How often do you have to feed baby chicks
Chick Care: Feeding and Watering Dos and Don’ts
by Gail Damerow in Farm Animals, Horses & Pets
Newly hatched chicks are not entirely helpless, but like any other babies, they must have access to clean water and be kept well fed. Gail Damerow shares some expert tips to ensure you’re ready for your new arrivals.
Buff Orpington chick. Photo © gina pina, via Wikimedia Commons.
Newly hatched chicks are not entirely helpless, but until they grow a full complement of feathers, you’ll need to keep them warm, dry, and safe. Like any other babies, they must also be kept clean and well fed. Here are a few dos and don’ts for making sure you’re meeting your new arrivals’ food and water needs.
DO make sure chicks must have access to fresh, clean water at all times. A waterer should be the correct size for your flock’s size and age — chicks should neither use up the available water quickly nor be able to tip over the fount. The basin should be high enough to keep the water level between a chick’s eye and the height of its back. This way, a chick drinks more and spills less. Chicks shouldn’t be able to roost over or step in the water. The easiest way to provide water to newly hatched chicks is to use a 1-quart (1 L) canning jar fitted with a metal or plastic watering base, available from most feed stores and poultry-supply catalogs.
DON’T be tempted to cut corners and provide water in an open dish or saucer. Chicks will walk in it, tracking litter and droppings that spread disease. They’ll tend to get wet and chilled, and the stress will open the way to disease. Some chicks may drown. Damp conditions in a brooder — whether caused by spilled water or a leaky waterer — are to be avoided.
To minimize stress, chicks should drink soon after they hatch and eat within five hours. Photo © Gail Damerow, excerpted from Storey’s Guide to Raising Chickens, 4th Edition.
DO clean waterers daily. Use warm water and vinegar or other poultry-approved sanitizer. When choosing a waterer for your chicks, make sure to select one with a drinker that is easy to clean. A fount that’s hard to clean won’t be sanitized as often as it should be.
Use warm water and vinegar or other poultry-approved sanitizer. When choosing a waterer for your chicks, make sure to select one with a drinker that is easy to clean. A fount that’s hard to clean won’t be sanitized as often as it should be.
DON’T make chicks travel far for their water. Initially place drinkers no more than 24 inches (60 cm) from the chicks’ heat source. Later, as you move the chicks to expanded housing, make sure they never have to travel more than 10 feet (3m) to get a drink. When upgrading to a larger waterer, DO leave old waterers in place for a few days — at least until the chicks get used to drinking from the new source.
DO make sure chicks are drinking before they start eating. They seem to experience less of a problem with sticky bottoms if they a good dose of water before they get a belly full of feed, especially when the feed is commercially formulated chick starter.
DON’T feed layer ration to chicks, not even as an emergency measure if you run out of starter. The high calcium content of layer ration can seriously damage a chick’s kidneys. If you run out of starter, or you forget to pick some up and you have chicks to feed, you can make an emergency starter ration by cracking scratch grains in the blender or, if you have no scratch, by running a little uncooked oatmeal through the blender and mixing it 50/50 with cornmeal. Don’t use this mixture any longer than necessary, though — grains are high in calories and low in the protein, vitamins, and minerals a chick needs for good growth and health.
The high calcium content of layer ration can seriously damage a chick’s kidneys. If you run out of starter, or you forget to pick some up and you have chicks to feed, you can make an emergency starter ration by cracking scratch grains in the blender or, if you have no scratch, by running a little uncooked oatmeal through the blender and mixing it 50/50 with cornmeal. Don’t use this mixture any longer than necessary, though — grains are high in calories and low in the protein, vitamins, and minerals a chick needs for good growth and health.
The end cut from a tissue box makes a handy first feeder to encourage baby chicks to peck for food. Photo © Gail Damerow, excerpted from Storey’s Guide to Raising Chickens, 4th Edition.
Soon after they hatch, chicks start looking for things to peck on the ground. If they don’t see anything else on the ground, they’ll peck their own feet.
DO sprinkle a little starter ration on a paper towel or paper plate to help them find feed. As soon as most chicks are pecking freely, remove the feed-covered paper before it starts to hold moisture that attracts mold. For the remainder of the first week, put the starter in a shallow lid or tray, such as a shoebox lid. When the chicks start scratching out the feed, switch to a regular chick feeder.
As soon as most chicks are pecking freely, remove the feed-covered paper before it starts to hold moisture that attracts mold. For the remainder of the first week, put the starter in a shallow lid or tray, such as a shoebox lid. When the chicks start scratching out the feed, switch to a regular chick feeder.
DO choose a feeder that works for your space. A good feeder prevents chicks from roosting over or scratching in feed and has a lip to prevent billing out (wasting feed by scratching it out with their beaks). If your space is limited, use a feeder that has a small footprint. One such style is a base, similar to a drinker base, that screws onto a feed-filled quart (1 L) jar, and has little openings through which the chicks can peck. If the brooder is roomy enough, a hanging feeder is ideal because it holds a lot of feed, so chicks are less likely to run out during the day; it minimizes feed wastage because chicks can’t scratch in it and are less likely to bill out feed if the feeder is maintained at the proper height (the same height as the birds’ backs). ; and it is easy to raise on the hanger to the proper height as the chicks grow.
; and it is easy to raise on the hanger to the proper height as the chicks grow.
A chick feeder that screws onto a quart (about a liter) jar has a small footprint, making it ideal where brooder space is limited. Photo © Gail Damerow, excerpted from Storey’s Guide to Raising Chickens, 4th Edition.
DON’T leave feeders empty for too long, and be careful not to let uneaten feed accumulate. Fill feeders in the morning, and let the chicks empty them before filling them again. Leaving feeders empty for long periods of time invites picking, but letting stale or dirty feed accumulate is unhealthful, so strike a healthy balance. Clean and scrub feeders at least once a week.
DO think about good gut health! Old-time poultry keepers spiked their chicks’ water with a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar per gallon (3.75 L). Chickens like it, and the poultry keepers saw positive effects. Could they have known that the beneficial bacteria and yeasts naturally colonizing a chick’s intestines prefer acidic conditions? I doubt it. The science of probiotics is all pretty new. But we know now some reasons why it was/is beneficial. Encouraging the growth of beneficial gut flora fends off harmful organisms through a process called competitive exclusion. Chicks raised in an incubator acquire beneficial gut flora more slowly than chicks raised under a hen. To enhance their immunity, probiotics are available that are either dissolved in water or sprinkled on feed to give the chicks an early dose of the same gut flora that will eventually colonize their intestines. A hand substitute is live-culture yogurt, but a little goes a long way — giving chicks too much yogurt will cause diarrhea.
The science of probiotics is all pretty new. But we know now some reasons why it was/is beneficial. Encouraging the growth of beneficial gut flora fends off harmful organisms through a process called competitive exclusion. Chicks raised in an incubator acquire beneficial gut flora more slowly than chicks raised under a hen. To enhance their immunity, probiotics are available that are either dissolved in water or sprinkled on feed to give the chicks an early dose of the same gut flora that will eventually colonize their intestines. A hand substitute is live-culture yogurt, but a little goes a long way — giving chicks too much yogurt will cause diarrhea.
Text excerpted and adapted slightly from
Storey’s Guide to Raising Chickens, 4th Edition © 2017, 2010, 1995 by Gail Damerow. All rights reserved.Gail Damerow
Gail Damerow has written extensively on raising chickens and other livestock, growing fruits and vegetables, and related rural know-how in more than a dozen books,… See Bio
Related Books
Articles of Interest
-
Give the gift of joy this holiday season with books that encourage readers to create, explore, and learn something new.
 From the ultimate guide to baking the perfect pie to an empowering collection of joyful verses for kids to sing out loud, these books offer … Read More
From the ultimate guide to baking the perfect pie to an empowering collection of joyful verses for kids to sing out loud, these books offer … Read MoreUncategorized
by Storey Digital Editors
-
After food is squeezed down the esophagus, the first destination is the stomach. As stomach muscles churn, food mixes with a pool of strong acid and enzymes. Stomach acid is about as acidic as lemon juice. In this activity, we can watch food break down … Read More
For Kids
by Betty Choi
-
Fermented foods sit at the intersection wherein the personal and individual meets the communal.
 Our fermented foods are, of course, filled with their own communities, teeming with bacteria, yeast, and fungi that intersect with our senses and our own microbiomes. But they connect us to … Read More
Our fermented foods are, of course, filled with their own communities, teeming with bacteria, yeast, and fungi that intersect with our senses and our own microbiomes. But they connect us to … Read MoreFood
by Julia Skinner
-
LIZ: When did you begin drawing? NDUBISI: I've always been drawing as far back as I can remember. It's been a long and beautiful journey. LIZ: Where do you get inspiration? NDUBISI: I get inspired by everything, literally, the way God … Read More
Author Interviews
by Liz Bevilacqua and Ndubisi Okoye
-
Squash is a fabulous storage crop that offers filling, sweet, comforting fall and winter fare.
 When it is the season, nothing makes me happier than the smell of hearty foods roasting in the oven and the bounty that greets me at the table. This stuffed … Read More
When it is the season, nothing makes me happier than the smell of hearty foods roasting in the oven and the bounty that greets me at the table. This stuffed … Read MoreRecipes
by Brittany Wood Nickerson
Baby Chick Care | Purina Animal Nutrition
Skip to Content (Press Enter)Backyard Poultry
Backyard Poultry
Starting a Flock : Caring for Chicks
Purina Animal Nutrition
Bringing home your baby chicks is an exciting milestone in raising backyard chickens. The three key essentials for raising strong baby chicks: Warm, water and feed. Start chicks strong by providing a complete chick starter feed from day 1 through week 18.
For those of us welcoming new chicks, how can we give them a solid start?
To best transition chicks into a flock, provide comfort, care and complete nutrition from day one. A chick never gets over a bad start. The actions we take before chicks arrive and the care we provide in the first few days can help set-up our chicks to be happy and healthy long-term.
Before baby chicks arrive: Set up the brooder
Set up your brooder about 48 hours before your chicks arrive. This allows time for bedding and equipment to dry and the temperature to set.
Equipment for day one includes:
- Brooder: The brooder is the first home of new chicks. Be sure it is comfortable, warm and draft-free with at least 3 to 4 square feet per chick. The area should be circular and expandable.
- Heat lamp: Assemble a heat lamp in the center of the brooder for bird warmth. Hang the heat lamp about 20 inches above the litter, with 2.
 5 to 3 feet between the lamp and the guard walls. The temperature under the heat lamp, or comfort zone, should be 95 degrees Fahrenheit and adequate room in the brooder should be available for the chicks to get out from under the heater if they get too hot. After week one, gradually reduce heat by 5 degrees Fahrenheit each week until reaching a minimum of 55 degrees.
5 to 3 feet between the lamp and the guard walls. The temperature under the heat lamp, or comfort zone, should be 95 degrees Fahrenheit and adequate room in the brooder should be available for the chicks to get out from under the heater if they get too hot. After week one, gradually reduce heat by 5 degrees Fahrenheit each week until reaching a minimum of 55 degrees. - Bedding: Add an absorbant wood shavings bedding to the floor of the brooder. Place bedding 3 to 4 inches deep to keep the area dry and odor free. Remove wet bedding daily, especially around waterers. Do not use cedar shavings or other types of shavings that have a strong odor because the odor could affect the long term health of the bird.
- Lights: Provide 18 – 22 hours of light for the first week. Then reduce light to 16 hours through the growing period or to the amount of light they will receive when they are 20 weeks of age. The amount of light intensity required would be provided by a 40 watt bulb for each 100 square feet (10’ x 10’) of floor space.

- Feeders: Offer 4 linear inches of feeder space for each bird. Clean egg cartons filled with feed make excellent and easily accessible feeders for young chicks. Provide low-lying feeders, or trough feeders, for after the transition.
- Waterers: For every 25 chicks, fill two 1-quart waterers with room temperature water and place them in the brooder. To help water stay at room temperature, place the waterers in the brooder, outside the comfort zone (do not position underneath the heat lamp), 24 hours prior to the chicks’ arrival.
Introduce baby chicks to water
Once chicks arrive, introduce them to the brooding area. Water, at room temperature, should be available, but wait a couple hours to introduce feed.
This gives chicks a couple hours to drink and rehydrate before they start eating, fresh, quality water is essential for healthy chicks. Dip the beaks of several chicks into the water to help them locate it. These chicks will then teach the rest of the group to drink. Monitor the group to ensure all chicks are drinking within the first couple hours.
These chicks will then teach the rest of the group to drink. Monitor the group to ensure all chicks are drinking within the first couple hours.
Teach baby chicks to eat
After chicks have had a chance to rehydrate, provide the nutrients they need through a complete chick starter feed.
Provide a chick starter feed with at least 18 percent protein to help support the extra energy needed for early growth. The feed should also include amino acids for chick development; prebiotics, probiotics and yeast for immune health; and vitamins and minerals to support bone health.
To provide all the nutrients chicks need for a strong start, choose a starter-grower feed from the Flock Strong® Feeding Program. Complete starter feed options include: Purina® Start & Grow®, Purina® Start & Grow® Medicated, Purina® Organic starter-grower and Purina® Flock Raiser.
First, teach the chicks to eat by placing feed on clean egg flats, shallow pans or simple squares of paper. On day 2, add proper feeders to the pens. Once chicks have learned to eat from the feeders, remove the papers, pans or egg flats.
Adjust feed as baby chicks develop
To keep feed fresh: Empty, clean and refill waterers and feeders daily. Also, raise the height of feeders and waterers so they are level with the birds’ backs as chicks grow.
As chicks mature, their nutritional needs change. At age 18 weeks, adjust the feed provided to meet the birds’ evolving nutrition needs.
Transition layer chicks onto a higher-calcium complete feed, like Purina® Layena® Crumbles or Pellets, when they begin laying eggs at age 18 to 20 weeks. For meat birds and mixed flocks, choose a complete feed with 20 percent protein, like Purina® Flock Raiser® Crumbles and feed this diet from day one through adulthood.
Thinking about getting your first chicks? Visit our Baby Chick Resource Center for everything you need to start chicks strong.
Related Education Content
Article
2- to 3-Week-Old Baby Chicks
Article
4- to 5-Week-Old Baby Chicks
Article
6- to 8-Week-Old Chicks: Moving to the Chicken Coop
Article
A Guide to Backyard Self-Sufficiency
Article
Adjust Nutrients in Chicken Feed as Birds Grow
Article
Backyard Chickens Are a Kids’ Best Friend
Article
Benefits of Raising Chickens
View All Backyard Poultry Education
diet in the first days of life, chicken feed norms
The diet of chickens, especially small ones, is different from the diet of adult chickens. Many breeders who raise chickens in the household are interested in how and what to feed the chicks so that they develop properly. For healthy growth, chickens require a balanced diet in sufficient quantities. The composition of the products depends on the direction and age of the chicks. Many breeders who raise chickens in the household are interested in how and what to feed the chicks so that they develop properly. For healthy growth, chickens require a balanced diet in sufficient quantities. The composition of the products depends on the direction and age of the chicks. |
Content:
- What does healthy chicks eat?
- General rules for formulating rations
- What to feed chickens?
- General rules for feeding
- Feed for chickens of various ages
- Feeding frequency
- Feeding Features
- Farmer's Councils
What does a healthy chicken diet consist of?
Sources of proteins, vitamins, micro and macro elements are products of plant and animal origin, as well as substances synthesized in the laboratory. For the production of finished formulations in the factory, only high-quality proven raw materials are used. In feed for laying hens and broilers are introduced:
|
It is quite difficult to independently calculate the proportions and mix the components thoroughly without the appropriate equipment.
General dietary guidelines
The terms of growing meat breeds are 1.5-2 months, laying hens - up to six months. During this time, the bird should gain weight of 2.5-3 kg. To accelerate the growth of muscle mass in broilers, it is recommended to use specialized feed. It fully meets the needs of the bird in proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. The composition and consumption of feed should be appropriate for the age of the chicks.
At 1-2 weeks of life, the foundation of the skeleton is laid in chickens, muscle mass increases at an average pace. At this time, it is necessary to introduce a sufficient amount of proteins, fiber, and mineral components into their diet.
In the growth phase, chickens are gaining weight intensively. They need as many amino acids and proteins as possible, which act as a building material for cells, as well as complex carbohydrates. The dose of vitamins and minerals received with food is increased.
The dose of vitamins and minerals received with food is increased.
At the finishing stage, the amount of carbohydrates is reduced so that the broilers gain more muscle mass, and not fat. At this stage, it is important to prevent weight loss. For these purposes, finishing compound feed is introduced into the diet.
What to feed chickens?
Cereals form the basis of the diet.
| Corn | One of the most useful and nutritious ingredients. Corn is the leader among grains in terms of protein content, while it contains less fiber than other cereals. The product is easily digested and well absorbed. |
|---|---|
| oats | Source of many amino acids. It is considered a dietary product, but contains a lot of fiber. In large quantities, it causes blockage of the intestines, so its share in the composition of the feed does not exceed 20%. Oats are given in a purified form, completely removing the film from the grains. The size of the fraction depends on the age of the bird. Sifted oatmeal is usually added to prestarter formulations. The size of the fraction depends on the age of the bird. Sifted oatmeal is usually added to prestarter formulations. |
| Wheat | Contains a large amount of vitamin E, B. Feed wheat is usually used in bird feed. The percentage can be up to 30%. |
| Rye | It is a source of a number of useful proteins, but contains too much mucus, which negatively affects the digestive system of chickens. It is added to some feeds in small quantities. |
| Barley | Practically not inferior to oats in useful properties, but also contains a lot of fiber. It is introduced into the composition only in a purified and sifted form. |
| Buckwheat | Despite the fact that the product contains components useful for poultry, it is rarely used. Basically, it is added to granulated feed, because. in loose form, chickens do not peck it. |
| Bran | Products of processing grain crops are introduced to increase the caloric content of the diet. By themselves, they have no nutritional value, so they are rarely used. By themselves, they have no nutritional value, so they are rarely used. |
Peeled vegetables are used as succulent feed.
| Potato | Improves poultry digestion, promotes the absorption of nutrients. It is introduced in boiled dehydrated form. In the process of preparing food, it is unacceptable to use green potatoes, since poisonous solanine has formed in them. |
|---|---|
| Beet | It normalizes the work of the intestines, prevents its blockage, provides the needs of chickens for vitamin B2, carotene, sugar. It can be given both fresh and boiled. The content of beets in the diet is about 15%. |
| Pumpkin | It contains a lot of vitamins and microelements. The product is added in an amount not exceeding 15% of the total volume. |
Protein components provide the daily requirement for amino acids. Protein sources are also rich in vitamins and minerals. They can be of plant and animal origin. Amino acids are well absorbed by the body. Animal proteins are obtained from various types of flour:
They can be of plant and animal origin. Amino acids are well absorbed by the body. Animal proteins are obtained from various types of flour:
- fish. This product makes up to 8% of the diet, but is not used in broiler feed so that the meat does not have a specific smell;
- bone. In terms of the amount of proteins, it is not inferior to cereals, and at the same time it is rich in fats (11%) and vitamins A and E. It is given to chickens from a month old;
- blood. The product is rich in essential amino acids, but in high concentrations it provokes indigestion. Its share in the diet should not exceed 4%;
- pen. This component is used as an available source of protein to balance the feed composition. It is added in small amounts (up to 2%).
Dairy products are also a source of well-digestible animal protein: cottage cheese or whey. Their inclusion in feed mixtures for laying hens increases the egg production and fertility of chickens.
Legumes are richest in vegetable proteins:
- soy in terms of percentage and qualitative composition of proteins and amino acids is practically not inferior to products of animal origin, it also contains vitamins and minerals;
- peas also provide protein requirements for poultry, although to a lesser extent; chickens do not eat it well because of the specific smell and taste, therefore, no more than 10% is introduced into the feed;
- soybean and sunflower meal and cake are an inexpensive, highly digestible source of amino acids. In compositions for adult chickens, their share is 15-17%, for chickens and young animals - 10%.
General feeding rules
Each individual should consume approximately 15-30 g of food per day: how much depends on the breed, weight of the chicks, and the intensity of their development. In general, the amount of feed each time should be such that the young hens will eat it in 30 or 40 minutes. The remains must be removed from the feeders so as not to deteriorate, and the feeders themselves must be washed and dried. The remains must be removed from the feeders so as not to deteriorate, and the feeders themselves must be washed and dried. |
If the chicks do not eat the feed given to them often, then its rate should be reduced. If, on the contrary, the food is eaten quickly, then it is desirable to increase its volume.
Feed for chickens of various ages
| PC-2 | Designed for chicks under 7 weeks old. It is produced in the form of finely ground grains, designed for an insufficiently unformed digestive system, easily digestible, contains all useful trace elements. |
|---|---|
| PC-3 | Balanced mix for young animals 8-20 weeks old. Promotes rapid growth and proper formation of the reproductive system. It is produced in the form of grains with medium-sized fractions. |
| PC-5 | Designed for broiler chickens from 2 weeks to 1 month of age. It consists of a complex of easily digestible components that stimulate a set of muscle mass. |
| PC-6 | It has similar characteristics, but is designed for broilers older than a month. |
All types of feed can be divided into three groups:
| carbohydrate | Protein | Vitamin |
|---|---|---|
| Promote accelerated growth and muscle mass gain. Their composition is dominated by cereals and vegetables. Chickens digest foods high in carbohydrates well, which cause a slowdown in metabolism and rapid weight gain. Such feeds are designed for broilers and increase the average carcass weight. | Such compound feeds are developed mainly for laying hens. A large amount of protein increases the productivity of the bird, improves the palatability of the eggs, and makes the shell stronger. | Strengthen the immune system, help to survive the winter period. Usually produced in the form of concentrates, which enrich the main diet. |
According to the form of release, the compositions are of 2 types.
| Loose ones consist of fine-grained components. The disadvantage of such compositions is that they are worse absorbed. The chicken chooses tasty crumbs from the feed, and the less appetizing ingredients are thrown away. As a result, the bird receives less nutrients. In addition, a lot of dust remains in the feeder. However, it is impossible to completely abandon loose compositions. Chickens in the first weeks of life are not able to swallow and digest large granules, therefore they can peck only small grains. For broilers, loose compound feed can be introduced into the diet from the first days of life, and for laying hens - from the second week. When using dry mixes, it is important to provide the hens with sufficient drinking water. |
Expanded feed is produced by short-term heat treatment under high pressure. Nutrient mixtures are in the form of granules and contain liquid components in their composition.
However, when heated, some of the vitamins are destroyed. |
Feeding frequency
The first time chickens are fed on the same day they are born. Then, until the age of 7 days, the chicks of meat breeds are fed 6-8 times a day, from the 2nd week of life - 6 times, from the 3rd - 4 times a day, by the age of one month, chickens are fed three times a day. Chicks of egg breeds up to 1.5 weeks are fed 5-6 times a day, and by the month they are gradually transferred to 3 meals a day.
When choosing a mixture, it is recommended to give preference to complete formulations. However, if the breeder has enough of his own food, you can limit yourself to concentrated additives to enrich it.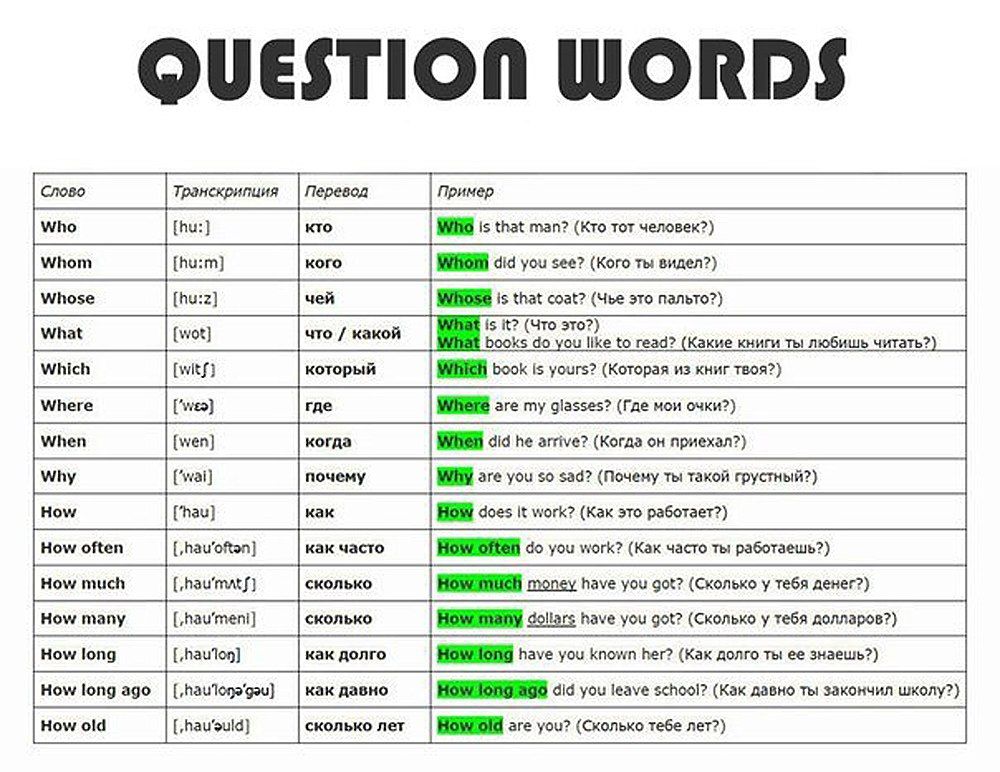 Such compositions are marked with the QC marking. Concentrates for meat and egg-bearing breeds solve different problems:
Such compositions are marked with the QC marking. Concentrates for meat and egg-bearing breeds solve different problems:
| for broilers | for laying hens |
|---|---|
|
|
It is unacceptable to use concentrates as the main feed, since an excess of nutrients is no less harmful than their deficiency. BVMB is introduced into the composition of the mash, taking into account the age of the chickens.
Feeding Features
| 1st day of life | Feeding of chickens of egg breeds begins immediately after they dry out. The first food for newborn chickens should be a hard-boiled egg. It is cut as small as possible so that the chicks can swallow small crumbs and roll it in semolina to prevent pieces from sticking to the paws and fluff. In the brooder where they are, they put a drinker with clean, boiled and cooled water. Newly hatched chicks are also fed boiled eggs under the brood hen. |
|---|---|
| 2nd day | On the 2nd day, the chicks are already given a mash of eggs and homemade low-fat fresh cottage cheese (the ratio of ingredients is 1 to 1). The formula for feeding day-old chicks should be fresh and fed every 3 hours. |
| Week 1 | From the 3rd day, chickens are fed with a more varied mixture of cottage cheese, boiled eggs, crumbly porridge from corn, oat or wheat chips (the share of cereals should be 65%). Finely chopped greens and boiled red carrots grated on a fine grater are added to them. You can give germinated grain or grass flour at the rate of 2-3 g per chicken per day. More than 5 g of such flour cannot be fed due to the high content of fiber in it. Separately, a little skimmed milk or yogurt is poured into the container; it is better not to add them to the mixers. Twice a week, a few crystals of potassium permanganate are added to the water so that it becomes slightly pink. Keep it in drinkers for no more than 0.5 hours, and then replace it with clean water. This protects chickens from stomach diseases. You can feed the chicks with special industrial compound feed for chickens from the first days of life. It is made up of products that are easily absorbed by the body of small chickens and fully satisfy all their needs. Finely chopped greens and boiled red carrots grated on a fine grater are added to them. You can give germinated grain or grass flour at the rate of 2-3 g per chicken per day. More than 5 g of such flour cannot be fed due to the high content of fiber in it. Separately, a little skimmed milk or yogurt is poured into the container; it is better not to add them to the mixers. Twice a week, a few crystals of potassium permanganate are added to the water so that it becomes slightly pink. Keep it in drinkers for no more than 0.5 hours, and then replace it with clean water. This protects chickens from stomach diseases. You can feed the chicks with special industrial compound feed for chickens from the first days of life. It is made up of products that are easily absorbed by the body of small chickens and fully satisfy all their needs. |
| 2-4 weeks | From 1.5 weeks of life, a little sunflower or soybean meal (3-4% of the total food volume), chalk or shells, bone meal (5-7% of the feed amount or 2-3 g per 1 chick). Particles of top dressing should not be more than 1-2 mm. Very fine gravel or sand washed in water is placed in a separate container. After 10 days, eggs are removed from the diet, but other components are introduced, for example, root crops (boiled potatoes, etc.). Salt, rice, rye, wheat bran (up to 10%), herbal flour (6-10%) are introduced into the menu of two-week-old chickens. From 3 weeks old, chicks gradually begin to accustom themselves to whole grains. Particles of top dressing should not be more than 1-2 mm. Very fine gravel or sand washed in water is placed in a separate container. After 10 days, eggs are removed from the diet, but other components are introduced, for example, root crops (boiled potatoes, etc.). Salt, rice, rye, wheat bran (up to 10%), herbal flour (6-10%) are introduced into the menu of two-week-old chickens. From 3 weeks old, chicks gradually begin to accustom themselves to whole grains. |
| 1 month | At this age, the young are already quite strong, they can spend time walking, where they independently find greenery, seeds of various plants, worms and beetles. If the birds are in a closed aviary and cannot pluck the grass, then they need to be given it along with grain and vegetables. In general, the share of green grass in the diet of one-month-old young animals should be about 1/3 part, no less. Grain can be given both ground and whole: the birds are already able to peck it. It can be anything: wheat, barley, corn, oats, etc. At this age, legumes can also be fed: peas, chickpeas, small beans, etc. In addition to grain products, you can feed root crops, fresh or boiled, to monthly chickens, vegetables from the garden and their tops, kitchen waste of both plant and animal origin, bran, meal and cake, compound feed. From mineral additives - bone and fish meal, chalk or lime, shell rock, salt. In addition to food, young animals should always have clean water in drinking bowls and pebbles that the bird needs for normal digestion. At this age, legumes can also be fed: peas, chickpeas, small beans, etc. In addition to grain products, you can feed root crops, fresh or boiled, to monthly chickens, vegetables from the garden and their tops, kitchen waste of both plant and animal origin, bran, meal and cake, compound feed. From mineral additives - bone and fish meal, chalk or lime, shell rock, salt. In addition to food, young animals should always have clean water in drinking bowls and pebbles that the bird needs for normal digestion. |
Chickens of meat breeds differ from egg breeds in that they need more complete proteins and vitamins, so their diet should be tailored to this feature. Therefore, it is necessary to give more protein feed, such as legumes (grains and green mass), meat and bone and fish meal, fresh kitchen waste. It should also be borne in mind that they eat more, so they need to be fed more often, especially in the first days of life.
Farmer's councils
When changing nutrition, the sensitivity of chickens to changes in composition should be taken into account. For this reason, birds should be transferred to a different diet gradually, over 3-5 days, daily adding new food to the usual food, gradually increasing its amount.
For this reason, birds should be transferred to a different diet gradually, over 3-5 days, daily adding new food to the usual food, gradually increasing its amount.
There should always be fresh water in the drinker, in which a little potassium permanganate is diluted - so much so that the liquid does not turn pink.
It is advisable to mix common salt (up to 5 g per 1 kg of the mixture) and ground egg shells into the feed.
The main disadvantage of self-prepared mixtures is the fragility of their storage. In contrast, prepared feed can be left in the feeder for as long as the chicks need to saturate.
In our company, you purchase safe, certified mixtures with high nutritional value. Products exceed the requirements of GOSTs in quality. At your request, it is possible to develop an individual recipe for specific chicken breeds.
The MEGAMIX company cooperates with a network of dealers in Moscow and regions. You can specify the terms of order and delivery by phone +7 (8442) 97-97-97 or on our website.
Free consultation
Ask a question to a specialist or order a price list
Telephone
Comment
09.11.2020
What and how to feed chickens from the first days of life: recommendations and photo review
Everyone who decides to have fluffy lumps - chickens, hopes that he will be able to grow a strong and strong livestock. Doing this at home is not so difficult if you approach nutrition and bird care in the right way. Unfortunately, very often the cause of the death of young animals is precisely the wrong diet. In order to prevent this from happening, you need to know what to feed the chickens, when and how to do it correctly in accordance with their age needs.
Features and rules of feeding
A chicken is essentially a child, and all children need to be fed correctly and nutritiously. To avoid possible negative consequences in the future, a balanced diet should be established literally from birth. If you are buying day old chicks from a hatchery in the market, ask how long ago they hatched and if they have been fed. Set the feeding schedule for your feathered babies. At first, they will have to be fed every 2 hours, but this is not for long, after the chickens celebrate their one-month anniversary, only 3 feedings will be enough for them.
If you are buying day old chicks from a hatchery in the market, ask how long ago they hatched and if they have been fed. Set the feeding schedule for your feathered babies. At first, they will have to be fed every 2 hours, but this is not for long, after the chickens celebrate their one-month anniversary, only 3 feedings will be enough for them.
In addition to a balanced diet, your chicks should always have clean and fresh water. Some breeders recommend periodically soldering chickens with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Others consider it poisonous and argue that with the slightest violation in the proportions in the process of preparing the solution, it can bring harm to the birds, not benefit.
Newly hatched chicks only
The first feeding of the chicks should take place immediately after they are dry. Nature has programmed the brain of a newborn chicken in such a way that immediately after he swallows something on his own for the first time in his life, this will start the mechanisms for the formation of the “correct” digestive system and the feeding reflex.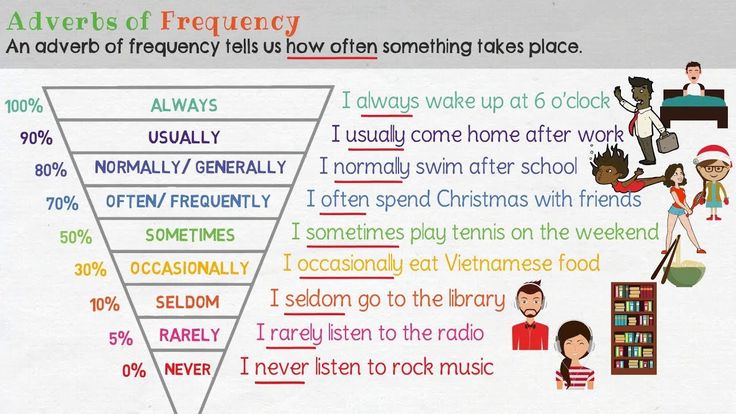 The process of leaving the egg itself is very energy-intensive. In order to somehow compensate for these energy costs, the so-called yolk sac is provided, which will serve as a source of nutrients for the newborn for the first 10-12 hours of life.
The process of leaving the egg itself is very energy-intensive. In order to somehow compensate for these energy costs, the so-called yolk sac is provided, which will serve as a source of nutrients for the newborn for the first 10-12 hours of life.
In order not to provoke a deficiency of these same nutrients in your hatched birds, immediately offer them food. Small corn grits are ideal for the first feeding. Scatter it simply on the floor of the cage or on the cardboard, so it will be more convenient for the chicks to peck at it. After that, take care of drinking, in the first 24 hours of life, the chicks will benefit from a 3-5% glucose solution - a powerful source of energy. It's great if you also add vitamin C there, at the rate of 10 g per 10 liters of liquid.
Day old
Many people are accustomed to feeding small day old chicks hard-boiled chicken eggs. And more recently, they began to talk about the fact that it is wrong to use such food for chickens in the first days of life.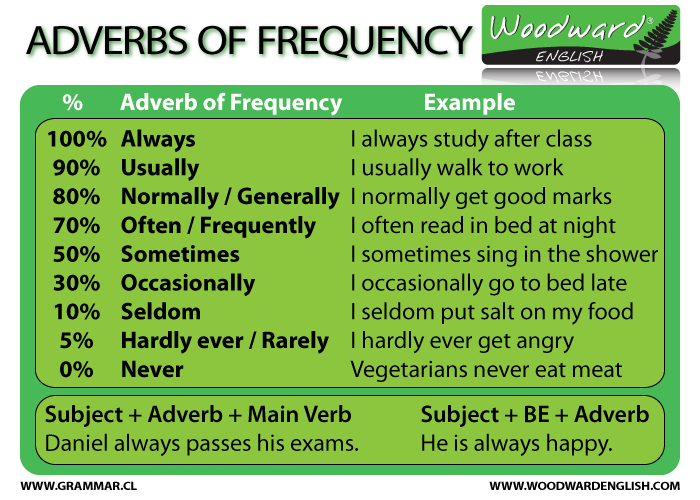 The egg does not give the proper load on the chicken stomach, which interferes with the formation of the correct muscles of the gastrointestinal tract. Protein oversaturates the body of the chick with proteins, and the yolk with fats. And this, in turn, negatively affects the process of assimilation of B vitamins, which are essential for the nervous system of chickens.
The egg does not give the proper load on the chicken stomach, which interferes with the formation of the correct muscles of the gastrointestinal tract. Protein oversaturates the body of the chick with proteins, and the yolk with fats. And this, in turn, negatively affects the process of assimilation of B vitamins, which are essential for the nervous system of chickens.
Although there is a successful experience of growing chickens at home on chicken eggs, it is probably not worth neglecting the latest research in this area either. Therefore, it is still preferable to dilute corn grits for chickens on the second day of life with such cereals as wheat, barley, semolina, oatmeal or millet. Make sure that all the chicks peck at the grain.
If a chick has an empty stomach, it is better to remove it from the common cage and feed it separately until its appetite returns to normal. Recall that daily babies need to be fed every two hours (that is, more than 10 times a day).
In addition to mixtures of cereals, starting from two or three days of age, finely chopped greens, cottage cheese, and wet mash are introduced into the diet of chickens.
Dairy products, a source of calcium and proteins, deserve special attention in the diet of feathered babies. In addition to cottage cheese, do not forget about kefir and yogurt. If the chicks refuse to voluntarily consume these products, they will have to drink yogurt from a pipette. Thanks to this, the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract of your small pets will be populated with beneficial microflora. Of course, he does not forget about greenery, from the third day of life, the chickens can already eat it. Young nettles, dandelions, clover, green onions from their own garden are the best food for chicks.
Weekly
At the age of one week (7 days) we continue to feed the chickens with mixtures of cereals, herbs and cottage cheese, the consumption rate during this period is 10 grams of feed per chick. We add wet mash with the same cereals and boiled potatoes or grated carrots to the diet, red carrots are especially useful. Starting from the 6-10th day of life, you can introduce mineral supplements, such as small shells, chalk, do not forget to water the chicks. We put a container with sand - in it the chickens not only swim with pleasure, but can also peck some grains of sand. For them, this is very useful - the esophagus is cleared and the food in the stomach is better ground.
We add wet mash with the same cereals and boiled potatoes or grated carrots to the diet, red carrots are especially useful. Starting from the 6-10th day of life, you can introduce mineral supplements, such as small shells, chalk, do not forget to water the chicks. We put a container with sand - in it the chickens not only swim with pleasure, but can also peck some grains of sand. For them, this is very useful - the esophagus is cleared and the food in the stomach is better ground.
Monthly
Three-week-old and one-month-old chicks can already spend most of their time in the pen. You can no longer chop the grass for them, as before, but hang bunches of herbs in bunches so that they can peck at the greens they like the most. You can give the birds more mash, but it's time to wean them off the "children's" cereals. For them, crushed grain is already suitable, and from the age of one and a half months and whole. Since the babies are in the stage of active growth, increase the proportion of minerals and vitamins in their feed.
Mix three-week-old chicks with meat and bone or fish meal, fish oil, pieces of sea fish. Some breeders prefer to feed their chicks with special baby food balanced for their age requirements.
Care considerations
In addition to a balanced diet, home chicks must be provided with the necessary comfort and care. It is better to settle them in well-ventilated cages, it is not bad if it is possible to provide them with walking. The cage needs to be cleaned every day. For convenience, a newspaper is laid on the floor where day old chicks live, which is easily removed as it gets dirty with droppings. The floor in the cage where chicks older than 10 days live is covered with sawdust. So that your feathered babies do not get stressed, feed them at the same time and keep the cage at a constant temperature and sufficient light.
Wash drinkers and feeders daily, especially after wet mashes. The slightest violation of sanitary conditions can entail not only diseases, but also pestilence among young animals.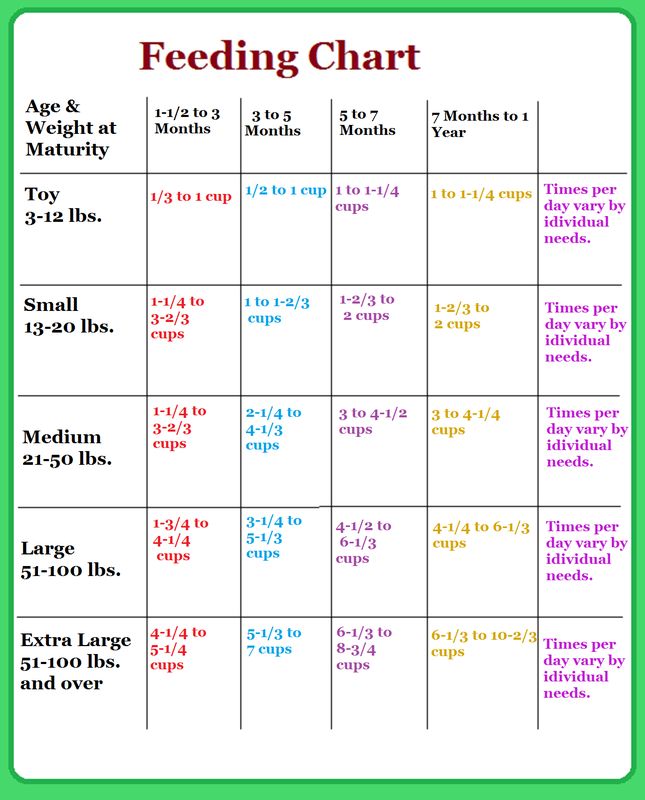


 The advantages of expanded compositions include:
The advantages of expanded compositions include: