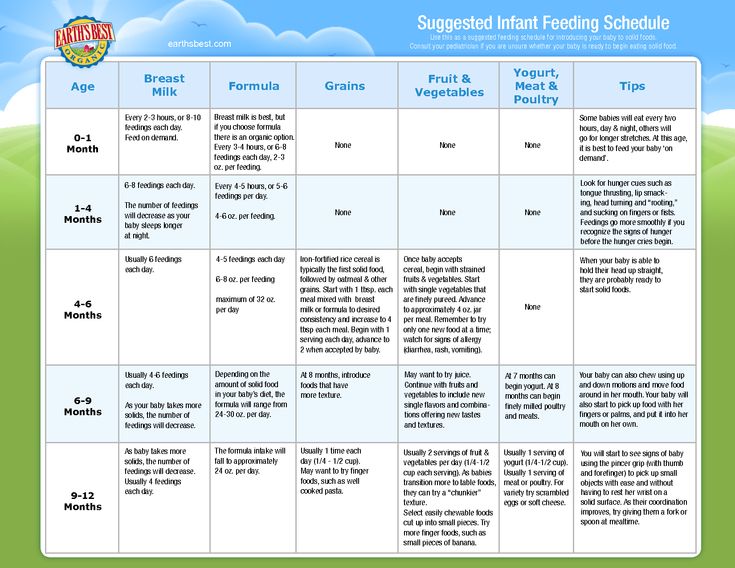
Starting feeding baby solids
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Feeding Your 4- to 7-Month-Old (for Parents)
Most babies this age are ready to try solid foods. Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Be sure to check with your doctor before giving any solid foods.
Is My Baby Ready to Eat Solid Foods?
How can you tell if your baby is ready for solids? Here are a few hints:
- Does your baby swallow food or push it out of their mouth? Babies have a natural tongue-thrust reflex that pushes food back out. Wait until this reflex disappears (typically when babies are 4–6 months old).
- Can your baby support their own head? To eat solid food, an infant needs good head and neck control and should be able to sit up.
- Is your baby interested in food? Babies who stare, reach and grab, and open their mouths for food are ready to try solid foods.
If your doctor gives the go-ahead but your baby seems frustrated or uninterested in solid foods, try waiting a few days before trying again. Breast milk and formula will still meet nutritional needs as your baby learns to eat solid foods.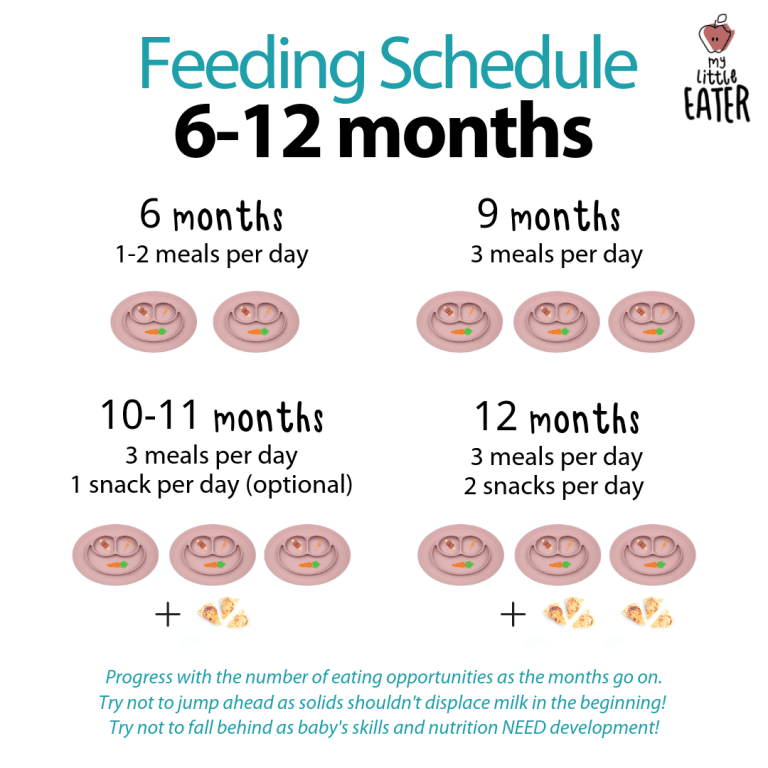 But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
Do not add cereal or other food to your baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain.
Watch for signs that your child is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your child stop when full. A child who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the breast or the bottle. With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
How Should I Start Feeding My Baby Solid Foods?
When your baby is ready and the doctor says it’s OK to try solid foods, pick a time of day when your baby is not tired or cranky. You want your baby to be a little hungry, but not so hungry that they’re upset. So you might want to give your baby a little breast milk or formula first.
Have your baby sit supported in your lap or in a high chair with a safety strap.
Most babies' first food is iron-fortified infant single-grain cereal mixed with breast milk or formula.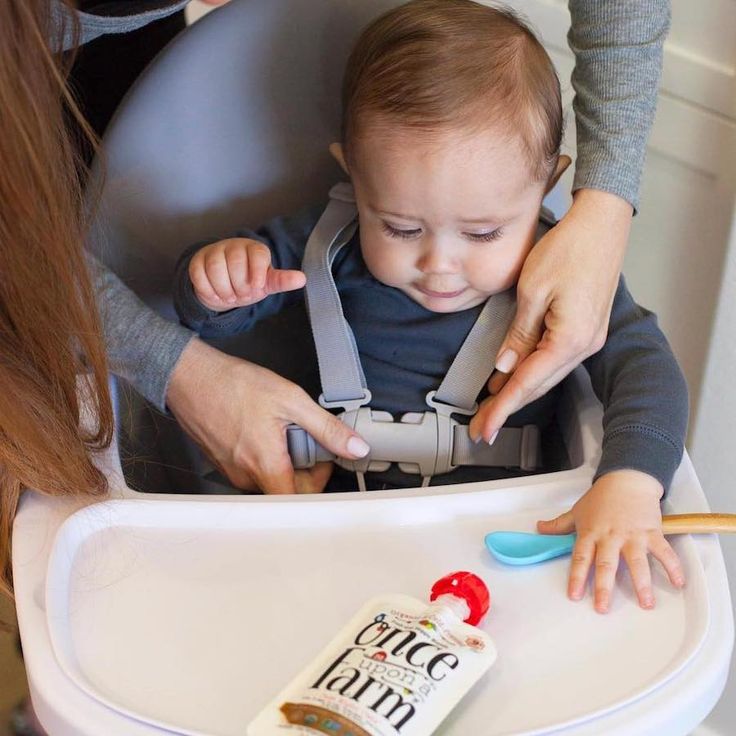 Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
When your little one gets the hang of eating cereal off a spoon, it may be time to try single-ingredient puréed meat, vegetables, or fruit. The order in which you give them doesn't matter, but go slow. Offer foods that are high in iron and zinc — such as meat, poultry, eggs, and beans — especially if your baby is breastfeeding. Try one food at a time and wait several days before trying something else new. This will let you identify any foods that your baby may be allergic to.
Which Foods Should I Avoid?
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
Possible signs of food allergy or allergic reactions include:
- rash
- bloating or an increase in gassiness
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Get medical care right away if your baby has a more severe allergic reaction, like hives, drooling, wheezing, or trouble breathing.
If your child has any type of reaction to a food, don't offer that food again until you talk with your doctor.
Babies shouldn't have:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy beverages before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula.
 It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese. - foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Tips for Feeding Your Baby Solid Foods
With the hectic pace of family life, most parents try commercially prepared baby foods at first. They come in small, convenient containers, and manufacturers must meet strict safety and nutrition guidelines.
If you prepare your own baby foods at home, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Follow the rules for food safety, including washing your hands well and often.
- To preserve the nutrients in your baby's food, cook it in ways that keep the most vitamins and minerals. Try steaming or baking fruits and vegetables instead of boiling, which washes away the nutrients.
- Freeze portions that you aren't going to use right away.
- Whether you buy the baby food or make it yourself, texture and consistency are important. At first, babies should have finely puréed single-ingredient foods.
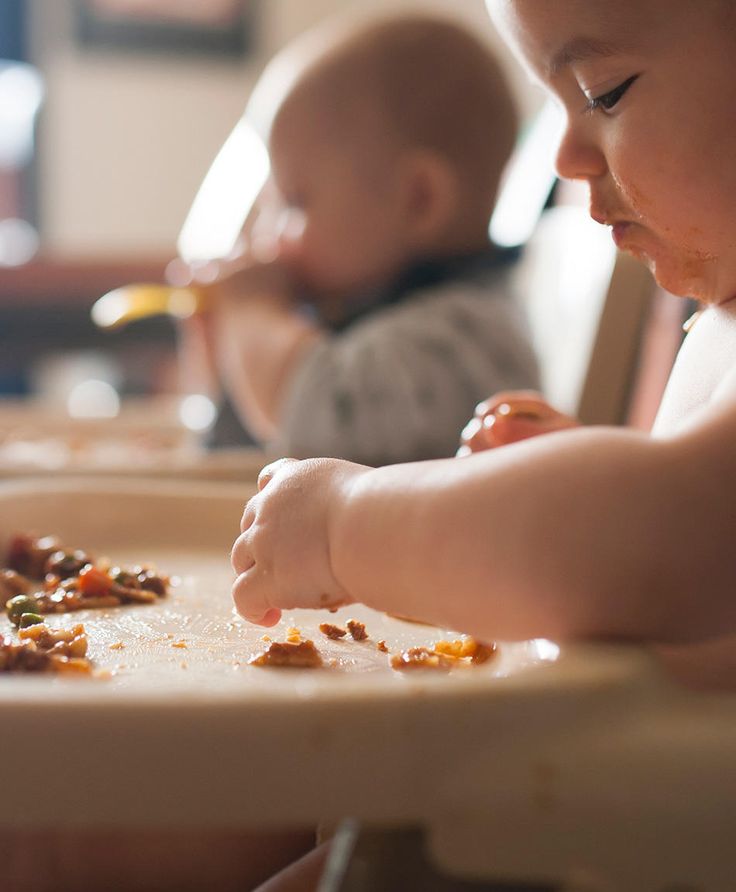 (Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.)
(Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.) - After your baby is eating individual foods, it's OK to offer a puréed mix of two foods. As babies get older, they will learn to eat a greater variety of tastes and textures.
- If you use prepared baby food in jars, spoon some of the food into a bowl to feed your baby. Do not feed your baby right from the jar — bacteria from the baby's mouth can contaminate the remaining food. If you refrigerate opened jars of baby food, it's best to throw away anything not eaten within a day or two.
- Around 6 months of age is a good time for your baby to try a cup. You might need to try a few cups to find one that works for your child. Use water at first to avoid messy clean-ups. Do not give juice to infants younger than 12 months.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
at what age to introduce with breastfeeding and artificial feeding, how to cook at home
When to introduce the first complementary foods
Today there are no hard and fast rules and deadlines for the introduction of complementary foods. Parents should first of all focus on the signs of the child's readiness for complementary foods. Here is what pediatrician, candidate of medical sciences Anna Levadnaya advises to pay attention to , the author of a blog about pediatrics and not only on Instagram.
The child holds his head confidently.
- Can sit with support, meaning it can be placed in a high chair or placed on an adult's lap.
- The kid shows an active food interest: he is interested in food, watches what adults eat.
- Breastfeeding or formula feeding is well organized and does not cause any problems.
- The child can put his hand to his mouth, puts various objects in his mouth, such as toys. In this case, the baby chews or champs.

As a rule, all these signs appear in the period from 5.5 to 7.5 - 8 months, but most often around 6 months. All babies develop differently, and one baby may be ready to try his first puree or porridge as early as 5 months, and another at 6 or 7 months will refuse the new food you offer.
What complementary foods a child needs in the first months
And here again, there are no strict recommendations and rules. On the contrary, many experts agree that it doesn’t matter which dish you start complementary foods with, the most important thing is to provide the right nutritional interest. In this case, the child will eat all the foods that you offer him.
In Russia, it is customary to focus on the following scheme for the introduction of complementary foods. The first to introduce cereals or vegetables, depending on the weight of the child. As a rule, vegetables are first, then cereals, then meat, then fruits, then cottage cheese. In some US states, for example, on the contrary, it is recommended to start complementary foods with meat. But the general message of the recommendations is to maximize the variety of tastes and textures in the first year of life. From vegetables in the first months, you can offer zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli, pumpkin, carrots, potatoes. Of the cereals, gluten-free are the first to be introduced: rice, buckwheat, corn. From fruits - apple, pear, banana, peach and others. From meat - it is better to start with a rabbit, turkey, chicken, veal.
But the general message of the recommendations is to maximize the variety of tastes and textures in the first year of life. From vegetables in the first months, you can offer zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli, pumpkin, carrots, potatoes. Of the cereals, gluten-free are the first to be introduced: rice, buckwheat, corn. From fruits - apple, pear, banana, peach and others. From meat - it is better to start with a rabbit, turkey, chicken, veal.
— At the very beginning, complementary foods should be puree-like, says Anna Levadnaya. - It is better to give preference to monocomponent purees so that the baby learns to distinguish between different tastes. As you introduce vegetables and cereals, add butter and vegetable oils to them. If there are no problems with the introduction of complementary foods, it is recommended to use the maximum variety of food textures as early as possible. Starting from 7-8 months, the baby can and should be introduced to semi-solid foods. This is very important for the correct formation of food interest, and for the development of chewing skills, the correct functioning of the tongue, the development of speech, the “tweezer” grip, and the coordination of the work of hands, mouth and eyes. If you do not introduce semi-solid food in time, then there may be problems with the introduction of already solid food, and after a year the child will refuse it completely. Therefore, starting from 7-8 months, the baby can be offered mashed or pureed food, such as a banana. From 8-9months, give the so-called "finger" food: cut into pieces soft fruits and vegetables, such as boiled carrots, potatoes, and put in front of the baby. By one year, the child is ready to eat solid food from the common table.
If there are no problems with the introduction of complementary foods, it is recommended to use the maximum variety of food textures as early as possible. Starting from 7-8 months, the baby can and should be introduced to semi-solid foods. This is very important for the correct formation of food interest, and for the development of chewing skills, the correct functioning of the tongue, the development of speech, the “tweezer” grip, and the coordination of the work of hands, mouth and eyes. If you do not introduce semi-solid food in time, then there may be problems with the introduction of already solid food, and after a year the child will refuse it completely. Therefore, starting from 7-8 months, the baby can be offered mashed or pureed food, such as a banana. From 8-9months, give the so-called "finger" food: cut into pieces soft fruits and vegetables, such as boiled carrots, potatoes, and put in front of the baby. By one year, the child is ready to eat solid food from the common table.
How to properly feed your baby
It used to be that complementary foods should be introduced very carefully and gradually, always in the morning, many parents still introduce each product over a week or two, very slowly increasing portions.
- These recommendations are relevant, perhaps, only for the very beginning of complementary foods, the first two or three weeks, - says Anna Levadnaya. - In general, in children without food allergies, the most rapid and varied expansion of the diet is recommended. That is, a new product can be safely introduced every 2-3 days. If you need to breed complementary foods, for example, baby cereals, then it is better to do this with breast milk or formula, and not with cow's. Whole milk is not recommended for children under one year of age.
Also with the introduction of complementary foods, offer your child water, either bottled for children or boiled. It is recommended to offer water from a cup so that the child learns to drink, and not from a drinking bowl, a bottle with a tube or a pacifier.
Monitor the child's well-being, in case of any changes that worry you, consult a doctor.
Complementary foods with natural and artificial feeding
Mothers often wonder if there are differences in the introduction of complementary foods with natural and artificial feeding. In both cases, the recommendations are the same: it is recommended to focus on food interest, signs of the child's readiness for the introduction of complementary foods. Usually, as we have already noted, the baby receives only breast milk or an adapted milk formula up to 6 months. With exclusive breastfeeding, it is not recommended to supplement the baby with water, especially in the first month, when lactation is established. Bottle-fed babies can be offered water.
For both breastfeeding and artificial feeding, it is recommended to offer the baby a new food before feeding, and then supplement it with breast milk or formula.
— It is desirable to keep breast milk or formula in the diet of a child up to a year, — says Anna Levadnaya.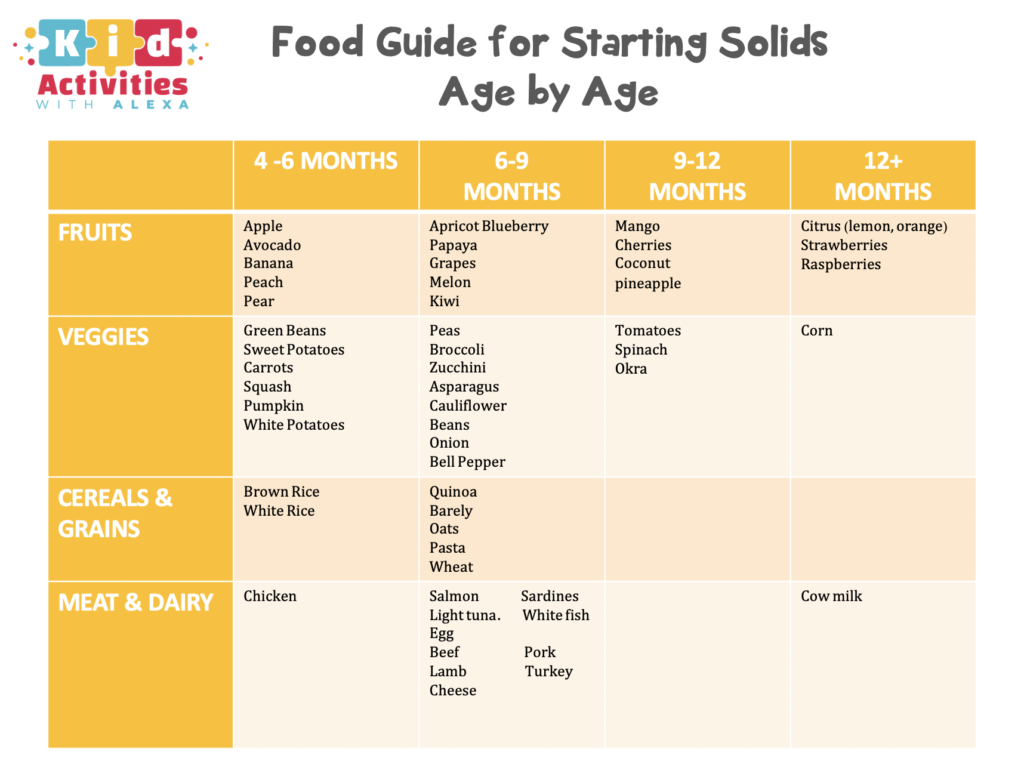 - After a year, it is better to leave the bottle completely, gradually reducing the amount of the mixture. After a year, preferably closer to one and a half, cow's milk can be offered if the child is not allergic to its protein. Breastfeeding can be continued as long as it brings pleasure to mother and child.
- After a year, it is better to leave the bottle completely, gradually reducing the amount of the mixture. After a year, preferably closer to one and a half, cow's milk can be offered if the child is not allergic to its protein. Breastfeeding can be continued as long as it brings pleasure to mother and child.
How to prepare the first complementary foods
Give canned puree and baby cereals or cook it yourself? This question worries many mothers.
“In fact, there is no universal advice here,” says Anna Levadnaya. - Do what is comfortable and best for you. But when choosing food, remember that you must be confident in the products you buy. If you are not sure, buy canned purees, industrial baby cereals. The main advantage of any industrial baby food is that the products from which it is made are tested for the content of pesticides, heavy metals, nitrates and other harmful substances (labeled up to 3 years). If you're cooking yourself, cook with either seasonal fruits and vegetables or frozen ones.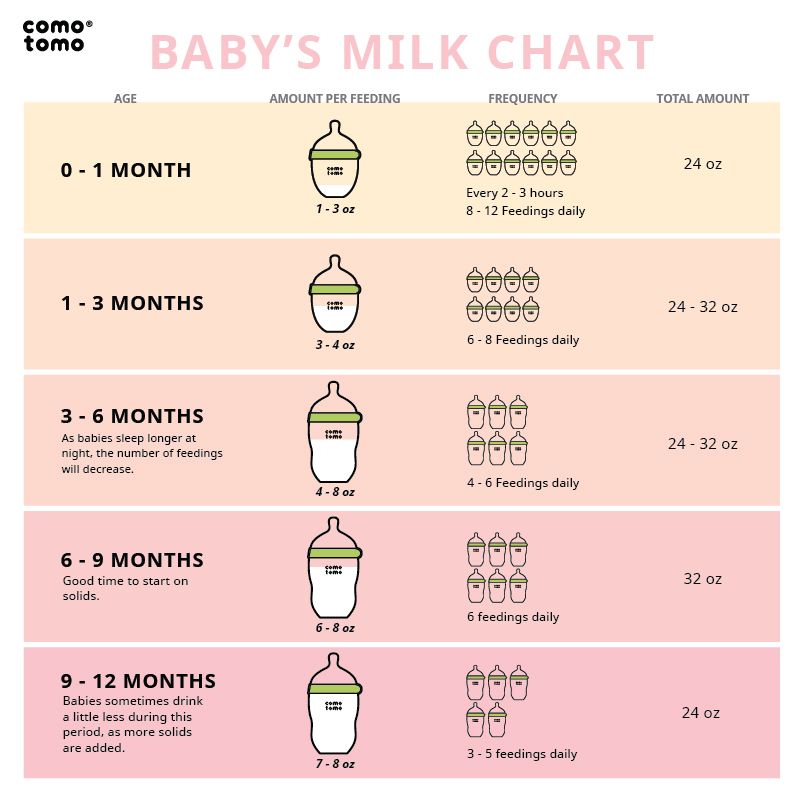 It is best to do it for a couple - this is how most vitamins and minerals are preserved. The advantage of homemade products is that we can provide the child with a different consistency, which is very important. But in any case, choose what is more convenient for you, more comfortable, including financially. The main principle is to provide the baby with a varied diet. Alternate between different foods.
It is best to do it for a couple - this is how most vitamins and minerals are preserved. The advantage of homemade products is that we can provide the child with a different consistency, which is very important. But in any case, choose what is more convenient for you, more comfortable, including financially. The main principle is to provide the baby with a varied diet. Alternate between different foods.
If you decide to cook on your own, follow our tips on how to prepare puree and porridge for the first feeding.
Vegetable puree
Zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower, carrots, pumpkin are suitable for the first feeding. The vegetable should be fresh, without dark spots. We clean it from the peel, boil or steam it. Then we pass through a blender. The vegetable should be quite soft to get the most uniform consistency (if necessary, you can add a little boiled water). If it did not work out, then additionally the mass can be rubbed through a fine sieve.
Fruit puree
To prepare fruit puree for your baby, such as apple or pear puree, fruit must first be baked in the oven, then peeled and passed through a blender or sieve to obtain the most homogeneous consistency. Choose fresh, ripe, seasonal fruits.
Porridges
Soak cereals (for the first feeding, we remind you, this is rice, buckwheat, corn) for 4-5 hours in warm water. Then dry, for example, in a preheated oven. Next, grind the porridge in a coffee grinder into the consistency of flour and cook in water until cooked, this is about 5 minutes. For one tablespoon you need about 50-70 ml of water.
The main mistakes of parents
In fact, there is nothing complicated in the management of complementary foods. Use the guidelines, common sense, and have fun introducing your little one to new foods. With Anna Levadna, we have compiled a list of mistakes that parents often make when introducing complementary foods. Try to avoid them.
In a hurry
It often happens that a child refuses the first complementary foods. Most often, this suggests that the baby is simply not ready for it yet. And the parents, by hook or by crook, are trying to feed him mashed potatoes or porridge. Under no circumstances should you force-feed your baby. It is worth postponing the introduction of complementary foods for one to two weeks.
Most often, this suggests that the baby is simply not ready for it yet. And the parents, by hook or by crook, are trying to feed him mashed potatoes or porridge. Under no circumstances should you force-feed your baby. It is worth postponing the introduction of complementary foods for one to two weeks.
Give mashed food from a bottle
Do not do this, because the child must learn to eat liquid and solid food separately.
Add salt or sugar
These components are not recommended to be introduced into complementary foods for a child under one year old, sugar is better up to three years old.
Only the bottle is used too long
For example, in addition to formula, if the child is on IV, they give water, compote and other drinks from the bottle. The danger is that long-term use of the bottle can reduce the child's desire to eat complementary foods and malocclusion, as well as lead to speech delay and swallowing problems.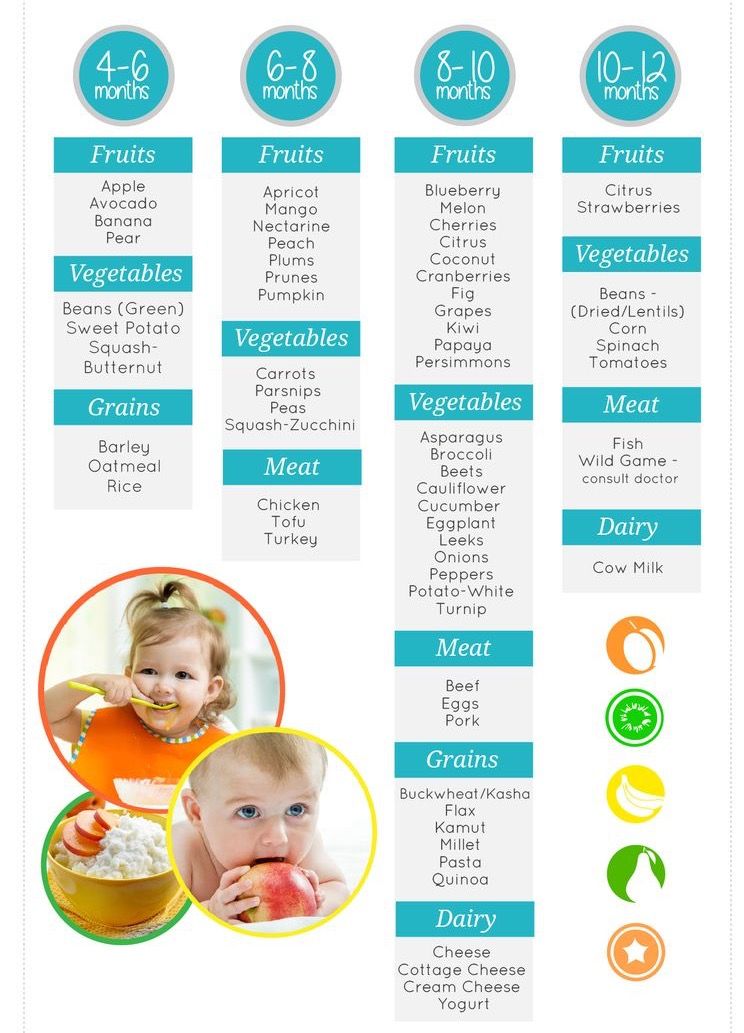 From 6-8 months, offer your baby to drink from a cup.
From 6-8 months, offer your baby to drink from a cup.
Children are not allowed to play with food
But freedom in dealing with food, the desire to take a spoon, move it around the plate and on the table, touch the food, knead it, and so on, is the key to a successful introduction of complementary foods.
when and how to start the first feeding of a child?
Weaning is the gradual transition of an infant from mother's milk or formula to more solid foods. Despite its naturalness, this process has some nuances. We will tell you when and where to start complementary foods so that this stage is as comfortable as possible for the baby.
Children develop in different ways: some are faster and some are slower. Therefore, at the beginning of complementary feeding of an infant, first of all, it is worth focusing not on his age, but on the presence of a number of skills. First of all, there should be food interest: the child usually “announces” this himself, starting to put his hands in his mouth, showing a desire to try food from his mother’s plate. It is also important that the baby confidently holds his head and sits, albeit with support, on the parent's lap or in a special chair. Of course, you need to make a decision about the start of complementary foods together with your doctor.
It is also important that the baby confidently holds his head and sits, albeit with support, on the parent's lap or in a special chair. Of course, you need to make a decision about the start of complementary foods together with your doctor.
When to start complementary foods? The "golden window" is an interval of four to six months. If you believe the statistics, most often the start of complementary foods for a baby falls on the age of five to six months. We emphasize once again that everything is individual, but it is also not recommended to delay the introduction of complementary foods too much. Starting complementary foods after seven months is fraught with a delay in the development of habits for eating thicker and denser foods, and then chewing skills. In addition, late feeding can negatively affect the formation of taste sensations and lead to a lack of a number of substances in the body: iron, zinc, calcium, copper, vitamin D and others. If closer to seven months the child does not have the skills necessary to start the first complementary foods, this must be reported to the pediatrician.
Where to start complementary foods
Of course, not every food is suitable for this. You need to move on to solid food gradually, and milk porridges (especially buckwheat, rice and corn) and vegetable purees are optimal as a “link”. This is stated in the National program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation, approved by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia (hereinafter referred to as the National Program) [1].
It is important to remember that the first complementary foods should be monocomponent, that is, contain only one product. Conventionally: mashed potatoes to start complementary foods can be squash or potato, but not a mix of these vegetables. By the way, babies with allergies are recommended mashed white or green vegetables. Complementary foods are better to start with microdoses, literally from a quarter of a teaspoon. Every day the volume should be increased. For convenience, you can keep a food diary and note all the dynamics in it.
The National Program recommends starting complementary foods with vegetables or cereals. Usually cereals are administered first if the child is underweight. After the baby is a little accustomed to porridge, you can add vegetables to his diet. If complementary foods begin with vegetables, the next, respectively, will be porridge. After two or three weeks, you can try giving your baby fruit puree made from apples, pears, or peaches. Later, you can add berry purees to the diet.
After the baby has become accustomed to mono-component complementary foods, two-component complementary foods can be introduced. For example, it can be porridge with fruit or vegetable puree. An important nuance: both components must first be “tested” separately to make sure that the child tolerates them well. You can not immediately feed the baby rice porridge with broccoli: first he needs to try rice, and the next time - broccoli. There is no need to draw hasty conclusions: for each new type of complementary foods, doctors advise taking five to ten days.
The next stage is the transition to semi-solid food. Of course, not all products are suitable here either. Cream soup, chopped pieces of boiled vegetables, meat and fish will be optimal. By the way, about meat - it should also be added carefully to the baby's diet, starting with monocomponent meat purees. At first, it is recommended to feed the baby with mashed rabbit and turkey and only then switch to beef, veal and chicken. It's the same with juices: we start with a clarified mono-fruit, apple or pear drink, and then you can expand the menu to carrot, pumpkin, plum, apricot and peach. It is worth remembering that the last three have a slight laxative effect. Closer to the year, you can try to give the child solid food - for example, small meatballs or the same cereals, only with unground cereals [2].
An equally important product in the complementary food menu is cottage cheese. Natural curds contain calcium and phosphorus, which positively affect the functioning of the heart. In addition, the calcium contained in the cottage cheese strengthens the bones and teeth of the baby, which is very important at a “tender” age. The composition of cottage cheese also includes albumin, a protein that produces antibodies that positively affect the development of the nervous system. In addition, the use of cottage cheese helps to normalize the work of the digestive tract and liver. Experts advise introducing curd complementary foods after vegetable puree and canned meat. It is worth starting with a small dose - half a teaspoon - once a day. It is important to remember that cottage cheese is allowed in the diet of babies only from six to eight months. It is not recommended to give such a product before, because the protein contained in it puts a strain on the kidneys.
In addition, the calcium contained in the cottage cheese strengthens the bones and teeth of the baby, which is very important at a “tender” age. The composition of cottage cheese also includes albumin, a protein that produces antibodies that positively affect the development of the nervous system. In addition, the use of cottage cheese helps to normalize the work of the digestive tract and liver. Experts advise introducing curd complementary foods after vegetable puree and canned meat. It is worth starting with a small dose - half a teaspoon - once a day. It is important to remember that cottage cheese is allowed in the diet of babies only from six to eight months. It is not recommended to give such a product before, because the protein contained in it puts a strain on the kidneys.
A few tips for mothers: how to introduce complementary foods without stress for the baby
If the baby does not like the product, do not categorically refuse it. It is better to remove it for four to eight weeks and then try to introduce it into the diet again, a little bit, like the first time.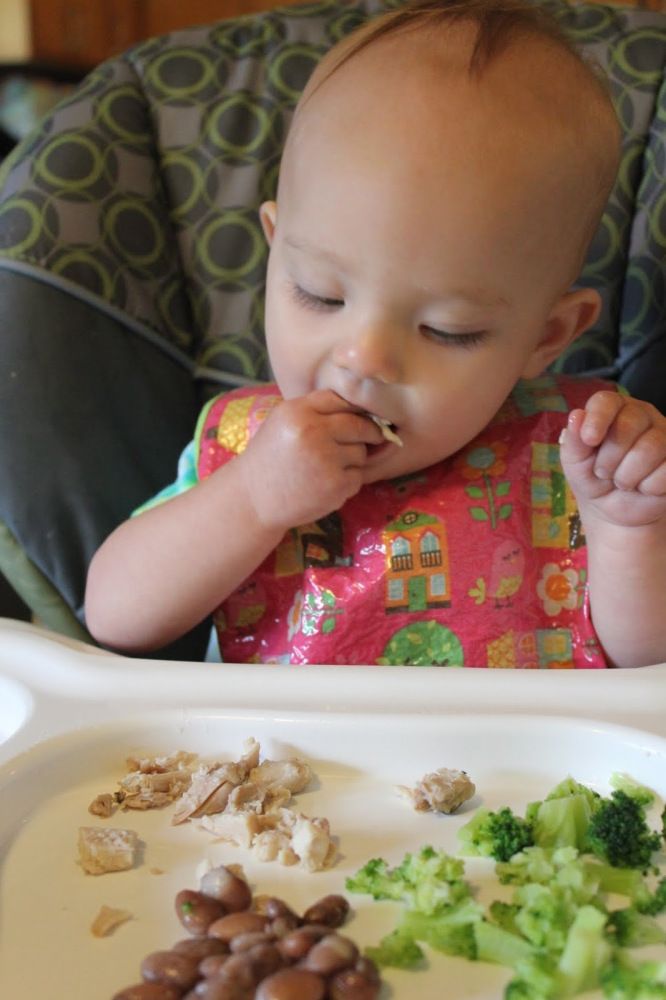 It is likely that the second experience will be successful: the main thing is to carefully monitor the reaction of the baby's body.
It is likely that the second experience will be successful: the main thing is to carefully monitor the reaction of the baby's body.
Many young mothers are also faced with a choice: cook it yourself or buy canned food? Making your own meals for your baby is usually cheaper, but it can be quite a hassle. First, you need to carefully choose the ingredients: store-bought vegetables can contain nitrates. Secondly, it is better not to cook with a margin: it is difficult to maintain sterility in the home kitchen, so it is undesirable to store baby food. It is best to cook before eating so that the food is fresh. When buying mashed potatoes in the store, you should pay attention to the expiration date and compliance with storage conditions [3].
As for cereals to start feeding a child, they can be divided into dairy-free (recommended for children with lactase deficiency and allergies) and dairy. The latter, in turn, are based on an adapted milk formula, goat's or cow's milk. Compared to cow's, goat's milk is closer to human breast milk in terms of protein and fat composition.
What's more, it contains a high dose of A2 protein (β-casein), which is easy to digest and improves the intestinal microflora. But the complex protein α-s1-casein, which is found in cow's milk, is practically absent in goat's milk. That is why goat milk baby food is digested five to six times faster. Another important feature of it is small evenly distributed fat globules. They are rich in medium chain triglycerides, which are quickly absorbed in the intestines and provide the baby with energy [4].
In order for the baby to easily switch to “adult food”, it is very important to start complementary foods correctly. How to start depends on the individual characteristics of the baby's body. It is important for mothers to know that industrial complementary foods are safe and contain all the necessary components for the normal development of the baby. The introduction of complementary foods is clearly not a question where you need to listen to the advice of friends and relatives.