Seven month baby foods
Solids, Food Chart And Recipes
This food chart will help ensure that your baby’s solid food diet meets their needs.
Research-backed
MomJunction believes in providing reliable, research-backed information to you. As per our strong editorial policy requirements, we base our health articles on references (citations) taken from authority sites, international journals, and research studies. However, if you find any incongruencies, feel free to write to us.
Image: Shutterstock
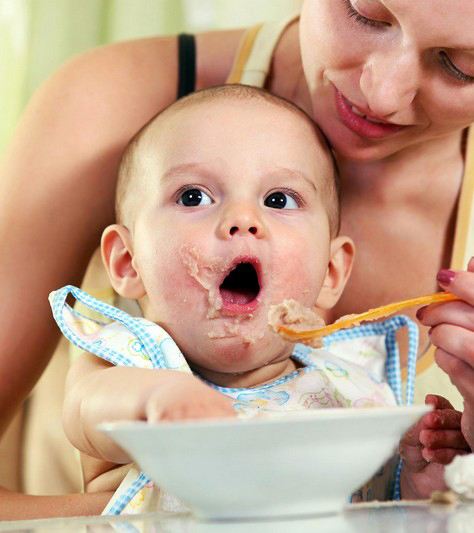
If your baby has been transitioning from breastmilk to solid foods, a 7-month-baby food chart can be a helpful guide. During the first six months of life, babies drink breast milk or formula milk to get their complete nutrition. However, after six months, their needs can increase, and it is time to introduce solid foods.
Keeping the transformation slow and introducing foods one by one is essential. Try offering easily digestible, cooked, and mashed food first, then move toward blends. Keep the quantity small and be cautious about choking hazards.
This post provides detailed information on what to feed your 7-month baby and what quantities. It also provides a food chart with some interesting recipes.
How Much Food Should A 7-Month-Baby Eat?
AAP recommends mothers to continue breastfeeding their baby for at least up to 12 months. At seven months, continue to breastfeed your baby while giving them some solid foods. According to the US Department of Agriculture (USDA), following portions of food from different food groups may be included in your seven months old baby’s diet (1) (2).
| Food group | Portion size (per day) |
|---|---|
| Breast milk or formula milk | 24 to 32 ounces (oz) |
| Grain products | 1 to 2oz |
| Fruits | 2 to 4oz; cooked, plain/strained/pureed/mashed |
| Vegetables | 2 to 4oz; cooked, plain/strained/pureed/mashed |
| Meat and protein-rich foods | 1 to 2oz; Cooked, plain/strained/pureed/mashed |
Food Options For Your Seven Months Old Baby
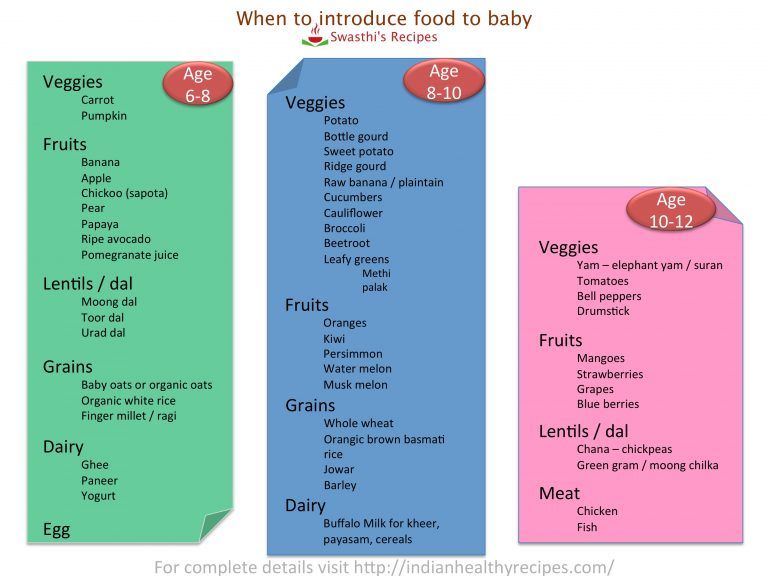
Traditionally, parents start with single-grain cereals (3) or single vegetable and fruit (blended, mashed or soft cooked). When your baby is around seven to nine months old, you may include a variety of foods from different groups (2) (4).
When your baby is around seven to nine months old, you may include a variety of foods from different groups (2) (4).
| Food group | Food items |
|---|---|
| Vegetables | Broccoli, cauliflower, peas, spinach, asparagus, parsnips, peppers, carrots, cabbage, avocado, green beans, kale, and pumpkin |
| Fruits | Banana, apple, mango, blueberries, kiwi, pears, strawberries, papaya, melon, peach, plums, and oranges. |
| Starch-rich foods | Potato, sweet potato, rice, porridge, oatmeal, oats, maize, millet, quinoa, cornmeal, and bread |
| Protein-rich foods | Meat (chicken, lamb, fish without bones), eggs, pulses, lentils, beans, and tofu |
| Dairy | Pasteurized full-fat yogurt without honey, sugar, and artificial sweeteners) Do not serve milk |
Boil and mash hard fruits like apples before serving it to the baby. You may blend fruits and vegetable purees with formula or breast milk. When choosing meat, you can also consider serving meat broth.
When choosing meat, you can also consider serving meat broth.
All foods should be soft to prevent the risk of choking. Make sure the baby eats slowly and in small portions.
Click here to view an enlarged version of this infographic.
10 Homemade Baby Food Recipes For Your Seven Months Old
You can try these simple nutrient-rich homemade recipes to introduce your child to different flavors and textures of food (5).
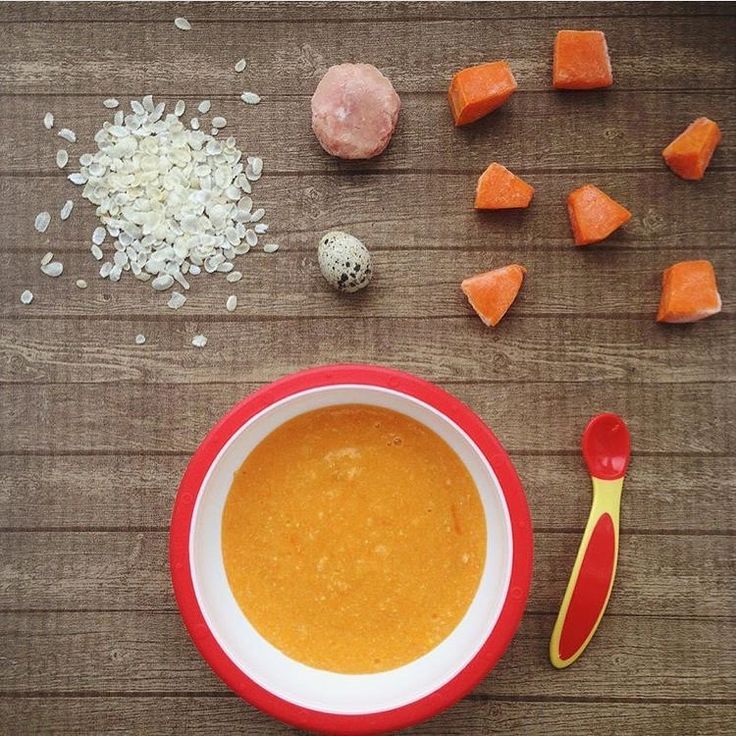
1. Steamed apple and pear puree
Image: Shutterstock
You will need:
- ½ apple, peeled and de-seeded
- ½ pear, peeled
How to:
- Cut the apple and pear into wedges or chunks. Put these pieces in a saucepan with water.
- Bring the water to boil and let it simmer for about 7-8 minutes. Allow it cool.
- You can make a puree and also use them as finger food (if your baby is ready to eat finger food). You can use yogurt as a dressing!
2.
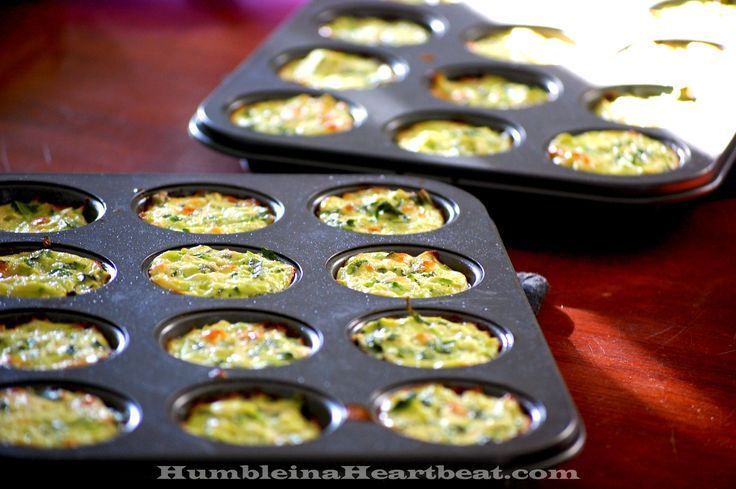
 Eggy omelet fingers
Eggy omelet fingers Image: Shutterstock
You will need:
- 1 small onion, peeled and chopped
- 1 egg
- ½ teaspoon oil
How to:
- Beat the egg. Cut the onion into small pieces and add it to the egg. Whip them together.
- Put oil in a frying pan. Once the pan is hot, add the mixture and let it cook.
- Let the omelet cool. Cut it into thin slices, and serve it to the baby.
3. Hot lentil soup
Image: Shutterstock
You will need:
- Handful of butternut squash peeled
- ¼ onion peeled and chopped
- 30 g red lentils
- ½ tsp oil
- Water
How to:
- De-seed and cut butternut squash into pieces. Finely chop the onions.
- Heat oil in a frying pan. Add all diced vegetables and let them soften.
- Then add water and washed/cleaned lentils to the pan. Bring the water to boil and let it simmer for about 20-25 minutes.

- Check if vegetables and lentils have cooked. Once cooked, let the mixture cool down and blend it before serving.
4. Berry porridge
Image: Shutterstock
You will need:
- 2 tablespoon porridge oats
- ¼ banana
- Frozen blueberries (you can use fresh blueberries too)
- 1 tablespoon yogurt
- Water
How to:
- Add oats and water in a saucepan. Let it cook till the mixture thickens and softens.
- Add small pieces or mashed bananas and blueberries as a topping before serving.
5. Tangy chicken fingers
Image: Shutterstock
You will need:
- Skinless chicken breast
- ½ lemon juice
How to:
- Take skinless chicken breast and slice it into thin medium-sized pieces.
- Preheat your oven to 200°C (about 400°F).
- Place the chicken slices in a tray and squeeze a few drops of lemon juice on them.

- Bake the chicken for 25 minutes. Once baked, you can mince it or give it as finger food.
6. Veggie hotpot
Image: Shutterstock
You will need:
- ½ leek
- ½ carrot, peeled and cut
- 1 potato, peeled and cut
- 1 tablespoon beans, chopped
- 1 small broccoli
- 1 teaspoon oil
- Water
How to:
- Peel and cut carrots and potatoes into small pieces. Cut beans and leeks.
- Take a saucepan with water and add leeks, potato, beans, and carrot. Bring it to boil and let it simmer for 15 to 20 minutes till all vegetables are cooked.
- Once cooked and cooled, blend these vegetables into a puree with pasteurized cream cheese.
- In another pan, cook pieces of broccoli in water for 3-4 minutes. Add these as finger food on top of the puree.
7. Pumpkin and thyme puree
Image: Shutterstock
You will need:
- ½ pumpkin peeled and cut
- Thyme leaves
How to:
- Peel, de-seed, and chop pumpkin into small pieces.
 Place the pieces on a baking tray.
Place the pieces on a baking tray. - Preheat oven to 175°C (about 350°F).
- Place the pumpkin and bake for 30 minutes. Once cooled, add thyme and blend it in a mixer.
8. Broccoli and spinach puree
Image: Shutterstock
You will need:
- 1 medium-sized broccoli, chopped
- 5-6 spinach leaves chopped
- Water
How to:
- Bring water to boil in a pan. Add spinach leaves and broccoli florets. Let it simmer for about 10-15 minutes.
- Once cooled, mash it with a fork or blend it before serving to the baby.
9. Avocado and banana mash
Image: Shutterstock
You will need:
- ½ avocado
- 1 banana, peeled
How to:
- Scoop out avocado and keep it in a pan. Add banana to it and mash.
- You can also add formula or breast milk to the mash and blend it before serving.
10.
 Root vegetables puree
Root vegetables puree Image: Shutterstock
You will need:
- 1 carrot, peeled and chopped
- 1 sweet potato, peeled and chopped
How to:
- Place the sweet potato and carrot pieces into a saucepan with water. Bring it to boil and let it simmer for around 10-15 minutes or till the vegetables are soft.
- Let the veggies cool down and mash it with a fork or blend before serving.
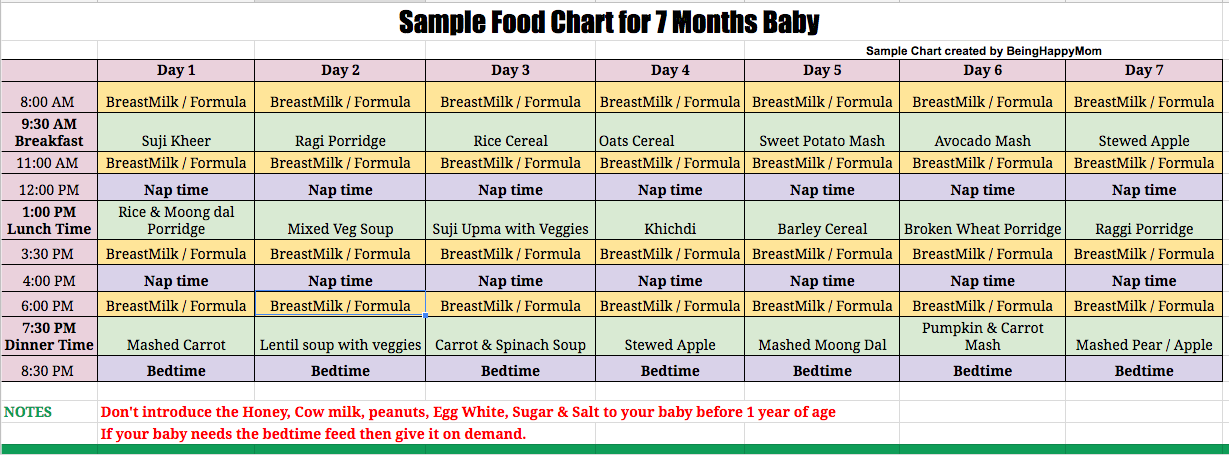
Seven Months Old Baby Food Chart
You may use this sample food chart for your seven months old baby as a reference (6) (7) (8).
| Meal name | Sample meal |
|---|---|
| Breakfast (morning) | Solid food: ● Iron-fortified infant cereal Liquid: ● Breast milk or formula milk |
| Snack (late morning) | Solid food: ● Pureed or mashed fruits such as banana, kiwi, strawberries, cooked apple, cooked pear with full-fat plain yogurt (unsweetened). Liquid: · Breast milk or formula milk |
| Lunch | Solid food: ● Cooked and finely chopped chicken, ● Cooked and mashed vegetables such as pumpkin, sweet potato, spinach, squash, etc. with cooked and mashed rice. Liquid: ● Breast milk or formula milk |
| Snack (evening) | Solid food: ● Cooked and mashed pear ● Cooked and finely chopped carrots or mashed chickpeas. ● Plain yogurt ● Whole-grain cracker Liquid: ● Breast milk or formula milk |
| Dinner | Solid food: ● Cooked and finely chopped green beans or other cooked vegetables. Liquid: ● Breast milk or formula milk |
Start with one or two tablespoons of food and see if your baby shows signs of being hungry or full. Remember, their bellies are small! You can alternate between solid food and liquids, depending on your baby’s hunger cues.
Try including a variety of colorful foods and textures in the baby’s diet.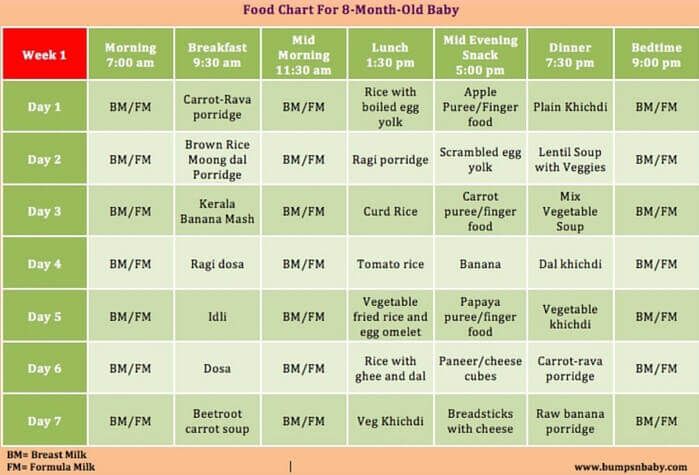 You can also slowly start introducing finger foods by the end of seven months to develop a habit of self-feeding (6).
You can also slowly start introducing finger foods by the end of seven months to develop a habit of self-feeding (6).
Seven Months Old Baby Food Schedule
According to World Health Organization (WHO), complementary foods (food items apart from breast milk) can be given to babies (six to eight months old) up to two to three times per day (9). In addition, the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that you should give your baby something to drink or eat every two to three hours, that is, about five to six times a day (10).
Tips and Precautions For Feeding A Seven Months Old Baby
These are a few points you should consider when feeding your little one (1) (11).
- Introduce one single ingredient at a time. Give the food item for three to five days, during which do not give any other new food. Observe the baby for any sign of an allergy.
- Gradually increase the variety and quantity of food ingredients; start with a teaspoon and then move to a tablespoon.
- You can also try to give finger foods if your baby seems ready. Your baby may start to grasp items with fingers when they are ready for finger foods. Make sure you are present when your baby is eating, to avoid any choking hazards.
- Wash, peel, and remove seeds and pits before giving fruits and vegetables to your baby.
- Use a spoon to feed your baby. Make sure your baby sits in a high chair with a table when feeding.
- Observe and respond to your baby’s hunger cues. Try to develop a predictable routine of all meals and snacks for your baby and limit the time of each meal from 15 to 20 minutes.
- Avoid added salt, sugar, and butter when making baby food at home. In addition, avoid cow’s milk and honey until your baby is at least 12 months old.
How to Know When a Baby Is Ready for Solid Food?
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), the following points could indicate that the baby is ready for solid food (3).
- Has good head control.
- Can sit upright in a high chair or a feeding seat (with no or little support).
- Tries to reach out (leans forward) for solid food.
- Opens mouth and seems eager to eat solid food when offered.
- Their fingers are able to grasp items, this is a sign that they are ready for solid/ finger foods.
According to UNICEF, delaying the introduction of solid foods may affect a baby’s healthy weight gain (12). So, encourage your baby to eat solids as soon as they show signs of readiness. A 7-month-old baby’s food chart can include various healthy foods, such as grains, pulses, meat, fish, poultry, fruits, and vegetables. With continued breastfeeding or formula feeding, babies can consume these foods in well-cooked puree or mash form.
They can also consume age-appropriate finger foods if they show signs of readiness. Feed them nutritious foods and drinks every two to three hours to support their proper growth and development. If the baby eats lesser than usual on some days, refrain from force-feeding. Remember, the main source of nourishment even for a seven-month-old is breast milk or formula. They can have solids but in small quantities, as they need time to adjust to weaning food’s taste, texture, and digestibility.
If the baby eats lesser than usual on some days, refrain from force-feeding. Remember, the main source of nourishment even for a seven-month-old is breast milk or formula. They can have solids but in small quantities, as they need time to adjust to weaning food’s taste, texture, and digestibility.
References:
MomJunction's articles are written after analyzing the research works of expert authors and institutions. Our references consist of resources established by authorities in their respective fields. You can learn more about the authenticity of the information we present in our editorial policy.
1. Guidelines for feeding healthy infants; The United States Department Of Agriculture. (2017)
2. Healthy Eating for 6 to 24 month old children (1) Getting Started; Family Health Service, The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. (2019)
3. Starting Solid Foods; American Academy of Pediatrics. (2018)
4. What to feed your baby; National Health Service, UK
What to feed your baby; National Health Service, UK
5. Recipes and meal ideas; National Health Service, UK
6. Menu planning for babies in childcare; Health Eating and Advisory Service
7. Feeding Your Baby: Sample Meals for Babies 6- 12 Months Old; HealthLinkBC. (2014)
8. Sample Meal Plans for Feeding Your Baby; UnlockFood.Ca. Dietitians of Canada. (2019)
9. What is the recommended food for children in their very early years?; World Health Organization (2011)
10. How much and how often to feed; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2018)
11. Feeding Guide for the First Year; Stanford Children’s Health
12. Feeding your baby: When to start with solid foods; UNICEF Parenting
The following two tabs change content below.
- Reviewer
- Author
Swati Patwal is a clinical nutritionist, a Certified Diabetes Educator (CDE) and a toddler mom with over eight years of experience in diverse fields of nutrition. She started her career as a CSR project coordinator for a healthy eating and active lifestyle project catering to school children. Then she worked as a nutrition faculty and clinical nutrition coach in different... more
She started her career as a CSR project coordinator for a healthy eating and active lifestyle project catering to school children. Then she worked as a nutrition faculty and clinical nutrition coach in different... more
Charmaine Dominguez is a plant-based online dietitian nutritionist. She has her own online nutrition practice. Charmaine is currently living in LA, California in the US, and pursuing Masters of Public Health at California State University, Long Beach. She has completed her Bachelor in Nutrition and Dietetics at California State University, Long Beach. Charmaine is passionate about helping others regain control... more
The Best First Foods for Babies 6 to 9 Months – Happiest Baby
By Happiest Baby Staff
On This Page
- Best Baby Foods at 6 Months
- Best Baby Foods at 7 Months
- Best Baby Foods at 8 Months
- Best Baby Foods at 9 Months
You've spent the first six months of your baby's life making sure that they are nourished with breastmilk or formula. As they grow and thrive, you might notice that your little sprout shows you some signs that they are ready to graduate from the bottle or breast to solid foods. If your baby can sit up and hold their head up, that's a great first sign! What's more, if they bring objects to their mouth and show an interest in what you are eating, your curious kiddo might be ready to start eating solid foods.
As they grow and thrive, you might notice that your little sprout shows you some signs that they are ready to graduate from the bottle or breast to solid foods. If your baby can sit up and hold their head up, that's a great first sign! What's more, if they bring objects to their mouth and show an interest in what you are eating, your curious kiddo might be ready to start eating solid foods.
But what should you feed your baby? Here’s a list of perfect starter foods for your baby from ages 6 to 9 months.
Best Baby Foods at 6 MonthsAt 6 months, babies may be starting to chew. Though this skill won’t be mastered just yet, they are typically ready to get messy with some mushy, pureed eats—helping them learn about flavor and texture. At this age, the goal is not to satiate your baby with full meals of solid foods but rather to get your child curious and excited about their culinary options.
Because babies are growing so fast, their needs for iron are high to prevent iron-deficiency and support their overall health.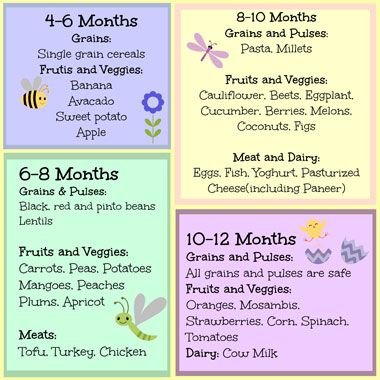 Offer your little one iron rich foods like—infant cereal (read up on why you may want to skip rice cereal), well-cooked meat, poultry, mashed beans, and lentils. To keep your baby safe from choking, avoid adding solids like cereal to baby bottles.
Offer your little one iron rich foods like—infant cereal (read up on why you may want to skip rice cereal), well-cooked meat, poultry, mashed beans, and lentils. To keep your baby safe from choking, avoid adding solids like cereal to baby bottles.
Here are some great first foods for Baby to try:
- Infant oat, grain, or barley cereals mixed with breastmilk or formula and spoon-fed to your baby
- Sweet potato puree
- Squash puree
- Pea puree
- Carrot puree
- Mashed banana
- Mashed avocado
- Mashed or pureed beans
- Mashed or pureed lentils
- Pureed meats (beef, chicken, or turkey)
- Soft, falling apart meats (salmon, beef, chicken, turkey)
Check out more of our favorite first food purees. Or, if purees aren’t your thing, read up on how to start baby-led weaning.
Best Baby Foods at 7 MonthsBy 7 months old, your baby will probably be eating more solids but not enough to replace breastmilk or formula as their primary source of food. The goal for this month is to keep introducing solid foods to your baby. What's fun is by 7 months, you can get more creative with mixing flavors and adding textures.
The goal for this month is to keep introducing solid foods to your baby. What's fun is by 7 months, you can get more creative with mixing flavors and adding textures.
Here are a few nutritious and delicious food combos to try with your baby:
- Peas pureed with breastmilk (or formula), sweet potatoes, or squash
- Kale pureed with blueberry, squash, potatoes, sweet potatoes, peas, pears, or bananas
- Apples pureed with cauliflower, carrots, pears, prunes, or beets
- Beef pureed with broccoli
- Chicken pureed with carrots and potatoes
- Chickpeas pureed with bananas, apples, or sweet potato
- Sweet potatoes pureed with red bell pepper
Seven months is also the perfect age to start giving your baby a plate, bowl, and plastic utensils so they can begin to practice feeding themselves. If your baby is teething, you can place frozen chunks of fruit in a sieve feeder/mesh bag that allows them to gnaw on the fruit without choking. Learn more about helping your baby use a fork and spoon!
Learn more about helping your baby use a fork and spoon!
By 8 months, your baby is likely eating more solids and relying a little less on milk as a primary meal (though it’s still where they get the bulk of their nutrition!). And they’re probably having lots of fun learning how to use their hands to feed themselves. Something else to consider: Babies should be exposed to potential allergen foods (like peanuts, tree nuts, eggs, and fish) before their first birthdays to help prevent future food allergies. Starting at 6 months of age, peanut butter is safe to introduce as long as you are comfortable giving it to your baby.
In fact, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans says that babies can begin having these foods when they start eating solids. But many families often feel more comfortable waiting to introduce these foods until around this age. Of course, consult with your little one’s pediatrician if you have concerns about potential allergen foods.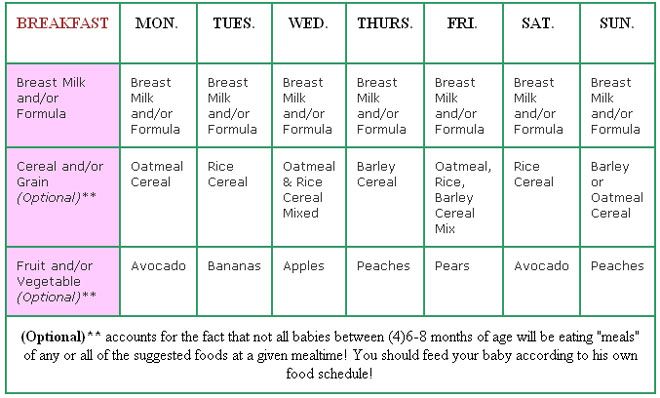
Here are some foods to add to your repertoire:
- Whole eggs, scrambled
- Nut butter thinned out with water and mixed with cereal (nut butters are sticky and can cause choking)
- Fully cooked fish, like salmon or tuna
- Full-fat yogurt
Here are some preparation ideas:
- Well-cooked (think over-cooked until falling apart) pasta such as elbows or alphabet shapes
- Mashed meat with mashed or ground vegetables such as peas and potatoes or kale and squash
- Rainbow on a plate: Using tiny pieces of soft, strained, pureed, and mashed food options, look for a variety of colors to offer. Some fun options could include banana, avocado, sweet potato, peas, blueberry, raspberry, cheese, and chicken.
Though there’s a greater variety of foods babies eat now, formula or breastmilk continues to be their primary source of nutrition until age 1. At 9 months old, babies get more comfortable with self-feeding and eating the foods their families enjoy. After all, eating solid foods is a sensory wonderland of texture, smells, and tastes. Not to mention all that fun making messes with those adorably curious fingers.
After all, eating solid foods is a sensory wonderland of texture, smells, and tastes. Not to mention all that fun making messes with those adorably curious fingers.
As you begin to focus on meal planning for your baby, there are few things to keep in mind:
- Babies need four to five servings of fruits and vegetables a day. A serving size for a 9-month-old is less than a quarter cup.
- "Eat the rainbow" is excellent advice because it gives your baby exposure to lots of different fruits, vegetables, grains, and starches.
Here are a few menu ideas to help meal plan for your baby…
Breakfast Ideas for Babies
These morning meals pack a nutritional punch—and don’t forget to check out all of our favorite breakfast ideas for babies:
- Soft fresh fruit cut up in small pieces (think: banana, raspberries, or blueberries)
- Whole-grain waffles or pancakes
- Unsweetened oatmeal made with breastmilk or formula combined with cut-up and cooked apples and pears or banana slices.
 (It is essential to steam the apples or pears to make them soft enough for your baby to mash with their gums.)
(It is essential to steam the apples or pears to make them soft enough for your baby to mash with their gums.) - Full-fat yogurt mixed with mashed or pureed berries such as blueberries, blackberries, strawberries, or raspberries
- Soft scrambled eggs
- Veggie frittata
Lunch Ideas for Babies
- Spread hummus on soft crackers or bread
- Grilled cheese sandwich with cooled tomato soup
- Macaroni and cheese with cooked veggies like peas and carrots mixed in
- Pizza bites with chopped bits of spinach in the sauce and melted shredded cheese
- Quesadilla made with pureed spinach, squash, or beans
Snack Ideas for Babies
Babies this young won’t likely need to snack too much (remember, breastmilk or formula will provide the majority of your little one’s nutrition). Still, it’s not a bad idea to have snacks on hand for when your mini muncher needs something to eat that’s not quite a meal. A few baby snack ideas:
- Apple and carrot slaw
- Cheese slices
- Full-fat plain yogurt
- Hard-boiled egg
- Avocado slices
- Muffins made with fruits, veggies, and/or whole grains
- Fruit and veggie pouches
- Sugar-free, whole-grain cereal, like plain Cheerios
Dinner Ideas for Babies
To help your baby get and stay excited about eating solid foods, serve a version of whatever the family is having for dinner. Remember to steam or mash, grind or chop foods into appropriate softness and sizes to prevent choking. Some baby dinner ideas:
Remember to steam or mash, grind or chop foods into appropriate softness and sizes to prevent choking. Some baby dinner ideas:
- Pasta with softened vegetables
- Well-cooked rice, soft veggies, and chicken
- Baked sweet potato with butter or cheese
- Beans or lentils served with rice and veggies
- Flaky fish served with steamed zucchini
There are endless variations on what you can serve your baby for dinner. As long as your baby is safe and happy, try to encourage lots of food exploration!
You must not feed any child under the age of 1 year honey, cow’s milk, juice, hard foods like candy, raw vegetables, popcorn, or sticky foods like peanut butter, as these each present choking hazards.
Learn more about feeding your baby:
- The Happiest Baby Feeding Guide
- The Benefits of Homemade Baby Food
- The Best Store-Bought Baby Food
***
REFERENCES
- Unlocking Opportunities in Food Design for Infants, Children, and the Elderly: Understanding Milestones in Chewing and Swallowing Across the Lifespan for New Innovations.
 Journal of Texture Studies, August 2017
Journal of Texture Studies, August 2017 - Complementary Feeding: A Position Paper by the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) Committee on Nutrition, Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, January 2017
- Infant Formula Feeding Practices Associated With Rapid Weight Gain: A Systematic Review, Maternal & Child Nutrition, July 2018
- Solid Food Introduction and the Development of Food Allergies, Nutrients, November 2018
- US Department of Agriculture: Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020-2025
View more posts tagged, feeding
Have questions about a Happiest Baby product? Our consultants would be happy to help! Connect with us at [email protected].
Disclaimer: The information on our site is NOT medical advice for any specific person or condition. It is only meant as general information. If you have any medical questions and concerns about your child or yourself, please contact your health provider.
It is only meant as general information. If you have any medical questions and concerns about your child or yourself, please contact your health provider.
Assignment of a monthly allowance for the purchase of children's assortment of goods and baby food
State service for the appointment of a monthly allowance for the purchase of children's assortment of goods and baby food
- Brief description of the service
Applicants who have the right to apply for the service are individuals from among one of the parents, guardians (custodians), who is a citizen of the Russian Federation, or a foreign citizen, or a stateless person living in the territory of the Leningrad Region together with a child until he reaches the age of 16 years, and if the child is studying in a general education organization, then until graduation, but no more than until he reaches the age of 18 years.
- To whom the service is provided
Individuals
- List of required documents
- Application for the provision of public services
Group 9 Documents0009
- State service application
- Consent to the processing of personal data
Group documents
- Consent to the processing of personal data
- Consent for the issuance of a case in Postamat
Documents of the group
- Consent for the issuance of the case in Postamat
- Documents proving the identity of the applicant, the representative of the applicant, a child who has reached the age of 14, the second parent
Documents of the group
- Certificate of a citizen subject to conscription for military service
- Temporary certificate issued in exchange for the military card of a reserve officer
- Temporary certificate issued in place of the military card of a soldier, sailor, sergeant, foreman, ensign, warrant officer Military officer
reserve
- Application for the provision of public services
- Military ID of a soldier, sailor, sergeant, foreman, warrant officer, midshipman
- Identity card of a serviceman of the Russian Federation
- Passport of a citizen of the USSR, model 1974
- Temporary identity card of a citizen of the Russian Federation in the form No.
 2-P
2-P - Passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation
Group documents
- Temporary residence permit
- Refugee certificate
- Residence permit
Documents of the group
- Documents on residence of family members
Documents of the group
- Individual rehabilitation program for a disabled person
- Certificate of disability
- Death certificate of the child
- Birth certificate of the child
- Certificate of paternity
- Marriage certificate
- Divorce certificate
- Proof of income
Documents of the group
- Birth certificate of a child issued by a consular office of the Russian Federation outside the territory of the Russian Federation Federation order translation into Russian
- Document confirming the birth and registration of a child, issued by the competent authority of a foreign state, translated into Russian and legalized by a consular office of the Russian Federation outside the territory of the Russian Federation
- Document confirming the birth and registration of a child, issued by the competent authority of a foreign state, translated into Russian and sealed with official seal
Group documents
- Certificates from the main place of work and from all places of additional work on income that is not subject to inclusion in the Form of information on income of individuals and amounts of tax on income of individuals "Certificate on income and amounts of tax on an individual" (Form 2 - personal income tax)
- Certificates of the amount of scholarships or compensation payments during the student's academic leave cannot find a job due to the lack of employment opportunities in their specialty and were recognized as unemployed in accordance with the established procedure, as well as during the period when the spouses of military personnel are forced not to work due to the health of their children, related to the living conditions at the place of military service of the spouse, if, according to the conclusion of a medical organization their children before reaching 18 years of age in need of care
- Certificates of the amount of monthly compensation payment to non-working wives of private and commanding officers of the internal affairs bodies of the Russian Federation and institutions of the penal system in remote garrisons and areas where there is no possibility of their employment
- Certificates of the amount of alimony received or an agreement on the payment of alimony child
- Certificates of monetary allowance for military personnel, employees of the internal affairs bodies of the Russian Federation, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system, customs authorities of the Russian Federation, other law enforcement agencies, as well as additional payments of a permanent nature, and food security established by the legislation of the Russian Federation Federation
- Certificates of a one-time allowance upon dismissal from military service, from the internal affairs bodies of the Russian Federation, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system, customs authorities of the Russian Federation, other law enforcement agencies (KDN 1122036)
- Certificate of registration (deregistration) of an individual as a taxpayer of professional income tax (KDN 1122035)
- Copies of tax declaration certified by tax authorities if the object of taxation is income not reduced by the amount of expenses)
Documents of the group
- Information about work activity
- Employment book
Group documents
- Certificate of the applicant (legal representative) caring for a child (children) living with him at the age of three years, registered for a place in a municipal educational organization in the Leningrad Region, implementing an educational program of preschool education, and who was not issued a referral to a municipal educational organization implementing an educational program of preschool education due to lack of places
- Conclusion (certificate) of a medical organization on the need of the spouse (wife), parents (parent), child (children) of the applicant (parents, children of the spouse (wife) of the applicant) in outside care or a certificate from the territorial body of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation on receipt by the spouse ( spouse) compensation payment as a person caring for a disabled citizen
- Certificate from a medical organization on registration for pregnancy and gestational age of at least 12 weeks upon registration
- Document (certificate) confirming being on outpatient or inpatient treatment (for the period of such treatment) (for non-working citizens) before entering the first grade of a general education organization) or about the presence of a disease in a child that prevents attendance at a general education organization
Documents of the group
- Certificate of study of a child (children) over 16 years old in a general education organization
Documents of the group
- Resolution of the body of guardianship and guardianship on the establishment of guardianship or guardianship
Group documents
- Court decision (extract from court decision)
- Agreement between parents
Documents of the group
- Certificate from the civil registry office on the basis for entering information about the father of the child in the birth certificate
Documents of the group
- Power of attorney in a simple written form
- Power of attorney in a simple written form for a social worker providing social services to the principal
- Power of attorney certified by a notary
- Power of attorney certified by the head and a specially authorized official of the LSG .
 6 by a person of the consular institution of the Russian Federation authorized to perform these actions
6 by a person of the consular institution of the Russian Federation authorized to perform these actions Group documents
- TIN
Group documents
- SNILS
Group documents
- Other document
- Federal Law No. 210-FZ dated July 27, 2010 On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services (as amended on December 30, 2020) dated November 24, 2020)
- Decree No. 250 dated March 18, 2015 On approval of the requirements for the preparation and issuance of paper documents to applicants confirming the content of electronic documents sent to the multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services based on the results of the provision of state and municipal services by authorities providing public services and bodies providing municipal services, and for issuance to applicants based on information from the information systems of bodies providing public services and bodies providing municipal services, including using information ion-technological and communication infrastructure, documents, including compilation on paper and certification of extracts from these information systems (ed.
 from 05.05.2016)
from 05.05.2016) - Decree No. 228 dated 05/20/2019 On approval of the list of standard compositions of interconnected public services provided by the executive authorities of the Leningrad Region upon a comprehensive request, and the procedure for organizing the provision of interconnected state and (or) municipal services upon a complex request in multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services of the Leningrad Region
- Decree No. 36 dated 01/30/2020 On approval of the procedure for electronic document management between the State Budgetary Institution of the Leningrad Region "Multifunctional Center for the Provision of State and Municipal Services", executive authorities of the Leningrad Region and organizations involved in the provision of public services (as amended by 04/13/2020)
- Decree No. 122 dated 04/22/2015 On approval of the List of public services provided on the basis of multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services of the Leningrad Region, including the list of public services that are not provided through a comprehensive request, and on the invalidation of certain resolutions of the Government of the Leningrad Region region (as amended on 07/03/2020)
- Order No.
 5 of 01/31/2020 On approval of administrative regulations for the provision of public services in the field of social protection of the population in the Leningrad region (as amended on 05/31/2021)
5 of 01/31/2020 On approval of administrative regulations for the provision of public services in the field of social protection of the population in the Leningrad region (as amended on 05/31/2021)
- Term for processing documents working days in the OGV: 12
- Term for the transfer of documents working days from the MFC to the OGV: 1
- Term for the transfer of documents working days from the OGV to the MFC : 1
The service is free.
- issuance of an order on the appointment of a public service;
- issuance of an order to refuse to appoint a public service.
- Submission by the applicant of documents that do not meet the requirements of the Administrative Regulations
- No right for the applicant to receive a public service
- Submission of an incomplete set of documents
- Repeated application for a public service during its provision
- Violation of the deadline for submitting an application and documents
- Absence (improper execution) of a document confirming the authority of the applicant's representative
State (Regional)
- Territorial branch of the State Institution of Public Institution "Center for Social Protection of the Population" of the Leningrad Region
where and how to get what they give in the dairy kitchen in Moscow and the regions
Yulia Shubina
refused dairy cuisine
Author profile
In Russia, expectant mothers and families with children can receive free food.
Each subject has its own rules. I received kits at a dairy kitchen in Moscow - I'll tell you who usually gets help and how to get it in different regions.
What is a dairy kitchen
The forerunners of the dairy kitchen were centers called "A Drop of Milk" where they gave out food for premature babies. They appeared in the Russian Empire in 1901.
Dairy cuisine - Big Medical Encyclopedia
There are more such organizations in the USSR. Dairy kitchens helped save the lives of many children during the Second World War: then they began to offer additional food, including to full-term babies. They continued to do so after the war.
Today there is no concept of "dairy cuisine" in Russian legislation. But there is a guarantee: according to the doctor, children under three years old, pregnant and lactating women must be provided with food. What to give and to what extent - the leadership of each region decides independently.
Art. 52 of the law "On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation"
How to get free food in Moscow
Only people with a Moscow residence permit can use dairy cuisine in Moscow.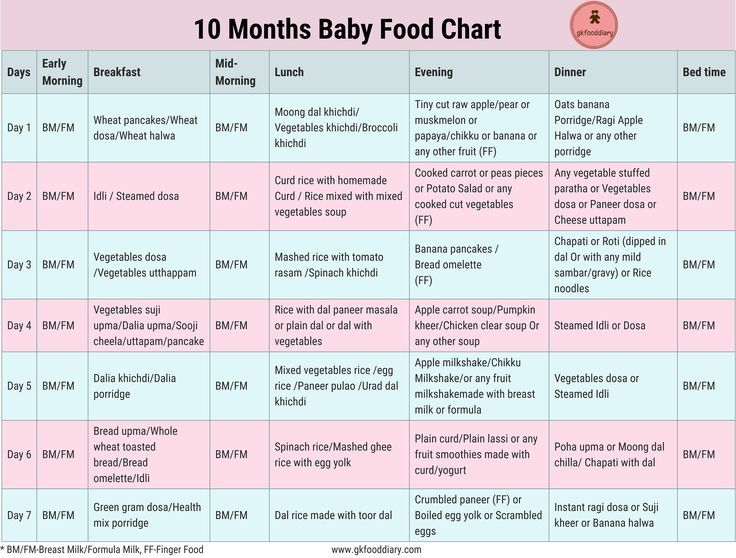 Here are the people who will receive food:
Here are the people who will receive food:
- pregnant and lactating women;
- mixed or formula-fed children under 6 months of age;
- children from 6 months to 3 years;
- children under 7 from large families;
- children under 15 with chronic diseases: glomerulonephritis, hemoblastosis, malignant neoplasms;
- disabled children under 18 years of age.
Regulation on the provision of free food for certain categories of children and women who are residents of the city of Moscow
But you can’t just go to the dairy kitchen for food: first you need to get a prescription from a doctor. For this, pregnant women need to contact the antenatal clinic, in all other cases, the prescription will be issued at the children's clinic where the child is assigned.
To confirm the right to receive products, the antenatal clinic or polyclinic will ask you to submit documents. They will need to be brought only once, after which all the necessary information will already be in the system.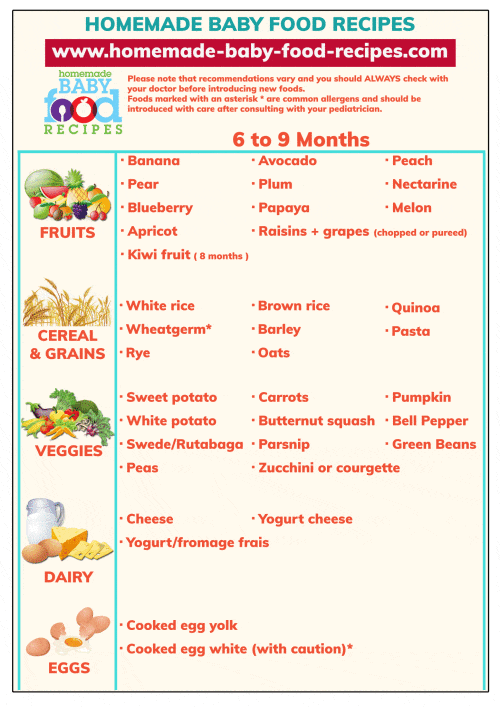 Here's what you need:
Here's what you need:
- Pregnant woman's passport or child's birth certificate together with the passport of either parent.
- MHI policy for a pregnant woman or child.
- Certificate of registration of a child in Moscow (form 8), pregnant women will need to show the registration page in their passport instead.
- If the child is under guardianship, you will additionally need a document confirming the establishment of guardianship.
- If the child is older than 3 years, you will need to confirm his benefits: a certificate of a large family, a certificate from a medical and social examination, or a medical certificate confirming the presence of a chronic disease will do.
They will also ask you to fill out an application for receiving products: a ready-made form will be provided at the clinic, you only need to sign it.
/kids-rule-everything-around-me/
Benefits for families with many children in Moscow until the 10th day of the month.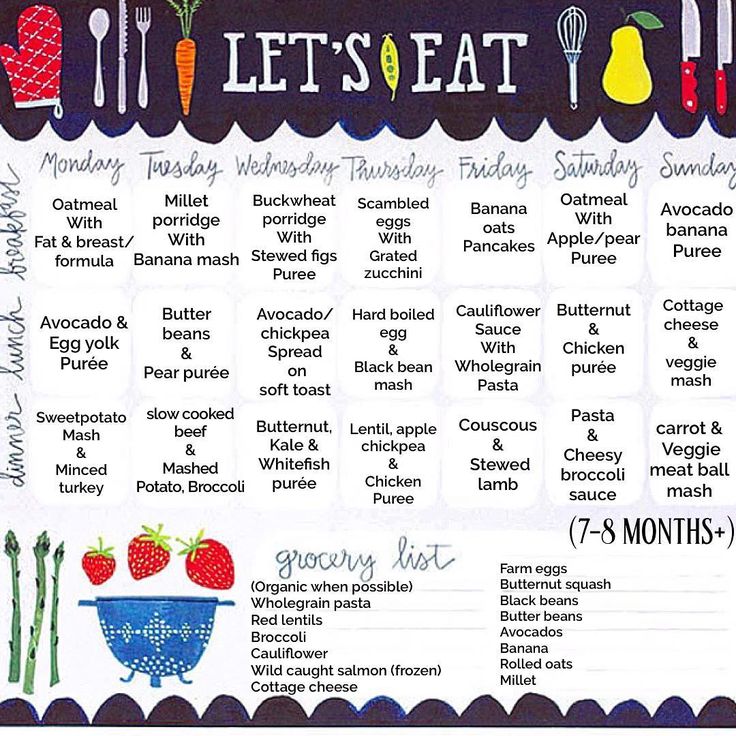 It was tiresome.
It was tiresome.
Now everything has changed: a doctor issues a benefit once through the EMIAS system and information about it is automatically transferred to the dairy kitchen until it expires. For example, this happens when a pregnant woman gives birth to a child or he reaches the age of three. Now you can go to the dairy kitchen right away, without wasting time getting a prescription from a doctor and without worrying about what date is on the calendar.
Where to go with a prescription
Each clinic has its own dairy kitchen - food packages will need to be received there. Sometimes several points are assigned to one clinic - then parents are offered to choose. You can find out what milk distribution points are in your area using the map on the Gormedtekhnika portal.
Those who come to buy food for the first time are assigned a number by the dairy kitchen staff. It must be remembered and called every time to get a set. Nothing critical will happen if the parents forget the number and instead ask to find a set by the child's last name, but it is more convenient for the kitchen staff to work with him.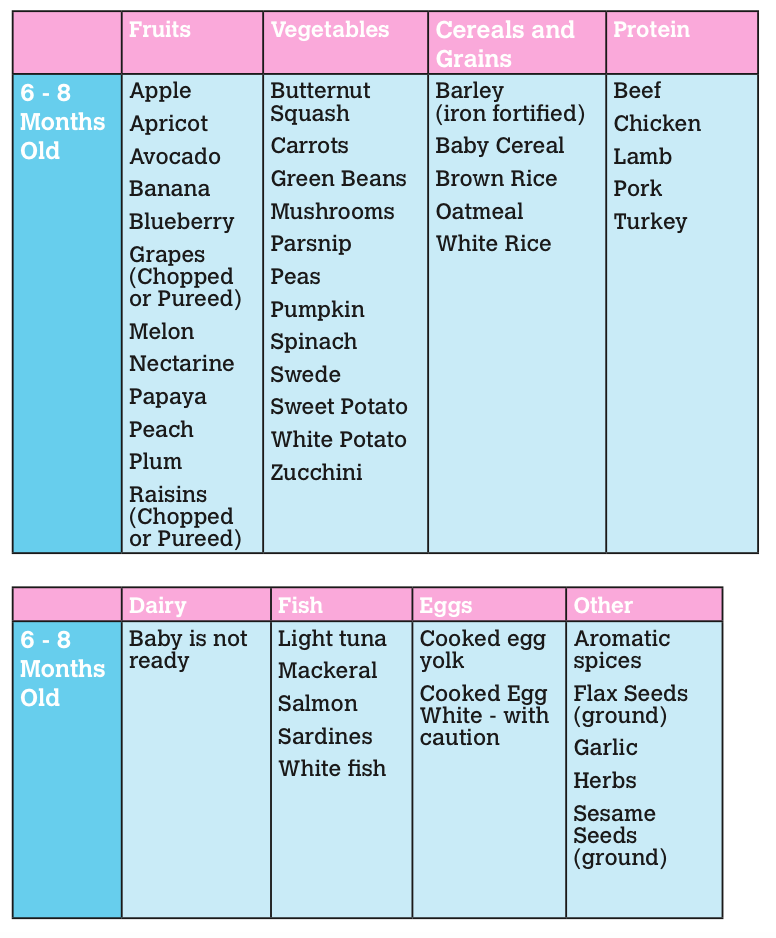
Normally, dairy kitchens distribute visitors by day of the week. In some kitchens, employees ask parents when it is more convenient for them to come for kits, while in others they appoint themselves: for example, they give out kits for pregnant women on Mondays, and for children under six months on Wednesdays. This rule is also not strict: if you miss the right day, you can safely come for a set on another.
/baby-cost/
How much does a child cost in the first year? We did not encounter this: even at the end of the month, my husband easily received a full set of products for 30 days.
Dairy kitchens in the capital are open from 06:30 to 15:00 from Monday to Saturday. From 12:30 to 13:00 - lunch break.
To get food, you will need to show your passport or other identification document - the husband usually shows the rights. According to the rules, dairy kitchens give out food packages only to parents, and if you need someone else to receive them, you need to issue a power of attorney. In reality, you can agree with the employees: sometimes my brother got the dairy kitchen and no one asked for additional papers - I think the point is that we have the same last name with him.
In reality, you can agree with the employees: sometimes my brother got the dairy kitchen and no one asked for additional papers - I think the point is that we have the same last name with him.
Before you go to the dairy kitchen, think about how you will collect food. We had to take a taxi, and other parents came with hiking backpacks: a set for a child of 6-12 months for 30 days weighs about 10 kg.
What foods are given in Moscow? Mothers are given juice and milk, and babies are given supplementary or complementary foods, depending on their age. These can be mixtures, canned purees, instant cereals and similar juices and milk, as for mothers.
Regulation on the provision of free food for certain categories of children and women who are residents of the city of MoscowPDF, 653 KB
| To whom they give | What is | How much per month |
|---|---|---|
| Formula-fed infants 0-3 months | Powdered and liquid milk formulas | 5. 5 kg 5 kg |
| Formula-fed babies 4 months old | Powdered and liquid milk formulas, fruit juice, fruit puree | 7.9 kg |
| Formula-fed babies 5 months old | Powdered and liquid milk formulas, fruit juice, vegetable puree, dry porridge, fruit puree | 9.8 kg |
| Children 6 months on any type of feeding | Dry and liquid mixtures, fruit juice, dry porridge, vegetable puree, fruit puree | 7.3 kg |
| Children 7-8 months | Dry and liquid mixtures, children's cottage cheese, fruit juice, dry porridge, vegetable puree, fruit puree, meat puree with vegetables, meat puree | 9.9 kg |
| Children 9-12 months | Dry and liquid mixtures, children's cottage cheese, kefir, fruit juice, dry porridge, vegetable puree, fruit puree, meat puree with vegetables, meat puree | 12.3 kg |
| Children 1-2 years old | Milk, kefir, cottage cheese, fruit puree, fruit juice | 9. 8 kg 8 kg |
| Children 2-3 years old | Milk, kefir, cottage cheese, fruit puree, fruit juice | 8.4 kg |
| Pregnant | Fruit juice, milk | 12.9L |
| Nursing | Milk, fruit juice | 16.2 L |
| Children from large families, disabled children | Milk | 18 l |
Children 0-3 months on artificial feeding
What
dry and liquid milk mixtures
volume
5.5 kg
Children 4 months on artificial feeding and liquid milk formulas, fruit juice, fruit puree
Volume per month
7.9 kg
Children 5 months on artificial feeding
, fruit puree
volume for a month
9,0008 kg
Children 6 months old on any type of feeding
that
Dry and liquid mixtures, fruit juice, vegetable porridge, fruit puree
,volume
,0008 7.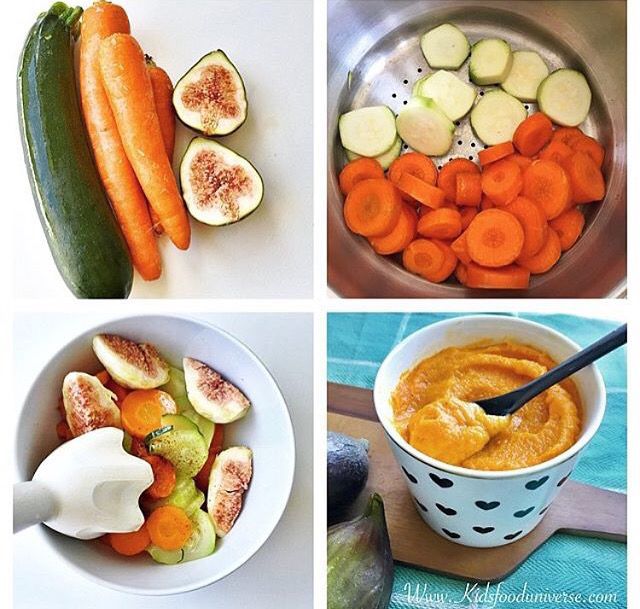 3 kg
3 kg
Children 7-8 months old
What
Dry and liquid mixtures, baby cottage cheese, fruit juice, dry porridge, vegetable puree, fruit puree, meat puree with vegetables, meat puree
909.9 kg
Children 9-12 months old
What
Dry and liquid mixtures, children’s cottage cheese, kefir, fruit juice, dry porridge, vegetable puree, fruit puree, meat puree with vegetables, 0
- Pregnant women - 400 R.
- Nursing mothers - 1000 R.
- Children from 0 to 1 year old on artificial or mixed feeding - 1000 to years old Children from years old on artificial or mixed feeding - 600 R.
volume for a month
12.3 kg
Children 1-2 years old
What
Milk, kefir, cottage cheese, fruit puree, fruit juice
,000 2-3 yearsWhat
Milk, kefir, cottage cheese, fruit puree, fruit juice
,0009Mounting
What
Milk, Fruit juice
volume
16.2 l
Children from large families, disabled children
volume volume
18L
Free food for 11 months baby for 30 daysMy experience with dairy food
I started getting free food when I was pregnant.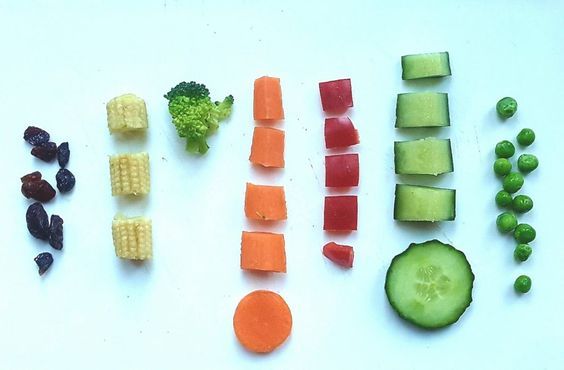 I was observed at the antenatal clinic by registration, so I was given a prescription for the nearest dairy kitchen. But due to the fact that I live in a different area, getting groceries was inconvenient. They found a way out quickly: my younger brother began to call for boxes. The products remained with him: I didn’t really need them.
I was observed at the antenatal clinic by registration, so I was given a prescription for the nearest dairy kitchen. But due to the fact that I live in a different area, getting groceries was inconvenient. They found a way out quickly: my younger brother began to call for boxes. The products remained with him: I didn’t really need them.
When our daughter was born, we assigned her to a polyclinic in our place of residence. They began to receive recipes for a dairy kitchen near the house. As a nursing mother, I was given juice and milk. I did not plan to take these products, but my brother liked them. Therefore, we used the recipe.
/guide/prikorm-detyam/
How to introduce complementary foods to children
Later, I learned that in the first six months we were also given a dairy kitchen for our daughter: she was mixed-fed. But for some reason, the pediatrician did not report this. True, this fact did not upset me much: I fed my daughter with Nutrilon Comfort, they are not given out in sets. And we would not change the mixture just to get it for free: for a baby, this is fraught with digestive problems.
And we would not change the mixture just to get it for free: for a baby, this is fraught with digestive problems.
What kind of purees, juices and mixtures did they give us
From the age of 5 months, on the recommendation of the pediatrician, we began to introduce complementary foods on our own. I read the advice of pediatricians on Instagram and decided, at least at first, to follow the composition of baby food. I didn’t want fanaticism in food, but mashed potatoes without unnecessary components were important to me. Therefore, in the first month of complementary foods, I carefully chose jars of mashed potatoes, which we bought with our own money.
From 6 months we began to receive dairy products. I was pleasantly surprised: there was nothing superfluous in the compositions. Therefore, for six months we actively used the food that was given to us. Monthly managed to save 1000-2000 R.
up to 2000 R
we saved on baby food
The variety of canned purees in the dairy kitchen made me happy. First, they gave the classic trio of vegetables that are recommended to start complementary foods with: broccoli, cauliflower and zucchini from Agushi. True, I didn’t really like the Agusha zucchini: it was too liquid and it was inconvenient to feed a child with it. Later, carrots and pumpkins of the same brand were added - with excellent composition and consistency.
First, they gave the classic trio of vegetables that are recommended to start complementary foods with: broccoli, cauliflower and zucchini from Agushi. True, I didn’t really like the Agusha zucchini: it was too liquid and it was inconvenient to feed a child with it. Later, carrots and pumpkins of the same brand were added - with excellent composition and consistency.
Meat puree was also varied: the sets included poultry, beef, and veal. From 9months, jars of “chicken and vegetables” and “beef and vegetables” began to be issued. My daughter still eats this, despite the fact that she mostly prefers a common table. By the way, for some reason, there were no fish in the set from the dairy kitchen, although the pediatrician's memo said that fish should be introduced from 10-11 months.
Meat puree from the dairy kitchen had a good composition. True, the smell was not very appetizing, but my daughter ate with pleasure Fruit puree was also given out by Agusha. The compositions were good, the tastes were different: we came across an apple, a pear, a peach. When my daughter got older, they began to give puree from several fruits and berries, for example, "apple, cherry, blueberry."
When my daughter got older, they began to give puree from several fruits and berries, for example, "apple, cherry, blueberry."
In addition, the set contained a mixture of two types: dry and liquid. We refused the liquid mixture: my daughter ate another, and in the kitchen they gave the same Agusha. The liquid mixture was packed in a separate box, so the husband immediately said: “We don’t take this.” We gave Nestogen dry mix to friends.
/list/fake-healthy-foods/
Corn flakes and "children's menu": what not to feed a child
My daughter fell in love with Agusha cottage cheese: she liked trying to eat from plastic packaging on her own.
What I didn't like about the dairy kitchen
First of all, the composition of some of the products that were given out on a monthly basis was contrary to the recommendations for complementary foods.
National program for optimizing the feeding of infants in the first year of life in the Russian Federation - methodological recommendations of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia, p. 45PDF, 4.45 MB
45PDF, 4.45 MB
Moreover, the recommendations were issued by a pediatrician in the very clinic where they wrote out a prescription for a dairy kitchen. The documents indicated that the products were issued in accordance with the age marking of the manufacturer, but in our case this did not always coincide with reality.
For example, milk porridges were not recommended until 9 months of age. In fact, we began to receive instant cereals with powdered milk from 7 months. Even the pediatrician did not advise giving fruit juice until a year old. And we began to receive it from 6 months - as a result, adults drank the juice from us.
Feeding and nutrition of infants and young children - guidelines for the WHO European RegionPDF, 1.28 MB0009
Secondly, cereals included fructose and milk powder. Rospotrebnadzor does not recommend introducing sugar up to a year. And WHO recommends to refrain from cow's milk in favor of breast milk, as cow's milk is too rich in protein and sodium.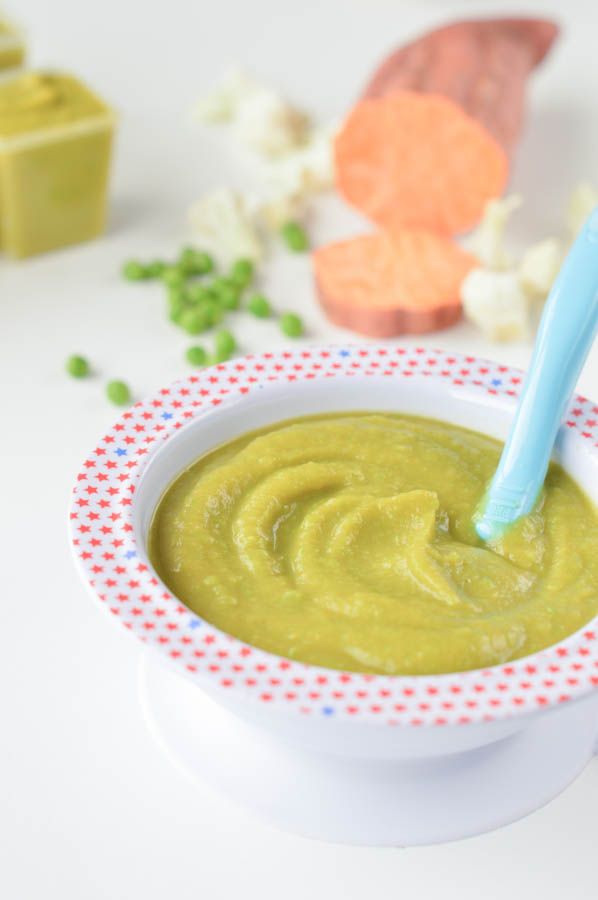
Thirdly, did not contain mashed potatoes with chunks in the packages. This was a little depressing: it is recommended to start introducing pieces from 9-10 months.
But in the end, I understand that mashing food with a fork is much easier than making a full-fledged puree on your own. In addition, I know that in other regions the level of support for the authorities is significantly lower compared to Moscow. So I was grateful for what I have.
Why we ended up dropping free products
This happened for two reasons at the same time. The first - by the year my daughter switched to a common table. The second - a set of products for children from the age of one did not suit her.
For example, I try to give cow's milk and juices as a treat, the rest of the time she drinks water. My daughter prefers grained cottage cheese and ordinary cereals to dry cereals and children's creamy cottage cheese: she likes to eat them with her hands or with a spoon. I never add sugar to buckwheat or rice - purchased cereals cannot boast of this.
I never add sugar to buckwheat or rice - purchased cereals cannot boast of this.
The only thing that could really be useful to us from the set for children from one year old is Agusha kefir, it has a good composition. But they give a lot of it, and the shelf life is short. On the one hand, this is good: it means that there are no preservatives in kefir, with which ultra-pasteurized milk is stored for months. But on the other hand, we had to drink kefir with the whole family until it got spoiled.
/farm-products/
I feed my family with farm products and save money
In addition, it was simply unprofitable to force my husband to go to the dairy kitchen for one yogurt.
How are things going with free meals in the regions
Each region independently determines what products, to whom and in what quantities to provide. In some regions, payments are assigned instead of products.
You can usually find out if there is a dairy kitchen in the region and who is eligible for it, usually at the children's clinic or social security departments. I will tell you about how things are in several large regions.
I will tell you about how things are in several large regions.
Moscow region. Dairy cuisine has been canceled in the Moscow region. You can get money instead. The amount of the monthly cash payment in 2022:
Decree of the Government of the Moscow Region dated November 26, 2019No. 868/41
If a woman has several children, she will receive payments for pregnant and lactating women in a single amount. If there are several children and they are formula fed, then a monthly cash payment is provided for each child.
Appointment of a monthly cash payment for food - the portal of public services of the Moscow region
St. Petersburg. In St. Petersburg there is neither a dairy kitchen nor compensation. But there is a "children's" card - it receives regional payments and benefits: for example, a one-time compensation payment for the birth of a child or a monthly allowance for a child up to one and a half years. You can only spend money on baby products in certain stores, including baby food.
But there is a "children's" card - it receives regional payments and benefits: for example, a one-time compensation payment for the birth of a child or a monthly allowance for a child up to one and a half years. You can only spend money on baby products in certain stores, including baby food.
Rules for using a "children's" card - St. Petersburg public services portal
You can order a card along with a one-time payment at the birth of a child. This is done online on the public services website or through the MFC. The card will be ready within three months, the service is free. You will need a passport to get it.
Nizhny Novgorod. Dairy products are distributed only to low-income families until the child is 2 years old. In order to receive food for children under one year old, the average per capita income of a family should not exceed two living wages, and if the child is from one to two years old, the average per capita income must be less than one living wage.
Regulations on the procedure for providing adequate nutrition for children under the age of 3 through special nutrition points (dairy kitchens) on the opinion of doctors in the city district of Nizhny Novgorod
What products are distributed in Nizhny Novgorod
| What is | How much per month | |
|---|---|---|
| Children under 5 months | Dry mix | 3.5 kg |
| Children 6-7 months | Dry milk porridge, dry mix, cottage cheese. By prescription, kefir | is issued4.13 kg + 12 liters of kefir |
| Children 8-12 months, depending on doctor's prescription | Dry milk porridge, dry mix, cottage cheese | 6 kg + 12 l kefir |
| Children 1-2 years old | Dry milk porridge, cottage cheese | 2 kg + 13.2 l kefir |
| Children 2-3 years old | Dry milk porridge, cottage cheese | 1.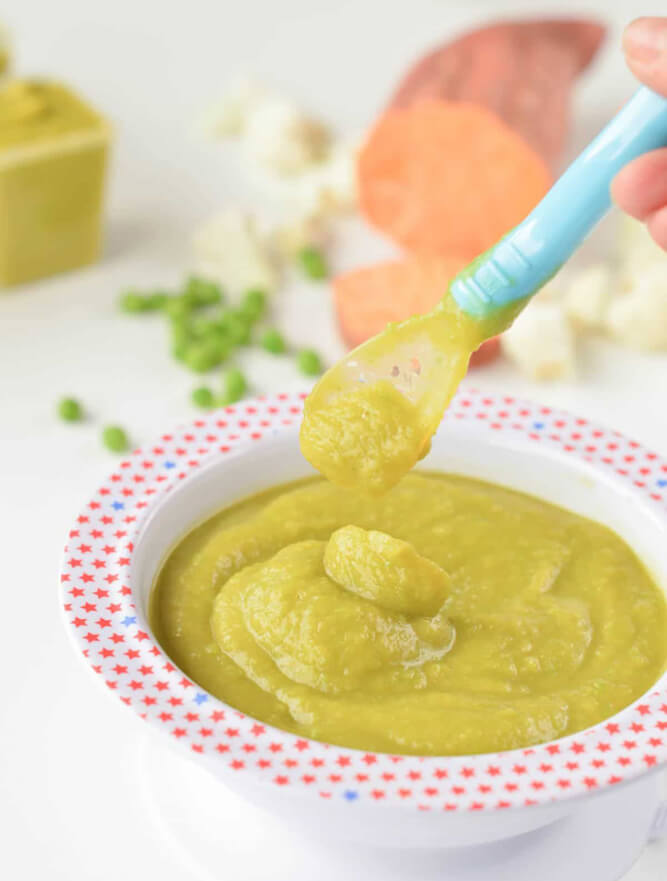 9 kg + 13.2 l kefir 9 kg + 13.2 l kefir |
Children up to 5 months
What
Dry mixture
volume
3.5 kg
Children 6–7 months
. Kefir is dispensed as prescribed by a doctorVolume per month
4.13 kg + 12 liters of kefir
Children 8-12 months old, depending on the doctor’s prescription
that
Dry milk porridge, dry mix, cottage cheese
volume
6 kg+ 12 l kefira
Children 1-2 years old
9000 month2 kg+ 13.2 l kefira
children 2-3 years old
What
Dry milk porridge, cottage cheese
volume
1.9 kg+ 13.2 l kefira
Kaluga region. Children of the first year of life on artificial and mixed feeding receive free meals. For children from 2 to 3 years old, the poor are paid compensation - up to 500 R. Explanations on the provision of adequate nutrition for children of the first year of life who are artificially and mixed-fed - the official portal of the authorities of the Kaluga region can apply if the income per family member does not exceed the regional subsistence minimum by more than 1,000 rubles.
What products are distributed in the Kaluga region
| To whom they give | What is | To what extent |
|---|---|---|
| Children up to 6 months | Dry mix | It is not known exactly, at the rate of 900 R per month per child |
| Children 6-12 months | Dry mix, dry porridge | It is not known exactly, at the rate of 900 R per month per child |
Babies under 6 months
What
Dry mixture
FILLOSE for a month
is not known exactly, at the rate of 900 r per month per child
children 6-12 months
What
Dry mix, dry porridge
,000 , at the rate of 900 R per month per child In Bashkiria. Products are provided to orphans, as well as children, lactating and pregnant women from low-income families. You can get a dairy kitchen if the family income per person does not exceed 10,015 R.
Dairy cuisine of the Republic of Bashkiria
Provision of specialized food for pregnant women and nursing mothers - Republican Center for Social Support of the Population
What products are distributed in Bashkiria
| What is | How much per month | |
|---|---|---|
| Pregnant | Pregnancy Powder | 2 kg |
| Lactating | Dry formula for nursing | 1 kg |
| Children up to 6 months | Powdered formula or specialty formula for medical reasons | 0.75 kg |
| Children 6-8 months | Dry or specialized formula for medical indications, dry porridge, cottage cheese | 2 kg |
| Children 8-12 months | Dry or specialized mixture for medical indications, dry porridge, milk, kefir, cottage cheese | 2 kg + 6.5 l milk and kefir |
| Children 1-2 years old | Dry porridge, cottage cheese, milk, kefir | 2 kg + 16.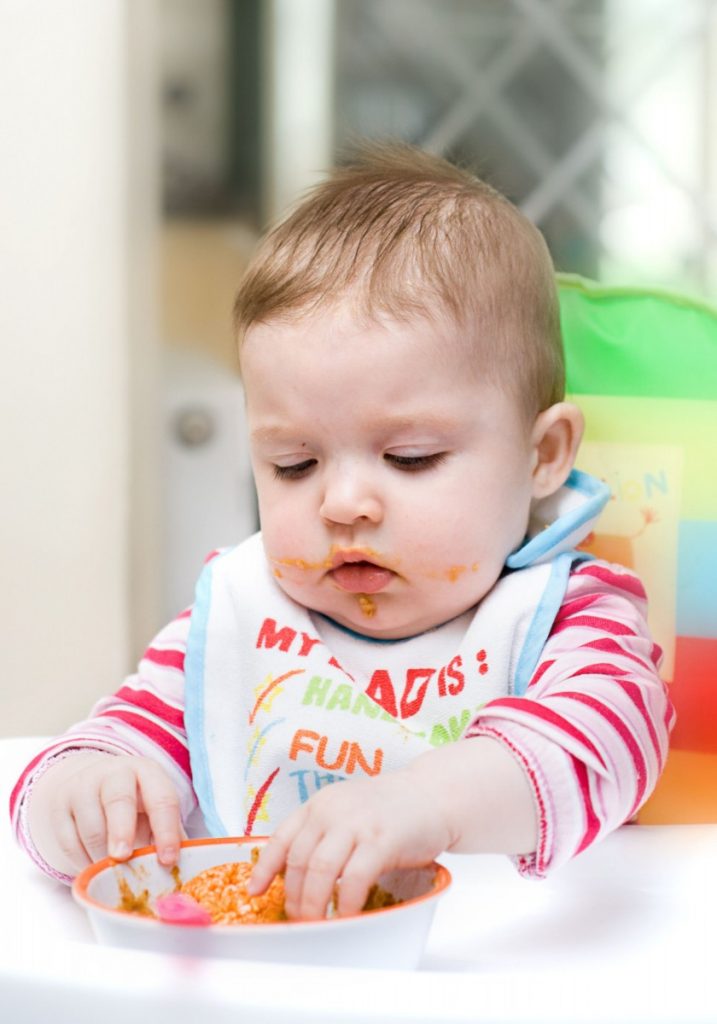 4 l milk and kefir 4 l milk and kefir |
| Children 2-3 years old | Curd, milk, kefir | 1.1 kg + 16.6 liters of milk and kefir |
Pregnant
What
Pregnancy powder
Monthly volume
2 kg
Nursing
that
Dry mixture for feeders
volume
1 kg
Children up to 6 months
that
Dry mix or specialized mixture for medical reasons
volume
0.75 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.75 kg
Children 6-8 months
What
Dry or specialized formula for medical indications, dry porridge, cottage cheese
Monthly volume
2 kg
Children 8-12 months
that
Dry or specialized mixture for medical reasons, porridge dry, milk, kefir, cottage cheese
volume
2 kg+ 6.5 l of milk and kefir
children 1-2 years oldthat
porridge dry, cottage cheese, milk, kefir
volume for a month
2 kg+ 16.