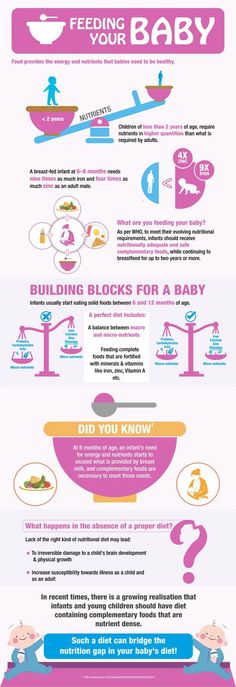
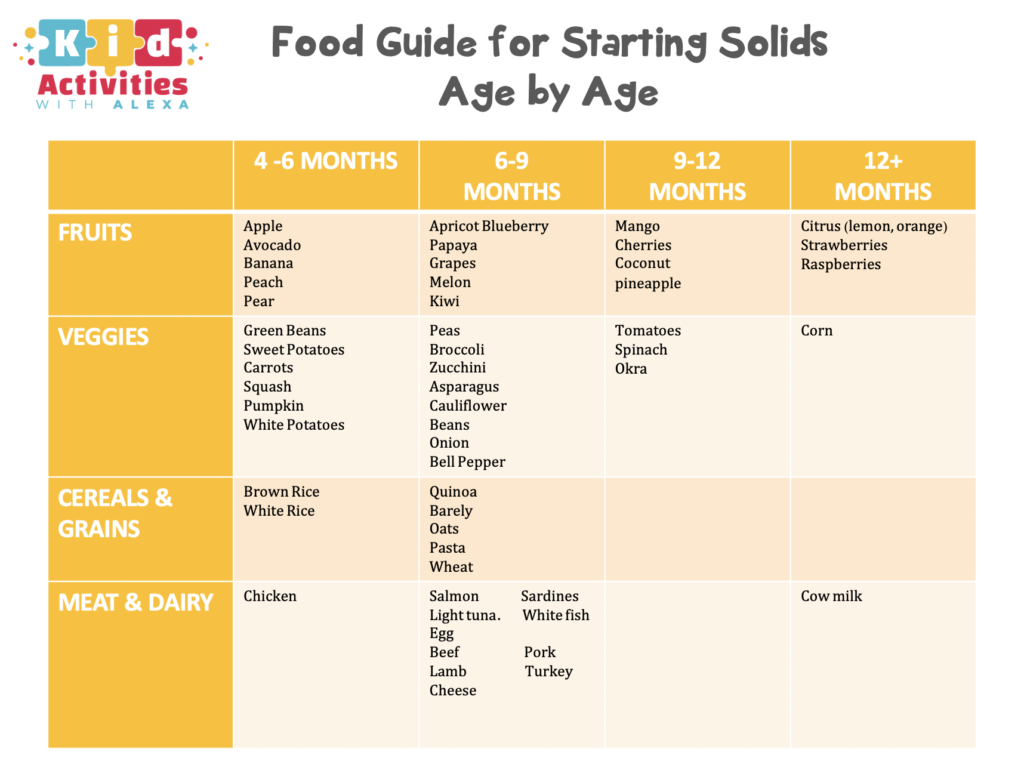
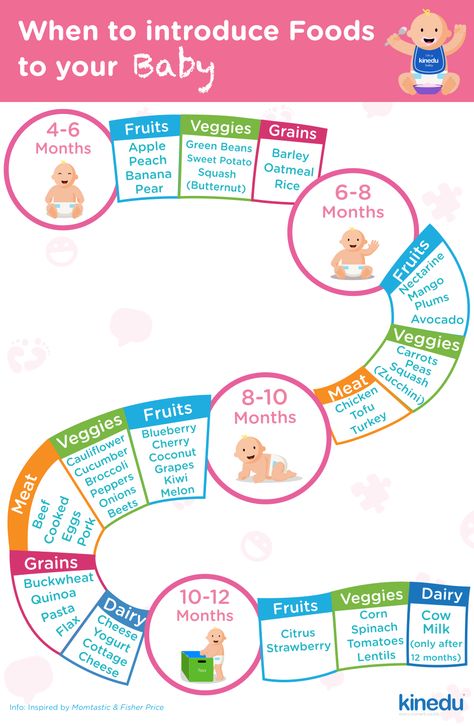
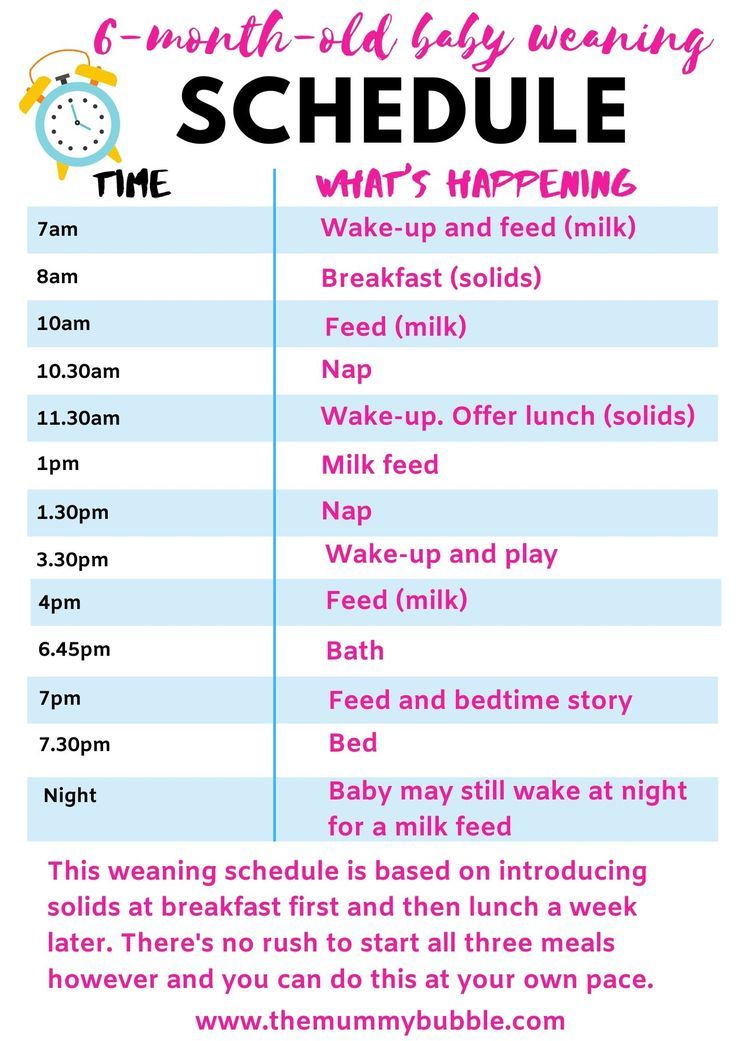
Introducing solid food to baby chart
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
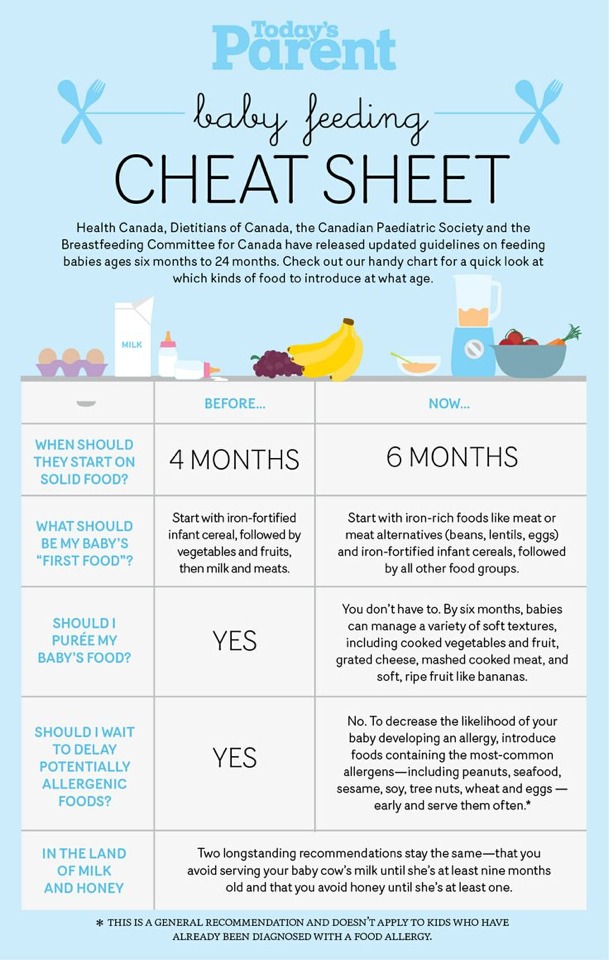
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
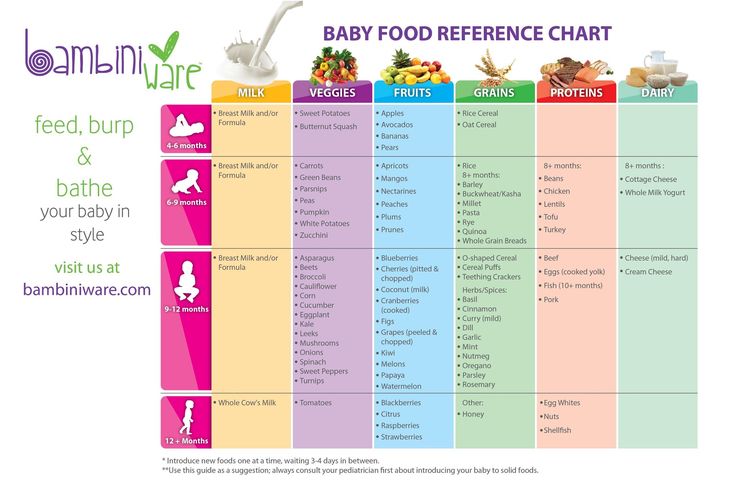
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Helpful Resources | Nutrition | CDC
If you would like more information on topics related to feeding your baby or toddler, here are some resources:
General
CDC’s Infant and Toddler Nutrition microsite syndication
CDC offers a free Web Content Syndication service that gives public health partners the opportunity to syndicate CDC content directly to their sites without having to monitor or copy updates. To search the CDC infant and toddler nutrition website available for syndication as well as other resources you can share, visit the CDC Public Health Media Library and browse or search for “infant and toddler nutrition”. Learn more about content syndication and how to add CDC syndicated content on your site.
To search the CDC infant and toddler nutrition website available for syndication as well as other resources you can share, visit the CDC Public Health Media Library and browse or search for “infant and toddler nutrition”. Learn more about content syndication and how to add CDC syndicated content on your site.
CDC’s Child and Teen Resources
This collection of resources provides parents and caregivers, health care providers, and partners with tools and information to help children and teens maintain a healthy weight and prevent obesity.
CDC’s Child Development Positive Parenting Tips (Infants)
This CDC website provides information about infants’ development, as well as tips for positive parenting and promoting the safety and health of infants.
CDC’s Learn the Signs. Act Early.
This website includes tools to track children’s milestones and resources about children’s development.
CDC’s Parent Information
This CDC website provides resources and information on pregnancy, infants and toddlers, children, and teens. Learn how to handle common parenting challenges through interactive activities, videos, and more. Healthcare professionals and researchers can also find information on children’s health and safety.
Learn how to handle common parenting challenges through interactive activities, videos, and more. Healthcare professionals and researchers can also find information on children’s health and safety.
CDC’s Division of Oral Health
Tooth decay (cavities) is one of the most common chronic diseases of childhood in the United States. Untreated tooth decay can cause pain and infections that may lead to problems with eating, speaking, playing, and learning. CDC’s Division of Oral Health provides information on what parents and caregivers can do to ensure good oral health for your child.
Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020–2025 pdf icon[PDF-30.6MB]external icon
These guidelines provide science-based advice for Americans on what to eat and drink to promote health, reduce chronic disease, and meet nutrient needs. The 2020–2025 edition provides recommendations for all life stages, including infants and toddlers.
Feeding Guidelines for Infants and Young Toddlers: A Responsive Parenting Approachexternal icon
This report presents recommendations for promoting healthy nutrition and feeding patterns for infants and toddlers from birth to 24 months, with an emphasis on dietary quality, portion sizes, and mealtime environment.
Healthy Childrenexternal icon
This website was developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics for parents. It features thousands of articles in English and Spanish on children’s health and safety, as well as interactive tools.
United States Department of Agriculture Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC)external icon
The WIC Program provides support to low-income pregnant, postpartum, and breastfeeding women, babies, and children up to age 5. WIC provides nutritious foods, information on healthy eating, breastfeeding promotion and support, and referrals to health care.
United States Department of Agriculture Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)external icon
SNAP provides benefits to low-income individuals and families and provides economic benefits to communities.
Feeding and Beverage Recommendationsexternal icon
Healthy Eating Research, a national program of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, offers science-based recommendations for parents and caregivers. Tips are available for feeding children from birth through 24 monthsexternal icon and beverages for children from birth through 5 yearsexternal icon. Tips for older children are also available.
Tips are available for feeding children from birth through 24 monthsexternal icon and beverages for children from birth through 5 yearsexternal icon. Tips for older children are also available.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Advice About Eating Fishexternal icon
The U.S. FDA and EPA provide advice regarding eating fish. This advice can help people make informed choices when it comes to the types of fish that are nutritious and safe to eat. It is especially important for those who might become pregnant, who are pregnant, or who are breastfeeding, as well as for parents and caregivers who are feeding children. This advice supports the recommendations of the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
Top of Page
Breastfeeding
CDC’s Breastfeeding Information
CDC’s Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity (DNPAO) is committed to increasing breastfeeding rates throughout the United States. CDC provides information for public health professionals and others to help support breastfeeding mothers, such as managing breastfeeding during various maternal and infant illnesses and conditions, any precautions for vaccines during breastfeeding, and recommendations for proper storage and handling of expressed human milk.
CDC provides information for public health professionals and others to help support breastfeeding mothers, such as managing breastfeeding during various maternal and infant illnesses and conditions, any precautions for vaccines during breastfeeding, and recommendations for proper storage and handling of expressed human milk.
International Lactation Consultant Association (ILCA)external icon
ILCA is the member association for professionals who care for breastfeeding families. ILCA’s “Find a Lactation Consultant Directory” can help you find a lactation consultant to get the breastfeeding support you need.
United States Lactation Consultant Association (USLCA)external icon
USLCA is a professional association for International Board Certified Lactation Consultants (IBCLCs) and other health care professionals who care for breastfeeding families. USLCA’s “Find an IBCLC” can help you find a lactation consultant to get the breastfeeding support you need.
WIC, the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children—Breastfeeding Support external icon
The United States Department of Agriculture Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) Breastfeeding Support website includes resources for expectant and current mothers about breastfeeding, overcoming common challenges, and thriving to make breastfeeding work for their families.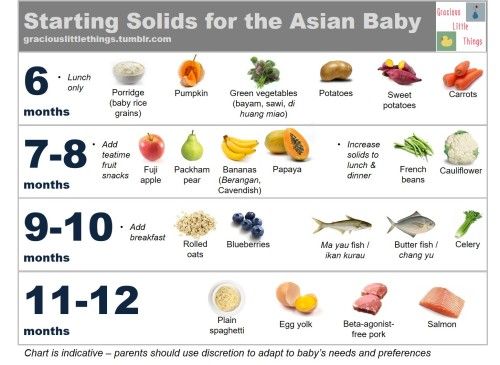
La Leche League USAexternal icon
La Leche League USA helps mothers to breastfeed through mother-to-mother support, encouragement, information, and education and promotes a better understanding of breastfeeding as an important element in the healthy development of the baby and mother.
Office on Women’s Healthexternal icon
The Office on Women’s Health’s vision is for all women and girls to achieve the best possible health outcomes. They provide information on breastfeeding to help women make infant feeding decisions and to guide mothers through the breastfeeding process.
Top of Page
Infant Formula
Questions & Answers for Consumers Concerning Infant Formulaexternal icon
The U.S. Food & Drug Administration regulates infant formula and has a list of questions and answers about infant formula.
Infant Formula Do’s and Don’tsexternal icon
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration provides information on infant formula preparation and storage, as well as other tips on how to keep infant formula safe.
Top of Page
Food Safety
Food Safety Concerns for Children Under Fiveexternal icon
Food safety is particularly important for young children. Foodsafety.gov provides information on safely preparing food for your child.
Top of Page
Meal Time
Fruits & Veggies—Have a Plant Movementexternal icon
A resource designed to help spread the word about the health benefits of adding more fruits and veggies to your diet.
USDA MyPlate Kitchenexternal icon
This online tool features a large collection of recipes and resources to support building healthy and budget-friendly meals. Site features include:
- Extensive search filters on cuisine, cooking equipment, nutrition content, and more.
- Detailed nutrition information.
- Cookbooks to browse and download or build your own.
- Recipe star ratings, review comments, and sharing on social networks.
Video Series on How to Introduce Solid Foods
1,000 Days has developed helpful videos about introducing solid foods to your baby. Topics include:
Topics include:
- Is your baby ready to start eating foods?
- What is a good first food for your baby?
- What to expect when introducing first foods
- How much should I feed my baby?
- How to win at mealtimeexternal icon
- What foods should my baby avoid?
- What should your baby eat in the first year?
Top of Page
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamin and Mineral Fact Sheetsexternal icon
The National Institutes of Health’s Office of Dietary Supplements has fact sheets for consumers and health professionals about vitamins, minerals, and dietary supplements.
Top of Page
how and when to introduce solid food to a child
Solid food: how and when to introduce solid food to a child Expecting new skills from the baby, do not rush things. It is necessary to acquaint the child with solid food no earlier than 6-7 months. At this time, the desire to scratch the gums, ready for the appearance of the first teeth, will coincide with the interest in adult food.
Dry initial milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 1 NutriValio for feeding children from birth to 6 months Read more
Follow-up dry milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 2 NutriValio for feeding children from 6 to 12 months More
Dry milk drink "Baby milk" Valio Baby 3 NutriValio for feeding children over 12 months Read more
Children are born with a vital, unconditioned reflex - sucking. They are ready to suck on their mother's breasts, but all solid objects that have fallen into their mouths are automatically pushed out so as not to choke (a protective reflex is triggered). Therefore, parents are not recommended to accustom the baby to solid foods too early. This will cause not only rejection, but sometimes vomiting. The ideal time is considered to be the start of complementary foods. When the first teeth begin to grow in the child, you can replace the homogenized puree with food with the addition of soft fibers. They will be to the taste of the baby, as they will massage itchy gums. An important clue for parents is also the child's interest in adult food. If the baby looks into your plate, tries not to suck on mashed potatoes in a spoon, but to remove it with his upper lip and chew - it's time to introduce more solid food into the children's menu. First, at the tip of the spoon, offer the baby vegetable and cereal side dishes, closer to 9months you can give pieces of well-boiled meat. The kid does not immediately learn to chew them, and the food will come out with a stool almost in its original form. It's not scary, over time the child will learn everything. It is important not to ignore his desire, you will have to pay for the pedagogical miscalculation and literally teach the child to chew.
The ideal time is considered to be the start of complementary foods. When the first teeth begin to grow in the child, you can replace the homogenized puree with food with the addition of soft fibers. They will be to the taste of the baby, as they will massage itchy gums. An important clue for parents is also the child's interest in adult food. If the baby looks into your plate, tries not to suck on mashed potatoes in a spoon, but to remove it with his upper lip and chew - it's time to introduce more solid food into the children's menu. First, at the tip of the spoon, offer the baby vegetable and cereal side dishes, closer to 9months you can give pieces of well-boiled meat. The kid does not immediately learn to chew them, and the food will come out with a stool almost in its original form. It's not scary, over time the child will learn everything. It is important not to ignore his desire, you will have to pay for the pedagogical miscalculation and literally teach the child to chew.
Of course, not everything can go according to plan. The most common reasons why a child refuses solid food:
The most common reasons why a child refuses solid food:
-
The pieces of food are too big.
-
You are using the wrong feeding technique.
-
The spoon is big for a child.
-
The child has unpleasant associations - perhaps you gave him medicine from this spoon. Do not use everyday baby utensils for unpleasant procedures.
-
The child is in a bad mood or does not feel well.
In no case do not force the baby to eat if he refuses. Gently try again and again. Set an example - eat the first spoon yourself, showing the crumbs how tasty his food is. If the child still cannot cope with solid food, it is worth contacting a pediatric osteopath. The baby may have a non-standard structure of the maxillofacial system, subluxation of the jaw associated with birth trauma, problems with muscle tone. The timely introduction of solid food is very important not only for the full nutrition of the child, it affects his future speech activity.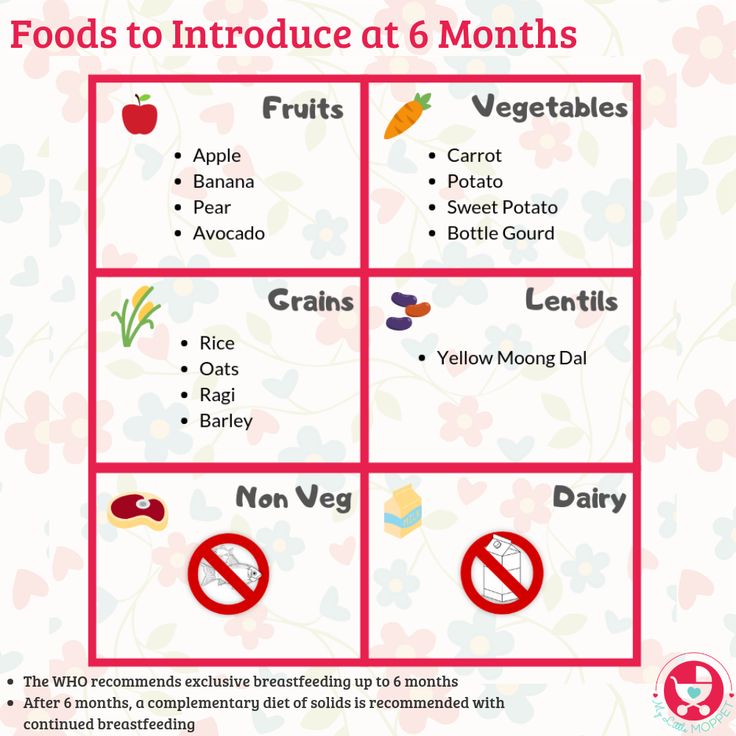 Breastfeeding is a good prevention of speech therapy problems. In order to suck milk from the breast, the child needs to make more efforts than when feeding from a bottle - this is a good (and what is valuable - natural) training of the jaws and muscles of the tongue, and it must be continued by introducing the crumbs to solid food in time. Of course, a baby with a piece of an apple in his hands (and in his mouth) must be looked after so that he does not choke. By the way, for the development of the chewing and speech apparatus, it is useful to grimace with the baby during the game - this strengthens the facial muscles well.
Breastfeeding is a good prevention of speech therapy problems. In order to suck milk from the breast, the child needs to make more efforts than when feeding from a bottle - this is a good (and what is valuable - natural) training of the jaws and muscles of the tongue, and it must be continued by introducing the crumbs to solid food in time. Of course, a baby with a piece of an apple in his hands (and in his mouth) must be looked after so that he does not choke. By the way, for the development of the chewing and speech apparatus, it is useful to grimace with the baby during the game - this strengthens the facial muscles well.
2.71 7
Power supplyShare:
Ivargizova Oksana
Medical Institute. Pavlova, specialization - pediatrics
Pavlova, specialization - pediatrics
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk. However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
Read
Author: Ivargizova Oksana
How to choose milk formula for a baby
Breast milk is the best food for a newborn baby. It contains all the necessary nutritional components that fully meet the needs of the child and are necessary for his healthy and harmonious development.
Read
Show all
We want to make our site more convenient for you, so we collect analytical data about your visit using cookies. By continuing to use the site, you agree to this. For more information on the collection and processing of data, please see the Personal Data Processing Policy.
By continuing to use the site, you agree to this. For more information on the collection and processing of data, please see the Personal Data Processing Policy.
Password recovery
To recover your password, enter your e-mail, which you specified during registration. We will send you a message with further instructions to this e-mail
Thank you for contacting us!
A letter with information to reset your password
has been sent to your mail
Back to the site
YOUR CITY -
?
Yes Change
We want to make our site more convenient for you, so we collect analytical data about your visit using cookies. By continuing to use the site, you agree to this. For more information on the collection and processing of data, please see the Personal Data Processing Policy.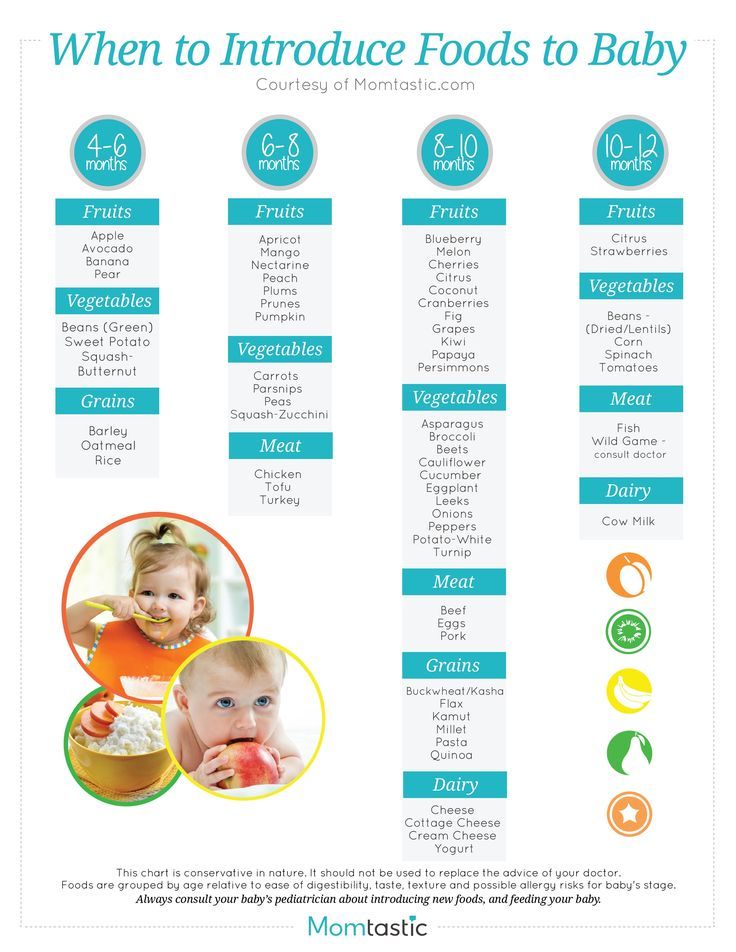
SELECT CITY
Complementary foods - what is it and how is it eaten?
home
Articles
Food
Loginevskaya Yana Vladimirovna Pediatrician
24.04.2019
What is weaning and when should we start it? These and many other issues related to child nutrition torment young parents. In the era of the Internet and easy access to information, this information can sometimes become too much.
Let's understand what is complementary foods
Complementary foods is the introduction into the diet of a healthy child at a certain age of any food, home or industrial preparation, which supplements breast milk or food imitating it, and contributes to the gradual transfer of the child to the general table. As a rule, complementary foods are thicker in consistency than the child's previous food. If the child has any health problems, the introduction of complementary foods may have its own characteristics.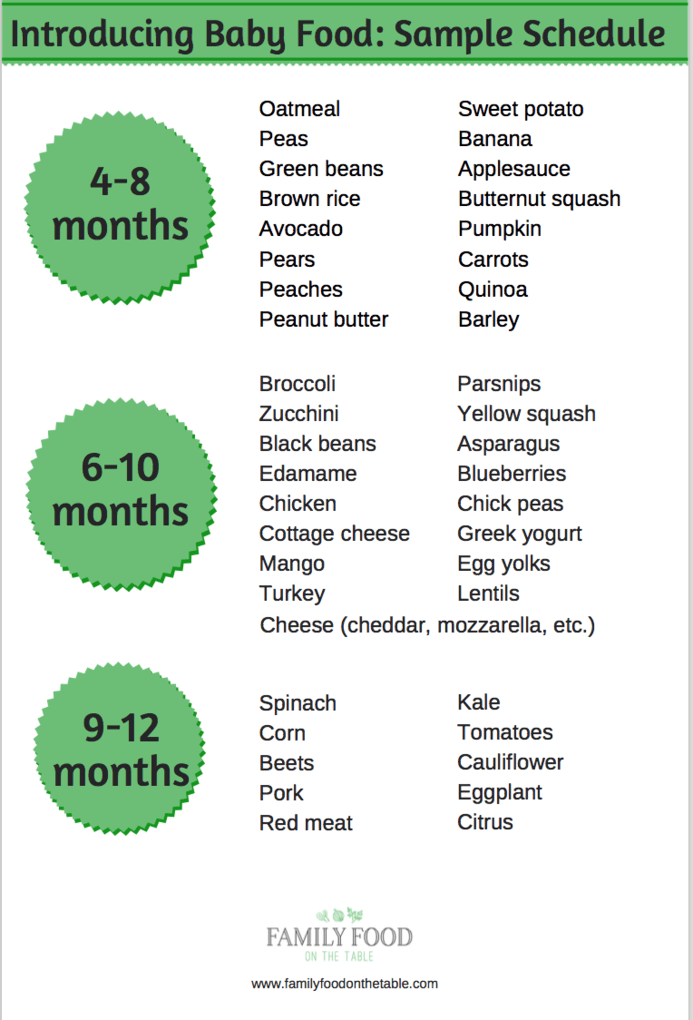
The purpose of complementary foods in the first year of life is to introduce the child to foods other than breast milk/or formula. Timely teach to swallow and chew solid food. And also to avoid deficiency of energy and micronutrients, and vitamins.
In the literature and other sources, you can find such names as "pediatric" and "pedagogical" complementary foods?
Pediatric Complementary Food , as its name implies, is a classic complementary feeding regimen recommended by the pediatrician at the appointment. Schemes in which there is a gradual replacement of breast milk / formula feeding with cereals, fruit / vegetable purees and other types of products.
Pedagogical complementary foods - "Pedagogical" means that first of all the child is taught - they are taught to eat, the correct behavior at the table, they teach that food is joy and pleasure, they show new tastes. The essence of pedagogical complementary foods is that the child’s nutrition begins with “microdoses” (grains of food) that the child receives from his mother’s plate, nothing is puréed or blended, or even warmed up.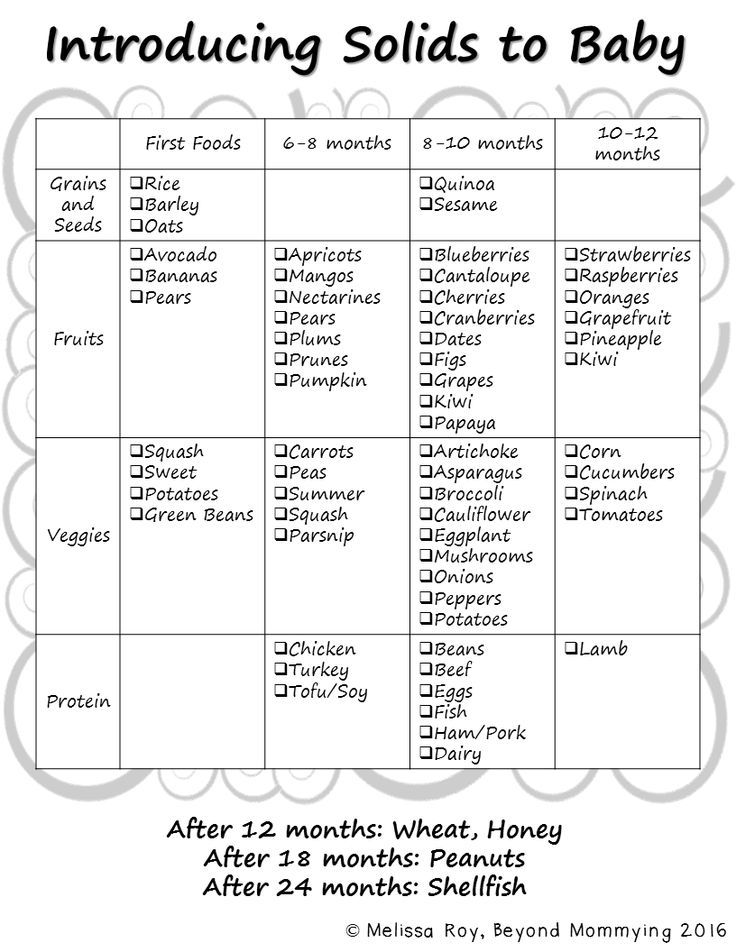 Nutrition of the child - together with the family, how much he will eat, he will eat so much. Nothing is specially prepared, the family is invited to switch to a healthy diet. The disadvantage of this type of complementary foods is that the child, starting with “micro doses”, does not adequately increase the volume of complementary foods, which can lead to malnutrition of the child at an older age.
Nutrition of the child - together with the family, how much he will eat, he will eat so much. Nothing is specially prepared, the family is invited to switch to a healthy diet. The disadvantage of this type of complementary foods is that the child, starting with “micro doses”, does not adequately increase the volume of complementary foods, which can lead to malnutrition of the child at an older age.
In my article, I will rely on modern research and recommendations primarily from the WHO (World Health Organization) and the National Program for Optimizing Feeding in Children in the First Year of Life in the Russian Federation.
What requirements must be met in relation to complementary foods:
- Complementary foods must be timely, introduced at the moment when the child's energy and nutrient requirements exceed what can be provided through breastfeeding (or formula).
- Complementary foods should be adequate, that is, with enough energy, protein and micronutrients to meet the nutritional needs of a growing child.

- Safe - stored or prepared hygienically and fed with clean hands using clean utensils - spoons, plates, not bottles and teats.
- Properly Administered - The child is fed appropriately for hunger cues, and feeding frequency and feeding methods should be appropriate for the child's age.
When do we introduce complementary foods
The optimal age for the introduction of complementary foods is 6 months.
If the child is premature, then the timing of the introduction of complementary foods is delayed by as much as this child was born earlier (that is, if the child was born not at 40 weeks, but, for example, at 36, we have the right to postpone the introduction of complementary foods for 4 weeks, but if we see that at 6 months the child is already quite ready for the introduction of complementary foods, then you can start as early as 6 months). It is advisable to postpone the introduction of complementary foods for no more than 2 months.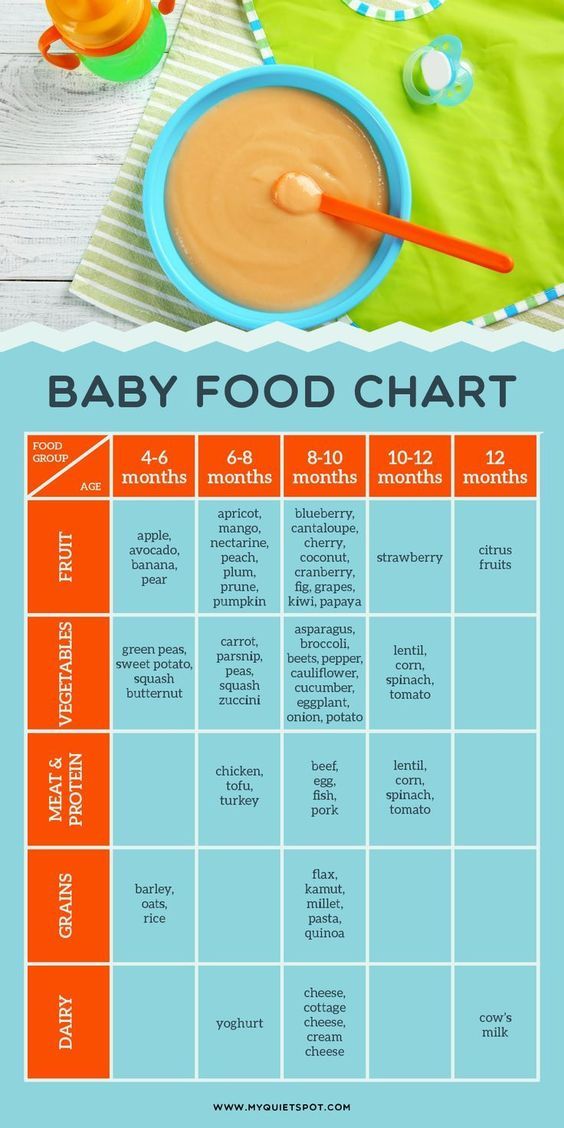 Try to start the introduction of complementary foods no later than 8 months of the child.
Try to start the introduction of complementary foods no later than 8 months of the child.
Up to 6 months, breastfeeding fully covers the energy needs of the child. Around 6 months of age, a baby's energy requirements increase dramatically, so it is necessary to add something to his diet in addition to liquid food. Breast milk in terms of its energy value contains 67-68 kcal / 100g, the mixture has approximately the same numbers. Breast milk remains a valuable energy product for children not only in the first year of life, but also after a year. At the same time, it should be taken into account that the volume of the child's stomach by 6 months is about 200 ml, so the food introduced to the child must be thicker than formula or breast milk, otherwise we will still not be able to meet the energy needs of the body. The optimal calorie content of complementary foods should be at least 100 kcal / 100 g.
Liquid food and liquid quickly fill the stomach. To fill the energy deficit, it is necessary to introduce foods with a higher energy value than breast milk or formula.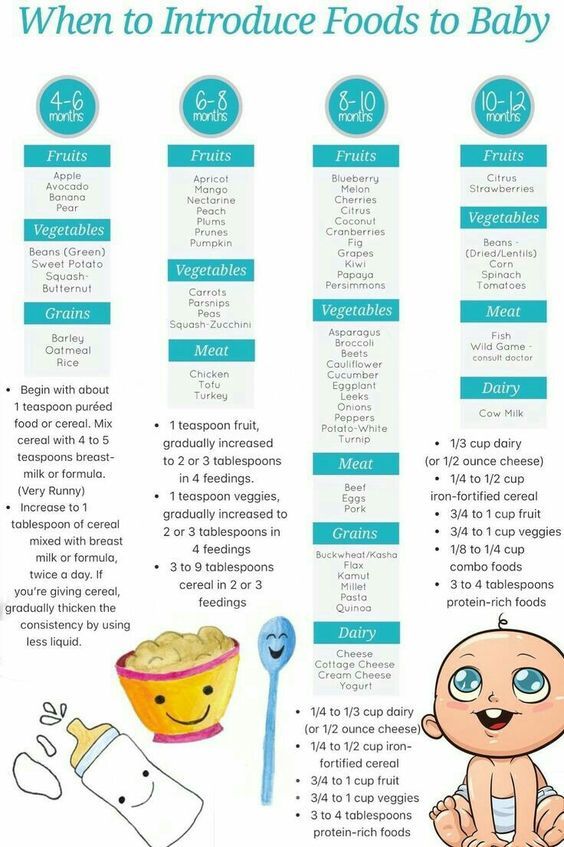
WHO ways to increase calories:
-
cook with less liquid
-
Replace part of the water for cooking with breast milk or a mixture (it must be borne in mind that breast milk contains enzymes (lipase) - which begin the digestion and breakdown of food even before it enters the child's body, so instant cereals, when breast milk is added, immediately become liquid, but their energy value is not lost.
What do we focus on when introducing complementary foods:
The main criterion is the readiness of the child to introduce complementary foods - the child shows interest in food, the so-called food interest - he is interested in what his mother eats, actively reaches for food from his parents' plate, wants to taste it.
Indirect criteria
- Child's age about 6 months
- Decreased ejection reflex for solid food (active interest in food is never shown until ejection reflex fades)
- Doubling birth weight (optional item, some babies double their weight before 6 months of age)
- Child can sit with support
- The first teeth appear in a child (again, not always)
Principles of maintaining interest in food
- Parents should remember that in order to form the main criterion for readiness for complementary foods, the child must see how his family eats.
 The formation of eating habits comes from the family and the immediate environment of the child. If, before 6 months, the child has never seen how mom or dad eats, how they eat at the table and what they eat, he may not have a food interest by 6 months. Food interest begins to gradually form as a skill of tracking the actions of an adult from 3 months of age. That is, somewhere from the age of 3 months the child, if you take him with you to the kitchen (dining room), the child begins to observe the process of eating, and gradually this interest - from the interest of "observation" goes to the "desire" to try just like mom or dad.
The formation of eating habits comes from the family and the immediate environment of the child. If, before 6 months, the child has never seen how mom or dad eats, how they eat at the table and what they eat, he may not have a food interest by 6 months. Food interest begins to gradually form as a skill of tracking the actions of an adult from 3 months of age. That is, somewhere from the age of 3 months the child, if you take him with you to the kitchen (dining room), the child begins to observe the process of eating, and gradually this interest - from the interest of "observation" goes to the "desire" to try just like mom or dad. - It is advisable not to feed the baby separately and try to eat with the baby what the baby eats. If you are feeding your child with industrial food (ready-made mashed potatoes in a jar), then try this food with your child. Try to bring the canned food as close as possible to the general view on the table - transfer the puree from the can to a plate, give a spoon.
 At the age of 8-10 months, the child learns to eat with his hands, so at this age it is advisable that the child has small pieces of food on the plate that he already eats - these can be pieces of boiled potatoes, broccoli, cauliflower, pieces of apple, banana. The pieces should be small, 1 x 1 cm, so that the child can grab them with his fingers. In parallel, the mother can supplement the child from the plate with the main food. The child learns to cope with more solid food, learns to chew, swallow. The sooner the skill of swallowing more solid food is worked out, the easier it is for parents in the future. At the age of 10-12 months, the child's fine motor skills are already improving, he is learning to eat with a spoon (be patient, different children do it in different ways and at different speeds)
At the age of 8-10 months, the child learns to eat with his hands, so at this age it is advisable that the child has small pieces of food on the plate that he already eats - these can be pieces of boiled potatoes, broccoli, cauliflower, pieces of apple, banana. The pieces should be small, 1 x 1 cm, so that the child can grab them with his fingers. In parallel, the mother can supplement the child from the plate with the main food. The child learns to cope with more solid food, learns to chew, swallow. The sooner the skill of swallowing more solid food is worked out, the easier it is for parents in the future. At the age of 10-12 months, the child's fine motor skills are already improving, he is learning to eat with a spoon (be patient, different children do it in different ways and at different speeds) - Be mindful of the child's physical condition - do not introduce new foods when the child is unwell or tired or teething or has undergone some medical procedure such as a vaccination
- Offer small portions.
 Some children undereat food because they are initially intimidated by the portion size. Do not insist that the child finishes the portion. Let it be better after some time to ask for another
Some children undereat food because they are initially intimidated by the portion size. Do not insist that the child finishes the portion. Let it be better after some time to ask for another - Try to keep the area around the child clean! This initially teaches the child to cleanliness at the table and to a neat diet. Some children are very sensitive to external stimuli - dirty hands, face, clothes can cause them severe discomfort
- Help the child if you see that the child is "interested" in food, but tired of fighting with it.
- No games, entertainment or persuasion while eating - in this way you replace food interest with interest in the game. The child will not be able to learn to adequately assess their desires in food. Don't turn food into a show.
Complementary feeding rules:
-
any new product is introduced only to a healthy child. A breastfed baby is given complementary foods up to the breast.
-
the introduction of new foods should not coincide with vaccinations, teething, vacations, or other stress for the child (when stressed, the child may refuse the proposed new product).
-
any new product is introduced in the morning (so parents have time to observe the child, look at his reaction, notice allergic manifestations) If the child has a reaction to a new product, then it is better to write it down, and try to introduce the product again after 5- 10 days. Because this reaction may not be related to the product, but caused by other factors. If the negative reaction is repeated, then the introduction of this product is postponed for 3 months.
-
it is advisable to introduce no more than one new product per day.
-
to get acquainted with the product, the child sometimes needs 10-15 sentences in order for him to start eating it. The reaction of the child in the form of wrinkling, pushing food, curvature of the face does not indicate that the child did not like the food, but only that the new taste is very bright for him and causes a large number of emotions.
 For children, even neutral tastes can seem very rich, due to the higher sensitivity of the receptors. Therefore, when introductory feeding, it is not recommended to use spices and salt in the preparation of food for the child.
For children, even neutral tastes can seem very rich, due to the higher sensitivity of the receptors. Therefore, when introductory feeding, it is not recommended to use spices and salt in the preparation of food for the child.
Basic complementary foods
For the first feeding, there are three main types of products: cereals, vegetables and meat.
-
Cereals - Dairy-free cereals are used to start complementary foods. Rice, corn, buckwheat are the first to be introduced - these can be special “instant” baby cereals (we carefully study the composition, make sure that there are no additives, sweeteners, flavor enhancers, vitamins), instant cereals are well suited to start complementary foods, at 6-7 months, in the future you can switch to ordinary "adult" cereals, you can grind ready-made buckwheat or rice with a blender or fork; instant porridges in the form of flakes are also good. Then the rest of the cereals (oatmeal, rye, millet) are introduced.
 With an allergic burden in the family, the introduction of milk porridges earlier than 12 months is not recommended.
With an allergic burden in the family, the introduction of milk porridges earlier than 12 months is not recommended. -
Vegetables - first we introduce green / white vegetables (zucchini, cucumber, broccoli, kohlrabi, cabbage and cauliflower), then legumes, colored vegetables (carrots, pumpkin, beets, tomatoes)
-
Meat - the beginning of complementary foods with the most easily digestible and hypoallergenic meats - rabbit, turkey, then veal, beef, pork, lamb. Children with an allergy to cow's milk protein start complementary foods first with pork, then they introduce beef. Children with allergies are also trying to limit the introduction of chicken into the diet, as it is a highly allergenic product. Lamb is introduced to children no earlier than 10 months. Poultry meat - duck, goose - contains refractory fats and is not recommended for introduction into the diet of babies under 3 years of age.
-
Fruit and dairy products are not considered essential complementary foods.
 Can be given for table variety. If the mother wants to give fruits, berries and juices to the child, it is better to use them as a flavoring additive to the main complementary foods or even postpone the introduction to an older age. In children with an allergic tendency, it is recommended not to introduce dairy products up to a year. You have to be careful with berries and fruits. It is best to start complementary foods with seasonal fruits and berries; the least and least likely to cause allergies are currants, blueberries, apples, pears, plums. Allergic reactions often occur on strawberries, bananas, citrus fruits.
Can be given for table variety. If the mother wants to give fruits, berries and juices to the child, it is better to use them as a flavoring additive to the main complementary foods or even postpone the introduction to an older age. In children with an allergic tendency, it is recommended not to introduce dairy products up to a year. You have to be careful with berries and fruits. It is best to start complementary foods with seasonal fruits and berries; the least and least likely to cause allergies are currants, blueberries, apples, pears, plums. Allergic reactions often occur on strawberries, bananas, citrus fruits. -
Fish and seafood. Not a staple complementary food. But fish, like meat, is a source of protein, rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, as well as minerals and vitamins. It is recommended to introduce fish no earlier than 9-10 months. Again, if the child is allergic, it is advisable to refrain from introducing fish products up to 1 year. We begin to introduce complementary foods with low-fat white varieties of fish in the form of mashed potatoes - ice fish, hake, cod, haddock, pollock, navaga, pike perch, sea bass, dorado.
-
Egg . A product that is rich in many different micro and macro elements, vitamins. However, the egg has a very high allergenicity (included in the very big eight allergens). Considering that a quarter (5-6 g) or half (10-12 g) of the yolk, which are recommended to be administered, contains very few nutrients and energy, it is easier not to give this product than to risk allergic reactions in a child.
-
Nuts, peanuts whole must not be present in a child's diet until at least three years of age. In a number of countries, communities, families, where, for example, peanuts are common as a staple food, they can be used as an additive to complementary foods in a pureed state. Nuts are included in the big eight allergens and are not recommended for introduction into complementary foods for children with allergies up to three years of age.
-
Water . After the introduction of complementary foods, children can begin to offer water as a drink.
 First as an introduction, later as an additional source of fluid, while reducing the volume of breast milk (mixture). It should be pure water without any additives. It is important to remember that breastfed babies may go without water for quite a long time, due to the fact that they receive enough liquid from breast milk.
First as an introduction, later as an additional source of fluid, while reducing the volume of breast milk (mixture). It should be pure water without any additives. It is important to remember that breastfed babies may go without water for quite a long time, due to the fact that they receive enough liquid from breast milk. -
Tea . The World Health Organization does not recommend including tea in the diet of children under 2 years of age. Why? First of all, because of the tannins that are present in tea and can help reduce the absorption of trace elements, including iron and cause anemia. Tea also contains caffeine (it is found in a state associated with tannins and is more often called theine), which can cause excessive stimulating effect on the fragile nervous system of the child., It can also lead to increased heart rate, increased peristalsis of the stomach, increased body temperature - all this can adversely affect the general condition of the child.