilk.”
Four processes or functions were selected for inclusion: gastrointestinal, immunologic, oral motor and the maternal reproductive processes that relate to the continuation of lactation and the provision of breastmilk.”
Following are some of the conclusions of this review:
- “Thus, exclusive breastfeeding to about six months allows the infant to have greater immunologic protection and limit the exposure to pathogens at a vulnerable age. This in turn permits the energy and nutrients that might otherwise be diverted to provide for immunologic responses to be available and utilized for other growth and developmental processes.”
- “These clinical reports indicate that the majority of normal full term infants are not developmentally ready for the transition from suckling to sucking or for managing semi-solids and solid foods in addition to liquids until between 6 and 8 months of age.”
- “Using this available information on the development of oral motor function, maternal reproductive physiology and development of the infant’s immunologic and gastrointestinal function, the expert review team concluded that the probable age of readiness for most full term infants to discontinue exclusive breastfeeding and begin complementary foods appears to be near six months or perhaps a little beyond.
 The also felt that there is probable convergence of such readiness across the several relevant processes.”
The also felt that there is probable convergence of such readiness across the several relevant processes.” - “The consensus opinion of the expert review group was that given the available information and the lack of evidence of significant harm to either normal mothers or normal infants, there is no reason to conclude that exclusive breastfeeding should not continue to six months.”
What about starting solids AFTER 6 months? At what point does baby need nutrition from solids that cannot be provided by breastmilk alone?
Medical research tells us that exclusive breastfeeding allows babies to thrive for the first 6 months. In the words of the World Health Organization,
“Breastfeeding is an unequalled way of providing ideal food for the healthy growth and development of infants… A recent review of evidence has shown that, on a population basis, exclusive breastfeeding for 6 months is the optimal way of feeding infants.”
But what if baby is not very interested in solids at six months? Babies who are not yet interested in solid foods can and do thrive on breastmilk alone until 9-12 months or later. You might hear people say, “Food before one is just for fun,” but perhaps this should be changed to “Food before one is mainly for fun.” As long as your baby is continuing to grow and develop as he should, your milk is meeting his needs well. Sometime after six months, however, babies will gradually begin to need more iron and zinc than that provided by breastmilk alone – at that point, additional nutrients can be obtained from small amounts of solids. If your baby chooses to continue exclusive breastfeeding, simply keep an eye on growth and iron status, continue to watch your baby for signs that he is ready for solids, and offer appropriate solids for him to try – baby can decide whether or not to eat them. No matter when baby begins solid foods, breastmilk should make up the majority of baby’s nutrition through the end of the first year.
You might hear people say, “Food before one is just for fun,” but perhaps this should be changed to “Food before one is mainly for fun.” As long as your baby is continuing to grow and develop as he should, your milk is meeting his needs well. Sometime after six months, however, babies will gradually begin to need more iron and zinc than that provided by breastmilk alone – at that point, additional nutrients can be obtained from small amounts of solids. If your baby chooses to continue exclusive breastfeeding, simply keep an eye on growth and iron status, continue to watch your baby for signs that he is ready for solids, and offer appropriate solids for him to try – baby can decide whether or not to eat them. No matter when baby begins solid foods, breastmilk should make up the majority of baby’s nutrition through the end of the first year.
What if my 4-5 month old seems developmentally ready for solids?
Four- to five-month-old babies are sometimes very eager to participate at mealtime, but it doesn’t necessarily mean that they are ready to eat solids – more often it’s just the normal developmental urge to do what everyone else is doing. Research studies tell us that there are many health advantages to delaying solids for about 6 months for all babies, not just the babies who are not yet interested in mealtime.
Research studies tell us that there are many health advantages to delaying solids for about 6 months for all babies, not just the babies who are not yet interested in mealtime.
There are a number of things you can do to let baby participate in mealtimes without starting solids:
- Let baby sit with the family at mealtime – in a lap, booster seat or high chair.
- Give baby a cup of water or expressed milk. Your baby can entertain himself at mealtime while learning to use a cup. 1-3 ounces of water in the cup should be plenty (often for the entire day). Many moms choose to use only water or a small amount of breastmilk to avoid wasting the “liquid gold” while baby learns to use the cup.
- Offer baby sips of water from your cup or straw. Even if baby hasn’t figured out how to use a straw yet, you can put your straw in water, block the top end of the straw with your finger to trap a little water in the straw, then let baby drink the water from the lower end of the straw (unblock the top end once it’s in baby’s mouth).

- Offer baby spoons, cups, bowls and other baby-safe eating utensils to play with during mealtime.
- Give baby an ice cube (if it’s a baby-safe size & shape) or ice chips to play with.
- Offer baby a momsicle (popsicle made from breastmilk) or slushy frozen breastmilk to eat with a spoon.
Myths about solids readiness
There are many myths and outdated information regarding how to tell if baby is ready for solids.
MYTH: Baby’s weight has reached a “magic” numberJust because your baby achieves “x” number of pounds, or has doubled birth weight, (or however much your baby weighs) does not mean that she is automatically ready for solids – particularly if she is under 6 months. The American Academy of Pediatrics/World Health Organization recommendations for starting solids at 6 months or later has no exceptions for babies who weigh more. The research that I’ve seen on the health benefits of starting solids at 6 months and later holds for all babies, no matter what their weight. It’s the maturity of the digestive tract and baby’s developmental readiness that makes the difference, not baby’s weight. |
It’s rather interesting to note that moms are told to start solids for both big and small babies. It’s not even uncommon to hear opposite arguments for both sides from the same person!
MYTH: “Your baby is big so you need to start solids.”Moms might be told to start solids for differing reasons when they have a large baby. Some are told that since baby is big, they won’t be able to produce enough milk to satisfy baby. This is quite untrue – almost all mothers have the ability to produce enough milk to exclusively breastfeed twins and even triplets. If you allow your baby to nurse on cue, your body will make enough milk for your baby. In addition, research tells us that exclusively breastfed babies do not increase the amount of milk they drink after the first 4 weeks or so – after the first month, milk intake stays constant (except for temporary appetite spurts) until sometime after six months when baby begins to eat more solid foods and decrease milk intake. Other moms are told that baby is eating too much, so mom should reduce baby’s intake by limiting nursing and/or starting solids. There is absolutely NO evidence that a large breastfed baby will become a large child or adult, and limiting nursing can be quite dangerous for a baby. Read more here: Is my exclusively breastfed baby gaining too much weight? |
MYTH: “Your baby is small so you need to start solids.”Another reason often given for starting solids is because baby is small (see Normal Growth of Breastfed Babies). I really don’t see the sense in this. Ounce for ounce, breastmilk has more calories than most baby-safe solid foods and significantly more nutrients than any type of solid food that you can feed your baby. Studies have shown that for babies under six months, solids tend to replace breastmilk in a baby’s diet – they do not add to baby’s total intake (WHO 2003,Cohen 1994, Dewey 1999). |
MYTH: Baby needs to start solids because there is not enough iron in breastmilk.An additional reason given for starting solids is the “lack of iron in breastmilk.” Breastmilk does have lower iron levels than formula, but the iron in breastmilk is more readily absorbed by the baby’s gut than the iron in formula. Also, formula-fed babies tend to lose iron through fissures that develop in their intestines as a result of damage from cow’s milk. Breastfed babies do not lose this iron. At some point after the first 6 months (later in the first year for a lot of babies), babies will require an additional source of iron other than mother’s milk. |
Signs that the child is ready for solid food. Your baby from birth to two years old
Signs that your baby is ready for solid foods. Your baby from birth to two yearsWikiReading
Your baby from birth to two years old
Sears Marta
Contents
Signs that a child is ready for solid food
The child may start begging - reaching for food on your plate, grabbing your spoon, looking at you with hungry eyes and imitating you, such as opening your mouth wide when you open yours while eating.
Sometimes children show more interest in cutlery than in the food itself. If your child is interested in watching you eat, try just letting him play with a spoon (preferably a plastic one - it makes less rumble when it is knocked on the table). If the child is satisfied with the spoon, then the toy is more desirable than the food. If the child continues to show interest and observe you, the pleasure is about to begin.
If the child is satisfied with the spoon, then the toy is more desirable than the food. If the child continues to show interest and observe you, the pleasure is about to begin.
In addition, other signs of a child's readiness are the ability to sit upright in a highchair and take food with thumb and forefinger.
Certain foods at certain ages?
The classic approach to baby food is that children should start with the softest and most insipid foods, moving on to more textured and richer foods after one year of age, and only after two years of age can they get the most allergenic and spicy foods. Our review of baby feeding follows these principles. However, many studies refute this approach, and many peoples give their children food that our Western civilization prefers to avoid. In fact, children can eat any food that is soft enough and difficult to choke on. Our table only suggests certain steps, you are not required to strictly follow this sequence. Children under one year old may well eat something from the list of one and a half year old children. When in doubt if your child is ready for a particular food, use common sense. There are some foods that should not be introduced into the diet for up to a year: peanut butter, cow's milk, seafood and honey . The conclusion is this: if the product is on your plate, it is soft enough for the child, does not belong to the four products that are prohibited for consumption up to a year, then this product can be given to the baby.
When in doubt if your child is ready for a particular food, use common sense. There are some foods that should not be introduced into the diet for up to a year: peanut butter, cow's milk, seafood and honey . The conclusion is this: if the product is on your plate, it is soft enough for the child, does not belong to the four products that are prohibited for consumption up to a year, then this product can be given to the baby.
This text is an introductory fragment.
Crisis 6-7 years, the problem of the child's readiness for school
Crisis of 6–7 years, the problem of the child's readiness for school On the basis of the emergence of personal consciousness, a crisis of 7 years appears. Here are its main signs: 1) loss of immediacy (between desire and action, the experience of what meaning this action will be is wedged
Childbirth readiness test
Test to determine readiness for childbirth • In order to determine if your baby is ready for childbirth, you can do this test: take a watch and put it next to you; sit or lie down comfortably, relax; irritate nipples and areolas with fingers 5-6 times for 1 minute every 3
Eating "Mine eats at fixed hours and never leaves anything on the plate!"
meal "Mine eats at fixed hours and never leaves anything on the plate!" This is one of the basic principles of French education. From the cradle, babies are taught to eat at strictly defined hours. Gathered around the newborn, parents make a schedule,
From the cradle, babies are taught to eat at strictly defined hours. Gathered around the newborn, parents make a schedule,
Auditory signs
Auditory signs Loves musical toys. However, if all sorts of sharp and nasty tweeters are installed there, he can flatly refuse such a gift, despite the colorful appearance. When watching movies or cartoons, he may not look at the screen at all. If
Signs of kinesthetic
Signs of kinesthetic What can be said about a child who perceives the world through touch? Yes, there are much fewer of them than auditory and even more so visual ones. But they are! Let's call this child "kinesthetic" and try to "calculate" him among other children. If you choose
43. Meals should be short and pleasant
43. Meals should be short and pleasant Dinner should not resemble a hostage situation. It is difficult for small children to sit at the table for more than half an hour. If they ask to be released, feel free to let them go. Growing up, children will linger at the table longer. В
Meals should be short and pleasant Dinner should not resemble a hostage situation. It is difficult for small children to sit at the table for more than half an hour. If they ask to be released, feel free to let them go. Growing up, children will linger at the table longer. В
11 Solid food introduction: when, what and how
eleven Introduction of solid food: when, what and how During a routine check-up at four or six months of age, I am waiting for the question: “Doctor, when should I start giving solid food?” One day I decided to take the initiative and asked an experienced mother of six children: “How do you determine
Further introduction of solid foods
Further introduction of solid food Starting with a trial dose, go to half a teaspoon, then to a teaspoon, to a tablespoon, then to about 60 g, or half a jar. Go from a soupy consistency to a thick one, and then to not quite homogeneous products, from
Go from a soupy consistency to a thick one, and then to not quite homogeneous products, from
How much food to give
How much food to give Remember that a baby's stomach is no bigger than his fist, so don't expect him to eat more in one meal. Be prepared for the fact that the child will eat every time at different times. One day he can eat a whole jar, and the next day only
Safety while eating
Safety while eating • Do you teach your children not to run around the house with a mouthful of food? (This can cause choking.) • Do you take any safety precautions when preparing food? (Whole sausages are dangerous because a bitten off piece can block the trachea
Signs of constipation in a child
Signs of constipation in a child If the child's stool is soft, then no problems arise, even if he pushes.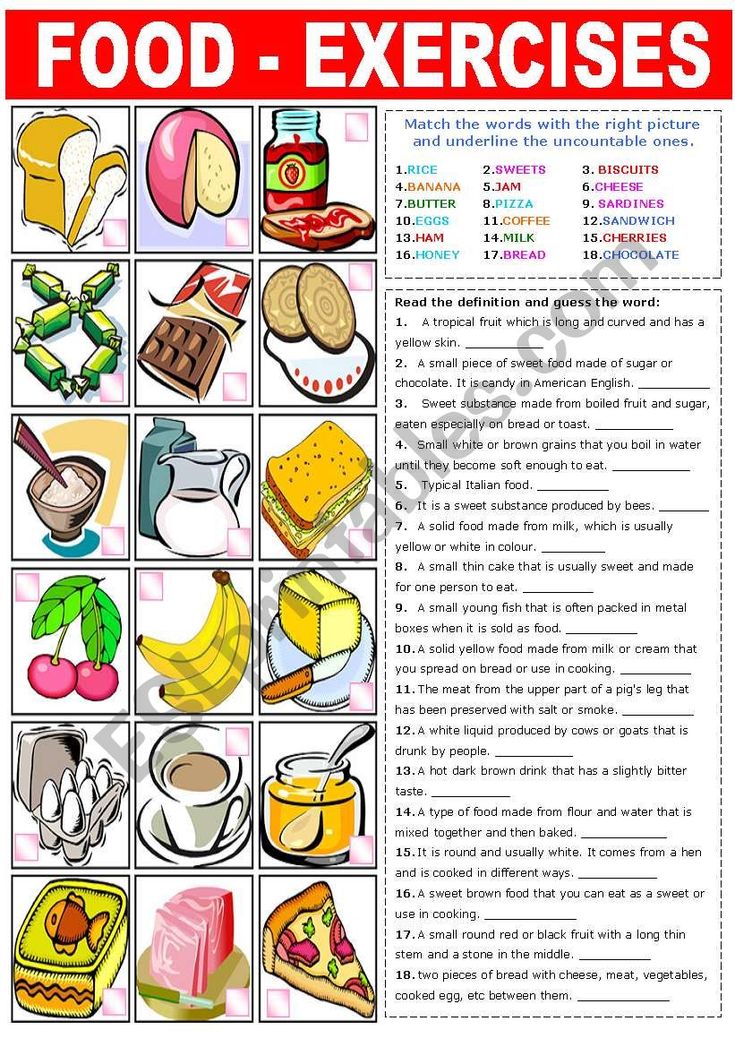 Rather, it is necessary to pay attention if the child hardly pushes out a dryish stool, more like a hard adult stool. This means that
Rather, it is necessary to pay attention if the child hardly pushes out a dryish stool, more like a hard adult stool. This means that
How to teach a child to chew solid food?
Shalunova Anastasia Ivanovna
Member of the Russian Union of Nutritionists, Nutritionists and Food Industry Specialists
Bring the spoon to your mouth, play with your food, twist the food with your tongue, spit it out, take a bite, try to chew it, and finally swallow a piece... What children do to cope with adult food, which at first seems so "difficult"! We tell you how to teach your child to chew solid food so that it does not become a family problem. Consulted by nutritionist Anastasia Ivanovna Shalunova.
- Anastasia Ivanovna, let's talk about how to teach a child to chew and swallow solid food. Why is age important here?
— It is important not to miss the right moment when chewing is the easiest to develop. The most optimal period is from 6 to 10 months, with the introduction of complementary foods with pieces. However, the boundaries of the norm are conditional, because a child can only eat liquid food at a year and a half.
The most optimal period is from 6 to 10 months, with the introduction of complementary foods with pieces. However, the boundaries of the norm are conditional, because a child can only eat liquid food at a year and a half.
Children begin to chew due to the development of the physiological and neuropsychological processes of the body - this is individual for each child. And here the influence of caesarean section and natural childbirth is also very important, how the birth process proceeded and how the baby developed from birth.
When to give your baby solid food
— How do parents know when their baby is ready to chew solid food?
— Food interest is conditionally formed from 4 to 6 months, when a child pulls a plate, a spoon towards himself, asks for food. During this period, complementary foods begin, gradually moving from homogeneous puree-like dishes to more dense, with pieces.
The child is ready to chew food if:
- he confidently picks up and holds a spoon;
- sits without adult support;
- receives complementary foods for three to four weeks.

From 6 to 10 months of age, it is easier for an infant to learn to eat and chew food in chunks. If the child does not gnaw, but sucks or licks what was given to him, there is no need to forbid him - perhaps he is not hungry or he is interested in something else at the moment.
In the absence of interest in food for up to a year, work with psychologists, neuropsychologists, and neurologists may be necessary. Each of them will look at the children's problem from their side and give recommendations.
— How many teeth are enough to start chewing?
— You can “chew” food even without teeth, rubbing the pieces with your gums. Some children have teeth late, but they are still given solid food in order to develop chewing skills. At the same time, chewing can stimulate blood circulation and tooth growth.
Read also
- What "adult" food can be given to a baby under one year old and when to start the transition to a common table.

— What problems can arise if a child does not chew food?
- Some parents complain that the child chokes on solid food or that he does not chew, but swallows immediately. This may be due to the late introduction of solid foods.
In addition, if a child does not chew food well, this provokes problems with digestion. You should not load the immature digestive system of the baby, as the child's body does not yet produce enough enzymes. In this case, the child will refuse food, will eat or chew less often.
What principles of nutrition should be followed:
- give the child a variety of foods, but in reasonable quantities, and watch the body's reaction;
- slow eating improves digestion and increases the feeling of satiety, so it is important to remember to chew your food thoroughly;
- with a healthy diet, it is better to avoid feeding in front of the TV and phone, or use them very pointwise. Gadgets distract from food, lead to unconscious and rapid consumption of food, and this can result in metabolic syndrome and subsequently lead to overweight or type II diabetes.
- How do you feel about tongue massage to improve food processing?
- Tongue massage is very often used by speech therapists to relieve muscle spasms in dysarthria in children, when pronunciation suffers. During massage, fingers, toothbrushes, probes are used, which can be traumatic for a child.
Parents of such children should be aware of the contraindications to speech therapy massage:
- skin rashes, swelling, wounds;
- herpetic infections of the oral cavity;
- colds;
- severe forms of chronic diseases;
- oncological, neuropsychiatric diagnoses.
- How to teach a child to chew food - where to start? What size should the pieces be?
— In order to make the chewing process effective and fun, the child must have an interest in food. Favorite product will be chewed best. It is also necessary to take into account the novelty of sensations and introduce new foods when the baby is hungry.
Nuances that parents should pay attention to:
- Be sure to develop food interest and build a diet, that is, the child should be hungry for the next meal.
- It is best to start with pieces in foods that the child has already eaten pureed. The taste will be familiar to him, but the texture will be slightly different.
- Cooking of vegetables is encouraged.
- It is important to look at whether the baby is coping with his portion. The first pieces are given no larger than a match head, then the size of a little finger nail, then everything is larger. You can give the baby in the hand slices of fresh fruits, baby cookies, crackers.
- Nibbler recommended for a smooth transition from puree to chunks. With him, the child eats on his own, and helps teeth erupt.
- Parental behavior influences child behavior at the table. If meeting at dinner or lunch is a family tradition, then the child automatically joins it and gets used to it, focusing on the example of the parents.

Do not give up trying to give solid food, even if the child spits out the food. But you don’t need to push the product either: you can offer it at a different moment, vary the pieces in size. Also, do not be afraid to give solid food to the child and be nervous during his training and feeding. Anxiety and panic are transmitted on a subconscious level - the baby can just hurry up and choke.
— What mistakes do parents make when feeding their baby?
— Most often, parents are in a hurry. They should pay attention to the formation of the oral apparatus and the psychological readiness of the baby to eat independently, chew and swallow the food bolus. It often happens that during the period of adaptation of the child, for example, after vaccination or moving, the mother begins to give him something unfamiliar and teach him new skills. This will only complicate the task.
If a child flatly refuses to chew solid food, do not force feed him, you need to find out the reason.
- And finally, probably one of the most popular parenting questions - cartoons while eating. What are the pros and cons?
- The child will be distracted from food by cartoons, which will negatively affect the whole process of eating. The purpose of eating is for the child to eat and realize that he is full. "If you're hungry, let's eat, if you want cartoons, watch them later" - these should be the rules. These actions must be distinguished, because watching cartoons is accompanied by other mental and motor processes.
Main recommendations:
- Take your time, stimulate chewing processes and do not forget about physiology: how ready the child's body, oral apparatus, communication systems are.
- Be more attentive to the baby, do not switch to your problems. The task of parents is to ensure that the child is fed, fed and develops correctly. To do this, it is important to build nutrition, taking into account the needs of the child and the processes occurring in the body.
Methods for teaching a child to chew are different, but two aspects are important in this matter: physiological and psychological. Solid foods are introduced from around six months of age, and children should be taught to chew solids before the age of one. In this case, the process depends on the received complementary foods, and on the home environment. It is important for parents to be patient during the learning process and gradually move from pureed food to regular feeding of the baby with solid food with pieces. Only then will he learn to chew and begin to enjoy the new food and his new abilities.
* Breast milk is the best food for babies. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of a child's life and continued breastfeeding after complementary foods are introduced until the age of 2 years. Before introducing new products into the baby's diet, you should consult with a specialist. The material is for informational purposes and cannot replace the advice of a healthcare professional.



 So starting solids will probably reduce (instead of increase) the amount of milk and calories that your baby is getting overall. One of the first recommendations for a baby who genuinely has slow weight gain is to decrease or eliminate solid foods and breastfeed more often.
So starting solids will probably reduce (instead of increase) the amount of milk and calories that your baby is getting overall. One of the first recommendations for a baby who genuinely has slow weight gain is to decrease or eliminate solid foods and breastfeed more often. This can most often be obtained through small amounts of solid food. Read more on iron and the breastfed baby here: Is Iron Supplementation Necessary?.
This can most often be obtained through small amounts of solid food. Read more on iron and the breastfed baby here: Is Iron Supplementation Necessary?.