What food for 7 month baby
Giving Baby Finger Foods at 7-8 Months
Written by Rebecca Felsenthal Stewart
In this Article
- Month 7, Week 3
- Month 7 Week 3 Tips
Month 7, Week 3
Once your baby is a pro at eating soft mashed foods, they may be ready to move on to finger foods around 8 months. They have the dexterity to pick the food up and release it or mash it, and will become more efficient and independent as they master the pincer grip around 9 months. At that point they'll be able to use their thumb and forefinger to pick up the small chunks of food.
Your baby may grab at everything on your plate, but follow these guidelines for healthy and safe feedings.
- Start with menu items like pieces of soft cheese; small pieces of pasta or bread; finely chopped soft vegetables; and fruits like bananas, avocado, and ripe peaches or nectarines. These foods should require minimal chewing, as your baby may not yet have teeth. Do NOT let them have hot dogs, raw vegetables, nuts, meats, hard candy, or sticky textures such as nut butters that have increased choking risks at this stage.
- Introduce new foods one at a time in case there are any concers about allergies.
- Chop all foods into soft, bite-sized pieces, 1/2 inch or smaller.
- Watch out for choking hazards: Avoid round, firm foods like carrots, grapes, and hot dogs and skip anything like raw veggies and peanuts. Raisins and popcorn are dangerous for babies.
- Keep up your formula or breastfeeding schedule, but as your baby eats more solids, they’ll naturally start to take less milk. Your baby needs to start eating more solids and drinking less milk for the nutritional value at this stage.
Your Baby's Development This Week
Your baby is getting stronger and may even be moving around, whether they are sliding around on their belly in reverse, scooting on their behind, or actually crawling forward. If you haven’t childproofed your house already, don’t wait any longer!
You may notice these growing signs of motor development:
- Your baby is probably now able to sit on their own for several minutes, without using their hands for support and they may be able to get up into a sitting position all by themselves.

- While you offer them support, they should be able to bounce up and down, and possibly even pull up to a stand.
- Their little hands are increasingly agile -- they are getting better at passing a toy back and forth from one to the other.
You might wonder about:
- Their vision. Your baby should be able to see nearly as far as an adult by now and can track moving objects with their eyes.
- Stranger anxiety. You’re not imagining it: They may fear new people and situations. So give them time to warm up and reassure them if they are upset.
- What they can understand. Your baby might comprehend more than you realize, so it’s important to keep talking to them about everything you’re doing and try to be consistent about the words you use for familiar objects.
Month 7 Week 3 Tips
- If food allergies run in the family, talk to your pediatrician about introducing highly allergenic foods like peanuts and eggs.

- Fried foods are not good choices for babies. If you offer them at all, do so rarely.
- Avoid feeding your baby juice unless it is fresh-squeezed.
- By now, your baby’s diet should include grains, fruits, vegetables, and meats, and they should be eating two to three meals a day.
- In addition to rice, barley, or oat cereal, you can introduce grain products your baby can grab, such as toast, crackers, and dry cereal. Avoid any colorful, sugary cereals.
- Sit baby in their high-chair for feeding time. If they eat finger foods while crawling around, they are more likely to choke.
- You’re not done with breast feeding or bottle feeding. Your baby is starting the transition, but breast milk and formula are still key.
- Pureeing or mashing vegetables may make them easier for your baby to eat when they are first transitioning from a liquid diet to solids.
The Best First Foods for Babies 6 to 9 Months – Happiest Baby
By Happiest Baby Staff
On This Page
- Best Baby Foods at 6 Months
- Best Baby Foods at 7 Months
- Best Baby Foods at 8 Months
- Best Baby Foods at 9 Months
You've spent the first six months of your baby's life making sure that they are nourished with breastmilk or formula. As they grow and thrive, you might notice that your little sprout shows you some signs that they are ready to graduate from the bottle or breast to solid foods. If your baby can sit up and hold their head up, that's a great first sign! What's more, if they bring objects to their mouth and show an interest in what you are eating, your curious kiddo might be ready to start eating solid foods.
As they grow and thrive, you might notice that your little sprout shows you some signs that they are ready to graduate from the bottle or breast to solid foods. If your baby can sit up and hold their head up, that's a great first sign! What's more, if they bring objects to their mouth and show an interest in what you are eating, your curious kiddo might be ready to start eating solid foods.
But what should you feed your baby? Here’s a list of perfect starter foods for your baby from ages 6 to 9 months.
Best Baby Foods at 6 MonthsAt 6 months, babies may be starting to chew. Though this skill won’t be mastered just yet, they are typically ready to get messy with some mushy, pureed eats—helping them learn about flavor and texture. At this age, the goal is not to satiate your baby with full meals of solid foods but rather to get your child curious and excited about their culinary options.
Because babies are growing so fast, their needs for iron are high to prevent iron-deficiency and support their overall health. Offer your little one iron rich foods like—infant cereal (read up on why you may want to skip rice cereal), well-cooked meat, poultry, mashed beans, and lentils. To keep your baby safe from choking, avoid adding solids like cereal to baby bottles.
Offer your little one iron rich foods like—infant cereal (read up on why you may want to skip rice cereal), well-cooked meat, poultry, mashed beans, and lentils. To keep your baby safe from choking, avoid adding solids like cereal to baby bottles.
Here are some great first foods for Baby to try:
- Infant oat, grain, or barley cereals mixed with breastmilk or formula and spoon-fed to your baby
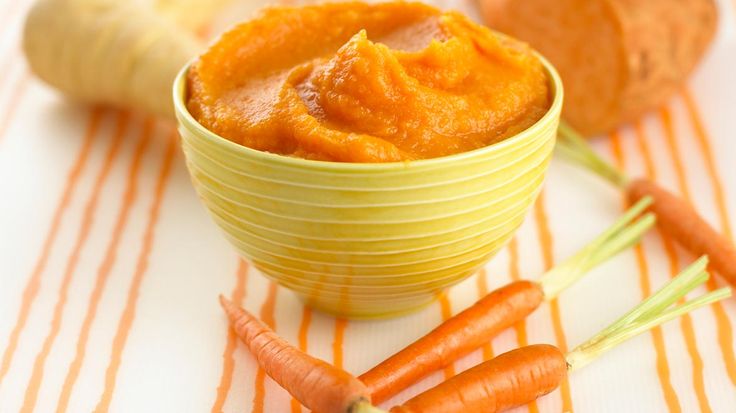
- Sweet potato puree
- Squash puree
- Pea puree
- Carrot puree
- Mashed banana
- Mashed avocado
- Mashed or pureed beans
- Mashed or pureed lentils
- Pureed meats (beef, chicken, or turkey)
- Soft, falling apart meats (salmon, beef, chicken, turkey)
Check out more of our favorite first food purees. Or, if purees aren’t your thing, read up on how to start baby-led weaning.
Best Baby Foods at 7 MonthsBy 7 months old, your baby will probably be eating more solids but not enough to replace breastmilk or formula as their primary source of food. The goal for this month is to keep introducing solid foods to your baby. What's fun is by 7 months, you can get more creative with mixing flavors and adding textures.
The goal for this month is to keep introducing solid foods to your baby. What's fun is by 7 months, you can get more creative with mixing flavors and adding textures.
Here are a few nutritious and delicious food combos to try with your baby:
- Peas pureed with breastmilk (or formula), sweet potatoes, or squash
- Kale pureed with blueberry, squash, potatoes, sweet potatoes, peas, pears, or bananas
- Apples pureed with cauliflower, carrots, pears, prunes, or beets
- Beef pureed with broccoli
- Chicken pureed with carrots and potatoes
- Chickpeas pureed with bananas, apples, or sweet potato
- Sweet potatoes pureed with red bell pepper
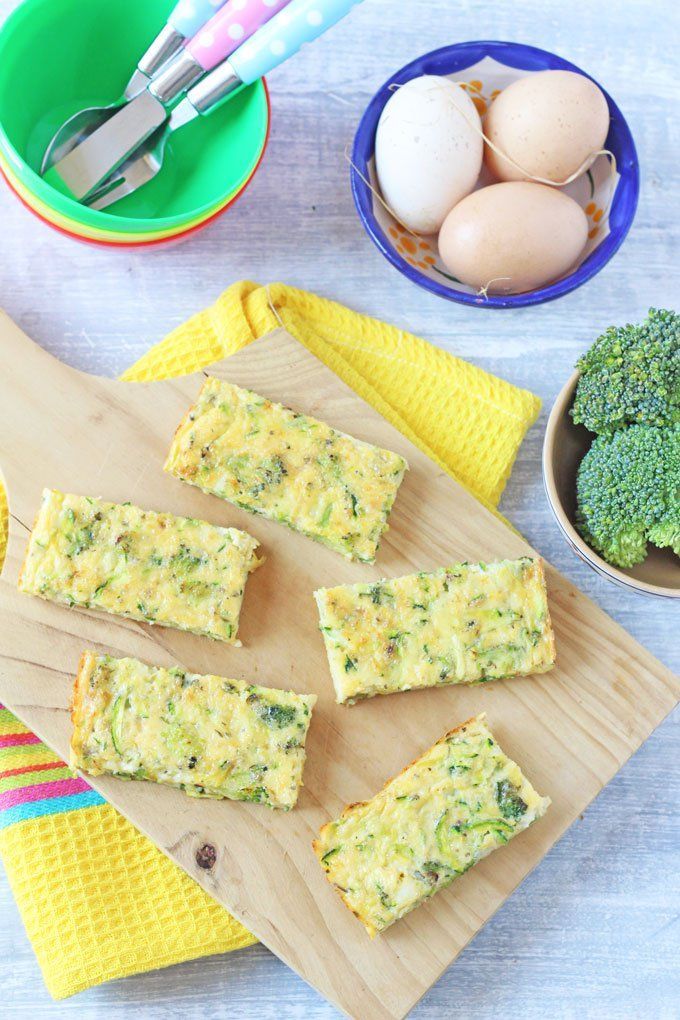
Seven months is also the perfect age to start giving your baby a plate, bowl, and plastic utensils so they can begin to practice feeding themselves. If your baby is teething, you can place frozen chunks of fruit in a sieve feeder/mesh bag that allows them to gnaw on the fruit without choking. Learn more about helping your baby use a fork and spoon!
Learn more about helping your baby use a fork and spoon!
By 8 months, your baby is likely eating more solids and relying a little less on milk as a primary meal (though it’s still where they get the bulk of their nutrition!). And they’re probably having lots of fun learning how to use their hands to feed themselves. Something else to consider: Babies should be exposed to potential allergen foods (like peanuts, tree nuts, eggs, and fish) before their first birthdays to help prevent future food allergies. Starting at 6 months of age, peanut butter is safe to introduce as long as you are comfortable giving it to your baby.
In fact, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans says that babies can begin having these foods when they start eating solids. But many families often feel more comfortable waiting to introduce these foods until around this age. Of course, consult with your little one’s pediatrician if you have concerns about potential allergen foods.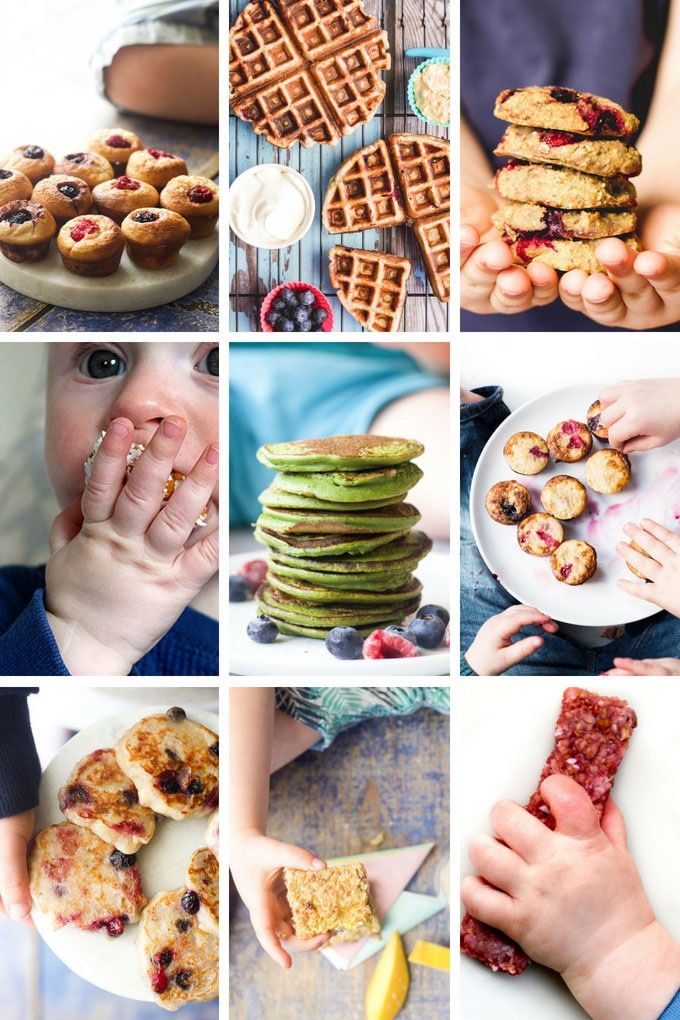
Here are some foods to add to your repertoire:
- Whole eggs, scrambled
- Nut butter thinned out with water and mixed with cereal (nut butters are sticky and can cause choking)
- Fully cooked fish, like salmon or tuna
- Full-fat yogurt
Here are some preparation ideas:
- Well-cooked (think over-cooked until falling apart) pasta such as elbows or alphabet shapes
- Mashed meat with mashed or ground vegetables such as peas and potatoes or kale and squash
- Rainbow on a plate: Using tiny pieces of soft, strained, pureed, and mashed food options, look for a variety of colors to offer. Some fun options could include banana, avocado, sweet potato, peas, blueberry, raspberry, cheese, and chicken.
Though there’s a greater variety of foods babies eat now, formula or breastmilk continues to be their primary source of nutrition until age 1. At 9 months old, babies get more comfortable with self-feeding and eating the foods their families enjoy. After all, eating solid foods is a sensory wonderland of texture, smells, and tastes. Not to mention all that fun making messes with those adorably curious fingers.
After all, eating solid foods is a sensory wonderland of texture, smells, and tastes. Not to mention all that fun making messes with those adorably curious fingers.
As you begin to focus on meal planning for your baby, there are few things to keep in mind:
- Babies need four to five servings of fruits and vegetables a day. A serving size for a 9-month-old is less than a quarter cup.
- "Eat the rainbow" is excellent advice because it gives your baby exposure to lots of different fruits, vegetables, grains, and starches.
Here are a few menu ideas to help meal plan for your baby…
Breakfast Ideas for Babies
These morning meals pack a nutritional punch—and don’t forget to check out all of our favorite breakfast ideas for babies:
- Soft fresh fruit cut up in small pieces (think: banana, raspberries, or blueberries)
- Whole-grain waffles or pancakes
- Unsweetened oatmeal made with breastmilk or formula combined with cut-up and cooked apples and pears or banana slices.
 (It is essential to steam the apples or pears to make them soft enough for your baby to mash with their gums.)
(It is essential to steam the apples or pears to make them soft enough for your baby to mash with their gums.) - Full-fat yogurt mixed with mashed or pureed berries such as blueberries, blackberries, strawberries, or raspberries
- Soft scrambled eggs
- Veggie frittata
Lunch Ideas for Babies
- Spread hummus on soft crackers or bread
- Grilled cheese sandwich with cooled tomato soup
- Macaroni and cheese with cooked veggies like peas and carrots mixed in
- Pizza bites with chopped bits of spinach in the sauce and melted shredded cheese
- Quesadilla made with pureed spinach, squash, or beans
Snack Ideas for Babies
Babies this young won’t likely need to snack too much (remember, breastmilk or formula will provide the majority of your little one’s nutrition). Still, it’s not a bad idea to have snacks on hand for when your mini muncher needs something to eat that’s not quite a meal. A few baby snack ideas:
- Apple and carrot slaw
- Cheese slices
- Full-fat plain yogurt
- Hard-boiled egg
- Avocado slices
- Muffins made with fruits, veggies, and/or whole grains
- Fruit and veggie pouches
- Sugar-free, whole-grain cereal, like plain Cheerios
Dinner Ideas for Babies
To help your baby get and stay excited about eating solid foods, serve a version of whatever the family is having for dinner.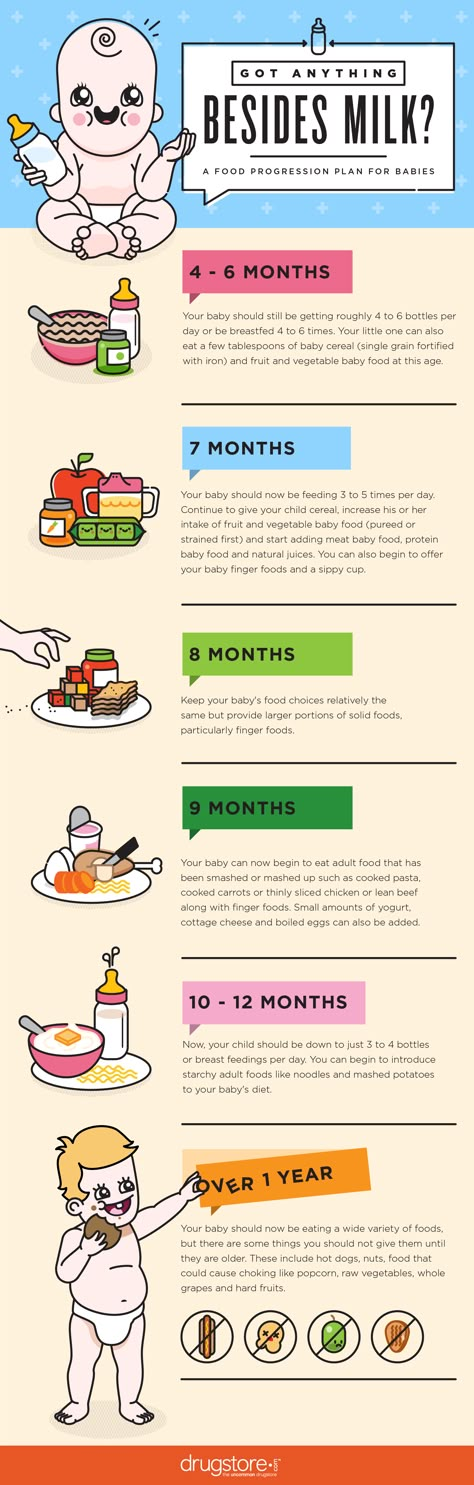 Remember to steam or mash, grind or chop foods into appropriate softness and sizes to prevent choking. Some baby dinner ideas:
Remember to steam or mash, grind or chop foods into appropriate softness and sizes to prevent choking. Some baby dinner ideas:
- Pasta with softened vegetables
- Well-cooked rice, soft veggies, and chicken
- Baked sweet potato with butter or cheese
- Beans or lentils served with rice and veggies
- Flaky fish served with steamed zucchini
There are endless variations on what you can serve your baby for dinner. As long as your baby is safe and happy, try to encourage lots of food exploration!
You must not feed any child under the age of 1 year honey, cow’s milk, juice, hard foods like candy, raw vegetables, popcorn, or sticky foods like peanut butter, as these each present choking hazards.
Learn more about feeding your baby:
- The Happiest Baby Feeding Guide
- The Benefits of Homemade Baby Food
- The Best Store-Bought Baby Food
***
REFERENCES
- Unlocking Opportunities in Food Design for Infants, Children, and the Elderly: Understanding Milestones in Chewing and Swallowing Across the Lifespan for New Innovations.
 Journal of Texture Studies, August 2017
Journal of Texture Studies, August 2017 - Complementary Feeding: A Position Paper by the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) Committee on Nutrition, Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, January 2017
- Infant Formula Feeding Practices Associated With Rapid Weight Gain: A Systematic Review, Maternal & Child Nutrition, July 2018
- Solid Food Introduction and the Development of Food Allergies, Nutrients, November 2018
- US Department of Agriculture: Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020-2025
View more posts tagged, feeding
Have questions about a Happiest Baby product? Our consultants would be happy to help! Connect with us at [email protected].
Disclaimer: The information on our site is NOT medical advice for any specific person or condition. It is only meant as general information. If you have any medical questions and concerns about your child or yourself, please contact your health provider.
It is only meant as general information. If you have any medical questions and concerns about your child or yourself, please contact your health provider.
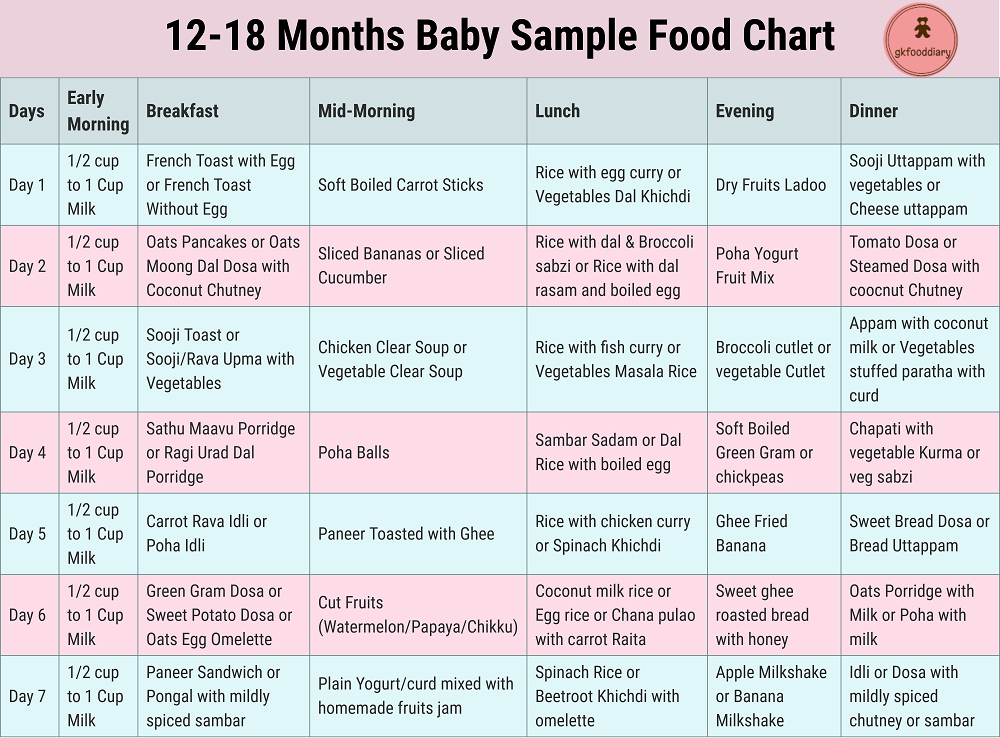
Diet for a child aged 7 months
When compiling a diet for a seven-month-old baby, distribute the products so that you get a certain prototype of the menu of an already grown-up child with breakfast and lunch.
At this age, the yolk of a boiled chicken egg, a valuable source of fat, vitamin B12, A, phosphorus and selenium, is introduced into the child's diet. Chopped yolk can be added to porridge or vegetable puree.
At the age of 7 months, you can already give your baby a cracker (in the form of dried bread) and baby biscuits.
The volume of fruit puree and juice is increased to 70 g.
It is still better to give preference to commercially produced complementary foods, given their high degree of safety and variety. If the baby does not perceive a new product the first time, it can be mixed with an already familiar product.
Approximate diet for a child aged 7 months.
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free or milk porridge ** Butter Boiled egg yolk Supplementation with breast milk or VHI | 150 g |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Vegetable oil Meat puree Fruit juice | 170 g approx. 1 tsp. 30 g 70 ml |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree Baby biscuits Breast milk supplement or VHI | 70 g |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or VHI | 200 ml |
* - infant formula
** - dairy-free porridge should be diluted with breast milk or infant formula that the child receives. Milk porridge is diluted with water.
Milk porridge is diluted with water.
Approximate diet of a 7-month-old child with cow's milk protein allergy:
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or formula for infants with intolerance to cow's milk proteins | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge* Vegetable oil Fruit puree (apple, pear) | 130 g approx. 1 tsp. 70 g |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Vegetable oil Meat puree (rabbit, turkey) | 170 g approx. 1 tsp. 30 g |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Vegetables or dairy-free porridge** Vegetable oil Meat puree | 180 g approx.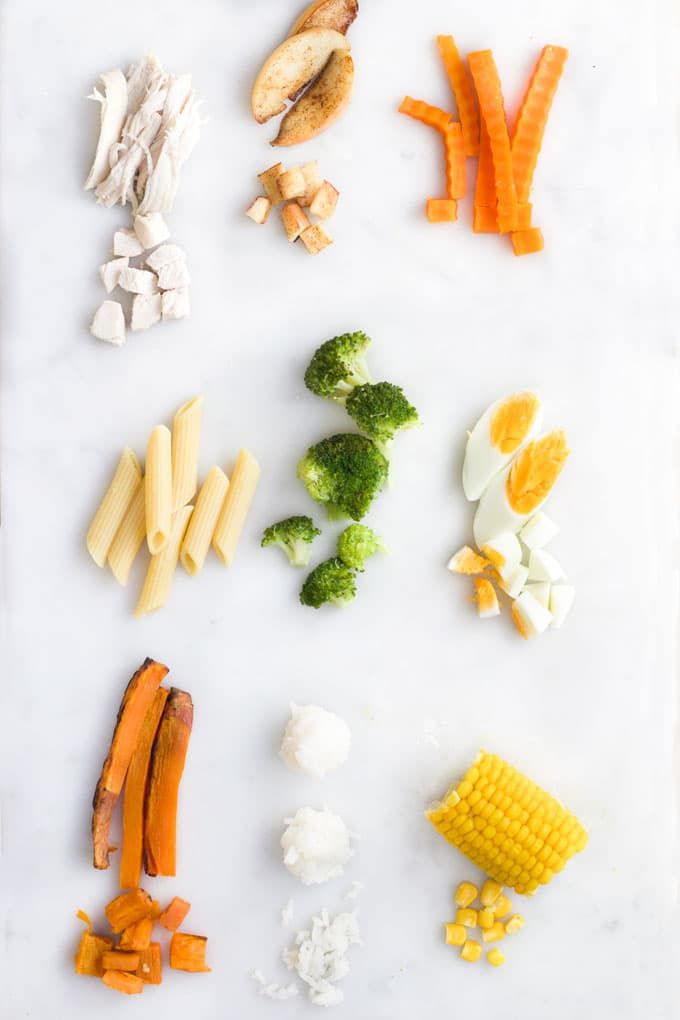  1 tsp. 1 tsp. 20 g |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or medicated formula for infants with cow's milk protein intolerance | 200 ml |
* - dairy-free porridge should be diluted with breast milk or formula for children with intolerance to cow's milk proteins.
** - you can either alternate porridge or vegetables, or offer a mixed dish - porridge with vegetables.
Baby menu at 7 months: what is possible and what is not yet
- Anastasia Ivanovna, what are the nutritional features of children at 7 months?
- The menu for a baby at seven months is different from the menu for a newborn and a baby at one year old. This difference exists due to the fact that a number of body systems, including the gastrointestinal tract and oral cavity, have not yet been formed in a newborn, he is only learning to suck. From four to six months, the diet begins to include complementary foods - food that is different from breast milk or infant formula. In the year of the child, in ideal conditions, they are transferred to a common table.
In the year of the child, in ideal conditions, they are transferred to a common table.
Some pediatricians recommend introducing complementary foods from five to six months, sometimes even from four. But the enzymatic system of the baby's body has not yet been formed, so pedagogical complementary foods are possible at four or five months, and pediatric complementary foods by six months.
— How to combine breastfeeding or bottle feeding with complementary foods?
— Pediatricians and nutritionists recommend separating these meals and giving the main dairy food and complementary foods in separate meals so that the child understands what he is eating.
If complementary foods started at 4-5 months
— What rules of baby food should parents know?
— The functions of the gastrointestinal tract are formed in such a way that the body needs to adapt to the incoming products. With proper complementary foods, it is important to monitor the child's condition in the food diary and, if necessary, consult a doctor.
Basic feeding recommendations for seven-month-old babies
- One new product is given in small doses at the beginning of the day every four days to monitor for allergies, constipation, peeling and other reactions.
- One new food can be given per feeding.
- Water is best offered between feedings and not given with complementary foods.
- Do not force-feed: if the child refuses a certain dish, it can be offered at another time and in a different form.
- The child is not given unfamiliar food when he is not in a very good mood, teething, or has just been vaccinated.
- How to identify food allergies and find the allergen?
- Observant mothers will see or hear the problem. The baby will have something on the body, constipation or indigestion will begin. A restless child will cry. To track the allergen, it is advisable to keep a food diary and keep your finger on the pulse. If there is a connection with the pediatrician, ask questions and, taking into account the vaccination calendar, the physiology of the development of your child, offer him certain products so as not to once again provoke an immune response.
What foods can be given at 7 months
Read also
- Why it is necessary to introduce meat complementary foods into the baby's diet and with what products it can be combined.
- What purees and cereals can be given at 7 months?
- If this is the first complementary food for a baby, then monocomponent purees, dairy-free and milk porridges with one cereal in the composition are good: they are easier to digest and it is easier to track the reaction of the body using them.
— In what order can complementary foods be given?
— If your baby is overweight by the age of seven months, it is better to feed him vegetable puree. If everything is in order with weight, then preference can be given to cereals. All new products are introduced gradually: they begin to feed in the amount of 5-10 g, gradually increasing the volume to 50 g. By seven months, a portion of porridge at one time can reach up to 200 g. The third option for complementary foods, if parents want, can be fruit. It is in this sequence, because fruits are sweet, and the child does not always eat unleavened vegetables or cereals after them.
It is in this sequence, because fruits are sweet, and the child does not always eat unleavened vegetables or cereals after them.
Each product will also have its own processing specifics:
- vegetables and fruits are given in the form of puree;
- purchased cereals are prepared according to the instructions;
- homemade porridges are boiled in water, then milk or mixture is added if desired;
- cottage cheese is properly stored in the refrigerator, tracking the expiration date;
- dairy, vegetable broths are brought to a single consistency (puree) so that the child develops the correct perception of the product.
— How many times to feed a baby at 7 months and how much food to give?
- You need to focus on five feedings per day. If your baby cannot tolerate the interval between meals, it is worth supplementing with breast or formula after the introduction of complementary foods.
How to calculate the amount of complementary foods
A child at seven months should weigh about eight kilograms. 1/8 of the child's weight is the daily amount of food, that is, approximately a kilogram of food, taking into account all feedings, or 200 grams per meal.
1/8 of the child's weight is the daily amount of food, that is, approximately a kilogram of food, taking into account all feedings, or 200 grams per meal.
Sample menu for a 7-month-old baby (Russian Federation)
— At what age can semi-solid and solid foods be introduced into a child's diet?
- By 6 months, most babies are ready for a new food: the baby realizes that something is hard in his mouth. By the age of seven months, the skill of palmar grip is formed: the child is able to hold solid food in his hand, and he can be given biscuits and crackers to grind. Allergists and pediatricians consider 6-10 months as the optimal period to begin the introduction of semi-solid and solid foods. But if the swallowing apparatus is not formed, there may be problems with chewing and swallowing disorders up to the gag reflex.











