Start feeding baby solid food
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.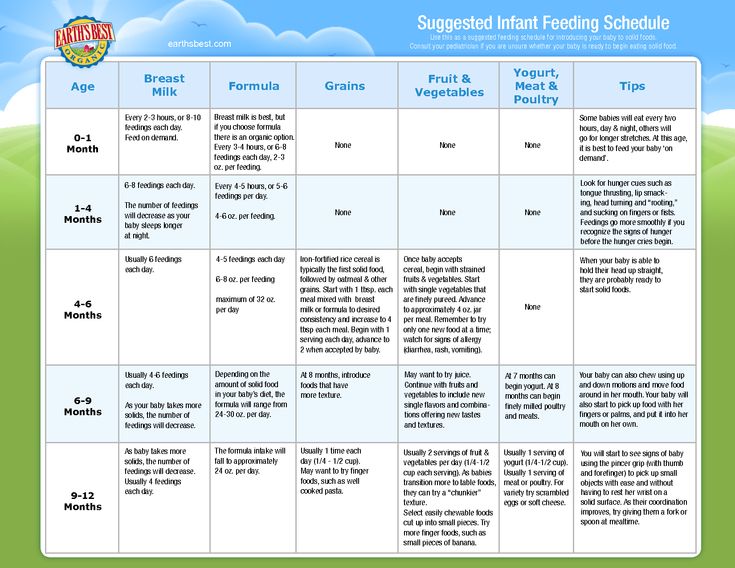
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.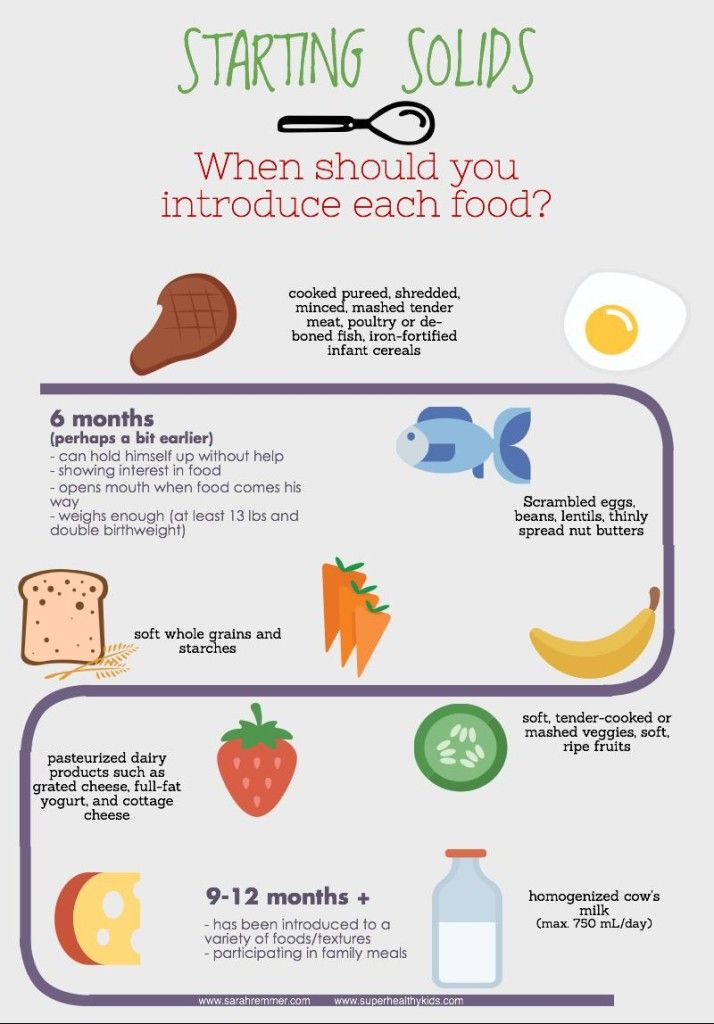
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Sample Menu for a Baby 8 to 12 Months Old
Log in | Register
Ages & Stages
Ages & Stages
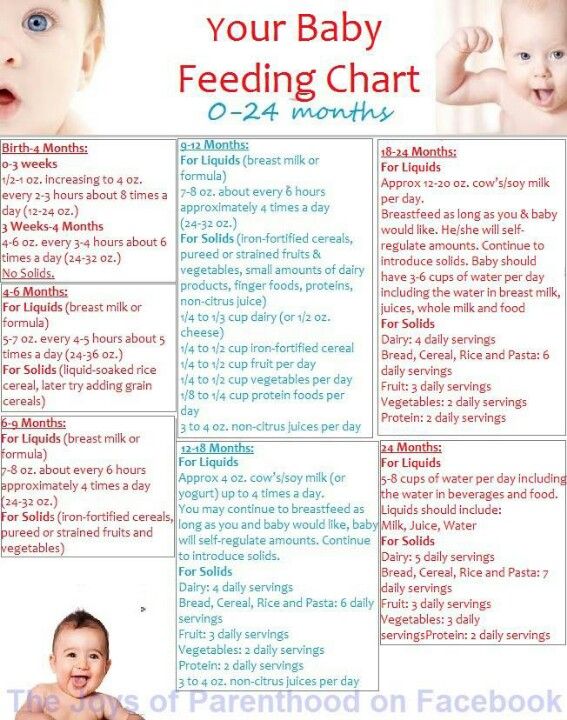
Now that your baby is eating solid foods, planning meals can be more challenging. At this age, your baby needs between 750 and 900 calories each day, of which about 400 to 500 should come from
breast milk or formula (if you are not breastfeeding)—roughly 24 ounces (720 mL) a day. Breast milk and formula contain vitamins, minerals, and other important components for brain growth.
At this age, your baby needs between 750 and 900 calories each day, of which about 400 to 500 should come from
breast milk or formula (if you are not breastfeeding)—roughly 24 ounces (720 mL) a day. Breast milk and formula contain vitamins, minerals, and other important components for brain growth.
At about eight months, you may want to introduce foods that are slightly coarser than strained pureed foods. They require more chewing than baby foods. You can expand your baby's diet to include soft foods such as yogurt, oatmeal, mashed banana, mashed potatoes, or even thicker or lumpy pureed vegetables. Eggs (including scrambled) are an excellent source of protein, as are cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, and avocado.
Sample menu ideas for an 8- to 12-month-old baby:
1 cup = 8 ounces = 240 ml
¾ cup = 6 ounces = 180 ml
½ cup = 4 ounces = 120 ml
¼ cup = 2 ounces = 60 ml
Breakfast
2 to 4 ounces cereal, or 1 mashed or scrambled egg
2 to 4 ounces mashed or diced fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Lunch
2 to 4 ounces yogurt or cottage cheese, or pureed or diced beans or meat
2 to 4 ounces cooked pureed or diced yellow or orange vegetables
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Dinner
2 to 4 ounces diced diced poultry, meat, or tofu
2 to 4 ounces cooked green vegetables
2 to 4 ounces cooked soft-whole grain pasta or potato
2 to 4 ounces diced or mashed fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Before bedtime
Breastmilk or 6 to 8 ounces formula, or water.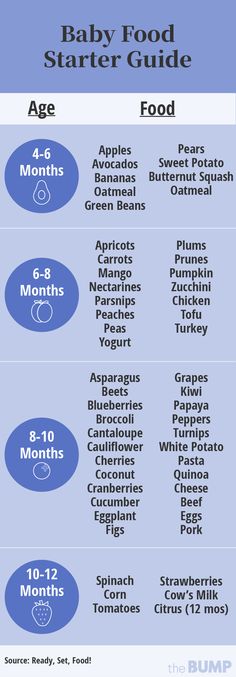 (If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
(If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
More information
- Sample Menu for a One-Year-Old
- Starting Solid Foods
- Breastfeeding Mealtime Milestones
- Ask the Pediatrician: Is it OK to make my own baby food?
- Last Updated
- 8/12/2022
- Source
- Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Introducing Solid Food: Why, When, What and How
Introducing Solid Food: Why Babies Need It
As babies grow older, the need for solid food arises, from which the body will receive enough iron and other nutrients necessary for growth and development.
During the first six months, the baby's body uses the iron stored in the womb. Some iron also comes from breast milk and/or formula. But as the baby grows, the reserves of this substance in the body decrease. And the iron that a child receives from breast milk or formula is already not enough at the age of about six months. nine0005
Through the introduction of solid foods, the child also learns to eat, gets to know new tastes and textures of different foods. At the same time, he develops teeth and jaws, and he also acquires skills that will later be needed for language development.
Signs it's time to introduce solid foods
You will know when it's time to introduce solid foods by how your baby develops and behaves.
Your child is ready for solid food if:
- holds head and neck well and can sit upright with support
- shows interest in food - for example, looking at the contents of your plate
- reaching for your food
- opens his mouth when you offer him food from a spoon.

Most children show these signs by about six months, but in general everyone is individual.
It is not recommended to introduce solid foods before four months of age.
If your baby is about seven months old and hasn't started solid foods yet, you can talk to a nurse or pediatrician. nine0005
The best time to offer solid food to your baby is when you and he are in a good mood for the first time.
He is also more likely to try new foods after breast milk or formula. The fact is that when a child is really hungry, he only wants milk or formula, because he knows that he will be satisfied. At the same time, there will still be room for other food in his tummy.
Over time, you will learn to tell if your baby is hungry or full, wants to try something or is tired. nine0005
Your child is hungry, if:
- brightens up when he sees you cooking for him
- leans towards you while sitting in a highchair
- opens its mouth when you are about to feed it.

Your child no longer wants to eat if:
- turns away
- loses interest or gets distracted
- repels spoon
- purses his lips.
In what portions should the new food be introduced to the child? Start with 1-2 teaspoons and increase according to your baby's appetite. By 12 months, he should be eating about three small meals a day, plus breast milk or formula. nine0005
Consistency of solid food
The first solid food can be smooth, pureed or in soft pieces , depending on your baby's preference. Then the child can quickly move on to finely chopped, and then just to finely chopped foods.
The child needs food of various consistencies. This will help him learn to chew, and chewing, in turn, contributes to the development of speech. It also encourages the child to learn to eat on his own and will prevent eating problems as he develops. nine0005
By 12 months, the baby should already be eating the same as the rest of the family.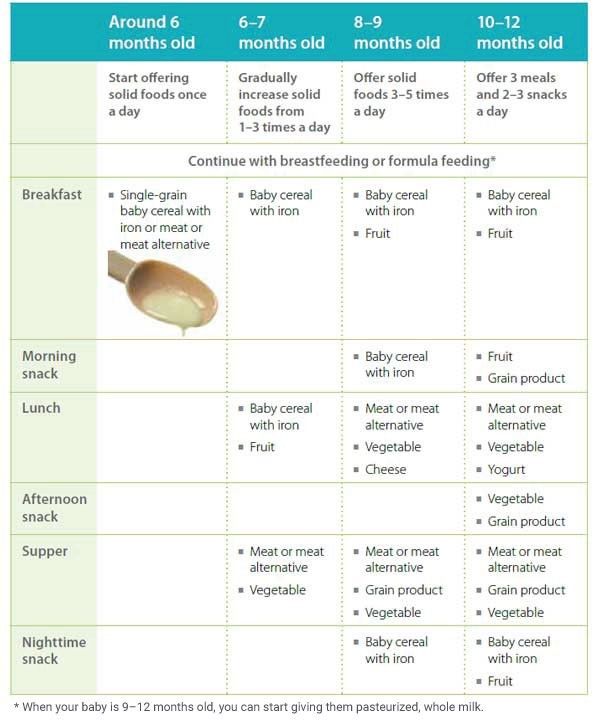 You may have to cut some foods into smaller pieces, and boil the vegetables well.
You may have to cut some foods into smaller pieces, and boil the vegetables well.
Do not leave the child unattended while eating, make sure that he does not choke. Be especially careful with foods such as nuts and small-boned meats, as they are easy to choke on. If the child can already move around, try to seat him while eating. If you sit next to each other while the baby is eating, he will most likely sit more quietly. nine0005
Types of foods when introducing solid foods
The child will be happy to try any new food, so there is no need to prepare something “special” for him.
You can introduce solid foods in any order, as long as you include iron-rich foods and cook foods of the right consistency.
Foods rich in iron include:
- iron-fortified baby cereals
- minced meat, poultry and fish
- tofu and legumes, cooked
- mashed or boiled eggs (do not give raw or soft-boiled eggs).
Iron-rich foods can be supplemented with other healthy foods:
- vegetables such as boiled potatoes, carrots or green vegetables such as broccoli
- fruit - e.
 g. banana, apple, melon or avocado
g. banana, apple, melon or avocado - cereals - e.g. oats, bread, rice and pasta
- Dairy products such as yogurt and full fat cheese.
These products can be combined as there is no need to administer only one product at a time. By offering your child a variety of foods, you will allow him to try a variety of new tastes and get a lot of nutrients. nine0005
With our solid food introduction tips, you can get your child interested in new foods and make the eating process smoother and playful.
Breast milk and formula when introducing solid food
Continue breastfeeding or formula until at least 12 months while introducing solid food.
If you are unsure if your baby is getting the right amount of milk once solids are introduced, pay attention to his behavior. nine0005
For example, if a child has eaten a lot of solid food and is not getting enough or is not getting enough milk, the daily milk feeds may need to be made less frequent but longer. If the baby does not want to eat solid food, he may have had too much milk. This may be a signal that portions of milk should be reduced.
If the baby does not want to eat solid food, he may have had too much milk. This may be a signal that portions of milk should be reduced.
By about nine months of age, babies usually develop enough chewing and swallowing skills to eat solid foods before milk, not after. nine0005
Solid food does not replace breast milk or formula. If the transition to solid foods instead of milk and/or formula occurs too quickly, a child may miss an important milestone in their diet.
Water administration
At the age of six months, the child may be offered chilled boiled water in a cup during meals or at other times. This is to help your baby learn to drink from a cup, but at this age, he still doesn't need liquids other than breast milk or formula. When the child is one year old, he can be offered fresh tap water without boiling. nine0005
Foods and drinks to avoid
Some foods should not be given to children under a certain age:
- honey under 12 months to avoid the risk of infant botulism
- raw eggs, soft-boiled eggs, and products containing raw eggs, such as homemade mayonnaise, up to 12 months - bacteria in raw eggs may be harmful to infants
- skim milk products up to two years
- Whole nuts and similar hard foods up to three years - due to risk of choking.
 nine0018
nine0018
Also, up to a certain age, children should not be given certain drinks :
- pasteurized whole cow's milk as a main drink up to 12 months
- soy, goat and sheep milk up to two years (fortified soy products may be given up to two years)
- rice, oatmeal, almond or coconut milk up to two years of age, unless advised otherwise by a pediatrician or nurse
- Unpasteurized milk of all kinds, tea, coffee or sugar-sweetened beverages for all ages
- fruit juice - should be limited at any age (fruits contain the nutrients a child needs).
Salt and sugar should not be added to baby food. Infants and young children are not suitable for highly processed foods and packaged foods that are high in fat, sugar and/or salt. These include cakes, cookies, chips and fried foods.
Food allergy and introduction of solid foods
Early introduction of allergenic foods may reduce risk development of food allergy in a child.
All children, including children at high risk of allergies, should try allergenic foods from about six months of age . These foods include hard-boiled eggs, peanut butter, wheat (in wheat bread, cereals, and pasta), and cow's milk (but not as a staple drink).
It is recommended to consult a physician, health visitor, nutritionist, pediatrician, allergist or immunologist if:
- the child already has a food allergy
- you have a family history of food allergies and are concerned about introducing solid foods to your child
- you are worried about his reaction to the products.
Children with severe eczema and children of parents with food allergies are more likely to develop food allergies. But most children with food allergies do not have food allergy parents.
How to teach your baby to chew: teaching your baby to chew solid food
01/29/2020 55778
- When to introduce the first complementary foods
- How to tell if a baby is ready for solid food
- Infant diet
- Common mistakes in complementary foods
- Prohibited products
- What to do if the child cannot eat hard pieces
- Meal Game
When a small child appears in the family, parents face a difficult task: not only to raise and educate, but also to instill in the baby all the necessary skills. For example, young parents are often concerned about the question of how to teach a child to chew. We have collected tips for you from well-known Russian and foreign pediatricians who will help you find the best solution. nine0005
For example, young parents are often concerned about the question of how to teach a child to chew. We have collected tips for you from well-known Russian and foreign pediatricians who will help you find the best solution. nine0005
What are the difficulties
For adults, the process of chewing food seems to be something completely natural. But the child has only a sucking reflex, and even liquid puree becomes an unusual and unfamiliar food for him. In addition, other reflex reactions are characteristic of the same period, due to which solid pieces of food that have fallen into the mouth are rejected. They weaken by 4 months, but it is not necessary to wean a child at this age: mother's milk "adjusts" to the needs of the baby, its composition changes over time. nine0005
When to introduce the first complementary foods
It was at this time - in the period from 4-6 months. Depending on various factors, it can be a monocomponent vegetable puree or dairy-free porridge from a single cereal. It is worth considering the weight, height, state of the digestive system and other features of the child's health.
It is worth considering the weight, height, state of the digestive system and other features of the child's health.
This is important!
Any new food should be given gradually, with caution: start with one teaspoon and supplement with mother's milk or formula. During the feeding period, you need to carefully monitor the condition of the child and possible allergic reactions. nine0230
How to tell if a baby is ready for solid food
As a rule, the baby himself makes it clear that he is interested in updating his diet. This can be seen from his behavior:
- Stops sucking food from a spoon by removing it with his lips
- Tries to chew
- Interested in "adult" food
- Pulls hard objects into mouth nine0025
- Opens mouth wide during feeding
- At 6-7 months, tiny particles up to 0.3 mm are acceptable. Grated vegetables are ideal
- At 8-9 months, food with particles up to 1.5 mm can be added to the diet. These can be cereal flakes in the composition of cereals, tiny pieces of well-cooked vegetables
- At 9-12 months, the baby can already chew food with pieces up to 3 mm.
- At 1 year of age and beyond, teach the child to chew solid food independently
- lozenges, caramel, toffee
- nuts and any seeds
- tough cuts of meat
- whole grapes
- large cuts of hard vegetables and fruits
- Prepare thick creamy soups and purees for your child, but leave a few tiny, boiled pieces of vegetables when blending with a blender
- Later vegetables can be chopped with a fork, the pieces will become larger, but not hard enough for a child to choke
- Foods that your child likes will help you achieve the best results.
 These can be baked apples and pears, bananas, children's cookies
These can be baked apples and pears, bananas, children's cookies - Food should be made not only tasty, but also beautiful so that it attracts the baby
This usually happens no earlier than 6-8 months - that's when you can start giving your child cereals and other foods with small dense particles.
How to choose a diet for young children
Common errors
Young parents may involuntarily make mistakes. This is normal and should not cause panic: the first child is always difficult. If the baby refuses solid food, there are several reasons. nine0005
Solids too large . The child has a protective reflex, due to which he often spits out food. And if the piece is very large, the baby may begin to vomit.
Complementary foods were introduced very late . Some "specialists" and "experienced relatives" convince young mothers that they need to breastfeed their baby for up to a year, without giving him any other food. The kid gets used to such food, and the chewing reflex is not formed in him. You should not be afraid, it is difficult, but you can fix it. nine0005
Some "specialists" and "experienced relatives" convince young mothers that they need to breastfeed their baby for up to a year, without giving him any other food. The kid gets used to such food, and the chewing reflex is not formed in him. You should not be afraid, it is difficult, but you can fix it. nine0005
The child does not like the taste . Yes, he is already an independent person who has his own preferences. So the baby can easily eat broccoli and refuse a baked pear. Or vice versa. You should not forcefully stuff the child with what he does not like, or force him to finish eating the entire portion.
Negative associations . Some psychologists believe that the refusal to eat from a spoon may be due to the fact that the child associates food with medicine (manifested in cases where the baby was given tasteless potions). nine0005
Too many new products . Don't try to include a wide variety of foods in your diet. As Ellyn Satter writes in Feeding and Feeding Your Child with Love and Common Sense, it's best to add "scary and unfamiliar" foods to what your child already loves, and in very small portions.
The child is fed like an adult . Larisa Surkova writes in the book “How cool it is with a child from 1 to 3 years old: a generator of useful tips”, you should not deny your baby tactile sensations. If he wants to crush food, sniff, smear on the table - let him do it. In the end, the table can be covered with oilcloth (and the floor, by the way, too). nine0005
Prohibited products
To avoid food allergies and digestive problems, a child under the age of four should never be given:
What to do if the child cannot eat hard pieces
In some cases, even a one-year-old baby cannot chew food and constantly chokes on small pieces. This means that the chewing reflex is not fully formed, and parents will have to act very delicately:
If, in the process of learning, the child continues to choke and is not able to swallow solid food, this is an occasion to consult a doctor who will find the cause of the problem.
Gameplay
The child needs to be interested. A game plot for eating is an absolute norm. In the process, the baby can be told an interesting story in which he will be involved. The well-known “airplane” flying to the “hangar” is a real way to feed a child without nerves and tantrums. However, it is important to understand that if the baby began to turn away, it means that he has already eaten. It is not necessary to supplement it with the remnants of mashed potatoes, even if it is the only spoon. Teaching a baby to eat “adult”, solid food is a really difficult task that requires attention and patience from parents.