How old for stage 2 baby food
What It Is, When to Start, and Options to Try
Accompanying your child through the different stages of learning how to eat real food is an exciting journey. Sometimes, along with the sense of pride — Look, they polished off the whole jar! — you can feel a little confused. How are you supposed to navigate the milestones?
Let’s start at the beginning: What do the stages of baby food mean, anyway?
Rome wasn’t built in a day, and your baby’s digestive system won’t make the leap from liquid to solid in one day either. That’s what the stages of baby food are for — to help your baby manage the mechanics of eating and to make the transition easier on your baby’s digestive system.
Defining the stages across the brands
While the different stages of baby food aren’t standardized (it would make your life easier if they were!), most popular brands more-or-less follow these four stages:
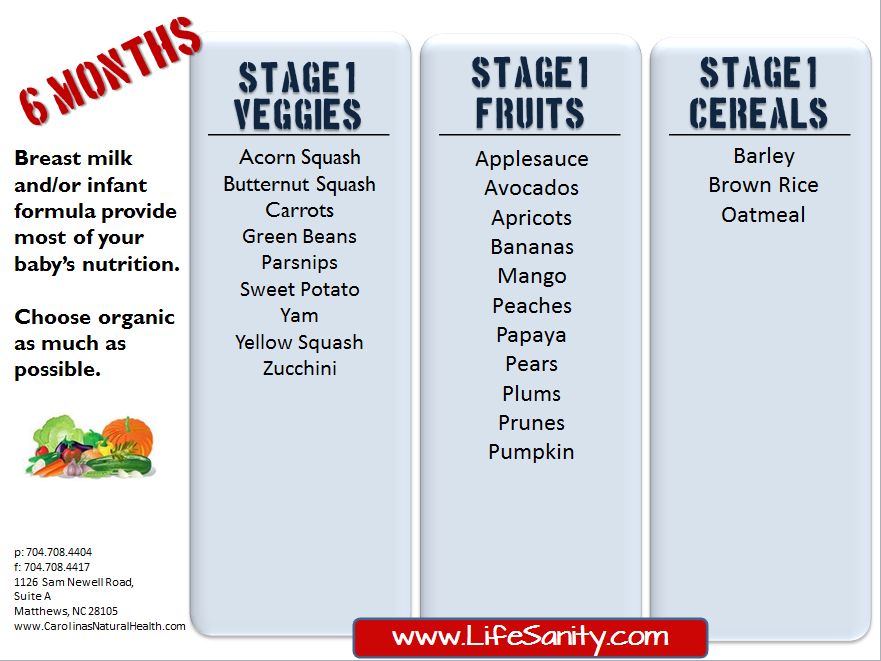
- Stage 1: 4 to 6 months (watery puree of a single ingredient)
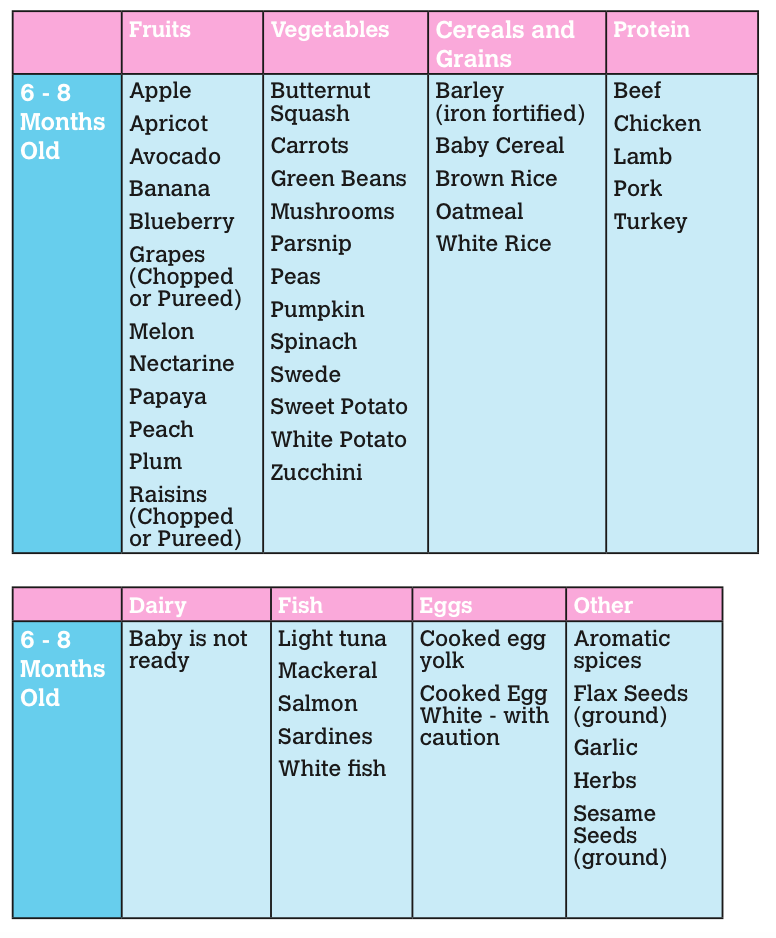
- Stage 2: 6 to 9 months (thicker texture that is strained or mashed)
- Stage 3: 10 to 12 months (mush that has soft, chewable, small chunks)
- Stage 4: After 12 months (finger foods and small, soft pieces of foods you share from your own supper)
What is the difference between stage 1 and stage 2 food?
Stage 1 foods are pretty watery. They’re pureed into a smooth paste that can drip off a spoon easily, so stock up on your bibs. These foods are usually made of a single ingredient: oatmeal cereal, apple, carrots. Your baby will start off eating about half a teaspoon of this.
Stage 2 foods get more exciting. These are strained or mashed into a dense paste. They’re made with a combination of foods that can include legumes and even meats or fish. They may combine flavors, like fruit and veggie blends. Your baby’s appetite is growing and you’ll have to keep pace with bigger portions.
At around 6 to 9 months, your baby is probably ready to move on to stage 2 foods. Not every baby will stick to this schedule simply because every child is a world to their own.
Here are some signs that your child is ready to move on:
- Tongue reflex: At around five months, your child will start losing their tongue thrust reflex and won’t immediately push out the food that you try to feed them.

- More please: They’ll easily polish off the stage 1 foods and look hungry for more.
- Variety: They’ll have eaten foods from all the food categories (vegetables, fruits, legumes, grains, meat) and shown no allergy or intolerance.
- Enjoyment: They’re managing spoonfuls of stage 1 foods easily, mouthing and swallowing happily.
At this exciting stage, feel free to give your baby most types of foods. By offering them a wide range of tastes and textures, you’re giving them a foundation for healthy eating habits — as well as making it easier for yourself. Keep in mind the following safety points:
- Choking hazards: Avoid nuts, seeds, and popcorn at this stage. And make sure to slice round foods like grapes and hot dogs lengthwise.
- No honey: Children younger than 12 months should not be given honey because it could lead to a botulism infection.
- No juice: Follow AAP guidelines and stick with breast milk, formula or a little water and steer clear of juices.

- Safe feeding: Always strap your child into their high chair and keep an eye on them while they’re eating.
And if you’re wondering about peanuts, here’s the scoop: A 2017 release from the National Institutes of Health suggests exposing children to peanut-containing foods as early as 4 months old. (Wait till 6 months for children with mild or moderate eczema.)
Surprised? Don’t be. A recent study suggested that Israeli kids rarely suffer from peanut allergies because they’re munching on Bamba, a peanut-based snack, from as early as 3 months. Talk to your doctor about suggested safe ways to incorporate peanut products into your little one’s diet.
What’s on the menu for stage 2 baby foods? Basically, you can go the store-bought or the homemade route. Or you can mix both depending on how much time you have. It’s up to you and your personal schedule.
Here are tasty ideas for both options.
Store-bought stage 2 baby food
- Plum: These organic blends come in easy-to-transport pouches.
 Try pear, spinach, and pea, or banana and pumpkin.
Try pear, spinach, and pea, or banana and pumpkin. - Beech-Nut: Options are available in jars and pouches. Serve up some apples and bananas or pineapple, pear, and avocado.
- Earth’s Best: Another organic option, in pouches or jars. Try sweet potato, barley, and garbanzo or pasta with tomato and white bean.
- Gerber: A classic, whether served up from plastic tubs, jars, or pouches. Flavor combinations include peach mango and oatmeal or chicken noodle dinner.
Remember to monitor your little one while they’re eating. Pouches are handy, but the caps can be a choking hazard. Glass jars are at risk of breaking, so keep them out of baby’s reach. Your baby should always enjoy snacks and meals with attentive adult supervision.
Homemade stage 2 baby food
Cooking up a storm for your baby’s budding taste buds at this stage doesn’t have to be challenging. Here are a few recipes to get you going. (You can find even more baby food recipes here. )
)
Don’t shy away from spices and herbs: your baby will appreciate the added flavor, and the micronutrients in them will give their immune system a boost.
- Apple, butternut, and carrot: Boil the ingredients until they test soft with a fork. Drain some of the water, but set it aside in case you need to thin the mixture. Sprinkle in a little curry and blend.
- Blueberries and chickpeas: You can cook up your own chickpeas or use a prepared version to save time. Mix equal amounts of blueberries and chickpeas. Blend and add breastmilk, formula, or water to get the right consistency. You can also add in some rice for extra oomph and texture.
- Salmon with roasted zucchini and fennel: Spray the salmon and vegetables with oil and broil for about 15 minutes. Add chopped parsley and blend. You can thin the mixture with breastmilk, formula, or water.
Enjoy this stage with your baby because it won’t be long before they move on to the next stages. And then, sooner than you think, you may be facing competition for that last slice of caramel-topped cheesecake.
And then, sooner than you think, you may be facing competition for that last slice of caramel-topped cheesecake.
When is a child ready to try a bit more texture?
Once your baby has mastered the art of slurping down smooth purees, it may be time to expand their culinary horizons with Stage 2 baby food. Your little gourmand isn’t quite ready to dine on a plate of spaghetti and meatballs just yet, but Stage 2 foods will give them the opportunity to sample new tastes, as well as consistencies.
Think your baby is ready to graduate onto the next stage of baby food? Here, parents and experts weigh in on Stage 2 baby food. Bon appetit!
What is Stage 2 baby food?
While the jarred Stage 2 baby food you find at the store is typically combinations of food (“sweet potato and chicken dinner”), it’s important to keep in mind this stage is more about the consistency of the food.
“While Stage 1 baby food is completely pureed, Stage 2 baby food has a bit more texture to it,” says Dr. Zulma Laracuente, a pediatrician in Alexandria, Louisiana. “The concept behind slowly transitioning baby from purees to thicker solids is to get them used to chewing and swallowing.”
Zulma Laracuente, a pediatrician in Alexandria, Louisiana. “The concept behind slowly transitioning baby from purees to thicker solids is to get them used to chewing and swallowing.”
Of course, every child develops at their own individual pace, so check with your child’s doctor for baby food recommendations during the first 12 months.
When to start Stage 2 baby food
The Stage 2 baby food age may vary based on when your infant started eating Stage 1 foods. The general age recommendation for Stage 1 baby food is between 4 and 6 months, so taking into consideration how long — and how well — your child has been eating these foods will help you determine if they’re ready to move up. According to Laracuente, babies are usually ready for Stage 2 between 6 and 8 months old — but make sure your little one has honed their Stage 1 skills before making the leap.
“Once your baby has done well with Stage 1 solids and has tried multiple foods, it is safe to advance to Stage 2 baby food,” says Dr. Melanie Custer, a pediatrician at at West Bend Pediatrics at Children’s Hospital of Wisconsin. “These foods usually have multiple ingredients, including some spices and are thicker in consistency.”
Melanie Custer, a pediatrician at at West Bend Pediatrics at Children’s Hospital of Wisconsin. “These foods usually have multiple ingredients, including some spices and are thicker in consistency.”
“These foods usually have multiple ingredients, including some spices and are thicker in consistency.”
DR. MELANIE CUSTER, PEDIATRICIAN
Signs baby is ready to start Stage 2 food
How do you know if your baby is nailing it with their Stage 1 foods and ready for the next step? Simply put, they’re eating and swallowing.
“As your baby’s oral skills develop and improve, you can move on to Stage 2 foods, which are purees with small chunks and texture,” says Jenifer Thompson, R.D., an advanced practice dietician at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore.
Thompson says in order to move on to Stage 2 foods, babies should be consistently taking the spoon in their mouth when you offer it to them, without spitting or pushing it back out.
“Once my baby was no longer grimacing or letting his food dribble onto his chin, I knew we were ready to move onto Stage 2 foods,” says mom of two Darcy McConnell of Garwood, New Jersey. “I actually have no idea how old he was when we made the switch since I based it off of how well he was eating!”
“I actually have no idea how old he was when we made the switch since I based it off of how well he was eating!”
What Stage 2 baby foods to start with
It’s important to expose your child to a number of foods, most of which are safe at this point.
“By the time they are 7 to 8 months, babies should be eating a variety of foods from different food groups, including cereals, meat and other proteins, yogurt, cheese, vegetables and fruits,” says Thompson.
“Most foods can be prepared for any stage, so long as they’re texturally age-appropriate,” says Dr. Kristen Treegoob, a pediatrician at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “When we think of Stage 2 baby food, we’re thinking of thicker purees with some mashable bits.”
Experts advise introducing as many different foods as possible during this stage of food development so your baby gets accustomed to them.
“While bananas, applesauce and peaches are good options and most babies like them, as they are naturally sweet, it is also important to try other foods that aren’t as common and popular, such as beets, rhubarb and asparagus, so they develop a taste for them,” says Custer.
Another thing to keep in mind is that the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) no longer recommends delaying the introduction of allergenic foods, particularly peanuts. While it was once advised to wait until your baby was at least 10 months to introduce peanut-containing foods, the AAP now recommends giving babies with no known egg allergy or eczema, infant-safe forms of peanut between 4 to 6 months old. Babies with mild eczema should wait until at least 6 months, and for babies with severe eczema, speak to their doctor before giving them peanut-containing foods. (To find out if your baby has an egg allergy, they must be tested by their pediatrician.)
Which foods to avoid during Stage 2
Even though your little one is venturing into new food texture territory with Stage 2, you should still avoid giving them chunks and small pieces of food, which can pose a serious risk. (Food may be thicker at Stage 2, but it’s still all about the purees and mashes at this point.)
“Infants may have any food that is texture-appropriate for their developmental feeding stage, but it’s important to stay away from choking hazards, such as whole grapes, nuts and seeds,” says Treegoob.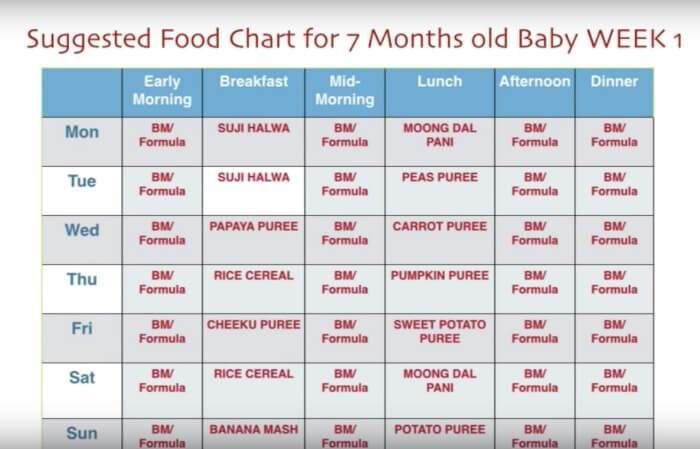
“Infants may have any food that is texture-appropriate for their developmental feeding stage, but it’s important to stay away from choking hazards, such as whole grapes, nuts and seeds.”
DR. KRISTEN TREEGOOB, PEDIATRICIAN
Also, avoid giving your baby honey — raw or cooked — before the age of 12 months, as it may cause a botulism infection.
And finally, when it comes to your baby’s beverage, steer clear of juice. The AAP recommends parents eschew juice, which has “no nutritional benefits over whole fruit,” until at least 1. “At this point, it’s best to stick with breast milk, formula or the odd bit of water (1 to 2 ounces a day), which is mainly for introducing your baby to the skill of using a sippy cup,” says Thompson.
How to start Stage 2 foods safely
Baby should be sitting in a highchair when eating and never left alone. You’ll still be spooning food into your baby’s mouth at this point, but don’t be afraid to let your little one take a whirl at self-feeding in order to get in some practice using utensils.
“At around 9 months, we started letting our son try his hand at feeding himself in his highchair,” says mom of two Erin Henderson, of Waltham, Massachusetts. “It was a mess, but he obviously enjoyed the learning experience.”
Also, during the latter half of your baby’s Stage 2 stint, they may learn how to grab things with their thumb and forefinger and bring them to their mouth.
“Between 8 and 12 months, babies develop the pincer grasp ability and should be able to pick up small pieces of finger food, such as Cheerios or puffs,” says Thompson.
As your baby grows and hones their eating skills, they’ll cut down a bit on how much breast milk or formula they drink — but keep in mind, that should still be their primary source of nutrients.
“Most infants will naturally start to moderate their breast milk or formula intake once their solid intake increases,” says Treegoob. “Solid food may start to account for a significant source of nutritional intake closer to 7 to 9 months. At this time, parents may notice that their baby shows interest in smaller or less frequent bottle or breastfeeds. As long as their weight remains on track and baby is drinking enough milk to stay well-hydrated, there should be no need for concern. Infants typically take somewhere between 24 to 40 ounces of breast milk or formula between 4 to 6 months and 24 to 32 ounces from 6 to 9 months.”
At this time, parents may notice that their baby shows interest in smaller or less frequent bottle or breastfeeds. As long as their weight remains on track and baby is drinking enough milk to stay well-hydrated, there should be no need for concern. Infants typically take somewhere between 24 to 40 ounces of breast milk or formula between 4 to 6 months and 24 to 32 ounces from 6 to 9 months.”
According to the AAP, babies should be eating about 4 ounces of solids (about one small jar of baby food) at each of their meals. And if you’re wondering how long baby food lasts, experts typically recommend 24-48 hours in the fridge or up to 3 months in the freezer.
Lastly, bear in mind that if at first you don’t succeed with a food, try, try again.
“At this age, if babies grimace when taking a bite or shake themselves, it is most often because of a texture issue, not the actual taste,” says Custer. “It is important to keep introducing these foods as it may take a baby up to 15 times to get used to a texture before you can say for sure he/she doesn’t like it. ”
”
Ready for the next stage?
- Stage 3 baby food
Canned nutrition - Understanding age
Viktoria Levchuk©
Parents often come across complementary food tables and schemes that indicate the approximate portion at each age stage, and when which product should be introduced into the child's diet. The dream of any mother is a unified policy for the introduction of complementary foods, so that the industrial production of baby food agrees with pediatricians and mothers on the age of introduction of the product into complementary foods. Some brand labels can be confusing when to use prepared foods, as well as how to combine canned food with home cooking.
The popular Gerber brand has registered trademarks labeled "1st Foods", "2nd Foods" and "3rd Foods". Other brands simply use "1", "2" or "3" or indicate the child's age in months, and some use it to indicate the stage at which a child is ready for a certain type of food consistency.
WHO baby feeding steps
Table of Contents:
The World Health Organization, in its booklet Infant and Young Child Feeding and Nutrition, divides childhood into several stages. These main stages are calculated up to the year of the child, they imply a smooth transition of the baby "from mother's milk to food from the family table." The most popular brands of baby food use the main stages of the transition of the child's diet in the labeling of canned food. There are four stages in total, starting at 4 months and ending at 12 months. These steps are not standardized. nine0005
You can read more about the age stages of baby food in the following articles:
- First stage of baby food: (4) 6-7 months
- Second stage of baby food: 7-8 months
- Third stage of baby food: 8- 10 months
- Fourth stage of infant feeding: 10-12 months
Food can label
Stage 1: Age at (4) 6 to 7 months
Start of complementary foods at (4) 6 to 7 months of age, includes foods from one-ingredient, smooth, light texture without a single lump, with a low level of allergy, without salt, sugar and seasonings, for example, rice porridge or zucchini puree.
Here are some examples of popular brands:
- Silent porridge Fleur Alpine from 4 months
- rice porridge HIPP from 4 months
- Rice porridge Sempler Sempler from 4 months
- puree from 4 months of
- zucchini Sady pridonya from 4 months
- Gerber zucchini puree from 4 months
Stage 2: Age 7 to 8 months
When children are 7 to 8 months old, they are given one-component and two-component products, simply pureed, medium density, sometimes products that seem to rubbed, i.e. food appears in pieces that are easy to swallow, but do not choke. Products are given with a low level of allergy, but slowly they begin to introduce the child to the average.
Second step product examples:
- Bebivita vegetable soup with beef from 8 months
- Bebivita mixed vegetable puree from 7 months
- Rabbit ragout with Gerber broccoli from 8 months
- Semper veg with veal liver from 8 months fritters
- Carrots with potatoes and salmon Hipp from 8 months
- Mixed vegetable puree Hipp from 7 months
- Welling oatmeal with banana and prunes Semper from 8 months
Stage 3: Age from 8 to 10 months
Between 8 and 12 months of age, babies receive a thicker textured meal that is easy to chew and swallow.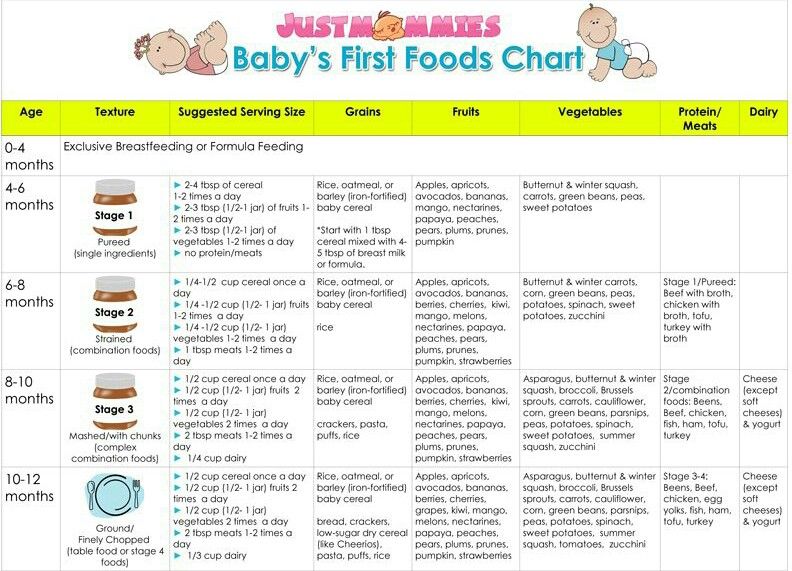 There are more three-component purees. Foods with small pieces help stimulate baby's chewing. Sugar, salt and spices are still missing from baby food.
There are more three-component purees. Foods with small pieces help stimulate baby's chewing. Sugar, salt and spices are still missing from baby food.
Examples of products from the third stage:
- Hipp noodles with sea fish and vegetables in creamy sauce from 10 months
- Mediterranean risotto with sea bream Semper from 10 months
- Gerber Italian treat from 10 months
- Marmaluzi mashed potatoes with fish pieces from 9 months
- Vegetable stew with salmon and Semper rice from 9 months
3-stage jar food is very easy to find in the store. Around this period, according to manufacturers of baby food, the child's appetite increases, respectively, and the portion he consumes, so we focus on jars of 200-250 grams per serving. But usually a child is not able to eat that much at the age of 9-10 months, even if this portion is written in all textbooks on baby food. But what about throwing away the leftovers?
Calm down, around this period, many mothers begin to cook for 2 times (the dish is stored in the refrigerator for about 24-36 hours), the child's body is already strong enough and adapted to complementary foods that pathogenic microbes in the finished dish are not dangerous to him. We just follow the rules of cleanliness, namely, we took a clean spoon, put a small portion from the jar into a separate plate, put the jar in the refrigerator with the rest of the food, and warmed up the postponed dish, fed the baby. nine0005
We just follow the rules of cleanliness, namely, we took a clean spoon, put a small portion from the jar into a separate plate, put the jar in the refrigerator with the rest of the food, and warmed up the postponed dish, fed the baby. nine0005
Stage 4: 10 to 12 months
Approximately one year old, the consistency of baby food is close to that of an adult table. If by 10 months the dish is thick with pieces of food, then closer to 12 months the baby eats small pieces of food, by 1.5 years it completely eats adult dishes, only occasionally large pieces that are difficult to chew, for example, meat, are crushed by adults.
By the age of 2, the child eats completely from the common table without the help of strangers. At this point, you can continue to feed the baby with canned food or completely transfer the baby to an adult table. Parents who initially fed the baby only canned food, by about 2 years old, are transferred to homemade food, i.e. up to 2 years they do not refuse jars, simply because they are used to it and it is convenient, safe, etc. nine0005
nine0005
Examples of products of the fourth stage:
- Young potatoes with green beans and Hipp rabbit from 12 months
- Italian pasta with trout in Semper cream sauce from 11 months
- Heinz0 apple-raspberry-blackcurrant milk porridge from 12 months 0 from 12 months
- Multi-cereal Semper porridge from 11 months
0005
- Vegetables with rice and beef stroganoff Semper from 18 months
- FrutoNyanya apple-raspberry puree (fruit pieces) from 12 months
- Fleur Alpine Organic apple marmalade cookies from 18 months 3 years.
However, it should be noted that after a year, all age restrictions indicated on canned food most likely carry information on products allowed for a given age, and not food consistency. We also take into account that the portion for a 3-year-old child is much larger than for a one-year-old baby. For example, Frutonyan has milk porridges of 200 ml from 6 months, and 500 ml from 3 years old, the porridge can be identical in composition, the difference is only in the portion. nine0005
nine0005
Canned food age recommendations
Please note that the age recommendations for each stage are only general recommendations. The age of introduction of complementary foods for each child is individual, so one will be ready at 5-6 months, and the other closer to 7 months. We look at signs of readiness for complementary foods, consult a pediatrician.
Moreover, the transition to a new consistency also occurs individually, as the baby is 7-8 months old, it is impossible to abruptly transfer the baby to thicker food or add hard pieces, there may be consequences in the form of vomiting or suffocation. It is important that the child gradually learns to chew food, with gradual complication, for effective skill acquisition. Don't forget our pediatricians, who can help a mother determine if a baby needs extra time to learn chewing skills or if it's time to move on to the next stage. nine0005
Consistency of food up to a year. Click on me!!!
And a little about baby food manufacturers. They indicate early dates for the introduction of complementary foods, this is a common marketing ploy to sell more, or they simply do not want to revise the layout of their labels, taking into account the recommendations of Russian pediatricians or the World Health Organization. Although recently, there is less and less canned food on sale, recommended from 3 months.
They indicate early dates for the introduction of complementary foods, this is a common marketing ploy to sell more, or they simply do not want to revise the layout of their labels, taking into account the recommendations of Russian pediatricians or the World Health Organization. Although recently, there is less and less canned food on sale, recommended from 3 months.
The main thing is that parents understand and know the rules and terms for the introduction of complementary foods, as well as listen to their intuition, which does not deceive. The appearance and abilities of the baby will tell parents more about the readiness for complementary foods than the age marking on canned food. nine0005
Chaos in canned food
A strange name for a subtitle, but it's hard to describe in another way what is happening in the industrial production of baby food. Each brand has its own recommendations for the introduction of complementary foods, based on their data, they label jars. Moreover, it is very difficult to understand their logic. The first two steps are easy for many parents because in general one or two ingredient purees are easier to navigate than multi-ingredient purees.
Moreover, it is very difficult to understand their logic. The first two steps are easy for many parents because in general one or two ingredient purees are easier to navigate than multi-ingredient purees.
Therefore, the first 2 stages parents either listen to a pediatrician, or look at a diagram from the Internet, or follow a complementary food table, which is listed on the website of their favorite canned food manufacturer. Although here, too, manufacturers can spoil the situation, so I met thickeners in the form of oatmeal in one-component baby purees (to which an allergy is possible at the beginning of complementary foods). Think for a moment, a one-component puree should contain 1 product and water, the only additional ingredient, but no, they can put any thickener, and it’s good if it’s rice or oat flour, but if the thickener is a preservative? Therefore ALWAYS read the composition of baby food before you buy it.
The first 2 stages seem to be not difficult, but as soon as the child approaches the 3rd stage or lumpy food, then it's just a disaster. Either some manufacturers do not produce food with pieces, then they do, but the composition is complex, there are many ingredients, more than half of the child was not introduced into complementary foods. Parents have to switch from one brand to another or choose 2-3 brands that inspire confidence.
Either some manufacturers do not produce food with pieces, then they do, but the composition is complex, there are many ingredients, more than half of the child was not introduced into complementary foods. Parents have to switch from one brand to another or choose 2-3 brands that inspire confidence.
Consider the situation on the example of milk. Now pediatricians, scientists and most parents agree that it is better to introduce dairy products into complementary foods gradually, starting with fermented milk, and milk is given after a year. But what do manufacturers of baby food offer us, milk porridge from 6 months old, or goat milk porridge from 4 months old. It seems that the recommendations of doctors for brands of baby food are empty space, the main thing for them is to offer an assortment, and parents will have to take care of the children. Therefore at the beginning of complementary foods, it is important to decide on a strategy, namely, to choose at least approximately a table of complementary foods or to make a list of the introduction of products, focusing on the recommendations of a pediatrician.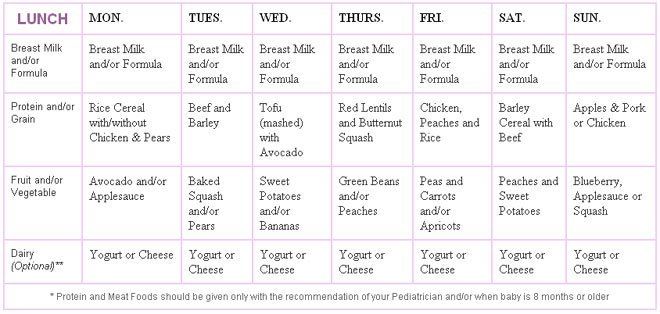 You can not blindly buy canned food, looking at the age on the label.
You can not blindly buy canned food, looking at the age on the label.
No one canceled the risk of an allergy to a product, and the earlier a child gets acquainted with a highly allergenic product, the stronger the reaction, read here for more details. If you feed the baby only canned food, focusing on age markings, that the child will eat delicate light food that will not teach him to chew, and then at 2 years old the question arises: Why does the child vomit on adult food? And the answer is simple, his body simply does not know how to chew, swallow and digest ordinary adult food. Therefore, as always0007 I speak and will speak and write, everything in moderation, the golden mean.
Canned nutrition is convenient, simple and easy, but should be in moderation. Up to a year, diversity, diversity, the first 2-3 months is a quiet pace, which grows and grows by the year. We offer the child different food, canned and homemade, but at stage 3 we try to give more homemade food, because it is always different, well, it is not possible to make mashed potatoes always the same, especially if you use only a fork, this is what the baby needs, different textures, different components, as in the game - different levels, for complication. nine0005
nine0005
Therefore, from the above, there are some rules to follow:
- Never look at the age marking on canned food;
- Always check the composition of the canned food;
- Always taste baby puree before giving to baby;
- Comply with safety measures for the quality of canned food, such as cotton when unscrewing the lid, storage temperature, etc.
- If the composition is multi-component, even if the products were introduced separately into complementary foods, give a jar very carefully, for example, give not all, but only 1/3 of it. nine0022
At what age can a child be given cow's milk
Reviewer Kovtun Tatyana Anatolievna
47111 views
December 16, 2021
Login or register to save articles and products to your favorites
Until recently, everyone was talking about the positive impact of milk on people of all ages. But recently the situation has changed, and now more and more experts disagree. At what age can you give milk to a child and what are the restrictions?
But recently the situation has changed, and now more and more experts disagree. At what age can you give milk to a child and what are the restrictions?
Benefits and harms of cow's milk
There was a belief that children have special lactoenzymes that can break down protein from cow's milk, but they disappear with age. Recent studies have refuted this theory - a person with a healthy digestive system, not allergic to cow's milk protein or lactose intolerance (lactase deficiency), can drink milk until old age. nine0005
Milk contains calcium in an easily digestible form: with it, the baby's teeth and bones will be strong. It is important to remember that milk is a nutritious product, so if the baby is thirsty, it is better to give him some water. Unlimited milk can cause digestive and metabolic disturbances, so moderation is important.
FrutoNyanya produces milk for baby food. It has a balanced content of calcium, prebiotic inulin and iodine. You can learn more about what stages it goes through from the video on the FrutoNyanya YouTube channel. nine0005
nine0005
When can children be given milk
Can babies drink cow's milk? Yes, but with certain restrictions. Babies of different ages have their own milk requirements. Most often, pediatricians advise giving milk in the following quantities:
- children under 12 months of age should not be given milk as a separate food product, only as part of a meal after consulting a pediatrician;
- children from 1 to 3 years old can drink one serving per day - this is 200 milliliters; nine0022
- after 3 years, the number of servings can be increased to two.
What kind of cow's milk to give to a child
As a first acquaintance, it is better to choose ultra-pasteurized milk. During ultra-pasteurization, bacteria die, due to which the milk begins to deteriorate quickly, and the beneficial components of the milk remain in place. Yes, the value of such milk will be slightly less than that of the freshest steam, but these measures guarantee the safety of the product for the child and increase the shelf life. It is also important that baby milk is produced in separate workshops where quality standards are strictly observed. nine0005
It is also important that baby milk is produced in separate workshops where quality standards are strictly observed. nine0005
Often, baby milk is enriched with vitamin complexes and prebiotics, which help the baby's digestive tract, protect the immune system and promote rapid growth.
How and in what form to give milk
It is better not to give milk immediately after a meal, as it does not go well with some foods. Optimally - for a second breakfast or afternoon snack, in combination with cookies or bakery products. You can also dilute milk-free baby cereals with milk or cook your baby’s favorite cereal cereals on its basis. nine0005
Even industrial ultra-pasteurized milk is better to warm up to 37 degrees - so the child will be more comfortable drinking it.
Why children under one year old should not have cow's milk
Babies under one year old should not be given cow's milk as a separate food product at all - their delicate gastrointestinal tract, immature excretory system and metabolism are not yet ready to assimilate this product [1] .
Signs of cow's milk intolerance in children
Some babies may not have enough lactase in their intestines, a special enzyme responsible for the breakdown of milk sugar. Usually, with age, the enzyme systems of the digestive tract mature and everything is getting better. And if lactase deficiency is congenital, then, depending on its severity, dairy products are excluded from the diet or replaced with low-lactose ones.
Pay close attention to your baby's reaction to the new product. An allergy to cow's milk in a child can be manifested by skin itching, upset stool, nausea or vomiting. In this case, it is better to refuse the product and seek the advice of a pediatrician. nine0005
Milk is a very useful addition to the diet, and if the child does not have an unpleasant reaction to it in the form of a skin rash or digestive disorders, then after consulting with a specialist, you can include it in the permanent menu.
*Breast milk is the best food for a young child.
Learn more