How much formula to feed your baby
Amount and Schedule of Baby Formula Feedings
- In the first week after birth, babies should be eating no more than about 1 to 2 ounces (30 to 60 ml) per feed.
- During the first month, babies gradually eat more until they take 3 to 4 ounces (90 to 120 ml) per feed, amounting to 32 ounces per day. Formula-fed babies typically feed on a more regular schedule, such as every 3 or 4 hours. Breastfed babies usually take smaller, more frequent feedings than formula-fed infants.
If your baby sleeps longer than 4 to 5 hours during the first few weeks after birth and starts missing feedings, wake them up and offer a bottle.
By the end of the first month: Your baby will be up to at least 3 to 4 ounces (120 mL) per feeding, with a fairly predictable schedule of feedings about every 3 to 4 hours.
By 6 months: Your baby will consume 6 to 8 ounces (180–240 mL) at each of 4 or 5 feedings in 24 hours.
Formula feeding based on body weight
On average, your baby should take in about 2½ ounces (75 mL) of infant formula a day for every pound (453 g) of body weight. But they probably will regulate their intake from day to day to meet their own specific needs, so let them tell you when they've had enough. If they become fidgety or easily distracted during a feeding, they're probably finished. If they drain the bottle and continues smacking their lips, they might still be hungry.
There are high and low limits, however. If your baby consistently seems to want more or less than this, discuss it with your pediatrician. Your baby should usually drink no more than an average of about 32 ounces (960 mL) of formula in 24 hours. Some babies have higher needs for sucking and may just want to suck on a pacifier after feeding.
On-demand feeding
Initially it is best to feed your formula-fed newborn a bottle on demand, or whenever they cry with hunger. As time passes, your baby will begin to develop a fairly regular timetable of their own. As you become familiar with their signals and needs, you'll be able to schedule their feedings around their routine.
As time passes, your baby will begin to develop a fairly regular timetable of their own. As you become familiar with their signals and needs, you'll be able to schedule their feedings around their routine.
Eating & sleeping patterns
Between 2 and 4 months of age (or when the baby weighs more than 12 lb. [5.4 kg]), most formula-fed babies no longer need a middle-of-the-night feedings. They're consuming more during the day, and their sleeping patterns have become more regular (although this varies considerably from baby to baby). Their stomach capacity has increased, too, which means they may go longer between daytime feedings—occasionally up to 4 or 5 hours at a time.
If your baby still seems to feed very frequently or consume larger amounts, try distracting them with play or with a pacifier. Sometimes patterns of obesity begin during infancy, so it is important not to overfeed your baby.
Getting to know your baby's feeding needs
The most important thing to remember, whether you breastfeed or bottlefeed, is that your baby's feeding needs are unique. No book―or website―can tell you precisely how much or how often they need to be fed or exactly how you should handle them during feedings. You will discover these things for yourself as you and your baby get to know each other.
No book―or website―can tell you precisely how much or how often they need to be fed or exactly how you should handle them during feedings. You will discover these things for yourself as you and your baby get to know each other.
More information
- How Often and How Much Should Your Baby Eat?
- Making Sure Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk
- Is Your Baby Hungry or Full? Responsive Feeding Explained (Video)
- Remedies for Spitty Babies
- Last Updated
- 5/16/2022
- Source
- Adapted from Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician.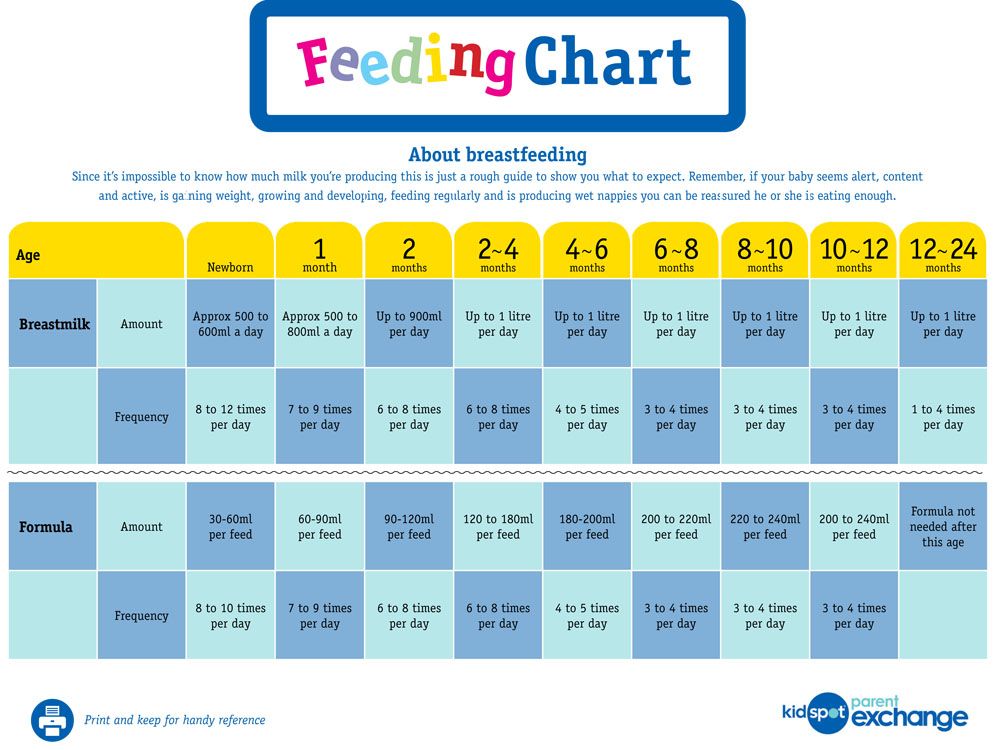 There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
How Often and How Much Should Your Baby Eat?
By: Sanjeev Jain, MD, FAAP
One of the most common questions new parents have is how often their baby should eat. The best answer is surprisingly simple: in general, babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry.
How do I know when my baby is hungry?
For babies born
prematurely or with certain medical conditions, scheduled feedings advised by your pediatrician are best. But for most healthy, full-term infants, parents can look to their baby rather than the clock for hunger cues. This is called feeding on demand, or
responsive feeding.
Hunger cues
A hungry baby often will cry. But it's best to watch for hunger cues before the baby starts
crying, which is a late sign of hunger and can make it hard for them to settle down and eat.
Some other typical hunger cues in babies:
Licking lips
Sticking tongue out
Rooting (moving jaw and mouth or head in search of breast)
Putting his/her hand to mouth repeatedly
Opening her mouth
Fussiness
Sucking on everything around
It is important to realize, however, that every time your baby cries or sucks it is not necessarily because he or she is hungry. Babies suck not only for hunger, but also for comfort; it can be hard at first for parents to tell the difference. Sometimes, your baby just needs to be cuddled or changed.
General guidelines for baby feeding
It is important to remember all babies are different―some like to snack more often, and others drink more at one time and go longer between feedings. However, most babies will drink more and go longer between feedings as they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk:
Most newborns eat every 2 to 3 hours, or 8 to 12 times every 24 hours.
 Babies might only take in half ounce per feeding for the first day or two of life, but after that will usually drink 1 to 2 ounces at each feeding. This amount increases to 2 to 3 ounces by 2 weeks of age.
Babies might only take in half ounce per feeding for the first day or two of life, but after that will usually drink 1 to 2 ounces at each feeding. This amount increases to 2 to 3 ounces by 2 weeks of age.At about 2 months of age, babies usually take 4 to 5 ounces per feeding every 3 to 4 hours.
At 4 months, babies usually take 4 to 6 ounces per feeding.
At 6 months, babies may be taking up to 8 ounces every 4 to 5 hours.
Most babies will increase the amount of formula they drink by an average of 1 ounce each month before leveling off at about 7 to 8 ounces per feeding. Solid foods should be started at about 6 months old.
Concerns about overfeeding or underfeeding your baby
Too full?
Babies are usually pretty good at eating the right amount, but they can sometimes take in more than they need. Infants who are
bottle feeding may be more likely to overfeed, because drinking from a bottle may take less effort than
breastfeeding.
Overfed babies can have stomach pains, gas, spit up or vomit and be at higher risk for obesity later in life. It's better to offer less, since you can always give more if your baby wants it. This also gives babies time to realize when they're full.
If you are concerned your baby wants to eat all the time―even when he or she is full―talk with your pediatrician. Pacifiers may be used after feeding to help sooth healthy-weight babies who like to suck for comfort, rather than nutrition. For babies who are breastfed, it's best to wait to offer pacifiers until around 3 to 4 weeks of age, when breastfeeding is well-established.
Trouble gaining weight?
Most babies will double their birth weight by 5 months of age and triple their birth weight by their first birthday. If your baby is having trouble gaining weight, don't wait too long between feeding―even if it means waking your baby. Be sure to talk with your pediatrician about how often and how much to feed your baby.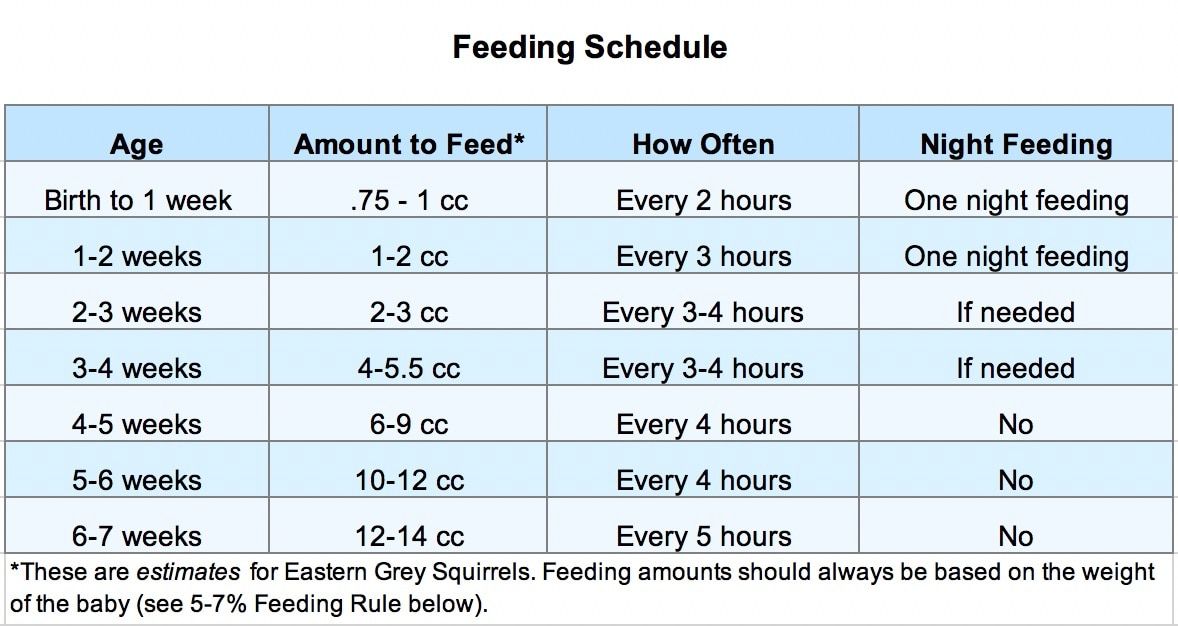
How do I know if my baby is getting enough to eat?
Daily diapers
A newborn's diaper is a good indicator of whether he or she is getting enough to eat. In the first few days after birth, a baby should have 2 to 3 wet diapers each day. After the first 4 to 5 days, a baby should have at least 5 to 6 wet diapers a day. Stool frequency is more variable and depends whether your baby is breastfed or formula fed.
Growth charts
During regular health check-ups, your pediatrician will check your baby's weight and plot it on a growth chart. Your baby's progress on the growth chart is one way to tell whether or not they are getting enough food. Babies who stay in healthy growth percentile ranges are probably getting a healthy amount of food during feedings.
Remember
Talk with your pediatrician if you have any questions or concerns about your baby getting the right amount to eat.
More information:
- Making Sure Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk
- Amount and Schedule of Formula Feedings
- Is Your Baby Hungry or Full? Responsive Feeding Explained (Video)
- Remedies for Spitty Babies
- Ask the Pediatrician: With the baby formula shortage, what should I do if I can't find any?
- Ask the Pediatrician: How should we feed our baby if we're running low on money?
-
Airplane Choo Choo: A Feeding Guide for Children (National Dairy Council)
About Dr.
 Jain:
Jain:
Sanjeev Jain, MD, FAAP, is a Clinical Associate Professor of General Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health. Within the American Academy of Pediatrics, he is a member of the Section on International Child Health and the Wisconsin State Chapter.
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
How to calculate infant formula by weight
A newborn from the first days should receive a certain amount of food. When breastfeeding, special calculations are not required: the baby himself eats as much as he needs. With artificial, when mother's milk is replaced with formula, it is important to calculate the amount of food and the daily number of feedings.
Average age mix
In the first days of life, the child eats colostrum, which is a high-calorie product and fully satisfies his needs. But "artists" are recommended to be fed strictly according to the scheme. Nutritional norms are derived by pediatricians based on the results of long-term observations, taking into account age, body weight, and health status. nine0003
The following formula is popular, according to which the daily dose is calculated: if the weight of a baby up to 10 days is less than 3200, then his age in days is multiplied by 70, if more - by 80. The result is the amount of food per day. For example, 2 (days) X 70 = 140 grams.
Table for calculating the volume of the mixture
| Age | Volume | The amount of mixture per day nine0018 |
|---|---|---|
| From 10 days to 2 months of life | 1/5 body weight | 700-850 ml |
| 2 to 4 months | 1/6 | 750-900 ml |
| 4 to 6 | 1/7 | 850-1000 ml | nine0023
| 6 to 12 | 1/8-1/9 | 950-1100 ml |
The data in the table are approximate, each child needs an individual diet, which is easy to calculate.
 For example, a baby who weighs 4300 g at 1.5 months should eat 860 ml of the mixture (4300: 5) per day.
For example, a baby who weighs 4300 g at 1.5 months should eat 860 ml of the mixture (4300: 5) per day. You can determine the rate of the mixture for one feeding, knowing how many times a day you need to feed. According to pediatricians, if the child is less than 2 months old, there should be 8-10 feedings (including nightly ones). With increasing age, this number decreases: nine0003
- 2-4 months - 7-8,
- 4-6 months - 6,
- over 6 months - 5-6.
We calculate the amount of food for one feeding using the example already given. Every day the child eats 860 ml of the mixture, he is 1.5 months old, he needs to be fed 8 times. The dose for one meal is 860:8 = 107.5 ml. An infant formula machine will also help you follow the rules, which will prepare food in 4-25 seconds, while maintaining the desired consistency. nine0003
Featured Products
Related Items
Dry cough in children - causes, symptoms and treatment of dry cough in children
Parents are always worried about the health of their children and hope that the baby will always be healthy. But, unfortunately, children get sick, and one of the common symptoms of childhood diseases is a dry cough.
But, unfortunately, children get sick, and one of the common symptoms of childhood diseases is a dry cough.
Read more
How much formula should a child eat?
nine0093 02/11/2022 Reading time: 6 min 158220
Article content
- How to tell if a child is full
- How much formula should a child eat per month
- How much formula should a baby eat at 2 months
- How much formula should a baby eat at 3 months
- Mixture Rate Chart
- What to do if the baby does not fill up with formula
A breastfed baby largely regulates the amount of food and the frequency of feeding. In the first month of life, he receives breasts on demand, and then a more or less stable diet is developed naturally. If for some reason the baby is deprived of breast milk and receives milk formula, then a free feeding schedule is impossible. The child eats according to the schedule, and the mother has to adhere to the recommended regimen. nine0003
In the first month of life, he receives breasts on demand, and then a more or less stable diet is developed naturally. If for some reason the baby is deprived of breast milk and receives milk formula, then a free feeding schedule is impossible. The child eats according to the schedule, and the mother has to adhere to the recommended regimen. nine0003
How to tell if a child is full
The signs that a child is full are universal: they are in a good mood, sound sleep, and regular stools.
If we consider not the momentary state of the child, but a longer period, then we need to monitor weight gain and skin condition. A baby who has enough nutrition will increase weight within the age norm - this will be assessed by the doctor during the control weighing. The baby's skin will be pink and firm. nine0121
Accordingly, a hungry child will worry, scream, cry, or may become lethargic and lethargic. He will rarely urinate and poop. A dry diaper for several hours is an alarming sign. Over time, the baby will begin to lag behind in weight, his skin may become pale, dry.
Over time, the baby will begin to lag behind in weight, his skin may become pale, dry.
But do not rush to give a supplement if the child has drunk the mixture and continues to grab the pacifier. Most likely, he ate, but did not satisfy the sucking reflex. Offer him a pacifier and watch for other signs: whether he will continue to worry, how his sleep will be. If you continue to doubt whether your baby is getting enough nutrition, check with your pediatrician. nine0121
How much formula should a child eat per month
A bottle-fed newborn should receive the mixture after 2.5-3 hours, that is, 8-10 times a day, including night feedings. The stomach of an infant in the first month of life is still too small to accommodate a large amount of food, so it is not recommended to take long night breaks between feedings at this age.
As for the volume of the mixture, it will depend not only on the age, but also on the weight of the baby. nine0121
In the first decade, that is, the first 10 days of life, the daily volume of the mixture is usually calculated as follows:
- if the baby's weight is less than 3 kg 200 g, then the number of days he lived is multiplied by 70;
- if the weight is more than 3 kg 200 g, then the age in days is multiplied by 80.
For example, a 6-day-old baby weighs 3 kg 400 g. Multiply 6 x 80 = 480 ml. We divide this volume by the number of feedings. Let's say you feed your baby 8 times, which means that in one feeding he should receive 60 ml of the mixture. nine0003
For a child older than 10 days, the formula calculation algorithm changes.
To calculate how much a child should eat mixtures in 1 month per day, you need to divide his body weight by 5. ⅕ of the child’s body weight is the daily amount of food.
For example, the same baby gained 4 kg by the 25th day of life. We divide 4 kg by 5, we get 800. Therefore, if the child continues to receive the mixture 8 times a day, then his single serving will be 100 g. nine0003
How much formula should a baby eat at 2 months
For a child of the second month of life, the same formula for calculating the mixture continues to operate: ⅕ of the weight is the daily volume. Divide by the number of feedings, we get a single serving.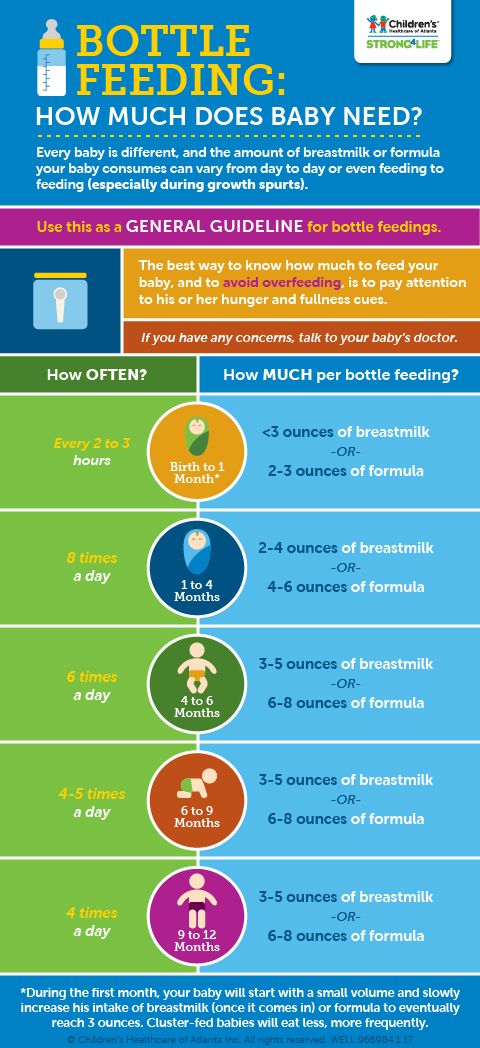
In the third month, the number of feedings is reduced to 7-8. If the child ate 10 times, gradually transfer to 8 times, if 8, then to 7.
But when calculating how much a child should eat mixtures at 2 months and older, we use a different formula. The daily volume of the mixture should now be ⅙ of the child's weight. On average, this is 750 ml or more. nine0003
How much formula should a baby eat at 3 months
To determine how much a child should eat formula at 3 months, you need to divide his weight again by 6. For example, the weight of a child is 5 kg 400 g. Divide it by 6, we get a daily volume of 900 g.
The number of feedings at 3 months remains the same - 7-8 times. Let our conditional child eat 7 times a day. We divide 900 by 7, we get approximately 130 g of the mixture per feeding.
Mixture Rate Chart
For the convenience of selecting the volume of the mixture, depending on the age and weight of the child, you can use the following table *. It contains average data, but since all children are different, the doctor should clarify the nutritional norm for a particular child.
It contains average data, but since all children are different, the doctor should clarify the nutritional norm for a particular child.
| Child's age | The ratio of nutrition and body weight per day | Daily volume of the mixture in ml | Number of feedings |
|---|---|---|---|
| From 10 days to 2 months | 1/5 | 700-850 | 8-10 |
| 2-4 months | 1/6 | 750-900 | 7-8 |
| 4-6 months | 1/7 | 850-1000 | 6 |
| Second half of life (6-12 months) | 1/8-1/9 | 950-1100 | 5-6 |
 nine0004 What to do if the child does not fill up with formula
nine0004 What to do if the child does not fill up with formula First of all, you need to understand by what signs you determined that the child did not eat enough. If he keeps asking for a bottle when he's finished formula, it doesn't necessarily mean he's hungry. Perhaps the child wants to continue the process itself, because the sucking reflex in children on artificial feeding is less satisfied than in children on breastfeeding.
If the baby starts to worry and cry much before the next feeding time, consider if the breaks between meals are too long. With pronounced "hungry" anxiety of the child, feed early, but the volume of the mixture should correspond to a single volume. nine0003
This is important!
It is impossible to make the mixture “thicker” for satiety, add more dry product than indicated in the instructions! This can lead to constipation and other health problems for the baby.
If the baby is not gaining weight well, often worries, sleeps poorly, consult a pediatrician.