How often to feed two month old baby
Breastfeeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Breastfeeding is a natural thing to do, but it still comes with its fair share of questions. Here's what you need to know about how often and how long to breastfeed your baby.
How Often Should I Breastfeed?
Newborn babies should breastfeed 8–12 times per day for about the first month. Breast milk is easily digested, so newborns are hungry often. Frequent feedings helps stimulate your milk production during the first few weeks.
By the time your baby is 1–2 months old, he or she probably will nurse 7–9 times a day.
In the first few weeks of life, breastfeeding should be "on demand" (when your baby is hungry), which is about every 1-1/2 to 3 hours. As newborns get older, they'll nurse less often, and may have a more predictable schedule. Some might feed every 90 minutes, whereas others might go 2–3 hours between feedings.
Newborns should not go more than about 4 hours without feeding, even overnight.
How Do I Count the Time Between Feedings?
Count the length of time between feedings from the time your baby begins to nurse (rather than at the end) to when your little one starts nursing again. In other words, when your doctor asks how often your baby is feeding, you can say "about every 2 hours" if your first feeding started at 6 a.m., the next feeding was around 8 a.m., then 10 a.m., and so on.
Especially at first, you might feel like you're nursing around the clock, which is normal. Soon enough, your baby will go longer between feedings.
How Long Does Nursing Take?
Newborns may nurse for up to 20 minutes or longer on one or both breasts. As babies get older and more skilled at breastfeeding, they may take about 5–10 minutes on each side.
How long it takes to breastfeed depends on you, your baby, and other things, such as whether:
- your milk supply has come in (this usually happens 2–5 days after birth)
- your let-down reflex (which causes milk to flow from the nipple) happens right away or after a few minutes into a feeding
- your milk flow is slow or fast
- the baby has a good latch, taking in as much as possible of your areola (the dark circle of skin around your nipple)
- your baby begins gulping right away or takes it slow
- your baby is sleepy or distracted
Call your doctor if you're worried that your baby's feedings seem too short or too long.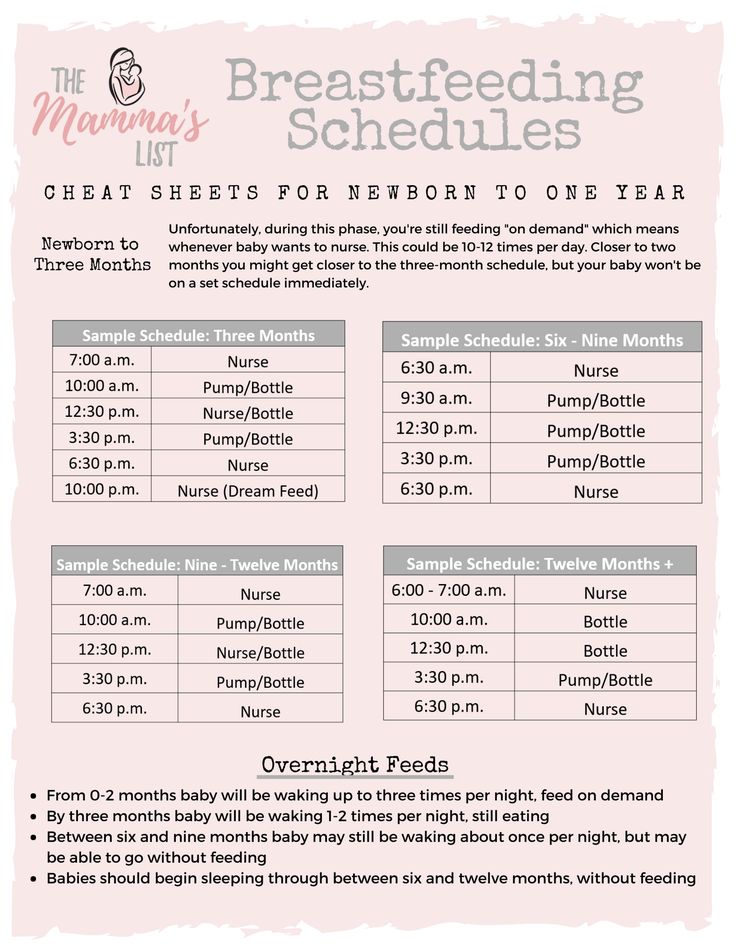
When Should I Alternate Breasts?
Alternate breasts and try to give each one the same amount of nursing time throughout the day. This helps to keep up your milk supply in both breasts and prevents painful engorgement (when your breasts overfill with milk).
You may switch breasts in the middle of each feeding and then alternate which breast you offer first for each feeding. Can't remember where your baby last nursed? It can help to attach a reminder — like a safety pin or small ribbon — to your bra strap so you'll know which breast your baby last nursed on. Then, start with that breast at the next feeding. Or, keep a notebook handy or use a breastfeeding app to keep track of how your baby feeds.
Your baby may like switching breasts at each feeding or prefer to nurse just on one side. If so, then offer the other breast at the next feeding. Do whatever works best and is the most comfortable for you and your baby.
How Often Should I Burp My Baby During Feedings?
After your baby finishes on one side, try burping before switching breasts.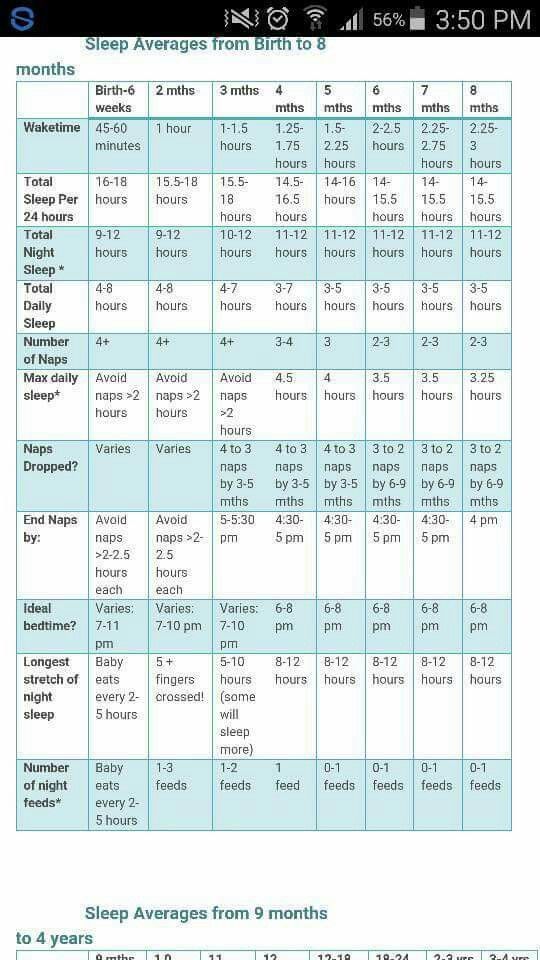 Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Some infants need more burping, others less, and it can vary from feeding to feeding.
If your baby spits up a lot, try burping more often. While it's normal for infants to "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, a baby should not vomit after feeding. If your baby throws up all or most of a feeding, there could be a problem that needs medical care. If you're worried that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
Why Is My Baby Hungrier Than Usual?
When babies go through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt), they want to eat more than usual. These can happen at any time. But in the early months, growth spurts often happen when a baby is:
- 7–14 days old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
During these times and whenever your baby seems extra hungry, follow your little one's hunger cues. You may need to breastfeed more often for a while.
How Long Should I Breastfeed My Baby?
That's a personal choice. Experts recommend that babies be breastfed exclusively (without formula, water, juice, non–breast milk, or food) for the first 6 months. Then, breastfeeding can continue until 12 months (and beyond) if it's working for you and your baby.
Breastfeeding has many benefits for mom and baby both. Studies show that breastfeeding can lessen a baby's chances of diarrhea, ear infections, and bacterial meningitis, or make symptoms less severe. Breastfeeding also may protect children from sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), diabetes, obesity, and asthma.
For moms, breastfeeding burns calories and helps shrink the uterus. In fact, breastfeeding moms might return to their pre–pregnancy shape and weight quicker. Breastfeeding also helps lower a woman's risk of diseases like:
- breast cancer
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
- heart disease
It also might help protect moms from uterine cancer and ovarian cancer.
How Often and How Much Should Your Baby Eat?
By: Sanjeev Jain, MD, FAAP
One of the most common questions new parents have is how often their baby should eat. The best answer is surprisingly simple: in general, babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry.
How do I know when my baby is hungry?
For babies born
prematurely or with certain medical conditions, scheduled feedings advised by your pediatrician are best. But for most healthy, full-term infants, parents can look to their baby rather than the clock for hunger cues. This is called feeding on demand, or
responsive feeding.
Hunger cues
A hungry baby often will cry. But it's best to watch for hunger cues before the baby starts crying, which is a late sign of hunger and can make it hard for them to settle down and eat.
Some other typical hunger cues in babies:
Licking lips
Sticking tongue out
Rooting (moving jaw and mouth or head in search of breast)
Putting his/her hand to mouth repeatedly
Opening her mouth
Fussiness
Sucking on everything around
It is important to realize, however, that every time your baby cries or sucks it is not necessarily because he or she is hungry.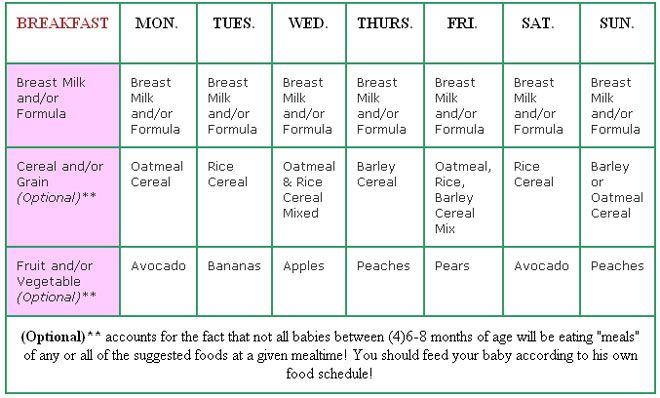 Babies suck not only for hunger, but also for comfort; it can be hard at first for parents to tell the difference. Sometimes, your baby just needs to be cuddled or changed.
Babies suck not only for hunger, but also for comfort; it can be hard at first for parents to tell the difference. Sometimes, your baby just needs to be cuddled or changed.
General guidelines for baby feeding
It is important to remember all babies are different―some like to snack more often, and others drink more at one time and go longer between feedings. However, most babies will drink more and go longer between feedings as they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk:
Most newborns eat every 2 to 3 hours, or 8 to 12 times every 24 hours. Babies might only take in half ounce per feeding for the first day or two of life, but after that will usually drink 1 to 2 ounces at each feeding. This amount increases to 2 to 3 ounces by 2 weeks of age.
At about 2 months of age, babies usually take 4 to 5 ounces per feeding every 3 to 4 hours.
At 4 months, babies usually take 4 to 6 ounces per feeding.

At 6 months, babies may be taking up to 8 ounces every 4 to 5 hours.
Most babies will increase the amount of formula they drink by an average of 1 ounce each month before leveling off at about 7 to 8 ounces per feeding. Solid foods should be started at about 6 months old.
Concerns about overfeeding or underfeeding your baby
Too full?
Babies are usually pretty good at eating the right amount, but they can sometimes take in more than they need. Infants who are bottle feeding may be more likely to overfeed, because drinking from a bottle may take less effort than breastfeeding.
Overfed babies can have stomach pains, gas, spit up or vomit and be at higher risk for obesity later in life. It's better to offer less, since you can always give more if your baby wants it. This also gives babies time to realize when they're full.
If you are concerned your baby wants to eat
all the time―even when he or she is full―talk with your pediatrician. Pacifiers may be used after feeding to help sooth healthy-weight babies who like to suck for comfort, rather than nutrition. For babies who are breastfed, it's best to wait to offer pacifiers until around 3 to 4 weeks of age, when breastfeeding is well-established.
Pacifiers may be used after feeding to help sooth healthy-weight babies who like to suck for comfort, rather than nutrition. For babies who are breastfed, it's best to wait to offer pacifiers until around 3 to 4 weeks of age, when breastfeeding is well-established.
Trouble gaining weight?
Most babies will double their birth weight by 5 months of age and triple their birth weight by their first birthday. If your baby is having trouble gaining weight, don't wait too long between feeding―even if it means waking your baby. Be sure to talk with your pediatrician about how often and how much to feed your baby.
How do I know if my baby is getting enough to eat?
Daily diapers
A newborn's
diaper is a good indicator of whether he or she is getting enough to eat. In the first few days after birth, a baby should have 2 to 3 wet diapers each day. After the first 4 to 5 days, a baby should have at least 5 to 6 wet diapers a day. Stool frequency is more variable and depends whether your baby is
breastfed or formula fed.
Growth charts
During regular health check-ups, your pediatrician will check your baby's weight and plot it on a growth chart. Your baby's progress on the growth chart is one way to tell whether or not they are getting enough food. Babies who stay in healthy growth percentile ranges are probably getting a healthy amount of food during feedings.
Remember
Talk with your pediatrician if you have any questions or concerns about your baby getting the right amount to eat.
More information:
- Making Sure Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk
- Amount and Schedule of Formula Feedings
- Is Your Baby Hungry or Full? Responsive Feeding Explained (Video)
- Remedies for Spitty Babies
- Ask the Pediatrician: With the baby formula shortage, what should I do if I can't find any?
- Ask the Pediatrician: How should we feed our baby if we're running low on money?
-
Airplane Choo Choo: A Feeding Guide for Children (National Dairy Council)
About Dr.
 Jain:
Jain:
Sanjeev Jain, MD, FAAP, is a Clinical Associate Professor of General Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health. Within the American Academy of Pediatrics, he is a member of the Section on International Child Health and the Wisconsin State Chapter.
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
what and how to feed a newborn at home
The daily amount of food for a child at 2 months
By two months, the child has to learn a lot - hold his head, distinguish between the voices of mom and dad, grow 3-4 centimeters and gain about 800 grams of weight Therefore, the baby must receive adequate nutrition. The daily amount of food for a child directly depends on what kind of feeding he is on. For example, when breastfeeding, the volume of milk may change over time, but the baby will be full. You should also not worry about the number of feedings - just put the baby to the chest at his first request.
For example, when breastfeeding, the volume of milk may change over time, but the baby will be full. You should also not worry about the number of feedings - just put the baby to the chest at his first request.
With artificial feeding, it is necessary to know when to stop. The daily volume of the mixture for a two-month-old is 800-850 ml of the mixture, which must be divided into 6-7 feedings with a three-hour interval.
What to feed a child at 2 months
At two months, the child still needs only mother's milk, and no complementary foods or water supplements. If for some reason the mother cannot breastfeed the baby, or there is not enough milk, the child is transferred to artificial or mixed feeding.
Breastfeeding
All paediatricians and breastfeeding specialists agree that nature has not invented anything better than mother's milk for feeding a baby. It is in breast milk that contains not only vitamins, minerals and other trace elements necessary for the healthy growth and development of the child, but also immunoglobulins that help to form and strengthen the baby's immunity. Surprisingly, breast milk can change its composition throughout the day and is produced exactly in the amount that the baby needs. Experts note that a breastfed baby is less likely to get colds, he has no digestive problems, and allergies and dermatitis rarely appear. Breastfeeding helps the child establish a special contact with the mother, forms a strong relationship between them. It has been proven that breastfed babies sleep better and more soundly at night and do not act up during the day.
Surprisingly, breast milk can change its composition throughout the day and is produced exactly in the amount that the baby needs. Experts note that a breastfed baby is less likely to get colds, he has no digestive problems, and allergies and dermatitis rarely appear. Breastfeeding helps the child establish a special contact with the mother, forms a strong relationship between them. It has been proven that breastfed babies sleep better and more soundly at night and do not act up during the day.
— The main principle of breastfeeding at two months is to put your baby to the breast as often as possible at his first request, so you will keep lactation for many months. Try to alternate breasts during feedings to avoid congestion and lactostasis. Also, do not forget about hygiene - wash your breasts with warm boiled water before and after feeding, and use a special healing ointment for cracked nipples, advises pediatrician, breastfeeding specialist Dina Nauruzova .
How do you know if your baby is getting enough breast milk? If a child behaves calmly during feeding, does not act up, and between feedings does not burst into hungry crying, then mother's milk is enough for him. Remember that by the age of two months, the baby's feeding regimen has not yet developed, so he may ask for a breast often, sometimes just to calm down.
In addition, every month at the appointment, the pediatrician conducts a control weighing of the child, which will also show whether the child is getting enough milk.
Find out more
Artificial feeding
If, for some reason, the mother cannot breastfeed her baby (for example, she is sick and takes medication, or she has no milk), then the baby is transferred to artificial feeding. Of course, not a single mixture, even the most expensive one, can replace mother's milk, but thanks to modern technologies, mixtures are now as close as possible in composition to breast milk.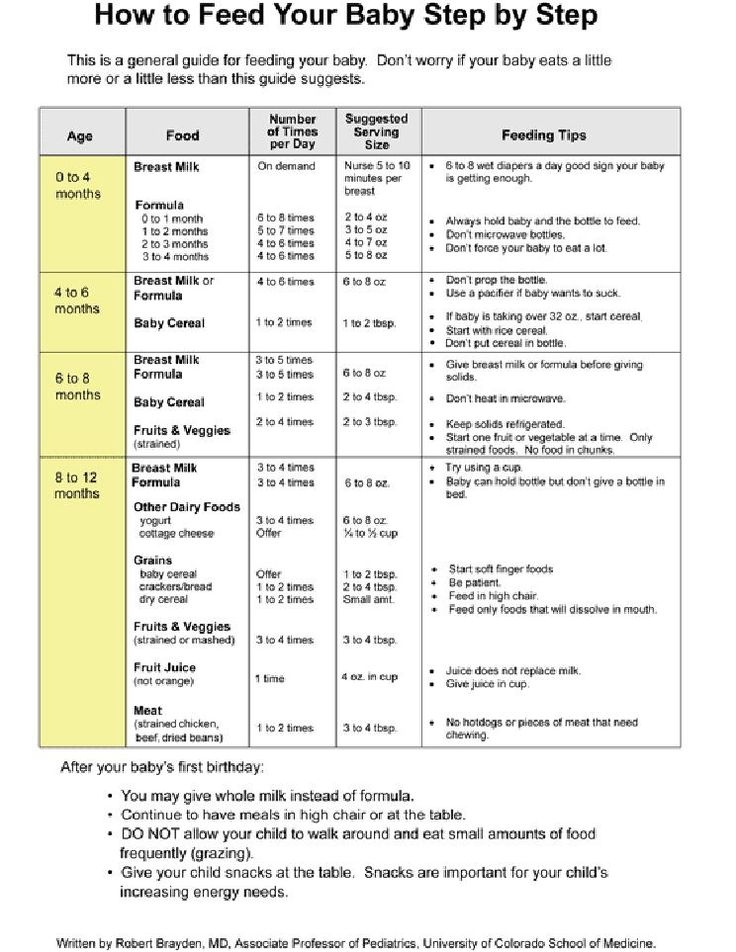
When choosing formula, it is best to consult your pediatrician first. In general, mixtures are of three types: conventional (for healthy children), therapeutic (with frequent colic and regurgitation, for premature babies) and hypoallergenic. The last two types are prescribed by the pediatrician after examining the child.
Because even expensive formula takes longer to digest than breast milk, a two-month-old baby's feeding regimen should be on schedule, with respect to 3-4 hour intervals. Approximately 6-7 feedings are required per day, and the volume of a single portion of the mixture is 120-150 ml.
- Do not worry if the child has not finished his formula, then he is not hungry. And even more so, you don’t need to force him to finish eating, otherwise his tummy will hurt or he will start spitting up, the pediatrician explains. – And remember, when a baby cries, it doesn't mean that he is necessarily hungry. He may have something to hurt, he is cold or hot, or the baby is just looking for maternal warmth.
Experts also remind that when bottle-fed, the baby needs to be supplemented with clean water, which is offered to him between feedings. The child will drink as much as he needs, it is not worth forcing him to drink.
Do not forget about the important rules of artificial feeding: the mixture must be prepared immediately before feeding, it cannot be stored for a long time even in the refrigerator. Bottles and nipples should be carefully sterilized and matched to the age of the child. The mixture must be diluted, strictly following the instructions on the package. Before feeding the baby, be sure to drip the mixture on your wrist so as not to burn the baby. Make sure that the mixture does not pour in a jet, otherwise the child may choke.
Mixed feeding
Mixed feeding is used when the baby is not full of breast milk, because there are problems with lactation, or the mother has to be away often, and then the baby is supplemented with formula or expressed milk.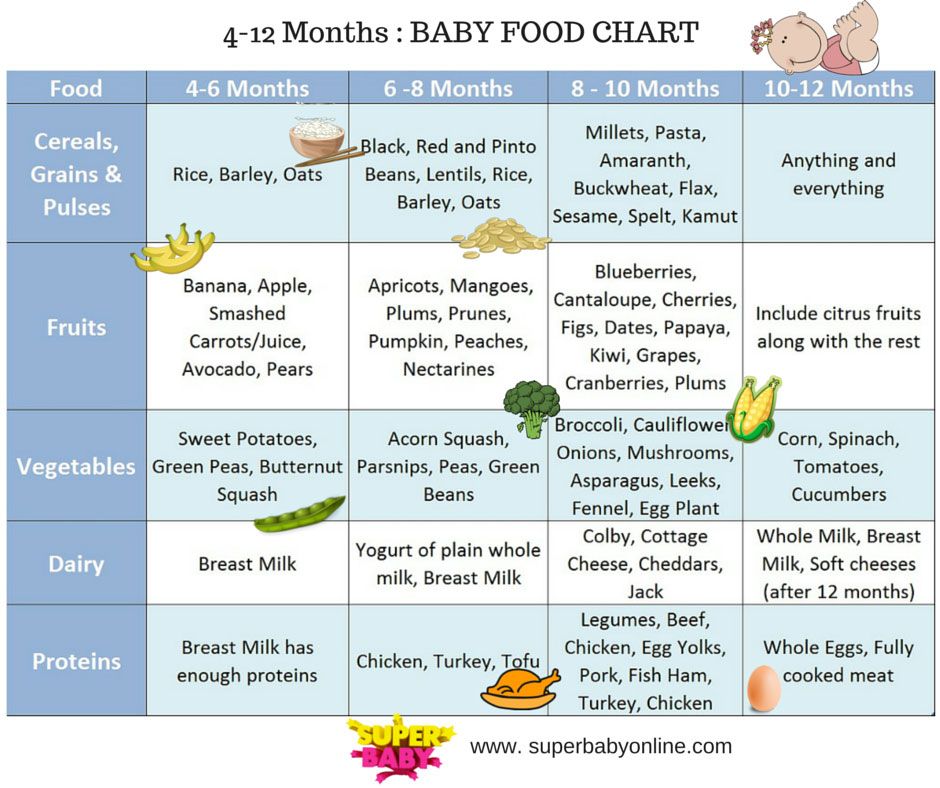
— Sometimes mothers think that their baby is not full, and they decide to supplement with formula on their own. This is wrong, you need to show the child to the pediatrician, who, at the control weighing, will conclude whether he is underweight, and hence the need for supplementary feeding, the pediatrician advises.
There are several options for supplementary feeding: supplementary feeding with expressed breast milk (well suited when the mother needs to go somewhere), donor breast milk (this is more difficult, since breast milk donation in Russia is still poorly developed, and an independent search for a wet nurse is undesirable - you you don’t know for sure if she has any health problems), or infant formula.
With mixed feeding, a two-month-old baby continues to be breastfed at his first request so that milk production does not stop at all, and one or two feedings are replaced by formula. Experts advise supplementing the baby with a syringe or spoon so that he does not prefer the bottle of the mother's breast.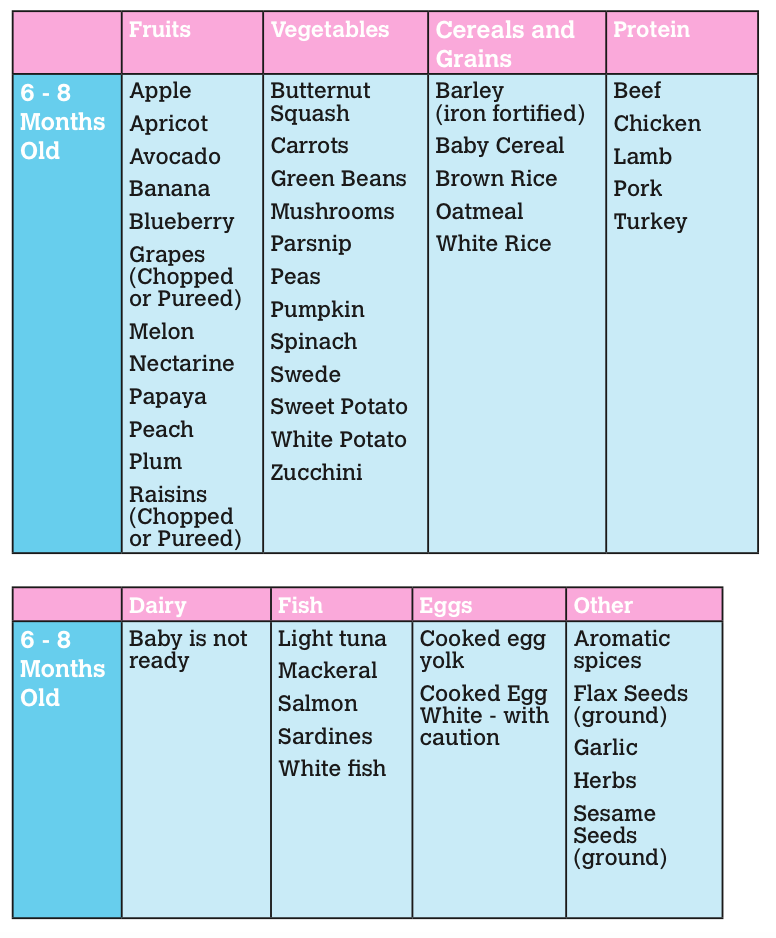 Whenever possible, you should try to return to natural breastfeeding, abandoning the mixture.
Whenever possible, you should try to return to natural breastfeeding, abandoning the mixture.
WHO Feeding Guidelines
The World Health Organization considers breastfeeding to be the ideal nutritional option for babies up to 6 months of age. According to experts, receiving a sufficient amount of mother's milk, up to six months the baby does not need any complementary foods or additional water. WHO also recommends that the baby be breastfed immediately after birth and that mother and baby be placed in the same room together. It is worth continuing breastfeeding for up to two years, because, contrary to speculation, mother's milk does not become “empty”, but adapts to the growing baby, providing him with the necessary vitamins, minerals and other useful substances.
WHO recommends that the first complementary foods should be introduced no earlier than 6 months, provided that the child is healthy and develops according to age norms. If you are underweight, complementary foods may be introduced a little earlier.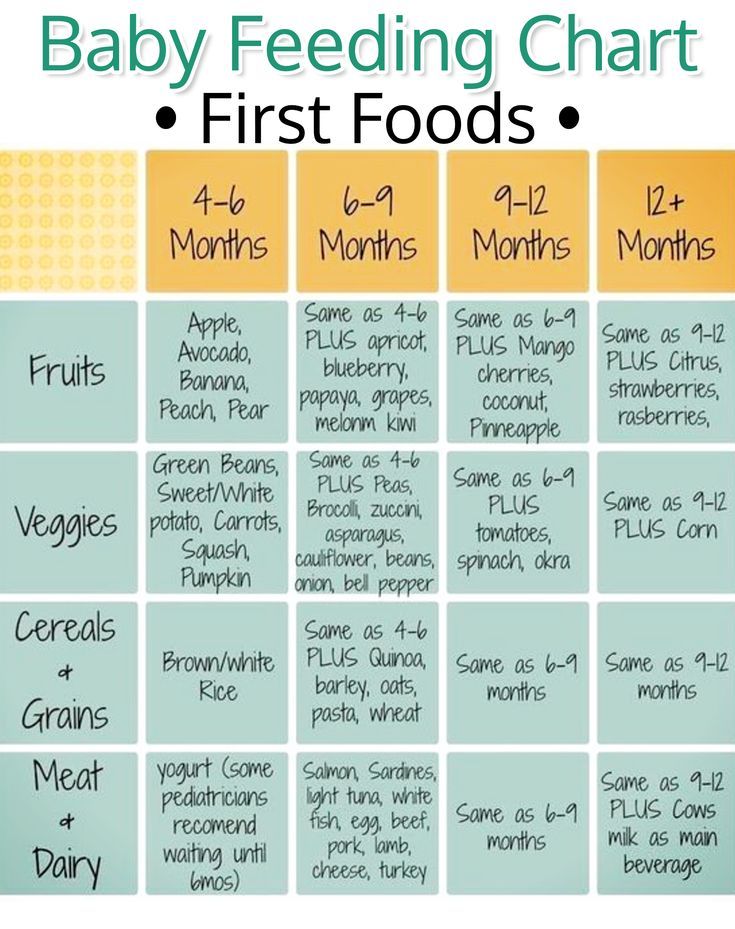
Recommendations of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia on feeding
The Union of Pediatricians of Russia is in solidarity with colleagues from WHO and calls breastfeeding the most natural and physiological nutrition for a child in the first year of life. According to experts, it is breast milk that plays an important role in the prevention of acute and chronic childhood infections, reduces the risk of otitis media, gastrointestinal disorders, infectious diseases of the respiratory system, and even non-specific ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
Photo: pexels.com, RODNAE Productions The Union of Pediatricians of Russia recommends not giving children from birth to six months (except for medical indications) any food or liquid other than breast milk. Also, doctors in the children's clinic should help the mother, if she has any questions about the organization of breastfeeding, explain the importance of this particular method of feeding, and only in case of emergency, choose the mixture.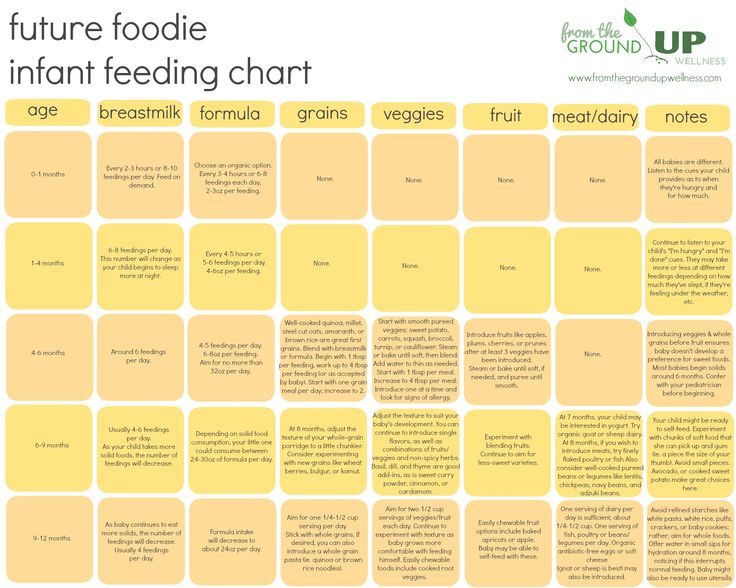
Frequently Asked Questions
How to start weaning?
— At two months, it is still too early for a baby, whether breastfed or formula-fed. In the old pediatric system, the introduction of juices at 2 months was practiced, but modern doctors assure that at this age, even for the juice of the gastrointestinal tract, the baby has not yet matured. If a child receives plenty of mother's milk, he does not need any complementary foods up to 6 months, and modern mixtures provide the child with all the necessary microelements, - explains pediatrician Dina Nauruzova.
How to prepare a diet for a child?
— At two months of age, the baby does not require any other food than breast milk or formula. Everything is simple: breastfeeding at the first request of the child, artificial feeding according to the schedule, the specialist clarifies.
What can mom eat during this period?
- If a mother is breastfeeding, then it is worth paying close attention to her diet, since many foods that get into breast milk can cause allergies or bloating.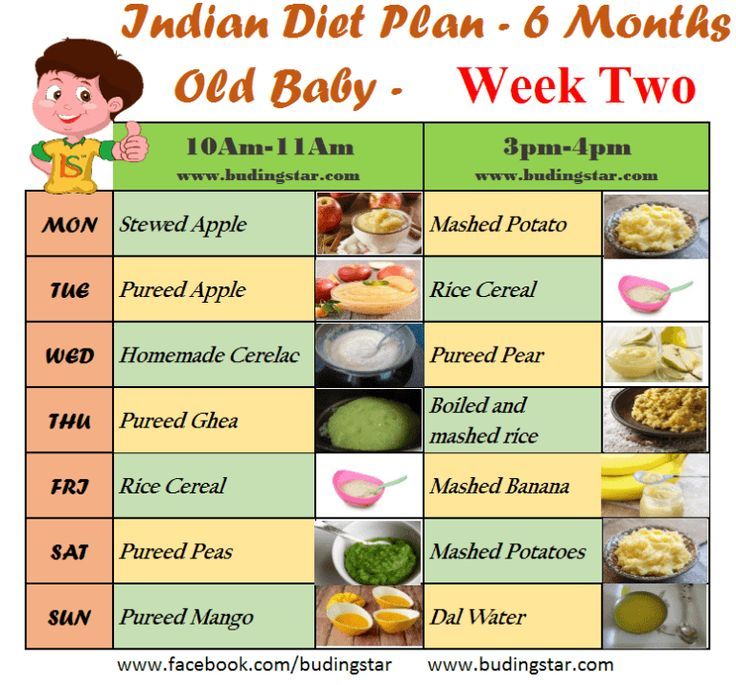 Also, the mother's diet should be varied and balanced. Lean meats are suitable: rabbit, turkey, chicken, beef, boiled or stewed green vegetables. At the same time, it is better to refuse cabbage, it can cause colic, and vegetables of bright colors can provoke an allergy. Allowed cereals, dairy products, mild cheese, cottage cheese. Apples - better baked, bananas, pears. Baking is better homemade, because the store may contain preservatives and dyes. Of course, no alcohol, nicotine, purchased "chemical" juices and carbonated drinks. In general, you should not limit yourself in everything and choke on boiled chicken breast and buckwheat. Everything is possible - the main thing is a little bit and be sure to monitor the reaction of the baby. It is better to keep a food diary and write down everything eaten there - it will be easier to track the product that caused colic or allergies in the baby, advises Dina Nauruzova.
Also, the mother's diet should be varied and balanced. Lean meats are suitable: rabbit, turkey, chicken, beef, boiled or stewed green vegetables. At the same time, it is better to refuse cabbage, it can cause colic, and vegetables of bright colors can provoke an allergy. Allowed cereals, dairy products, mild cheese, cottage cheese. Apples - better baked, bananas, pears. Baking is better homemade, because the store may contain preservatives and dyes. Of course, no alcohol, nicotine, purchased "chemical" juices and carbonated drinks. In general, you should not limit yourself in everything and choke on boiled chicken breast and buckwheat. Everything is possible - the main thing is a little bit and be sure to monitor the reaction of the baby. It is better to keep a food diary and write down everything eaten there - it will be easier to track the product that caused colic or allergies in the baby, advises Dina Nauruzova.
How can you tell if your baby is getting enough milk?
— Some mothers, having heard the cry of the baby, run to feed him as soon as possible, but the child cries not only when he is hungry.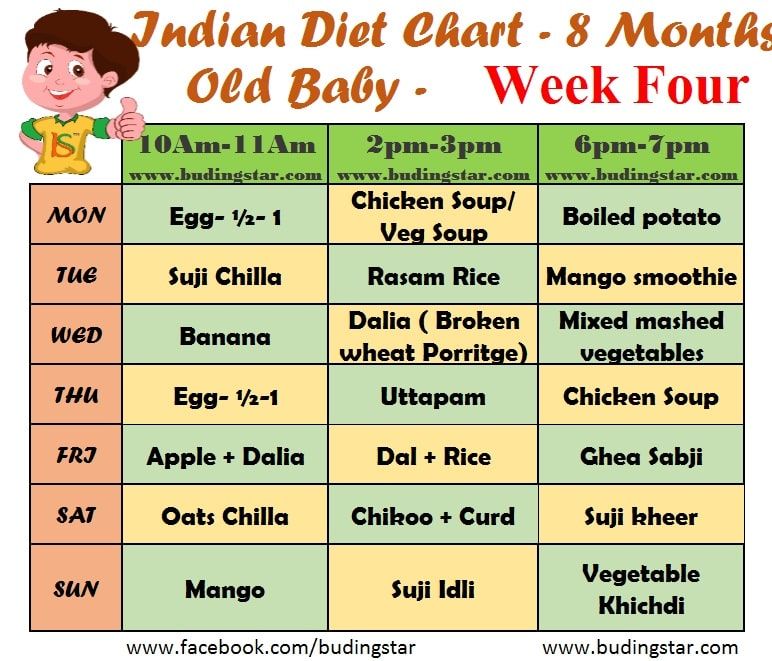 He may be hot or cold, in pain, or he does not want to lie alone, and he expresses all his needs through crying. If the child, even after feeding, continues to move his head, as if looking for a breast or a bottle, smacks his lips, tries to suck his own fists, most likely he is hungry. You can also understand that a child has enough milk if he has regular urination. And of course, control weighing at the pediatrician - if the child receives enough milk, he steadily gains weight, - the specialist explains.
He may be hot or cold, in pain, or he does not want to lie alone, and he expresses all his needs through crying. If the child, even after feeding, continues to move his head, as if looking for a breast or a bottle, smacks his lips, tries to suck his own fists, most likely he is hungry. You can also understand that a child has enough milk if he has regular urination. And of course, control weighing at the pediatrician - if the child receives enough milk, he steadily gains weight, - the specialist explains.
Should the baby be given water during the heat?
- In general, it is not necessary to supplement the child with water if he is breastfed, but if he is on a mixture, then between feedings you can supplement him with a spoon or syringe. It is also necessary to solder if the temperature in the room is above +24 degrees, otherwise dehydration may occur. As for the common myth that when hiccups, the baby must be given water, then if the hiccups do not bother the child all the time, then you can generally wait until it passes on its own, the pediatrician clarifies.
The daily routine of a child at 2 months: development, sleep, feeding
03/21/2019
90
At 2 months, your baby is no longer the same as it was only 4 weeks ago. The baby becomes more active, his sense organs develop, his sleep and wakefulness change. We tell you what you need to consider when shaping the daily regimen of two-month-old children on breastfeeding and artificial feeding.
Sleep at night
By 2 months you will notice that your baby's sleep patterns have begun to change. The biological rhythms of the baby continue to form, and the duration of night sleep gradually increases. The child will begin to go into the night earlier - at 22.00-23.00 hours. But for the time being, bedtime is not as important as whether the baby gets enough sleep. Many children sleep around 9-10 hours at night with awakenings for feeding. How long you should be between night feeds is best discussed with your pediatrician. The time of the morning rise is also not yet constant and not always at 7 in the morning.
Daytime sleep
The duration and time of daytime naps are still different, as well as the time of wakefulness between them. In general, a two-month-old baby sleeps approximately 4-5 hours during the day. And sleep segments are now usually from 30-40 minutes to an hour. During the day, the child sleeps from 4 to 6 times - depending on the time of getting up and leaving at night.
Baby can be active for up to 1 hour or 1 hour and 15 minutes. But you should not allow overwork and focus also on the signs of fatigue and the duration of the previous sleep.
If a two-month-old baby calms down, loses interest in surrounding objects, starts rubbing his eyes, directs his eyes to one point, for no reason starts to get nervous and asks for food, then he wants to sleep and it's time to go to bed.
How many hours of sleep do you need in general? A newborn needs 14-16 hours of sleep a day.
By this age, you already understand your baby better, and it will be easier to follow a more or less understandable schedule. Although the exact daily routine has not yet been organized.
Although the exact daily routine has not yet been organized.
Why can a two-month-old baby not sleep?
If bedtimes are long and it is difficult for the child to fall asleep during the day, the causes of sleep disturbances should be found out and, if possible, eliminated:
-
At this age, the baby begins to be distracted by the surrounding objects, so be sure to darken the room. Darkness will help calm the baby and set him to sleep. This is especially important if you have trouble falling asleep in the evening. From 2.5 months, the sleep hormone melatonin begins to be produced. Therefore, remember that bright light destroys it, and darkness, on the contrary, contributes to the formation of melatonin in the child's body.
-
At 2 months, the sense organs are actively developing in babies. Now the child reacts to any rustle. And those sounds that he did not notice before can now wake him up during sleep.
 The use of a white noise generator will help here to protect the baby from extraneous noise. It is not recommended to buy special white noise toys that are placed in the crib, as this is unsafe.
The use of a white noise generator will help here to protect the baby from extraneous noise. It is not recommended to buy special white noise toys that are placed in the crib, as this is unsafe. -
Even an extra 5-10 minutes can affect the child's well-being this month and lead to more overwork. If this happens, use different ways to calm the baby and put him to bed.
Now is the time to introduce a ritual that will help set the baby up for sleep. Daily repetition of activities facilitates the process of falling asleep and improves night sleep. Start by bathing, lightly massage your baby, swaddle, feed in dim light, walk with your baby upright to ease spitting up.
At the end, read a story or sing a lullaby. Separating feeding and falling asleep will help your baby learn to fall asleep on his own in the future, not relying only on the breast. Gradually, food will become part of the ritual, and not the only way for the child to fall asleep.
Sleepy, but awake, baby in bed, stroking head and tummy if necessary.
If it’s hard to adjust the baby’s sleep and routine on your own, come to the Club REGIME FROM A TO Z.
How to avoid confusion between day and night
.
When you are awake, take your baby outside, turn on the lights and open the curtains. Let the child be surrounded by familiar everyday sounds while playing.
Avoid bright lights at night, feed and change diapers with minimal light if possible. If the baby wakes up at night, be quiet and do not play with him.
In the table you will find the norms of sleep and wakefulness of a child at 2 months
Feeding and daily routine of a child of 2 months
The daily routine of a 2-month-old baby on breastfeeding and on artificial feeding is almost the same. The only difference is the feeding schedule. Since the mixture is digested more slowly, meals will be less frequent. The feeding regimen should be discussed with the doctor observing the child. As in the case if the baby was born prematurely or does not gain weight.
The feeding regimen should be discussed with the doctor observing the child. As in the case if the baby was born prematurely or does not gain weight.
At two months, the number of applications with natural feeding during the day is about 6-9, at night - from 2 to 4 times. For a two-month-old baby, about 800-900 ml is enough. milk or 700-750 ml. mixture per day. The menu should not include other fluids while breastfeeding. Feeding on demand usually occurs at 2 months for 15-20 minutes.
A baby of the second month of life has a need for contact with the outside world. He begins to be distracted by environmental stimuli during breastfeeding and eats less milk or formula during the day than he needs. Have you noticed this with your child?
Therefore, offer breasts during sleep and after waking up. And during feeding, retire with the baby in a quiet place, darken the room so that nothing distracts the baby, and offer him the breast in a calm environment.
Baby development at 2 months
At this age, babies develop a reflex that makes them look at their outstretched arms when they wave them. The child gets used to his body and learns it. Surely, your baby loves to take his fingers in his mouth and touch his legs with his hands! And now you will notice the first smile - smile and you will respond in order to establish contact with the child.
A 2-month-old baby turns its head to sounds, follows objects with its eyes, holds its head and starts pushing with its arms while on its stomach.
2 months is a period of active development of the child's strength, balance and coordination, which is important for the formation of the baby's motor skills.
During waking hours it is useful to walk in the fresh air with the baby, communicate and play with the child.⠀
Continue to use the developmental mat, on which toys can already be hung, Place them on the sides so that the baby turns his head, follows them and reaches for them.