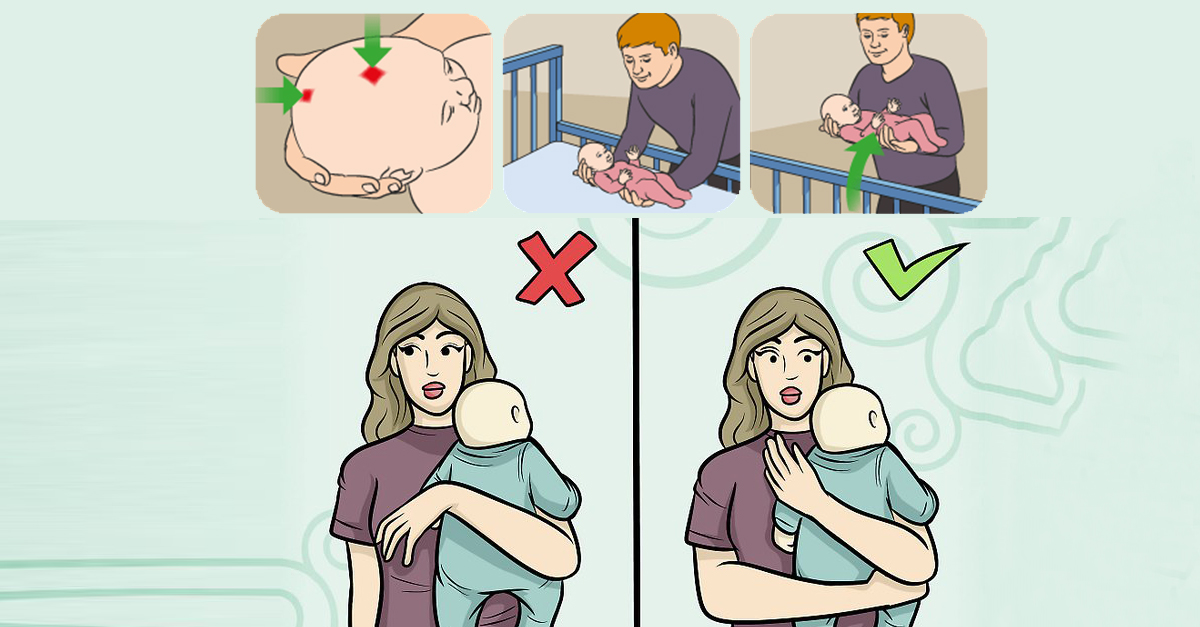
How to bottle feed a baby with breast milk
How to combine breast and bottle feeding
It can take several weeks for you and your baby to feel happy and confident with breastfeeding.
Once you've both got the hang of it, it's usually possible to offer your baby bottles of expressed milk or formula alongside breastfeeding.
This is sometimes called mixed or combination feeding.
Why combine breast and bottle?
You may want to combine breastfeeding with bottle feeding if you:
- are breastfeeding and want to use a bottle to offer your baby some expressed breast milk
- want to breastfeed for some of your baby's feeds, but give bottles of formula for 1 or more feeds
- are bottle feeding your baby and want to start breastfeeding
- need to leave your baby and want to make sure they have some milk while you're away
Introducing formula feeds can affect the amount of breast milk you produce. There is also a small amount of evidence to show babies may not breastfeed as well because they learn to use a different kind of sucking action at the bottle than at the breast.
These things can make breastfeeding more difficult, especially in the first few weeks when you and your baby are still getting comfortable with breastfeeding.
Your breastmilk supply will usually not be affected if you start bottle feeding your baby when they are a bit older, you are both comfortable with breastfeeding, and you breastfeed every day.
Introducing formula feeds
If you're combining breastfeeding with formula feeds both you and your baby can carry on enjoying the benefits of breastfeeding.
If you choose to introduce infant formula:
- it's best to do it gradually to give your body time to reduce the amount of milk it makes – this helps lower your chance of getting uncomfortable, swollen breasts, or mastitis
- if you're going back to work, start a few weeks beforehand to give both of you time to readjust
- if your baby is 6 months old or more and can drink milk from a cup, you may not need to introduce a bottle at all
For more information, see drinks and cups for babies.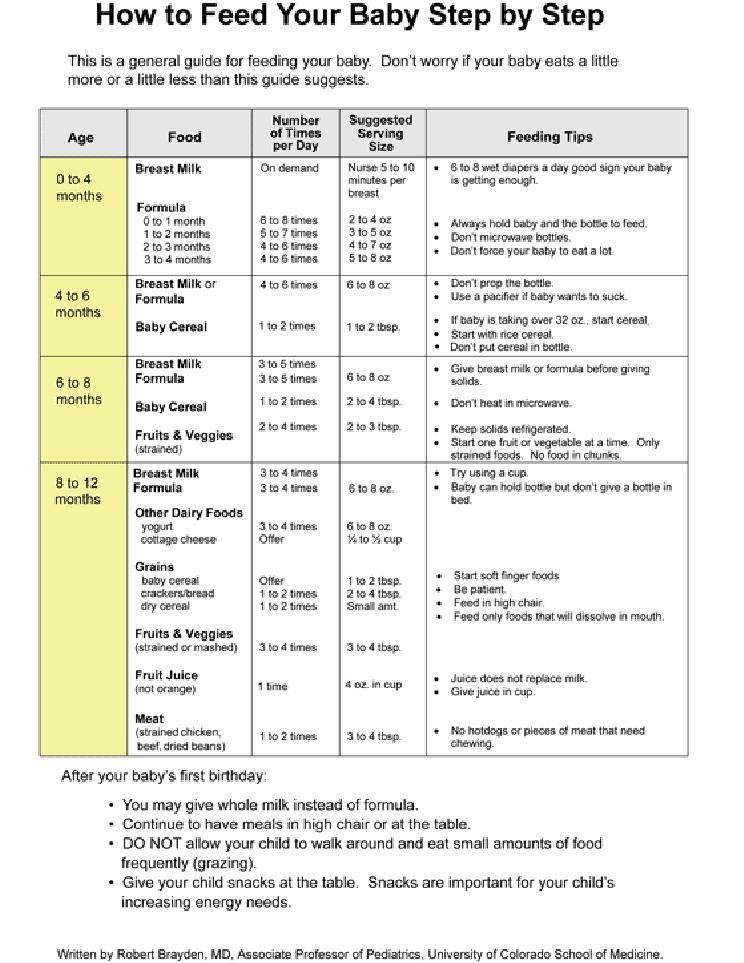
Giving your baby their first bottle
It may take a while for a breastfed baby to get the hang of bottle feeding, because they need to use a different sucking action.
- it usually helps to give the first few bottles when your baby is happy and relaxed – not when they're very hungry
- it may help if someone else gives the first bottle feeds, so that your baby is not near you and smelling your breast milk
- you might want to try using a different position for bottle and breastfeeding
See more advice on how to bottle feed.
Restarting breastfeeding
If you want to start breastfeeding more and give your baby fewer bottles, it's a good idea to ask your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter for support.
These tips may help too:
- Hold and cuddle your baby as much as possible, ideally skin to skin. This will encourage your body to make milk and your baby to feed.
- Express your breast milk regularly. Expressing releases the hormone prolactin, which stimulates your breasts to make milk. About 8 times a day, including once at night is ideal. It may be easier to express by hand to begin with – your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter can show you how.
- Try bottlefeeding while holding your baby skin to skin and close to your breasts.
- If your baby is latching on, feed little and often. Do not worry if your baby does not feed for long to begin with. See tips on how to get your baby properly positioned and attached.
- Choose times when your baby is relaxed, alert and not too hungry, and do not force your baby to stay at the breast.

- Decrease the number of bottles gradually, as your milk supply increases.
- Consider using a lactation aid (supplementer). A tiny tube is taped next to your nipple and passes into your baby's mouth so your baby can get milk via the tube as well as from your breast. This helps to support your baby as they get used to attaching to the breast. Your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter can give you more information.
See more tips on boosting your milk supply.
Help and support with mixed feeding
If you have any questions or concerns about combining breast and bottle feeding:
- talk to your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter
- call the National Breastfeeding Helpline on 0300 100 0212 (9.30am to 9.30pm, every day)
- find breastfeeding support near you
Video: why combine breast and bottle feeding?
In this video, 3 mothers discuss ways to combine breast and bottle feeding.
Media last reviewed: 22 March 2020
Media review due: 22 March 2023
Page last reviewed: 8 October 2019
Next review due: 8 October 2022
Introducing a Bottle to a Breastfed Baby
The information in this post is also contained in our Working & Breastfeeding.
Here is one approach to beginning pumping and introducing bottles that has worked well for many mothers as they prepared to return to work:
- Once breastfeeding is well established – usually after about four weeks – begin pumping after one feeding a day where your breasts still feel a little full. Remember you are pumping “leftovers” and should only expect a small amount.
- Freeze that first pumping immediately. You can add other pumpings to it after they have been cooled in the freezer.
- Your pediatrician may have given you a total number of ounces your baby may feed in a day or a range from the smallest probable amount to the largest, based on your baby’s weight.
- If dealing with a total volume over a 24-hour period, divide that by the typical number of times your baby feeds for a target volume for the first bottle.
- If dealing with a range, store volumes of the lower amount.
- Store some extra small volumes in case baby is hungrier than expected.
- When you have enough stored to equal the expected volume and a bit more, you can begin to plan a time to introduce a bottle.
- EXAMPLE for offering the first bottle:
- Your pediatrician suggests that your baby probably takes about 24 ounces a day.
- You know that he feeds between eight and 12 times a day.
- That means he could take anywhere from 2 to 3 ounces.
- You pump until you have a 2-ounce bottle and then have several 1/2 ounce bottles to equal at least three ounces or more saved.
- Choose a day that your primary support person will be available and a feeding time where baby tends to be more pleasant and patient for his feeding.

- Baby may accept a bottle more easily from someone other than you. He knows milk comes from you and may not understand why he’s not going there instead of to this foreign object.
- Thaw out the 2-ounce bottle in the refrigerator overnight.
- When baby begins to stir, place the bottle from the refrigerator in a bowl of warm water (bath temperature) or a bottle warmer while the person offering the bottle goes to get baby from his bed, changed and ready for the feeding.
- Often it helps to run the bottle nipple under warm water, if it was also in the refrigerator, to make it more acceptable to the baby.
- Baby should be held in an upright, almost sitting, position that is similar to the position usually used by the support person.
- The warmed bottle should be held at an angle tilted just enough to fill the nipple to allow baby to keep control of when and how fast the milk comes.
- Tickle the baby’s mouth to encourage an open mouth then bring baby up onto the bottle nipple, aiming the nipple toward the palate.

- Some have found that it can help to have an article of clothing you have worn, like a nightgown or t-shirt, to place on their arm, shoulder, or chest where the baby can smell your scent.
- It is usually best if you are close but not present in the room during this first “experiment” with bottle feeding. Your baby is very wise and will wait for you to come feed her if she knows you are nearby.
Once the feeding is completed, you will pump to create a bottle equal to what the baby consumed. Remember that the baby is always better than a pump! If you do not pump as much as the baby took, it is more likely a pump issue than an issue of not enough milk. Just pump after another breastfeeding and add that amount to what you pumped to get the amount baby took.
You will continue this pattern until you have enough milk stored in your freezer to get you through a normal work day plus a few extra for any hectic day at work where you may not have been able to pump as often. Plan to fully breastfeed for all feedings when not separated from your baby.
Plan to fully breastfeed for all feedings when not separated from your baby.
Working and Breastfeeding
Feeding Breastmilk From a Bottle
Pumping
Cleaning and Sanitizing Pumping Accessories
Hand Expressing
Published August 2018.
Feeding with expressed milk | breastfeeding
When can I start breastfeeding my baby with expressed breast milk? How to do it right? Is it worth worrying that the child will confuse the pacifier with the breast? In this article we will answer your questions.
Share this information
When can I start breastfeeding my baby?
If your baby is healthy and breastfeeding well, there is no need to give him expressed milk. For the first four weeks, you work together to start and increase milk production, and your baby also learns to suckle properly at the breast. There is not enough scientific data on this yet, 1 but there is an opinion that bottle feeding in the first month may adversely affect the process of establishing breastfeeding.
However, if the newborn is unable to latch on or suckle for some reason, start expressing milk as soon as possible after delivery. Read more about this in our articles on coping with problems in the first week, breastfeeding premature babies and babies with special needs, and seeking help from your healthcare provider.
How can I feed my baby with expressed breast milk?
There are many expert feeding solutions that allow you to give your baby expressed milk in a variety of ways, depending on your and your baby's needs.
For example, the innovative Calma smart pacifier only lets milk through when the baby creates a vacuum by suckling. This means that when feeding from a bottle, he will make the same movements with his tongue and jaws as when sucking at the breast. 2.3 Calma was developed with the help of breastfeeding experts from the University of Western Australia. When using this pacifier, the baby can suck, swallow, pause and breathe in the same way as when breastfeeding. 4 Preserving natural sucking habits allows baby to transition easily from breast to bottle and back.
4 Preserving natural sucking habits allows baby to transition easily from breast to bottle and back.
In addition, Medela also offers regular bottle teats* in two versions that produce milk at different rates. All Medela* nipples can be placed directly on bottles used for expressing milk, minimizing the risk of spillage.
If you need to feed your baby with expressed milk, but you do not want to bottle feed him until he is learning to breastfeed, you can use a sippy cup* for temporary feeding. The baby will be able to drink milk from such a mug, but you should be careful not to spill the milk. For the first time, it is advisable to feed the child from a drinking cup under the supervision of the attending physician in order to learn how to do it correctly.
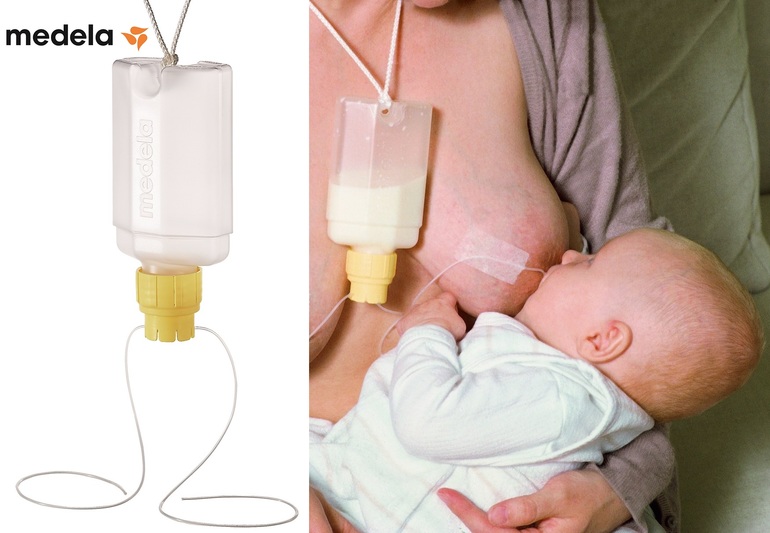
If your baby needs to be supplemented with expressed milk in addition to regular breastfeeding, the Supplementary Feeding System (SNS)* can be used. It is equipped with a thin, flexible capillary that can be clipped close to the nipple to give your baby expressed milk while breastfeeding.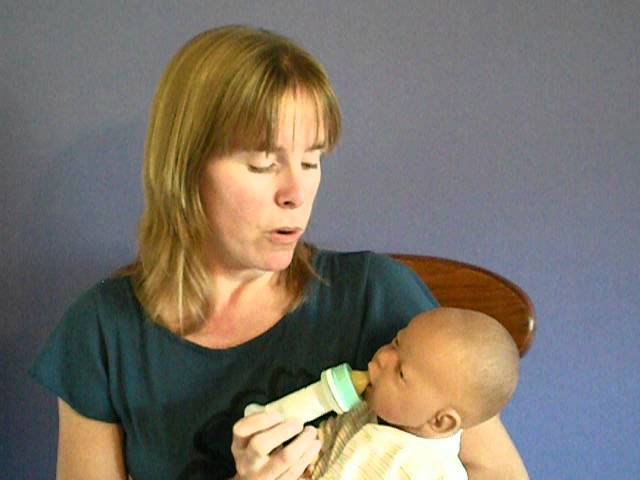 Thanks to this, the baby suckles the breast for longer, thereby developing sucking skills and stimulating the production of milk from the mother. This can be helpful when there is a shortage of breast milk, as well as when feeding adopted or surrogate children.
Thanks to this, the baby suckles the breast for longer, thereby developing sucking skills and stimulating the production of milk from the mother. This can be helpful when there is a shortage of breast milk, as well as when feeding adopted or surrogate children.
If the baby is unable to breastfeed because he is too weak or has a congenital disease, you can use the Special Needs Cup*, which releases milk with gentle pressure, making it suitable for feeding these babies.
How to teach a child to bottle feed?
If breastfeeding is going well and you decide to start bottle feeding your baby with expressed breast milk, follow these guidelines.
Start early and take your time
Don't wait until the first day of work or the first time you leave the house to start bottle feeding your baby. Start accustoming your baby to small portions of expressed milk a couple of weeks before the desired date, calmly and without haste. Gradually build up to one full serving of pumped milk from a bottle.
Choose a time
Ideally, at the first bottle feeding, the baby should be hungry, but not too hungry - in this state, he is as relaxed as possible.
Let others feed
Your baby is used to feeding from your breast, so when you offer him a bottle it can be confusing. The process can go faster if the first time the baby is bottle-fed by someone else while you are not in the room, so that your sight and smell do not embarrass the baby.
Maintain optimal temperature
Your baby will be more willing to eat expressed milk if the temperature is around 37°C, close to body temperature.
Dip the nipple in milk
Try dipping the nipple in expressed milk before offering it to your baby. This way it will taste and smell like your breast milk. Lightly touch the baby's upper lip with the nipple to open the mouth.
Choose the right position for bottle feeding
Feed your baby on demand and keep him reclining during feeding. Never bottle feed your baby when he is lying or sitting, otherwise he may choke. Listen to the wishes of the child - take as many pauses as he needs. You can even try to shift it from one hand to another during feeding.
Never bottle feed your baby when he is lying or sitting, otherwise he may choke. Listen to the wishes of the child - take as many pauses as he needs. You can even try to shift it from one hand to another during feeding.
Be patient
Don't worry if your baby doesn't take the bottle right away - it may take several tries. If he pushes the bottle away or starts crying, calm him down, wait a few minutes and try again. If he still doesn't want to bottle feed, wait a few more minutes and breastfeed him as usual. Repeat the bottle experiment at a different time of day.
How much pumped milk should I give my baby?
All children are different. Research shows that between the ages of one and six months, a baby can consume between 50 and 230 ml of milk per feeding. To start, prepare about 60 ml and observe how much your baby needs - more or less. You will soon realize how much milk he usually eats. Just never force him to finish the cooked portion.
How can I keep my baby safe when bottle feeding?
Always clean and sterilize your pump and bottles according to the manufacturer's instructions. Wash your hands before expressing, pouring milk, and feeding your baby. Follow our instructions for safely storing and thawing your expressed milk.
If breastmilk needs to be warmed, place the bottle or bag in a bowl of warm water or a heater or under running water at a maximum of 37°C. Never heat breast milk in the microwave or on the stove.
Will the baby be able to transition from breast to bottle?
Some mothers worry that if they start bottle feeding too early, the baby will get used to the artificial nipple and not want to breastfeed. Others, on the contrary, are worried that if the child is not immediately accustomed to the bottle, then he will no longer eat from it. In general, in these cases, they say that the child confuses the nipple with the breast.
Experts disagree on whether such confusion is a problem. 1 Without a doubt, it is easier for a baby to suckle milk from a regular bottle with a nipple, which does not require a vacuum, than from the breast, since the milk flows faster, also under the influence of gravity. And some babies really have clear preferences: only the breast or only the nipple. However, many babies are comfortable suckling both the breast and the pacifier.
1 Without a doubt, it is easier for a baby to suckle milk from a regular bottle with a nipple, which does not require a vacuum, than from the breast, since the milk flows faster, also under the influence of gravity. And some babies really have clear preferences: only the breast or only the nipple. However, many babies are comfortable suckling both the breast and the pacifier.
If you are unable to feed your baby with expressed breast milk, seek help from a lactation consultant or specialist.
Literature
1 Zimmerman E, Thompson K. Clarifying nipple confusion. J. Perinatol. 2015;35(11):895-899. - Zimmerman I., Thompson K., "On the issue of breastfeeding." Zh Perinatol (Journal of Perinatology). 2015;35(11):895-899.
2 Geddes DT et al. Tongue movement and intra-oral vacuum of term infants during breastfeeding and feeding from an experimental teat that released milk under vacuum only. Early Hum Dev . 2012;88(6):443-449. - Geddes D.T. et al., "Language Movements and Oral Vacuum Generation in Term Infants During Breastfeeding and Feeding from an Experimental Vacuum-Delivery Teat". Airlie Hume Dev. 2012;88(6):443-449.
2012;88(6):443-449. - Geddes D.T. et al., "Language Movements and Oral Vacuum Generation in Term Infants During Breastfeeding and Feeding from an Experimental Vacuum-Delivery Teat". Airlie Hume Dev. 2012;88(6):443-449.
3 Segami Y et al. Perioral movements and sucking pattern during bottle feeding with a novel, experimental teat are similar to breastfeeding. J. Perinatol. 2013;33(4):319-323. - Segami I. et al., "Perioral movements and sucking during bottle feeding with a new experimental nipple are very similar to sucking from the breast." Zh Perinatol (Journal of Perinatology). 2013;33(4):319-323.
4 Sakalidis VS et al. Oxygen saturation and suck-swallow-breathe coordination of term infants during breastfeeding and feeding from a teat releasing milk only with vacuum. Int J Pediatr. 2012;2012:130769. - Sakalidis V.S. et al., "Oxygenation and Coordination of Sucking, Swallowing, and Breathing in the Term Infant During Breastfeeding and Feeding from a Purely Vacuum Teat". Int J Pediatrician 2012;2012:130769.
Int J Pediatrician 2012;2012:130769.
Read instructions before use. Consult a specialist about possible contraindications.
* RC № ФСЗ 2010/07353 of 07/19/2010
Feeding a baby with breast milk from a bottle
Establishing breastfeeding is one of the most significant processes for a mother in the first month after the birth of a baby. This is a sacrament in which a lot of important moments for the development of the baby are hidden: ideal food for the baby, contact between the baby and the mother, normalization of sleep. In addition, for many mothers, this is a very pleasant and healing process in the postpartum period. The release of the hormone oxytocin contributes to the contraction of the uterus and the restoration of its former shape. The production of milk by the body helps mom lose extra pounds. Long-term breastfeeding acts as a prophylactic against a number of female diseases.
However, not everyone succeeds in easily coping with this process (albeit natural). In the first month, many women may experience difficulties: unprepared nipples, irregular or insufficient milk production, etc. These problems are the norm and should not become a reason for the growth of anxiety and self-blame. Most likely, in a month the process will improve. But even if this is not the case, alternative options can be used, for example: feeding with expressed milk from a bottle or supplementing with formula. In any case, it is worth remembering: you are the best mother for your child.
In the first month, many women may experience difficulties: unprepared nipples, irregular or insufficient milk production, etc. These problems are the norm and should not become a reason for the growth of anxiety and self-blame. Most likely, in a month the process will improve. But even if this is not the case, alternative options can be used, for example: feeding with expressed milk from a bottle or supplementing with formula. In any case, it is worth remembering: you are the best mother for your child.
At what age can you bottle feed your baby with expressed milk?
If there is significant difficulty in breastfeeding, you can use the bottle almost immediately. Today, a feeding bottle with a teat labeled "0+" is available in every pharmacy or baby store. There are bottles of foreign and domestic manufacturers on sale (for example, DINO & RHINO bottles are produced in Russia).
Bottle feeding may also be recommended if the baby is not suckling well at the breast, has a weak latch on the nipple, and is not gaining weight (this is sometimes the case with babies who were born a little early).
In other cases, in the first month it is recommended to establish a natural process of breastfeeding. In the future, you can use the bottle as an aid, for example, if you need to go away on business, and leave the child with dad, grandmother, nanny.
How to feed your baby with expressed milk?
To begin with, the bottle must be sterilized. How to do it correctly, you can read in our other article. Then fresh or thawed, warmed to body temperature (37 ° C) expressed breast milk is poured into a bottle, and the baby sucks it out through the nipple.
Modern bottle nipples are designed so that when sucking, the baby must make the same movements and efforts as when sucking milk from the breast. The nipples have a flow rate close to the anatomical shape and the actual age of the baby. They are made from safe and hypoallergenic BPA-free materials, so you don't have to worry about your child's health.
How to offer the baby a bottle for the first time and teach the child to eat from it?
Usually this does not cause difficulties, many children begin to actively drink from a bottle the first time. But sometimes it takes several tries. The baby may push the pacifier away, crying is normal. Try again and again.
But sometimes it takes several tries. The baby may push the pacifier away, crying is normal. Try again and again.
To offer a bottle for the first time, wait until the baby is hungry (but not too hungry) and bring the nipple to the mouth in the same way as you do with the breast nipple, at the same angle. Lightly touch her lips to the child so that he opens his mouth. The optimal position of the baby when feeding is reclining.
If up to this point you have been breastfeeding for a long time and the child has a clear connection in the head (mother - breast), ask one of the relatives to offer him a bottle, so he will not be distracted by your smell and expect the usual way of feeding.
If the baby does not want to take the nipple in any way, dip its tip in expressed milk, perhaps he will readily react to the smell.
If he wants to pause, listen to his desire.
How much expressed milk should you give your baby?
There are norms recommended by pediatricians: how many ml of milk a child of one age or another should eat. For example, at the stage of 1-6 months, the average child should eat 50-230 ml of milk per meal (you can find a detailed table by month in the relevant reminders). But there is also an individual norm. If your child eats less or more than the average amount, but is healthy and developing well, there is no reason to worry.
For example, at the stage of 1-6 months, the average child should eat 50-230 ml of milk per meal (you can find a detailed table by month in the relevant reminders). But there is also an individual norm. If your child eats less or more than the average amount, but is healthy and developing well, there is no reason to worry.
How to make bottle feeding as safe as possible?
- Choose a nipple with an age-appropriate flow and ensure your baby is in the correct feeding position to prevent choking.
- Sterilize the nipple, bottle, and pump before each feeding during the first few months of your baby's life.
- Be sure to wash your hands before feeding and pumping.
- Store expressed milk correctly: no more than 4 hours at room temperature. If you need to store longer, use the refrigerator or freezer.
Can I alternate between breastfeeding and bottle feeding?
Yes, for most children this does not cause discomfort.