Newborn baby bottle feeding times
Formula Feeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
How Often Should I Feed My Baby?
Newborns and young babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry. This is called on-demand feeding.
After the first few days of life, most healthy formula-fed newborns feed about every 2–3 hours. As they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk, they usually eat about every 3–4 hours. As babies get older, they’ll settle into a more predictable feeding routine and go longer stretches at night without needing a bottle.
Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about feeding your baby, especially if your baby is very small, is not gaining weight, or was born early (prematurely).
How Can I Tell When My Baby Is Hungry?
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands, fingers, and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling again their mothers' breasts
- showing the rooting reflex (when a baby moves its mouth in the direction of something that's stroking or touching its cheek)
Babies should be fed before they get upset and cry. Crying is a late sign of hunger. But every time your baby cries is not because of hunger. Sometimes babies just need to be cuddled or changed. Or they could be sick, tired, too hot or too cold, in pain, or have colic.
How Much Should My Baby Drink?
In the first few weeks, give 2- to 3-ounce (60- to 90-milliliter) bottles to your newborn. Give more or less depending on your baby’s hunger cues.
Here's a general look at how much your baby may be eating at different ages:
- On average, a newborn drinks about 1.5–3 ounces (45–90 milliliters) every 2–3 hours. This amount increases as your baby grows and can take more at each feeding.
- At about 2 months, your baby may drink about 4–5 ounces (120–150 milliliters) every 3–4 hours.
- At 4 months, your baby may drink about 4–6 ounces (120-180 milliliters) at each feeding, depending on how often they eat.
- By 6 months, your baby may drink 6–8 ounces (180–230 milliliters) about 4–5 times a day.

Watch for signs that your baby is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your baby stop when full. A baby who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the bottle.
Why Does My Baby Seem Hungrier Than Usual?
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. Still, there may be times when your little one seems hungrier than usual.
Your baby may be going through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt). These can happen at any time, but in the early months are common at around:
- 7–14 days old
- between 3–6 weeks
- 4 months
- 6 months
During these times and whenever your baby seems especially hungry, follow their hunger cues and continue to feed on demand, increasing the amount of formula you give as needed.
Is My Baby Eating Enough?
At times, you may wonder whether your baby is getting enough nutrients for healthy growth and development. Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
At your baby’s checkups, the doctor will review your baby’s growth chart, track your little one’s development, and answer any questions. Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about your baby’s feeding and nutrition.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
Tips for the First Year
Eat, sleep, pee, poop, repeat. Those are the highlights in a day of the life of a brand new baby.
And if you’re a new parent, it’s the eating part that may be the source of many of your questions and worries. How many ounces should your baby take? Do you wake a sleeping baby to eat? Why do they seem hungry all the time? When can your child start solids?
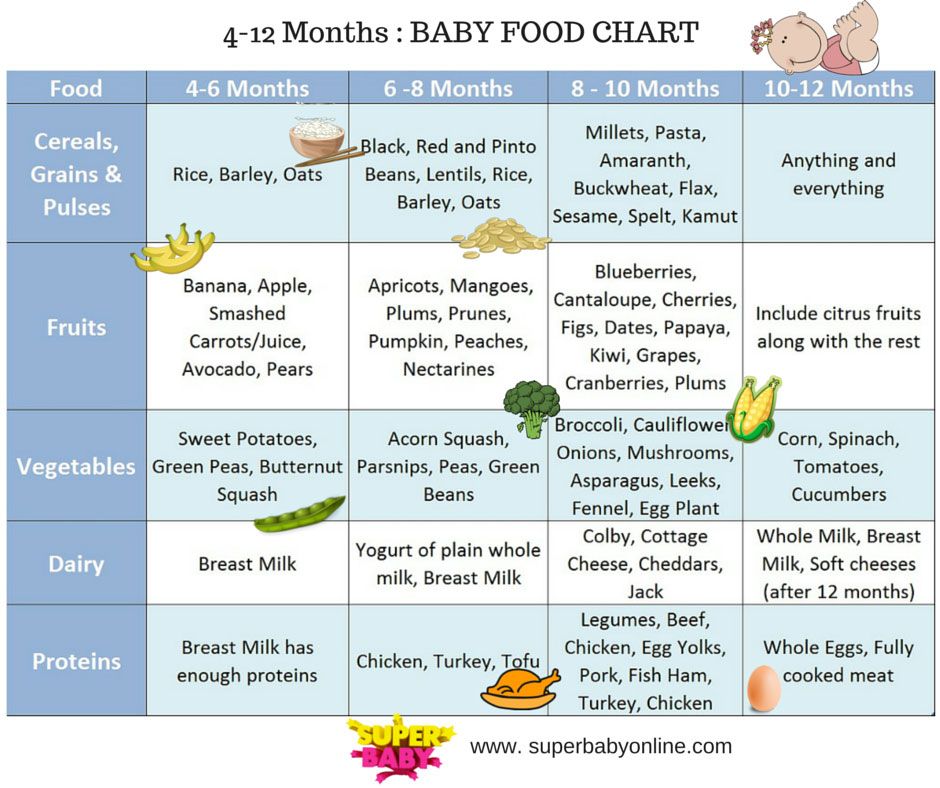
Questions abound — and, despite Grandma’s insistence, the answers have changed since you were a tot. It’s now recommended that newborns, even formula-fed ones, eat on demand (consider it good preparation for the teenage years) and that babies wait to start solid foods until they’re 4 to 6 months old.
On day one of life, your baby’s stomach is the size of a marble and can only hold 1 to 1.4 teaspoons of liquid at a time. As your baby gets older, their stomach stretches and grows.
It’s hard (or impossible, really) to know how much milk your baby is taking in while breastfeeding. But if you’re bottle feeding due to any number of valid reasons, it’s a bit easier to measure.
Here, from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), a typical feeding schedule for bottle-fed babies.
| Age | Ounces per feeding | Solid foods |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 2 weeks of life | .5 oz. in the first days, then 1–3 oz. | No |
| 2 weeks to 2 months | 2–4 oz. | No |
| 2–4 months | 4-6 oz. | No |
| 4–6 months | 4–8 oz. | Possibly, if your baby can hold their head up and is at least 13 pounds. But you don’t need to introduce solid foods yet. |
| 6–12 months | 8 oz. | Yes. Start with soft foods, like one-grain cereals and pureed vegetables, meats, and fruits, progressing to mashed and well-chopped finger foods. Give your baby one new food at a time. Continue supplementing with breast or formula feedings. |
Every baby is unique — but one thing that’s pretty consistent is that breastfed babies eat more frequently than bottle-fed ones. That’s because breast milk is easily digested and empties from the stomach a lot quicker than formula.
Breastfed babies
There’s no rest for the weary. According to La Leche League International, you should begin nursing your baby within 1 hour of birth and provide about 8 to 12 feedings daily in the first few weeks of life (yeah, we’re exhausted for you).
At first, it’s important not to let your baby go more than 4 hours without feeding. You’ll likely need to wake them up if necessary, at least until breastfeeding is well established and they’re gaining weight appropriately.
As your baby grows and your milk supply amps up, your baby will be able to take in more milk in less time at one feeding. That’s when you might start to notice a more predictable pattern.
- 1 to 3 months: Your baby will feed 7 to 9 times per 24 hours.
- 3 months: Feedings take place 6 to 8 times in 24 hours.
- 6 months: Your baby will feed around 6 times a day.
- 12 months: Nursing may drop to about 4 times a day. The introduction of solids at about 6 months helps to fuel your baby’s additional nutritional needs.
Keep in mind that this pattern is just one example. Different babies have different paces and preferences, along with other factors that influence the frequency of feedings.
Bottle-fed babies
Like breastfed babies, bottle-fed newborns should eat on demand. On average, that’s about every 2 to 3 hours. A typical feeding schedule may look like this:
- Newborn: every 2 to 3 hours
- At 2 months: every 3 to 4 hours
- At 4 to 6 months: every 4 to 5 hours
- At 6+ months: every 4 to 5 hours
For both breastfed and bottle-fed babies
- Don’t give liquids other than formula or breast milk to babies under a year old.
 That includes juices and cow’s milk. They don’t provide the right (if any) nutrients and can be upsetting to your baby’s tummy. Water can be introduced around 6 months when you start offering a cup.
That includes juices and cow’s milk. They don’t provide the right (if any) nutrients and can be upsetting to your baby’s tummy. Water can be introduced around 6 months when you start offering a cup. - Don’t add baby cereal to a bottle.
- It can create a choking hazard.
- A baby’s digestive system isn’t mature enough to handle cereal until about 4 to 6 months of age.
- You could overfeed your baby.
- Don’t give your baby any form of honey until after their first birthday. Honey can be dangerous for a baby, occasionally causing what’s called infant botulism.
- Do adjust your expectations based on your baby and their unique needs. Premature babies are likely to follow feeding patterns according to their adjusted age. If your baby has challenges like reflux or failure to thrive, you may need to work with your doctor on the appropriate feeding schedule and amount they should be eating.
Schedules are the holy grail of every parent. Your child will naturally start to fall into a feeding pattern as their tummy grows and they can take in more breast milk or formula at one sitting.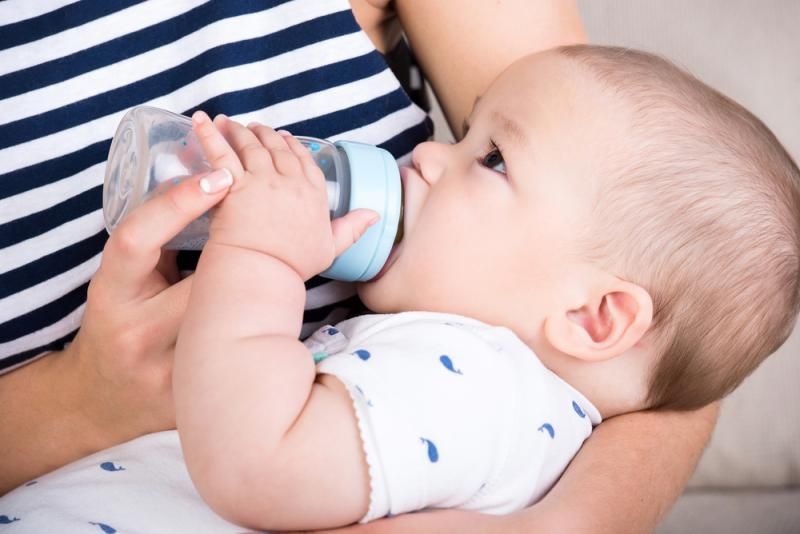 This may begin to happen between 2 and 4 months of age.
This may begin to happen between 2 and 4 months of age.
For now, though, focus on learning your baby’s hunger cues, such as:
- rooting around your chest, looking for a nipple.
- putting their fist in their mouth
- smacking or licking their lips
- fussing that can escalate quickly (don’t wait until your baby’s hangry to feed them)
Once your baby is a few months old, you may be able to introduce a sleep/feed schedule that works for you.
Let’s say, for example, your 4-month-old wakes every 5 hours for a feeding. That means if you feed at 9 p.m., your baby wakes around 2 a.m. But if you wake and feed the baby at 11 p.m., just before you go to bed, they may not rouse until 4 a.m., giving you a decent chunk of nighttime winks.
In general, if your baby seems hungry, feed them. Your baby will naturally eat more frequently during growth spurts, which typically occur around 3 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months of age.
Some babies will also “cluster feed,” meaning they’ll feed more frequently during certain periods and less at others. For example, your baby may cluster feed during the late afternoon and evening and then sleep longer at night (yay!). This is more common in breastfed babies than bottle fed babies.
For example, your baby may cluster feed during the late afternoon and evening and then sleep longer at night (yay!). This is more common in breastfed babies than bottle fed babies.
Worried about overfeeding? While this isn’t really possible to do with an exclusively breastfed baby, you can overfeed a baby who’s taking a bottle — especially if they’re sucking on the bottle for comfort. Follow their hunger cues, but talk to your pediatrician if you’re worried your little one may be overeating.
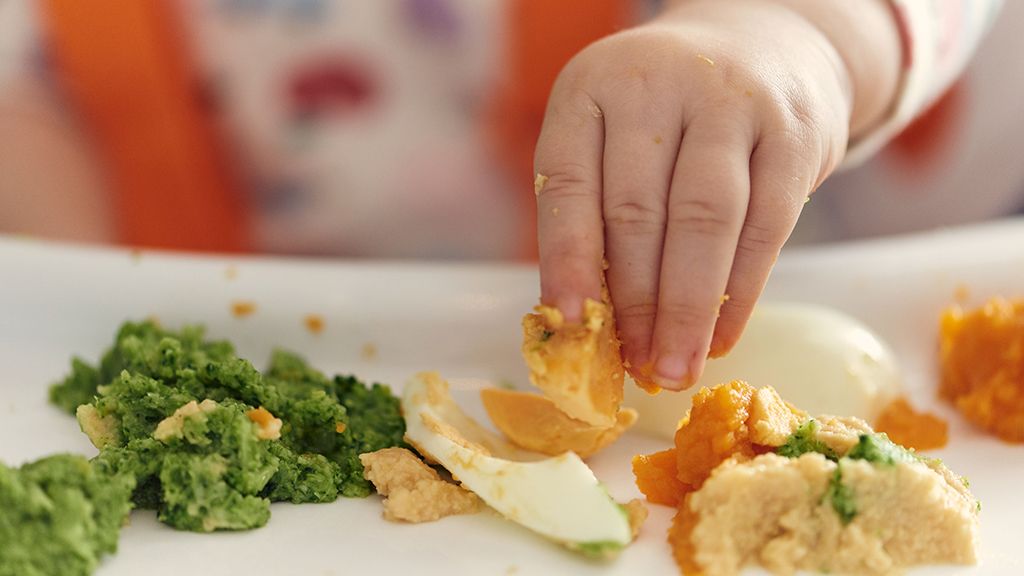
Your baby is probably ready for solids if they’re 4 to 6 months old and:
- have good head control
- seem interested in what you’re eating
- reach for food
- weigh 13 or more pounds
Which food to start with? The AAP now says it doesn’t really matter much in what order you introduce foods. The only real rule: Stick with one food for 3 to 5 days before offering another. If there’s an allergic reaction (rash, diarrhea, vomiting are common first signs), you’ll know which food is causing it.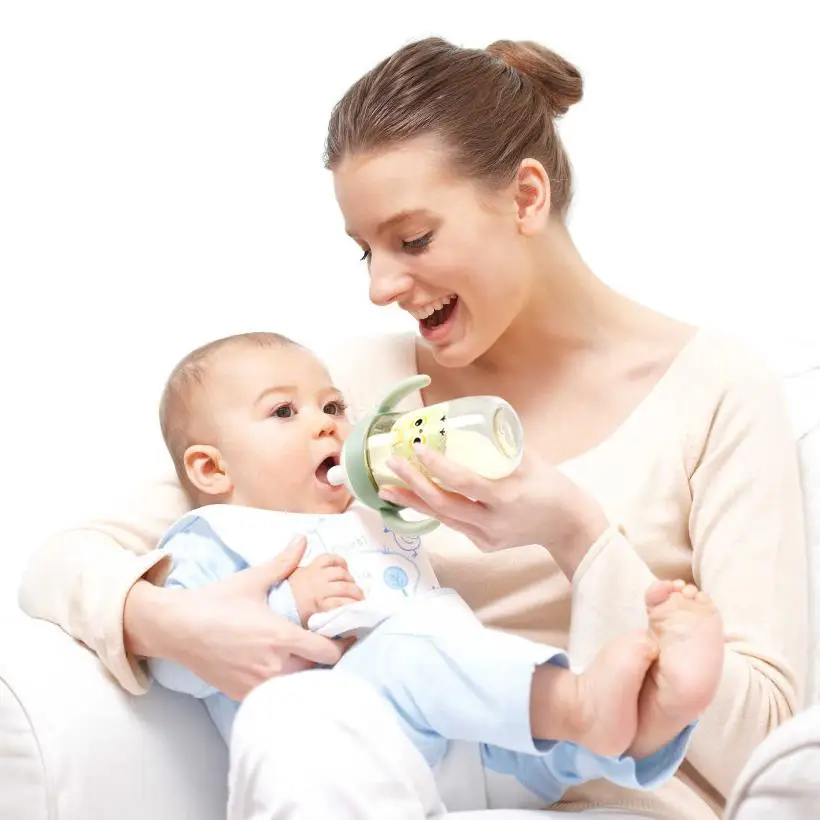
As your baby grows, move from pureed baby food to ones that have more texture (for example, mashed banana, scrambled egg, or well-cooked, chopped pasta). This generally happens around 8 to 10 months of age.
Your supermarket offers a variety of baby food products, but if you want to make your own, keep it sugar and salt free. Additionally, at this stage, don’t feed your baby anything that could be a choking hazard, including:
- hard foods, such as popcorn or nuts
- hard, fresh fruits, like apples; cook to soften or chop into very small pieces
- any meat that isn’t well cooked and very well chopped (this includes hot dogs)
- cheese cubes
- peanut butter (though talk to your pediatrician about this one — and the benefits of introducing diluted peanut butter before the age of 1)
As your baby nears their first birthday, they should be eating a variety of foods and taking in about 4 ounces of solids at each meal. Continue to offer breast milk or formula.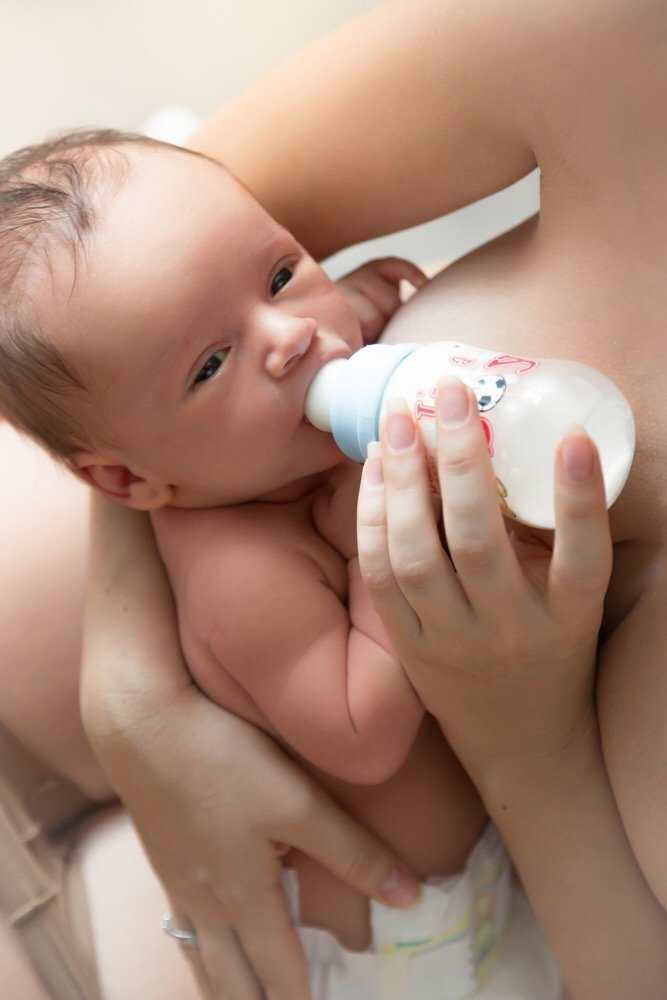 By 8 months, babies are drinking about 30 ounces a day.
By 8 months, babies are drinking about 30 ounces a day.
Oh yeah, and buy some stock in a company that makes stain-fighting laundry detergent. It’ll pay for college.
Babies aren’t cookie cutter. Some will gain weight easily, while others will have problems. Things that can affect a baby’s weight gain include:
- having a birth defect like a cleft lip or palate, which creates problems feeding
- having a milk protein intolerance
- being premature
- being fed with a bottle versus the breast
A 2012 study of more than 1,800 babies found that the infants who were fed with a bottle — regardless of whether the bottle contained breast milk or formula — gained more weight in the first year than babies who nursed exclusively.
Your baby’s doctor is the best one to advise you on a healthy weight range for your baby.
How, when, and what to feed a baby are top worries of every parent — but there’s good news: Most babies are pretty good judges of when they’re hungry and when they’re full — and they’ll let you know it.
You just need to present them with the right choices at the right time and pay attention to their cues. If you have any questions or concerns, your pediatrician is there to help you along the way.
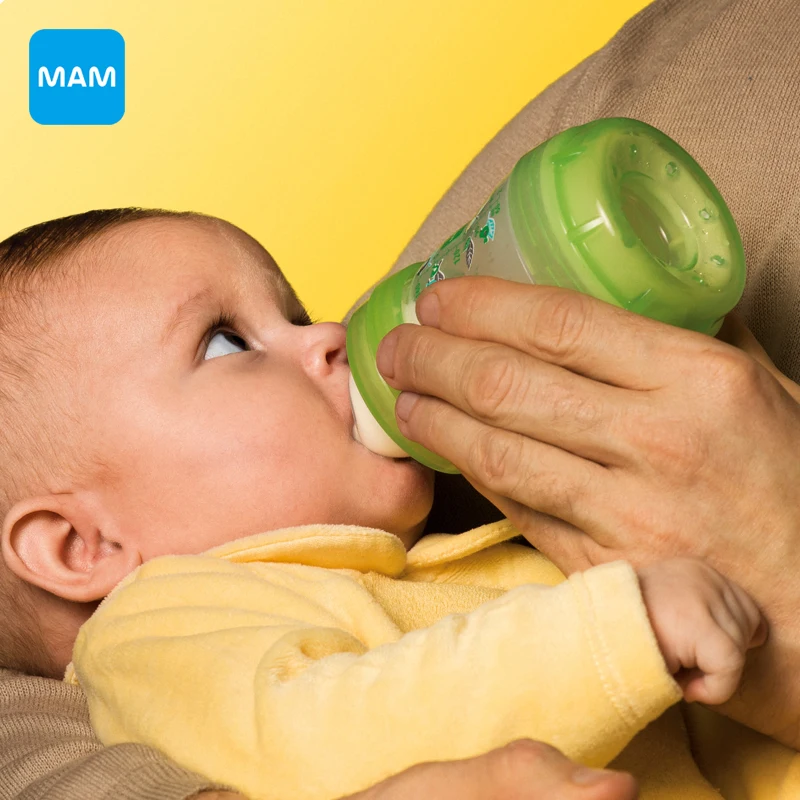
How to properly bottle feed
Feeding your baby is not only an important process for healthy growth and development, but also a way to establish close emotional contact with the baby and build trusting and loving relationships. The transition from breastfeeding to bottle feeding should be carried out after the mother and the child are fully prepared for this. We are talking about both the moral aspect, and about choosing the right bottle and getting adults the necessary skills so that eating brings only positive emotions and benefits to the baby. In this article, we will talk more about how to properly bottle feed your baby and where to start.
How to prepare your baby for bottle feeding
If this method of feeding is a completely new experience for the baby, or if parents decide to bottle feed their baby from a very young age, slow flow nipples should be preferred. So you protect the child from the possibility of choking while eating. Over time, you can gradually switch to bottles with nipples, which would provide faster and more intense feeding.
So you protect the child from the possibility of choking while eating. Over time, you can gradually switch to bottles with nipples, which would provide faster and more intense feeding.
Feeding bottle selection and daily care
All baby accessories should be kept clean and sterilized regularly and thoroughly.
There are several ways to sterilize dishes:
- select the appropriate mode when using the dishwasher;
- or place the bottle and teat in a vessel of boiling water for 5 minutes.
Before using this method of cleaning the bottle, make sure that the material it is made of can be exposed to high temperatures. Since some types of plastic contain various chemicals in their composition, after sterilization they can become dangerous for their little user. For this reason, experts recommend choosing glass bottles.
The need for thorough cleansing of everything that the baby will touch is caused by the fact that in the first months of life, the child's immune system is just beginning to strengthen. Before sterilizing the teat, it can be cleaned with dishwashing detergent. There are special products for washing children's dishes, without a strong odor and with a safe composition.
Before sterilizing the teat, it can be cleaned with dishwashing detergent. There are special products for washing children's dishes, without a strong odor and with a safe composition.
How to bottle feed your baby
Before starting a meal, mom or dad should wash their hands well with soap and warm running water. Particular attention should be paid to the area between the fingers and under the nails. The hand washing process should take at least 20 seconds. And after carrying out this hygienic procedure, hands should be wiped dry with a paper towel or clean towel.
The next step is to prepare for the meal. If you plan to fill the bottle with formula, then dilute it with water in accordance with the instructions in the instructions. Improper proportions can lead to dehydration or bloating. It should also be remembered that for the preparation of the mixture you need to use only clean drinking water.
Breast milk is the most beneficial for a newborn.![]() Despite this, pediatricians advise breastfeeding babies for as long as possible. Even if the mother is ready to give up breastfeeding, milk can be expressed into a bottle and gradually accustom the baby to the nipple. If, for one reason or another, the mother does not have the opportunity to feed herself, then the only alternative is feeding with a special mixture.
Despite this, pediatricians advise breastfeeding babies for as long as possible. Even if the mother is ready to give up breastfeeding, milk can be expressed into a bottle and gradually accustom the baby to the nipple. If, for one reason or another, the mother does not have the opportunity to feed herself, then the only alternative is feeding with a special mixture.
In the first six months after birth, cow's or goat's milk or its substitute in the form of soy milk should not be included in the baby's diet. Valid options for supporting healthy development of a newborn are breast milk or formula milk only.
What temperature should the bottle filler be? Under no circumstances should the bottle be heated on the stove or in the microwave. If the temperature of the bottle and its filling exceed 37°C, the baby may be burned. It is recommended to use special bottle warmers. If this is not possible, then use the following method:
- put a saucepan on the stove with a little water;
- bring the water to a boil, then remove the pan from the heat;
- place a bottle of milk in a vessel and heat it up to 37◦С;
- check the temperature with a pre-cleaned thermometer or a special device for measuring the temperature of foodstuffs.
You can also check the temperature of the ready-to-use bottle as follows:
- turn the bottle over;
- drip several times into your wrist area.
In this way, you can check not only the temperature of the milk or formula, but also how well the liquid flows out of the bottle. If you have to shake or squeeze the bottle hard to drip, the nipple is blocked and needs to be cleaned out. If, on the contrary, the filler pours out when the bottle is turned over, this means that the nipple is damaged and another nipple should be used to feed the baby, having previously sterilized it.
How to bottle feed your baby lying down
There are several techniques for feeding your baby. However, it is the feeding of the child lying down from the bottle that young parents consider the most comfortable. It is worth noting that eating in this position will only be safe when the baby's head is slightly raised. Otherwise, the child may simply choke. In the prone position, the child should be placed on his arm bent at the elbow. After feeding, you should place the baby in an upright position, taking him in your arms and putting his stomach to your chest.
In the prone position, the child should be placed on his arm bent at the elbow. After feeding, you should place the baby in an upright position, taking him in your arms and putting his stomach to your chest.
Make sure that the feeding bottle is closed correctly: the ring at the connection of the nipple to the bottle must not be too tight. Air must enter the bottle, otherwise a vacuum will be created there, which, in turn, will complicate the consumption of food for the child.
How to bottle feed without spitting up
Since the newborn is not able to fully control the process of feeding, along with milk, he can also take in air. This may be the reason that at one meal the child could not master the planned portion. In view of this, it is recommended to take small breaks during feeding.
As soon as you notice that the baby has stopped sucking on the pacifier, is tired or thoughtful, pick him up and press his face to you, holding his head and back. To help burp excess air, you can make a light massage between the shoulder blades, pat on the back or pope.
To help burp excess air, you can make a light massage between the shoulder blades, pat on the back or pope.
The air will quickly rise up and the baby will burp it without any extra effort. However, you should be prepared for the fact that, along with the air, part of the consumed mixture or milk may also return. Therefore, before taking the baby in your arms, cover yourself with a diaper, because it will be easier to wash it than clothes.
Never leave your baby alone with the bottle or let him fall asleep while using it. After eating, mom or dad must help their child burp. This will help to avoid colic, bloating and other manifestations of stomach discomfort.
Where to buy baby accessories
It's safe to say that I Love Mommy online store is one of the best places to buy baby food. Our catalogs feature products from world-famous brands, the quality of which you will not have to doubt for a minute. Bottles, baby dishes, pacifiers, baby bibs - all this and much more you can buy for your son or daughter from us at affordable prices in just a few minutes.
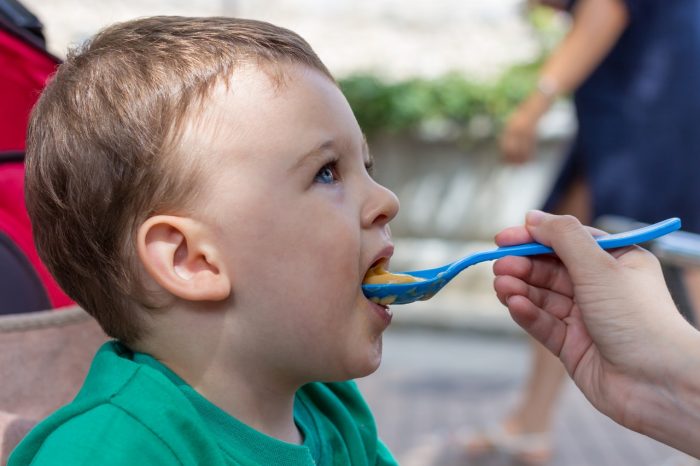
How to bottle feed your baby
There is no better food for a newborn baby than breast milk. But sometimes breastfeeding is contraindicated for the mother.
Website editor
Tags:
Children
newborns
Philips
There is no better food for a newborn baby than breast milk. But sometimes breastfeeding is contraindicated for the mother.
Do not self-medicate! In our articles, we collect the latest scientific data and the opinions of authoritative health experts. But remember: only a doctor can diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Mother's milk has an optimal composition, it contains substances that help the baby fight infections and strengthen his immunity.
However, unfortunately, there are often situations in which it is impossible to continue breastfeeding:
- mother's illness when she has to take medicines that affect the quality of breast milk;
- mother's going to work;
- lack of breast milk.
Depending on the situation, breast milk can be expressed and bottle fed to the baby; transfer the baby to artificial feeding; alternate breast milk feeding with bottle feeding. In each of these cases, the mother is faced with the question of how to feed the baby from a bottle.
Bottle feeding technique
To ensure that the baby does not experience discomfort during bottle feeding, some basic rules must be observed:
- Try to give your baby warm milk or formula - most babies prefer to be fed warm. To check the temperature of the mixture, drop it on the inner surface of your wrist - the feeling should be comfortable.
- If you are formula feeding your baby, be sure to check the expiration date on the box and follow the directions for preparation carefully.
- For bottle feeding, choose a position that is comfortable for both you and your baby.
- The pacifier should be pressed lightly against the baby's lower lip so that he opens his mouth wide enough. Make sure that the tongue is located below, under the nipple. If the baby's lips close around the wide part of the nipple, closer to the base, it means that he took the nipple correctly.
Make sure that the tongue is located below, under the nipple. If the baby's lips close around the wide part of the nipple, closer to the base, it means that he took the nipple correctly.
- Do not rush the child and do not force him to eat the whole portion: some children eat quickly, others slowly, and some like to eat with breaks. Be patient.
- Always hold the bottle in a tilted position: this helps the nipple fill with milk or formula, which means that the baby will not swallow air. Make sure that the nipple does not become clogged or flattened. If this happens, change the pacifier.
- After the child has eaten, pour out the rest of the mixture so as not to provoke a bacterial infection.
- After eating, gently pat your baby on the back to help expel the swallowed air.
We hope this bottle feeding technique will help you and your baby.
Bottle selection
The first thing to consider is the material the bottle is made of. Glass bottles tend to be heavier than plastic bottles and break easily. But they have a longer service life, while plastic bottles can become cloudy or crack quite quickly. But you can’t do without a plastic bottle on a walk and when the baby begins to learn to hold it on his own.
Glass bottles tend to be heavier than plastic bottles and break easily. But they have a longer service life, while plastic bottles can become cloudy or crack quite quickly. But you can’t do without a plastic bottle on a walk and when the baby begins to learn to hold it on his own.
Another important nuance - when choosing a bottle, be sure to pay attention to the presence of clear divisions that will help you determine the volume of breast milk or formula.
Most baby bottles from well-known manufacturers are equipped with anti-colic protection. They are equipped with various mechanisms that prevent air from entering the baby's stomach and thereby reduce the likelihood of colic.
Philips AVENT bottles have a unique one-piece valve in the nipple skirt that lets air in and prevents a vacuum. Such a valve is easy to clean and does not break, and due to the lack of vacuum, the baby can suck in his usual rhythm, which brings bottle feeding closer to breastfeeding.
For bottles Dr. Browns has developed a special ventilation system that prevents the air entering the bottle from contacting the liquid. As the baby sucks and the liquid decreases, the bottle fills with air and no vacuum occurs.
The presence of a special valve in bottles Nuby also does not allow air to mix with formula or milk, thereby relieving the child of stomach cramps.
Just as important is choosing the right pacifier. Most nipples today are made from latex or silicone. Silicone teats are odorless, more durable and easy to disinfect. The second important point when choosing a nipple is the intensity of the flow. For the smallest, it is better to choose a nipple with one or two small holes, for an older child - with several holes.
Some manufacturers offer large-diameter nipples that mimic the shape of a woman's breasts to prevent breast rejection during mixed feeding.
Bottle and nipple care
If your baby is under a year old, it is important to practice good hygiene when bottle feeding. The immune system of young children is still weak enough to successfully resist all infections. If you do not pay enough attention to the handling of the bottle, pacifier and other feeding items, the baby may experience indigestion or diarrhea.
Wash items thoroughly with warm soapy water after each feeding and sterilize before the next feeding to remove all bacteria from the surface. For sterilization, it is best to use bottled or clean filtered water - this will help to avoid the appearance of plaque on the dishes. One of three sterilization methods can be used:
1. Boiling. Items that need to be sterilized should be placed in a saucepan, filled with water and placed on the stove. Boil 5 minutes.
2. Microwave processing. Place the items in a glass saucepan, fill with water, cover with a lid and put in the microwave for 5-8 minutes.
3. Treatment in a special sterilizer for bottles.
Advice from Leyla Namazova-Baranova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of MMA named after.