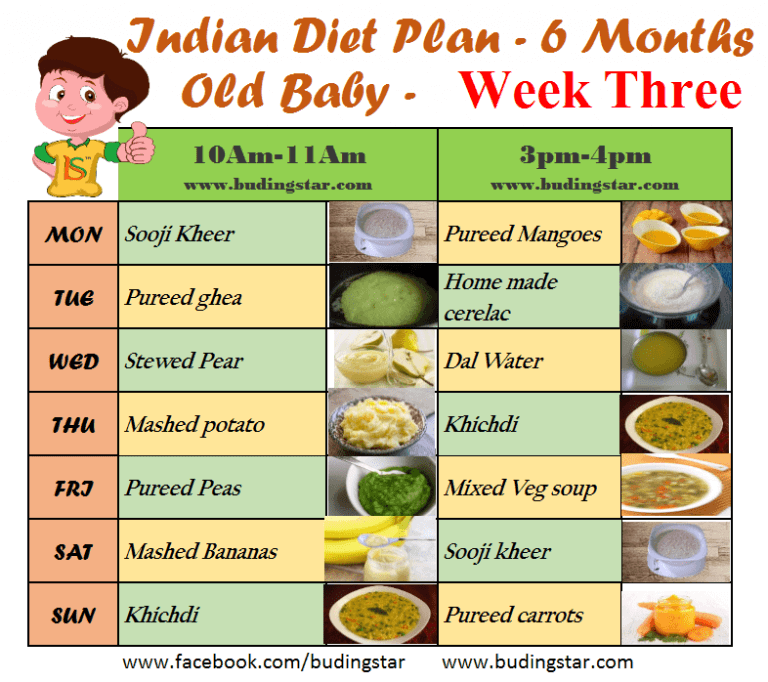
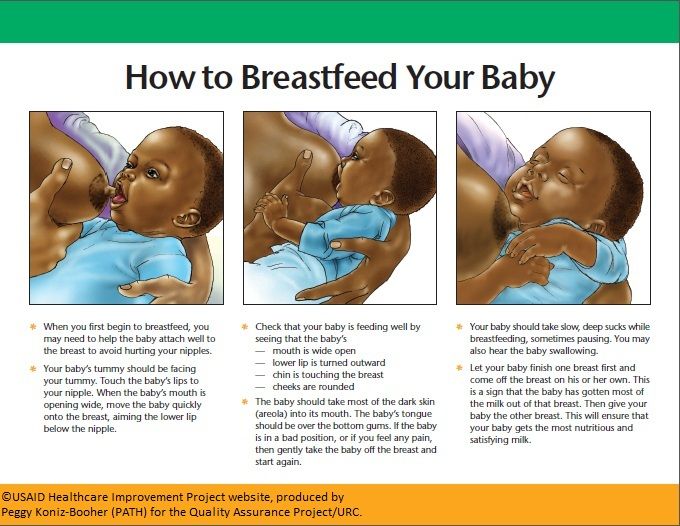
Problem feeding baby
How to tell if your baby has a feeding problem
COVID-19 Information Center: get the latest on vaccines, testing, screening, visitor policy and post-COVID support >>
Back to Healthy Driven Blog Home
November 26, 2019 | by Alexis Rodriguez, M.D.
Categories: Healthy Driven Moms
Some babies have trouble eating and drinking at first. They may spit up, avoid new foods or refuse to eat certain foods. They may have trouble holding food and liquid in their mouth. These issues are usually normal and temporary.
A child with a feeding problem or disorder will keep having trouble. Twenty-five percent of all children will experience feeding difficulties during infancy and early childhood that can affect their overall health and development.
When a baby doesn’t like solids, it’s easy to assume they are a “picky eater.” But poor feeding is different from picky eating, which doesn’t usually start until your baby becomes a toddler. A baby may have a feeding problem when they can’t eat or drink enough of the right things to stay healthy.
Feeding problems may include difficulty swallowing, called dysphagia. This is the inability of food or liquid to pass easily from the mouth to the throat, through the esophagus and into the stomach. Dysphagia can result in aspiration, which may cause pneumonia and/or other serious lung conditions.
How do you know if your baby has a feeding problem or disorder? Some common red flags include:
- Refuses to eat and drink
- Isn’t gaining weight or growing as expected
- Arches back or stiffens when feeding
- Cries or fusses when feeding
- Regularly takes a long time to eat (more than 30 minutes)
- Falls asleep or isn’t alert when feeding
- Avoids foods with certain textures
- Drools a lot, coughs or gags when feeding
- Has problems chewing and swallowing
- Has trouble breathing while eating and drinking
- Frequently spits up or vomits
- Has a hoarse or raspy voice during or after feeding
Feeding difficulties in babies may happen because of breastfeeding challenges.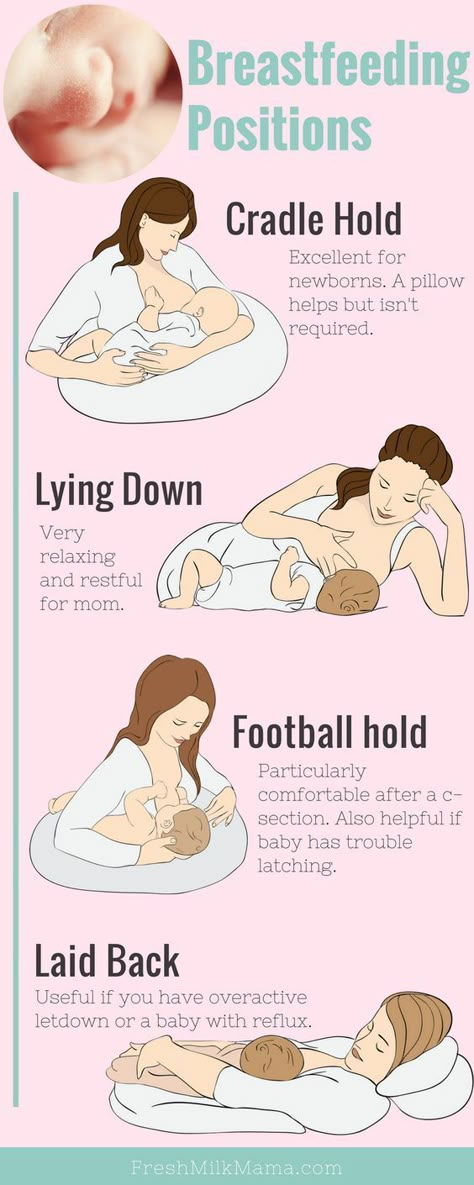 Lactation consultants can teach you how to feed your baby and help with latching difficulties, painful nursing, low milk production and other issues.
Lactation consultants can teach you how to feed your baby and help with latching difficulties, painful nursing, low milk production and other issues.
Poor feeding may also be caused by temporary illnesses, including ear infections and colds. These can make feeding uncomfortable for babies and will normally stop when the illness is treated. Other factors that may affect a baby’s ability to feed are stress, pain from teething and medication side effects.
Babies with certain health problems or conditions may also have feeding difficulties. Some possible causes for infant feeding and swallowing problems include:
- Prematurity, low birth weight
- Certain traumatic birth injuries (cerebral palsy)
- Structural abnormalities (cleft lip, cleft palate)
- Reflux or other stomach problems
- Lung or respiratory problems (asthma)
- Heart disease
- Nervous system or muscle problems (muscular dystrophy)
- Developmental delays or disabilities (autism)
If left untreated, feeding problems can negatively affect your baby’s health. Malnutrition is a top concern. Babies need to feed and digest the necessary nutrients to develop and grow properly. If they don’t get the necessary nutrition, it can lead to a condition known as failure to thrive.
Malnutrition is a top concern. Babies need to feed and digest the necessary nutrients to develop and grow properly. If they don’t get the necessary nutrition, it can lead to a condition known as failure to thrive.
Feeding issues can also put infants at risk for dehydration, aspiration, pneumonia or other lung infections, and delayed physical and mental development which can lead to speech, cognitive and behavioral problems.
The earlier the problem is addressed, the better the long-term outcome. Treatment for feeding disorders varies based on what’s causing the issue and the symptoms involved. A team approach, including the child’s doctor, dietitians and speech-language pathologists, is often the best way to treat these issues.
For instance, babies and children with dysphagia are often able to swallow thick fluids and soft foods better than thin liquids. A speech-language pathologist can suggest techniques for feeding that may help improve swallowing problems.
Treatment may also include medicines for reflux, trying different foods or textures, changing the temperature of food, changing the feeding schedule (e. g., smaller, more frequent meals), changing your child’s position while eating, and/or switching feeding methods. In severe cases, your child may need to get nutrition in other ways, such as through a feeding tube.
g., smaller, more frequent meals), changing your child’s position while eating, and/or switching feeding methods. In severe cases, your child may need to get nutrition in other ways, such as through a feeding tube.
If you think your baby is having trouble with feeding, let your child’s doctor know right away. While feeding problems are usually minor, your doctor will want to rule out an underlying medical issue.
Some warning signs of feeding problems include wetting fewer than four diapers per day, infrequent or hard stools in the first month, your baby becomes more yellow instead of less during the first week.
If your baby shows any signs of emergency, such as a fever over 100 degrees, wheezing, bloody vomit or stool, or constant crying, get immediate medical attention. Signs of an allergy or digestive disturbance include vomiting after feeding, frequent loose or watery stools, blood in the stools or a severe skin rash.
The Edward-Elmhurst Health Pediatric Feeding Clinic takes a comprehensive approach to the full spectrum of feeding disorders in children of all ages and concentrates on feeding, nutrition and growth.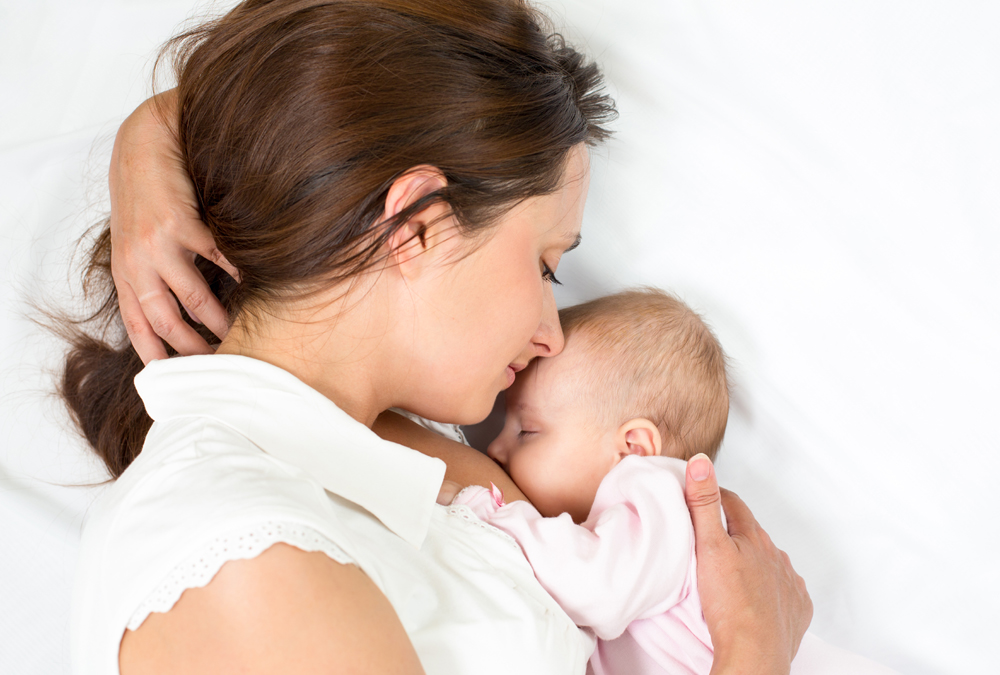 Our multidisciplinary team includes a pediatric dietitian, pediatric speech-language pathologist, pediatric gastroenterologist and a pediatric nurse. For questions, please call 630-527-5409.
Our multidisciplinary team includes a pediatric dietitian, pediatric speech-language pathologist, pediatric gastroenterologist and a pediatric nurse. For questions, please call 630-527-5409.
Explore children’s services at Edward-Elmhurst Health.
Related blogs:
Should I be worried about my baby’s growth?
Breast or bottle? Which will you choose?
Is my newborn normal?
How to teach your child to love her body
Know the signs of an eating disorder and when to get help
KidsMatter: Helping youth say “yes” to endless possibilities
Featured Expert
Alexis Rodriguez, M.D. Specialty: Pediatric Gastroenterology
Dr. Rodriguez specializes in pediatric gastroenterology. Read More >>
Rodriguez specializes in pediatric gastroenterology. Read More >>
Blog Category
Healthy Driven Stories with Mary Lou Mastro
Our very own President & CEO Mary Lou Mastro will post about what our patients want to know, from the latest buzz in our hospitals to what’s new in health care.
Healthy Driven Life
We’ve got fresh new ideas about how to lead a healthier life! Our physicians and other experts will post about exercise and fitness, recipes, wellness advice and more.
Healthy Driven Heroes
Our stories about patients who bravely and proactively improved their health, and the caregivers who helped them along the way, are sure to motivate and inspire.
Healthy Driven Moms
Our physicians and other experts will post about all things moms and moms-to-be want to know.
Healthy Driven Cancer Fight
Our physicians and other experts will post about issues that matter most to people affected by cancer.
Healthy Driven Hearts
Our physicians and other experts will post about the latest treatments and more for living a heart healthy life.
Healthy Driven Minds
Our physicians and other experts will post about improving mental health and well-being.
Healthy Driven Voices of Diversity
By creating platforms and opportunities that allow us to come together, we can begin to know and understand each other.
Healthy Driven Community
Read stories that illustrate our commitment to keeping our community healthy.
Healthy Driven Chicago®
Our physicians and other experts will post about the steps you can take today to stay healthy and fit for years to come.
Feeding Problems | Pediatrics
Feeding can become a problem when your child is losing weight or having trouble gaining the right amount of weight for their age. Your child or baby has feeding problems when:
Your child or baby has feeding problems when:
- They can’t eat or drink anything.
- They can’t eat and drink enough of the right things to stay healthy.
- They choose not to eat or drink enough of the right things to stay healthy.
With a baby, you might have breastfeeding problems. Other baby feeding problems might come from your baby not being able to suck, chew, or swallow.
Eating disorders in young children are called feeding disorders. They might also be called toddler eating disorders. (Usually, the term eating disorder is used for pre-teens, teenagers, and adults.)
Sometimes problems with eating get better without treatment. Sometimes your baby or child will need to be seen by a doctor.
With treatment, feeding disorders can get better. Eating can turn into a safer, easier, and happier experience for your child and the rest of the family. Treatment can also help your child become healthier.
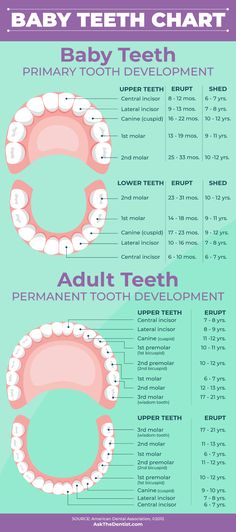
Sometimes feeding problems are due to a child not being able to suck, chew, or swallow. This might stem from a physical problem such as a cleft palate or tongue tie. When the cause is less clear, you can look for these signs:
This might stem from a physical problem such as a cleft palate or tongue tie. When the cause is less clear, you can look for these signs:
- Not gaining weight well
- Coughing, choking, or gagging when eating or drinking
- Throwing up often
- Choking on food or drink once during a meal and not eating again
- Eating and breathing coordination problems
- Not eating baby food purees by 8 months old
- Not eating table foods by 12 months old
- Not using a cup by 16 months old
- Eating baby foods at 16 months old
- Avoiding foods with a certain texture or from a certain food group (such as fruits and vegetables)
- Eating fewer than 20 kinds of food, especially when they stop eating certain foods and don’t replace them with other foods
- Crying or arching the back at most meals
- Taking more than 30 minutes to eat meals on a regular basis
Other signs within your family can include:
- Arguing with your child about food and feeding
- When feeding your child is difficult for everyone
- Eating problems you have that your child may get from you
If your baby or child is losing weight or having trouble gaining the right amount of weight for their age, you should see a doctor. While some feeding problems can get better without treatment, it is best to make sure that the cause isn’t serious.
While some feeding problems can get better without treatment, it is best to make sure that the cause isn’t serious.
If your baby is very uncomfortable when eating or their spit up is green or bloody, you should take them to a doctor right away.
Feeding disorders are more than picky eating. Feeding difficulties in children are almost always caused by some other medical problem, including:
- Gastroesophageal reflux [GAS-troh-ih-SOF-oh-JEE-uhl REE-fluhks]. This is a condition where acid from the stomach flows back into the esophagus, the tube that connects your child’s mouth to their stomach.
- Eosinophilic esophagitis [EE-oh-sin-oh-fil-ik EE-sof-a-jai-tis] or inflammation of the esophagus
- Other stomach or intestine problems
- Seizures
- Nervous system problems
- Premature birth
- Sensory system problems
- Autism
- Craniofacial [CRAY-nee-oh-FAY-she-awl] syndromes or abnormalities of the face or head
- Heart or lung problems
- Face and mouth muscle problems
- Problems swallowing certain liquids and food textures
When a baby has a problem with breastfeeding, these medical problems might not be the cause.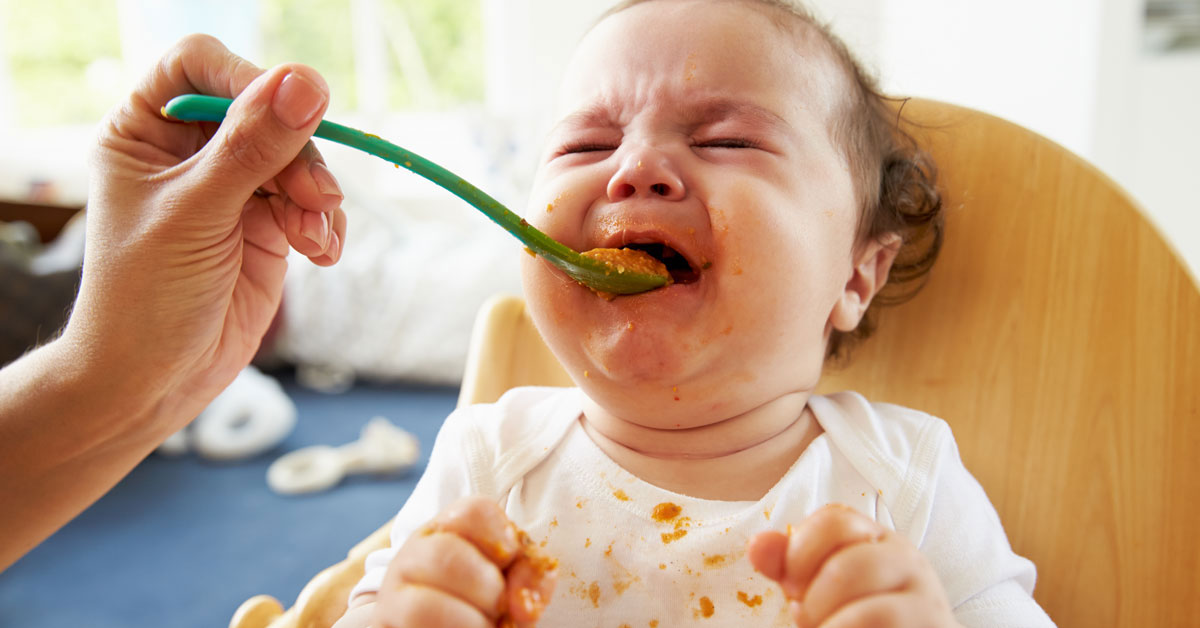 Breastfeeding doesn’t necessarily come easily for everyone. You may have difficulty with positioning your baby or have sore or tender nipples. Your baby might be spitting up. Some spitting up is normal for all babies. It happens when they eat too fast or swallow air. Remember that it takes practice and patience to find a pattern that works best for you and your baby.
Breastfeeding doesn’t necessarily come easily for everyone. You may have difficulty with positioning your baby or have sore or tender nipples. Your baby might be spitting up. Some spitting up is normal for all babies. It happens when they eat too fast or swallow air. Remember that it takes practice and patience to find a pattern that works best for you and your baby.
Your child will have a clinical feeding evaluation at a therapy center. The feeding specialist (either a speech-language pathologist or an occupational therapist) will talk with you about:
- The foods your child eats
- Where and when your child eats
- Who feeds your child
The therapist will look at your child’s mouth and face. They will watch your child eat or be fed. By watching children eat, the specialist can learn how they move their mouths, think while eating, and control their bodies. They can also see a child’s general ability to eat. If the therapist thinks your child may not be swallowing safely, they will schedule another evaluation.
After the feeding evaluations, the therapist may recommend several ways to help your child, including:
- Putting your child in certain safe eating and drinking positions
- Giving your child certain drinks and foods that are safe for them
- Helping your child to eat a wider variety of foods, and drink assorted drinks
- Teaching you and your child safe feeding and drinking skills
- Coordinating services with other medical and therapy professionals
Most causes of feeding problems cannot be prevented. Some steps you can take to make eating a healthy time that your child likes include:
- Not arguing about food
- Making food fun
- Avoiding power struggles over food
- Being patient when giving your baby or child new foods to try
- Healthy Children
Your child or baby has feeding problems when they can’t eat or drink or when they can’t eat and drink enough of the right things to stay healthy. If your child is losing weight or having trouble gaining the right amount of weight for their age, they might have a feeding disorder. With treatment, feeding disorders can get better.
If your child is losing weight or having trouble gaining the right amount of weight for their age, they might have a feeding disorder. With treatment, feeding disorders can get better.
© 2018 Intermountain Healthcare. All rights reserved. The content presented here is for your information only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, and it should not be used to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease. Please consult your healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns.
Solving six breastfeeding problems in the first week
Having difficulty breastfeeding your newborn baby? Read on for expert advice on tackling the main challenges of the first week of breastfeeding.
Share this information
Cathy Garbin, child health nurse, midwife and lactation consultant:
Cathy, a mother of two, was a research fellow at the renowned Human Lactation Research Institute, founded by Peter Hartmann, for seven years, providing support to breastfeeding mothers in clinics and at home. Today, she still works as a family counselor, and also conducts seminars for attending physicians and speaks at international conferences.
Today, she still works as a family counselor, and also conducts seminars for attending physicians and speaks at international conferences.
Breastfeeding is not always easy, so if
you are having difficulty, know that you are not alone. A US study found that out of 500 new mothers surveyed, 92% experienced breastfeeding problems by the third day. 1 Fortunately, most early breastfeeding problems are easy to resolve. Below you can read recommendations for solving the main problems that mothers often face in the first week of feeding.
Problem #1. Breastfeeding hurts!
Pain during feeding is usually associated with tenderness or inflammation of the nipples, especially when milk "comes" on the second to fourth day after birth. 2 The baby will beg for a breast every couple of hours, and this can quickly aggravate the problem: some mothers' nipples crack, bleed, or blister. This is, of course, very annoying.
Solutions 3
- Check how the baby latch on.
 An incorrect latch is one of the most common causes of pain during breastfeeding. A newborn baby should take most of the lower half of the areola (dark skin around the nipple) into his mouth, and your nipple should rest against his palate, supported from below by the tongue.
An incorrect latch is one of the most common causes of pain during breastfeeding. A newborn baby should take most of the lower half of the areola (dark skin around the nipple) into his mouth, and your nipple should rest against his palate, supported from below by the tongue. - Contact a lactation consultant or healthcare professional to make sure your baby's mouth and torso are properly positioned during feeding and there are no other latch-on problems. The doctor may also examine the baby's mouth for physical abnormalities.
- Try other feeding positions. Reclining, cross cradle, underarm, or lying positions can relieve pressure on the most painful areas of your breasts.
- Gently wipe soaked nipples with water-soaked cotton swabs after each feed to remove milk residues that can cause infection.
- Air dry nipples or blot with a clean, soft muslin or flannel cloth to prevent bacterial growth in a humid environment.
 Use disposable or reusable bra pads to absorb leaking milk and remember to change them regularly.
Use disposable or reusable bra pads to absorb leaking milk and remember to change them regularly. - Soften your nipples. An ultra-pure lanolin treatment will help relieve inflammation and dry skin. You can also apply a few drops of your own breast milk to your nipples. In both cases, you do not have to wash your breasts before the next feeding. You can also apply refrigerated hydrogel pads* to your nipples. They soothe the nipples and help relieve pain during feeding, as well as speed up healing.
- Protect your nipples. Nipple shields* protect the sore area from rubbing against clothing.
- Be patient. The inflammation usually resolves after a few days as your body adjusts to breastfeeding and your baby learns to suckle.
- Seek medical attention, if pain during feeding does not go away after a few days. Constant inflammation of the nipples may indicate an infection that requires prompt treatment.
Problem #2. Baby doesn't latch on properly
Some newborns do not latch on properly right away. Maybe both of you just need more time to learn how to breastfeed, or maybe the baby was born prematurely, feels unwell after a difficult birth, or mom has flat or inverted nipples.
Solutions
- Contact a lactation consultant or healthcare professional who can help identify the cause of the problem and suggest solutions.
- Flat or inverted nipples must be pulled out. Nipple formers* fit comfortably in the bra and apply gentle pressure to the nipples to help them come out for easier feeding.
- Try different positions and ways to support your newborn. The baby needs to feel supported. He must be comfortable and breathe freely in order to suckle properly. Do not hold the child by the head and do not put pressure on it. Lean back and let your child take the lead.
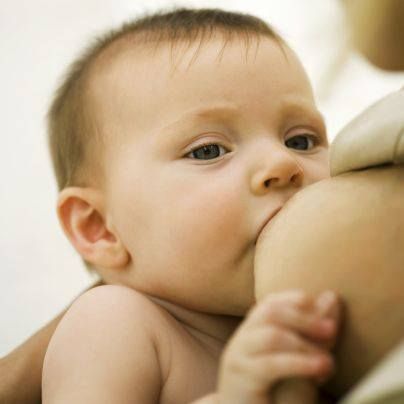 This stimulates his natural reflexes and helps him find and latch on to his breasts. 4
This stimulates his natural reflexes and helps him find and latch on to his breasts. 4 - When feeding, try to find the optimal position. Instead of putting your baby on and off, stressing both of you, try to position him in a way that is easy and comfortable for him. Hold the torso and legs of the baby close to you, support him by the shoulders and hold him firmly so that he feels safe. Let the baby's head rest freely on your arm so that he can tilt it back slightly and breathe freely. The chin should be pressed against your chest. If these small adjustments don't make feeding more comfortable for your baby, seek help from a lactation consultant or healthcare professional.
- Use nursing pads. If your baby is having difficulty latch-on, a lactation consultant or healthcare professional may suggest trying nursing pads*. A nipple with an overlay is more convenient to take in the mouth, so it is larger and more rigid. Do not use nursing pads for a long time.

Problem #3. Not enough breast milk
You will produce little breast milk at the very beginning, as the hormonal changes that trigger milk production occur slowly and do not end until the second or fourth day after birth. 2 You may be worried that your baby is not getting enough milk, but in the early days his stomach is still too small and feedings are frequent, so don't worry. The only things to worry about these days are excessive weight loss, too few wet and soiled diapers, or signs of dehydration in the baby. For more information on how often a newborn should urinate and void, see Breastfeeding Newborns: What to Expect in the First Week.
Solutions
- Contact a Lactation Consultant or your healthcare provider who can determine if you have problems with milk production. The sooner you do this, the better.
- Feed your baby on demand, not on a schedule. In the first week after birth, your baby will ask to breastfeed every two to three hours (or more often!), both day and night.
 Such frequent feeding helps to establish the production of breast milk.
Such frequent feeding helps to establish the production of breast milk. - Take care of yourself. It's not always easy with a newborn, but try to rest whenever you can, eat right, and accept any help around the house or with older children that your loved ones can give you to fully focus on breastfeeding.
- Try expressing milk. If a baby is feeding frequently but not gaining any weight, a lactation consultant or doctor may recommend pumping to increase breast milk production. If milk is not coming out at all, you can try the Medela Symphony Dual Electric Clinical Breast Pump**. It features an Initiate program that mimics a baby's natural sucking rhythm for the first few days.
Problem #4. Breast full and heavy
Your breasts will become fuller and heavier as milk comes in.
If the baby suckles well and often, this should not cause any problems. However, in some women, the breasts become so full that they become hard and painful. This condition, called breast swelling, can cause discomfort. The swollen chest seems to be “burning”, now all the activity of your body is concentrated in it, resembling a busy traffic at rush hour. Fortunately, this condition usually resolves within 24 to 48 hours. However, due to the swelling of the mammary glands, the nipples can become flat and the baby may have difficulty latch-on. 5
Solutions
- Feed your baby often. Try to breastfeed at least 8-12 times a day. This is the main way to alleviate this condition. For more tips and tricks, see the article on Breast Swelling. 6.7
- Call your healthcare provider, if symptoms persist for more than 48 hours, you have a fever, or your baby is unable to breastfeed due to swelling.
Problem #5. Milk is leaking
Breast leakage is very common in the early days of breastfeeding when milk production begins. Milk may leak from one breast while you are feeding the other, when you sleep on your stomach, or when something accidentally triggers the milk flow reflex, such as when you hear a baby crying in a store. The leakage usually stops after about six weeks.
Solutions
- Protect clothes from stains will help disposable or reusable bra pads to be used day and night.
- Don't waste precious drops! Breast milk collection pads* fit inside the bra and allow you to collect any leaking milk. This is a very useful thing when there is too much milk and the pads are not absorbing well, or when one breast is leaking while you are feeding the other. If you want to save the collected milk, use only the milk collected at the feeding. Place it in a sterile container and refrigerate immediately if you are not supplementing with it right away. Collected milk must be used within 24 hours. The breast milk collection sleeves should not be worn for more than two to three hours at a time.
Problem #6. There seems to be too much milk
Sometimes when milk comes in, too much is produced! In the first few weeks there may be an excess of milk, but usually everything returns to normal soon. 7 Up to this point, the breasts may be heavy and sore almost all the time, even immediately after a feed, and a lot of milk may leak. A strong flush can cause a baby to cough or choke, vomit immediately after a feed, have tummy discomfort, or have hard, frothy, greenish stools. These are all signs that you are having too much milk, but the problem may resolve itself as your breasts get used to the new function.
Solutions
- Express some milk by hand at the beginning of each feed to ease the force of the flush.
- Try to feed while leaning back: this will help your baby control the flow of milk. The "cradle" position is also good: hold the baby obliquely by the shoulders so that the head can lean back slightly while on your arm.
The torso of the baby will be located diagonally on you.
- Be kind and patient. Let your baby rest and absorb milk both during and after feeding. Don't move your baby too much or too fast, as this can make him nauseous. As the baby grows, he will learn to better cope with the rush of milk, which is likely to weaken anyway.
- Use the towel or swaddle to soak up spilled milk if the baby can't handle the flush, and place the breast milk collection pad on the other breast to catch any spilled milk.
- Contact a lactation consultant or doctor if problems persist after a few weeks . He will examine you and may suggest one-sided feedings or hourly breast changes (“breast duty”) to reduce your milk supply.
Related materials: Difficulties in breastfeeding in the next few weeks and problems with breastfeeding after the first month
Literature
1 Wagner EA et al. Breastfeeding concerns at 3 and 7 days postpartum and feeding status at 2 months. Pediatrics . 2013: peds -2013. - Wagner I.A. et al., "Breastfeeding Problems at Days 3 and 7 of a Baby's Life and Type of Feeding at 2 Months of Age". Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2013:e865–e875.
2 Pang WW, Hartmann PE. Initiation of human lactation: secretory differentiation and secretory activation. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2007;12(4):211-221. - Pang, W.W., Hartmann, P.I., "Lactation initiation in the lactating mother: secretory differentiation and secretory activation." G Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12(4):211-221.
3 Cadwell K. Latching - On and Suckling of the Healthy Term Neonate: Breastfeeding Assessment. J Midwifery & Women ’ s 2007;52(6):638-642. — Cadwell, K., "Latching and sucking in healthy newborns: evaluation of breastfeeding." F Midwifery Women Health. 2007;52(6):638-642.
4 Colson SD et al. Optimal positions for the release of primitive neonatal reflexes stimulating breastfeeding. Early Hum Dev . 2008;84(7):441-449. - Colson S.D. et al., "Optimal Positions for Provoking Primitive Innate Reflexes to Induce Breastfeeding." Airlie Hume Dev. 2008;84(7):441-449.
5 Jacobs A et al. S3-guidelines for the treatment of inflammatory breast disease during the lactation period. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2013;73(12):1202-1208. - Jacobs A. et al., "Recommendations S -3 for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the breast during breastfeeding. Geburtskhilfe und Frauenheilkünde. . ABM Clinical Protocol# 4: Mastitis , Revised MARCH 2014. Breastfeed : 5): 5) H., Academy of Breastfeeding Protocol Committee, AVM Clinical Protocol #4: Mastitis, March 2014 edition of Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2014;9(5):239-243.
7 Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine Protocol Committee. ABM clinical protocol # 20: Engorgement. Breastfeed Med . 2009;4(2):111-113. - Protocol Committee of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine, "AVM Clinical Protocol No. 20: Engorgement, Revision 2016". Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2009;4(2):111-113.
Read instructions before use. Consult a specialist about possible contraindications.
* RU No. ФСЗ 2010/07352 of 07/19/10
** RU No. ФСЗ 2010/06525 of 03/17/2021
What is breast swelling? | Breast swelling
Some mothers experience breast swelling when milk begins to flow in the first days after childbirth. Usually this phenomenon is temporary and easily eliminated. Read our article to find out how to help yourself.
Share this information
Sioned Hilton, health visitor, neonatal nurse and lactation consultant:
A mother of three, Sioned Hilton has been supporting families with newborns and young children for over 30 years. She provides advice on breastfeeding and pumping, both in clinics and at home. In addition, Schoned writes articles for parenting magazines, attends conferences, and conducts seminars for attending physicians.
When you start breastfeeding, you first produce a small amount of colostrum, which gradually increases over the first few days. After about two to four days, production increases significantly. This phenomenon is called the "arrival" of milk. 1
One of the signs that milk is starting to come in is a change in the breast - it fills up and becomes firmer. This is due not only to an increase in the amount of milk, but also to increased blood flow and additional lymphatic fluid to the breast tissues. 2
If the child eats well and often, then for most mothers this feeling of heaviness disappears over time without any complications. However, some women produce so much milk that their breasts fill up and become painful and very hard. This condition is called breast swelling. And although everything usually passes in a day or two, this period can be quite painful.
How does breast swelling manifest itself?
Swelling may affect one or both breasts. It can cause swelling, sometimes down to the armpits, and a throbbing sensation. The chest becomes quite hot, sometimes lumps are felt in it. All this is due to the fact that a huge number of processes take place inside. You may also notice other symptoms, such as the skin on your breasts becoming shiny and tight, and your nipples becoming hard and flat. Swelling of the mammary glands can even cause a temperature to rise to 37.5–38.3°C (99–101°F). 3
In addition to pain, swollen breasts are also dangerous because they can make breastfeeding difficult, and this, in turn, will worsen the situation even more. If the baby finds it difficult to latch on because the nipples have become flat and the breast tissue is firmer, nipples may become inflamed. In addition, in the event of a poor grip, he will not be able to completely empty the chest. Thus, if left untreated, swelling of the mammary glands can lead to blockage of the milk ducts, mastitis, and reduced milk production.
What causes breast swelling?
Usually breast swelling is due to the fact that the child does not feed often enough (less than eight times a day). In principle, this can happen to any mother, but women who have undergone various breast surgeries, including breast augmentation, are more prone to swelling of the mammary glands. 2 Wearing a bra that is the wrong size or that is too tight can increase discomfort and lead to clogged milk ducts and even mastitis.
Breast swelling can occur in both breastfeeding mothers and mothers who are not or cannot breastfeed. The hormonal changes that occur after the birth of a baby and the release of the placenta and increase milk production are independent of whether you are breastfeeding or not. Swelling can also occur if the number of feedings is drastically reduced, for example, if the child becomes ill, sleeps longer, starts eating solid foods, or goes to nursery.
How to treat breast swelling?
2The best cure for swollen breasts is a hungry baby! Try to empty your breasts as much and as often as possible to facilitate the release of milk. To do this, feed your baby on demand, preferably eight to twelve times a day.
Maintain skin-to-skin contact with your baby, cuddling as often as possible during the day and at night when you are awake. This will allow him to smell the attractive smell of your milk and have easy access to the breast, and you will be able to better monitor signs that he is hungry and, accordingly, feed more often. Let the baby eat enough from one breast before offering the second.
It's a good idea to see a lactation consultant or specialist to check if your baby is properly grasped and positioned. It depends on how well he will eat and empty his chest. The tips below will also help you relieve the symptoms of breast swelling.
Tips for Relieving Swollen Breast Symptoms 2
- Breastfeed at least eight times a day.
- Make sure your baby is latching on well.
- Try other feeding positions.
- Gently massage your breasts during feeding to improve the flow of milk.
- Express some milk by hand or with a breast pump before feeding to soften the nipple and make it easier for your baby to latch on.
- If your breasts are still firm and full after a feed, pump more until you feel better.
- If your baby is unable to breastfeed, express milk for him. Pumping must be continued until the breast becomes softer, and do this at least eight times a day.
- Try the areola pressure softening technique. This helps to remove excess fluid from the breast. A lactation consultant or specialist will show you how to do this.
- If milk is leaking, try taking warm showers or applying a warm flannel to your breasts just before feeding or expressing to soften your breasts and make it easier for your milk to flow.
You should not, however, warm the chest for more than two minutes, as this can only increase swelling.
- If your milk isn't leaking, try applying cold compresses, chilled gel pads, or even frozen green peas wrapped in a towel for ten minutes after feeding to reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Put clean cabbage leaves in your bra. Yes Yes! For many moms, it really helps reduce swelling and discomfort, and there are scientific explanations for this. 4
- Take an anti-inflammatory pain reliever. While breastfeeding, you can take some medications, in consultation with your doctor. Always consult your doctor, follow the drug manufacturer's instructions and the pharmacist's recommendations. To learn more about medications and breastfeeding, read our article on breastfeeding when sick.
- Wear an appropriately sized and comfortable nursing bra, avoid underwire or no bra at all.
- Do not skip feedings or stop breastfeeding abruptly as this may increase breast swelling.
Seek medical attention if your temperature 5 rises above 38 °C or if your baby is unable to suckle due to breast swelling.
And in any case, try to remain calm. Your body is just getting used to producing milk and feeding your baby. Breast swelling should go away on its own soon after you both get comfortable with breastfeeding.
Literature
1 Pang WW, Hartmann PE. Initiation of human lactation: secretory differentiation and secretory activation. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12(4):211-221. - Pang, W.W., Hartmann, P.I., "Lactation initiation in the lactating mother: secretory differentiation and secretory activation." G Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12(4):211-221.
2 Berens P, Brodribb W. ABM Clinical Protocol# 20: Engorgement, Revised 2016. Breastfeed Med . 2016;11(4):159-163. - Behrens P, Brodrhibb W, "AVM Clinical Protocol #20: Engorgement, 2016 edition". Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2016;11(4):159-163.
3 Affronti M Low-grade fever: how to distinguish organic from non-organic forms. Int J Clin Pract. 2010;64(3):316-321. - Affronti M. et al., "Subfebrile temperature: how to distinguish organic from non-organic cases." Int Zh Klin Prakt. 2010;64(3):316-321.
4 Boi B et al. The effectiveness of cabbage leaf application (treatment) on pain and hardness in breast engorgement and its effect on the duration of breastfeeding. JBI Libr Syst Rev . 2012;10(20):1185-1213. - Boys B. et al., "Effectiveness of cabbage leaf (as a drug) for breast pain and engorgement, and its effect on the duration of breastfeeding." JBAi Libr Sist Rev. 2012;10(20):1185-1213.
5 NHS Choices. How do I take someone's temperature? [Internet].