Taurine in baby food
The role of taurine in infant nutrition
Review
. 1998;442:463-76.
doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-0117-0_56.
R W Chesney 1 , R A Helms, M Christensen, A M Budreau, X Han, J A Sturman
Affiliations
Affiliation
- 1 University of Tennessee College of Medicine, Memphis, USA.
- PMID: 9635063
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4899-0117-0_56
Review
R W Chesney et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998.
. 1998;442:463-76.
doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-0117-0_56.
Authors
R W Chesney 1 , R A Helms, M Christensen, A M Budreau, X Han, J A Sturman
Affiliation
- 1 University of Tennessee College of Medicine, Memphis, USA.
- PMID: 9635063
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4899-0117-0_56
Abstract
The importance of taurine in the diet of pre-term and term infants has not always been clearly understood and is a topic of interest to students of infant nutrition. Recent evidence indicates that it should be considered one of the "conditionally essential" amino acids in infant nutrition. Plasma values for taurine will fall if infants are fed a taurine-free formula or do not have taurine provided in the TPN solution. Urine taurine values also fall, which is indicative of an attempt by the kidney to conserve taurine. The very-low-birth-weight infant, for a variety of reasons involving the maturation of tubular transport function, cannot maximally conserve taurine by enhancing renal reabsorption and, hence, is potentially at greater risk for taurine depletion than larger pre-term or term infants, and certainly more than older children who have taurine in their diet. Taurine has an important role in fat absorption in pre-term and possibly term infants and in children with cystic fibrosis. Because taurine-conjugated bile acids are better emulsifiers of fat than glycine-conjugated bile acids, the dietary (or TPN) intake has a direct influence on absorption of lipids.
Recent evidence indicates that it should be considered one of the "conditionally essential" amino acids in infant nutrition. Plasma values for taurine will fall if infants are fed a taurine-free formula or do not have taurine provided in the TPN solution. Urine taurine values also fall, which is indicative of an attempt by the kidney to conserve taurine. The very-low-birth-weight infant, for a variety of reasons involving the maturation of tubular transport function, cannot maximally conserve taurine by enhancing renal reabsorption and, hence, is potentially at greater risk for taurine depletion than larger pre-term or term infants, and certainly more than older children who have taurine in their diet. Taurine has an important role in fat absorption in pre-term and possibly term infants and in children with cystic fibrosis. Because taurine-conjugated bile acids are better emulsifiers of fat than glycine-conjugated bile acids, the dietary (or TPN) intake has a direct influence on absorption of lipids. Taurine supplementation of formulas or TPN solutions could potentially serve to minimize the brain phospholipid fatty acid composition differences between formula-fed and human milk-fed infants. Taurine appears to have a role in infants, children, and even adults receiving most (> 75%) of their calories from TPN solutions in the prevention of granulation of the retina and electroencephalographic changes. Taurine has also been reported to improve maturation of auditory-evoked responses in pre-term infants, although this point is not fully established. Clearly, taurine is an important osmolyte in the brain and the renal medulla. At these locations, it is a primary factor in the cell volume regulatory process, in which brain or renal cells swell or shrink in response to osmolar changes, but return to their previous volume according to the uptake or release of taurine. While there is a dearth of clinical studies in man concerning this volume regulatory response, studies in cats, rats, and dog kidney cells indicate the protective role of taurine in hyperosmolar stress.
Taurine supplementation of formulas or TPN solutions could potentially serve to minimize the brain phospholipid fatty acid composition differences between formula-fed and human milk-fed infants. Taurine appears to have a role in infants, children, and even adults receiving most (> 75%) of their calories from TPN solutions in the prevention of granulation of the retina and electroencephalographic changes. Taurine has also been reported to improve maturation of auditory-evoked responses in pre-term infants, although this point is not fully established. Clearly, taurine is an important osmolyte in the brain and the renal medulla. At these locations, it is a primary factor in the cell volume regulatory process, in which brain or renal cells swell or shrink in response to osmolar changes, but return to their previous volume according to the uptake or release of taurine. While there is a dearth of clinical studies in man concerning this volume regulatory response, studies in cats, rats, and dog kidney cells indicate the protective role of taurine in hyperosmolar stress. The infant depleted of taurine may not be able to respond to hyper- or hyponatremic stress without massive changes in neuronal volume, which has obvious clinical significance. The fact that the brain content of taurine is very high at birth and falls with maturation may be a protective feature, or compensation for renal immaturity Defining an amino acid as "conditionally essential" requires that deficiency result in a clinical consequence or consequences which can be reversed by supplementation. In pre-term and term infants, taurine insufficiency results in impaired fat absorption, bile acid secretion, retinal function, and hepatic function, all of which can be reversed by taurine supplementation. Therefore, this small beta-amino acid, taurine, is indeed conditionally essential.
The infant depleted of taurine may not be able to respond to hyper- or hyponatremic stress without massive changes in neuronal volume, which has obvious clinical significance. The fact that the brain content of taurine is very high at birth and falls with maturation may be a protective feature, or compensation for renal immaturity Defining an amino acid as "conditionally essential" requires that deficiency result in a clinical consequence or consequences which can be reversed by supplementation. In pre-term and term infants, taurine insufficiency results in impaired fat absorption, bile acid secretion, retinal function, and hepatic function, all of which can be reversed by taurine supplementation. Therefore, this small beta-amino acid, taurine, is indeed conditionally essential.
Similar articles
-
Taurine in infant nutrition.
Karan S. Karan S.
 Indian J Pediatr. 1991 May-Jun;58(3):311-6. doi: 10.1007/BF02754955. Indian J Pediatr. 1991. PMID: 1937640 Review.
Indian J Pediatr. 1991 May-Jun;58(3):311-6. doi: 10.1007/BF02754955. Indian J Pediatr. 1991. PMID: 1937640 Review. -
Taurine depletion in very low birth weight infants receiving prolonged total parenteral nutrition: role of renal immaturity.
Zelikovic I, Chesney RW, Friedman AL, Ahlfors CE. Zelikovic I, et al. J Pediatr. 1990 Feb;116(2):301-6. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82898-7. J Pediatr. 1990. PMID: 2105387
-
Influence of dietary taurine on vitamin D absorption.
Zamboni G, Piemonte G, Bolner A, Antoniazzi F, Dall'Agnola A, Messner H, Gambaro G, Tatò L. Zamboni G, et al. Acta Paediatr. 1993 Oct;82(10):811-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1993.tb17616.x. Acta Paediatr. 1993. PMID: 8241636
-
Effect of taurine supplementation on growth and development in preterm or low birth weight infants.

Verner A, Craig S, McGuire W. Verner A, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Oct 17;2007(4):CD006072. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006072.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. PMID: 17943882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taurine in pediatric nutrition: review and update.
Gaull GE. Gaull GE. Pediatrics. 1989 Mar;83(3):433-42. Pediatrics. 1989. PMID: 2645571 Review.
See all similar articles
Cited by
-
Integration of metagenomic and metabolomic insights into the effects of microcystin-LR on intestinal microbiota of Litopenaeus vannamei.
Duan Y, Xing Y, Zeng S, Dan X, Mo Z, Zhang J, Li Y. Duan Y, et al. Front Microbiol.
 2022 Sep 23;13:994188. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.994188. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36212851 Free PMC article.
2022 Sep 23;13:994188. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.994188. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36212851 Free PMC article. -
Taurine: A Maternally Derived Nutrient Linking Mother and Offspring.
Tochitani S. Tochitani S. Metabolites. 2022 Mar 5;12(3):228. doi: 10.3390/metabo12030228. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35323671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Taurine in Mitochondria Health: More Than Just an Antioxidant.
Jong CJ, Sandal P, Schaffer SW. Jong CJ, et al. Molecules. 2021 Aug 13;26(16):4913. doi: 10.3390/molecules26164913. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34443494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactive Compounds in Infant Formula and Their Effects on Infant Nutrition and Health: A Systematic Literature Review.

Almeida CC, Mendonça Pereira BF, Leandro KC, Costa MP, Spisso BF, Conte-Junior CA. Almeida CC, et al. Int J Food Sci. 2021 May 14;2021:8850080. doi: 10.1155/2021/8850080. eCollection 2021. Int J Food Sci. 2021. PMID: 34095293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taurine Increases Zinc Preconditioning-Induced Prevention of Nitrosative Stress, Metabolic Alterations, and Motor Deficits in Young Rats following Intrauterine Ischemia.
Gonzalez-Vazquez A, Aguilar-Peralta AK, Tomas-Sanchez C, Blanco-Alvarez VM, Martinez-Fong D, Gonzalez-Barrios JA, Treviño S, Millán-Perez Peña L, Alatriste V, Soto-Rodriguez G, Brambila E, Leon-Chavez BA. Gonzalez-Vazquez A, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 May 6;2021:6696538. doi: 10.1155/2021/6696538. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34040692 Free PMC article.
See all "Cited by" articles
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grant support
- DK 37223/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD-11129/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10-HD-31326/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
etc
Added Choline, Taurine and Nucleotides in Formula Products – Are They As Good As They Claimed?
Added Choline, Taurine and Nucleotides in Formula Products – Are They As Good As They Claimed?
Reported by Ms. Melissa LIU, Scientific Officer,
Melissa LIU, Scientific Officer,
Risk Assessment Section,
Centre for Food Safety
In the previous issues, we have discussed the micronutrients, macronutrients and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in formula products and foods for infants and young children (0-36 months). In this issue, we will look at some other substances added to these products and study whether they could bring additional health benefit to infants and young children.
Addition of Choline, Taurine and Nucleotides to Formula Products
As explained in the previous issues, the Codex Alimentarius Commission (Codex) has required formula products for infants and young children to contain a number of nutrients in prescribed amounts to ensure they meet the normal nutritional requirements of infants and young children. However, on top of these essential compositions, manufacturers often add other substances to formula products, claiming that they bring additional nutritional benefit on various aspects. Choline, taurine and nucleotides are some of the examples.
Choline, taurine and nucleotides are some of the examples.
Benefits of choline, taurine and nucleotides added to formula products still lack international consensus
Choline
Choline plays a role in the structural integrity of cell membranes, as well as in lipid and cholesterol transport and metabolism. Concerning its function in brain development, information mainly came from animal studies. As for claims related to the function of dietary choline intake on eye development of infants, support of such claims from internationally recognised scientific evidence is still pending. The Codex considers choline as an essential composition for infant formula but not for follow-up formula. Egg yolk, meat and nuts are good sources of choline.
Taurine
Taurine is a major constituent of bile salts and is abundant in foetal and neonatal human brain. It plays an important role in the absorption of fat and fat soluble vitamins and maintenance of normal liver functions. Although taurine is commonly added to formula products because of the anticipated benefits on visual, auditory and intestinal development of infants, relevant evidence from human studies is lacking. The Codex considers mandatory addition of taurine is not necessary in formula products. Taurine is available from human breastmilk, and also in seafood and meat.
Although taurine is commonly added to formula products because of the anticipated benefits on visual, auditory and intestinal development of infants, relevant evidence from human studies is lacking. The Codex considers mandatory addition of taurine is not necessary in formula products. Taurine is available from human breastmilk, and also in seafood and meat.
Nucleotides
Nucleotides are core structural units of DNA and RNA. They are involved in protein synthesis and metabolic regulatory processes. Nucleotides are added to formula products to mimic breastmilk with the anticipated benefits of enhancing immune functions and promoting growth of infants. However, evidences of beneficial effects from nucleotide supplementation of infant formulae are not conclusive. The Codex does not require the addition of nucleotides in formula products. In fact, nucleotides could be produced in the human body and are widely available in foods.
Should I Give My Child Products With Added "Nutritive" Substances?
At present, the benefits from adding a number of substances voluntarily by manufacturers to formula products still lack international consensus. In the case of choline, taurine and nucleotides, although claims on their functions or health benefits may have been made on some formula products, only a few have been accepted in individual overseas jurisdictions, notably Singapore . These claims include those related to choline and overall mental function, taurine and overall mental and physical development, nucleotides and body's natural defence or normal cell function. Nevertheless, similar claims have not been permitted in other jurisdictions such as the European Union. Claims on choline, taurine and nucleotides made on formula products for infants and young children still need more scientific support, in particular from human studies.
In the case of choline, taurine and nucleotides, although claims on their functions or health benefits may have been made on some formula products, only a few have been accepted in individual overseas jurisdictions, notably Singapore . These claims include those related to choline and overall mental function, taurine and overall mental and physical development, nucleotides and body's natural defence or normal cell function. Nevertheless, similar claims have not been permitted in other jurisdictions such as the European Union. Claims on choline, taurine and nucleotides made on formula products for infants and young children still need more scientific support, in particular from human studies.
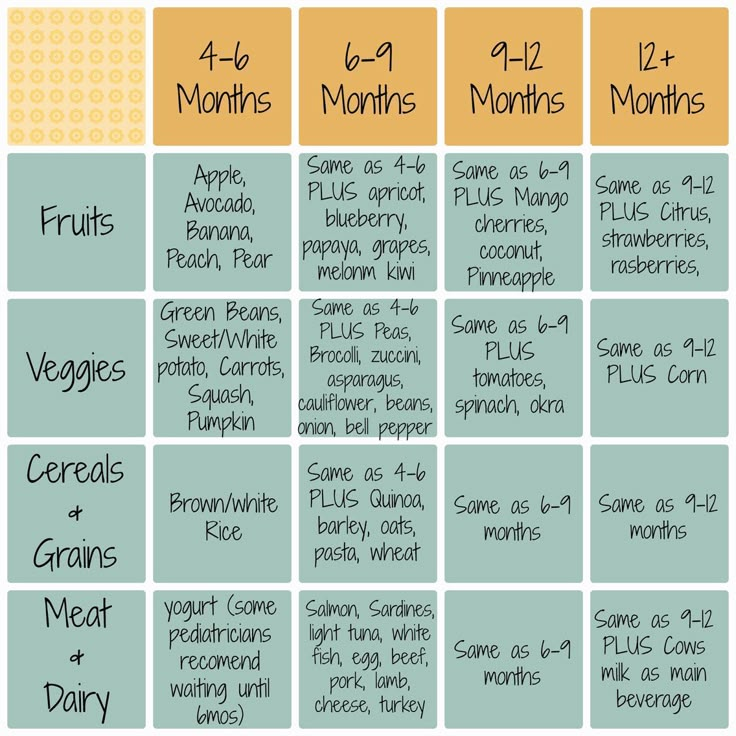
All in all, there is no international consensus that formula products with additional "nutritive" substances provide added benefits to infants and children. In fact, normal infants below six months old could usually obtain adequate nutrients from breastmilk or infant formulae meeting the Codex basic compositional requirements. For older infants and young children who have started weaning, maintaining a balanced diet and consuming a variety of foods are crucial to obtaining different types of nutrients to support their growth and development.
For older infants and young children who have started weaning, maintaining a balanced diet and consuming a variety of foods are crucial to obtaining different types of nutrients to support their growth and development.
Roskachestvo investigated baby food: what parents should be afraid of
Komsomolskaya Pravda
The experts found out how true they are
The results of the study showed that the products of all brands are safe for the health of babies Photo: Evgenia GUSEVA
The World Health Organization constantly reminds that there is nothing better for a child than mother's milk. Pediatricians talk about the same. But it often happens that, for one reason or another, mothers cannot feed their baby and are forced to switch to artificial mixtures.
According to the Research Institute of Baby Nutrition, Federal Research Center for Nutrition, Biotechnology and Food Safety, today in the country 40% of children are bottle-fed . Are formulas a potential hazard to children? To answer these and other questions, Roskachestvo experts examined 21 trademarks of dry mixes from Belarus (1), Germany (2), Denmark (3), Ireland (1), Spain (2), the Netherlands (4), New Zealand (1), Russia (4), Finland (1), Switzerland (1) and Estonia (1).
Are formulas a potential hazard to children? To answer these and other questions, Roskachestvo experts examined 21 trademarks of dry mixes from Belarus (1), Germany (2), Denmark (3), Ireland (1), Spain (2), the Netherlands (4), New Zealand (1), Russia (4), Finland (1), Switzerland (1) and Estonia (1).
Only one is the best
Blends, as well as other goods, were not only subject to GOST requirements, but increased requirements of Roskachestvo. They corresponded only to the Belarusian trademark "Bellakt Optimum 1".
But this does not mean that other mixtures are bad. nine0004
No safety violations
The study found no safety excesses and no GMOs.
Roskachestvo experts tested breast milk substitutes for microbiological safety, for the presence of preservatives and antibiotics. The results of the study showed that the products of all brands are safe for the health of babies and do not contain dangerous microorganisms (including salmonella), mold and yeast, preservatives and antibiotics, lead, mercury, cadmium and arsenic. nine0004
nine0004
Problems - only in labeling
True, it turned out that the content of vitamins and nutrients does not always coincide with the information indicated on the label. At the same time, most mixtures fit into the range necessary for the full nutrition of a healthy child.
- Nevertheless, incorrect information creates inconvenience when choosing baby food, - says Elena Saratseva, deputy head of Roskachestvo. - So, mixtures that claim to contain more calcium, or vitamin C, may not actually turn out to be so. This problem may be related to the methods of "dry" mixing in production - this method of manufacture does not allow achieving uniformity of the composition. nine0004
Top 5 questions about infant formula
1. Can formula be compared to breast milk?
All studies are unambiguous: it is impossible to completely reproduce the composition of breast milk. Firstly, its composition, balance is constantly changing depending on the health of the child, adjusting to the body of a particular little person. The composition of milk changes even depending on the time of day (for example, at night they “give” fatter). And, of course, the age of the child. Unfortunately, none of even the best mixture can replace breast milk 100 percent. nine0004
The composition of milk changes even depending on the time of day (for example, at night they “give” fatter). And, of course, the age of the child. Unfortunately, none of even the best mixture can replace breast milk 100 percent. nine0004
But each manufacturer of mixtures tries as much as possible to bring the composition closer to the properties of human milk. The metabolism, digestion of children, the balance of acids, vitamins and nutrients in milk are constantly being studied.
2. Why is milk fat replaced with vegetable oils?
- To improve lipid metabolism, milk fat is partially or completely replaced with vegetable oils (corn, palm, rapeseed, soybean, coconut, sunflower) containing polyunsaturated fatty acids essential for the child's body, - clarifies the head of the department of the Research Institute of Baby Nutrition of the branch of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "Federal Research Center for Nutrition and Biotechnology" Elena Simonenko.
According to the study, the mass fraction of fat in all studied adaptable mixtures meets the requirements. That is, the fat content is close to the mother's.
3. Is palm oil dangerous in mixtures?
Many manufacturers, in response to consumer fears, are excluding palm oil from infant formulas. In fact, this is not always a good move. nine0004
- The main essential fatty acid of breast milk is palmitic, which is found in the fruits of the oil palm, - explains Executive Director of the Association of Producers and Consumers of Oil and Fat Products Ekaterina Nesterova. - And palm oil is about 47% palmitic acid. Infant milk formulas are made as close as possible in composition to breast milk and palm oil is an important component. Requirements for the indicators of raw materials used in the production of infant formula are established in the technical regulation of the Customs Union "On food safety" (TR CU 021/2011),
4. Why do we need taurine?
Why do we need taurine?
- For the health of the baby, it is important that the mixture is balanced in terms of the content of amino acids, vitamins and minerals, which are an obligatory component of human milk, - notes the head of the department of the Research Institute of Baby Nutrition of the branch of the FGBUN "Federal Research Center for Nutrition and Biotechnology" Elena Simonenko. - Particular attention should be paid to the presence of taurine in the composition - an essential amino acid necessary for the proper development of the child's body. nine0004
Taurine is an important component of women's milk, which affects the formation of the central nervous system, vision and brain of a child, the absorption of minerals (magnesium, sodium, calcium), the digestion and absorption of fats.
Research by Roskachestvo showed that the content of taurine in the products of all brands meets the established requirements.
5. Will casein hurt?
In addition, for adapted mixtures intended for young children, manufacturers adjust the amount of protein in the product. nine0004
nine0004
According to Elena Simonenko, the ratio of whey proteins and casein in mixtures for children from birth to 6 months should be 60:40, for older children - 50:50. At the same time, it is important that the casein proteins in the milk formula are replaced with whey proteins, since the latter are absorbed much faster.
The experts determined that there were no violations in the number and ratio of proteins in any brand.
TIP
Where vitamins and minerals are lacking
Any adapted milk formula, according to the recommendations of the FAO/WHO Codex Alimentarius Commission, must contain at least 11 minerals and 15 vitamins.
According to the results of the study, it turned out that in mixtures of Frisolac (Netherlands), the content of calcium and magnesium in the diluted mixture is below the established norms. Experts found no violations in the content of mineral substances in the products of other brands.
The level of vitamins in adapted mixtures should be higher than in human milk, on average by 15–20%, since their digestibility is lower than from breast milk. The audit showed that the products of nine brands lack vitamin C: Malysh Istra (Russia), Bebi Premium (Denmark), Frisolac Gold (Netherlands), Frisolac (Netherlands), Humana Expert (Germany), Nestogen (Russia), " Nutricia Malyutka (Russia), Nutrilon Premium (Ireland), Similac (Denmark). nine0004
However, this cannot be attributed to violations: due to the volatility of dry components, it is incorrect to say that this indicator was lower due to the fault of the manufacturer. Its content may have decreased during storage.
BTW
Melamine scandal does not threaten us
In 2008, more than 6,000 children in China were poisoned by baby food, in which the content of melamine was 500 times higher than the permissible norm. This chemical is actively used in the production of plastics, varnishes, furniture, etc. It often contaminates various food products, but in small concentrations it does not pose a danger. nine0004
It often contaminates various food products, but in small concentrations it does not pose a danger. nine0004
Melamine was not found in any of the investigated mixtures sold in Russia.
- According to the most common version, the reason for the Chinese melamine crisis was the deliberate addition of melamine to baby food and dairy products, explains Dmitry Makarov, senior researcher at the FGBU VGNKI Rosselkhoznadzor. - This was done in order to increase the protein value of products. The fact is that the generally accepted method for determining protein does not distinguish between protein and melamine, which is probably why the manufacturers hoped that their scam would go unnoticed. However, they did not take into account the fact that in high concentrations, melamine causes the formation of crystals in the urinary tract, which leads to disruption of the kidneys. nine0004
Age category of the site 18+
The online publication (website) is registered by Roskomnadzor, certificate El No. FS77-80505 dated March 15, 2021.
FS77-80505 dated March 15, 2021.
EDITOR-IN-CHIEF OF THE SITE - KANSK VICTOR FYODOROVICH.
THE AUTHOR OF THE MODERN VERSION OF THE EDITION IS SUNGORKIN VLADIMIR NIKOLAEVICH.
Messages and comments from site readers are posted without preliminary editing. The editors reserve the right to remove them from the site or edit them if the specified messages and comments are an abuse of freedom mass media or violation of other requirements of the law. nine0004
JSC "Publishing House "Komsomolskaya Pravda". TIN: 7714037217 PSRN: 1027739295781 127015, Moscow, Novodmitrovskaya d. 2B, Tel. +7 (495) 777-02-82.
Exclusive rights to materials posted on the website www.kp.ru, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation for the Protection of the Results of Intellectual Activity belong to JSC Publishing House Komsomolskaya Pravda, and do not be used by others in any way form without the written permission of the copyright holder. nine0004
nine0004
Acquisition of copyright and communication with the editor: [email protected]
harm or benefit to the child?
Taurine is responsible for the full development of the baby from birth to adulthood. Its presence in the body in the right doses is provided by infant formulas.
Content
- Sulfonic acid taurine
- Health benefits of tauric acid
- Tuarine deficiency
- Enriched infant formula Free sulfonic acid, which is responsible for many biochemical reactions in the body, including the brain, taurine - babies get from mother's milk. The substance taurine in infant formulas is the most important component of nutrition, without which the body will not function normally, and the child will not grow up healthy. nine0004
Interestingly, in full-term infants, taurine synthesis begins only 1.5 months after birth. Before that and in the future, up to a certain age, babies receive wonderful sulfoamic acid from breast milk or baby food.
 And even adults consume taurine only with certain types of foods:
And even adults consume taurine only with certain types of foods: - butter and cheese;
- eggs;
- meat and liver;
- seafood.
Taurine sulfonic acid
To get an idea of taurine, to understand what it is, let's turn to the facts. This sulfoamic acid is the result of a synthesis involving the organic molecules cysteine and methionine.
The resulting compound taurine, in contrast to the parent amino acids, is in the body in an unbound state and is not directly involved in the construction of proteins. Nevertheless, it is found in almost any of our tissues, being responsible for its normal functioning.
Elevated concentrations of taurine are present in the retina, cardiac muscle, skeletal muscles, spinal cord. The content of sulfoamic acid taurine in the brain of an infant is many times greater than the concentration in the brain of an adult. nine0004
The norm for the body is the amount of taurine 1 milligram per 1 kg of weight.
 With lactation and breastfeeding, its content corresponds to 4-5 mg per 100 milliliters. For formula-fed babies, the correct dosage of taurine present in infant formula cannot be overestimated.
With lactation and breastfeeding, its content corresponds to 4-5 mg per 100 milliliters. For formula-fed babies, the correct dosage of taurine present in infant formula cannot be overestimated. Useful properties of tauric acid
Theoretical and practical studies of the "wonderful molecule" taurine have shown how its presence in the body affects the child. Responsible for the normal functioning of most organs and systems, tauric acid provides a general healthy state of a person. Its presence contributes:
- correct functioning of the heart muscle with a normal rhythm of contractions;
- prevention of platelet fusion and blood thinning;
- normal cholesterol content, regulating its level;
- binding and excretion of acids from the gallbladder and ducts;
- uninterrupted metabolism of fats and sugars;
- full-fledged work of the organs of vision.
For babies under the age of three months, taurine is the most valuable active biological substance and is responsible for:
- formation of the brain, retina;
- construction of tissues of the nervous system and the formation of their "zones of responsibility";
- strengthening of immunity;
- enhanced antioxidant protection;
- absorption of mineral trace elements - calcium, potassium, magnesium, etc.
 , as well as fat-soluble vitamins and digestion of fats;
, as well as fat-soluble vitamins and digestion of fats; - regulation of adrenaline levels, reducing anxiety and irritability.
Tuarine deficiency
It is clear that tuarinic acid is a useful substance for humans. But, perhaps, its effect is exaggerated, and the absence is not so scary? After all, both in mother's milk and in the baby's body itself, taurine does not appear immediately, but in industrial baby food it may be completely absent. So is there any harm or benefit from a taurine deficiency?
According to the results of numerous scientific studies, it was found that with a lack of taurine for a growing organism, very serious consequences are possible. It turned out not immediately, because. in the first months and even years of life, the child seems to develop normally. But the consequences can be dire. nine0004
Experts have determined that the risk group sensitive to tauric acid deficiency primarily includes:
- preterm infants;
- newborns with functional and/or morphological immaturity;
- who received hypoxia and CNS damage during childbirth.

And even artificial feeding without taurine or with cow's milk, where the acid is contained in minimal amounts, leads to a decrease in intellectual potential, hearing loss, poor eyesight and diseases of the biliary system. nine0004
An overdose of taurine in the body leads to lethargy, a feeling of satiety, and drowsiness. Regular artificial administration of sulfonic acid in large quantities suppresses the natural function of the body to synthesize it, which leads to metabolic disorders, overweight, reduced immunity, and so on. An irregular excess of tauric acid can be excreted from the body through the kidneys and intestines.
Fortified infant formula
Today it is clear that in the absence of breastfeeding, feeding with adapted formulas is indispensable. And thanks to numerous research and development, the composition of canned baby food is constantly improving. That is why taurine in baby food is an indispensable component, which is especially indicated for children in the 1st half of a year of life.
 nine0004
nine0004 The "Technical Regulations" for adapted powdered milk formulas and dry and liquid milk drinks set the content of tauric acid to be no more than 80 mg per 1 liter of liquid product. The total amount of a vital component in baby food, as practice shows, varies. It can range from 32 mg to 60 mg.
For the vast majority of partially/less and highly adapted both starter and transitional milk formulas, the average taurine value corresponds to 40 - 50 milligrams per 1 liter. As usual, you should carefully review the data on the product packaging when choosing a formula for your baby. nine0004
The following labeling is practiced:
- Pre - for small/premature babies;
- 1 - for newborns from 0 to 6 months;
- 2 - from 5-6 months;
- 0-12 - from the age of 2 months.
Tauric acid is an indispensable element for the healthy growth and development of the child. Do not neglect this essential component of nutrition, but do not exaggerate its doses by introducing milk formulas and complementary foods.