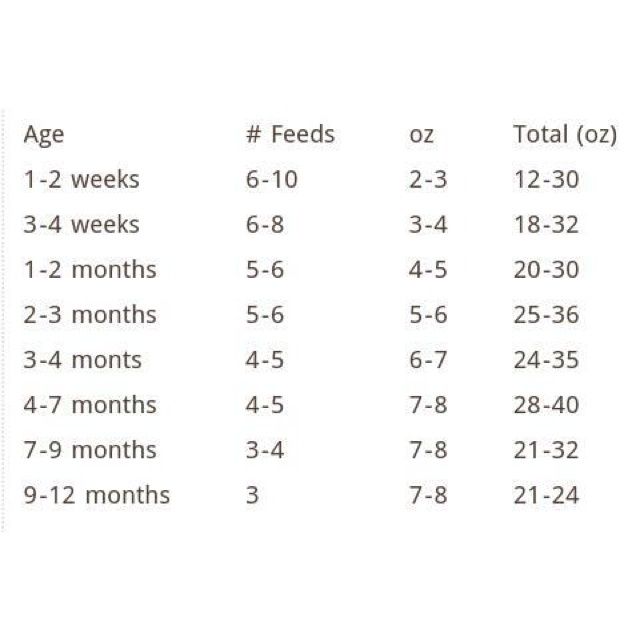
How many ounces to feed 1 month old baby
Amount and Schedule of Baby Formula Feedings
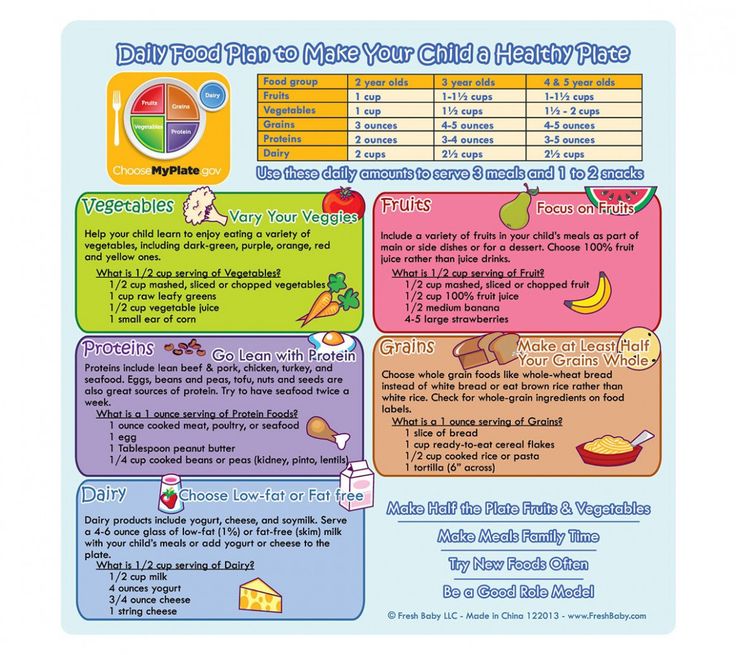
- In the first week after birth, babies should be eating no more than about 1 to 2 ounces (30 to 60 ml) per feed.
- During the first month, babies gradually eat more until they take 3 to 4 ounces (90 to 120 ml) per feed, amounting to 32 ounces per day. Formula-fed babies typically feed on a more regular schedule, such as every 3 or 4 hours. Breastfed babies usually take smaller, more frequent feedings than formula-fed infants.
If your baby sleeps longer than 4 to 5 hours during the first few weeks after birth and starts missing feedings, wake them up and offer a bottle.
By the end of the first month: Your baby will be up to at least 3 to 4 ounces (120 mL) per feeding, with a fairly predictable schedule of feedings about every 3 to 4 hours.
By 6 months: Your baby will consume 6 to 8 ounces (180–240 mL) at each of 4 or 5 feedings in 24 hours.
Formula feeding based on body weight
On average, your baby should take in about 2½ ounces (75 mL) of infant formula a day for every pound (453 g) of body weight. But they probably will regulate their intake from day to day to meet their own specific needs, so let them tell you when they've had enough. If they become fidgety or easily distracted during a feeding, they're probably finished. If they drain the bottle and continues smacking their lips, they might still be hungry.
There are high and low limits, however. If your baby consistently seems to want more or less than this, discuss it with your pediatrician. Your baby should usually drink no more than an average of about 32 ounces (960 mL) of formula in 24 hours. Some babies have higher needs for sucking and may just want to suck on a pacifier after feeding.
On-demand feeding
Initially it is best to feed your formula-fed newborn a bottle on demand, or whenever they cry with hunger. As time passes, your baby will begin to develop a fairly regular timetable of their own. As you become familiar with their signals and needs, you'll be able to schedule their feedings around their routine.
As time passes, your baby will begin to develop a fairly regular timetable of their own. As you become familiar with their signals and needs, you'll be able to schedule their feedings around their routine.
Eating & sleeping patterns
Between 2 and 4 months of age (or when the baby weighs more than 12 lb. [5.4 kg]), most formula-fed babies no longer need a middle-of-the-night feedings. They're consuming more during the day, and their sleeping patterns have become more regular (although this varies considerably from baby to baby). Their stomach capacity has increased, too, which means they may go longer between daytime feedings—occasionally up to 4 or 5 hours at a time.
If your baby still seems to feed very frequently or consume larger amounts, try distracting them with play or with a pacifier. Sometimes patterns of obesity begin during infancy, so it is important not to overfeed your baby.
Getting to know your baby's feeding needs
The most important thing to remember, whether you breastfeed or bottlefeed, is that your baby's feeding needs are unique. No book―or website―can tell you precisely how much or how often they need to be fed or exactly how you should handle them during feedings. You will discover these things for yourself as you and your baby get to know each other.
No book―or website―can tell you precisely how much or how often they need to be fed or exactly how you should handle them during feedings. You will discover these things for yourself as you and your baby get to know each other.
More information
- How Often and How Much Should Your Baby Eat?
- Making Sure Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk
- Is Your Baby Hungry or Full? Responsive Feeding Explained (Video)
- Remedies for Spitty Babies
- Last Updated
- 5/16/2022
- Source
- Adapted from Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
How Many Ounces Should a Newborn Eat?
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.D. — By Chaunie Brusie on December 7, 2018
Overview
Let’s be honest: Newborns don’t do a lot. There’s eating, sleeping, and pooping, followed by more sleeping, eating, and pooping. But don’t be fooled by your little one’s lax schedule.
Your baby is actually doing important work in those first few weeks of life. All of that sleeping and eating is helping them grow at a rather astonishing rate.
But you may be wondering just how much your newborn really needs to eat. Here’s a feeding guide for new parents.
How much should newborn babies eat the day they’re born?
You may be anxious about getting your baby started eating as soon as possible. But on the first day of life, it’s possible that your baby is just as tired as you after going through birth.
It’s not uncommon for babies to be very sleepy in the first 24 hours of life. That first 24-hour period after birth can be a learning curve for the baby to literally learn how to eat and be alert enough to eat. Don’t fret too much if your baby isn’t showing interest in eating every two hours on schedule.
One study found that, on average, infants who were breastfed ate around eight times and had three wet or dirty diapers in the first 24 hours of life. This is less than they’ll eat and eliminate later.
You may be shocked to see how little your newborn is actually eating through breastfeeding in that first day of life, too. This is normal so don’t be worried. Keep in mind that until your milk comes in (around postpartum day three), your baby is drinking colostrum only.
Colostrum is like concentrated superfood full of calories and nutrients, which is why it is adequate even in its small amounts the first couple days. Think quality over quantity.
On average, a healthy newborn will only drink about a 1/2 ounce in colostrum over the first 24 hours of life. Of course, every baby is different.
Of course, every baby is different.
When should you start feeding your newborn baby?
Newborns especially are most alert an hour or two after birth, which is why it’s important to start breastfeeding as soon as possible. If you miss that very active stage, your baby may be sleepier later, which makes it harder to practice latching on for that first initial feeding.
If your baby’s not showing signs of wanting to latch, you should continue to offer your baby the breast every two to three hours. It can take a lot of practice, so it’s important to be patient as your baby is figuring out the best way to latch.
Write down the feeding times and number of wet and dirty diapers your baby has had while you’re in the hospital. Your nurse and doctor will be able to help you determine if your baby needs some additional encouragement to nurse or supplement.
Feeding by weight
- As a rough estimate, your baby should eat 2.5 ounces for every pound they weigh.
 So if your baby weighs 10 pounds, they should eat a total of 25 ounces per day.
So if your baby weighs 10 pounds, they should eat a total of 25 ounces per day.
How many ounces do formula-fed babies need each day?
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) explains that after the first few days, your formula-fed newborn will drink around 2 to 3 ounces (60 to 90 milliliters) of formula with every feeding.
They’ll need to eat about every three to four hours. This is compared to a breastfed baby, who will usually eat every two to three hours.
By the time your baby is 1 month old, they should be eating around 4 ounces every four hours.
How much do breastfed babies need to eat?
If you’re exclusively breastfeeding, you won’t be measuring your baby’s ounces for feedings. Instead, you’ll simply be feeding your baby on demand, or whenever they want to eat.
In general, for the first months of life, a newborn will eat around every two to three hours, but this will vary. The feeding timeline starts from the time your baby starts breastfeeding.
For example, in the first few weeks, if your baby starts eating at 2 p.m. and nurses for 40 minutes, they may be ready to eat again at 4 p.m. Hello, human milk bar!
Sometimes your baby may nurse more or less frequently. Your baby may want to nurse more if they’re sick. Nursing is a comfort mechanism and immune booster. They may want to eat more if they’re going through a growth spurt and need some extra calories.
Both the AAP and the World Health Organization recommend breastfeeding a baby on demand. So don’t worry, you can’t overfeed an exclusively breastfed baby.
Your baby will signal to you when they are full by pushing away or by stopping latching on their own, until they are ready again. And if you’re exclusively pumping, follow self-care practices to help keep your milk supply up and watch your baby’s cues for how much to feed them.
Next steps
It’s best to feed your baby when they’re hungry, rather than follow a strict schedule. Work with your doctor to make sure your baby is growing and developing properly.
Q:
How can you tell if you’re feeding your baby a healthy amount?
Anonymous patient
A:
Your baby will show signs that they are full by showing less interest in the milk and pulling away. Don’t force your baby to eat more than what they are interested in if they continue growing well. One sign you may be feeding too much is seeing your baby spit up a lot with every feed. If this occurs even without feeding too much, remember to ask your pediatrician about it. At the pediatrician visit, discuss how well your baby is growing in weight and height. Consistent growth along their growth curve is always a good sign that your baby is eating a healthy amount.
Nancy Choi, MDAnswers represent the opinions of our medical experts. All content is strictly informational and should not be considered medical advice.
Last medically reviewed on December 7, 2018
- Parenthood
- Baby
- 06 Months
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Amount and schedule of formula feedings. (2015, November).
healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/feeding-nutrition/Pages/Amount-and-Schedule-of-Formula-Feedings.aspx - Breastfeeding. (n.d.).
who.int/topics/breastfeeding/en/ - Cobb MA, et al. (2012). Breastfeeding frequency during the first 24 hours of life for the normal newborn. DOI:
doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6909.2012.01362_39.x - Santoro W, et al. (2010). Colostrum ingested during the first day of life by exclusively breastfed healthy newborn infants. DOI:
doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.07.009
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Dec 7, 2018
Written By
Chaunie Brusie
Edited By
Nizam Khan (TechSpace)
Medically Reviewed By
Karen Richardson Gill, MD
Share this article
What is normal breastfeeding? | Interview with Dr.
.jpg) Jacqueline Kent
Jacqueline Kent It can be difficult for new mothers to understand if breastfeeding is going well, so we decided to ask the expert if it is possible to talk about the norms when it comes to breastfeeding.
Share this information
Dr Jacqueline Kent, Research Fellow, Hartmann Human Lactation Research Group:
Jacqueline joined the University of Western Australia research team in 1986 and received her PhD in 1999. She is currently researching the biochemical and physiological aspects of breast milk synthesis and release in search of scientific information to help mothers breastfeed longer.
Dr. Jacqueline Kent and her colleagues have been studying breastfeeding for many years. As it turned out, for all mothers and babies, this process occurs in its own way.
What were the most surprising results of your research?
Variety. It turns out that the limits of the norm are extremely wide.
We are used to textbooks that say that an infant should eat 8-12 times a day and gain 150 grams per week. But babies don't read textbooks and do things their own way! Some gain weight more slowly, others very quickly.
But babies don't read textbooks and do things their own way! Some gain weight more slowly, others very quickly.
We observed infants aged one to six months who were exclusively breastfed. As our studies have shown, on average, a child is breastfed 4 to 13 times a day, and the duration of one feeding varies from 12 minutes to 1 hour. 1
How much milk do breastfed babies usually consume?
According to our research, the volume of milk consumed by baby
ranges from 54 to 234 ml per feeding. 1
Sometimes it seems to the mother that the baby ate well, but when weighed, it turns out that he ate very little milk. And it happens the other way around: the child is distracted, breastfeeds for only a few minutes and still eats 100 ml of milk. Even if the baby is restless, this does not mean at all that he is malnourished.
All babies are different, but they all get the amount of milk they need in one way or another. One needs 500 ml of milk per day, while others eat up to 1356 ml!
By the way, boys on average eat 76 ml more milk per day than girls. The main thing is that you have enough milk, and the baby will decide when and how much he will eat.
The main thing is that you have enough milk, and the baby will decide when and how much he will eat.
Should I offer my baby a second breast?
I advise offering the second breast to the baby after the first has been completely emptied. If he accepts it, then he hasn't finished eating. If not, don't worry. Let the baby decide for himself - only he knows when he is full. According to our research, 30% of babies get enough milk from one breast, 13% eat from two breasts at each feed, and 57% from time to time. 1
How do you know if a baby is getting enough milk?
In my experience, mothers often blame themselves for not producing enough milk. Ask yourself: Is my child growing? Is he putting on weight? Is he cheerful? Is his skin healthy? How often does he get diapers dirty? If the answer is “yes”, then the baby is getting enough milk, no matter if he eats a lot or a little.
What is the most common misconception about breastfeeding?
Mothers usually think that the older the child gets, the more often
he needs to be fed and the more milk he will eat. They are often surprised to learn that between the 4th and 26th weeks, total milk production normally does not change. 2
They are often surprised to learn that between the 4th and 26th weeks, total milk production normally does not change. 2
In the first few months, the baby grows very quickly and his metabolism is accelerated. The milk that the child consumes during this period is almost completely used for growth and maintenance of metabolism.
Between the ages of three and six months, metabolism slows down and growth slows, so the same amount of milk is sufficient for the baby. In other words, the baby does not have to consume more and more milk as they grow older. On the contrary, feedings become shorter and less frequent, but at the same time the child receives the same amount of milk, because he suckles better.
Do studies say anything about the age at which breastfed babies start sleeping through the night?
Most babies need to be fed at night.
A baby's stomach is not large enough to go all night without a feed, and breast milk is digested very quickly. Therefore, it is natural for the baby to wake up at night - and this usually continues for at least the first six months. Feeding at night is normal. When you feed your baby at night, do not even hesitate - all over the world at this moment other mothers of babies of the same age are doing the same. Be patient - it usually only lasts a few months. 1
Therefore, it is natural for the baby to wake up at night - and this usually continues for at least the first six months. Feeding at night is normal. When you feed your baby at night, do not even hesitate - all over the world at this moment other mothers of babies of the same age are doing the same. Be patient - it usually only lasts a few months. 1
What worries new mothers the most during the first few weeks of breastfeeding?
The most common concern is whether the baby latch on properly, sucks well, and is full during feeding. Often mothers also worry about sore nipples. The main thing is to find the right position for feeding from the very beginning and ensure that the baby is latching on correctly. Practice shows that this significantly affects the flow of milk and the convenience of feeding.
What breastfeeding symptoms should be of concern?
Milk production usually returns to normal levels two weeks after delivery. If the child does not begin to gain weight on the fifth or sixth day of life, it's time to sound the alarm. You should contact your doctor to make sure that milk is being produced and that its composition is changing from colostrum to mature breast milk.
You should contact your doctor to make sure that milk is being produced and that its composition is changing from colostrum to mature breast milk.
What advice would you give to a new breastfeeding mother?
Try to ensure skin-to-skin contact with the baby as soon as possible after delivery. If possible, feed your baby within the first hour of life, or at least breastfeed. As soon as possible, contact a specialist to correct the position and grip of the breast during feeding and thus avoid damage to the nipples.
Feed frequently. Young mothers do not immediately succeed in correctly recognizing the signals that the child gives. Be sure to feed your baby on demand, and not at set intervals. Offer the breast as soon as you notice any signs of hunger - as a rule, the baby suckles better when he is calm. If he cries, it is more difficult for him to take the breast. If you are not sure what the child wants, offer him the breast. He decides whether he wants to eat or not.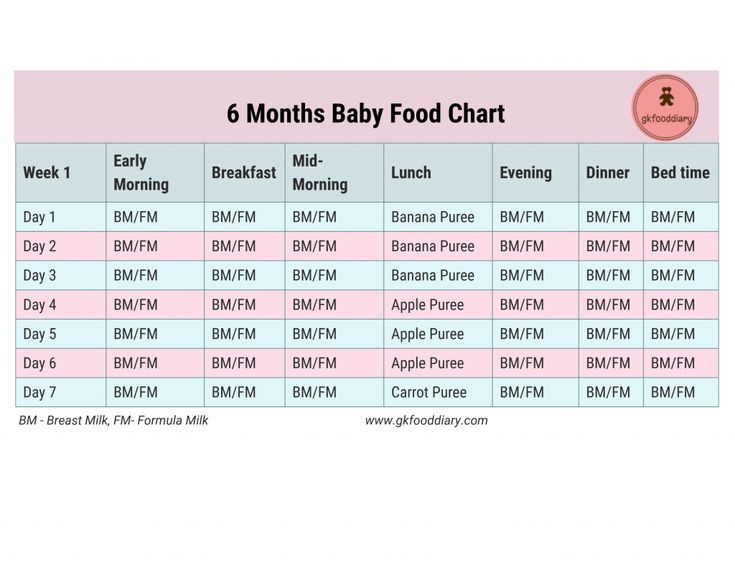
To learn more about Dr. Kent's research, download infographic "How to determine the limits of normal when it comes to breastfeeding" or see it below.
Literature
1 Kent JC et al. Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics . 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
2 Kent JC et al. Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Breastfeeding Medicine . 2013;8(4):401-407. - Kent J.S. et al., Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Brest Med. 2013;8(4):401-407.
Breastfeeding in the first month: what to expect
Not sure how to establish lactation and increase milk production? If you need help, support, or just want to know what to expect, read our First Month Breastfeeding Recommendations
Share this information
The first weeks of breastfeeding are a very stressful period. If at times you feel like you can't handle it, know that you are not alone. Feeding your baby all day long is completely natural and helps produce breast milk, but can be quite tiring at times. Be patient, think about yourself and remember: after the first month, when milk production stabilizes, it will become easier.
If at times you feel like you can't handle it, know that you are not alone. Feeding your baby all day long is completely natural and helps produce breast milk, but can be quite tiring at times. Be patient, think about yourself and remember: after the first month, when milk production stabilizes, it will become easier.
How often should a baby be breastfed?
Babies are born with a small stomach that grows rapidly with increasing milk production: in the first week it is no larger than an apricot, and after two weeks it is already the size of a large chicken egg. 1.2 Let the child eat as much as he wants and when he wants. This will help him quickly regain the weight lost after birth and grow and develop further.
“Be prepared to feed every two to three hours throughout the day. At night, the intervals between feedings can be longer: three to four or even five hours, says Cathy Garbin, a recognized international expert on breastfeeding. Some eat quickly and are satiated in 15 minutes, while others take an entire hour to feed.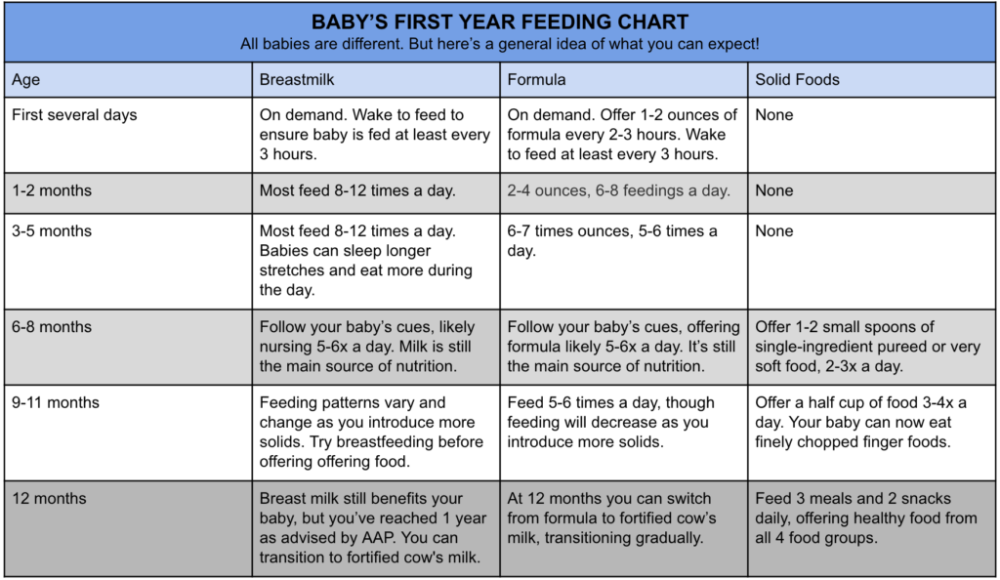 Do not compare your breastfeeding regimen with that of other mothers - it is very likely that there will be nothing in common between them.
Do not compare your breastfeeding regimen with that of other mothers - it is very likely that there will be nothing in common between them.
At each feed, give your baby a full meal from one breast and then offer a second one, but don't worry if the baby doesn't take it. When the baby is full, he lets go of his chest and at the same time looks relaxed and satisfied - so much so that he can immediately fall asleep. The next time you feed, start on the other breast. You can monitor the order of the mammary glands during feeding using a special application.
Why does the child always ask for a breast?
The first month is usually the hardest time to breastfeed. But do not think that because the baby is constantly hungry and asks for a breast almost every 45 minutes, then you do not have enough milk.
In the first month, the baby needs to eat frequently to start and stimulate the mother's milk production. It lays the foundation for a stable milk supply in the future. 3
3
In addition, we must not forget that the child needs almost constant contact with the mother. The bright light and noise of the surrounding world at first frighten the baby, and only by clinging to his mother, he can calm down.
Sarah, mother of three from the UK, confirms: “Crying is not always a sign of hunger. Sometimes my kids just wanted me to be around and begged for breasts to calm them down. Use a sling. Place the cradle next to the bed. Don't look at the clock. Take advantage of every opportunity to relax. Forget about cleaning. Let those around you take care of you. And not three days, but six weeks at least! Hug your baby, enjoy the comfort - and trust your body."
Do I need to feed my baby on a schedule?
Your baby is still too young for a strict daily routine, so
forget about breastfeeding schedules and focus on his needs.
“Volumes have been written about how to feed a baby on a schedule, but babies don't read or understand books,” Cathy says. - All children are different. Some people can eat on a schedule, but most can't. Most often, over time, the child develops his own schedule.
- All children are different. Some people can eat on a schedule, but most can't. Most often, over time, the child develops his own schedule.
Some mothers report that their babies are fine with scheduled feedings, but they are probably just the few babies who would eat every four hours anyway. Adults rarely eat and drink the same foods at the same time of day - so why do we expect this from toddlers?
Offer your baby the breast at the first sign of hunger. Crying is already the last stage, so be attentive to early signs: the baby licks his lips, opens his mouth, sucks his fist, turns his head with his mouth open - looking for the breast. 4
What is a “milk flush”?
At the beginning of each feed, a hungry baby actively suckles the nipple,
thereby stimulating the milk flow reflex - the movement of milk through the milk ducts. 5
“Nipple stimulation triggers the release of the hormone oxytocin,” Cathy explains. “Oxytocin circulates throughout the body and causes the muscles around the milk glands to contract and the milk ducts to dilate. This stimulates the flow of milk.
This stimulates the flow of milk.
If the flushing reflex fails, milk will not come out. This is a hormonal response, and under stress it may not work at all or work poorly. Therefore, it is so important that you feel comfortable and calm when feeding.
“Studies show that each mother has a different rhythm of hot flashes during one feed,” Katie continues, “Oxytocin is a short-acting hormone, it breaks down in just 30-40 seconds after formation. Milk begins to flow, the baby eats, the effect of oxytocin ends, but then a new rush of milk occurs, the baby continues to suckle the breast, and this process is repeated cyclically. That is why, during feeding, the child periodically stops and rests - this is how nature intended.
The flow of milk may be accompanied by a strong sensation of movement or tingling in the chest, although 21% of mothers, according to surveys, do not feel anything at all. 5 Cathy explains: “Many women only feel the first rush of milk.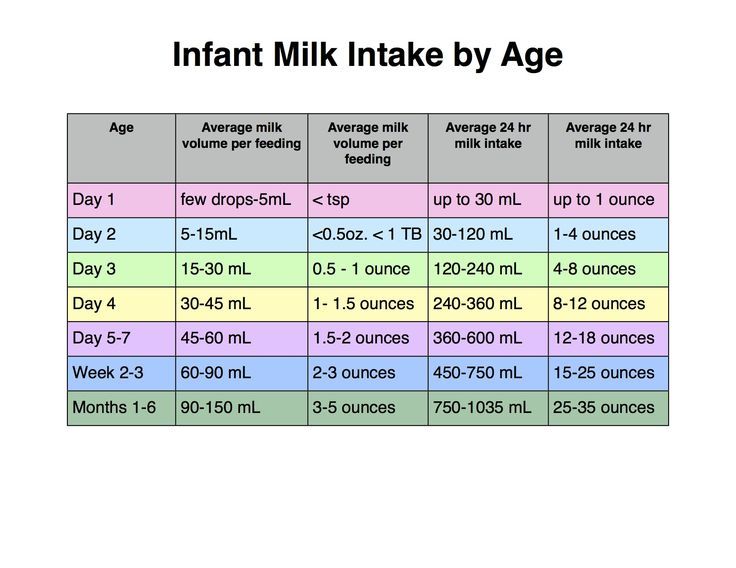 If you do not feel hot flashes, do not worry: since the child eats normally, most likely, you simply do not understand that they are.
If you do not feel hot flashes, do not worry: since the child eats normally, most likely, you simply do not understand that they are.
How can you tell if your baby is getting enough milk?
Since it is impossible to track how much milk a baby eats while breastfeeding, mothers sometimes worry that the baby is malnourished. Trust your child and your body.
After a rush of milk, the baby usually begins to suckle more slowly. Some mothers clearly hear how the baby swallows, others do not notice it. But one way or another, the child himself will show when he is full - just watch carefully. Many babies make two or three approaches to the breast at one feeding. 6
“When a child has had enough, it is noticeable almost immediately: a kind of “milk intoxication” sets in. The baby is relaxed and makes it clear with his whole body that he is completely full, says Katie, “Diapers are another great way to assess whether the baby is getting enough milk. During this period, a breastfed baby should have at least five wet diapers a day and at least two portions of soft yellow stool, and often more. ”
”
From one month until weaning at six months of age, a baby's stool (if exclusively breastfed) should look the same every day: yellow, grainy, loose, and watery.
When is the child's birth weight restored?
Most newborns lose weight in the first few days of life. This is normal and should not be cause for concern. As a rule, weight is reduced by 5-7%, although some may lose up to 10%. One way or another, by 10–14 days, almost all newborns regain their birth weight. In the first three to four months, the minimum expected weight gain is an average of 150 grams per week. But one week the child may gain weight faster, and the next slower, so it is necessary that the attending physician monitor the health and growth of the baby constantly. 7.8
At the slightest doubt or signs of dehydration, such as
dark urine, no stool for more than 24 hours, retraction of the fontanel (soft spot on the head), yellowing of the skin, drowsiness, lethargy, lack of appetite (ability to four to six hours without feeding), you should immediately consult a doctor. 7
7
What is “cluster feeding”?
When a baby very often asks to breastfeed for several hours, this is called cluster feeding. 6 The peak often occurs in the evening between 18:00 and 22:00, just when many babies are especially restless and need close contact with their mother. Most often, mothers complain about this in the period from two to nine weeks after childbirth. This is perfectly normal and common behavior as long as the baby is otherwise healthy, eating well, gaining weight normally, and appears content throughout the day. 9
Cluster feeding can be caused by a sharp jump in the development of the body - during this period the baby especially needs love, comfort and a sense of security. The growing brain of a child is so excited that it can be difficult for him to turn off, or it just scares the baby. 9 If a child is overworked, it is often difficult for him or her to calm down on his own and adult assistance is needed.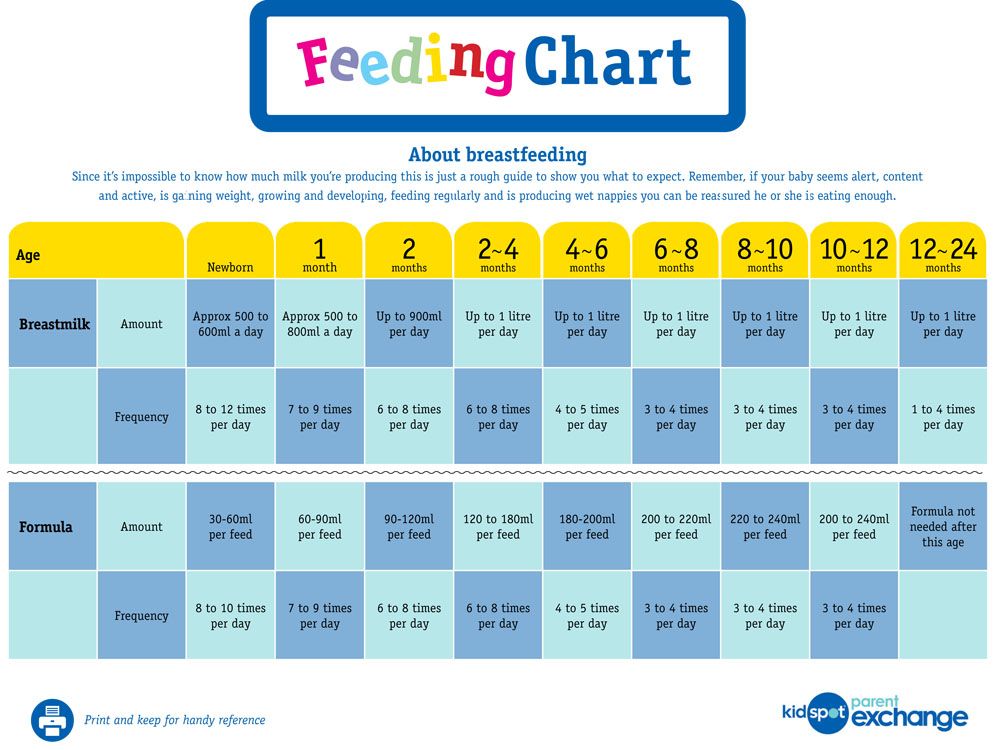 And breastfeeding is the best way to calm the baby, because breast milk is not only food, but also pain reliever and a source of happiness hormones. 10
And breastfeeding is the best way to calm the baby, because breast milk is not only food, but also pain reliever and a source of happiness hormones. 10
“Nobody told me about cluster feeding, so for the first 10 days I just went crazy with worry - I was sure that my milk was not enough for the baby,” recalls Camilla, a mother from Australia, “It was a very difficult period . I was advised to pump and supplement until I finally contacted the Australian Breastfeeding Association. There they explained to me what was happening: it turned out that it was not about milk at all.
Remember, this is temporary. Try to prepare dinner for yourself in the afternoon, when the baby is fast asleep, so that in the evening, when he begins to often breastfeed, you have the opportunity to quickly warm up the food and have a snack. If you are not alone, arrange to carry and rock the baby in turns so that you have the opportunity to rest. If you have no one to turn to for help and you feel that your strength is leaving you, put the baby in the crib and rest for a few minutes, and then pick it up again.
Ask your partner, family and friends to help you with household chores, cooking and caring for older children if you have any. If possible, hire an au pair. Get as much rest as possible, eat well and drink plenty of water.
“My daughter slept a lot during the day, but from 23:00 to 5:00 the cluster feeding period began, which was very tiring,” recalls Jenal, a mother from the USA, “My husband tried his best to make life easier for me — he washed, cleaned, cooked, changed diapers, let me sleep at every opportunity and never tired of assuring me that we were doing well.
If you are concerned about the frequency of breastfeeding, it is worth contacting a specialist. “Check with a lactation consultant or doctor to see if this is indicative of any problems,” recommends Cathy. “Resist the temptation to supplement your baby with formula (unless recommended by your doctor) until you find the cause. It may not be a matter of limited milk production at all - it may be that the child is inefficiently sucking it.
When will breastfeeding become easier?
This early stage is very special and does not last long. Although sometimes it seems that there will be no end to it, rest assured: it will get easier soon! By the end of the first month, breast milk production will stabilize, and the baby will become stronger and learn to suckle better. 2.3 Any problems with latch on will most likely be resolved by this time, and the body will be able to produce milk more efficiently, so inflammation and leakage of milk will begin to subside.
“The first four to six weeks are the hardest, but then things start to get better,” Cathy assures. It just needs to be experienced!”
The longer breastfeeding continues, the more benefits it brings, from saving on formula and improving sleep quality 11–13 to boosting your baby's immune system 14 and reducing your risk of developing certain types of cancer. 15
“When you feel like you're pushing yourself, try to go from feed to feed and day to day,” says Hannah, a UK mom. “I was sure I wouldn’t make it to eight weeks. And now I have been breastfeeding for almost 17 weeks, and I dare say it is very easy.”
“I was sure I wouldn’t make it to eight weeks. And now I have been breastfeeding for almost 17 weeks, and I dare say it is very easy.”
Read the resource Breastfeeding After the First Month: What to Expect
Readings
1 Naveed M et al. An autopsy study of relationship between perinatal stomach capacity and birth weight. Indian J Gastroenterol .1992;11(4):156-158. - Navid M. et al., Association between prenatal gastric volume and birth weight. Autopsy. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1992;11(4):156-158.
2 Neville MC et al. Studies in human lactation: milk volumes in lactating women during the onset of lactation and full lactation .Am J Clinl Nutr . 1988;48(6):1375-1386. at the beginning and at the peak of lactation." Am F Clean Nutr. 1988;48(6):1375-1386.
3 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
4 Australian Breastfeeding Feeding cues ; 2017 Sep [ cited 2018 Feb ]. - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Feed Ready Signals; September 2017 [cited February 2018]
5 Kent JC et al. Response of breasts to different stimulation patterns of an electric breast pump. J Human Lact . 2003;19(2):179-186. - Kent J.S. et al., Breast Response to Different Types of Electric Breast Pump Stimulation. J Human Lact (Journal of the International Association of Lactation Consultants). 2003;19(2):179-186.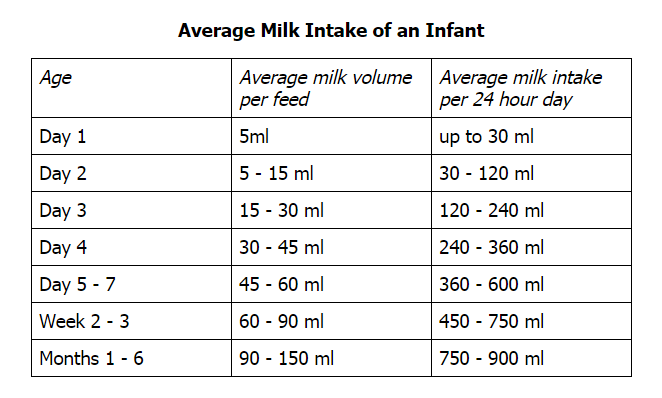
6) Kent JC et al . Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
7 Lawrence RA, Lawrence RM. Breastfeeding: A guide for the medical profession. 7th ed. Maryland Heights MO, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. 1128 p . - Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.M., "Breastfeeding: A guide for healthcare professionals." Seventh edition. Publisher Maryland Heights , Missouri, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. P. 1128.
8 World Health Organization. [Internet]. Child growth standards; 2018 [cited 2018 Feb] - World Health Organization. [Internet]. Child Growth Standards 2018 [cited February 2018].
[Internet]. Child Growth Standards 2018 [cited February 2018].
9 Australian Breastfeeding Association [ Internet ]. Cluster feeding and fussing babies ; Dec 2017 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Cluster Feeding and Screaming Babies; December 2017 [cited February 2018].
10 Moberg KU, Prime DK. Oxytocin effects in mothers and infants during breastfeeding. Infant . 2013;9(6):201-206.- Moberg K, Prime DK, "Oxytocin effects on mother and child during breastfeeding". Infant. 2013;9(6):201-206.
11 U.S. Department of Health & Human Services [Internet]. Surgeon General Breastfeeding factsheet; 2011 Jan 20 [cited 2017 Feb] - Department of Health and Human Services [Internet], "Breastfeeding Facts from the Chief Medical Officer", Jan 20, 2011 [cited Feb 2017]
12 Kendall-Tackett K et al. The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression. clinical lactation. 2011;1;2(2):22-26. - Kendall-Tuckett, K. et al., "Influence of feeding pattern on sleep duration, maternal well-being and the development of postpartum depression." Clinical Lactation. 2011;2(2):22-26.
The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression. clinical lactation. 2011;1;2(2):22-26. - Kendall-Tuckett, K. et al., "Influence of feeding pattern on sleep duration, maternal well-being and the development of postpartum depression." Clinical Lactation. 2011;2(2):22-26.
13 Brown A, Harries V. Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med . 2015;10(5):246-252. - Brown A., Harris W., "Night feedings and infant sleep in the first year of life and their association with feeding frequency, daytime supplementation, and infant weight." Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252.
14 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk.