One year baby foods
12 Healthy and Practical Foods for 1-Year-Olds
Your 1-year-old is changing, growing, and discovering at a whirlwind pace. Making sure they’re getting the foods they need may be a concern.
Inconsistent food choices and a fickle appetite are par for the course at this age. As frustrating as it might be, this is entirely normal as your toddler establishes independence and learns to discern their body’s fullness and hunger cues.
By the time they reach 12 months, toddlers need about 1,000 calories, 700 mg of calcium, 600 IU of vitamin D, and 7 mg of iron each day to support proper growth, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics (1).
With so much going on, you might be wondering how to best feed your 1-year-old without spending all day in the kitchen or chasing after them.
Here are 12 healthy and practical foods for 1-year-olds.
Around this time your 1-year-old starts to develop their pincer grasp, which involves pinching and maneuvering food with their fingertips, as they endeavor to self-feed. This is a great time to introduce finger-friendly foods.
Softer, fresh fruits are wonderful options for this transitional time and beyond. They not only deliver needed nutrients and a host of beneficial plant chemicals but also help cement healthy eating habits (2).
Slice bananas, clementines, strawberries, peaches, or mango, and slowly introduce them to your child. Avoid large pieces of fruit, as they may pose a choking hazard. Cut grapes into halves or quarters and never feed these to your child whole.
If your child doesn’t immediately take to the new fruit, don’t stress. In fact, studies show a child typically needs to be exposed to a new food 6–15 times before accepting it into their diet (3).
Soft fresh fruits can also be easily made into a smoothie or make an excellent snack when you’re on the go.
However, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, make sure your child eats any cut-up fruit within 2 hours after being out of the fridge. If you’re outside and it’s over 90°F (32°C), that time shrinks to within 1 hour (4).
If you’re outside and it’s over 90°F (32°C), that time shrinks to within 1 hour (4).
SummarySoft, bite-sized bits of fruit are excellent choices, especially as your child experiments with self-feeding. Be sure they eat any cut-up fruit that’s been out of the fridge within 2 hours, or within 1 hour if you’re in hot temperatures.
As your child may be slowly weaning off breast milk or formula, it’s a good time to introduce cow’s milk.
Milk and yogurt are great sources of protein and bone-building calcium, which also benefits their developing teeth. One glass (244 ml) of whole milk offers 39% of the Daily Value (DV) for calcium that your 1-year-old needs each day, as well as 8 grams of protein (5).
While you may continue to offer breast milk until 2 years of age or longer, whole fat dairy milk or yogurt may also be introduced at mealtimes or as a snack. Yogurt can be topped with diced fresh fruit or a drizzle of honey.
Honey can be introduced now at this age, but be sure to never feed it to a child under 12 months of age. Doing so can put them at risk of botulism, a serious infection (6).
Doing so can put them at risk of botulism, a serious infection (6).
Though dairy is generally safe at this age, be sure to watch for signs of a casein allergy.
Casein is a protein in milk. It’s different from lactose, which is a sugar found in milk that many adults don’t digest well (7).
A casein allergy manifests in about 2–3% of children under the age of 3, although more than 80% outgrow it. It seems to be most prevalent in children who were introduced to cow’s milk in infancy when breastfeeding was not an option (7, 8).
Be sure to introduce new foods, including milk and dairy products, to your child slowly. In fact, it’s a good idea to do so one food at a time and wait 3–5 days between the introduction of another new food to see how their body reacts (7).
Symptoms of casein allergy include wheezing, hives, vomiting, and diarrhea. If your child experiences these or other reactions when you are introducing them to a new food, stop feeding them this food and speak to their healthcare provider (7, 9).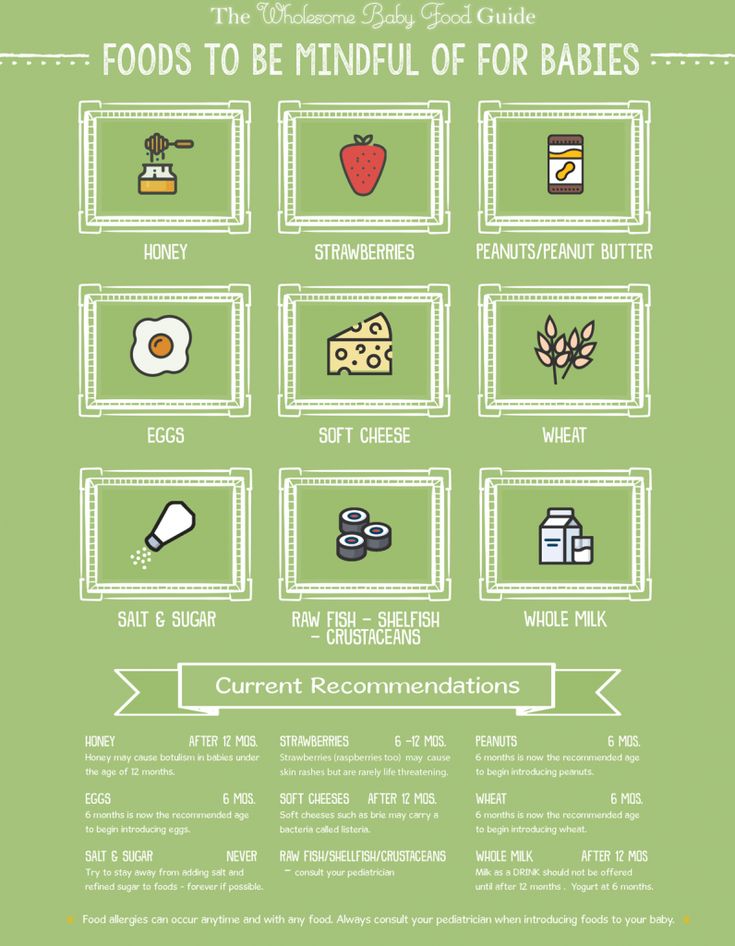
Also, consult your child’s pediatrician before giving them plant-based milk alternatives, as these are generally not recommended for toddlers due to their lack of essential nutrients for growth.
SummaryWhole milk and yogurt are great options as your child weans off formula or breast milk. These provide protein and support bone growth. You can offer them at mealtimes or as snacks.
Little ones won’t master the jaw-grinding motion, which helps with proper chewing, until they’re about 4 years old. In the meantime, their food must be mashed or cut up into small, easy-to-chew pieces (10).
Oatmeal is a wonderful option as your child makes this transition into chewing. It’s easy to swallow and boasts an impressive nutritional profile with a hearty heap of protein, carbs, vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats (11).
What’s more, oats provide ample amounts of fiber, which helps keep their digestive tracts healthy and regular (12).
While premixed packages are tempting, opt for your own homemade blend when possible to limit their intake of added sugar. If you’re strapped for time, consider making overnight oats by simply soaking them in the fridge overnight.
Mixing your oats with milk instead of water will also pack a bit more nutrients into your child’s bowl. Serve these topped with diced strawberries, bananas, or your child’s favorite raw fruit.
SummaryOatmeal is a nutritional powerhouse and offers an easy-to-swallow texture, which is helpful as your child develops the skills for proper chewing. Opt for homemade oatmeal over packets to limit added sugar, or try overnight oats.
Pancakes are popular among kids, and whole grains are a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Thus, whole grain pancakes are a natural solution to what to serve your 1-year-old (13).
Whole grain pancakes deliver gut-friendly prebiotics, which help feed beneficial gut bacteria.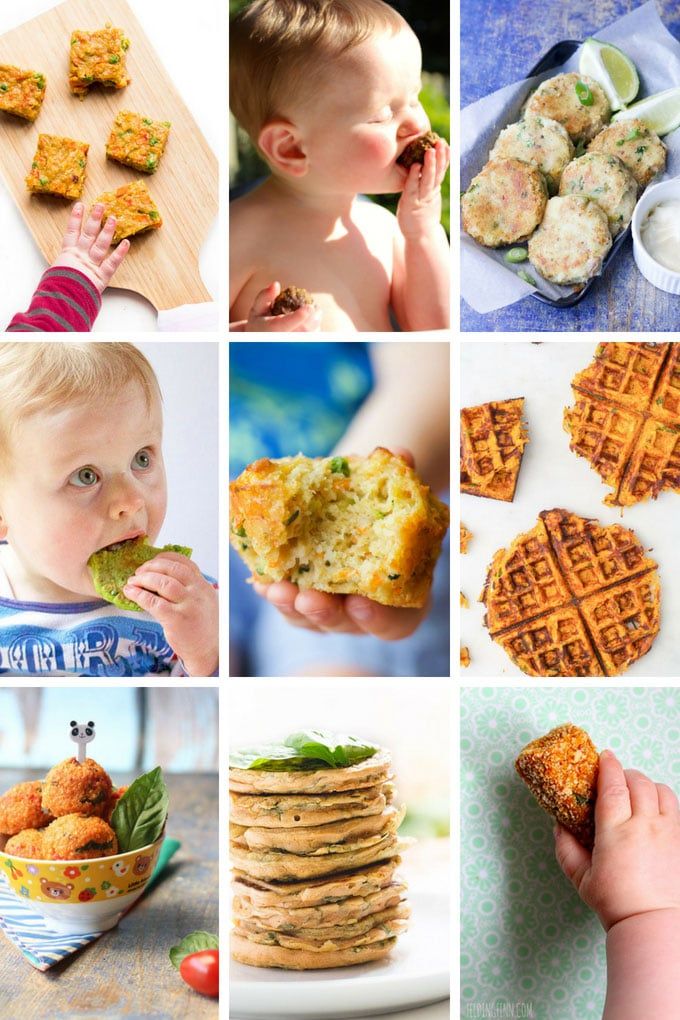 They’re also finger-friendly when cut into bite-sized pieces (14).
They’re also finger-friendly when cut into bite-sized pieces (14).
Whip these up or buy a mix with 100% whole grains. After sizzling them on a skillet or griddle, top them with freshly sliced soft fruits, applesauce, or a drizzle of honey.
You can even smear a very thin layer of creamy nut butter to add extra protein. Although, given that tree nuts are a common allergen, be sure to introduce this food into their diet slowly.
SummaryWhole grain pancakes are a practical and healthy choice for your 1-year-old. Whip up your own mix or buy a premade 100% whole grain mix. Top them with your child’s favorite soft fruit, a thin layer of nut butter, or a drizzle of honey.
Eggs are a powerhouse food for kids and adults alike.
They support eye health and proper brain development, and they’re rich in protein, healthy fats, and a host of other nutrients (15, 16, 17, 18).
Scramble them or serve them hard-boiled and peeled. Be sure to cut either of these into bite-sized pieces, especially as your toddler endeavors to self-feed.
Be sure to cut either of these into bite-sized pieces, especially as your toddler endeavors to self-feed.
Note that eggs are among the eight most common allergy-causing foods for children. Most children outgrow the allergy, but it’s important to watch for symptoms, which can include hives, nasal congestion, digestive issues, coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
Eggs can but rarely cause anaphylaxis, a severe life threatening reaction that can constrict airways or cause lightheadedness or loss of consciousness. Speak with a pediatrician if you are concerned about an egg allergy (19).
SummaryEggs are excellent for toddlers and adults alike. They’re particularly supportive of eye health and proper brain development. Plus, they boast an impressive nutritional profile and can be part of a healthy meal or snack.
Tofu is a great source of iron, calcium, and protein — with firm tofu boasting the greatest concentrations (20).
A 2-ounce (56-gram) portion of firm tofu provides almost 1 mg of iron, or nearly 14% of the DV for your child. The same serving also provides 12% of their daily calcium needs (20).
Served sweet or savory, tofu is wonderfully versatile. Silken tofu can be blended into smoothies or mashed into bananas, avocado, or cottage cheese. Its flavor is neutral, so all this will do is provide some hearty nutrition.
Toss cubed firm tofu into soups, or stir-fry it with your favorite gentle seasonings. You can also break firm tofu up with your hands and scramble it with your favorite soft vegetables, such as diced bell peppers, tomatoes, and onions.
If your child has a diagnosed soy allergy, you want to avoid tofu. If this allergy runs in your family, you should speak with your pediatrician.
SummaryTofu, whether silken or firm, is packed with iron, calcium, and protein. It is wonderfully versatile and can accompany sweet or savory dishes. Add silken tofu to smoothies or scramble firm tofu with soft veggies.

Soft bits of chicken or ground turkey can be great ways to incorporate more protein into your child’s diet. This nutrient is needed for proper growth (21).
Begin by feeding them puréed chicken, turkey, or soft cuts of meat. Poach the protein first, then add milk, broth, or yogurt to soften this mix in the blender or food processor. As they get more comfortable with self-feeding, sauté ground meat or cut it into small, bite-sized pieces.
Avoid any tough or stringy cuts of meat, as these might be too difficult for your child to chew or swallow. Also, steer clear of spicy or strong seasonings, which might upset their gentle stomachs.
SummarySofter cuts of meat like chicken or turkey can be a fountain of protein for your growing tot. Feed them puréed poached meats. As they get better at chewing, sauté ground or small bite-sized pieces. Avoid strong flavors.
Avocados are a fantastic food to feed your 1-year-old. Their creamy texture is especially helpful during this transitional period, while their impressive nutritional profile supports your child’s growth (22).
Their creamy texture is especially helpful during this transitional period, while their impressive nutritional profile supports your child’s growth (22).
What’s more, 30–40% of your toddler’s calories should come from fat, according to the American Heart Association (23).
Avocados are packed with healthy fats, which benefit your child’s brain and heart. Half a cup (75 grams) of diced, raw avocado provides nearly 9 grams of healthy unsaturated fats (24).
Cube or mash them and smear them on whole grain toast or a cracker. Experiment with blending avocado with other soft-textured fruits and vegetables, such as cooked butternut squash or sweet potato.
SummaryAvocados pack healthy fats and fiber while providing an ideal transitional texture for your toddler. Cube or mash them or blend them with other favorite fruits and veggies.
As your tyke weans off breast milk or formula, they need to hydrate. Water is an optimal choice.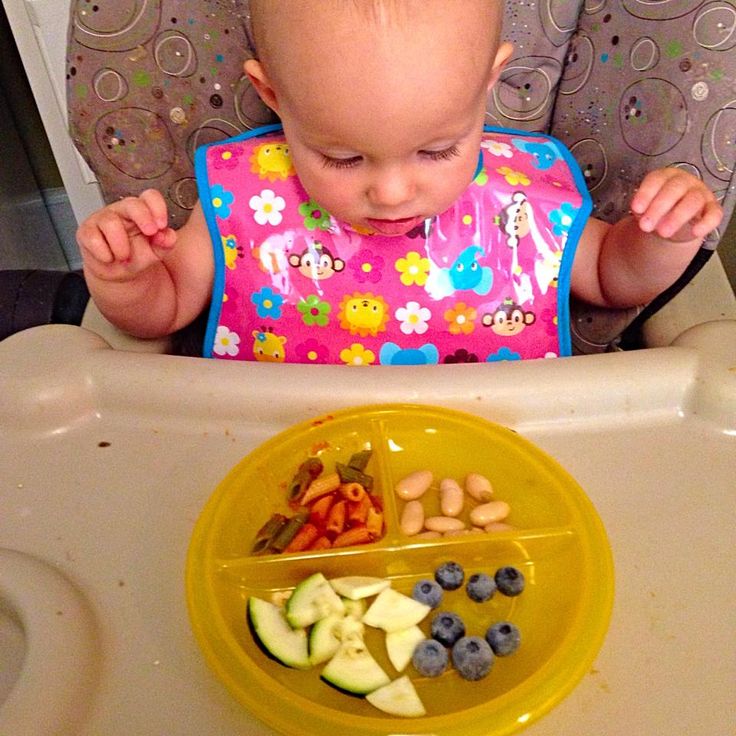 Fill up their sippy cups and replenish as often as they need.
Fill up their sippy cups and replenish as often as they need.
Your 1-year-old should be getting at least one 8-ounce glass (237 ml) of water a day. They may need more if they’re active, ill, or in hot temperatures. Also, they will need more as they get older (25).
When in doubt, check their diapers — they should be urinating at least every 6 hours.
SummaryWater should be provided as your tyke weans off breast milk or formula. At this age, they should get at least 1 cup (237 ml) each day.
Steaming vegetables, such as broccoli, peas, and carrots, is an excellent way to introduce your child to this important food group.
Broccoli, carrots, and peas pack fiber and vitamin C. What’s more, carrots contain lutein, which supports eye health, while peas pack muscle-building proteins (26, 27, 28).
Venture out with other veggies, including steamed parsnips, sweet potatoes, and butternut squash, too. Serve these with a lemony yogurt dip or hummus.
You’ll want to hold off on serving any of these raw, as they’re still too tough to chew.
SummarySteaming veggies softens them to an ideal texture for your growing tot. Broccoli, carrots, and peas are great choices, but feel free to venture out.
Half a cup (130 grams) of mashed beans provides nearly 39% of the DV for iron for your child (29).
Mashed beans — whether they’re black, kidney, or white beans — are a rich source of iron, which your child needs to keep their blood cells healthy (30).
Serving these alongside a food high in vitamin C, such as broccoli, diced tomatoes, or mashed sweet potatoes, will help them absorb iron much more efficiently (31).
This iron and vitamin C combo is especially important if your toddler doesn’t eat meat, as the body absorbs heme iron from animal sources more efficiently than nonheme iron from plant sources (31, 32).
SummaryMashed beans boast impressive nutrients, including iron.
This is especially important for your child’s health and helps keep their blood cells healthy. Eat beans with vitamin-C-rich foods to help boost iron absorption.
Hummus blends chickpeas and sesame butter, which pair to provide a bounty of protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals (33).
Spread hummus on some whole grain crackers or serve it alongside your child’s favorite protein source, a piece of cheese, or steamed veggie.
There are great store-bought options, but if you’re feeling inspired, this is an easy one to whip up. Simply combine a bit of garlic, sesame butter (tahini), chickpeas, and olive oil in a food processor until smooth.
Still, keep in mind that sesame seeds, which are used to make sesame butter, are among the top 10 most common food allergens, accounting for 17% of food allergies in children. Only 20–30% of affected kids outgrow it (34).
For this reason, be sure to introduce this and other sesame-containing foods to your child in very small amounts and watch for common reactions like hives and vomiting (34).
SummaryHummus is a great food to introduce at this age, as it provides a bounty of protein, healthy fats, and other nutrients.
A lot is going on with your 1-year-old. They’re experimenting with feeding themselves, learning to sense hunger and fullness, and asserting their independence, among several other developmental milestones.
As you navigate this period of growth and change, there are many practical and healthy food choices, including fresh, soft fruits, steamed veggies, tofu, and eggs.
The key points are selecting foods that are easy-to-chew, soft, and highly nutritious.
It’s a good idea to introduce new foods in small amounts and one at a time. With each new food, watch for adverse reactions, and stop feeding them this food if you observe signs of intolerance or allergy.
However, if you suspect it’s simply a matter of taste, or if your child doesn’t immediately take to these or other new foods, keep trying. It might take 6–15 exposures to a new food for your child to accept it into their diet.
It might take 6–15 exposures to a new food for your child to accept it into their diet.
Don’t stress if their appetite is fickle or their food choices vary like the wind — this is all part of their process.
Sample Menu for a 1-Year-Old Child
Ages & Stages
Listen
Español
Text Size
Babies and young toddlers should get about half of their calories from fat. Healthy fats are very important for normal growth and development at this stage of their development.
All fats are not created equal, though. Healthy fats like those found in avocado, olive oil, fish, nut butters, and dairy are good for your child (and you). Unhealthy fats such as those found in fried foods, fast foods and many packaged foods are not healthy at any age. If you keep your child's daily caloric intake at about 1,000 calories, you needn't worry about overfeeding and risk of weight gain
Here is a sample menu for a one-year-old child who weighs about 21 pounds (9.
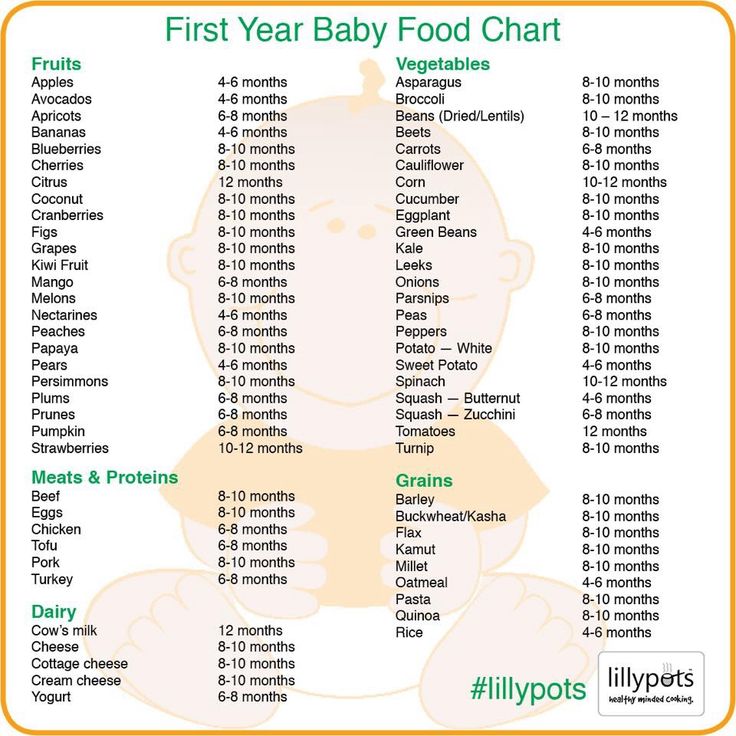 5 kg):
5 kg):1 cup = 8 ounces = 240 ml
1 ounce = 2 tablespoons = 30 ml
½ ounce = 1 tablespoon = 15 ml = 3 teaspoons
1 teaspoon = ¹⁄³ tablespoon = 5 ml
BREAKFAST
½ cup iron-fortified breakfast cereal or 1 cooked egg
½ cup whole or 2% milk
½ banana, sliced
2 to 3 large sliced strawberries
SNACK
1 slice toast or whole-wheat muffin with 1–2 tablespoons cream cheese or peanut butter, or ½ cup yogurt with cut-up fruit
Water or ½ cup whole or 2% milk
LUNCH
½ sandwich: sliced turkey or chicken, tuna, egg salad or peanut butter
½ cup cooked green vegetables
½ cup whole or 2% milk
SNACK
1 to 2 ounces cubed or string cheese, or
2 to 3 tablespoons fruit or berries
Water or ½ cup whole or 2% milk
DINNER
2 to 3 ounces cooked meat, ground or diced
½ cup cooked yellow or orange vegetables
½ cup whole-grain pasta or potato
½ cup whole or 2% milk
Remember
Talk with your child's pediatrician if you have any questions or concerns about your baby's diet.
More information
- Discontinuing the Bottle
- Unsafe Foods for Toddlers
- Selecting Snacks for Toddlers
- Water & Juice
- Last Updated
- 8/12/2022
- Source
- Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Nutrition for a child under one year old - "Our Joy"
Balanced nutrition - one of the main components of health at any age - is of particular importance for children. It is important to make the right diet and diet for the child.
It is important to make the right diet and diet for the child.
At the same time, the younger the child, the more significant the influence of nutrition on his current and subsequent development and health.
The first 1000 days of life is a critical period when nutrition and other factors determine the way to implement the genetic program, program the future.
In our articles, we will talk about the organization of nutrition for a child up to a year, as the most vulnerable period of childhood, and we will touch on the period from 12-36 months, during this period, high growth rates and development of the child continue, the improvement of the functions of individual organs and body systems continues, which requires an adequate supply of nutrients and energy to ensure these processes.
Brain. The baby's brain develops the fastest in the first two years of life. Between the age of one and three years, 50% of all energy is spent on brain activity, and in an adult - only 20%
Immunity . The protection that the baby received from the mother during breastfeeding in the first months of life is gradually reduced, and his body needs to learn to protect itself. The correct introduction of complementary foods helps to form a healthy intestinal microflora, which supports the child's immunity.
The protection that the baby received from the mother during breastfeeding in the first months of life is gradually reduced, and his body needs to learn to protect itself. The correct introduction of complementary foods helps to form a healthy intestinal microflora, which supports the child's immunity.
Digestion. The baby's stomach is very delicate and unable to digest heavy food. How well the digestive system will function depends largely on what kind of nutrition the baby receives. Therefore, the additional nutrition of the baby should be balanced and natural in order to ensure easy absorption of nutrients.
Teeth are being cut. In order for a child's milk teeth to be healthy, with strong enamel, his body needs the appropriate micro and macro elements. Proper nutrition will provide the baby with them in full
Eating habit. Optimal food consistency helps baby learn to chew, while a variety of natural flavors (and their flavor profiles) build healthy eating habits.
Complementary foods - introduction of other products in the diet of a child in the first year of life, in addition to breast milk .
The need to introduce complementary foods to the child by the end of the first six months of life is due to the following points:
- An increase in the child's need for food ingredients, including vitamins and minerals, which can no longer be satisfied by exclusive breastfeeding
- The introduction of food other than breast milk is necessary for the formation of food tolerance, the prevention of allergic diseases in the future
- Thick food is necessary to stimulate the motility of the gastrointestinal tract, the formation of the masticatory apparatus of the child.
The timing of the introduction of complementary foods. In accordance with the "National program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation", developed by leading experts in the field of baby nutrition, the introduction of complementary foods is recommended at the age of 4-6 months. Focusing on the individual characteristics of your baby, you should not forget that both early and too late introduction of complementary foods equally adversely affect the growth and development of the child. So, with the early appointment of complementary foods (up to 4 months), the frequency of dyspepsia, allergies, intestinal dysbacteriosis increases, mother's milk or infant formula is unreasonably ousted, and the enzymatic activity of the gastrointestinal tract is sharply stimulated.
Focusing on the individual characteristics of your baby, you should not forget that both early and too late introduction of complementary foods equally adversely affect the growth and development of the child. So, with the early appointment of complementary foods (up to 4 months), the frequency of dyspepsia, allergies, intestinal dysbacteriosis increases, mother's milk or infant formula is unreasonably ousted, and the enzymatic activity of the gastrointestinal tract is sharply stimulated.
Late feeding (after 6 months) leads to a pronounced deficiency of micronutrients (iron, zinc, etc.) perception of new tastes and textures of food.
The readiness of the baby to introduce complementary foods The pediatrician will help determine the following signs of the child's development:
- Baby sitting with support,
- He confidently holds and turns his head
- His weight has doubled since birth
- After 8-10 breastfeeds or formula, he is still hungry
- The baby stopped spitting out thick food (it is necessary to give the child a little puree from a spoon; if all the puree is on the chin, then it is too early to introduce complementary foods; if the child does not stick out his tongue, but swallows puree, then complementary foods can be introduced
- The baby gets excited at the sight of food and opens its mouth like a little chick
Complementary feeding rules.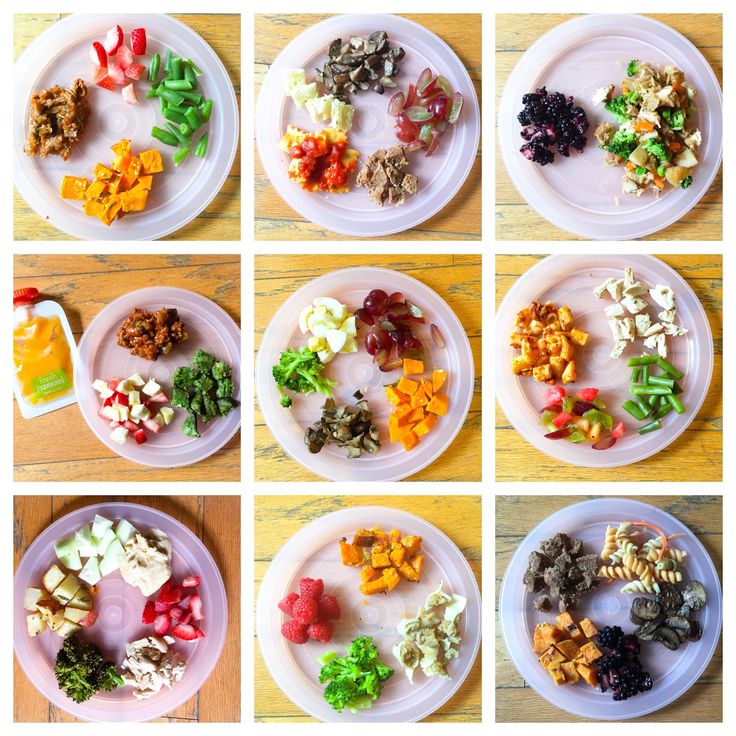 When introducing complementary foods, the following rules should be followed:
When introducing complementary foods, the following rules should be followed:
- The introduction of new products is not started if the child is sick, as well as during preventive vaccinations;
- Complementary foods given by spoon before breastfeeding or infant formula;
- The introduction of each new product starts with a small amount. Gradually. in 5-10 days. Increasing it to the required volume4, while carefully monitoring the tolerance of the product;
- The introduction of complementary foods is possible only after the child gets used to the previous one. Simultaneous introduction of more than one new dish is unacceptable;
- The introduction of any new complementary foods should start with monocomponent foods;
- The consistency of complementary foods changes gradually depending on the age of the child, passing through successive stages - first homogeneous (4-6 months), then puree and small pieces (7-9 months), and by the end of the year and more dense and large pieces.

how to choose the right baby food and what is the best?
The ideal "baby food" for an infant is breast milk. However, not all mothers can breastfeed their baby, usually this is due to the health of the mother or child. It happens that the woman herself has a serious condition after childbirth and in the early postoperative period, reduced lactation or diseases in which breastfeeding is contraindicated. In such cases, the baby is given formula milk - this is the only alternative to mother's milk. Subsequently, at four to seven months, complementary foods should be introduced into the child's diet, regardless of whether he is breastfed or artificial. The mother is faced with the task of choosing the right baby food for complementary foods.
In this article, we will talk about what foods for babies are and how to choose the best baby food.
Legislation defines "baby food" as food products that meet the physiological needs of a child under 14 years of age. And nutrition for young children is food intended for children from birth to three years[1]. It is necessary to make a diet taking into account the age of the baby and the characteristics of his physical condition.
And nutrition for young children is food intended for children from birth to three years[1]. It is necessary to make a diet taking into account the age of the baby and the characteristics of his physical condition.
The Union of Pediatricians of Russia created the National Program for feeding children in the first year of life and the National Program for optimizing the nutrition of children from one to three years old [2]. They describe recommendations regarding what formula to feed the baby from birth, how to introduce complementary foods and expand the baby's diet. These programs provide detailed information on what nutrients and nutrients should be included in the diet of children of different ages.
First you need to figure out what kind of baby food is [3]. Products for toddlers can be divided into two categories:
Infant formula. There are for children from birth to six months (formula 1 mixtures, or initial), from six months to a year (formula 2) and from a year (formula 3).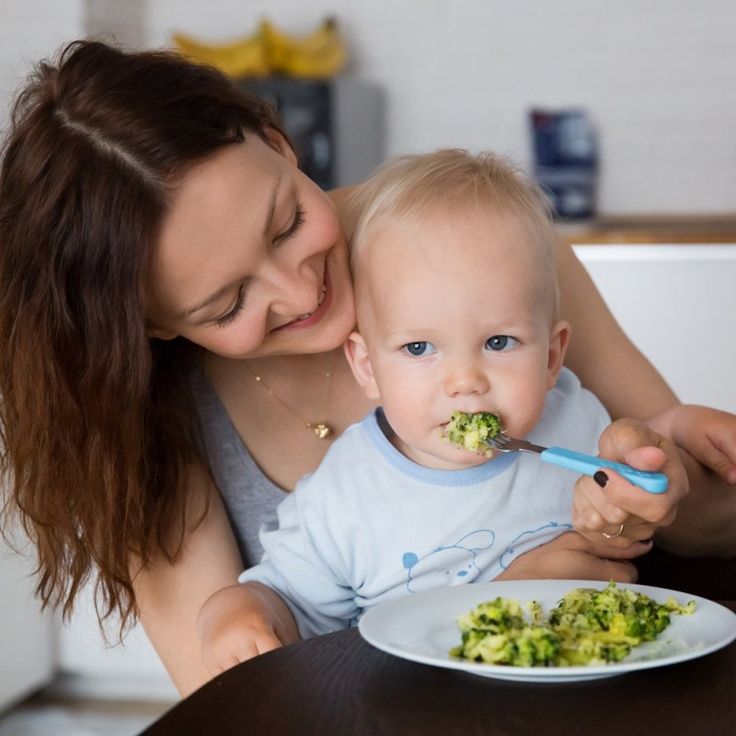 The composition of such baby food is adapted, that is, as close as possible to the composition of breast milk.
The composition of such baby food is adapted, that is, as close as possible to the composition of breast milk.
- In the initial mixtures, the amount of protein is reduced to 1.2-1.5 g / 100 ml - in accordance with the composition of breast milk. They also changed the fat and mineral profile. The initial mixtures are enriched with such an essential amino acid as taurine, and micronutrients, probiotics, vitamins.
- After six months, the baby's need for protein increases, mother's milk changes its composition. And babies on artificial feeding begin to be fed with a more nutritious mixture of formula 2. Taurine is no longer always needed: the body of a baby aged from six months to a year is able to synthesize this amino acid itself. Meanwhile, the content of iron, calcium, zinc increases compared to the initial mixtures, because by this age the child's reserves of minerals received from the mother during pregnancy are depleted, and they need to be replenished.
- A child's diet changes after one year - he is already able to eat a variety of solid foods.
 However, it is advisable to continue to feed him with a mixture, though already formula 3. Pediatricians recommend it as a source of vitamins and minerals that the baby can easily absorb.
However, it is advisable to continue to feed him with a mixture, though already formula 3. Pediatricians recommend it as a source of vitamins and minerals that the baby can easily absorb.
Complementary foods As we have already noted, it is introduced when the baby is four to seven months old. This interval is referred to as the "critical window" and is considered optimal for initiating complementary foods for several reasons:
- The baby needs a wider range of minerals, vitamins and other nutrients. In addition, his baby's digestive system is already ready to accept more solid and complex foods than mother's milk or infant formula.
- At this age, the child develops an interest in food, and it is necessary to offer him the right foods to develop his taste.
- During this period, the risk of developing a food allergy to a new product is lower.
- Timely introduction of complementary foods prevents the risk of micronutrient deficiencies and iron deficiency anemia.

Usually the first food is vegetable puree or monocomponent gluten-free cereals, milk or dairy-free. Over time, cereals containing gluten, supplements from fruits and berries, and also consisting of several cereals are added. A six-month-old child can already be given several types of vegetables and cereals. Also, at about six months, they begin to give meat puree, then fruit, and from eight months - fish. A child from seven months is allowed the yolk.
From the age of 12 months, complementary foods already make up the majority of your baby's diet. At this age, it is especially important to diversify the child's diet: he can be given soups with small pieces of vegetables, meat, fish and cereals.
For information
During the first feeding, the child's eating habits are laid, and it depends on the parents how correct they will be. Often, mothers introduce fruit juices into complementary foods too early. And because babies have an innate preference for sweet tastes, they can become naughty and stop eating the unsweetened foods they need, especially vegetables. Unhealthy taste habits are formed, which can later provoke obesity.
Unhealthy taste habits are formed, which can later provoke obesity.
Domestic doctors are concerned about such irrational nutrition of young children - due to the wrong approach to nutrition, many babies experience a deficiency of vitamins and an excess of fast carbohydrates.
How to choose baby foods
Finding the right foods for your baby is not an easy task. Store shelves are bursting with boxes, jars and bottles, and manufacturers write on every second package that the baby will be healthy, strong and cheerful after feeding. Of course, the baby will receive the necessary substances, no matter what product his parents choose, because all the production of baby food is strictly controlled by the state. By the way, Russia has some of the most stringent requirements for the quality of baby food in the world.
However, products for children differ in their properties. It is necessary to select food so that by the end of the first year of life the baby has actively developed chewing skills and an interest in independence, and the diet of complementary foods is reasonably varied.
For children from one to three years of age, the diet should be even more varied. It is important that the child receives daily something new from the main food groups: dairy, vegetables and fruits, meat and fish, cereals, butter and vegetable oil. Of course, the baby's diet should be expanded taking into account his state of health.
When organizing the nutrition of a child from the moment of introduction of complementary foods and up to three years, a mother needs not only to know what can be fed, but also to consider what foods should not be included in the diet. Among the prohibited products for children under three years of age:
- any mushrooms, vegetables and fruits in the marinade;
- pickles, preserves in tomato sauce;
- commercial juice concentrates, carbonated drinks, coffee and strong tea;
- various condiments - mustard, ketchup, hot sauces, horseradish, pepper, vinegar, mayonnaise;
- products containing flavors, industrial colors, including chewing gum;
- margarine and refractory fats - lamb, pork;
- chocolates, sweets, other sweets.

To choose the right baby food, you need to know exactly what you should pay attention to and what you don't need to worry about.
When choosing mixtures it is important to check:
- Absence of palm oil. Formula manufacturers may use palm oil (more specifically palm oil extract) because, like breast milk, it is rich in palmitic acid. However, in human milk, palmitic acid is in the beta position, while in palm oil it is in the alpha position. Such alpha-palmitic acid can interfere with the absorption of calcium and fats and is generally less well absorbed by the child's body. This can negatively affect the work of the intestines, lead to constipation, regurgitation. Milk fat is better suited for baby food as a source of palmitic acid[4][5].
- Protein ratio. Breast milk protein is primarily whey proteins and casein. A child needs both types of protein, while proteins are easily digested, which cannot be said about casein.
 If baby food contains a lot of casein, it stays longer in the digestive tract, which can cause problems with the baby's stool.
If baby food contains a lot of casein, it stays longer in the digestive tract, which can cause problems with the baby's stool. - The presence of additional functional elements in the composition - lutein, nucleotides, pre- and probiotics. The task of lutein is to protect vision from ultraviolet rays. Nucleotides are low molecular weight compounds that promote the growth of beneficial bifidobacteria in the intestines. And pre- and probiotics in the composition of infant formulas help to establish comfortable digestion.
When choosing complementary foods, pay attention to:
- Age appropriate. It is important that in the diet of a child under three years old who receives complementary foods, special children's products prevail - in their composition the components are selected taking into account the age-related needs of the baby's body. It is impossible at an early age to transfer children to "adult" foods like pickles, smoked foods, fast food, and so on.

- Fortified products. It is important that the composition contains vitamins and minerals. The National Child Nutrition Optimization Program recommends choosing complementary foods that contain elements designed to prevent anemia, rickets, and vitamin deficiencies.
- Dietary diversity. The menu for a baby up to six months is quite monotonous. But as they grow older, the baby needs more various nutrients - proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals.
- The individual reaction of the baby. If the child is already receiving complementary foods, then it is worth introducing a new product only after the previous one has been fully introduced. If the baby is allergic to the product, then it should be administered carefully, carefully checking the reaction of the body.
Ingredient safety testing is optional. Of course, the content of any "chemistry" in the product for feeding a child, whether it be a mixture or complementary foods, is unacceptable. There is no need to worry about this: baby food is carefully checked. If it is registered on the territory of the Customs Union and hit the shelves, then it complies with SanPiN 2.3.2.1940-05 and there will be no "prohibited" components in its composition. Also, contrary to popular misconception, in Russia it is forbidden to use GMOs in children's products.
There is no need to worry about this: baby food is carefully checked. If it is registered on the territory of the Customs Union and hit the shelves, then it complies with SanPiN 2.3.2.1940-05 and there will be no "prohibited" components in its composition. Also, contrary to popular misconception, in Russia it is forbidden to use GMOs in children's products.
Note
Baby food in jars (usually puree) has a short shelf life after opening, as it does not contain preservatives. However, before the jar is opened, the products can stand for quite a long time on the shelves of stores or in the refrigerator at home. This is possible thanks to a special production technology, sterilization and vacuum packaging. If a soft pop is heard when opening the jar, this is a good sign: the puree is not spoiled. But products in jars with swollen lids or a protruding bottom should not be used: microorganisms already multiply in such food, it is not suitable for food.
Features of the choice of dairy products
It is necessary to choose dairy products for babies, following the doctor's recommendations. The specialist will take into account the health of the baby, especially if he is allergic to cow protein. In Russia, such an allergy occurs in 30–40% of children [6]. Such a reaction may occur due to hereditary predisposition and immaturity of the body. But most often, allergies go away when the child grows up.
Goat milk baby food may be a suitable option for young children with a predisposition to allergies. Its protein is perceived by the body better than cow's: alpha-s1-casein, contained in large quantities in cow's milk, makes a product based on it difficult to digest - food stagnates in the baby's gastrointestinal tract, motor skills are disturbed, as a result, allergies often occur. In goat milk, as in breast milk, there is practically no alpha-s1-casein [7]. Therefore, goat's milk, and hence the mixture based on it, are better absorbed.