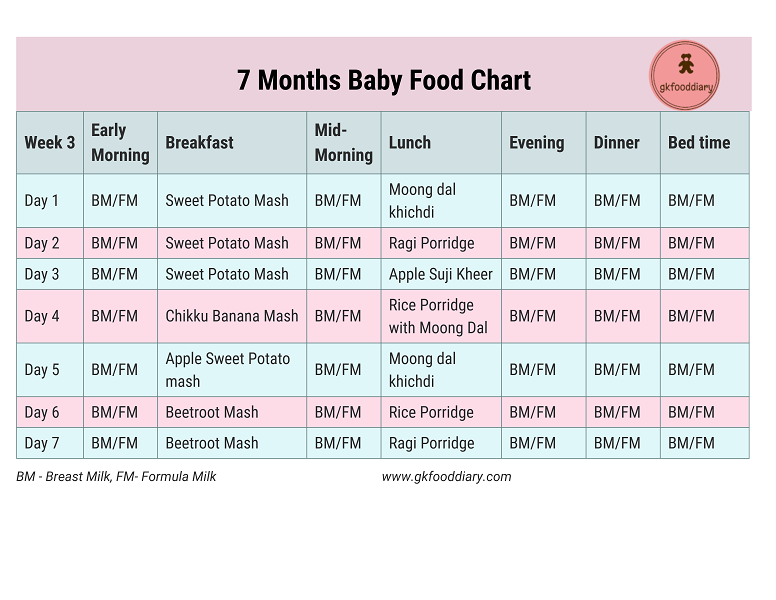
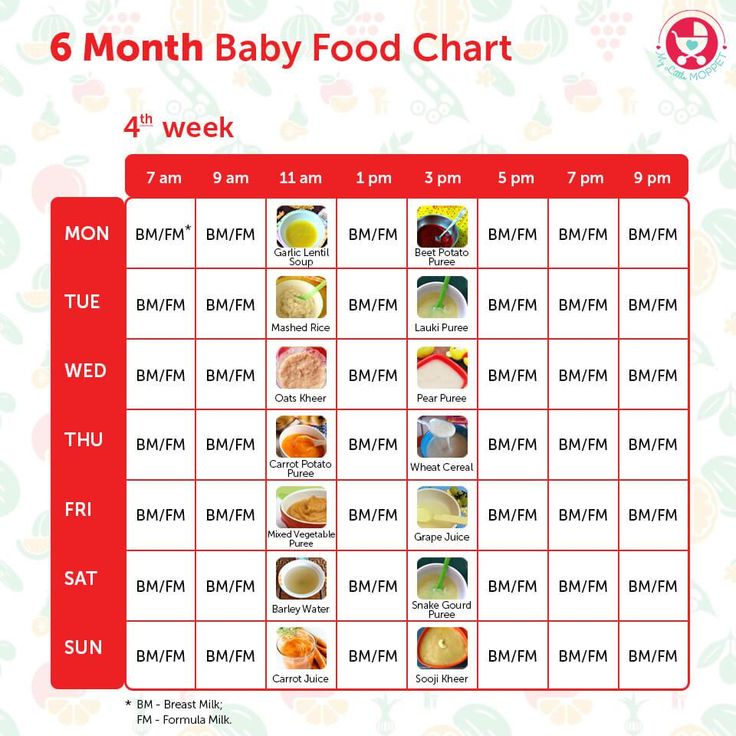
Are baby food pouches safe
Do Baby Food Pouches Cause Eating Problems?
Written by Lisa Marshall
Walk the baby food aisle and you'll quickly notice that those miniature glass jars of baby food from your childhood are being overtaken by squeezable, suck-able, disposable pouches.
A decade after they hit the shelves, billed as a mess-free portable option for on-the-go families, the puree-filled packages now make up more than a quarter of baby food sales in the United States. Nearly a third of 2-year-olds' packed lunches at day care contain at least one pouch, one recent University of Texas Austin study found, and some toddlers are getting more than half of their midday calories in pouch form.
That concerns child health experts who say that while the pouches are fine as an occasional snack, their overuse could potentially breed poor eating habits and stunt development of feeding skills and motor coordination at a critical stage of life.
"Many of us in the medical field have a love-hate relationship with pouches," says Kara Larson, a speech language pathologist and feeding specialist at Boston Children's Hospital. "They're convenient and travel well and are often a better choice than cookies or chips. But parents need to use them in moderation."
For infants and toddlers, Larson says, eating is an important learning experience. Scraping a spoon across a bowl and lifting it to the mouth develops motor coordination. Plucking cut-up bits of banana from a high-chair tray develops grasping skills. And unlike sucking from a pouch -- which requires a front-to-back tongue motion -- chewing soft foods requires a child to develop side-to-side tongue motions needed for eating and speech later in life.
"If children are just sucking from a pouch all the time, we worry that some of that tactile experience with food might be lost," she says.
Parents often like pouches for their wide variety of seemingly healthy flavors, ranging from quinoa and kale mixtures to organic vegetable blends. But experts warn that the actual taste of those vegetables and grains is often masked with sugar, which could pose dental problems and breed picky eaters.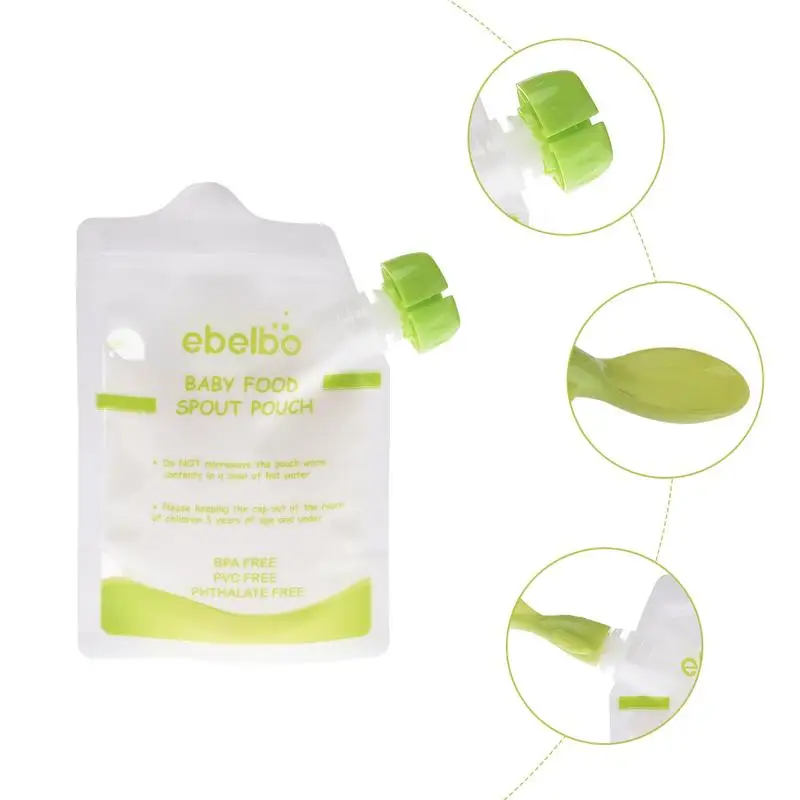
"Children at this age are developing taste preferences that will follow them throughout life," says Courtney Byrd-Williams, PhD, a behavioral scientist at UTHealth School of Public Health in Austin, TX. "If they are used to eating overly sweet fruit or aren't exposed to plain vegetables, they are less likely to like them as adults."
She also worries that because pouches are far easier to suck down quickly, they might encourage children to keep eating, even when they're already full -- a bad habit that could cause problems in adulthood.
All that said, Larson and Byrd-Williams see no harm in offering babies 6 months or older and toddlers an occasional pouch -- in the grocery store, in the car, at big brother's soccer game -- when sitting down for a snack isn't practical. Just don't exceed one or two pouches per day, look for low-sugar/high-fiber options, and don't let convenience trump health.
"When we consider what convenience food has done to adult health, there are plenty of reasons to pause before passing your child another pouch," Byrd-Williams says.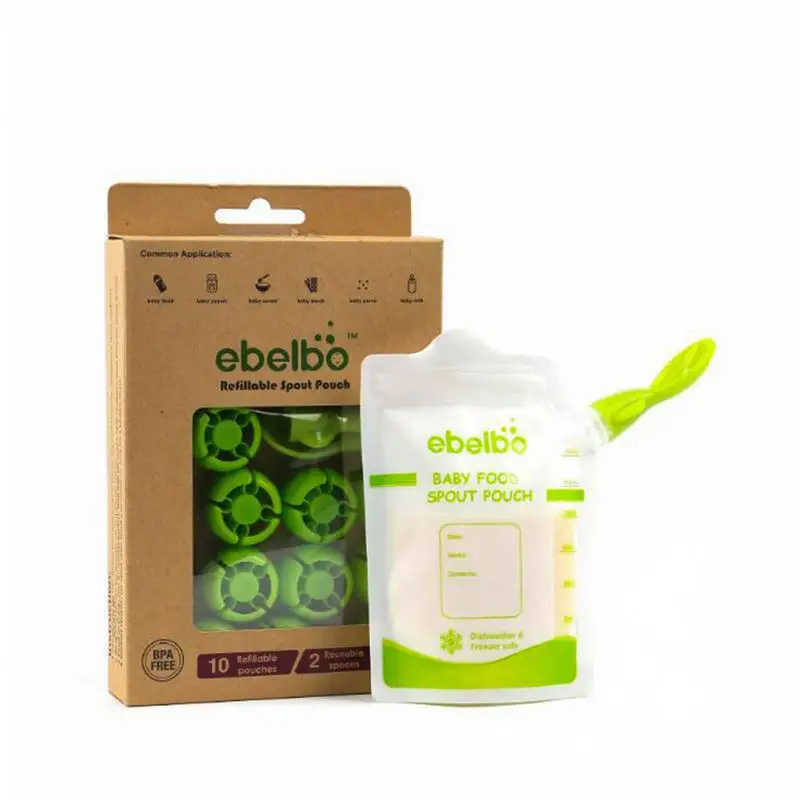
28%: Percentage of day-care lunches for children 6 months to 3 years old that contain at least one pouch; 10% contain two or more pouches. In 4%, half of lunchtime calories came from pouches.
0: Number of packed-lunch pouches that contained purely vegetables.
12 grams: Average amount of sugar in a single pouch.
25%: Percentage of the total baby food market made up of pouches in 2018, according to Nielsen Total Food View.
The (ugly) Truth About Baby Food Pouches | Are Homemade Pouches For Babies Good Or Bad | Do Baby Food Packets Grow Mold | Amara
The (Ugly) Truth About Baby Food Pouches
It’s hard to believe that baby food pouches only came on the market about a decade ago, give or take. To put it mildly, these things became insanely popularfast. In 2018, theNew York Times reported that pouches account fora full quarter of the baby food market —wow. This is a pretty staggering rise to prominence, when you think about it.
This is a pretty staggering rise to prominence, when you think about it.
In real life, the prominence bears out. I see pouches everywhere, and it’s true: pouches take up at least 25% of the shelf space on the baby food aisle (which is itself a dizzying array of products and options…).
If you’re a parent, we probably don’t have to tell you why pouches became so popular so quickly: they’re the epitome of convenience. Besides the fact that kidsreally like them, pouches require no prep, no feeding, no refrigeration, no mess, and virtually no clean up. They’re easy to pack, easy to store, easy to hand over, and given that so many of them are organic and/or contain exotic fruits and vegetables, they’re really easy to feel good about.
But too much of anything is not always a good thing.
Pouches are a great option for any number of circumstances and situations (more on this shortly…), but according to the best experts, over relying on them is actually problematic. Here’s why:
Here’s why:
-
Pouches don’t teach young children about food and eating.
Every time a baby or toddler sits down to eat presents a learning opportunity in more ways than one. And unfortunately, pouches detract from that learning more than they contribute to it.
Eating — whether it’s by hand or getting spoon-fed — entails using fine motor skills, coordination, and specific oral mechanics. It’s a tactile experience that furthers a child’s developmental abilities in multiple areas. If eating is an actual activity, “eating” from a pouch is passive. It is, in a way, a lost developmental learning opportunity.
When children eat solids — including purees — they’re learning to take bites, to move food around in their mouths, to use their tongues, and to chew. Pouches demand none of this of children. As Kara Larson, a feeding specialist and speech language pathologist at Boston Children’s Hospital said in an interview: “if children are just sucking from a pouch all the time, we worry that some of that tactile experience with food might be lost. ”
”
Eating is also a sensory experience, and this is another area in which pouches come up short. Babies and toddlers learning to eat take ineverything about foods — feeling, seeing, and smelling are a huge part of how they learn about different foods. With pouches, all this sensory intake is essentially lost: children can’t see what color their “food” is, can’t smell it by and large, and don’t feel its textures.
Not to mention, to a large extent,they also can’t even really taste it. Here’s what I mean…
The main ingredient in most pouches tends to be a sweet food, usually a fruit. And those sweet foods effectively dominate the entire flavor profile. So even if a pouch does contain spinach or broccoli or the like,children can’t taste it. Like, at all.
Indeed, partly because of this sweet-taste-masking effect, young children usually can’t differentiate between any of the flavors in any given pouch. I found it helpful to consider what’s going on for me whenever I have a smoothie — I can often pull outsome of the individual flavors, but not all of them. And even the singular tastes I can detect,I can only detect because I already know what they taste like.
And even the singular tastes I can detect,I can only detect because I already know what they taste like.
Babyhood and toddlerhood together comprise a critical period of time for learning about foods — and learning to like foods! If toddlers don’t have experience with actual vegetables, they may be less likely to enjoy them down the road. As pediatrician Dr. Natalie Muth told the Times, “kids need the taste of what the actual food is to come to like it later.” IOW, apple-pear-kale pouches aren’t helping children learn to love kale.
All of this is to say that children don’t learn much about foods (if anything at all) from pouches — they’re not becoming familiar with the foods or even the flavors included — which is a problem because this is a huge piece of how children come to actually like foods.
-
Pouches aren’t as nutritious as manufacturers would like us to believe.
There is ahuge problem in the way these pouches are marketed — it’s totally misleading, in my opinion.
We parents are led to believe that pouches are a great way to “get” our children to eat healthy, and that we can trust a pouch to put plenty of fruits and vegetables into our kids’ systems. Many pouches also contain foods you won’t find in conventional baby food jars, like quinoa or kale or pomegranate or avocado — and the message we are led to believe is that these inclusions make poucheseven more healthy. They contain all these awesome foodie foods! But pouches actually aren’t all that healthy, and as mentioned above, the delivery mechanism — single-texture blends that children “drink” more than they “eat” — isn’t teaching children to come to know and loveactual fruits and vegetables.
Some pouches contain added sugars (grrr), and even among those that don’t the sugar content is still disproportionate compared to the real foods they started out as. This is true of jarred baby food in general (the high-heat processing that ensures shelf-stability also nukes all the “good stuff,” including vitamins, minerals, fiber, and flavor, while leaving undesirable contents like sugar) — but some research indicates that pouches in particular tend to have higher sugar contents than baby food jars.
The lack of fiber and texture is also a huge loss — because fiber is super important for digestive health and also contributes to feeling satiated. In fact, some experts worry that because children can suck down pouches so much more quickly than they could eat the same thing (and they aren’t getting any measurable amounts of fiber from them), pouches might actually impact children’s learning about feelings of satiety.
The convenience factor, too, can be so damntempting. Because they are so easy and children like them so much, many parents (myself included — guilty) use pouches as a sort of management strategy in moments of “crisis,” to put an end to things like public tantrums or epic stretches of whining. Admittedly, this probably sends our kids some mixed messages, namely that emotional or inappropriate behavior can and will be tamed with food (read: sugar). Without being alarmist about it, it’s not unreasonable to think that these aren’t necessarily the healthy, ideal lessons many of us are aiming to teach our kids.
______
All this said — there is a time and a place for everything, and you don’t need to empty your pantry of pouches for all eternity or swear them off entirely. The problem with pouches, as it were, is only apparent if babies and toddlers are consuming them A LOT. As in, multiple pouches per day. As in, so-many-pouches are displacing other sources ofreal food.
Here are some helpful thoughts from experts on when and how to incorporate pouches:
Pouches may be a parent’s best friend in certain situations — and the hands-down “winner” in that category is TRAVEL. Whether you are making a road trip, day trip, plane trip, or whatever, having a pouch on hand for a snack can be life-saving. These kinds of situations are often about getting through them, so do what you need to anddon’t feel guilty about it!
Experts suggest having some sort of “ground rules,” so to speak, about using pouches — as opposed to using them randomly, on the fly, or as a reactive strategy to calm down your child. Put another way, they recommend making decisions about when and how you plan to use pouches ahead of time, rather than in the moment.
Put another way, they recommend making decisions about when and how you plan to use pouches ahead of time, rather than in the moment.
Look for products with no added sugar, and consider buying smaller sized pouches if they’re available.
Simply choosing to feed your child the contents of a pouch can change a lot about the situation — it reintroduces the feedingexperience to the equation, is much more interactive, and also takes more time.
If you’re going to “need” some sort of easy, on-the-go packaged food for whatever reason, don’t necessarily discount pouches. They are certainly a better choice than much of the ultra-processed food options available, such as candy or chips or cookies and the like. Sure, pouches aren’t blueberries or peas or carrots, but they’re not M&M’s. This isn’t to say that children need pouches — not at all. Pouches were made for and marketed toUS, parents. And there are plenty of reasons to like them. But our children don’t need them, and they’re certainly not benefitting from them.
This isn’t to say that children need pouches — not at all. Pouches were made for and marketed toUS, parents. And there are plenty of reasons to like them. But our children don’t need them, and they’re certainly not benefitting from them.
As we said, there’s a time and a place for everything — and pouches aren’t “all bad”! When we offer them with intention and in moderation, pouches can be wonderful. But it’s also important to see beyond the deceptive marketing that would have us believe pouches are a boon to any child’s culinary education. Not so — as always, in the end, real food wins…
How Baby Food Pouches are Made (A Behind the Scenes Look) & How We're Different
Most parents can admit to staring and staring at the supermarket shelf, looking the baby food aisle up and down, wondering what is the best possible baby food to give their baby. There are more flavors of baby food pouches available than there are cereals, but there is one thing they all have in common: the way the baby food pouches are made.
But wait, they’re 100% fruit right? They don’t list “sugar” as an ingredient… They are “organic,” brain smart, and filled with fiber. How can these squeeze pouches be badfor your little one?
When we started Amara, we knew that no one was getting more time anytime soon. So we searched high and low for the best way to bring fresh food to supermarket shelves without sacrificing essential nutrients and vitamins.
We stumbled across a technique that was used centuries ago by the Incans to preserve food. The Incans didn’t just store their food where they lived. They would climb up to the highest mountains, at a much higher elevation than where they lived, and store their food there. Why would they store their food so far away from where they cooked? It turns out the Incans were not just trying to get exercise, they were on to something. The pressure and cold of the high mountains actually preserved the food, all while maintaining the taste, texture and nutrients of fresh fruits and vegetables.
Crazy right? Well, we started researching more to see how we could use this ancient wisdom. That’s when we found the technique we use today. At Amara, we minimally process the fruits, veggies and grains so you can get the closest thing to homemade when you don’t have time to make it yourself. We just take out the water, so you can take homemade with you, anytime, anywhere.
Now that’s what we do. But what do other baby food companies do? Why are those pouches so high in sugars? Why do they have the same texture and consistency, all kind of tasting like apples?
Creating a shelf-stable pouch of baby food
Shelf-stable means that the food can sit on a shelf without refrigeration or spoilage for quite some time. Jarred shelf-stable baby food lasts for about two years. Pouch-stored shelf-stored baby food lasts for one year. This lets supermarkets and baby food companies take their time in selling the product because they don’t have to worry about spoilage.
Unfortunately, the way they create shelf-stable food isn’t exactly good for its nutritional value. They have to use processes that remove the causes of spoilage (the bad stuff), but these same processes also reduce nutrition (the good stuff).
The extraordinary high levels of heat the traditional jars and pouches are using is the major culprit. Heat breaks down vitamins and destroys enzymes that are needed for proper digestion. Now, after so much heat – you are left with a boiled down mixture that is closer to jam than wholesome fresh food.
So let’s follow how traditional baby food is made….
First, most shelf-stable baby food companies don’t process raw vegetables and fruits themselves. They buy them from other companies in the form of a puree or a concentrate. These purees and concentrates start by chopping and washing vegetables and grinding them down (which heats up the puree.) Next, stones, skins, and seeds are removed, but along with these, the fiber is also removed. This creates a smooth consistency, but babies need fiber!
This creates a smooth consistency, but babies need fiber!
So far, it’s like making homemade baby food, only maybe not so much heat because you’re not using industrial equipment (you don’t normally heat your food over 185 degrees F for a long period of time)…. But that’s not it.
Then, the puree is “deareated” to remove oxygen (which causes food to spoil) and then pasteurized. As we all know, pasteurization requires high heat for a long time to kill bacteria. This high heat-processed puree is sent to the baby food companies. If a concentrate is called for, the puree goes through an evaporator to draw out water before shipping. If you’ve ever tasted frozen juice concentrate, you know it’s like swallowing a spoonful of sugar.
Now, enter baby food companies:
Baby food companies buy these pureed (can we still call them fruits and vegetables?) and blend them to create their flavors. They sometimes add water for consistency, and they can also add other things. Acids (e.g. citric acid) is added for further bacterial control as well as to prevent browning of the product over time. Nutrient powders may also be added to make up for the lost nutritional value caused by the earlier processes.
So let’s go over that….
- Company X grinds fruit or vegetable down to a puree. Heat step to keep it shelf stable and ready to ship to Baby Company.
- Baby Company blends said purees with their recipes. May add nutrient powders, emulsifiers or acids to keep it looking presentable.
- Usually another heat step here to make sure nothing is alive (remember, we have to kill the bad stuff….Oops! There goes the good stuff too.)
Ok, so now we have that pureed recipe of baby food company X. What next?
Then the puree has to get packaged. If it’s in a jar, it’s the same process used for home canning, which requires high levels of heat. But did you know that pouches have to be heated as well? This has to be done to kill any bacteria in the pouch, but again, it raises the temperature of the food. These pouches, while convenient, do contain compounds that might leach into the food under high heat such as BPA and aluminum.
These pouches, while convenient, do contain compounds that might leach into the food under high heat such as BPA and aluminum.
So now you have your pureed heated mix according to the recipe for baby food company X. Then it’s put in a pouch. The pouch is heated AGAIN at high levels to make sure that there is no bacteria or mold in the pouch.
…. Pausing. We’re pretty far from those fresh fruits and veggies you pinned right?
Right.
So. Shelf-stability may help consumers know they’re getting unspoiled baby food, but by the end of it, fruits and vegetables have been turned into a kind of jam with no texture and not the best nutrition. (Ever wonder why your baby loves the pouches but doesn’t like the real veggies when you make them?)
Now, I want to pause here. We are all feeling pretty bad about those pouches and jars right? I mean, we didn’t paint the prettiest picture here. Because it’s not. BUT. I do want to stress here, there are moments that your baby is screaming or you’re in the car and the pouch really is the easiest option. And THAT’S OKAY. We don’t walk around in a perfect white onesie all the time, do we? We know there are times for the pouch, but just treat it as an occasional snack or dessert, not an everyday kind of thing.
And THAT’S OKAY. We don’t walk around in a perfect white onesie all the time, do we? We know there are times for the pouch, but just treat it as an occasional snack or dessert, not an everyday kind of thing.
How Amara differs
We look carefully at every single ingredient and source it the best possible way. That’s right. We don’t just use one co packer that hands us a finished product. We look at every ingredient and find the best process and combination for your little one. We don’t use additives; we don’t use emulsifiers or any of those funny fillers. We just do real food, real ingredients. We bring you the best possible baby food, without you having to chop and cook everything yourself. It's a difference you can see:
Imagine the fruits and veggies just without the water. Now that's a pouch you can actually feel proud of. At Amara, baby food is made better to taste better.
Get 15% off your first purchase with us with code:
ONLYTHEBEST
Sources:
https://www.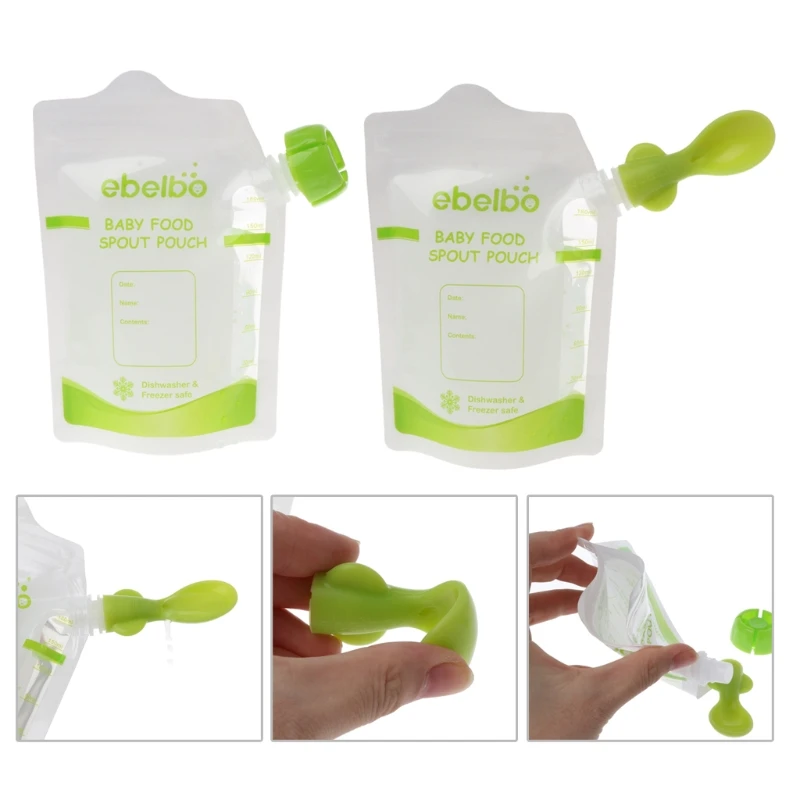 stlouischildrens.org/health-resources/pulse/pros-and-cons-baby-food-pouches
stlouischildrens.org/health-resources/pulse/pros-and-cons-baby-food-pouches
https://www.firstfiveyears.org.au/child-development/the-important-facts-on-baby-food-pouches
https://www.cleveland.com/news/2019/03/baby-food-pouches-may-pose-risks-for-development-health-when-overused.html
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31340487/
https://www.nytimes.com/2018/06/19/well/rethinking-baby-food-pouches.html
https://www.nytimes.com/2020/04/17/parenting/baby-food-pouches.html
http://science.howstuffworks.com/innovation/inventions/5-ancient-incan-inventions5.htm
USDA Table of Nutrient Retention Factors
http://nutritiondata.self.com/topics/processing#ixzz1fPecqOzH
http://www.livestrong.com/article/547867-what-does-cooking-do-to-vitamin-c/
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/raw-veggies-are-healthier/
http://www.beyondveg.com/tu-j-l/raw-cooked/raw-cooked-2f.shtml
http://feedkids.com/2010/09/freeze-dried-dehydrated-fresh-frozen-or-canned-what-is-the-best-source-of-nutrition/
Gupta et al 2013, Retention of nutrients in green leafy vegetables on dehydration; J Food Sci Technol 50 (5), 918-925.
Happy baby 15051 Baby food storage bags
Our advantages
Delivery on the day of order
Delivery works 7 days a week across the Crimea from 10:00-20:00
Wide range
children under 5 years old.
Quality Assurance
All items in my Lvenok stores carry a manufacturer's warranty. nine0004
Promotions and discounts
Be the first to know about promotions, discounts and special offers from moy Lvenok store.
Convenient self-delivery
You can pick up the order yourself in one of the stores in Simferopol.
Own warehouse
All goods are placed in moy Lvenok's warehouse equipped for storing children's goods.
Payment methods
You can pay for the purchase in any way: cash to the courier, bank card to the courier, card according to the details.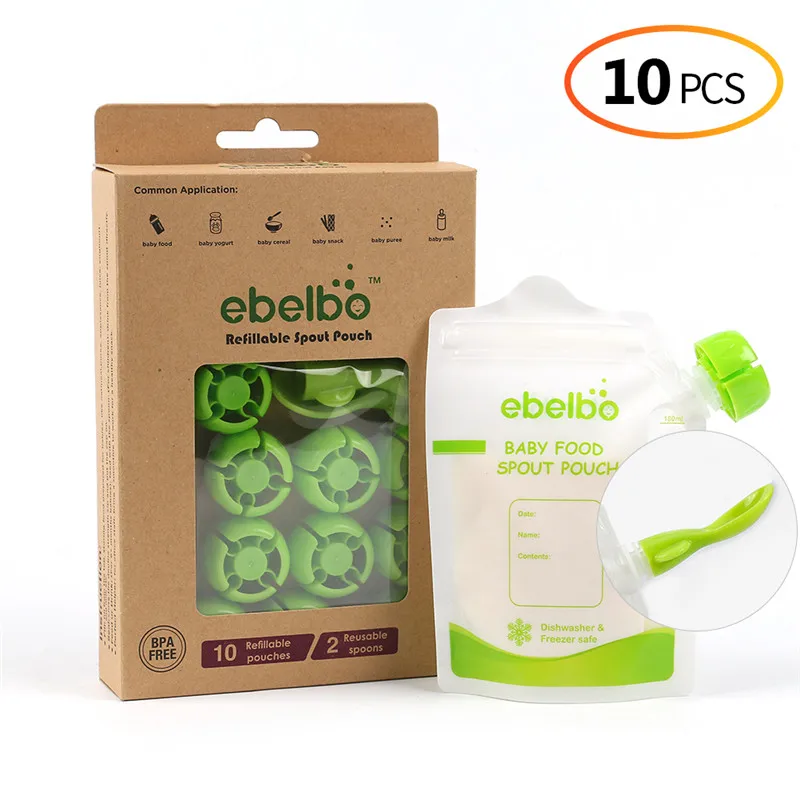 nine0004
nine0004
- 590 rub
In stock
531 r
VIP discount card price in retail stores
FOOD POUCH reusable baby food storage bags with lids and a spoon will help out on the road, on a walk or on a trip. They keep food fresh, are completely safe for the baby and are suitable for feeding the baby outside the home right from the bag. Screw the spoon onto the bag - no additional utensils are required. Packages are easily sealed, and a reliable zipper will not open during storage or transportation. Suitable for freezing and perfectly washed in the dishwasher. nine0004
COMPOSITION:
- Polyethylene terephthalate, LDPE/HDPE, polypropylene.

Reviews
Happy baby 15051 Baby food storage bags
Previous Next
Our advantages
Delivery on the day of order
Delivery works 7 days a week in the Crimea from 10:00-20:00
Wide assortment
We offer the most complete range of products for expectant mothers, newborns and children up to 5 years of age.
Quality Assurance
All items in my Lvenok stores carry a manufacturer's warranty.
Promotions and discounts
Be the first to know about promotions, discounts and special offers from moy Lvenok store.
Convenient self-delivery
You can pick up the order yourself in one of the stores in Simferopol. nine0004
Own warehouse
All goods are placed in moy Lvenok's warehouse equipped for storing children's goods.
Payment methods
You can pay for the purchase in any way: cash to the courier, bank card to the courier, card according to the details.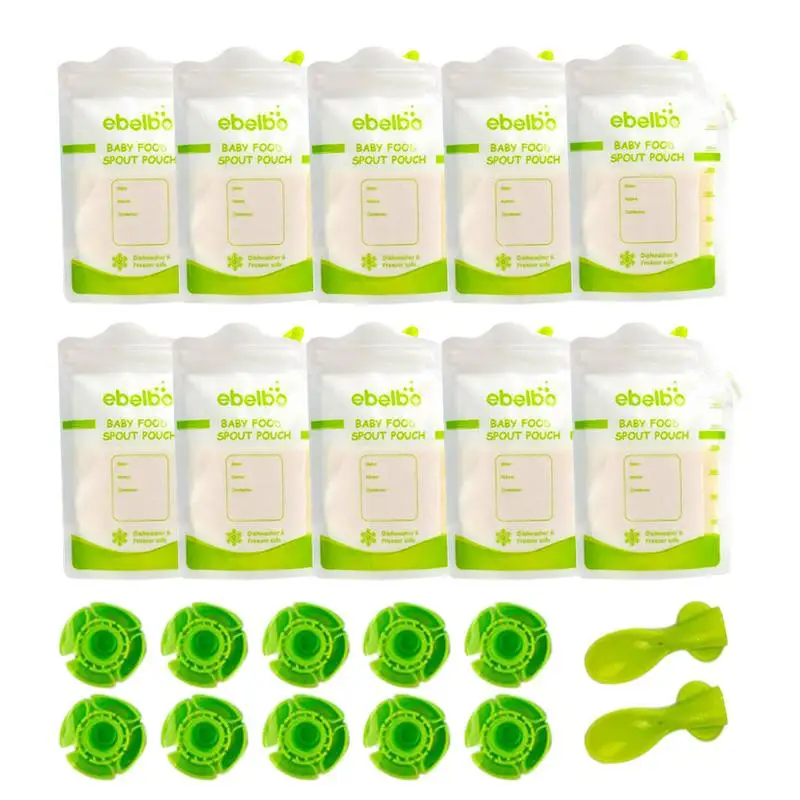
Products of this brand
Buy with this product
Do not forget to also buy
What is the safest plastic: Ecology articles ➕1, 06/15/2021
Plastic has become an integral part of our lives. Grocery containers, packages for household chemicals, children's toys, clothes, CDs, toothbrushes... If you care about your own health and the health of your loved ones, it is important to know what type of plastic the things around us are made of.
You can determine how safe a particular type of plastic is by labeling it. It is marked on the packaging with a number. Unmarked plastic is prohibited in Russia, but nevertheless it is common. Using such plastic means knowingly risking your health. nine0004
1
- PET (PET/PETE) - polyethylene terephthalate. This is plastic from which bottles, disposable cups, plates and other utensils, other containers and packaging (for sauces, cosmetics, spices) are made.
2
- HDPE (LDPE) - high density polyethylene (low pressure). Liquid containers, disposable bags, food utensils, toys, jars and containers for cosmetics and household chemicals, cans, buckets are made from this plastic.
3
- PVC - polyvinyl chloride. Food wrap is made from it, sometimes also bottles, bags, toys, since the material is quite flexible.
4
- LDPE (HDPE) - low density polyethylene (high pressure). Bags, bottles, various containers and containers, children's toys are made from it.
5
- PP (PP) - polypropylene. This material is used to produce food utensils (plates, spoons, forks, cups), jars and packaging for sour cream, yogurt, curds. nine0004
6
- PS (PS) - polystyrene. This type of plastic is most often used for the manufacture of disposable tableware, as well as foam substrates for meat, eggs, vegetables and fruits.
7
- OTHER (O) - other types of plastic. This group includes all types of plastics that are not assigned their own letter code. A wide variety of products are made from such materials, including food storage and packaging.
PET or PETE is the most common type of plastic. When reused, it releases substances that are toxic to the human body. nine0004
HDPE (HDPE) is considered relatively safe for humans, but it can release formaldehyde (a colorless gas) that adversely affects the respiratory and nervous systems.
LDPE (HDPE) is food safe. But when heated and decomposed, it can release formaldehyde.
PP (PP) can also be considered relatively safe, but it releases formaldehyde at high temperatures. In other words, absolutely safe plastic does not exist, each type of it can harm human health. nine0004
And now - plastics that are always dangerous, and not just when heated, decomposed, reused or in contact with alcohol.
Use plastic marked OTHER with care. If the dishes made from it are damaged or after the expiration date, it begins to release a carcinogen that can cause diabetes or hormonal failure. A large amount of carcinogen also releases PS (PS).
The most dangerous type of plastic is PVC. When burned, it releases very toxic dioxins into the air. The plasticizers contained in it can cause damage to the liver and kidneys, infertility, and cancer. If possible, limit the use of PVC products. nine0004
Plastic cannot be safely disposed of at home. This is possible only at specially equipped stations and factories. Plastic waste should not be thrown into the general garbage, but collected and placed in a blue container in the yard or special collection points.
In many Russian cities, containers for separate collection of recyclables are installed in the yards. From there it goes to processing.