What can i feed my baby
How much should my baby eat? A guide to baby food portions
- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
Wondering how much to feed your baby? This can be hard to figure out, especially when you're starting solids and most of your baby's food ends up on your little one or the floor. It's also difficult to determine how much an 8-month-old (or older baby) should eat – babies this age are more interested in solid foods but still get most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula. This visual guide to baby food portions can help you figure out how much your baby should eat at every stage.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby eat?
Do you worry that your baby is eating too little or too much? Your baby will self-regulate her food intake based on what their body needs, so let their appetite be your guide.
It's helpful to have a reference point, however. Here are photos of how much solid food a baby typically eats in a day. You can also ask your baby's doctor for feeding advice.
This visual guide shows:
- Portions for infants who are new to solids (typically 4 to 6 months)
- Two sample meals for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
- Three sample meals and two snacks for an older baby (8 to 12 months) from a menu developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)
Your little one may eat less or more than what's shown here. Your job is to provide a variety of healthy foods at regular intervals without pressure, and their job is to decide what and how much to eat.
Photo credit: iStock.com / UntitledImages
Watch for signs your baby is full
Lots of factors – including activity level, growth spurts or plateaus, illness, and teething – will affect your baby's appetite, which can vary daily.
End feeding when they signal that they're done. Signs of being full include:
Signs of being full include:
- Turning their head away
- Refusing to open their mouth for another bite after they've swallowed (resist the urge to encourage your baby to have one last spoonful)
- Leaning back in their chair
- Playing with the spoon or food rather than eating
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 4- to 6-month-old should eat
When your baby is developmentally ready for solids, typically around 4 to 6 months, talk to their doctor about introducing solid foods. The first bites are mostly about them getting used to the idea of having something different in their mouth.
- Start with a very small amount, 1 to 2 teaspoons, of a single-ingredient puree.
- Gradually increase to 1 to 2 tablespoons of food once a day.
- Follow your baby's fullness cues.
Popular first foods include pureed mango, banana, chicken, turkey, beef, peas, sweet potatoes, and infant cereal. It's up to you what food to start with, but wait 3 to 5 days between introducing each new food to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction or food intolerance. (And remember, no cow's milk or honey until age 1.)
It's up to you what food to start with, but wait 3 to 5 days between introducing each new food to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction or food intolerance. (And remember, no cow's milk or honey until age 1.)
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 6- to 8-month-old should eat
As your little one gets more comfortable with solids, you can increase the frequency of meals and variety of food.
- Transition from one to two meals a day, typically by 8 months.
- Over time, add a second food to each meal. The photo above is an example of a meal with two foods.
- Once you've worked up to two meals with two foods each, aim for a balance of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains in their daily diet.
- Whenever you introduce a new food, start with a very small amount, a teaspoon or two, to allow your baby to get used to its flavor and texture.
- Start with a soupy consistency. Gradually add more texture as their eating skills improve.

Expect their intake of breast milk or formula to go down. They'll start drinking less of it as they eat more solid foods. Provide healthy options at mealtimes, and let them choose how much to eat.
Note: The jars in all photos are standard 4-ounce baby food jars.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
Cereal and fruit make an easy combination for a morning meal.
Grain: Iron-fortified, whole-grain infant cereal is a popular first grain. At 6 months, a typical daily portion of infant cereal mixed with breast milk or formula might be 2 to 3 tablespoons, increasing to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) by 8 months. (It's best to avoid rice cereal, though.)
Fruit: Babies love the natural sweetness of fruits like pears, apples, berries, prunes, and stone fruits. Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of fruit puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) of mashed or minced fruit.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
If you serve a grain and fruit in the morning, consider offering a protein-rich food and vegetable later in the day. Your child may eat more or less than the amounts shown.
Protein: A baby might transition from eating 1 to 2 tablespoons of meat puree at 6 months to 2 to 4 tablespoons at 8 months, for example. Other good protein sources include cheese, unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt, tofu, beans, and lentils.
Vegetables: Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of vegetable puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup). Try classic favorites like carrots, spinach, or butternut squash, as well as less traditional first foods such as parsnips, beets, or asparagus.
As your child's eating skills improve, gradually add more texture by dicing or mincing foods.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much an 8- to 12-month-old should eat
By 8 months or so, your baby is likely getting the hang of eating and needs to eat more calories to support their growing body. But since their little belly can't hold a lot of food, they'll need to eat more often. Every baby is different, but this may be a good time to try offering a third solid food meal.
But since their little belly can't hold a lot of food, they'll need to eat more often. Every baby is different, but this may be a good time to try offering a third solid food meal.
During this period:
- Continue to give your baby breast milk or formula.
- Add morning and afternoon snacks. (Some babies this age are happy with breast milk or formula as their snack, while others gravitate toward solid foods.) Once you've added a third meal and snacks, your baby will be eating or drinking something about every two to three hours.
- Continue to aim for a mix of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains.
- Introduce coarser and chunkier textures, for example, by dicing or mincing food instead of pureeing it, and graduate to soft finger foods as your baby's eating skills improve.
- Avoid foods with added sugars. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and try to steer clear of foods that list 1 gram or more of "Added Sugars.
 "
" - Provide healthy options, and let your baby choose how much to eat.
To visualize daily portions for an 8- to 12-month-old, check out the following photos of a typical day's menu for a baby this age, developed by the AAP.
Your child may eat more or less than these amounts. If you're concerned about how much your baby is eating, talk to their doctor for advice.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a breakfast consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) whole-grain infant cereal mixed with formula or breast milk
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Morning snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a morning snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced cheese or cooked vegetables
Note: This is an example of a morning snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Lunch for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a lunch consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt or cottage cheese, or minced meat
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced or mashed yellow or orange vegetable
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Afternoon snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features an afternoon snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit or unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt
- 1 whole-grain teething biscuit or cracker
Note: This is an example of an afternoon snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a dinner consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) minced or ground poultry or meat, or diced tofu
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2) cup diced, cooked green vegetable
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) noodles, pasta, rice, or potato
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby drink once they start eating solids?
Breast milk or formula will fully meet your child's hydration needs until they're about 6 months old. They may start drinking less as solid foods become a bigger part of their diet. Here are typical daily amounts by age – your baby's intake may be different, however.
6 to 8 months: 24 to 32 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
8 to 12 months: 24 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
Water: You can offer your baby water once they start eating solids, but let them self-regulate how much they drink. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends giving babies who are 6 to 12 months old 4 to 6 ounces of water a day, but what your baby decides to drink may vary. They may drink more on a hot day, for example.
Avoid juice: Juice isn't recommended for babies younger than 12 months.
Photo credit: iStock.com / SDI Productions
Your baby has the final say
Keep in mind that these portions are an estimate. The truth is, every baby is different, and there's no set amount of food that's appropriate for every baby at every stage.
If you're worried about whether your baby is eating enough – or too much – the best advice is to look for and respond to signs that your baby is full.
Your baby's doctor will chart their weight gain at regular intervals. If the doctor sees a consistent growth curve and doesn't have other concerns, your baby is most likely eating the right amount of food.
Hungry for more?
Age-by-age guide to feeding your baby
The 10 best foods for babies
The worst foods for babies
Using spices and seasoning in baby food
Elizabeth Dougherty
Elizabeth Dougherty is a veteran parenting writer and editor who's been contributing to BabyCenter since 2015. She's an intrepid traveler, devoted yogi, and longtime resident of Silicon Valley, where she lives with her husband and son.
Advertisement | page continues below
Baby formula feeding chart: How much formula by weight and age
Is your baby getting too much or too little formula? It's an important question that worries many new parents, especially those with newborns. When deciding how much formula to give your baby, it's important to watch their hunger cues as well as looking at guidelines based on age and weight. In general, before they're eating solids, babies need 2.5 ounces of formula per pound of body weight each day.
In general, before they're eating solids, babies need 2.5 ounces of formula per pound of body weight each day.
These guidelines are for babies who are exclusively formula-fed for the first 4 to 6 months, and then fed a combination of formula and solids up to age 1. If your baby is getting a combination of breast milk and formula, talk to their doctor for separate advice.
Your pediatrician can tell you where your baby falls on the growth charts, make sure they're growing steadily on their own growth curve, and help you ensure that they're getting a healthy amount of formula. If you're ever worried about your baby's growth, behavior, or development, talk with their doctor.
How much formula for a newborn
For the first few days, offer your newborn 1 to 2 ounces of formula every 2 or 3 hours. (At first, newborns may only take a half ounce of formula at a time.)
After the first few days, give your newborn 2 to 3 ounces of formula every 3 to 4 hours.
Initially it's best to feed your formula-fed newborn on demand, whenever they show signs that they're hungry. Because your little one can't tell you when they want a bottle, you'll need to learn to read their hunger cues. Crying is often a late sign of hunger, so if you can, try to catch the earlier signs that it's time for a feeding.
Because your little one can't tell you when they want a bottle, you'll need to learn to read their hunger cues. Crying is often a late sign of hunger, so if you can, try to catch the earlier signs that it's time for a feeding.
Here are some hunger cues to watch for:
- Smacking or licking their lips
- Rooting (moving their jaw, mouth, or head in search of food)
- Putting their hands to their mouth
- Opening their mouth
- Fussiness
- Sucking on things
- Becoming more alert
- Crying
As time passes, your newborn will begin to develop a fairly regular feeding schedule. You'll become familiar with their cues and needs, and knowing when and how much to feed them will be much easier.
Formula feeding chart by weight
During the first 4 to 6 months, when your baby isn't eating solid foods, here's a simple rule of thumb: Offer 2.5 ounces of formula per pound of body weight every 24 hours, with a maximum of about 32 ounces.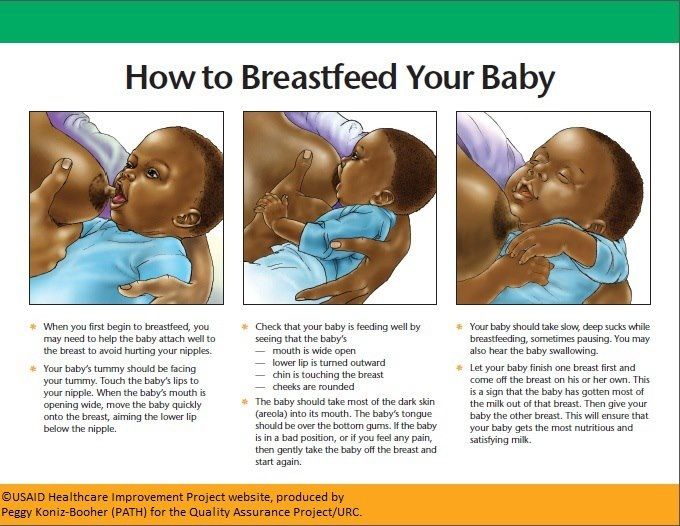
| Weight | Ounces of formula |
|---|---|
| 6 pounds | 15 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 7 pounds | 17.5 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 8 pounds | 20 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 9 pounds | 22.5 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 10 pounds | 25 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 11 pounds | 27.5 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 12 pounds | 30 fl oz every 24 hours |
These numbers aren't rigid rules. They offer a rough estimate for what your baby may need. Some babies will grow well while taking less than the recommended amount, while others consistently need more. Your baby's daily feedings will also vary according to their individual needs – in other words, they may want a bit more on some days and a bit less on others.
Formula feeding chart by age
Here are typical amounts per day based on age:
| Age | Ounces of formula |
|---|---|
| Full-term newborn | 2 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 1 month old | 3 to 4 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 2 month old | 4 to 5 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 3 month old | 4 to 6 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 4 month old | 4 to 6 ounces per bottle, 4 to 6 times a day |
| 5 month old | 4 to 6 ounces per bottle, 4 to 6 times a day |
| 6 month old | 6 to 8 ounces per bottle, 4 to 5 times a day |
| 7 month old | 6 to 8 ounces per bottle, 3 to 5 times a day |
From 8 months old until their first birthday, you can expect your baby to have 7 to 8 ounces per bottle, 3 to 4 times a day.
As your baby gets older – and their tummy gets bigger – they'll drink fewer bottles a day with more formula in each. It's important not to overfeed your baby so they'll stay at a healthy weight. Your baby shouldn't have more than 32 ounces of formula in 24 hours.
When they reach their first birthday, they can stop drinking formula and transition to cow's milk in a bottle, sippy cup, straw cup, or open cup. Limit your toddler to 16 to 24 ounces (2 to 2.5 cups) a day of whole milk, so they have room for other healthy foods.
Signs that your baby's getting enough formula
Here are signs that your baby's getting all the formula they need:
- Steady weight gain. They continue to gain weight after their first 10 days and follow a healthy growth curve during their first year. (Most babies lose up to 7 to 10 percent of their birth weight in the first few days and then regain it by the time they're about 2 weeks old.)
- Happy baby.
 They seem relaxed and satisfied after a feeding.
They seem relaxed and satisfied after a feeding. - Wet diapers. They wet two to three diapers a day in the first few days after birth. Over the next few days, the amount should increase to at least five to six wet diapers a day.
Signs your baby's getting too much formula
Babies are usually good at eating the amount they need, but bottle-fed babies can drink too much at times. Here are the signs that they're getting too much formula:
- Vomiting after a feeding may be a sign that your baby had too much. (Spitting up is normal, vomiting isn't.)
- Tummy pain after a feeding can also be a sign of overfeeding. If your baby draws up their legs or their tummy seems tense, they may be in pain. (See other possible reasons for stomach pain in babies.)
If your baby seems to want to eat all the time, even after finishing a bottle, talk to your pediatrician. Using a pacifier may help soothe their need to suck.
Formula-feeding tips
- In general, babies eat when they're hungry and stop when they're full, so resist the temptation to encourage your baby to finish each bottle. Overfeeding during infancy can contribute to obesity later in life.
- Don't respond to your baby's every cry with a bottle. They may be crying because their diaper is wet, they're cold or hot, they need to be burped, or they want to be close to you. (Learn more about why babies cry, and how to soothe them.)
- Your baby may be hungrier than usual during growth spurts. These typically occur 10 to 14 days after birth and around 3 weeks, 6 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months of age.
Read more:
- Formula Feeding Problem Solver
- How to safely store and use formula
advertisement | page continues below
Various breastfeeding positions
Try different breastfeeding positions to find the one that works best for you and your baby. You can see the options in our selection of photos
Share this information
There is no right or wrong way to hold the baby while
feeding, and mom and baby are sure to find their favorite position.
It is important that both you and your child feel comfortable. 1.2 It's good to learn a few different breastfeeding positions and techniques because life's circumstances often require us to be flexible, especially as your baby gets older and you start to leave the house more often.
Whatever position you choose to breastfeed your baby, remember a few simple rules.
- Prepare everything you need before feeding, including drinks, food, mobile phone, TV remote control, book or magazine. And do not forget to go to the toilet - the feeding process can take a long time!
- Make sure your baby is comfortable. Whichever position you choose, it's important to keep your baby firm, level, and provide good support for their head, neck, and spine.
- You should also be comfortable. Don't stress. If necessary, use pillows of different sizes or rolls of towels to support your back or arms.
- Make sure your baby is latching on correctly. Proper grip is the key to comfort when breastfeeding.

- If your baby does not latch on well or you experience pain while feeding, contact a lactation consultant for help. The specialist will also be able to show you how to hold your baby more comfortably.
1. Relaxed feeding or reclining position
The relaxed feeding position, also known as biological feeding, 1 is often the first position for most mothers. If, immediately after birth, the baby is placed on the mother’s chest or stomach, normally, he instinctively reaches for the breast and tries to grab the nipple. This phenomenon is known as the breast seeking reflex. Skin-to-skin contact stimulates the infant's feeding instinct, and gravity helps him to latch onto the breast and maintain balance.
But it's not just newborns that can be fed in the reclining position - this position is great for babies of all ages. It can be especially helpful if your baby does not latch well in other positions or does not like to be touched during feeding, and also if you have too much milk flow or too large breasts. Isabelle, a mother from the UK, shares her experience: “I had large breasts, and the baby was born small - 2.7 kg, so it was not easy to find a comfortable position at first. After a few weeks, it became clear that there was no “correct” posture for me. As a result, I most often fed lying down, putting the baby on my chest. ”
Isabelle, a mother from the UK, shares her experience: “I had large breasts, and the baby was born small - 2.7 kg, so it was not easy to find a comfortable position at first. After a few weeks, it became clear that there was no “correct” posture for me. As a result, I most often fed lying down, putting the baby on my chest. ”
It is more convenient to feed not lying flat on your back, but half-sitting, leaning on pillows. So you will have a back support and you will be able to watch the baby during feeding.
2. Cradle position
This is the classic
first thought of breastfeeding. Mom sits straight
, and the baby lies on her side on her arm, pressing his stomach against her stomach. 3 Although this is a very popular position, it is not always easy to master with newborns because it gives the baby less support. Try putting a pillow under your back, and put a special breastfeeding pillow on your knees and lean on it with your hands. So you can more reliably support the child, without overstraining your back and shoulders. Just make sure that the baby does not lie too high on the pillow for feeding. The breast should remain at a natural level so that the baby can grab it without effort, otherwise sore nipples cannot be avoided.
Just make sure that the baby does not lie too high on the pillow for feeding. The breast should remain at a natural level so that the baby can grab it without effort, otherwise sore nipples cannot be avoided.
“I breastfed in the cradle position because it suited me perfectly! It was comfortable and I loved just sitting and looking at my little one,” recalls Rachel, a mother of two from Italy.
3. Cross Cradle
This breastfeeding position looks almost the same as Cradle, but the baby is on the other arm. 3 This gives your baby support around the neck and shoulders so he can tilt his head to latch on. This position is great for breastfeeding newborns and small babies, as well as for babies who do not latch well. Since the baby lies completely on the other hand, it becomes easier to control his position and you can adjust the chest with your free hand.
Julie, a UK mother of two, finds this position very practical: “I usually breastfeed my youngest in the cross cradle position.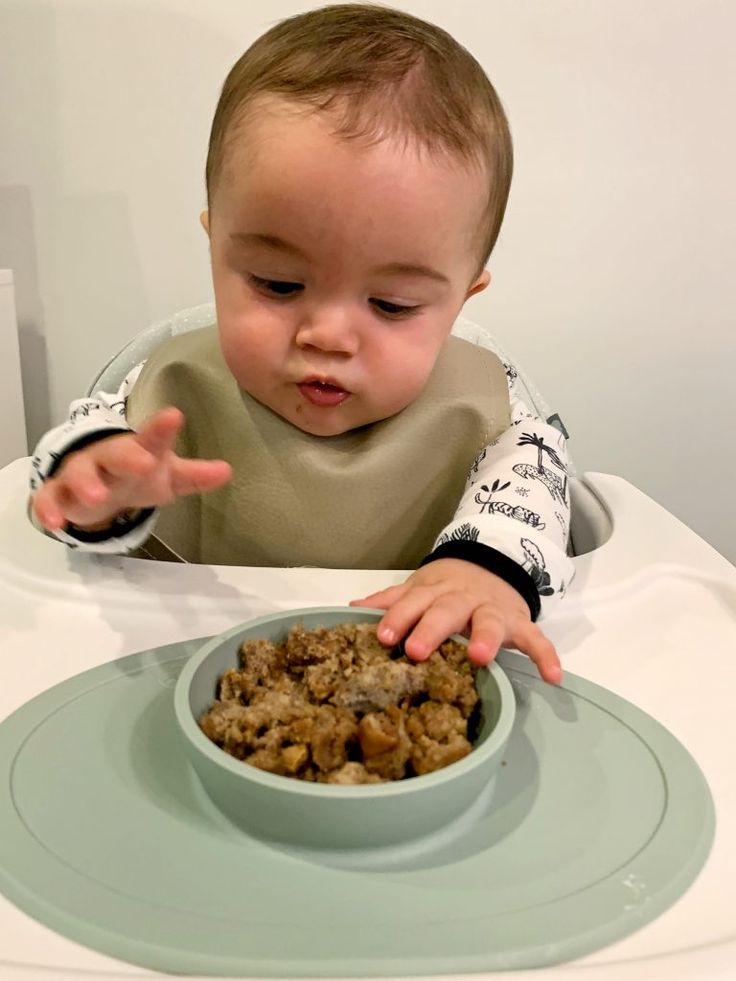 So I have a free second hand, and I can take care of an older baby at the same time. ”
So I have a free second hand, and I can take care of an older baby at the same time. ”
Do not hold the baby's head at first, otherwise you may inadvertently press his chin against his chest. Because of this, the child will not be able to take the breast deeply, because the nipple will rest against the base of the tongue, and not against the palate, which will lead to inflammation of the nipples. As the child grows, this position becomes more comfortable, and he can rest his head on your palm (as shown in the photo above).
4. Underarm breastfeeding
In this position, also known as the “ball grip”, the mother sits with the baby lying along her arm at the side, legs towards the back of the chair (or any other seat). 3 Another comfortable position for newborn breastfeeding, you can give your baby good support, full control of his position and a good view of his face. And the baby feels safe in close contact with the mother's body. This position is especially good for those who have had a caesarean section or a premature birth, as well as mothers of twins and women with large breasts.
“When I breastfed my first daughter, I had very large K-sized breasts—twice the size of her head,” recalls Amy, an Australian mother of two. - I put rolls of towels under each breast, because they were very heavy, and fed my daughter in a pose from under the arm, but only sitting straighter so as not to crush her. This position was also convenient because I had a caesarean section and could not put the baby on my stomach.”
5. Side-lying position
The side-lying position is ideal for a relaxed
nighttime feeding in bed or on the couch. If you had a
caesarean section or ruptures during childbirth, this position may be more comfortable than sitting down. 3 In this position, mother and baby lie side by side, tummy to tummy.
“It was difficult for me to sit during endless night feedings, firstly because of the caesarean section, and secondly because of lack of sleep,” recalls Francesca, a mother from the UK. “And then I discovered that you can feed your baby lying on your side and rest at the same time.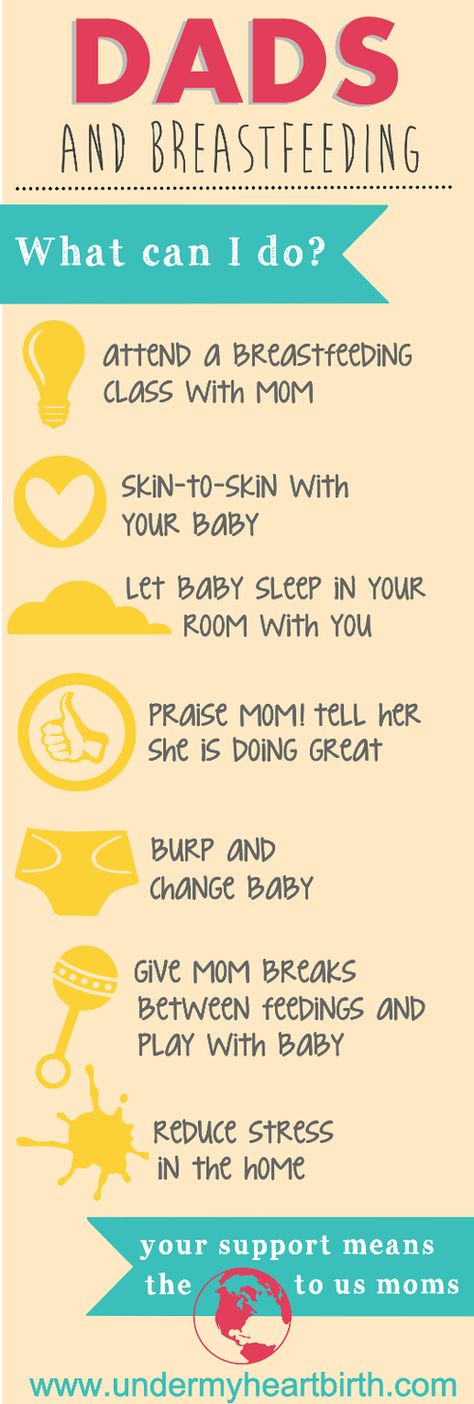 ”
”
“Because of the short tongue frenulum, Maisie could only properly latch on to her breasts while lying on her side. The lactation consultant showed me how it's done. In this position, the flow of milk was optimal for my daughter, and it was easier for her to keep the nipple in her mouth. As she got older, she became much better at grabbing her breasts in normal positions,” says Sarah, mother of two from Australia.
6. Relaxed breastfeeding after caesarean section
If you can't find a comfortable position for breastfeeding after caesarean section, 3 try holding the baby on your shoulder in a reclining position – this does not stress the postoperative suture and allows you to breastfeed your baby comfortably. You can also try side feeding.
7. Sitting upright breastfeeding or “koala pose”
When breastfeeding in an upright position or “koala pose”, the baby sits with a straight back and a raised head on the mother's hip. 4 This position can be tried even with a newborn if it is well supported, but it is especially convenient for feeding a grown child who can already sit up by himself. The upright sitting position, or “koala pose,” is great for toddlers who suffer from reflux or ear infections and feel better sitting. In addition, this pose may be suitable for children with a shortened frenulum of the tongue or reduced muscle tone.
The upright sitting position, or “koala pose,” is great for toddlers who suffer from reflux or ear infections and feel better sitting. In addition, this pose may be suitable for children with a shortened frenulum of the tongue or reduced muscle tone.
“When my daughter got a little older, I would often feed her in an upright position, which was more comfortable for both of us, and I could still hold her close,” recalls Peggy, a mother from Switzerland. “Besides, it was possible to discreetly breastfeed her in public places.”
8. Overhanging position
In this position, the baby lies on his back, and the mother bends over him
on all fours so that the nipple falls directly into his mouth. 4 Some moms say this breastfeeding position is good to use occasionally for mastitis, when touching the breasts is especially unpleasant. Some say that this breastfeeding position helps with blockage of the milk ducts, although there is no scientific evidence for this yet. You can also feed in the “overhanging” position while sitting, kneeling over the baby on a bed or sofa, as well as reclining on your stomach with support on your elbows. Pillows of various sizes that you can lean on will help you avoid back and shoulder strain.
You can also feed in the “overhanging” position while sitting, kneeling over the baby on a bed or sofa, as well as reclining on your stomach with support on your elbows. Pillows of various sizes that you can lean on will help you avoid back and shoulder strain.
“I have breastfed several times in the 'overhang' position for clogged milk ducts when no other means of dissolving the blockage worked. And this pose seems to have helped. I think it's because of gravity, and also because the breasts were at a completely different angle than with normal feeding, and my daughter sucked her differently, ”says Ellie, a mother of two from the UK.
Feeding in the "overhanging" position is unlikely to be practiced regularly, but in some cases this position may be useful.
“I used to breastfeed in the overhang position when my baby was having trouble latch-on,” says Lorna, mother of two in the UK. - This, of course, is not the most convenient way, but then I was ready for anything, if only he could capture the chest. We succeeded and have been breastfeeding for eight months now!”
We succeeded and have been breastfeeding for eight months now!”
9. Breastfeeding in a sling or in a sling
Breastfeeding in a sling takes some practice, but it can be used to go out, look after older children, or even do a little household chores.
The sling is also useful if the baby does not like to lie down or is often attached to the breast. Lindsey, a mother of two in the US, notes: “I used the carrier frequently for both of my children. When we were out, I tied the sarong around my neck and covered the carrier with it. Under such a cape, the baby can eat as much as he wants until he falls asleep.
This breastfeeding position is best when the baby is already good at breastfeeding and can hold his head up by himself. Any slings are suitable for breastfeeding, including elastic and rings, as well as carrying bags. Whatever option you choose, the main thing is that you can always see the face of the child, and his chin does not rest against his chest.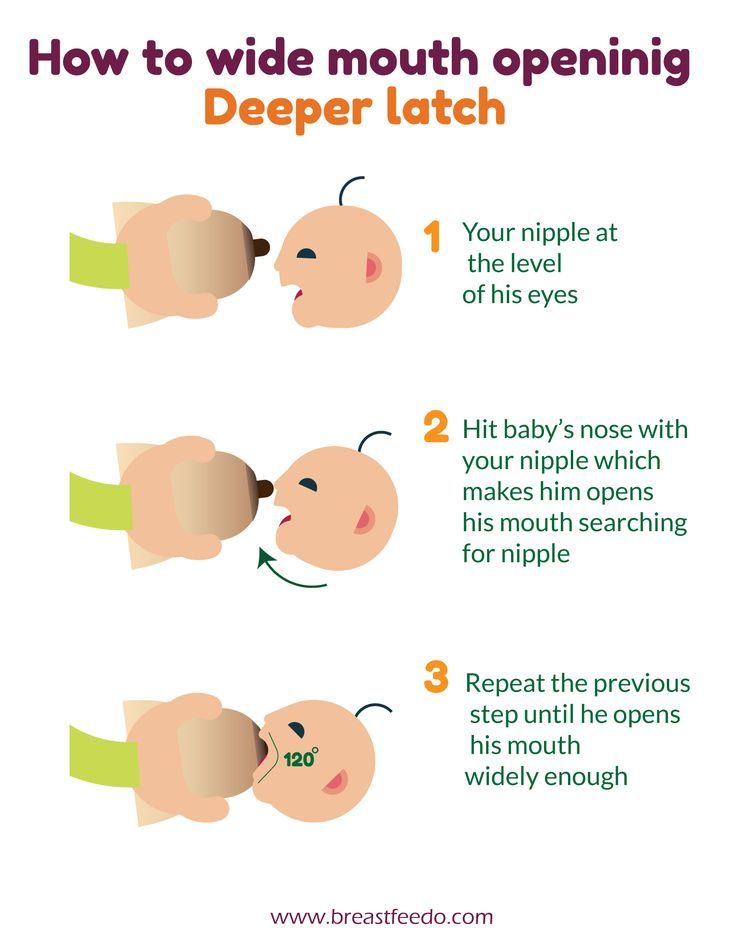
10. Double hand-held breastfeeding
Double hand-held breastfeeding (or “double-ball grab”) is great for mothers of twins—you can breastfeed both at the same time and keep your arms relatively free. 4 When feeding in this position, it is advisable to use a special pillow for breastfeeding twins, especially at first. It will provide extra support and help keep both babies in the correct position, as well as reduce the burden on the abdomen if you had a caesarean section. In addition, the hands are freer, and if necessary, you can deal with one child without interfering with the second.
“My twins were born very tiny and had to be fed every two hours at any time of the day or night. Very soon it became clear: if I want to do anything besides feeding, I need to feed them both at the same time, - says Emma, mother of two children from the UK. “I breastfed them two by hand using a breastfeeding pillow.”
Other good positions for breastfeeding twins are two criss-cross cradles, one baby in the cradle and the other close at hand, reclining feeding, or sitting upright (one baby on one side, the other on the other).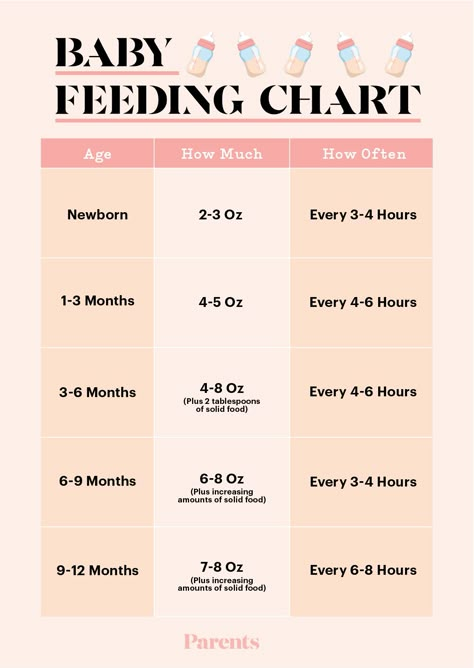
11. Breastfeeding in the "hand-supported" or "dancer's hand" position
muscle tone (which is typical for premature babies, children suffering from various diseases or Down syndrome), try supporting his head and your chest at the same time. 4 Grasp your chest with your palm underneath so that your thumb is on one side and all the others are on the other. Move your hand slightly forward so that your thumb and forefinger form a "U" just in front of your chest. With the other three fingers, continue to support the chest. With your thumb and forefinger, hold the baby's head while feeding so that his chin rests on the part of the palm between them, your thumb gently holds the baby on one cheek, and your index finger on the other. So the baby gets excellent support, and you can control his position and see if he is holding his breast.
Literature
1 Colson SD et al. Optimal positions for the release of primitive neonatal reflexes stimulating breastfeeding. Early Hum Dev . 2008;84(7):441-449. - Colson S.D. et al., "Optimal Positions for Provoking Primitive Innate Reflexes to Induce Breastfeeding." Early Hume Dev. 2008;84(7):441-449.
Early Hum Dev . 2008;84(7):441-449. - Colson S.D. et al., "Optimal Positions for Provoking Primitive Innate Reflexes to Induce Breastfeeding." Early Hume Dev. 2008;84(7):441-449.
2 UNICEF UK BFHI [ Internet ]. Off to the best start ; 2015 [ cited 2018 Feb ]. - UNICEF UK, Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative, Start the Best You Can [Internet]. 2015 [cited February 2018].
3 Cadwell K. Latching - On and Suckling of the Healthy Term Neonate: Breastfeeding Assessment. J Midwifery & Women's Health. 2007;52(6):638-642. — Cadwell, K., "Latching and sucking in healthy newborns: evaluation of breastfeeding." F Midwifery Women Health. 2007;52(6):638-642.
4 Wambach K, Riordan J, editors. Breastfeeding and human lactation. Jones & Bartlett Learning ; 2014. 966 p . - Wambach K., Riordan J., "Breastfeeding and female lactation". Burlington, MA: Publishing House Jones & Bartlett Learning ; 2014. Pp. 966.
Breastfeeding and human lactation. Jones & Bartlett Learning ; 2014. 966 p . - Wambach K., Riordan J., "Breastfeeding and female lactation". Burlington, MA: Publishing House Jones & Bartlett Learning ; 2014. Pp. 966.
Breastfeeding in public | Tips for breastfeeding moms
Open breastfeeding in public takes some getting used to. Here are some tips to help you and your baby feel more confident
Share this information
The beauty of breastfeeding is that everything you need is always at your fingertips: you can feed your baby wherever you are, and the temperature of the milk will always be just right. But while there's nothing more natural than breastfeeding, the very idea of breastfeeding in front of everyone, especially the first time, can be a little unsettling. Whether you are worried about what others will think or not, our tips will help you prepare for this event.
Whether you are worried about what others will think or not, our tips will help you prepare for this event.
1: Rehearse
If you are embarrassed by the prospect of breastfeeding your baby for the first time in a public place, practice at home in front of a mirror to imagine how you will look from the outside. You will surely notice that the chest is not so open at the same time: it is blocked by the head of the child.
First, try breastfeeding in public in a friendly environment. In the company of other mothers or in a cafe with a friend, you will obviously be more comfortable than alone in the train or in a noisy shopping center.
2: Dress comfortably
When it comes to comfortable clothing for breastfeeding in general and in public places in particular, there are many options. If breastfeeding is going well and you intend to continue, it's worth picking up a few pieces of nursing clothing that will make feeding easier.
“I had a very comfortable nursing shirt. It was possible to discreetly feed the child in it even in winter, since nothing had to be removed. Just put the baby on the slit in the T-shirt and you're done. You can feed anywhere and anytime!” says Caroline, mother of two from France.
It was possible to discreetly feed the child in it even in winter, since nothing had to be removed. Just put the baby on the slit in the T-shirt and you're done. You can feed anywhere and anytime!” says Caroline, mother of two from France.
However, it is not necessary to buy special nursing clothes - you can just wear two regular T-shirts. “I solved the problem with a stretch blouse that I wore under a loose top. When it was necessary to feed the child, I pulled the jacket under my chest and lifted the top. He covered my chest, and the jacket - my stomach. So it was possible to feed discreetly anywhere, while not freezing and not showing anyone your tummy that sagged after childbirth,” recalls Suzanne, a mother of two children from the UK.
Other handy options are tops and dresses with buttons or front zips, with straps or side slits. You can also try wraparound styles, collar collars or shawl collars.
“Wrap-around cardigans have been a lifesaver when I have to feed in public,” says Natalie, a UK mom. - I just untied one floor and covered my baby's head with it during feeding or when she cried. And you didn’t have to carry anything with you to disguise.”
- I just untied one floor and covered my baby's head with it during feeding or when she cried. And you didn’t have to carry anything with you to disguise.”
3: Know your surroundings
Before you go anywhere with your baby, make a list of good places to feed in advance so you don't have to rush around looking at the last minute. Shopping malls, department stores and children's clothing stores often have mother and baby rooms where you can feed your baby in peace and quiet, sitting on a comfortable chair, or use the changing table. Many cafes and hotel restaurants also try to create comfortable conditions for nursing mothers.
“If you're worried, look ahead for breastfeeding friendly places so you know where to go if you need to. Feeding in public can be difficult at first, but over time it gets better and better. And then you do it so quickly and imperceptibly that people around you don’t even realize that you are breastfeeding a baby, ”says Rachel, a mother from the Maldives.
Other potentially suitable locations are fitting rooms in department stores, furniture stores, community centers, libraries, museums, and parks. Ask around moms you know - they can probably share their experience about suitable feeding places nearby.
“In the UAE, children under the age of two are legally allowed to breastfeed. Breastfeeding is highly encouraged here, shopping malls have dedicated facilities for breastfeeding, and mothers who breastfeed in public places like restaurants are treated with respect,” says Fay, mother of two from the UAE.
4: Try a breastfeeding cape
Some moms prefer to cover themselves and their baby with a cape when breastfeeding in public. The choice here is huge - from simple shawls and ponchos to special capes and aprons with a rigid semicircular hole on top, which allows you to watch the baby during feeding. There is a solution for every taste. And you can also feed your baby in a sling or carrier - this is both convenient and shelters you from prying eyes.
“I recommend buying a carrier,” says Caroline, mother of two in the US. “With a little practice, you can feed on the go, without looking up from other things.”
However, the last word often rests with the baby. Some babies do not tolerate any capes when feeding, and someone, on the contrary, is distracted if he is not covered. “Both of my babies didn’t like it when I tried to cover them with a shawl during feeding, so I just had to rely on their heads to cover their breasts enough,” recalls Esther, mother of two from the UK.
5: Know your rights
Breastfeeding in all public places is legal in many countries. Moreover, there are laws aimed at protecting breastfeeding mothers. If you are not sure if there are such laws in your country, search the Internet for information. The best place to start is with the websites of government and health agencies. Or try asking your doctor. You can also ask familiar mothers, friends and relatives about their own experiences. The answers may surprise you.
The answers may surprise you.
"Breastfeeding is widely accepted in Australia, and it's quite normal to sit bare-chested in a cafe while a nice waiter takes your order for a fat-free latte!" says Amy, mother of two from Australia.
If someone is upset that you are breastfeeding your baby in a public place, politely remind them of your rights. If you believe that asking you not to breastfeed in a store, cafe, or similar establishment violates your rights, you can file a formal complaint—if you are willing and supported by local law.
“One day I decided to breastfeed my baby in a diner after I had eaten myself, and I did it right at the table because they didn't have a feeding room. A confused junior manager was sent to me asking if I could move to the women's room for this. I replied that no - do they eat there? Then I was asked to move to a side booth. But I refused here and didn’t budge until we were done!” recalls Maya, a mother of two from Spain.
“My advice is don't worry! I was worried at first, but I regularly had to breastfeed my baby in public places, both in the city and in the countryside.