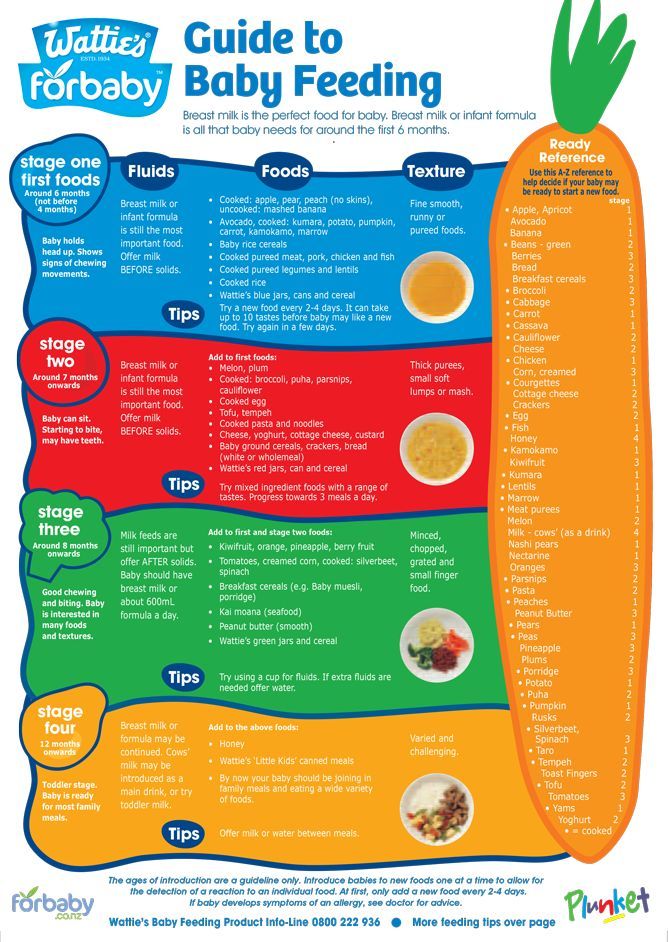
How long should babies eat baby food
When to Stop Pureed Food for Infants | Healthy Eating
By Krista Sheehan Updated December 12, 2018
Knowing when to stop pureed foods in your baby's diet isn't as easy as knowing when to change his diaper. There is no one-size-fits-all rule for feeding your baby -- but he'll let you know when he's ready. Adding pureed foods to your baby’s diet at around 4 months of age introduces a new world of tastes and textures. But knowing when to stop pureed foods -- usually around 1 year of age -- is important for helping your baby develop chewing and swallowing skills.
Developmental Timeline
Typically, infants are started on pureed foods between 4 to 6 months of age. In the beginning, choose pureed foods with only one ingredient. As the infant becomes more accustomed to the new texture, include pureed foods with a combination of ingredients -- this typically occurs around 6 to 8 months of age. As your baby moves into the 8- to 10-month time frame, chunkier pureed foods can be introduced. If your baby does well with these foods, introduce soft, cooked vegetables and cooked fruits, breads, soft cereals, scrambled eggs and yogurt around 10 to 12 months of age. If your baby manages these soft foods easily, stop pureed foods. Ideally, your baby should not be eating pureed foods after 1 year of age.
Baby’s Readiness Cues
Your baby will give you certain clues that indicate he’s ready for solid and finger foods. These cues might include picking up foods with his thumb and forefinger, easily transferring items from one hand to the other and moving his mouth in a chewing motion. Your baby will also be ready to stop eating pureed foods as he develops more teeth and gains more control of his tongue. However, if you attempt to stop pureed foods at 12 months and your baby is struggling with solid and finger foods, adding pureed foods back into the diet might be necessary. Consult your pediatrician if you have any concerns or questions about your baby’s specific diet.
Allergy Considerations
When adding new foods to a baby’s diet, add only one new ingredient at a time. This feeding plan allows you to more easily identify a baby’s allergies or sensitivities to specific foods. Allow your baby to eat the new ingredient for a few days -- unless an allergic reaction occurs, of course. If no reactions occur after a few days, you can safely add another new ingredient to your baby’s diet.
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods and ingredients should be completely avoided in a baby’s diet. According to the Florida Department of Health, your baby should never be given pureed foods made with honey, corn syrup, added sugar, artificial sweeteners, spices, seasonings or salt.
References- March of Dimes: Feeding Your Baby
- Cooking Light: Baby Feeding Timeline
- BabyCenter: Age-by-Age Guide to Feeding your Baby
Krista Sheehan is a registered nurse and professional writer. She works in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) and her previous nursing experience includes geriatrics, pulmonary disorders and home health care. Her professional writing works focus mainly on the subjects of physical health, fitness, nutrition and positive lifestyle changes.
She works in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) and her previous nursing experience includes geriatrics, pulmonary disorders and home health care. Her professional writing works focus mainly on the subjects of physical health, fitness, nutrition and positive lifestyle changes.
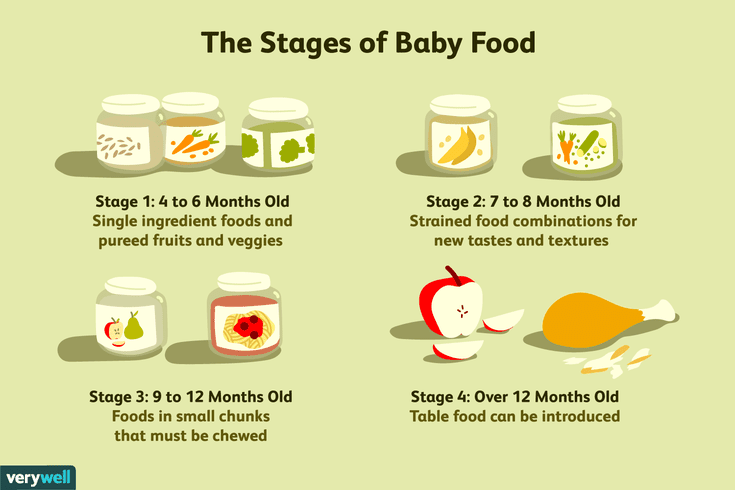
The 3 baby food stages: What foods and when
Making the leap from breast milk or formula to solids and then eventually to table food is an exciting time. But it’s also a little confusing because there isn’t a one-size-fits-all rule when it comes to baby food stages. While one child may happily take to pureed carrots at 6 months, another may purse their lips at anything but a breast or bottle until 8 months.
To simplify the whole process, here’s a general rule of thumb to keep in mind: Most foods are OK to give to babies in the first year, as long as they’re properly prepared. And if you’re concerned about food storage, read more from our experts on how long baby food lasts.
Here’s the quick lowdown on what to feed baby and when:
- Stage 1: Purees (4 to 6 months).

- Stage 2: Thicker consistency (6 to 9 months).
- Stage 3: Soft, chewable chunks (10 to 12 months).
“With the exception of raw or cooked honey, which shouldn’t be consumed until 12 months because of the risk of infantile botulism, babies can have any food that is texturally appropriate for their developmental feeding stage,” says Dr. Kristen Treegoob, a pediatrician at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
In other words, it’s perfectly fine to give both a 6- and 12-month-old peas, but for the 6-month-old, they need to be pureed.
In the past, parents have been advised to start their baby with single-grain cereals, such as rice cereal, but the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) now says there’s “no medical evidence that introducing solid foods in any particular order has an advantage for your baby” — nutritionally or when it comes to long-term food preferences. (So, when your Aunt Joanne tells you that your baby will be a vegetable-hater for life if you start off with applesauce, she’s wrong. )
)
All of this said, there is a method to the messy madness that is the three stages of baby food. In order to make things less complicated — and more delicious — we tapped top experts and veteran parents to find out everything you need to know about feeding little ones at every stage (plus, we included a handy baby food stages chart). All you have to do now is serve the food and clean the high chair!
Stage 1 (4 to 6 months): What you need to know
The fun begins! Stage 1 baby food is typically for babies who are between the ages of 4 months and 6 months. But as with all things parenting-related, it’s important to keep in mind that each baby is different, and there’s no hard and fast rule for starting solids.
“While the AAP recommends exclusively breastfeeding from birth to age 6 months, it’s important to remember that not every baby is exclusively breastfed,” says Dr. Zulma Laracuente, a pediatrician in Alexandria, Louisiana. “Also, some babies show signs of readiness to start food earlier than others. You know your baby best.”
You know your baby best.”
Solids that fall under the Stage 1 category are thin and smooth in texture — not much thicker than breast milk or formula — and contain a single ingredient. If you’re making your baby’s food at home, make sure it’s blended to an almost-watery puree.
“Stage 1 baby foods should have no chunks whatsoever,” says Jenifer Thompson, registered dietician and advanced practice dietician at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore. “Formula or breast milk can be added to the purees to make them thinner.”
While there’s no specific food parents need to start with, many pediatricians recommend beginning with iron-rich foods, such as iron-fortified cereals or pureed meats.
“The reason we advise introducing solids at 6 months and starting with iron-containing foods is because iron stores that were built up during pregnancy are depleting, and iron is important for infants’ brain development,” says Dr. Melanie Custer, a pediatrician at Deaconess Clinic in Evansville, Indiana.
Custer also says that babies should “absolutely not” decrease their breast milk or formula when they first start off with solids.
“Infants still should receive 24 to 32 ounces of formula or breast milk each day,” she says. “Solids at this point are more of a snack, with baby eating about 3 to 4 tablespoons once or twice a day.”
How to tell your baby is ready for Stage 1
According to Treegoob, here are the signs your baby is prepared to start Stage 1 foods:
- They’re showing an interest in what family members are eating.
- They’re learning to open their mouths for a spoon.
- They’ve outgrown the involuntary habit of pushing food and spoons out of their mouth with their tongue.
- They have steady head control.
- They have the ability to move food from a spoon to their throat and swallow without choking.
Stage 2 (6 to 9 months): What you need to know
Time to mix it up! While Stage 2 solids are still basically mush, food has a little more texture at this point, as well as a few soft chunks.
“Stage 2 baby foods are thicker in consistency than Stage 1 purees, and many of the jars you find in stores have some small mashable bits in them,” says Treegoob. “These are great for infants who have done well with Stage 1 but who are not quite ready to chew. The typical age for Stage 2 is between 6 to 9 months.”
Treegoob also notes that the 7 to 9 month time frame is also when many babies begin modifying their breast milk or formula intake.
“As long as an infant’s weight remains on track and they’re drinking enough to stay hydrated, there isn’t a reason to worry if baby is showing interest in smaller or less frequent bottle or breastfeeds,” she says. “Infants typically take in somewhere between 24 to 32 ounces a day when they’re between 6 to 9 months.”
Whether you’re making your little one’s food on your own or getting it pre-made at the store, you have a little more room to play once you hit Stage 2.
“In addition to being thicker in consistency, Stage 2 foods usually have multiple ingredients, including some spices,” says Custer. “At this point, baby is usually taking in more food than they were in Stage 1, so it’s important to make sure they’re being introduced to a wide variety of foods from different food groups.”
“At this point, baby is usually taking in more food than they were in Stage 1, so it’s important to make sure they’re being introduced to a wide variety of foods from different food groups.”
According to the AAP, babies should be eating about 4 ounces of solids — about one small jar of baby food — at each of their meals.
How to tell your baby is ready for Stage 2
Once your baby has consistently been eating Stage 1 foods, they’re likely ready for the next step. Here are other signs to look for, according to Thompson:
- Their oral skills are continuing to develop.
- They’re consistently taking food in and swallowing when you offer it (and not spitting it out).
Stage 3 (9 to 12 months): What you need to know
Now, the true culinary adventure begins — Stage 3 foods! While some babies will still happily have mom and dad spoon-feed them mashed food at this age, many babies will have what you’re having at this point — and they’ll do it themselves, thank you very much.
“As soon as we thought he was ready — at about 9 months — we started giving my son softer, cut-up versions of whatever we were having for dinner,” says mom of two Jennifer Reilly, of New York City. “There was more cleanup, but I actually got to sit down and eat my meal!”
Once babies hit the age range for Stage 3 foods, most have the oral and fine motor skills to self-feed.
“Between 8 to 12 months, babies develop the pincer grasp ability and should be able to pick up small pieces of finger foods with their finger and thumb and bring it to their mouth,” says Thompson.
Technically speaking, Stage 3 solids are thicker, more sophisticated versions of the baby food your little one has already been eating (think vegetable and beef pilaf or tender chicken and stars), but also, they’re not necessary for everyone.
“Stage 3 food is starting to have chunks mixed in, in order to prepare baby for table foods,” says Custer. “But some babies wind up skipping this stage altogether and go straight to soft table foods. ”
”
While it’s perfectly fine to continue with Stage 3 foods up to your child’s first birthday, Treegoob advises letting your baby try their hand at “real food.” “Well-cooked veggies, ripe fruits, shredded meat, scrambled eggs, soft cheese and cooked pasta are all great options for babies this age,” she notes.
Between 9 months and 12 months is also when you’re likely to see a significant drop in how much breast milk or formula your baby is drinking.
“As babies continue to eat table foods, I’ve seen their breast milk or formula intake drop to as low as 16 to 20 ounces per day,” Treegoob says. “That said, some infants continue to show a heavy preference for breast milk or formula despite months of solid introduction. If you feel like your baby may be drinking excessive amounts of breast milk or formula, and they have no interest in food, I would recommend speaking with your pediatrician.”
How to tell your baby is ready for table food
Your child’s readiness to start table food will likely be more discernible than any other baby food stage. As long as they’re continuing to hone their oral skills, as well as their ability to pick food up and bring it to their mouth, you can count on them to let you know they’re ready for “big kid” food.
As long as they’re continuing to hone their oral skills, as well as their ability to pick food up and bring it to their mouth, you can count on them to let you know they’re ready for “big kid” food.
“My daughter looked like she was ready for pasta, eggs and basically anything we were eating shortly after she started solids,” says mom of two Julie Cortez of Brooklyn, New York. “We waited until about 8 months, when we knew she knew how to properly eat, and sure enough, she ate her whole plate on the first go! We completely skipped the Stage 3 jars of food.”
Follow these safe feeding must-knows
Even though your baby’s eating skills will continue to progress as they gain more experience, it’s important baby is always sitting upright, strapped in a high chair and never left unattended while eating. Also, make sure table food is always soft and cut into small pieces to avoid choking hazards. When first starting out with solids, be sure to wait a few days before giving them something new.
“This allows for observation for any adverse reaction or intolerance to the new food,” Thompson says.
And finally, be sure to give your baby a wide range of healthy food in order to expose them to a variety of tastes and textures — and don’t be discouraged if they don’t take to a specific food at first.
“If baby refuses a food or makes a strange face when eating, this may simply mean that it is a new food and unfamiliar to them,” Thompson says. “Try again. It may take 10 to 20 exposures of a new food before they accept it.”
Here’s more on every baby food stage:
- Stage 1 baby food.
- Stage 2 baby food.
- Stage 3 baby food.
Union of Pediatricians of Russia
Nutrition for children from 1 to 3 years of age
The period from 1 to 3 years of life is a crucial stage in the transition to an adult type of nutrition, which has certain features. In order to ensure that all the necessary nutrients enter the child's body and at the same time prevent an excess of individual nutrients, nutrition should be balanced and varied.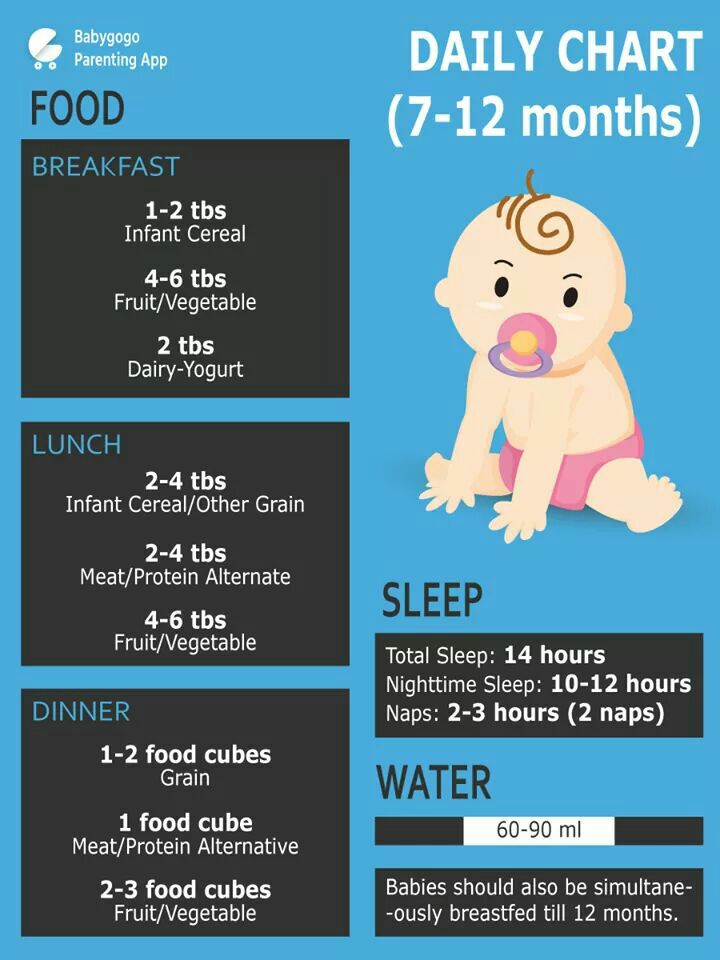 nine0003
nine0003
The daily amount of food for children aged 1 to 1.5 years should be 1000-1200 g, from 1.5 to 3 years - 1200-1500 g, the amount of food in one feeding should not exceed 300-350 ml. The diet consists of three main meals per day and two snacks. It is considered optimal when breakfast is 25% of the total energy density of the diet, lunch is 30–35%, dinner is 20%, and additional meals are about 10%. In general, the child can eat the same food as the rest of the family. nine0003
In the diet of a child of 1–3 years of age , must be present daily: meat of animals or poultry, dairy and sour-milk products, vegetables, fruits, bread, cereals, vegetable and butter; fish and eggs are included in the diet 2-3 times a week.
Cereal products: bread - 2-3 servings per day, cereals and side dishes - 1 time per day
Fruit and/or vegetables: at least 5 times a day
Dairy products: at least 3 servings per day (including those used to make cereals, yoghurts, fermented milk drinks, cottage cheese, infant formula or breast milk).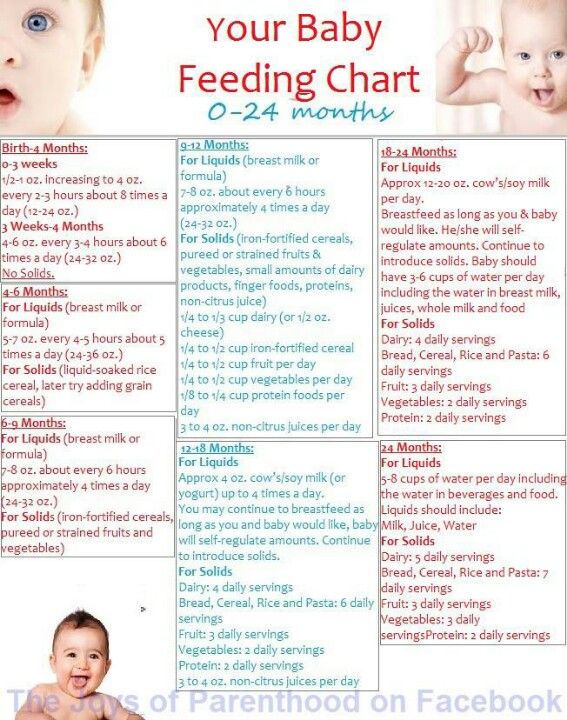 nine0003
nine0003
Domestic pediatricians recommend, when compiling a diet for children aged 1–3 years, preference should be given to specialized children's dairy products of industrial production that meet high quality requirements and safety indicators for this age. Most children's dairy products are additionally enriched with vitamins and/or minerals and other biologically active components, taking into account the physiological needs of children of this age. At the same time, in foreign recommendations, children over 1 year old are offered the gradual introduction of whole cow's milk, which is rich in fats necessary for proper growth and development, the absorption of vitamins A and D, the development of the child's brain and nervous system. nine0003
Meat dishes: 2-3 times a day
Fish dishes: 2-3 servings per week
Eggs: 2-3 per week
Dietary fats: 3-4 teaspoons of butter and/or vegetable oils per day
When cooking, use the minimum amount of salt and sugar, and do not add them to industrial products.
Offer your child a variety of foods and let them choose for themselves. Children love to eat on their own, so if possible, offer food that the child can eat with their hands. nine0003
It is important to remember that a baby can choke on pieces of food, so whatever you give your baby should be crushed or cut into small pieces that can be easily chewed.
Do not give to a small child: nuts, whole grapes, cherry tomatoes (unless quartered), whole carrots, seeds (such as pumpkin or sunflower seeds), round candies, legumes, raisins, because a child can eat them choke.
Also in the diet of children of the first 3 years of life should not be present:
Mushrooms; canned snacks, pickled vegetables and fruits
Home canned food
Dry concentrates for side dishes
Hot sauces, mustard, horseradish, pepper, vinegar, mayonnaise
Natural coffee
Juices and drinks in the form of dry concentrates; sweet carbonated drinks
Products containing food additives (flavorings, dyes of artificial origin, including chewing gum), popcorn
Combined fats; cakes and pastries
It is important to remember that children of this age should not be given too spicy and spicy foods.
How much should a newborn eat: feeding chart
0-6 months
Article
5/5 2 reviews
As soon as the long-awaited event has happened and the baby is born, the mother is faced with many questions. One of the most frequently asked: how to feed and how much should a newborn eat? Indeed, this is a very important point, since a properly selected and debugged diet allows the child to grow and develop harmoniously, promotes good health and strengthens the immune system. How to calculate the norm for a baby from the first days of life to a year? nine0003
8 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
Contents
Listen to the experts
Calculation norms
- First weeks of life
- One to four months
- Five-six months
- Seven to twelve months
How much breast milk a newborn should eat: table
Not enough breast milk or not at all: what to do
Norms and stages of introducing complementary foods
- First stage - vegetables
- Second stage - cereals
- Third stage - fruits
- Fourth stage - meat
- Fifth stage - new flavors
An example of a daily diet for a 6-8 month old baby
Frequently Asked Questions
Listen to the experts baby's age.
 All these data are usually voiced to parents during a doctor's appointment and entered into the card for further assessment of the child's condition. Comparison of the actual weight and the prescribed norms allows you to find out whether the child is eating well enough and, if necessary, to correct mistakes made during feeding. If something is not clear to you at the appointment with the pediatrician, do not be afraid to ask again and clarify. After all, only a specialist can give competent recommendations specifically for your baby, based on the results of an examination or analysis. The advice of friends, grandmothers and mothers from various forums may be good, but they do not take into account the individual characteristics and needs of your child's body. So, they may not work or even hurt. nine0003
All these data are usually voiced to parents during a doctor's appointment and entered into the card for further assessment of the child's condition. Comparison of the actual weight and the prescribed norms allows you to find out whether the child is eating well enough and, if necessary, to correct mistakes made during feeding. If something is not clear to you at the appointment with the pediatrician, do not be afraid to ask again and clarify. After all, only a specialist can give competent recommendations specifically for your baby, based on the results of an examination or analysis. The advice of friends, grandmothers and mothers from various forums may be good, but they do not take into account the individual characteristics and needs of your child's body. So, they may not work or even hurt. nine0003 Be part of Nestle Baby&Me®
Each stage of a baby's development is unique and is associated with new questions from parents. Get advice from experts.
Registration
Calculated norms
1.
 First month of life
First month of life As soon as the baby is born, it is immediately brought to the mother's breast to be fed. This helps to strengthen the immunity of the baby and stimulates lactation in the mother. During this period, there is still no milk in the breast, but there is a very nutritious transparent sweetish liquid - colostrum. It is released in the first two or three days after birth and supplies the child with all the necessary substances. To eat, the baby needs a few drops: on the first day of life, the small stomach holds only 7 milliliters. On the second day of life, the baby begins to eat more often. It needs to be fed on demand or every two to three hours, while the baby eats within 10-20 milliliters at one time. Thus, per day the norm will be approximately 90 milliliters. Starting from the third day after birth, the mother actively produces breast milk, the volume of which increases as the child grows. In the first week of life, the baby should eat from 50 to 80 milliliters of milk at a time, and 400 milliliters per day.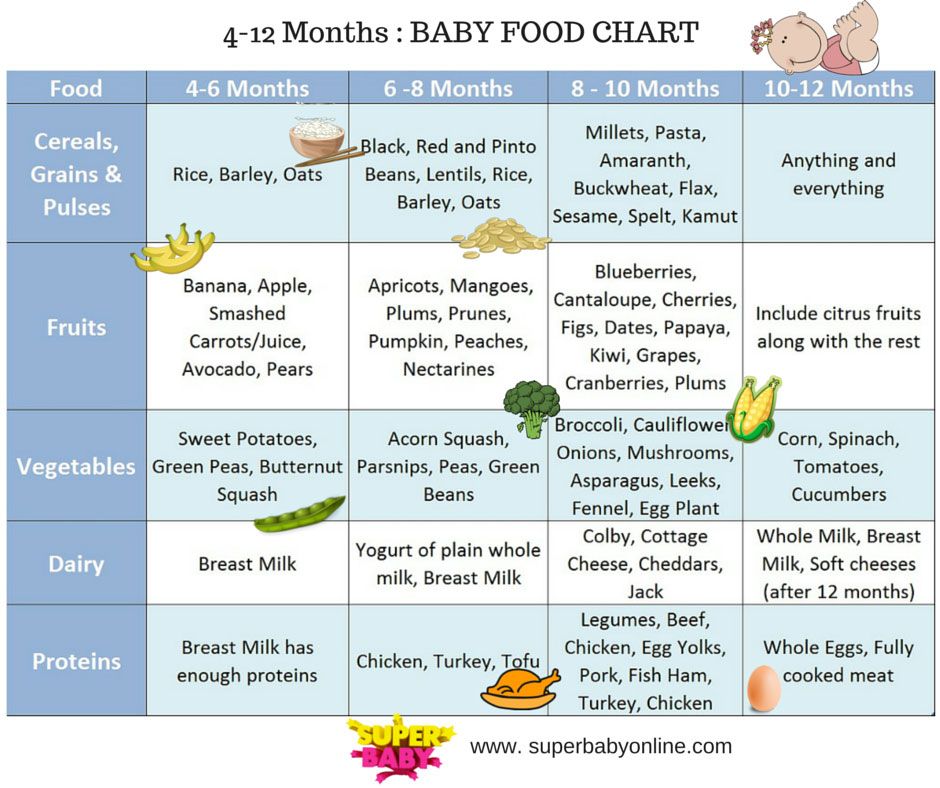 At two weeks of age, the daily ration should be 20% of the weight of the newborn, and closer to a month - about 600 milliliters. It is important to note that these figures are approximate. Each baby needs its own, certain amount of milk or mixture, depending on individual characteristics: height, weight, mother's milk quality, calorie content of the mixture and the rate of development of the baby. nine0003
At two weeks of age, the daily ration should be 20% of the weight of the newborn, and closer to a month - about 600 milliliters. It is important to note that these figures are approximate. Each baby needs its own, certain amount of milk or mixture, depending on individual characteristics: height, weight, mother's milk quality, calorie content of the mixture and the rate of development of the baby. nine0003
See also: Breastfeeding: the first steps after childbirth
2. From one to four months
Every day the baby grows, gains weight and increases its daily portions of milk. Having reached the month, the baby is already eating 90-100 milliliters six to seven times a day. After one month, the norms become as follows:
- At two months, the child should eat from 120 to 150 milliliters at a time. The daily norm, therefore, is 700-800 milliliters. nine0076
- A three-month-old baby should eat between 150 and 180 milliliters. In this case, it is recommended to observe the frequency of feeding no more than six to seven times a day.
- From the fourth month, babies need 180-210 milliliters of milk or infant formula. The average amount per day is not less than 1/6 of the baby's weight.
3.Five-six months
A six-month-old child normally eats 210-240 milliliters at a time, and the total amount of food per day should be 1/7 of body weight, or 800-1000 milliliters. Also, if there are no contraindications, complementary foods are introduced from six months. nine0003
4. From seven to twelve months
During this period, a single portion of breast milk for a baby ranges from 210 to 240 milliliters. At the same time, the average amount per day is not less than 1/8 of the child's body weight. Vegetable, fruit and meat purees, dairy-free and milk porridges are introduced into the diet (if the baby is not allergic to cow's milk proteins).
Below is a table that describes in detail the daily intake of a newborn for each age up to a year.
How much breast milk should a newborn eat: table
| Child's age | The amount of milk eaten per feeding, ml | The amount of milk eaten per day, ml |
| 3-4 days | 20–60 | 200–300 |
| 1 week | 50–80 | 400 |
| 2 weeks | 60–90 | 1/5 child weight |
| 1 month | 100–110 | 600 |
| 2 months | 120–150 | 800 |
| 3 months | 150–180 | 1/6 child weight |
| 4 months | 180-210 | 1/6 child weight |
| 5-6 months | 210-240 | 1/7 baby weight (800-1000) |
| 7-12 months | 210-240 | 1/8 weight baby |
Important!
Remember that every child is unique, has individual characteristics and needs. Therefore, slight deviations from the standard indicators are quite possible.
Therefore, slight deviations from the standard indicators are quite possible.
Not enough breast milk or not at all: what to do
When a baby cries after waking up, he is hungry. Modern doctors do not advise mothers to maintain any strict feeding schedule. If the mother gives the baby a breast when he asks, and the baby eats for her own pleasure and at the same time sleeps soundly and well, smiles and is not naughty, then she is full and completely satisfied. nine0003
But if the baby cries and sleeps badly, then perhaps he does not have enough milk. In this case, check if the baby is eating his age norm, and try to keep track of this indicator in the future. Found that you don't have enough breast milk? Do not worry, it is better to immediately consult a doctor. The specialist will help you find a way to support milk production and improve lactation.
If you cannot solve the problem and normalize lactation, consult a pediatrician and find the right supplemental formula for your child.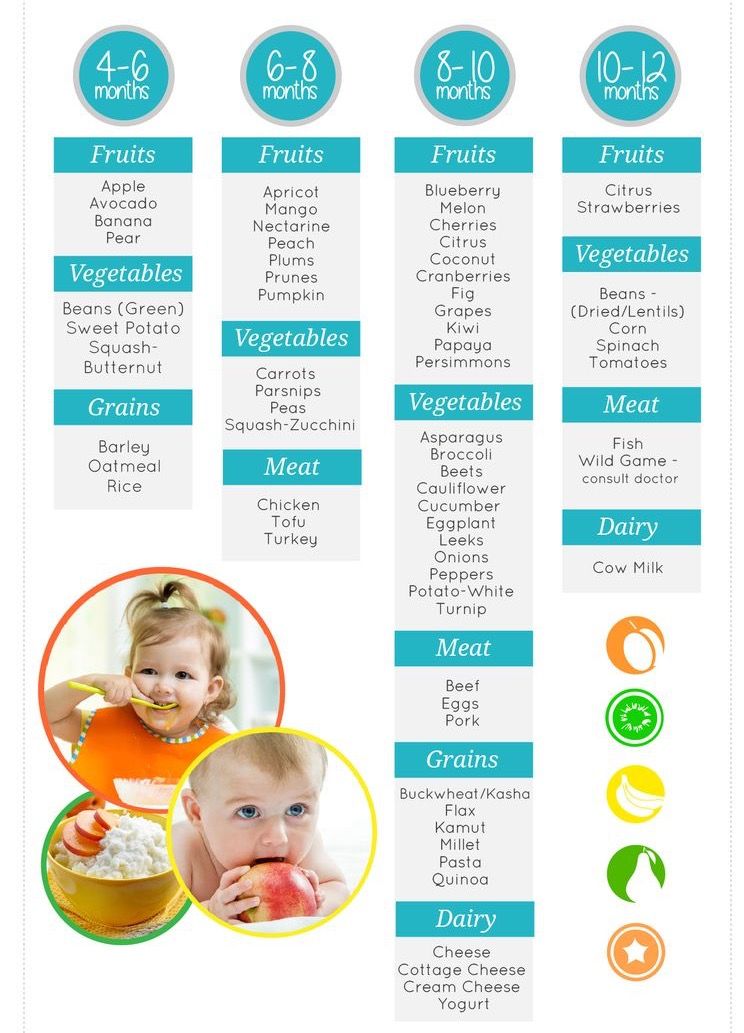 With strict observance of all the doctor's recommendations, instructions for preparation and dosages indicated on the package, the mixture makes it possible to compensate for the lack of breast milk and provide the baby with the necessary amount of nutrients. nine0003
With strict observance of all the doctor's recommendations, instructions for preparation and dosages indicated on the package, the mixture makes it possible to compensate for the lack of breast milk and provide the baby with the necessary amount of nutrients. nine0003
Important!
Even if you don't have enough breast milk to fully meet your baby's needs, try to remain on partial breastfeeding for as long as possible. After all, the ideal food for a child is mother's milk.
Complementary feeding rules and stages
As a rule, complementary foods are introduced from the age of six months. Before you start exploring new products, you should consult with your pediatrician. In general, different types of food are introduced in stages, starting with very small portions. nine0003
1.First step - vegetables
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) the best starting food is a one-component vegetable puree, such as zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower or potatoes.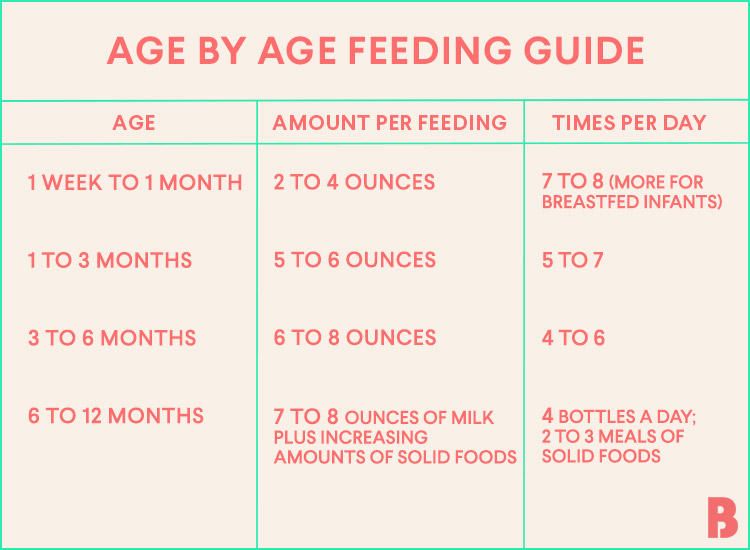 If everything goes well, you can try pumpkin, carrot, pea and tomato puree a little later.
If everything goes well, you can try pumpkin, carrot, pea and tomato puree a little later.
It takes seven to ten days to fully introduce the product into the baby's diet. We start with half or a whole teaspoon once a day until breastfeeding. If there are no allergic or other adverse reactions, you can continue the introduction of this product, gradually increasing the dose to a full serving - 100-150 grams. nine0003
2. The second stage - cereals
After the introduction of vegetable puree, we recommend diversifying the baby's menu with cereals. For acquaintance, it is better to choose liquid one-component gluten-free cereals, for example, rice or buckwheat. Then you can add oatmeal or semolina.
The initial portion of porridge is half or one teaspoon. Gradually increase the portion to a full - 150 grams.
3.Third stage — fruits
We also start fruit complementary foods with one-component low-allergenic purees, such as apple, pear, plum, banana. These products are not only tasty, but also contain vitamins and minerals necessary for the child. nine0003
These products are not only tasty, but also contain vitamins and minerals necessary for the child. nine0003
Fruit purees are also introduced with caution, starting with half or a whole teaspoon. Gradually, the portion increases to 100-150 grams.
Find out more: Gerber Baby Food: Puree Range
4.Stage Four - Meat
Meat is an essential product for development, rich in iron and protein, which is well absorbed in the body. It is introduced in the form of a homogeneous one-component puree from dietary turkey, rabbit, chicken, veal or lamb. nine0003
At the beginning we give a try - half or one teaspoon, over time we bring the portion to 60 grams.
5. The fifth stage - new tastes
After the successful introduction of the above products, the baby forms a full-fledged varied menu. So you can introduce the young gourmet to new flavors that could previously provoke an allergy: multi-component purees, fruit and cereal cocktails, children's snacks, pieces of fresh fruits and vegetables.
See also: Introduction of complementary foods to children with food allergies
Example of a daily diet for a baby at 6-8 months
A child from six to eight months should be given complementary foods three times a day. Further, at the age of nine to eleven months, the amount is increased to four times a day. To make it easier and clearer, check out two options for a full-fledged daily diet, which outlines what and how much a newborn should eat.
See also: Nutrition for a 7-month-old baby: making a menu for a baby
Popular questions
1. How to warm up breast milk?
Use the bottle warmer to warm breast milk that has been stored in the refrigerator. If this is not at hand, put a tightly closed bottle in a container of warm water and hold it there until the milk warms to body temperature - 37 ° C.
2. How often should a newborn eat? nine0126
A newborn needs to be fed every 2-3 hours, ie 10-12 times a day.
3. How much milk does a newborn eat?
During the first days of life, the baby has a very small stomach and a poorly developed sucking reflex. Therefore, for one feeding, the newborn eats 7-9 milliliters of colostrum. Breast milk from the mother appears only on the third or fourth day.
4. How to calculate how much a child should eat? nine0126
To understand how much a newborn should eat, you need to know his age and weight. Data for calculation: from 10 days to 1.5 months, the baby needs such an amount of food, the weight of which is approximately 1/5 of the child's body weight; from 1.5 to 4 months - 1/6, from 4 to 6 months - 1/7; from 6 to 8 months - 1/8; from 8 to 12 months - 1/9 of the body weight.
Articles on the topic:
Breastfeeding: benefits for the baby, health for the mother 12 rules of healthy nutrition for children Baby does not eat well, how to feed? nine0126
Latest reviews
Average customer rating
2 customer ratings
Snapshot of community ratings
- five 2
- 4 0
- 3 0
- 2 0
- one 0
Recommended Articles
0-6 months
Article nine0003
Quantity and quality of protein in breast milk
The amount of protein in breast milk is perfectly adapted to your baby's age and needs at every stage of their development.
0-6 months
Article
Buying and storing baby food
Establishing a safe and wholesome diet is an important task that is entirely the responsibility of adults. This means that every parent must know the rules for choosing, storing and feeding the smallest. nine0003
0-6 months
Article
Diet during lactation
During lactation, the mother's body uses nutrients primarily for milk production and then for itself.
0-6 months
Article
The diet of a child at 7 months: we make a menu for the baby
What should be the menu of a child at 7 months? What foods and in what quantity can be introduced into the diet at this age? When and at what intervals to give the baby to eat? We will help develop an approximate menu for a 7-month-old baby and answer the most exciting questions regarding the nutrition of a baby up to a year old. nine0003
nine0003
0-6 months
Article
Feeding a nursing mother
Most of the nutrients your baby gets through breast milk comes from your body's stores. Therefore, do not forget that the menu of a nursing mother plays an important role!
0-6 months
Article
Proper nutrition is the basis of future health nine0111
During the first 1000 days of a baby's life, optimal nutrition largely determines the growth and development of the child in the present and future. A balanced diet, which contains the most important macro and micronutrients, is an important investment in a child's future health.
0-6 months
Article
Major food allergens
An allergic reaction in a child, just like in an adult, occurs when the body mistakenly perceives a substance as harmful, in other words, it is a defensive reaction to an invasion that actually did not occur. nine0003
nine0003
0-6 months
Article
Basic principles of breastfeeding
0 reviews
Are you planning to breastfeed your baby but don't know what it takes? Here is a list of breastfeeding tips to help you get ready.
0-6 months
Article nine0003
How can a new mother cope with feelings of loneliness?
0 reviews
Even with the abundance of online parenting forums, new moms often feel lonely. Here is a list of activities for parents and children, from organizing games together to children's yoga, that will help you feel less isolated.
0-6 months
Article nine0003
Vomiting in a child: what to do to help the baby
0 reviews
What can cause a child to vomit and how to provide first aid before the doctor arrives.
0-6 months
Article
Physical development of the child by months
All parents are worried about whether their baby is developing normally, whether he is gaining enough weight and whether the growth of the baby is normal, whether he is acquiring all the skills appropriate for an early age. nine0003
0-6 months
Article
Menu for breastfeeding: what can a nursing mother eat?
0 reviews
If you are breastfeeding, it is important to eat a healthy diet because breastfeeding can affect your baby as much as you. We have collected information about what you can eat for a nursing mother, and what is not recommended to eat while breastfeeding. nine0003
0-6 months
Article
Immunization schedule in Ukraine: vaccination rules
During the first year of life, a baby is recommended to have a number of vaccinations against various life-threatening diseases. In order to determine the order and time of vaccination, there is a special vaccination schedule recommended by the Ministry of Health of Ukraine.
In order to determine the order and time of vaccination, there is a special vaccination schedule recommended by the Ministry of Health of Ukraine.
0-6 months
Article nine0003
How to remove the stomach after childbirth: TOP 8 tips
0 reviews
A few proven methods to trim the belly after childbirth . Follow simple recommendations, and soon you will return to your figure, which was before pregnancy.
0-6 months
Article
How to care for the navel of a newborn?
0 reviews
The baby's umbilical cord is the link between the baby and mother throughout life inside the mother's womb.
0-6 months
Article
How to be a good parent
0 reviews
Becoming a parent for the first time and bringing a newborn home is the most exciting moment. Along with all the joy and love you experience, it's perfectly normal to feel unprepared and overwhelmed. If you're worried about becoming a mom or dad soon, we've put together some tips on how to be a good parent. nine0003
Along with all the joy and love you experience, it's perfectly normal to feel unprepared and overwhelmed. If you're worried about becoming a mom or dad soon, we've put together some tips on how to be a good parent. nine0003
0-6 months
Article
How to teach a child to roll over from his stomach to his back?
In the first year of life, the baby grows and develops very quickly. Parents rejoice at each new success of the crumbs. Here he is already holding his head, and now he is turning over from his back to his side. But sometimes the baby does not get coups from the back to the stomach and vice versa. In this case, mom and dad can help him. How to teach a child to roll over from his stomach to his back and vice versa? nine0003
0-6 months
Article
First walk with a newborn: useful tips
0 reviews
Preparing for a child's first walk can be difficult.











