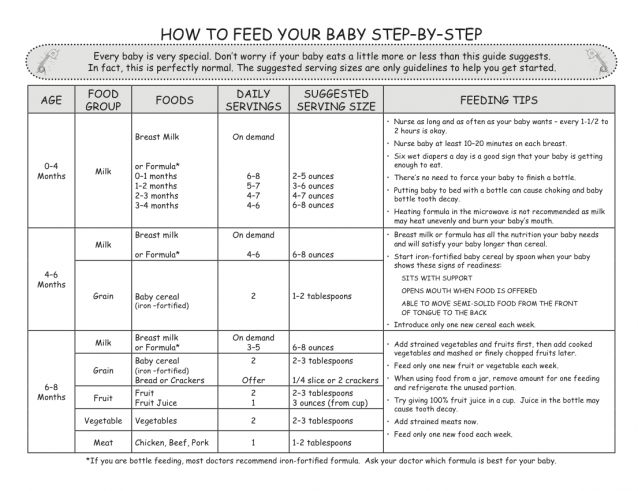
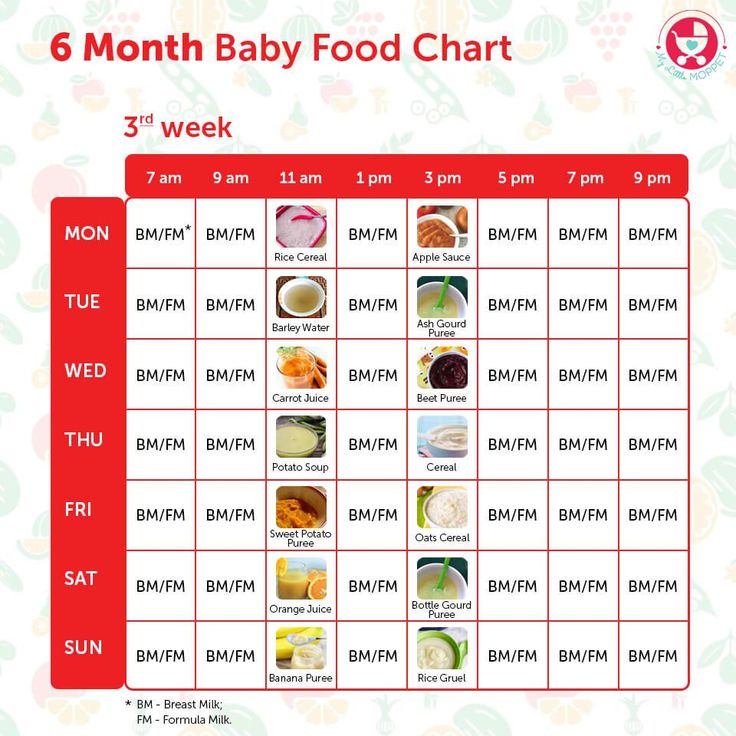
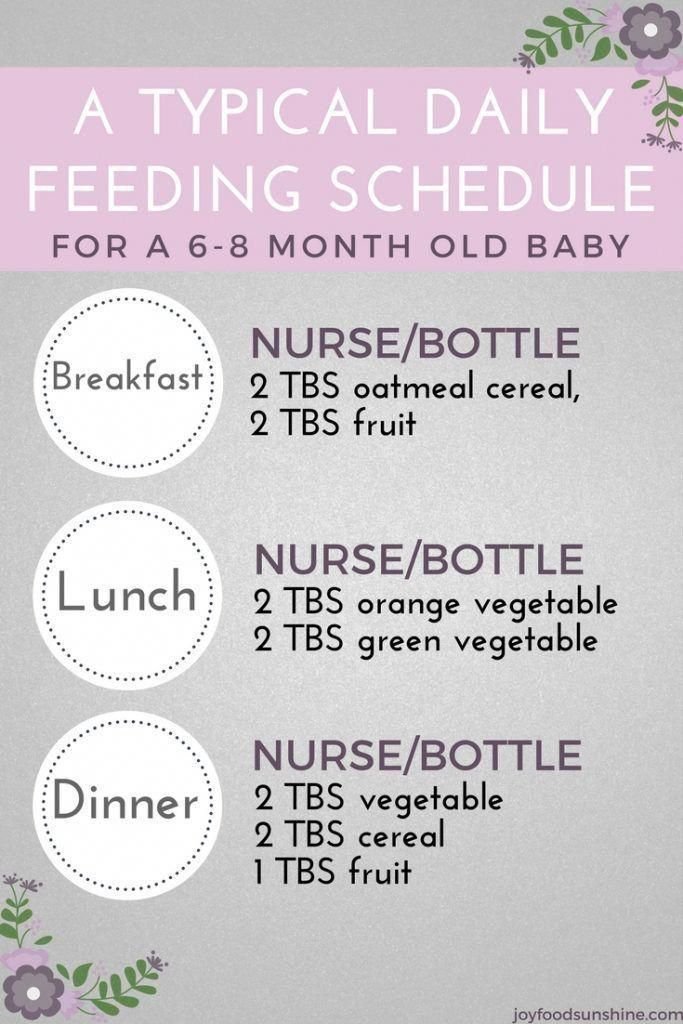
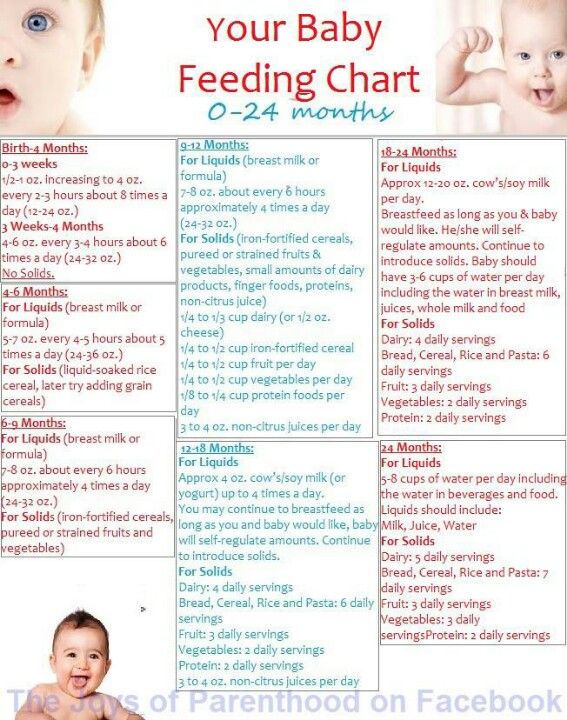
How often to feed 1 year old baby
1 Year Old Feeding Schedule (With Sample Meal Plans)
Here’s a look at sample one year old feeding schedules to help you manage (or create!) your routine. I have options for one year olds taking bottles, being breastfed, or being on all solids—plus sample menu plans!
One Year Old Feeding Schedule
Once a baby turns one and is eating meals and snacks, it can help to establish a routine to make it all easier on you to manage. Feeding kids is a lot of work and a basic feeding schedule is a great place to start.
This is meant to offer guidance and to be adjusted for your reality, whatever that may look like, since I know that no two families have the same schedules or eating preferences.
Sample 1 Year Old Feeding Chart
I’m going to share three versions of a sample feeding charts to give you an idea of the time intervals between meals based on when the kiddo wakes up and goes to bed. Generally speaking, 2-3 hours between solid food is a good rule of thumb—though always remember that your child may be hungrier some days than others and may need that timeframe adjusted.
Version 1
This example is for a toddler who’s taking milk in a sippy cup with meals (or drinks water with meals). Let’s assume wake up time is a little after 6 and bedtime is 7 pm. There may or may not be a morning nap, but there is an assumed afternoon nap from about 1-3 pm.
- 6:30 am: Breakfast
- 9 am: Snack
- 12 pm: Lunch
- 3 pm: Snack
- 5:30 pm Dinner
TIP: There could be a simple Bedtime Snack in the mix if needed before bed.
Version 2
This example is for a toddler who’s still drinking bottles and has water with meals. Let’s assume wake up time is 7 and bedtime is 8 pm. There may or may not be a morning nap, but there is an assumed afternoon nap from about 1-3 pm.
- 7 am: bottle
- 8 am: Breakfast
- 10 am: Snack
- 12 pm: Lunch
- 1 pm: bottle
- 4 pm: Snack
- 6 pm Dinner
- 7:30 pm: bottle
TIP: We want to wean kids from bottles by 2 at the latest, and the sooner you do it, the easier it often is. Work on transitioning the milk consumption to be with meals during the one year old year, rather than separate standalone bottles, especially if it seems to be limiting hunger for solids.
Work on transitioning the milk consumption to be with meals during the one year old year, rather than separate standalone bottles, especially if it seems to be limiting hunger for solids.
Version 3
This example is for a toddler who’s breastfed and has water with meals. Let’s assume wake up time is 6:30 am and bedtime is 7:30 pm. There may or may not be a morning nap, but there is an assumed afternoon nap from about 1-3 pm. There of course may be more nursing sessions in the mix here if the child is nursed on demand, so adjust as needed for your real life.
- 6:30 am: breastfeeding
- 7:30 am: Breakfast
- 9:30 am: Snack
- 12 pm: Lunch
- 1 pm: breastfeeding
- 4 pm: Snack
- 6 pm: Dinner
- 7 pm: breastfeeding
TIP: If the child doesn’t seem hungry for snacks, you don’t always have to do them. They may be full from the breastmilk and solids. If breast feeding seems to be limiting hunger for solids, you can consider tapering down the daytime sessions if you want.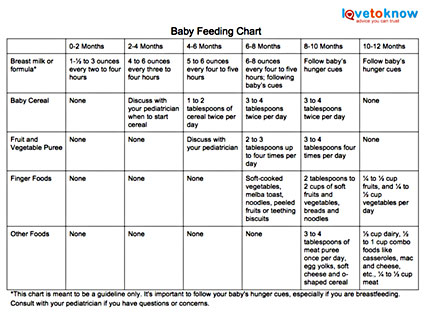 (No pressure, just know that some kids aren’t hungry enough for all meals and snacks and breastmilk during their one year old year so something could be adjusted if desired.
(No pressure, just know that some kids aren’t hungry enough for all meals and snacks and breastmilk during their one year old year so something could be adjusted if desired.
1 Year Old Meal Plan
I prefer to have a general framework for when meals happen because it helps me to plan the rest of the day. It also helps the kids to generally know what to expect and when, even if it’s as simple as learning that we go outside after morning snack and do our bedtime routine after dinner.
TIP: Find a week’s worth of Sample Meals for Toddlers here.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often do you feed a 1 year old?
Toddlers generally eat around every 2-3 hours, but that may vary depending on their own unique hunger.
How many bottles should a 1 year old have per day?
After turning 1 year, a child may be having a few bottles, but we want to transition over to sippy cups of milk served with meals by 18-24 months. If the child doesn’t seem hungry for solids, that could be a good reason to start tapering down separate milk feedings.
If the child doesn’t seem hungry for solids, that could be a good reason to start tapering down separate milk feedings.
How many meals should a one year old have each day?
Most one year olds eat 3 main meals and 2 snacks. That may vary based on whether there are bottles or breastfeeding in the mix.
How many oz should a one year old eat?
The best guide for the amount of food any child should eat is their own unique hunger. Start with smaller portions and allow more according to their hunger. (Read more about the Division of Responsibility in Feeding for more of the reason behind approaching meals this way.)
Why doesn’t my one year old eat foods they loved as a baby?
There are may possible reasons, but there are two common ones. First, one year olds grow less rapidly than they did as babies and are often less hungry. This may mean they eat fewer and less foods than they used to. Second, there is a normal developmental phase known as neophobia where kids are more fearful of new and less familiar foods.
This may mean they eat fewer and less foods than they used to. Second, there is a normal developmental phase known as neophobia where kids are more fearful of new and less familiar foods.
Both can happen at this age and can look like “pickiness” to parents. (It’s frustrating, I know, but my goal is to simply point out that there are often clear reasons behind the behavior we’re seeing.)
Picky Eating in One Year Olds
I hear from a lot of parents with 14-19 month olds who are suddenly “picky” and aren’t interested in the food that they used to love as a baby. Here’s what to keep in mind if that describes your situation:
It is very normal for one year olds to grow less rapidly than they did as babies, and to have a correspondingly lower appetite. It is very common for parents to see kids eating less and fewer foods and assume it’s “pickiness” when in fact the child is simply not as hungry as we expect them to be.
Try serving smaller portions, spacing out meals or snacks a bit, and letting it be okay if the child eats less than you expect.
Also developmentally, kids this age are exploring all of their boundaries—from the color of their socks to the fork they prefer to whether or not they want to walk on the sidewalk—so it’s normal to see some of this show up at the dinner table.
This is not a sign that anything is necessarily wrong, but is it usually a normal part of the kids realizing they are independent from us, have the power to say “no” (and get a reaction), and voice their opinions.
Remember: It’s not your job to “get” your child to eat. It’s your job to offer a variety of food that is tasty, easy for them to chew, and developmentally appropriate. It’s also our job to set the routine for when and where meals happen and what things are like during meals—we sit in our chairs, we don’t throw our food, etc. It’s their job to decide how much of the food to eat and which foods.
If we expect these factors during toddlerhood, it’s much easier to empathize and understand why they are happening—and realize that our kids are doing the normal work of figuring out their world.
TIP: Toddlers go through a normal phase called “neophobia” where they are naturally more skeptical of less familiar foods (or even foods they haven’t seen in a few days or weeks). Read up on that developmental stage so you can keep what you’re experiencing in perspective.
How do I know if my toddler is eating enough?
The general rule of thumb is to consider if the child is growing, gaining weight, and meeting milestones. Do they mostly seem happy? If the answers to all of those are yes, chances are very high that the kiddo is eating plenty. But, if your gut tell you that something is off or your pediatrician is concerned with growth (such as falling off of the child’s own unique growth curve), you may need additional help from your pediatrician or a feeding therapist.
TIP: I recommend Thrive by Spectrum Pediatrics and Lutz, Alexander & Associates Nutrition Therapy for personalized feeding therapy. My ebook How to Relax about Picky Eating can help too.
Best Tips for Success
- Plan to have a general feeding schedule, that can adjust to realities of life, to make it easier on you to plan—and easier for the kids to know what to expect from their day.
- Allow 2-3 hours between solids, adjusting for the child’s hunger as needed.
- Aim to transition off of bottles by 18-24 months. (And learn why you don’t need Toddler Formula unless medically advised.)
- Here are more Sample Toddler Meal Plans to refer to as the kids grow and a basic Toddler Nutrition Chart.
- Learn more about how to Wean a Toddler and how to Night Wean.
- If you’re worried about picky eating, this post on what’s normal will help.
- For help on understanding how to trust the kids to eat to their own unique fullness, start with the Division of Responsibility and then see this post with FAQ on Picky Eating.
I’d love to hear your feedback on this post, so please comment below to share!
Feeding Your 1- to 2-Year-Old (for Parents)
Toddlers this age are moving toward a diet more like your own. Keep introducing new flavors and textures. Food preferences are set early in life, so help your child develop a taste for healthy foods now.
Keep introducing new flavors and textures. Food preferences are set early in life, so help your child develop a taste for healthy foods now.
Toddlers have little tummies, so serve foods that are packed with the nutrients they need to grow healthy and strong. Avoid sweets and empty calories. Don’t give your child sugar-sweetened drinks, such as soda, juice drinks, sports drinks, and flavored milks. Limit 100% fruit juice to no more than 4 ounces a day, and serve juice in a cup, not in a bottle.
Your toddler will continue to explore self-feeding, first with their fingers and then with utensils at around 15–18 months of age. Give your child lots of chances to practice these skills, but lend a hand when frustrations arise. As skills develop, step back and let your little one take over.
Toddlers like to assert their independence, and the table is one place to give yours some sense of control. Serve a variety of healthy foods from all the food groups and let your child decide which of those foods to eat and how much.
What About Milk?
Milk is an important part of a toddler's diet because it provides calcium and vitamin D, which help build strong bones. Most kids under age 2 should drink whole milk. If a toddler is overweight or there is a family history of obesity, high cholesterol, or heart problems, your doctor might recommend switching to reduced fat (2%) milk.
If your child can’t drink cow’s milk, choose unsweetened soy drinks fortified with calcium and vitamin D. Other milk alternatives (such as almond, oat, rice, or coconut) have less protein and may not be fortified.
Kids this age don’t need special toddler milk or formulas, which contain added sugars. Toddlers can get all the nutrition they need by drinking cow’s milk or a fortified soy drink and eating a variety of solid foods.
When your child is 2, you can switch to low-fat or nonfat milk.
Between 12 and 18 months of age is a good time to move to a cup. Instead of stopping bottles all at once, slowly drop them from the feeding schedule, starting with mealtime. Offer whole milk in a cup after your child has begun the meal.
Offer whole milk in a cup after your child has begun the meal.
Why Is Iron Important?
Iron makes the red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body. Low iron levels can affect growth and may lead to learning and behavior problems and anemia (a low number of red blood cells).
After 12 months of age, toddlers may not get enough iron because they no longer drink iron-fortified formula and they may not get enough iron-rich foods in their diet.
To help prevent iron deficiency:
- Limit your child's milk intake to 16–24 ounces (480–720 milliliters) a day.
- Include iron-rich foods in your child's diet, like meat, poultry, fish, beans, and iron-fortified foods.
- Continue serving iron-fortified cereal until your child is eating a variety of iron-rich foods.
Talk with your doctor if your child drinks a lot of cow's milk, isn't getting enough iron-rich foods, or if you're thinking of giving your child a multivitamin.
What Foods Should We Avoid?
Offer your child a variety of healthy foods. Watch for allergic reactions when trying new foods.
Toddlers between 12 and 24 months should avoid:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners, including sugar-sweetened and diet drinks
- high-sodium foods
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw vegetables, grapes, hard cheese, popcorn, and nuts
Always supervise when your child is eating. Make sure your child sits up in the high chair or other safe place.
How Much Should My Toddler Eat?
Schedule three meals and two or three healthy snacks a day. But expect your toddler to sometimes eat less or skip meals. This can be hard for many parents, but kids should be allowed to respond to their own feelings of hunger and fullness. Toddlers who are full may push food away, close their mouths or turn their heads away from food, use hand gestures, or make sounds to let you know they have had enough. Don't push food on a child who's not hungry.
Don't push food on a child who's not hungry.
If you have any questions about what and how much your child is eating, talk with your doctor.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
The diet of a one-year-old child / What and how to feed a baby - an article from the "What to feed" section on Food.ru
Principles of nutrition for a child per year
If a child has 6-8 teeth per year, and he looks with interest into the plates of his parents , this does not mean that it is time for him to change to a common table. At the very least, the diet of a one-year-old child should be very different from that of an adult.
Adult food is often unbalanced, prepared in an unsuitable way for a baby, contains a lot of sugar, salt and spices. Such food harms the growing organism. Therefore, first of all, build the right diet.
-
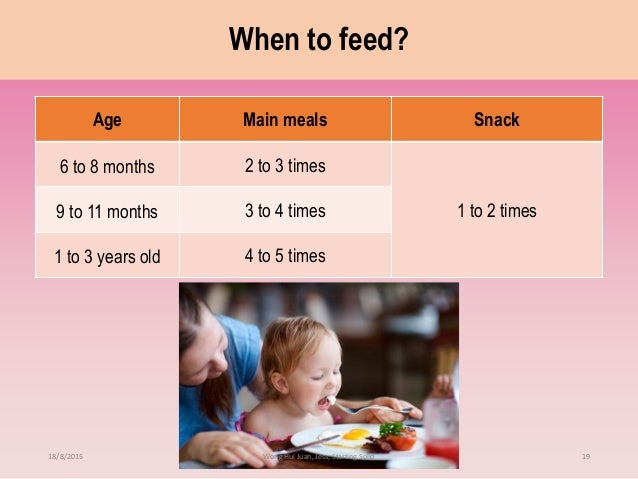
It is recommended to eat 3-4 times a day for 300-400 g plus 1-2 snacks between feedings.

-
From the first year of life, the baby can chew solid food.
-
If lactation continues, breastfeed until 2 years of age.
-
Avoid fast food and sugary sodas.
A one-year-old's diet might look like this:
-
8:00 - breakfast.
-
12:00 - lunch.
-
16:00 - afternoon tea.
-
19:00 - dinner.
-
21:00 - snack.
Advice
600 ml is the recommended amount of milk for a baby to drink daily.
If breastfeeding, feed your baby after waking up, in the afternoon after dinner, or before bed. You need to feed at the same time with a delay of 15-20 minutes.
Proper nutrition helps to form reflexes, which improves the absorption of nutrients in the body.
How much should a one year old child eat
A baby's diet should include 1000-1400 kcal per day. The calculation is as follows: multiply the weight of the child by 100 kcal.
The calorie content is distributed as follows:
-
Breakfast - 250 kcal;
-
lunch - 350 kcal;
-
afternoon tea - 200 kcal;
-
dinner - 200 kcal.
Healthy food contains enough vitamins, minerals and nutrients: proteins, carbohydrates and fats. It is necessary to include fatty foods in the child's diet: milk, butter, sour cream, cream. Fatty food promotes the absorption of trace elements in the body.
Interesting fact
10% of one-year-old children in Russia are overweight. They are not properly fed, they are allowed to eat fast food and drink soda. Obesity at an early age leads to vascular disease, heart disease, diabetes, mental disorders and other serious disorders.
Child's menu per year
Balanced menu includes specialty meals designed to meet the needs of children, plus "adult" foods: meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, fruits, vegetables, cereals, bread, pastries and legumes.
It is good to eat milk porridge for breakfast. It is a rich source of vitamins, minerals and fiber. Fiber is good for intestinal microflora: it regulates the balance of beneficial and harmful bacteria.
Meat is a source of animal protein, indispensable for a growing organism. WHO recommends that children eat 60–70 g of meat per day. It can be served as steam cutlets, meatballs in soup, or any other attractive form. Offal and meat products are harmful to a one-year-old child.
It is also desirable to gradually expand the vegetable menu. Vegetables contain many vitamins, minerals, trace elements and organic acids that are beneficial to the body. Gradually introduce boiled carrots, cabbage, zucchini, turnips, beets into the baby's diet.
Legumes are a source of vegetable proteins. Beans, lentils, green peas diversify the baby's diet. They contain useful trace elements, vitamins, as well as coarse fiber. Therefore, legumes need to be boiled and chopped in a blender. Beans should not be eaten too often either, as they cause bloating and, in rare cases, diarrhea.
Beans should not be eaten too often either, as they cause bloating and, in rare cases, diarrhea.
Fruit diet improves immunity, especially in winter when the body is weakened. Fruit goes well with cereals or served as smoothies and juices.
Sugar and salt lead to nutritional imbalances, cardiovascular problems and obesity. Avoid cakes, pastries, chocolate bars and other sweets. Replace sugar with fructose, which is abundant in fruits, or honey.
What to drink? Water, lots of water. It is advisable to make sure that the child has drunk a glass of liquid after eating. He himself will not ask, because he still does not know how. When a one-year-old child is thirsty, he begins to act up. Sweet soda should be excluded from the diet of the baby.
What foods should not be given to a one-year-old child
Approach the baby's menu carefully. Do not rush to transplant him to an adult table. Among the forbidden foods for a one-year-old child:
-
Fried foods, including chips, snacks and fast food.
-
Meats and offal such as sausages and sausages, other than liver, heart and tongue.
-
Curds, ice cream, condensed milk, koumiss.
-
Mushrooms.
-
Products containing colorants and flavors.
-
Cream confectionery containing vegetable protein.
-
Carbonated drinks.
-
Concentrates like Doshirak.
-
Caramel and gum.
-
Pickled vegetables and fruits.
-
Spices and condiments, including ketchup, mayonnaise and other sauces.
-
Smoked products.
Advice
Buy food from stores labeled "Baby Food". The label often says for what age this product is intended. There are no additives, GMOs, artificially grown products and other things in baby food. Read the contents of the label carefully. Often unscrupulous manufacturers use false labels for marketing purposes.
What to do if the child does not want to eat
It is difficult to persuade children to try unusual food. There are four ways to deal with this problem:
There are four ways to deal with this problem:
-
Lead by example before introducing new foods. When he sees that adults eat with appetite, he involuntarily wants to try it. But remember that the baby gets used to a new food only from the tenth time.
-
Try one new product at a time. A child needs time to get used to it. New food should be combined with what is already loved.
-
Don't force your child to eat something they don't like. Let him choose what he wants.
-
Food should be as simple and familiar as possible. Children do not like dishes with many obscure ingredients like casseroles.
Tip
Babies eat better when they are relaxed. Work up an appetite during a walk or after a game. Never teach children to watch TV or smartphones while eating. Eating should be extremely calm.
Benefits of pre-mixed formula
Don't be afraid to switch babies to formula instead of breastfeeding. They benefit the baby's body, unlike, say, goat's milk. Goat's or cow's milk is too low in nutrients and high in protein. Its digestion increases the load on the gastrointestinal tract of the child and leads to obesity.
They benefit the baby's body, unlike, say, goat's milk. Goat's or cow's milk is too low in nutrients and high in protein. Its digestion increases the load on the gastrointestinal tract of the child and leads to obesity.
Three advantages of mixtures:
-
Contains polyunsaturated fatty acids that are beneficial for the baby's body.
-
Rich in probiotics and prebiotics, live bacteria that maintain normal intestinal microflora.
-
Give your child the necessary balanced intake of vitamins and minerals.
Tip
Formula will not replace breast milk.
What can be done?
Set a clear power mode. Make a menu for every day: breakfast, lunch, afternoon tea, dinner, snack. Write down the products and their quantity. The children's menu should be varied and balanced, contain sufficient nutrients, minerals and vitamins. Introduce new foods gradually and do not force the child to eat something that he does not want in a year.
Read more about children's nutrition:
-
How to improve your child's health during the off-season. Simple tips from an expert
-
How to improve your child's appetite. Instructions for parents
-
6 healthy fiber foods. What to feed your child to be healthy
Russian Union of Pediatricians
Nutrition for children aged 1 to 3 years
The period from 1 to 3 years of life is a crucial stage in the transition to an adult type of nutrition, which has certain features. In order to ensure that all the necessary nutrients enter the child's body and at the same time prevent an excess of individual nutrients, nutrition should be balanced and varied.
The daily amount of food for children aged 1 to 1.5 years should be 1000-1200 g, from 1.5 to 3 years - 1200-1500, the amount of food in one feeding should not exceed 300-350 ml. The diet consists of three main meals per day and two snacks. It is considered optimal when breakfast is 25% of the total energy density of the diet, lunch is 30–35%, dinner is 20%, and additional meals are about 10%. In general, the child can eat the same food as the rest of the family.
It is considered optimal when breakfast is 25% of the total energy density of the diet, lunch is 30–35%, dinner is 20%, and additional meals are about 10%. In general, the child can eat the same food as the rest of the family.
In the nutrition of a child of 1–3 years of age , must be present daily: animal or poultry meat, dairy and sour-milk products, vegetables, fruits, bread, cereals, vegetable and butter; fish and eggs are included in the diet 2-3 times a week.
Cereal products: bread - 2-3 servings per day, cereals and side dishes - 1 time per day
Fruit and/or vegetables: at least 5 times a day
Dairy products: at least 3 servings per day (including those used to make cereals, yoghurts, fermented milk drinks, cottage cheese, infant formula or breast milk).
Domestic pediatricians recommend, when compiling a diet for children aged 1–3 years, preference should be given to specialized children's dairy products of industrial production that meet high quality requirements and safety indicators for this age. Most children's dairy products are additionally enriched with vitamins and/or minerals and other biologically active components, taking into account the physiological needs of children of this age. At the same time, in foreign recommendations, children over 1 year old are offered the gradual introduction of whole cow's milk, which is rich in fats necessary for proper growth and development, the absorption of vitamins A and D, the development of the child's brain and nervous system.
Most children's dairy products are additionally enriched with vitamins and/or minerals and other biologically active components, taking into account the physiological needs of children of this age. At the same time, in foreign recommendations, children over 1 year old are offered the gradual introduction of whole cow's milk, which is rich in fats necessary for proper growth and development, the absorption of vitamins A and D, the development of the child's brain and nervous system.
Meat dishes: 2-3 times a day
Fish dishes: 2-3 servings per week
Eggs: 2-3 per week
Dietary fats: 3-4 teaspoons of butter and/or vegetable oils per day
When cooking, use the minimum amount of salt and sugar, and do not add them to industrial products.
Offer your child a variety of foods and let them choose their own. Children love to eat on their own, so if possible, offer food that the child can eat with their hands.
It is important to remember that a baby can choke on pieces of food, so whatever you give your baby should be crushed or cut into small pieces that can be easily chewed.