Introducing foods to baby guideline
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
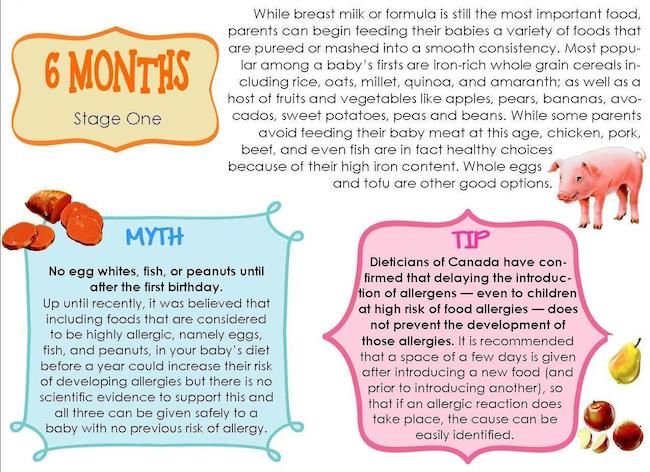
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
The Complete Guide to Starting Solids
Ready to start solid foods with your baby? Get the details as to what and how much baby should be eating with this comprehensive guide to starting solids!
Warning. This post is LONG. But comprehensive. So say what you will! I was inspired to write this post because a very good friend of mine called me up one night asking all sorts of questions about starting solids with her baby. I shared what my plan was with Lily [similar to what I had done with Anthony and Joey]. I took her questions and essentially have made an easy-to-follow blog post on the topic of starting solids with baby. And if you want MORE than this post, be sure to scroll down to the bottom of this post for additional resources I’ve found helpful on this topic.
This post is LONG. But comprehensive. So say what you will! I was inspired to write this post because a very good friend of mine called me up one night asking all sorts of questions about starting solids with her baby. I shared what my plan was with Lily [similar to what I had done with Anthony and Joey]. I took her questions and essentially have made an easy-to-follow blog post on the topic of starting solids with baby. And if you want MORE than this post, be sure to scroll down to the bottom of this post for additional resources I’ve found helpful on this topic.
Note: The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that breastmilk or formula be the sole source of your baby’s nutrition for the first 6 months of life. That’s why I waited to feed Lily solids until then. However, if your baby is physically showing signs of readiness then your doctor may give you the OK to start solids anywhere between 4-6 months.
There are essentially two schools of thought when it comes to starting solids with your baby. The first, the traditional start with purees around 6 months of age [earlier if your baby is showing signs of readiness] and gradually starting introducing chopped or soft finger foods 8-9 months of age. OR, there’s baby led weaning, where you skip the purees all together and start with soft finger foods around 6 months of age, or when baby has developed a stronger pincer grasp. With Joey I did the traditional route. And with Anthony and Lily I did [or am doing] more of a modified baby led weaning approach. So a mix of both! I’d encourage you to listen to your baby and your own instincts— if baby led weaning makes you nervous, then heck, start with purees! That’s what the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends. But if you feel like your baby is developmentally ready for SOLID solids and is strong enough to pick up pieces of food and put it directly in their mouth, then baby led weaning might be for you.
The first, the traditional start with purees around 6 months of age [earlier if your baby is showing signs of readiness] and gradually starting introducing chopped or soft finger foods 8-9 months of age. OR, there’s baby led weaning, where you skip the purees all together and start with soft finger foods around 6 months of age, or when baby has developed a stronger pincer grasp. With Joey I did the traditional route. And with Anthony and Lily I did [or am doing] more of a modified baby led weaning approach. So a mix of both! I’d encourage you to listen to your baby and your own instincts— if baby led weaning makes you nervous, then heck, start with purees! That’s what the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends. But if you feel like your baby is developmentally ready for SOLID solids and is strong enough to pick up pieces of food and put it directly in their mouth, then baby led weaning might be for you.
I’ve compiled the most important information from this blog post and put it into a printer-friendly PDF just for you. You can also pin this image to save and read this post later too!
You can also pin this image to save and read this post later too!
Fast Facts about Starting Solids
- Look for physical signs that your baby is ready for solids, such as she can sit up with limited support, and has good head and neck control, and she can keep most of the food in her mouth, swallowing it.
- Solid foods can be introduced between 4-6 months of age. After 6 months finger foods or other table foods can be introduced based on your discretion and your baby’s readiness.
- Wait three to four days before introducing another allergenic food [peanuts, tree nuts, soy, eggs, wheat, shellfish, fish] to your baby. If you suspect a reaction, stop feeding your baby the new food and contact your pediatrician.
- Offer a variety of healthy foods, even multiple vegetables, at each meal. It is also important to offer protein/meat and iron-rich foods, particularly for breastfed infants.
- Don’t stop breast or formula feeding. Continue providing breastmilk or formula as the main source of your baby’s nutrition and calories for the first year of life.

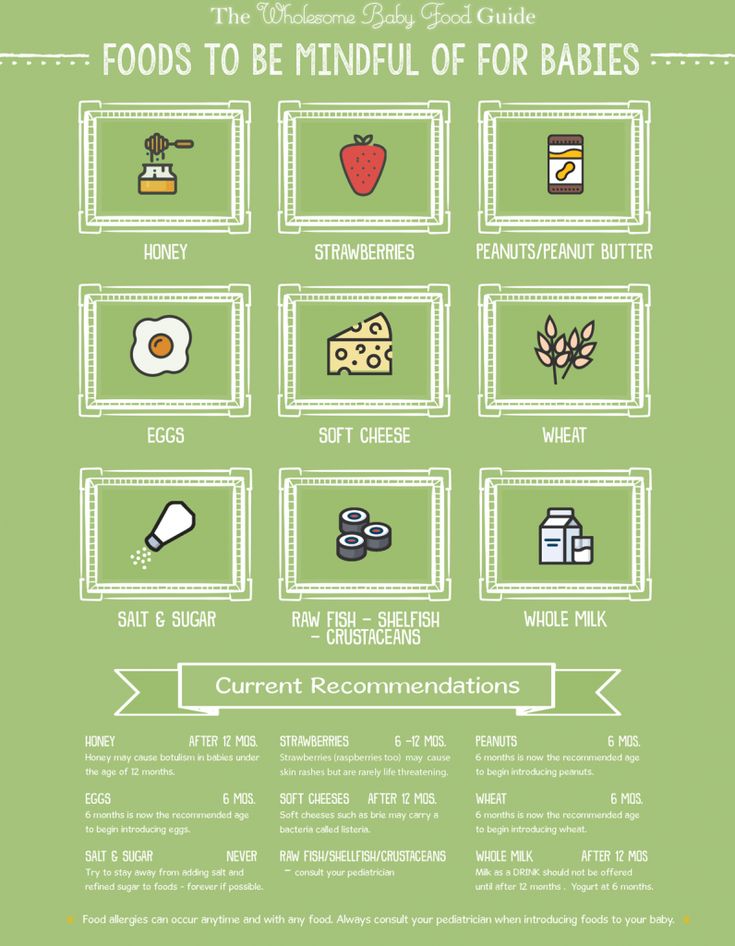
- Never add honey, salt, or sugar to baby food. These should never be added to “entice” or “trick” your baby into liking a certain food.
- Try to relax: Most of the first few solid-food feedings wind up on your baby’s face, hands, and bib.
- Never feed your baby solid foods from a bottle. Always spoon-feed from a bowl, not from the jar of baby food unless she will finish it.
- Never force-feed your baby. Stop feeding your baby when she turns head away from spoon or keeps her mouth closed.
Division of Responsibility in Feeding
I follow the Ellyn Satter division of responsibility when it comes to feeding. Parents or caregivers provide the food, and when and where the child is fed, and then the children decide what and how much they’ll eat. Learning to feed a child is an experience for both the parents and child. Children are not only learning to eat, but they are eating the amount THEY need. For example, for this stage of feeding babies, when your baby is turning their head away from you or pushing food off their tray, they are a. finished or b. not a huge fan of that particular food!
finished or b. not a huge fan of that particular food!
Sample Baby Feeding Schedule
Here’s a quick, sample schedule that I roughly followed with the kids when they were babies. And I use the word schedule lightly. This isn’t EVERYDAY. Some days are busier than others and baby might miss a taste or two of food. And sometimes baby nurses more than 4 times a day and more than once at night. But again, we aren’t feeding babies solids because they need a certain amount of calories from solid foods. We are feeding them solids at this age so they can learn to explore, taste, and have fun with new foods and textures! You could make life even easier by thinking of your mealtime as the same mealtime for your baby.
- Wakeup + breastmilk/formula
- Breakfast 1-1.5 hours later
- Breastmilk/Formula after morning nap
- Lunch 1-1.5 hours later
- Breastmilk/Formula after afternoon nap
- Dinner 1-1.5 hours later
- Breastmilk/Formula before bed
- Wakeup at night for breastmilk/formula
Baby Led Weaning Approach to Feeding
Some people skip the purees and feed their babies with a method called Baby Led Weaning [BLW] around 6 months of age.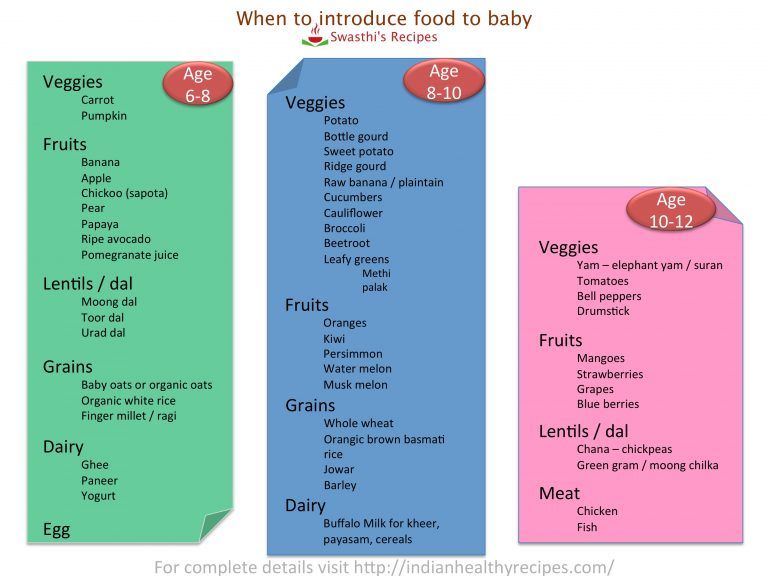 Baby-led weaning essentially means you skip pureed, spoon-feeding with your baby and your baby starts self-feeding around 6 months of age [with the continuation of breast milk or formula]. This method is a great option if you find your baby has developed a pincer grasp [which most babies do around 8-10 months], which means she’ll be able to pick up smaller objects/pieces of food between her thumb and forefinger. According to multiple BLW resources, babies are developmentally capable of feeding themselves by 6 months of age, so there is no need for pureed food. Your job is to offer your baby bite-sized or soft pieces of food at the table [essentially the same food the rest of the family is eating] and it is up to your baby whether or not he or she eats it, and how much they eat.
Baby-led weaning essentially means you skip pureed, spoon-feeding with your baby and your baby starts self-feeding around 6 months of age [with the continuation of breast milk or formula]. This method is a great option if you find your baby has developed a pincer grasp [which most babies do around 8-10 months], which means she’ll be able to pick up smaller objects/pieces of food between her thumb and forefinger. According to multiple BLW resources, babies are developmentally capable of feeding themselves by 6 months of age, so there is no need for pureed food. Your job is to offer your baby bite-sized or soft pieces of food at the table [essentially the same food the rest of the family is eating] and it is up to your baby whether or not he or she eats it, and how much they eat.
This is in contrast to the spoon-feeding, traditional pureed method to start solids with babies. While both methods can work well for your baby, one is not superior to the other. What is most important is that you, as the parent, are comfortable with starting solids with your baby, and that your pediatrician gives you the go ahead.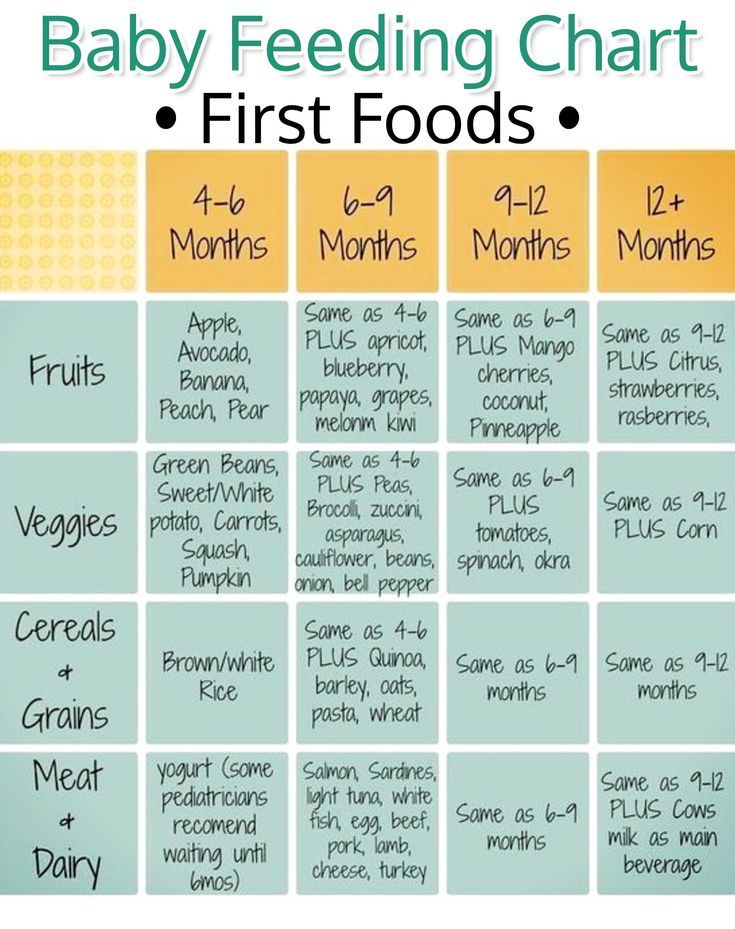 Ultimately both methods can be seen as baby-led as long as you watch your baby carefully and allow them to control their own hunger and fullness cues.
Ultimately both methods can be seen as baby-led as long as you watch your baby carefully and allow them to control their own hunger and fullness cues.
Concerned about allergies? Me too!
Guess what? The recommendations of when to introduce highly allergenic foods have changed. Now we can introduce 7 of the 8 allergenic foods when we introduce solids, as early as 6 months of age [peanuts, tree nuts, eggs, soy, fish, shellfish, and wheat]. Research points at the fact that the longer we waited on giving children these highly allergenic foods, the likelihood for them having an allergy was greater. Note: If a history of severe food allergies runs in your family, talk to your primary care provider before introducing allergenic foods. Also, it is safe to introduce cow’s milk based cheese and yogurt before age one, however it is recommended to wait until after age one to introduce cow’s milk. When giving your baby one of these allergenic foods, introduce one food at a time, wait a couple of days and then try another one to watch out for any reactions, which would indicate a sensitivity or allergy. Also, if you do have food allergies in your family, you may want to talk to you pediatrician about when to introduce peanuts, eggs, etc.
Also, if you do have food allergies in your family, you may want to talk to you pediatrician about when to introduce peanuts, eggs, etc.
I’M DONE!
Phew! When it comes to starting solids here’s what I know: do your very best to offer a variety of foods and textures and flavors, and your little one will decide how much or what to eat. Also, the period of pureed foods for babies is over so quickly. So do not stress too much about it. Just beware: things get a whole lot messier from 12 months and beyond during toddlerhood. Soon enough the stage of purees and chopped foods will be over, and your baby will be eating exactly what everyone else in the family eats!
If you have ANY other questions, don’t be shy. Please email me at [email protected]
Additional Baby Feeding Resources
Age-By-Age Guide to Feeding Your Baby by BabyCenter
Feeding & Nutrition by American Academy of Pediatrics
How To Modify Baby Led Weaning by The Lean Green Bean
5 Tips for Successful Baby Led Weaning by Sarah Remmer, RD
Russian Union of Pediatricians
Introduction of complementary foods
How to introduce complementary foods correctly is one of the most pressing issues that concern parents.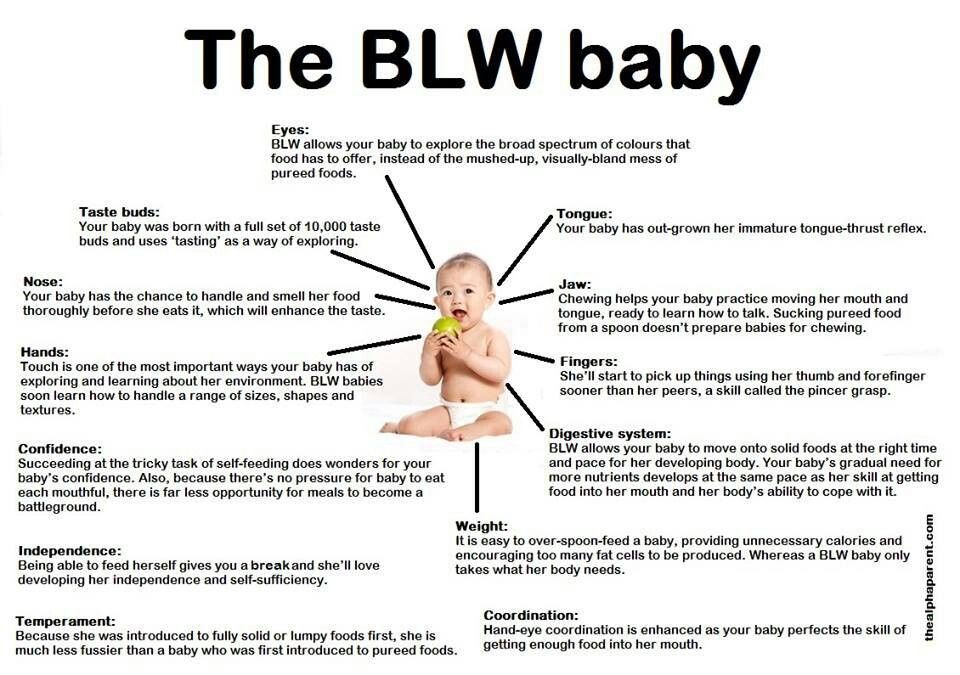
In the first months of life, the main food for the baby is breast milk or an adapted milk formula, however, as the child grows and develops, this becomes insufficient and it is necessary to think about the introduction of complementary foods.
Your baby is over 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines them and reaches for them. The child's emotional reactions have become much richer: he smiles happily at all people, makes various sounds. Perhaps you notice that the child looks into your plate with interest, closely monitors what and how you eat, does this mean that it is time to introduce complementary foods? And where is the best place to start? Let's figure it out!
When should complementary foods be started?
According to the Program for optimizing the feeding of infants in the first year of life in the Russian Federation (2019), the recommended age for the introduction of complementary foods is in the range from 4 to 6 months.
The following points will help determine the readiness of the baby for the introduction of complementary foods:
1. Food interest - you can check its presence as follows: during your meal, give the baby an empty spoon or fork, and if he plays with it, licks it, then there is no food interest yet; but if the child is dissatisfied with the fact that the spoon is empty, food interest has probably appeared. “But how does a child understand that there should be food in a spoon?” Parents often ask. The answer is quite simple: take your baby to the table with you so that he can see how you eat!
2. The child can sit alone or with support. It is unacceptable to feed the child lying down, because he may choke.
3. Extinction of the “pushing out” reflex - when the baby pushes out of the mouth both the offered food and the pacifier, etc.
Why is it not recommended to introduce complementary foods before 4 and after 6 months of life?
Before 4 months of life, the baby is not yet ready to digest food other than breast milk or infant formula. By this age, a number of digestive enzymes mature, a sufficient level of local immunity is formed, which reduces the risk of developing allergic reactions, the child acquires the ability to swallow semi-liquid and thicker food, which is due to the extinction of the “spoon ejection reflex”. The introduction of complementary foods after 6 months can cause a pronounced deficiency of micronutrients (iron, zinc, etc.) and lead to a delay in the formation of chewing skills for thick foods. Too late the introduction of a variety of products increases the risk of allergic reactions. Remember that the timing of the introduction of complementary foods is set individually, taking into account the readiness of the child to accept new foods.
By this age, a number of digestive enzymes mature, a sufficient level of local immunity is formed, which reduces the risk of developing allergic reactions, the child acquires the ability to swallow semi-liquid and thicker food, which is due to the extinction of the “spoon ejection reflex”. The introduction of complementary foods after 6 months can cause a pronounced deficiency of micronutrients (iron, zinc, etc.) and lead to a delay in the formation of chewing skills for thick foods. Too late the introduction of a variety of products increases the risk of allergic reactions. Remember that the timing of the introduction of complementary foods is set individually, taking into account the readiness of the child to accept new foods.
Complementary feeding guidelines:
1. introduce a new product in the first half of the day to track possible reactions to it;
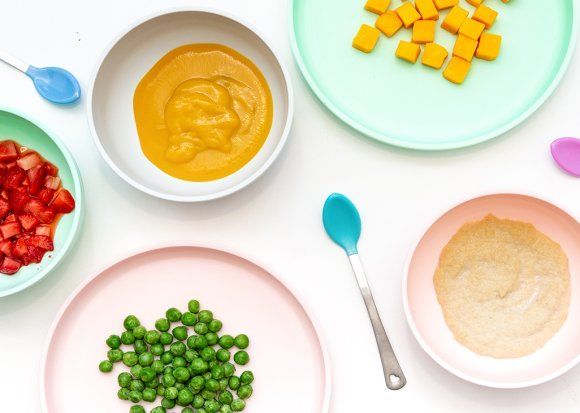
2. cereals, vegetable / fruit / meat purees should be introduced, starting with monocomponent ones, gradually adding other products of this group;
3. start giving a new product with 1/2 teaspoon, gradually increasing the volume to the age norm within a week;
start giving a new product with 1/2 teaspoon, gradually increasing the volume to the age norm within a week;
4. It is not recommended to introduce new products during acute infectious diseases or at some special moments (moving to another apartment, leaving the city, on vacation, illness of parents, etc.).
What is the best way to start complementary foods?
The first complementary food can be anything. Often parents worry that if the child first tries the fruit, then because of its sweet taste, he will refuse other foods. We hasten to reassure you: breast milk is also sweet, so babies may like sweet fruits / berries more, but this does not mean at all that he will refuse vegetables or cereal. Traditionally, they begin to introduce complementary foods in the form of mashed potatoes, but if the child shows interest in “pieces”, then, observing the safety rules, you can give them. Also, along with the introduction of complementary foods, you can offer the child water.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to a 5-time feeding regimen. If the baby shows that he is full and no longer wants to eat (for example, leaning back or turning away from food), then you should not continue to force him to feed, because this can lead to eating disorders in the future. Also, do not force the child to eat as much as possible before bedtime in the hope that he will not wake up for nightly feedings.
Traditionally, in our country, complementary foods begin with vegetables or cereals.
Vegetables: zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower, pumpkin, etc. If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up on your plan and continue to offer this vegetable in small quantities daily, you can even not once, but 2-3 times, and after a while (7-14 days) the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies his diet, will help form the right taste habits in the child.
As for cereals, it is worth starting with dairy-free gluten-free ones - buckwheat, corn, rice. You can use commercial baby food porridge, which is enriched primarily with iron. In addition, such porridge is already ready to eat, you just need to dilute it with water, which will save you a lot of time.
You can use commercial baby food porridge, which is enriched primarily with iron. In addition, such porridge is already ready to eat, you just need to dilute it with water, which will save you a lot of time.
It is also recommended to add oil to food, for example, vegetable puree to vegetable puree, and butter to porridge.
Of meat products, lean meats, such as mashed turkey or rabbit, are most preferred to start complementary foods. Meat puree contains iron, which is easily absorbed, and adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of this micronutrient from them. Subsequently, the daily use of children's enriched porridge and mashed meat allows you to meet the needs of babies for iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
When introducing fruit purees (apple, pear, peach, prunes, etc.) into your baby's diet, you should pay special attention to the composition of the product - it is important that it does not contain added sugar.
Fish is a source of easily digestible protein and contains a large amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids, including the omega-3 class, as well as vitamins B2, B12, and minerals. Preference should be given to oceanic fish, preferably white (cod, hake, pollock, sea bass, etc.), salmon can be recommended from red, and pike perch from river.
Preference should be given to oceanic fish, preferably white (cod, hake, pollock, sea bass, etc.), salmon can be recommended from red, and pike perch from river.
Fermented milk products are prepared using a special starter culture that breaks down milk protein, so that the baby can get an indispensable set of amino acids in a well-available form. Some foods have added prebiotics, certain vitamins and minerals. Their regular use favorably affects the functioning of the intestines, increases appetite and the absorption of micronutrients.
Recommendations and timing of the introduction of complementary foods for children at risk of developing food allergies and suffering from food allergies are the same as for healthy children. Delayed introduction of highly allergenic foods has previously been recommended to prevent the development of allergic diseases in children at risk. There is now evidence that this practice may lead to an increase rather than a decrease in the incidence of food allergies. The most common highly allergenic foods include cow's milk, chicken eggs, soybeans, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish and fish. If a child has a high risk of developing allergies or an existing allergic disease, it is recommended to consult a pediatrician, an allergist-immunologist before introducing highly allergenic products.
The most common highly allergenic foods include cow's milk, chicken eggs, soybeans, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish and fish. If a child has a high risk of developing allergies or an existing allergic disease, it is recommended to consult a pediatrician, an allergist-immunologist before introducing highly allergenic products.
By the age of 8 months, when all the main food groups have already been introduced and your baby is improving his skills to eat on his own, special attention should be paid to the diversity of the composition of dishes and the change in food consistency - from puree to finely and coarsely ground. Soft foods cut into small pieces (fruits, vegetables, meat, etc.) are perfect for a little gourmet, which diversifies his diet and will contribute to the formation of chewing skills.
By 9-12 months, most babies have the dexterity to drink from a cup (holding with both hands) and to eat foods prepared for other family members. This behavior needs to be encouraged, but combined with regular feeding to meet energy and nutrient requirements.
It is advisable to use industrial products that are designed specifically for young children after a year.
What should not be given to the baby?
It is not recommended to add salt or sugar to food to enhance the taste.
Drinks that should be avoided include fruit juices, whole cow and goat milk (whole milk is not recommended for children under one year old, and even longer, due to a high risk of developing iron deficiency and increased kidney stress), sweet fruit drinks, compotes and carbonated drinks.
Also, some foods should be excluded from the diet of infants: solid round foods (for example, nuts, grapes, raw carrots, raisins, peas, etc.), due to the fact that the child can choke on them.
It is not recommended to eat products with added sugar, for example, confectionery (marshmallow, marshmallow, marmalade, jam, jam, cookies, waffles, etc.), etc.
You should not give your child the meat of large predatory fish (shark, bigeye tuna, king mackerel, swordfish): these types of fish accumulate more harmful substances than others.
It is forbidden to give honey to children under one year old due to the fact that it may contain spores of Clostridium botulinum bacteria, which in the still immature digestive system of babies are able to multiply, produce toxins directly inside the intestines and, thus, cause infant botulism, which can be fatal. outcome.
Do not give babies raw meat, fish, eggs, caviar, salted fish, soft pickled cheeses because of the risk of intestinal infections.
If you follow all these simple rules, your baby will grow up healthy and happy!
Diets for different ages
References:
1. Methodological recommendations. The program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation. [Internet]. - M.: Union of Pediatricians of Russia, 2019. [Methodicheskie rekomendaczii. Programma optimizaczii vskarmlivaniya detej pervogo goda zhizni v Rossijskoj Federaczii. [Internet]. – Moscow: Soyuz pediatrov Rossii, 2019. (In Russ.).] Available: http://www.pediatr-russia.ru/information/dokumenty/other-docs/nacprog1year_2019.pdf Link active as of 20.04.2020
(In Russ.).] Available: http://www.pediatr-russia.ru/information/dokumenty/other-docs/nacprog1year_2019.pdf Link active as of 20.04.2020
2. Duryea T.K. Introducing solid foods and vitamin and mineral supplementation during infancy. In: Post T, ed. UpToDate . Waltham, Mass.: UpToDate; 2020. www.uptodate.com. Accessed April 20, 2020.
3.Fleischer D.M. Introducing highly allergenic foods to infants and children. In: Post T, ed. UpToDate . Waltham, Mass.: UpToDate; 2020. www.uptodate.com. Accessed April 20, 2020.
Recommendations for the introduction of complementary foods in babies
Support Support icon ofKeywords for search for
HOME DO NEW
9000 9000 9000 901 many precious moments that arise in the process of close communication. You are now preparing for another exciting milestone - introducing solid foods to your baby's diet. This is an exciting moment when your baby becomes more independent in eating. But, like all other stages of a child's development, this period requires a long adaptation. Like most parents, you probably want to know when to start introducing solid foods and how to introduce solid foods to your baby.
But, like all other stages of a child's development, this period requires a long adaptation. Like most parents, you probably want to know when to start introducing solid foods and how to introduce solid foods to your baby.
This article contains important information about introducing solid foods to your baby's diet (age-appropriate), tips for introducing complementary foods, and techniques to help you and your baby transition smoothly to the next level of nutrition.
At what age should complementary foods be introduced?
Be sure to check with your doctor when you think your child is ready to introduce new foods to their diet. There is no exact age at which complementary foods should be introduced. However, the introduction of complementary foods to children, both breastfed and bottle-fed, is recommended to start at the age of 4-6 months. At 6 months of age, a baby's energy and mineral needs increase. However, all babies are different and some may be ready for it as early as four months. Four months is the earliest age at which complementary foods can be introduced. Until then, the baby's gastrointestinal tract is not ready to absorb any other food besides breast milk or formula. Only a doctor will be able to assess the individual readiness of each child; no matter what his decision is, it is important to continue breastfeeding, gradually introducing solid foods along with it.
Four months is the earliest age at which complementary foods can be introduced. Until then, the baby's gastrointestinal tract is not ready to absorb any other food besides breast milk or formula. Only a doctor will be able to assess the individual readiness of each child; no matter what his decision is, it is important to continue breastfeeding, gradually introducing solid foods along with it.
The doctor will try to identify key signs that your baby is ready for solid foods: [1]
- The baby can sit up without help or can sit on mom's lap and hold her head.
- The “spoon push” reflex, a natural reaction of rejection of food, in which the child pushes the spoon out with the tongue (the child no longer sticks out his tongue when eating), has disappeared in the baby.
- The child has an active food interest (desire to try something from the table while adults are eating).
After your baby has mastered the skills necessary for independent feeding, including holding his head well, you can begin to introduce more solid foods into the diet.
Your baby's first foods
The moment you've been waiting for is finally here: your baby is ready to try solid food! Usually the products of the first complementary foods are vegetables and cereals.
If the baby is healthy, has no digestive problems and is gaining weight well, then, as a rule, weaning foods start with the introduction of vegetables.
Monocomponent vegetable purees are good for the first feeding. Vegetables are a source of organic acids, potassium, iron, fiber. It is recommended to start vegetable complementary foods with zucchini, broccoli and cauliflower. Initially, vegetable puree should consist of one type of vegetable. Then you can make a combination of various vegetables. Start with 1 spoon, then bring the volume to 180 grams. By the year, the amount of vegetable purees consumed per day is 200 grams.
If the child is underweight or anemic, industrial cereals can be given as the first complementary food. As the first cereals, in order to avoid allergic reactions, it is recommended to introduce dairy-free gluten-free cereals. Mix one to two tablespoons of single-grain cereal with breast milk, or infant formula, or water. If the child is breastfed, give him complementary foods only after the main feeding, so that the child can first get enough breast milk; keep doing this until he is about
As the first cereals, in order to avoid allergic reactions, it is recommended to introduce dairy-free gluten-free cereals. Mix one to two tablespoons of single-grain cereal with breast milk, or infant formula, or water. If the child is breastfed, give him complementary foods only after the main feeding, so that the child can first get enough breast milk; keep doing this until he is about
[2]
Once your child gets used to their first meal, continue to introduce new foods such as fruit purees, cottage cheese, eggs, dairy products, and meat and fish purees. Before introducing each next product, you must wait three to five days to find out if the child is allergic to the previous one.
Steaming!
The inclusion of various foods in the diet is very important for the formation of taste habits in the baby. Steam a variety of healthy meals!
Steaming is one of the healthiest ways to cook baby food. Steamed products are very soft and juicy, unlike fried products, which, of course, is very popular with children. And most importantly, steamed foods preserve the most important vitamins and minerals.
Steamed products are very soft and juicy, unlike fried products, which, of course, is very popular with children. And most importantly, steamed foods preserve the most important vitamins and minerals.
Make healthy cooking easy and enjoyable with the Philips Avent 4 in 1 Steamer Blender. The 4 in 1 healthy baby food maker allows you to steam and grind food in one jug. In addition, with the Philips Avent Steamer Blender, parents can make solid foods for babies of all ages, from purees to chunks. Jug with a volume of 1l. designed to cook several servings at a time. So you can prepare several meals at once to feed your baby now, and also freeze the puree for next time in a special container that comes with the steamer. The defrost and keep warm functions will help you prepare lunch or dinner for your baby even faster.
The 4 in 1 Steamer Blender also comes with a recipe booklet developed with pediatric nutritionist Emma Williams. In the brochure you will find interesting recipes for preparing tasty and fresh children's meals, as well as useful tips on the introduction of complementary foods and interesting menu ideas. Instill healthy habits in your baby from an early age for healthy development.
Instill healthy habits in your baby from an early age for healthy development.
In addition to the joy your child will experience from a change in diet, it is important to be aware of the various food allergies that can occur during the introduction of complementary foods. Experts recommend starting to introduce commonly known food allergens when the baby is 4-6 months old. In addition, recent studies have shown that with a later introduction of complementary foods in children, the risk of developing food allergies increases, therefore, it is necessary to introduce such foods into the baby’s diet on time and not put them off for later. The most well-known G8 food allergens include: [2] [3]
- cow's milk;
- chicken eggs;
- fish;
- seafood;
- nuts;
- peanuts;
- wheat;
- soybeans.
If you or a family member has a food allergy, be sure to consult your pediatrician for the best solution for introducing the foods listed above to your child's diet.
In addition to introducing new foods into the child's diet, it is also necessary to teach him to drink water from the age of 6 months. During the first six months of a child's life, mother's milk provides him with the necessary amount of fluid, even in hot climates. But once your baby is 6 months old, you can start giving him little by little to drink from a non-spill cup.
Check out Avent's Soft Non-Spill Training Cup from the Natural series with comfortable handles to help your child learn to drink without help. It is easy to drink from it, because the liquid begins to flow out only when the child bites or sucks on the spout of the cup. The design of the cup makes it easy to hold with little hands.
From pureed to finely chopped foods
Once your child has mastered the motor skills needed to eat more solid foods, you can move on to finely chopped foods. Each child is different, but usually chopped vegetables and meat can be introduced into the diet from nine months. [4]
[4]
When you introduce crushed foods into your child's diet, try to get your child to take an active part in family meals. The baby can be offered boiled vegetables, pieces of soft fruit, well-boiled pasta, or small pieces of chicken.
Remember to check that the ground food is soft and well cooked so that the child can easily grind it into mush with his mouth. Meat, for example, has a tougher structure and fibers, and therefore requires more thorough grinding compared to fruits that are delicate in texture.
With the Philips Avent 4 in 1 Steamer Blender, you can customize your food consistency from puree to chunks. Also, the recipe book that comes with the double boiler will allow you to easily choose the right recipe for the age of the child.
Tips on how to start introducing solid foods to your baby
Here are the main recommendations for introducing complementary foods to infants. As you introduce solid foods into your child's diet, we also recommend following other tips to help your child get used to the new food: [1]
- Offer food only when the child wants it.
 In a quiet environment or when other family members are having lunch, offer your baby a new food if he wants to try it.
In a quiet environment or when other family members are having lunch, offer your baby a new food if he wants to try it. - Introduce a new product in small portions in the morning. A new product should be administered in the morning to monitor possible reactions to the product. Remember that the introduction of new foods into the diet should not be considered a complete meal for the child. It is only about giving the child the opportunity to taste different foods, as well as to get a feel for their structure, gradually increasing their portions as the baby grows older.
- Only offer your child a new product when they are healthy. Do not introduce new foods when the child is sick or during the vaccination period.
- If the child does not like the product, postpone the tasting until a later date. This is a new experience for your baby, associated with new tastes and sensations. Therefore, do not be discouraged and do not worry if the child did not like the food the first time! Simply postpone taking this product until a later time.

- Never leave your child alone with food. Although the child is already taking the first steps in independent nutrition, this does not mean that he can be completely independent.
- Do not give your child foods that are too hard or slippery, rounded or choking on. These precautions will prevent the child from suffocation. Any rounded foods, such as grapes or carrots, should be cut into two or four pieces.
Goodbye liquid diet!
Proper weaning is an unforgettable experience for you and your baby. Complementary foods are very different from breastfeeding and bottle feeding, and you will certainly feel a sense of pride as your baby matures. Enjoy these precious moments. After all, before you know it, your child will grow out of his highchair and move on to a full three-course meal!
Download the app and use trackers to track your child's development and growth, and keep those special moments forever.