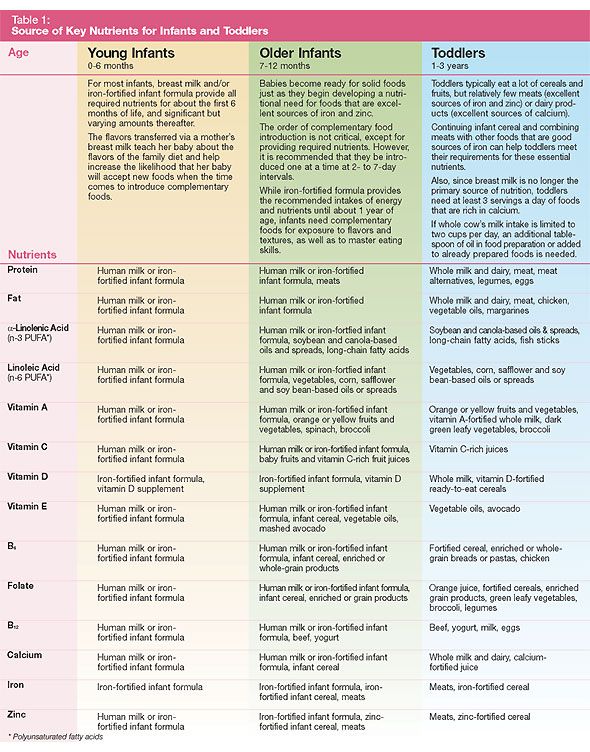
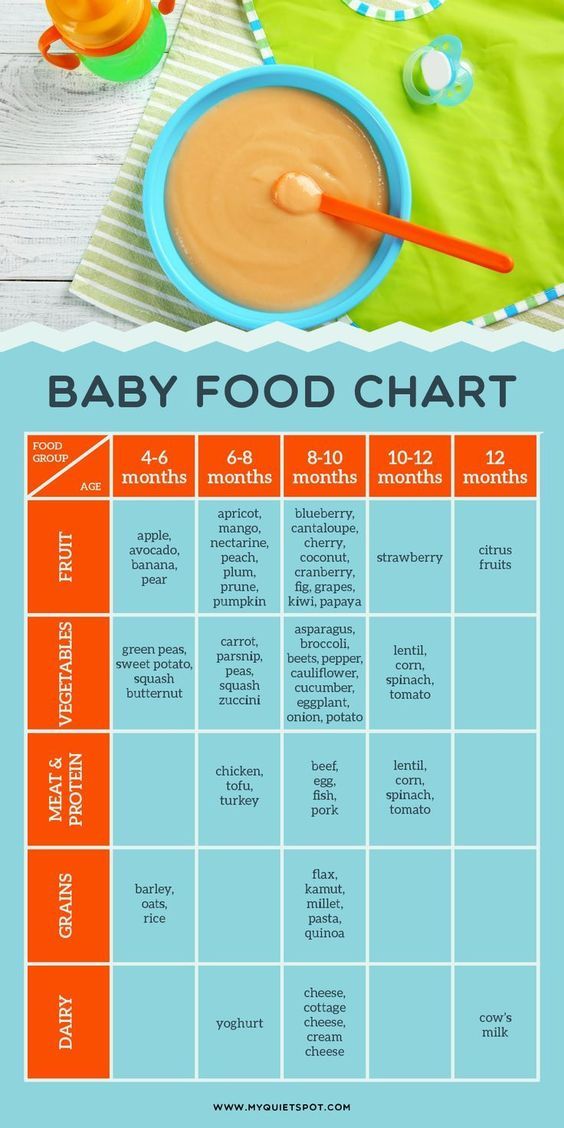
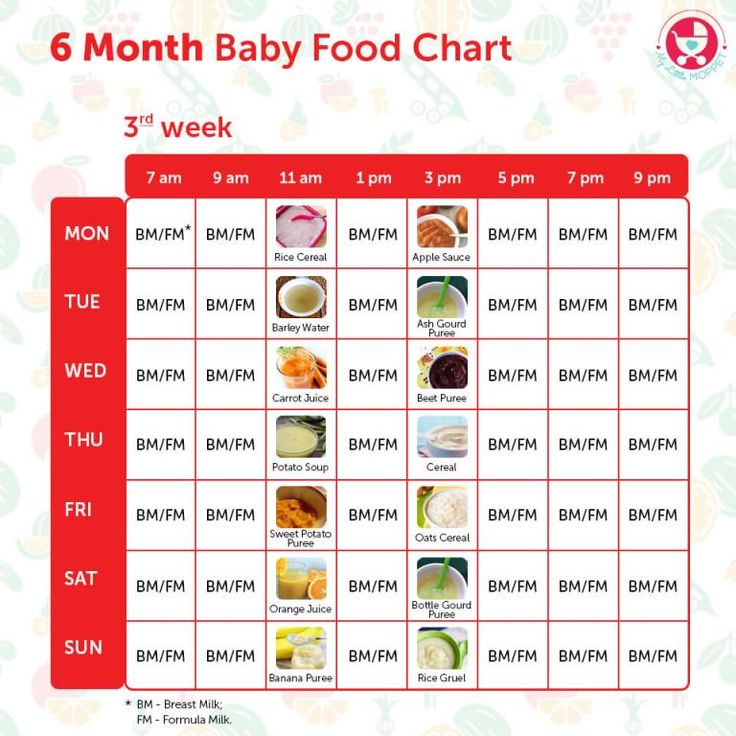
Six month old baby foods
How much should my baby eat? A guide to baby food portions
- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
Wondering how much to feed your baby? This can be hard to figure out, especially when you're starting solids and most of your baby's food ends up on your little one or the floor. It's also difficult to determine how much an 8-month-old (or older baby) should eat – babies this age are more interested in solid foods but still get most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula. This visual guide to baby food portions can help you figure out how much your baby should eat at every stage.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby eat?
Do you worry that your baby is eating too little or too much? Your baby will self-regulate her food intake based on what their body needs, so let their appetite be your guide.
It's helpful to have a reference point, however. Here are photos of how much solid food a baby typically eats in a day. You can also ask your baby's doctor for feeding advice.
This visual guide shows:
- Portions for infants who are new to solids (typically 4 to 6 months)
- Two sample meals for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
- Three sample meals and two snacks for an older baby (8 to 12 months) from a menu developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)
Your little one may eat less or more than what's shown here. Your job is to provide a variety of healthy foods at regular intervals without pressure, and their job is to decide what and how much to eat.
Photo credit: iStock.com / UntitledImages
Watch for signs your baby is full
Lots of factors – including activity level, growth spurts or plateaus, illness, and teething – will affect your baby's appetite, which can vary daily.
End feeding when they signal that they're done.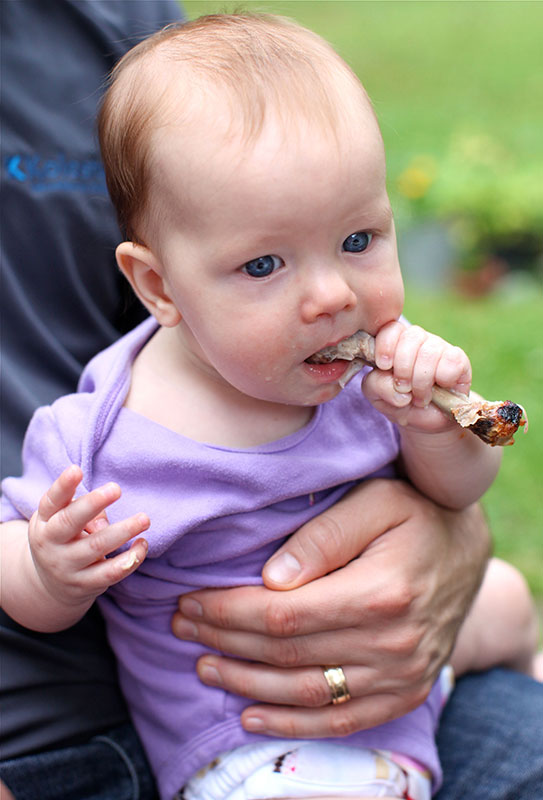 Signs of being full include:
Signs of being full include:
- Turning their head away
- Refusing to open their mouth for another bite after they've swallowed (resist the urge to encourage your baby to have one last spoonful)
- Leaning back in their chair
- Playing with the spoon or food rather than eating
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 4- to 6-month-old should eat
When your baby is developmentally ready for solids, typically around 4 to 6 months, talk to their doctor about introducing solid foods. The first bites are mostly about them getting used to the idea of having something different in their mouth.
- Start with a very small amount, 1 to 2 teaspoons, of a single-ingredient puree.
- Gradually increase to 1 to 2 tablespoons of food once a day.
- Follow your baby's fullness cues.
Popular first foods include pureed mango, banana, chicken, turkey, beef, peas, sweet potatoes, and infant cereal. It's up to you what food to start with, but wait 3 to 5 days between introducing each new food to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction or food intolerance. (And remember, no cow's milk or honey until age 1.)
It's up to you what food to start with, but wait 3 to 5 days between introducing each new food to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction or food intolerance. (And remember, no cow's milk or honey until age 1.)
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 6- to 8-month-old should eat
As your little one gets more comfortable with solids, you can increase the frequency of meals and variety of food.
- Transition from one to two meals a day, typically by 8 months.
- Over time, add a second food to each meal. The photo above is an example of a meal with two foods.
- Once you've worked up to two meals with two foods each, aim for a balance of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains in their daily diet.
- Whenever you introduce a new food, start with a very small amount, a teaspoon or two, to allow your baby to get used to its flavor and texture.
- Start with a soupy consistency. Gradually add more texture as their eating skills improve.
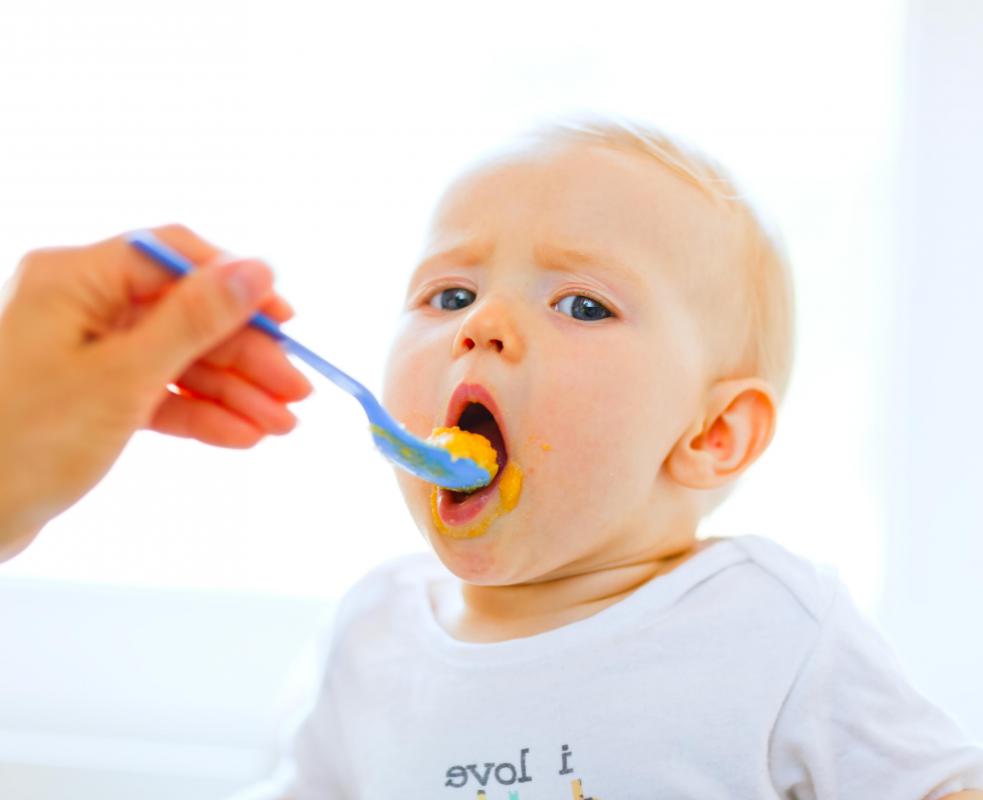

Expect their intake of breast milk or formula to go down. They'll start drinking less of it as they eat more solid foods. Provide healthy options at mealtimes, and let them choose how much to eat.
Note: The jars in all photos are standard 4-ounce baby food jars.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
Cereal and fruit make an easy combination for a morning meal.
Grain: Iron-fortified, whole-grain infant cereal is a popular first grain. At 6 months, a typical daily portion of infant cereal mixed with breast milk or formula might be 2 to 3 tablespoons, increasing to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) by 8 months. (It's best to avoid rice cereal, though.)
Fruit: Babies love the natural sweetness of fruits like pears, apples, berries, prunes, and stone fruits. Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of fruit puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) of mashed or minced fruit.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
If you serve a grain and fruit in the morning, consider offering a protein-rich food and vegetable later in the day. Your child may eat more or less than the amounts shown.
Protein: A baby might transition from eating 1 to 2 tablespoons of meat puree at 6 months to 2 to 4 tablespoons at 8 months, for example. Other good protein sources include cheese, unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt, tofu, beans, and lentils.
Vegetables: Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of vegetable puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup). Try classic favorites like carrots, spinach, or butternut squash, as well as less traditional first foods such as parsnips, beets, or asparagus.
As your child's eating skills improve, gradually add more texture by dicing or mincing foods.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much an 8- to 12-month-old should eat
By 8 months or so, your baby is likely getting the hang of eating and needs to eat more calories to support their growing body. But since their little belly can't hold a lot of food, they'll need to eat more often. Every baby is different, but this may be a good time to try offering a third solid food meal.
But since their little belly can't hold a lot of food, they'll need to eat more often. Every baby is different, but this may be a good time to try offering a third solid food meal.
During this period:
- Continue to give your baby breast milk or formula.
- Add morning and afternoon snacks. (Some babies this age are happy with breast milk or formula as their snack, while others gravitate toward solid foods.) Once you've added a third meal and snacks, your baby will be eating or drinking something about every two to three hours.
- Continue to aim for a mix of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains.
- Introduce coarser and chunkier textures, for example, by dicing or mincing food instead of pureeing it, and graduate to soft finger foods as your baby's eating skills improve.
- Avoid foods with added sugars. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and try to steer clear of foods that list 1 gram or more of "Added Sugars.
 "
" - Provide healthy options, and let your baby choose how much to eat.
To visualize daily portions for an 8- to 12-month-old, check out the following photos of a typical day's menu for a baby this age, developed by the AAP.
Your child may eat more or less than these amounts. If you're concerned about how much your baby is eating, talk to their doctor for advice.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a breakfast consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) whole-grain infant cereal mixed with formula or breast milk
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Morning snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a morning snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced cheese or cooked vegetables
Note: This is an example of a morning snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Lunch for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a lunch consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt or cottage cheese, or minced meat
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced or mashed yellow or orange vegetable
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Afternoon snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features an afternoon snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit or unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt
- 1 whole-grain teething biscuit or cracker
Note: This is an example of an afternoon snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months.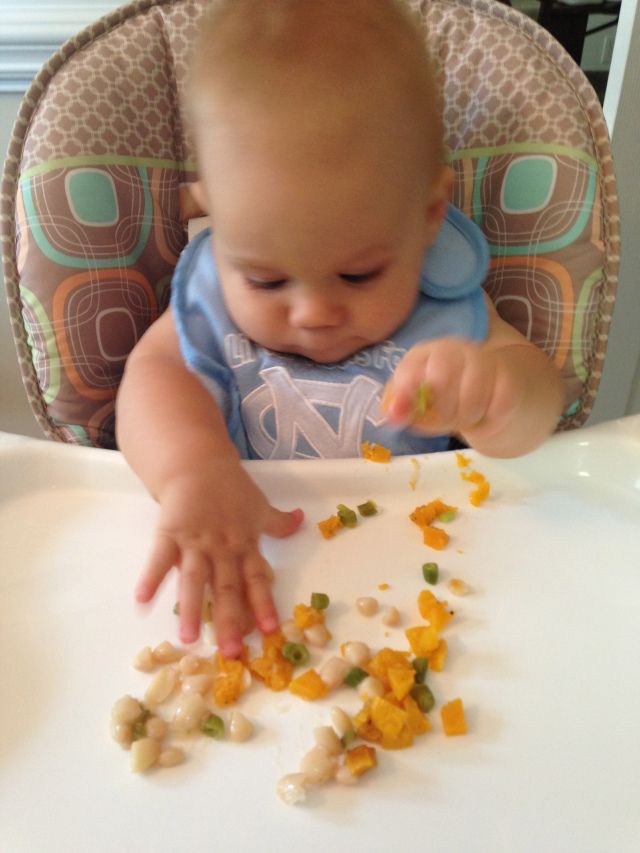 Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a dinner consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) minced or ground poultry or meat, or diced tofu
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2) cup diced, cooked green vegetable
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) noodles, pasta, rice, or potato
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby drink once they start eating solids?
Breast milk or formula will fully meet your child's hydration needs until they're about 6 months old. They may start drinking less as solid foods become a bigger part of their diet. Here are typical daily amounts by age – your baby's intake may be different, however.
6 to 8 months: 24 to 32 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
8 to 12 months: 24 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
Water: You can offer your baby water once they start eating solids, but let them self-regulate how much they drink. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends giving babies who are 6 to 12 months old 4 to 6 ounces of water a day, but what your baby decides to drink may vary. They may drink more on a hot day, for example.
Avoid juice: Juice isn't recommended for babies younger than 12 months.
Photo credit: iStock.com / SDI Productions
Your baby has the final say
Keep in mind that these portions are an estimate. The truth is, every baby is different, and there's no set amount of food that's appropriate for every baby at every stage.
If you're worried about whether your baby is eating enough – or too much – the best advice is to look for and respond to signs that your baby is full.
Your baby's doctor will chart their weight gain at regular intervals. If the doctor sees a consistent growth curve and doesn't have other concerns, your baby is most likely eating the right amount of food.
Hungry for more?
Age-by-age guide to feeding your baby
The 10 best foods for babies
The worst foods for babies
Using spices and seasoning in baby food
Sources
BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies.
AAP. 2021. Starting solid foods. American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren. org/English/ages-stages/baby/feeding-nutrition/Pages/Starting-Solid-Foods.aspx [Accessed February 2022]
org/English/ages-stages/baby/feeding-nutrition/Pages/Starting-Solid-Foods.aspx [Accessed February 2022]
AAP. 2021. Sample menu for an 8 to 12 month old. American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/feeding-nutrition/Pages/Sample-One-Day-Menu-for-an-8-to-12-Month-Old.aspx [Accessed February 2022]
CDC. 2020. How much and how often to feed. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/nutrition/InfantandToddlerNutrition/foods-and-drinks/how-much-and-how-often.html [Accessed February 2022]
Stanford University. Undated. Feeding guide for the first year. Stanford Children's Health and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital Stanford. https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=feeding-guide-for-the-first-year-90-P02209 [Accessed February 2022]
USDA. 2020. ChooseMyPlate.gov. U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://www.choosemyplate.gov/ [Accessed February 2022]
USDA. 2020. Infant nutrition and feeding. U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://wicworks.fns.usda.gov/resources/infant-nutrition-and-feeding-guide [Accessed February 2022]
U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://wicworks.fns.usda.gov/resources/infant-nutrition-and-feeding-guide [Accessed February 2022]
USDA and DHHS. 2020. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025. 9th Edition. U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://DietaryGuidelines.gov [Accessed February 2022]
Elizabeth Dougherty
Elizabeth Dougherty is a veteran parenting writer and editor who's been contributing to BabyCenter since 2015. She's an intrepid traveler, devoted yogi, and longtime resident of Silicon Valley, where she lives with her husband and son.
Baby formula feeding chart: How much formula by weight and age
Is your baby getting too much or too little formula? It's an important question that worries many new parents, especially those with newborns. When deciding how much formula to give your baby, it's important to watch their hunger cues as well as looking at guidelines based on age and weight. In general, before they're eating solids, babies need 2. 5 ounces of formula per pound of body weight each day.
5 ounces of formula per pound of body weight each day.
These guidelines are for babies who are exclusively formula-fed for the first 4 to 6 months, and then fed a combination of formula and solids up to age 1. If your baby is getting a combination of breast milk and formula, talk to their doctor for separate advice.
Your pediatrician can tell you where your baby falls on the growth charts, make sure they're growing steadily on their own growth curve, and help you ensure that they're getting a healthy amount of formula. If you're ever worried about your baby's growth, behavior, or development, talk with their doctor.
How much formula for a newborn
For the first few days, offer your newborn 1 to 2 ounces of formula every 2 or 3 hours. (At first, newborns may only take a half ounce of formula at a time.)
After the first few days, give your newborn 2 to 3 ounces of formula every 3 to 4 hours.
Initially it's best to feed your formula-fed newborn on demand, whenever they show signs that they're hungry. Because your little one can't tell you when they want a bottle, you'll need to learn to read their hunger cues. Crying is often a late sign of hunger, so if you can, try to catch the earlier signs that it's time for a feeding.
Because your little one can't tell you when they want a bottle, you'll need to learn to read their hunger cues. Crying is often a late sign of hunger, so if you can, try to catch the earlier signs that it's time for a feeding.
Here are some hunger cues to watch for:
- Smacking or licking their lips
- Rooting (moving their jaw, mouth, or head in search of food)
- Putting their hands to their mouth
- Opening their mouth
- Fussiness
- Sucking on things
- Becoming more alert
- Crying
As time passes, your newborn will begin to develop a fairly regular feeding schedule. You'll become familiar with their cues and needs, and knowing when and how much to feed them will be much easier.
Formula feeding chart by weight
During the first 4 to 6 months, when your baby isn't eating solid foods, here's a simple rule of thumb: Offer 2.5 ounces of formula per pound of body weight every 24 hours, with a maximum of about 32 ounces.
| Weight | Ounces of formula |
|---|---|
| 6 pounds | 15 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 7 pounds | 17.5 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 8 pounds | 20 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 9 pounds | 22.5 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 10 pounds | 25 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 11 pounds | 27.5 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 12 pounds | 30 fl oz every 24 hours |
These numbers aren't rigid rules. They offer a rough estimate for what your baby may need. Some babies will grow well while taking less than the recommended amount, while others consistently need more. Your baby's daily feedings will also vary according to their individual needs – in other words, they may want a bit more on some days and a bit less on others.
Formula feeding chart by age
Here are typical amounts per day based on age:
| Age | Ounces of formula |
|---|---|
| Full-term newborn | 2 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 1 month old | 3 to 4 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 2 month old | 4 to 5 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 3 month old | 4 to 6 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 4 month old | 4 to 6 ounces per bottle, 4 to 6 times a day |
| 5 month old | 4 to 6 ounces per bottle, 4 to 6 times a day |
| 6 month old | 6 to 8 ounces per bottle, 4 to 5 times a day |
| 7 month old | 6 to 8 ounces per bottle, 3 to 5 times a day |
From 8 months old until their first birthday, you can expect your baby to have 7 to 8 ounces per bottle, 3 to 4 times a day.
As your baby gets older – and their tummy gets bigger – they'll drink fewer bottles a day with more formula in each. It's important not to overfeed your baby so they'll stay at a healthy weight. Your baby shouldn't have more than 32 ounces of formula in 24 hours.
When they reach their first birthday, they can stop drinking formula and transition to cow's milk in a bottle, sippy cup, straw cup, or open cup. Limit your toddler to 16 to 24 ounces (2 to 2.5 cups) a day of whole milk, so they have room for other healthy foods.
Signs that your baby's getting enough formula
Here are signs that your baby's getting all the formula they need:
- Steady weight gain. They continue to gain weight after their first 10 days and follow a healthy growth curve during their first year. (Most babies lose up to 7 to 10 percent of their birth weight in the first few days and then regain it by the time they're about 2 weeks old.)
- Happy baby.
 They seem relaxed and satisfied after a feeding.
They seem relaxed and satisfied after a feeding. - Wet diapers. They wet two to three diapers a day in the first few days after birth. Over the next few days, the amount should increase to at least five to six wet diapers a day.
Signs your baby's getting too much formula
Babies are usually good at eating the amount they need, but bottle-fed babies can drink too much at times. Here are the signs that they're getting too much formula:
- Vomiting after a feeding may be a sign that your baby had too much. (Spitting up is normal, vomiting isn't.)
- Tummy pain after a feeding can also be a sign of overfeeding. If your baby draws up their legs or their tummy seems tense, they may be in pain. (See other possible reasons for stomach pain in babies.)
If your baby seems to want to eat all the time, even after finishing a bottle, talk to your pediatrician. Using a pacifier may help soothe their need to suck.
Formula-feeding tips
- In general, babies eat when they're hungry and stop when they're full, so resist the temptation to encourage your baby to finish each bottle. Overfeeding during infancy can contribute to obesity later in life.
- Don't respond to your baby's every cry with a bottle. They may be crying because their diaper is wet, they're cold or hot, they need to be burped, or they want to be close to you. (Learn more about why babies cry, and how to soothe them.)
- Your baby may be hungrier than usual during growth spurts. These typically occur 10 to 14 days after birth and around 3 weeks, 6 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months of age.
Read more:
- Formula Feeding Problem Solver
- How to safely store and use formula
advertisement | page continues below
how to choose and what kind of baby food is better?
The ideal "baby food" for an infant is breast milk. However, not all mothers can breastfeed their baby, usually this is due to the health of the mother or child. It happens that the woman herself has a serious condition after childbirth and in the early postoperative period, reduced lactation or diseases in which breastfeeding is contraindicated. In such cases, the baby is given formula milk - this is the only alternative to mother's milk. Subsequently, at four to seven months, complementary foods should be introduced into the child's diet, regardless of whether he is breastfed or artificial. The mother is faced with the task of choosing the right baby food for complementary foods.
It happens that the woman herself has a serious condition after childbirth and in the early postoperative period, reduced lactation or diseases in which breastfeeding is contraindicated. In such cases, the baby is given formula milk - this is the only alternative to mother's milk. Subsequently, at four to seven months, complementary foods should be introduced into the child's diet, regardless of whether he is breastfed or artificial. The mother is faced with the task of choosing the right baby food for complementary foods.
In this article, we will talk about what foods for babies are and how to choose the best baby food.
Legislation under "baby food" means food products that meet the physiological needs of the body of a child under 14 years of age. And nutrition for young children is food intended for children from birth to three years[1]. It is necessary to make a diet taking into account the age of the baby and the characteristics of his physical condition.
The Union of Pediatricians of Russia created the National Program for feeding children in the first year of life and the National Program for optimizing the nutrition of children from one to three years old [2]. They describe recommendations regarding what formula to feed the baby from birth, how to introduce complementary foods and expand the baby's diet. These programs provide detailed information on what nutrients and nutrients should be included in the diet of children of different ages.
First you need to figure out what kind of baby food is[3]. Products for toddlers can be divided into two categories:
Infant formula. There are for children from birth to six months (formula 1 mixtures, or initial), from six months to a year (formula 2) and from a year (formula 3). The composition of such baby food is adapted, that is, as close as possible to the composition of breast milk.
- In the initial mixtures, the amount of protein is reduced to 1.
 2-1.5 g / 100 ml - in accordance with the composition of breast milk. They also changed the fat and mineral profile. The initial mixtures are enriched with such an essential amino acid as taurine, and micronutrients, probiotics, vitamins.
2-1.5 g / 100 ml - in accordance with the composition of breast milk. They also changed the fat and mineral profile. The initial mixtures are enriched with such an essential amino acid as taurine, and micronutrients, probiotics, vitamins. - After six months, the baby's need for protein increases, mother's milk changes its composition. And babies on artificial feeding begin to be fed with a more nutritious mixture of formula 2. Taurine is no longer always needed: the body of a baby aged from six months to a year is able to synthesize this amino acid itself. Meanwhile, the content of iron, calcium, zinc increases compared to the initial mixtures, because by this age the child's reserves of minerals received from the mother during pregnancy are depleted, and they need to be replenished.
- A child's diet changes after one year - he is already able to eat a variety of solid foods. However, it is advisable to continue to feed him with a mixture, though already formula 3. Pediatricians recommend it as a source of vitamins and minerals that the baby can easily absorb.

Complementary foods As we have already noted, it is introduced when the baby is four to seven months old. This interval is called the "critical window" and is considered optimal for the initiation of complementary foods for several reasons:
- The baby needs a wider range of minerals, vitamins and other nutrients. In addition, his baby's digestive system is already ready to accept more solid and complex foods than mother's milk or infant formula.
- At this age, the child develops an interest in food, and it is necessary to offer him the right foods to develop his taste.
- During this period, the risk of developing a food allergy to a new product is lower.
- Timely introduction of complementary foods prevents the risk of micronutrient deficiencies and iron deficiency anemia.
Usually the first food is vegetable puree or monocomponent gluten-free cereals, dairy or dairy-free. Over time, cereals containing gluten, supplements from fruits and berries, and also consisting of several cereals are added. A six-month-old child can already be given several types of vegetables and cereals. Also, at about six months, they begin to give meat puree, then fruit, and from eight months - fish. A child from seven months is allowed the yolk.
A six-month-old child can already be given several types of vegetables and cereals. Also, at about six months, they begin to give meat puree, then fruit, and from eight months - fish. A child from seven months is allowed the yolk.
From the age of 12 months, complementary foods already make up the majority of your baby's diet. At this age, it is especially important to diversify the child's diet: he can be given soups with small pieces of vegetables, meat, fish and cereals.
Information
During the first feeding, the baby's eating habits are laid, and it depends on the parents how correct they will be. Often, mothers introduce fruit juices into complementary foods too early. And because babies have an innate preference for sweet tastes, they can become naughty and stop eating the unsweetened foods they need, especially vegetables. Unhealthy taste habits are formed, which can later provoke obesity.
Domestic doctors are concerned about such irrational nutrition of young children - due to the wrong approach to nutrition, many babies experience a deficiency of vitamins and an excess of fast carbohydrates.
How to choose baby foods
Finding the right foods for your baby is not an easy task. Store shelves are bursting with boxes, jars and bottles, and manufacturers write on every second package that the baby will be healthy, strong and cheerful after feeding. Of course, the baby will receive the necessary substances, no matter what product his parents choose, because all the production of baby food is strictly controlled by the state. By the way, Russia has some of the most stringent requirements for the quality of baby food in the world.
However, products for children differ in their properties. It is necessary to select food so that by the end of the first year of life the baby has actively developed chewing skills and an interest in independence, and the diet of complementary foods is reasonably varied.
For children from one to three years of age, the diet should be even more varied. It is important that the child receives daily something new from the main food groups: dairy, vegetables and fruits, meat and fish, cereals, butter and vegetable oil. Of course, the baby's diet should be expanded taking into account his state of health.
Of course, the baby's diet should be expanded taking into account his state of health.
When organizing the nutrition of a child from the moment of introduction of complementary foods and up to three years, a mother needs not only to know what can be fed, but also to consider what foods should not be included in the diet. Among the prohibited products for children under three years of age:
- any mushrooms, vegetables and fruits in a marinade;
- pickles, preserves in tomato sauce;
- commercial juice concentrates, carbonated drinks, coffee and strong tea;
- various condiments - mustard, ketchup, hot sauces, horseradish, pepper, vinegar, mayonnaise;
- products containing flavors, industrial colors, including chewing gum;
- margarine and refractory fats - lamb, pork;
- chocolates, sweets and other sweets.
To choose the right baby food, you need to know exactly what you should pay attention to and what you don't need to worry about.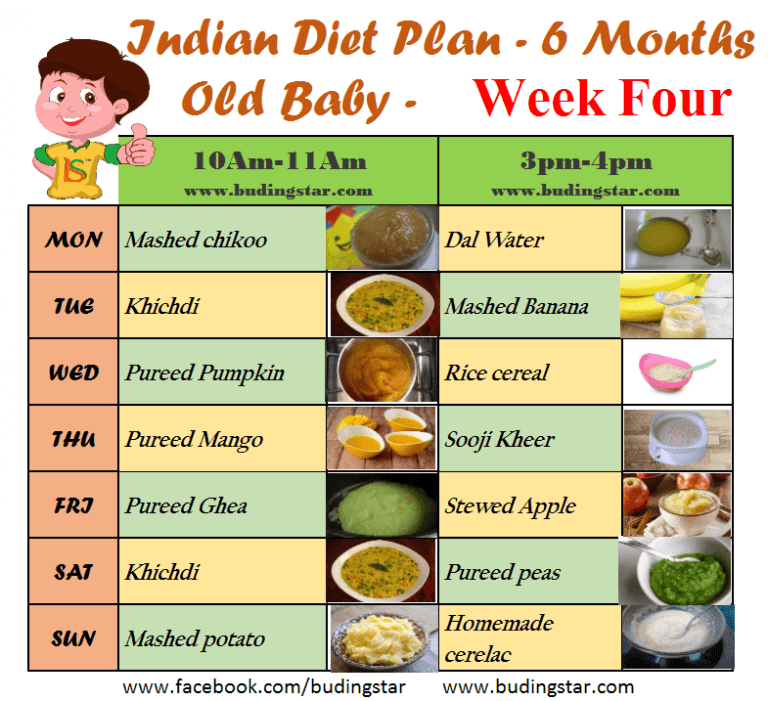
When choosing mixtures, it is important to check:
- Absence of palm oil. Formula manufacturers may use palm oil (more specifically palm extract) because, like breast milk, it is rich in palmitic acid. However, in human milk, palmitic acid is in the beta position, while in palm oil it is in the alpha position. Such alpha-palmitic acid can interfere with the absorption of calcium and fats and is generally less well absorbed by the child's body. This can negatively affect the work of the intestines, lead to constipation, regurgitation. Milk fat is better suited for baby food as a source of palmitic acid[4][5].
- Protein ratio. Breast milk protein is primarily whey proteins and casein. A child needs both types of protein, while proteins are easily digested, which cannot be said about casein. If baby food contains a lot of casein, it stays longer in the digestive tract, which can cause problems with the baby's stool.

- The presence of additional functional elements in the composition - lutein, nucleotides, pre- and probiotics. The task of lutein is to protect vision from ultraviolet rays. Nucleotides are low molecular weight compounds that promote the growth of beneficial bifidobacteria in the intestines. And pre- and probiotics in the composition of infant formulas help to establish comfortable digestion.
When choosing complementary foods, pay attention to:
- Age appropriate. It is important that in the diet of a child under three years of age who receives complementary foods, special children's products predominate - in their composition the components are selected taking into account the age-related needs of the baby's body. It is impossible at an early age to transfer children to "adult" foods like pickles, smoked foods, fast food, and so on.
- Fortified products. It is important that the composition contains vitamins and minerals.
 The National Child Nutrition Optimization Program recommends choosing complementary foods that contain elements designed to prevent anemia, rickets, and vitamin deficiencies.
The National Child Nutrition Optimization Program recommends choosing complementary foods that contain elements designed to prevent anemia, rickets, and vitamin deficiencies. - For a varied diet. The menu for a baby up to six months is quite monotonous. But as they grow older, the baby needs more various nutrients - proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals.
- For the individual reaction of the baby. If the child is already receiving complementary foods, then it is worth introducing a new product only after the previous one has been fully introduced. If the baby is allergic to the product, then it should be administered carefully, carefully checking the reaction of the body.
Ingredient safety testing is optional. Of course, the content of any "chemistry" in the product for feeding a child, whether it be a mixture or complementary foods, is unacceptable. There is no need to worry about this: baby food is carefully checked. If it is registered on the territory of the Customs Union and hit the shelves, then it complies with SanPiN 2. 3.2.1940-05 and there will be no "prohibited" components in its composition. Also, contrary to popular misconception, in Russia it is forbidden to use GMOs in children's products.
3.2.1940-05 and there will be no "prohibited" components in its composition. Also, contrary to popular misconception, in Russia it is forbidden to use GMOs in children's products.
Note
Baby food in jars (usually mashed potatoes) has a short shelf life after opening because it does not contain preservatives. However, before the jar is opened, the products can stand for quite a long time on the shelves of stores or in the refrigerator at home. This is possible thanks to a special production technology, sterilization and vacuum packaging. If a soft pop is heard when opening the jar, this is a good sign: the puree is not spoiled. But products in jars with swollen lids or a protruding bottom should not be used: microorganisms already multiply in such food, it is not suitable for food.
Features of the choice of dairy products
It is necessary to choose dairy products for babies, following the doctor's recommendations. The specialist will take into account the health of the baby, especially if he is allergic to cow protein. In Russia, such an allergy occurs in 30–40% of children [6]. Such a reaction may occur due to hereditary predisposition and immaturity of the body. But most often, allergies go away when the child grows up.
The specialist will take into account the health of the baby, especially if he is allergic to cow protein. In Russia, such an allergy occurs in 30–40% of children [6]. Such a reaction may occur due to hereditary predisposition and immaturity of the body. But most often, allergies go away when the child grows up.
Goat milk baby food may be a suitable option for young children with a predisposition to allergies. Its protein is perceived by the body better than cow's: alpha-s1-casein, contained in large quantities in cow's milk, makes a product based on it difficult to digest - food stagnates in the baby's gastrointestinal tract, motor skills are disturbed, as a result, allergies often occur. In goat milk, as in breast milk, there is practically no alpha-s1-casein [7]. Therefore, goat's milk, and hence the mixture based on it, are better absorbed.
Of course, with the introduction of complementary foods, other dairy products will appear in the baby's diet. Unadapted fermented milk drinks, such as kefir, yogurt, biolact, can be introduced into the diet from eight months and in an amount not exceeding 200 ml. Also during this period, it is recommended to give cottage cheese - no more than 50 g per day, but according to indications, it can also be prescribed from the age of six months. Whole milk cannot be used as the main food, and it is advised to introduce it into the diet of babies no earlier than a year (in the amount of 100-150 ml per day) [8]. As mentioned above, it must be adapted infant milk or formula 3 formula.
Also during this period, it is recommended to give cottage cheese - no more than 50 g per day, but according to indications, it can also be prescribed from the age of six months. Whole milk cannot be used as the main food, and it is advised to introduce it into the diet of babies no earlier than a year (in the amount of 100-150 ml per day) [8]. As mentioned above, it must be adapted infant milk or formula 3 formula.
To choose the best baby food, it is necessary to take into account the health of the baby, his tastes, as well as individual reactions of the body. Therefore, before going to the store, you should consult a doctor. The specialist will not only tell you which baby food to choose, but also give recommendations on how to make the child's diet balanced and healthy.
Ingredients | Bibikol - Baby food based on goat milk
ORGANIC. WHOLE. USEFUL
As you know, the nature of a child's nutrition in the nine months that he is in the womb, and the first couple of years of life, programs and forms the state of health for the rest of his life.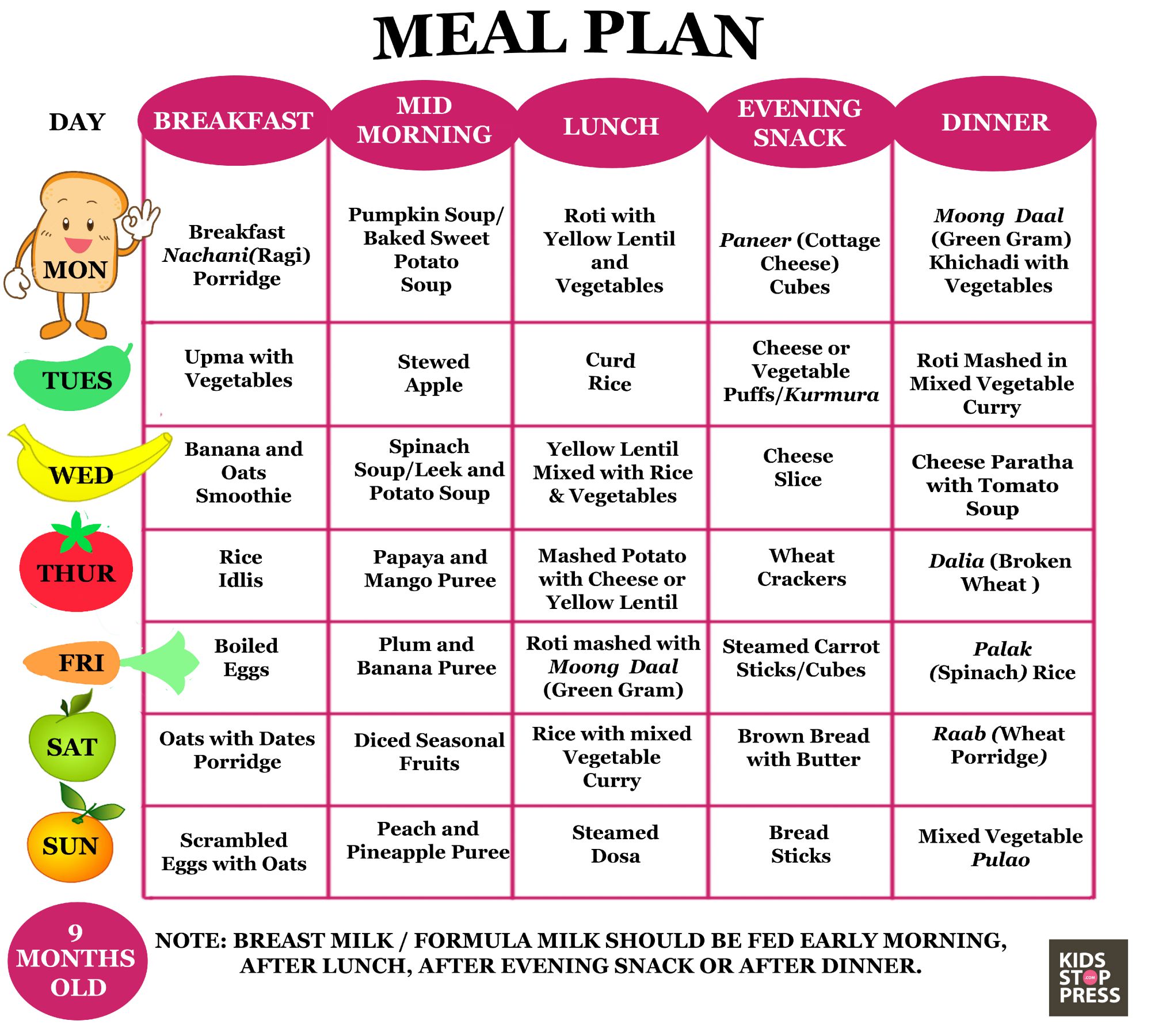 What the baby eats during this period of development is no less important than genetic prerequisites.
What the baby eats during this period of development is no less important than genetic prerequisites.
It is unlikely that anyone will argue that the "gold standard" of nutrition in infancy is breast milk. The World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding until six months of age and, if possible, continued breastfeeding with complementary foods until two years of age. However, sometimes this is not possible for objective medical or social reasons. Then the pediatrician transfers the child to mixed or artificial feeding. And here the problem immediately arises - how to choose the most suitable breast milk substitute.
Infant formula should be as close as possible to it not only in its chemical composition, but also in the presence of important functional components.
Recently, one of the most promising areas in the creation of food products for young children is the use of whole goat milk. Throughout the history of mankind, it has been highly valued for its special dietary and even medicinal properties. This is confirmed by numerous studies conducted both in our country and abroad.
This is confirmed by numerous studies conducted both in our country and abroad.
It is known that the milk of different breeds of goats, moreover, living in different climatic conditions, is very different in composition. That is why, for example, the company "BIBIKOL" - a leader in the production of baby food based on whole goat milk - turned its attention to New Zealand with its mild climate and a network of farms practicing organic farming and animal husbandry. A special breed of New Zealand goats has the opportunity to eat fresh grass all year round, which, of course, has a positive effect on the properties of milk. In addition, the genetic trait of these goats is that their milk contains low levels of the highly allergenic milk protein alpha-S1-casein. The protein of this goat milk has a high biological value.
BIBIKOL has set up on-site production of adapted NANNY mixtures in New Zealand. From the milking process to the packaging of the finished mixture, no more than eight hours pass. Thanks to a special technology, NANNY manages to preserve the unique nutritional and functional components of natural whole goat milk and bring the mixtures as close as possible to breast milk. NANNIE formulas retain milk fat, so there is no need to add palm oil as a source of palmitic acid.
Thanks to a special technology, NANNY manages to preserve the unique nutritional and functional components of natural whole goat milk and bring the mixtures as close as possible to breast milk. NANNIE formulas retain milk fat, so there is no need to add palm oil as a source of palmitic acid.
As a source of beneficial ω-3- and ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids, NANNIE is supplemented with marine fish oil and a blend of high quality vegetable oils.
The carbohydrate component in the "NANNIE" mixture is represented by milk sugar - lactose, which provides energy for the rapidly growing body of the child and improves the absorption of calcium. The NANNIE 1.2 mixture contains a complex of vegetable prebiotics Orafti®Synergy1, which has a pronounced positive effect on the functioning of the child's intestines, comparable to the effect of breast milk.
In addition to dry mixes, "BIBIKOL" produces "BIBIKASHI" with organic cereals and fruit and vegetable purees with cottage cheese, also based on goat's milk, and "AMALTEYA" powdered milk for pregnant and lactating women.