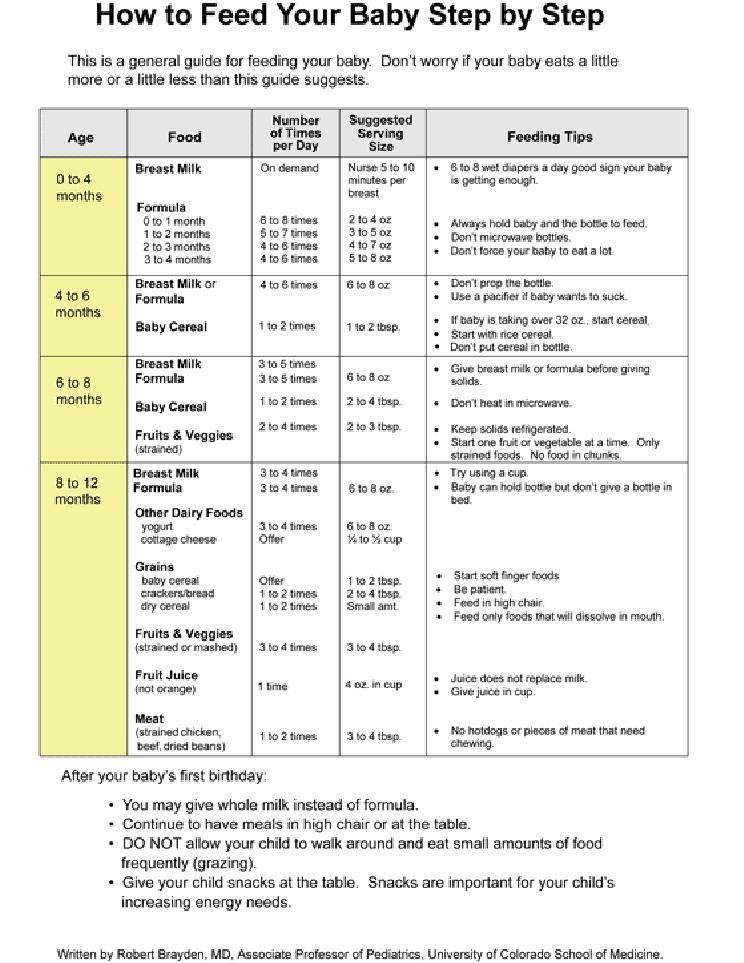
How much to feed 1 year old baby
Feeding & Nutrition Tips: Your 1-Year-Old
Log in | Register
Ages & Stages
Ages & Stages
After your child's first birthday, you'll probably notice a sharp drop in his or her appetite. Maybe your child is suddenly turning his or her head away after just a few bites and/or is resisting coming to the table at mealtimes. Despite this behavior and increased activity, there's a good reason for the change. Your child's growth rate has slowed; he or she really doesn't require as much food now.
Tips for Parents:
One year olds need about 1,000 calories divided among three meals and two snacks per day to meet their needs for growth, energy, and good nutrition. Don't count on your child always eating it that way though—the eating habits of toddlers are erratic and unpredictable from one day to the next! For example, your child may:
Eat everything in sight at breakfast and almost nothing else for the rest of the day.
Eat only the same food for three days in a row—and then reject it entirely.
Eat 1,000 calories one day, but then eat noticeably more or less over the next day or two.
Encourage, but don't pressure or force your child to eat at a particular time. Hard as it may be to believe, your child's diet will balance out over several days if you make a range of wholesome foods available.
One year olds need foods from the same basic nutrition groups that you do. If you provide your child with selections from each of the basic food groups and let him or her experiment with a wide variety of tastes, colors, and textures, he or she should be eating a balanced diet with plenty of vitamins.
Don't restrict fats from your one-year-old's menu. Babies and young toddlers should get about half of their calories from fat. Cholesterol and other fats are also very important for their growth and development at this age.
 Once your child has reached age two, you can gradually decrease fat consumption (lowering it to about one-third of daily calories by ages four to five). See Preschoolers' Diets Shouldn't Be Fat-Free: Here's Why for more information.
Once your child has reached age two, you can gradually decrease fat consumption (lowering it to about one-third of daily calories by ages four to five). See Preschoolers' Diets Shouldn't Be Fat-Free: Here's Why for more information. Be sure the food is cool enough to prevent mouth burns. Test the temperature yourself, because he or she will dig in without considering the heat.
Don't give foods that are heavily spiced, salted, buttered, or sweetened. These additions prevent your child from experiencing the natural taste of foods, and they may be harmful to long-term good health.
Your little one can still choke on chunks of food. Children don't learn to chew with a grinding motion until they're about four years old. Make sure anything you give your child is mashed or cut into small, easily chewable pieces.
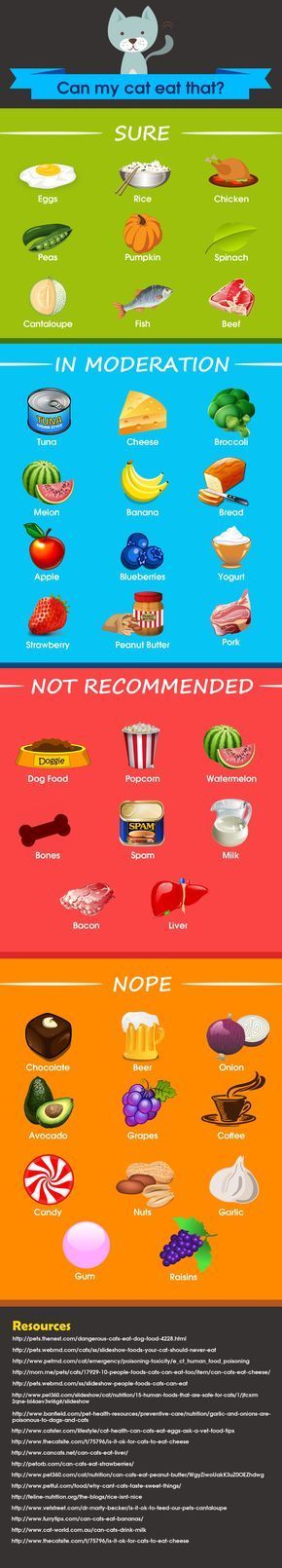
Never offer peanuts, whole grapes, cherry tomatoes (unless they're cut in quarters), whole carrots, seeds (i.
 e., processed pumpkin or sunflower seeds), whole or large sections of hot dogs, meat sticks, or hard candies (including jelly beans or gummy bears), or chunks of peanut butter (it's fine to thinly spread peanut butter on a cracker or bread).
e., processed pumpkin or sunflower seeds), whole or large sections of hot dogs, meat sticks, or hard candies (including jelly beans or gummy bears), or chunks of peanut butter (it's fine to thinly spread peanut butter on a cracker or bread). Hot dogs and carrots— in particular—should be quartered lengthwise and then sliced into small pieces.
Make sure your child eats only while seated and while supervised by an adult. Although your one-year-old may want to do everything at once, "eating on the run" or while talking increases the risk of choking. Teach your child as early as possible to finish a mouthful prior to speaking.
Additional Information from HealthyChildren.org:
- Sample Menu for a One-Year-Old
- Making Sure Your Child is Eating Enough
- Serving Sizes for Toddlers
- Selecting Snacks for Toddlers
- Airplane Choo Choo: A Feeding Guide for Children (National Dairy Council)
- Last Updated
- 10/29/2020
- Source
- Section on Obesity (Copyright © 2016 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
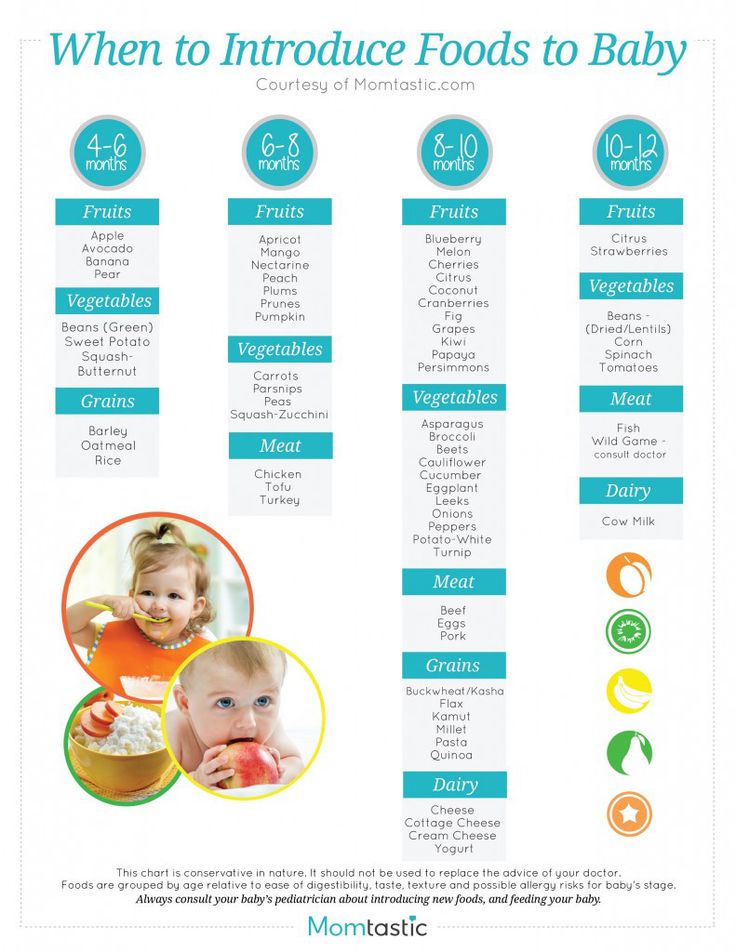
Age-by-age guide to feeding your toddler
- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby Names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
Your growing toddler can enjoy a wide range of foods. Expect your little one to have about 2 cups of milk or yogurt, 3 ounces of whole grains, 1 cup each of fruit and vegetables, and 2 ounces of protein a day. Help your toddler eat well by offering healthy foods including dairy products, iron-fortified cereals, whole grains, fruit, vegetables, and protein. Limit added sugars and watch out for choking hazards. It's fine to give your toddler a vegan or vegetarian diet as long as you make sure to include enough essential nutrients.
Photo credit: Thinkstock
Use this guide to find out what and how much to feed your toddler. Don't worry if your child eats more or less than the amounts suggested – they're meant as general guidelines.
Your toddler may actually seem to eat less than before, and that's perfectly normal at this stage. If you wonder whether your child is getting enough calories, follow this guideline: The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children get about 40 calories a day for every inch of height.
(See our article about what to feed children younger 12 months.)
What to feed a 1-year-old
Developmental milestones
- Can use a spoon (though proficiency will take a while!)
What to feed
- Whole milk
- Other dairy products (soft pasteurized cheese, full-fat yogurt and cottage cheese)
- Iron-fortified cereals (oats, barley, wheat, mixed cereals)
- Other grains (whole wheat bread, pasta, rice)
- Fruits (melon, papaya, apricot, grapefruit)
- Vegetables (broccoli and cauliflower "trees," cooked until soft)
- Protein (eggs, beans, thinly spread peanut butter, small pieces of meat, poultry, boneless fish, or tofu)
- Honey
How much per day
- 2 cups milk, or 2 cups yogurt, or 1 1/2 to 2 ounces cheese
- 3 ounces grains, at least half whole grains (1 ounce = 1 cup cold cereal, 1/2 cup pasta or rice, one slice of bread)
- 1 cup fruit (fresh, frozen, or canned.
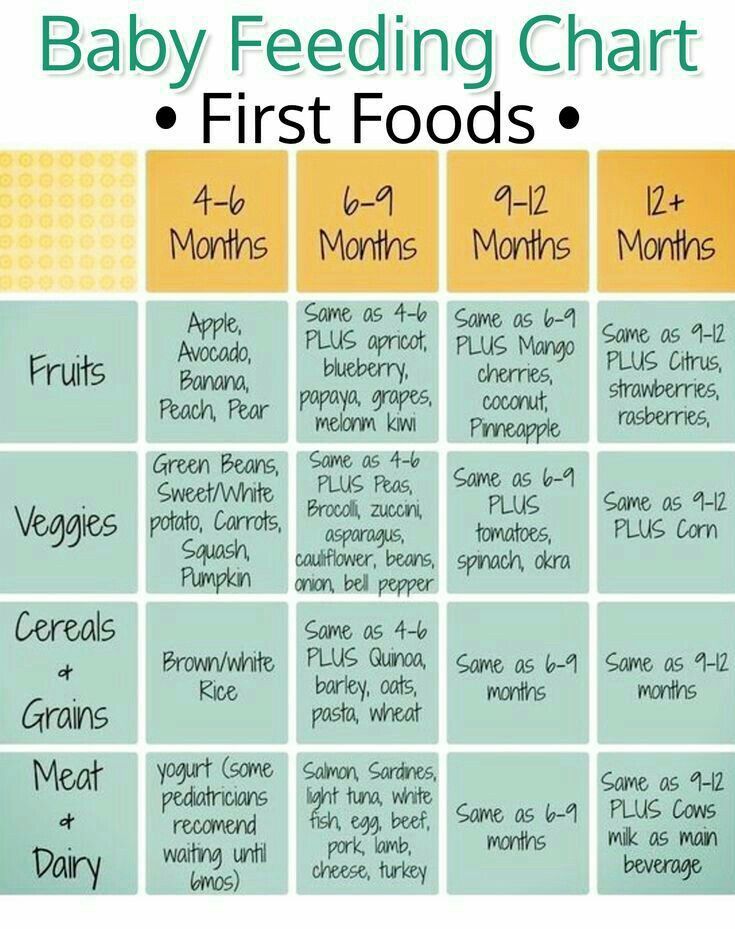 Cut fresh fruits into very small pieces.)
Cut fresh fruits into very small pieces.) - 1 cup vegetables (a variety cut in small pieces and cooked well)
- 2 ounces protein (1 ounce = one slice of sandwich meat, about 1/3 of a chicken breast, 1/4 can of tuna, 1/4 cup cooked dry beans, or one egg)
Advertisement | page continues below
Feeding tips
- Experts used to say you shouldn't give a young child eggs, fish, or peanut products because the child might develop a food allergy. But the latest research from the American Academy of Pediatrics found no evidence to support this claim. Talk to your child's doctor if you have a family history of food allergies.
- Limit added sugars. Toddlers' added-sugar intake should be no more than 10 percent of their total daily calories. Keep in mind that these sugars and syrups creep into common foods toddlers love, from breakfast bars to mac n' cheese to flavored drinks. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and try to steer clear of foods that list 1 gram or more of "Added Sugars.
 "
" - Choking is still a danger. Learn more about which foods pose the greatest hazard.
What to feed a 2-year-old
Developmental milestones
- Self-feeding
- Eagerness to make own food choices
What to feed
- Low-fat milk (It's okay to switch to low-fat or nonfat milk once your child is older than 2, but check with your child's doctor if you have questions.)
- Other dairy products (diced or grated cheese, low-fat yogurt, cottage cheese, pudding)
- Iron-fortified cereals (oats, barley, wheat, mixed cereals)
- Other grains (whole wheat bread and crackers, bagel pieces, pretzels, ready-to-eat cereal, pasta, rice)
- Fruits (sliced fresh or canned)
- Dried fruit, soaked until soft to prevent choking (apples, apricots, peaches, pears, dates, pitted prunes)
- Vegetables (a variety cut in small pieces and cooked well)
- Protein (eggs, beans, thinly spread peanut butter, small pieces of meat, poultry, boneless fish, or tofu)
- Combo foods like macaroni and cheese, casseroles
How much per day
- 2 cups milk, or 2 cups yogurt, or 1 1/2 to 2 ounces cheese
- 3 ounces grains, at least half whole grains (1 ounce = one slice of bread, 1 cup ready-to-eat cereal, or 1/2 cup of cooked rice, cooked whole wheat pasta, or cooked oatmeal)
- 1 cup fruit (fresh, frozen, canned, or dried.
 Cut fresh fruits into very small pieces.)
Cut fresh fruits into very small pieces.) - 1 cup vegetables (a variety cut in small pieces and cooked well)
- 2 ounces protein (1 ounce = 1/4 cup cooked dry beans or peas, one egg, 1 ounce of meat, poultry, or fish)
Feeding tips
- Experts used to say you shouldn't give a young child eggs, fish, or peanut products because the child might develop a food allergy. But the latest research from the American Academy of Pediatrics found no evidence to support this claim. Talk to your child's doctor if you have a family history of food allergies.
- Limit added sugars. Toddlers' added-sugar intake should be no more than 10 percent of their total daily calories. Keep in mind that these sugars and syrups creep into common foods toddlers love, from breakfast bars to mac n' cheese to flavored drinks. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and try to steer clear of foods that list 1 gram or more of "Added Sugars."
- At this age, children can have strong opinions about food.
 Let your child have a say in what to eat, while you provide the balance, boundaries, and encouragement to make healthy choices.
Let your child have a say in what to eat, while you provide the balance, boundaries, and encouragement to make healthy choices. - Choking is still a danger. Learn more about which foods pose the greatest hazard.
What if we're vegetarians?
If you're a vegan or vegetarian, you can still provide your infant or toddler with everything she needs. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and American Academy of Pediatrics agree that well-planned vegetarian and vegan diets are fine for infants and toddlers. Just pay attention to make sure your child gets plenty of the following nutrients:
- Vitamin B12: Vegetarians can get this nutrient from milk products and eggs. Vegans can use fortified soy beverages, cereals, and meat substitutes.
- Vitamin D: Breastfed babies should get an additional 400 IU per day from fortified cow's milk or soy milk.
- Calcium: Vegan babies may need calcium-fortified foods, beverages, or supplements.
 Check with your doctor or a dietitian.
Check with your doctor or a dietitian. - Zinc: This important nutrient helps the immune system and can be found in beans, fortified cereal, milk, and wheat germ.
- Iron: You can find this mineral in iron-fortified cereal or supplements. Serve with foods high in vitamin C – like oranges, tomatoes, and strawberries – to improve iron absorption.
- Protein: Vegetarians can get added protein from yogurt and eggs. Vegans can get plant proteins from beans, cereals, and fortified soy milk.
- Fiber: Good sources of fiber include whole grain breads, fortified cereals and pastas, and high-fat plant foods like sunflower butter and avocados.
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
Karisa Ding
Karisa Ding is a freelance health writer and editor with expertise in preconception, pregnancy, and parenting content. A mother of two, Ding finds great joy in supporting new and expectant parents by providing information they need for the life-changing journey ahead. Ding lives in San Francisco with her family.
Ding lives in San Francisco with her family.
Advertisement
The diet of a one-year-old child / What and how to feed a baby - an article from the "What to feed" section on Food.ru
Principles of nutrition for a child per year
If a child has 6-8 teeth per year, and he looks with interest into the plates of his parents , this does not mean that it is time for him to change to a common table. At the very least, the diet of a one-year-old child should be very different from that of an adult.
Adult food is often unbalanced, prepared in an unsuitable way for a baby, contains a lot of sugar, salt and spices. Such food harms the growing organism. Therefore, first of all, build the right diet.
-
It is recommended to eat 3-4 times a day for 300-400 g plus 1-2 snacks between feedings.
-
From the first year of life, the baby can chew solid food.
-
If lactation continues, breastfeed until 2 years of age.
-
Avoid fast food and sugary sodas.
A one-year-old's diet might look like this:
-
8:00 - breakfast.
-
12:00 - lunch.
-
16:00 - afternoon tea.
-
19:00 - dinner.
-
21:00 - snack.
Advice
600 ml is the recommended amount of milk for a baby to drink daily.
If breastfeeding, feed your baby after waking up, in the afternoon after dinner, or before bed. You need to feed at the same time with a delay of 15-20 minutes.
Proper nutrition helps to form reflexes, which improves the absorption of nutrients in the body.
How much should a one year old child eat
A baby's diet should include 1000-1400 kcal per day. The calculation is as follows: multiply the weight of the child by 100 kcal.
The calorie content is distributed as follows:
-
Breakfast - 250 kcal;
-
lunch - 350 kcal;
-
afternoon tea - 200 kcal;
-
dinner - 200 kcal.

Healthy food contains enough vitamins, minerals and nutrients: proteins, carbohydrates and fats. It is necessary to include fatty foods in the child's diet: milk, butter, sour cream, cream. Fatty food promotes the absorption of trace elements in the body.
Interesting fact
10% of one-year-old children in Russia are overweight. They are not properly fed, they are allowed to eat fast food and drink soda. Obesity at an early age leads to vascular disease, heart disease, diabetes, mental disorders and other serious disorders.
Child's menu per year
Balanced menu includes specialty meals designed to meet the needs of children, plus "adult" foods: meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, fruits, vegetables, cereals, bread, pastries and legumes.
It is good to eat milk porridge for breakfast. It is a rich source of vitamins, minerals and fiber. Fiber is good for intestinal microflora: it regulates the balance of beneficial and harmful bacteria.
Meat is a source of animal protein, indispensable for a growing organism. WHO recommends that children eat 60–70 g of meat per day. It can be served as steam cutlets, meatballs in soup, or any other attractive form. Offal and meat products are harmful to a one-year-old child.
It is also desirable to gradually expand the vegetable menu. Vegetables contain many vitamins, minerals, trace elements and organic acids that are beneficial to the body. Gradually introduce boiled carrots, cabbage, zucchini, turnips, beets into the baby's diet.
Legumes are a source of vegetable proteins. Beans, lentils, green peas diversify the baby's diet. They contain useful trace elements, vitamins, as well as coarse fiber. Therefore, legumes need to be boiled and chopped in a blender. Beans should not be eaten too often either, as they cause bloating and, in rare cases, diarrhea.
Fruit diet improves immunity, especially in winter when the body is weakened. Fruit goes well with cereals or served as smoothies and juices.
Sugar and salt lead to nutritional imbalances, cardiovascular problems and obesity. Avoid cakes, pastries, chocolate bars and other sweets. Replace sugar with fructose, which is abundant in fruits, or honey.
What to drink? Water, lots of water. It is advisable to make sure that the child has drunk a glass of liquid after eating. He himself will not ask, because he still does not know how. When a one-year-old child is thirsty, he begins to act up. Sweet soda should be excluded from the diet of the baby.
What foods should not be given to a one-year-old child
Approach the baby's menu carefully. Do not rush to transplant him to an adult table. Among the forbidden foods for a one-year-old child:
-
Fried foods, including chips, snacks and fast food.
-
Meats and offal such as sausages and sausages, other than liver, heart and tongue.
-
Curds, ice cream, condensed milk, koumiss.
-
Mushrooms.

-
Products containing colorants and flavors.
-
Cream confectionery containing vegetable protein.
-
Carbonated drinks.
-
Concentrates like Doshirak.
-
Caramel and gum.
-
Pickled vegetables and fruits.
-
Spices and condiments, including ketchup, mayonnaise and other sauces.
-
Smoked products.
Advice
Buy food from stores labeled "Baby Food". The label often says for what age this product is intended. There are no additives, GMOs, artificially grown products and other things in baby food. Read the contents of the label carefully. Often unscrupulous manufacturers use false labels for marketing purposes.
What to do if the child does not want to eat
It is difficult to persuade children to try unusual food. There are four ways to deal with this problem:
-
Lead by example before introducing new foods.
 When he sees that adults eat with appetite, he involuntarily wants to try it. But remember that the baby gets used to a new food only from the tenth time.
When he sees that adults eat with appetite, he involuntarily wants to try it. But remember that the baby gets used to a new food only from the tenth time. -
Try one new product at a time. A child needs time to get used to it. New food should be combined with what is already loved.
-
Don't force your child to eat something they don't like. Let him choose what he wants.
-
Food should be as simple and familiar as possible. Children do not like dishes with many obscure ingredients like casseroles.
Tip
Babies eat better when they are relaxed. Work up an appetite during a walk or after a game. Never teach children to watch TV or smartphones while eating. Eating should be extremely calm.
Benefits of pre-mixed formula
Don't be afraid to switch babies to formula instead of breastfeeding. They benefit the baby's body, unlike, say, goat's milk. Goat's or cow's milk is too low in nutrients and high in protein. Its digestion increases the load on the gastrointestinal tract of the child and leads to obesity.
Its digestion increases the load on the gastrointestinal tract of the child and leads to obesity.
Three advantages of mixtures:
-
Contains polyunsaturated fatty acids that are beneficial for the baby's body.
-
Rich in probiotics and prebiotics, live bacteria that maintain normal intestinal microflora.
-
Give your child the necessary balanced intake of vitamins and minerals.
Tip
Formula will not replace breast milk.
What can be done?
Set a clear power mode. Make a menu for every day: breakfast, lunch, afternoon tea, dinner, snack. Write down the products and their quantity. The children's menu should be varied and balanced, contain sufficient nutrients, minerals and vitamins. Introduce new foods gradually and do not force the child to eat something that he does not want in a year.
Read more about children's nutrition:
-
How to improve your child's health during the off-season.
 Simple tips from an expert
Simple tips from an expert -
How to improve your child's appetite. Instructions for parents
-
6 healthy fiber foods. What to feed your child to be healthy
Russian Union of Pediatricians
Nutrition for children aged 1 to 3 years
The period from 1 to 3 years of life is a crucial stage in the transition to an adult type of nutrition, which has certain features. In order to ensure that all the necessary nutrients enter the child's body and at the same time prevent an excess of individual nutrients, nutrition should be balanced and varied.
The daily amount of food for children aged 1 to 1.5 years should be 1000-1200 g, from 1.5 to 3 years - 1200-1500, the amount of food in one feeding should not exceed 300-350 ml. The diet consists of three main meals per day and two snacks. It is considered optimal when breakfast is 25% of the total energy density of the diet, lunch is 30–35%, dinner is 20%, and additional meals are about 10%. In general, the child can eat the same food as the rest of the family.
In general, the child can eat the same food as the rest of the family.
In the nutrition of a child of 1–3 years of age , must be present daily: animal or poultry meat, dairy and sour-milk products, vegetables, fruits, bread, cereals, vegetable and butter; fish and eggs are included in the diet 2-3 times a week.
Cereal products: bread - 2-3 servings per day, cereals and side dishes - 1 time per day
Fruit and/or vegetables: at least 5 times a day
Dairy products: at least 3 servings per day (including those used to make cereals, yoghurts, fermented milk drinks, cottage cheese, infant formula or breast milk).
Domestic pediatricians recommend, when compiling a diet for children aged 1–3 years, preference should be given to specialized children's dairy products of industrial production that meet high quality requirements and safety indicators for this age. Most children's dairy products are additionally enriched with vitamins and/or minerals and other biologically active components, taking into account the physiological needs of children of this age. At the same time, in foreign recommendations, children over 1 year old are offered the gradual introduction of whole cow's milk, which is rich in fats necessary for proper growth and development, the absorption of vitamins A and D, the development of the brain and nervous system of the child.
At the same time, in foreign recommendations, children over 1 year old are offered the gradual introduction of whole cow's milk, which is rich in fats necessary for proper growth and development, the absorption of vitamins A and D, the development of the brain and nervous system of the child.
Meat dishes: 2-3 times a day
Fish dishes: 2-3 servings per week
Eggs: 2-3 per week
Dietary fats: 3-4 teaspoons of butter and/or vegetable oils per day
When cooking, use the minimum amount of salt and sugar, and do not add them to industrial products.
Offer your child a variety of foods and let them choose their own. Children love to eat on their own, so if possible, offer food that the child can eat with their hands.
It is important to remember that a baby can choke on pieces of food, so whatever you give your baby should be crushed or cut into small pieces that can be easily chewed.
Do not give a small child: nuts, whole grapes, cherry tomatoes (unless quartered), whole carrots, seeds (such as pumpkin or sunflower seeds), round candies, legumes, raisins, because a child can eat them choke.