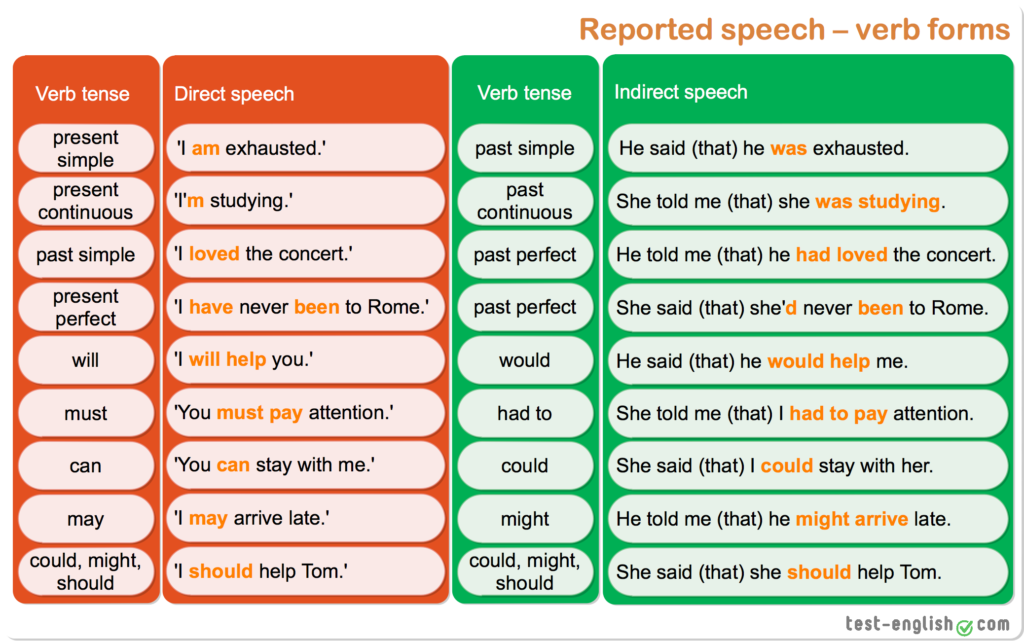
What is the best food to start my baby on
Do's and Don'ts for Baby's First Foods
Breastfeeding has been shown to improve infant, child and maternal health outcomes and help control healthcare costs, but how long should breastfeeding last and when should parents introduce solid foods?
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend exclusive breastfeeding, meaning the infant receives only breast milk, during the first six months of life for optimal nutrition and health benefits.
Once solid foods are introduced, health professionals recommend continuing breastfeeding through 12 months of age and, after that, as desired by mother and baby. Introducing your baby to solid foods is an exciting milestone. When you start introducing children to the world of solid foods, you are helping them shape their relationship with food and establish a healthy eating style. The timing for introducing solid foods will depend on the infant, but it is not recommended before the age of four months or after the age of six months.
Not sure how to get your baby started on solid foods? Consider these helpful tips.
Is Your Baby Ready to Transition?
Each child's readiness for solid food depends on their own rate of development. Signs a baby may be ready to start solid foods include sitting up with minimal support, demonstrating good head control, bringing objects to the mouth or grasping at small objects. Check with your pediatrician before starting solid foods.
Getting Started With Solids
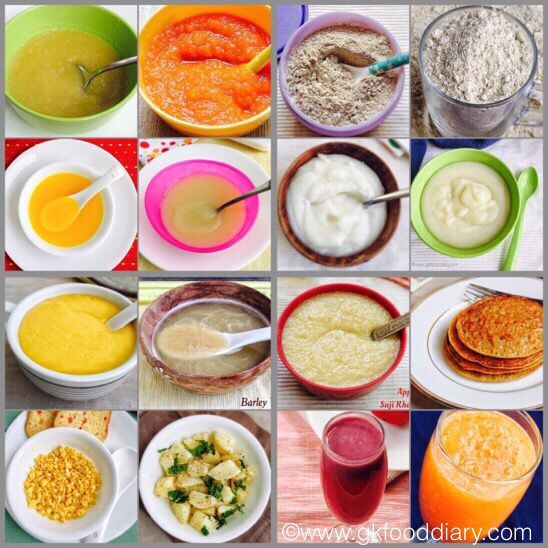
Solid foods may be introduced in any order. However, puréed meats, poultry, beans and iron-fortified cereals are recommended as first foods, especially if your baby has been primarily breastfed, since they provide key nutrients. Only one new single-ingredient food should be introduced at a time.
Softer textures are very important when first introducing foods. Infants usually start with pureed or mashed foods around six months. As infants develop chewing and motor skills, they are able to handle items like soft pieces of fruit and finger foods. As the child ages, a variety of healthful foods is encouraged.
As the child ages, a variety of healthful foods is encouraged.
Weaning From Breastfeeding
When deciding if you should wean your baby to a bottle or a cup, consider their developmental readiness. Between 7 and 8 months, most infants will drink small amounts of liquid from a cup or a glass when someone else holds it. Older babies and toddlers often have the coordination to drink fluids from a cup by themselves.
If your baby is under 12 months of age and you are not continuing to breastfeed, wean from breast milk to iron-fortified infant formula. If your baby is 12 months or older, whole cow’s milk is appropriate.
Food Safety Do’s and Don’ts
Food safety concerns for infants and toddlers include food allergies, choking and risks for foodborne illness. Keep the following safety tips in mind:
Do talk with your pediatrician about the risk of food allergies. Introducing one new food at a time, every several days, allows time to monitor for allergic reactions. Current evidence does not indicate needing to wait beyond 4 to 6 months before introducing potential allergy-causing foods such as eggs, dairy, soy, peanuts and fish. In fact, introducing peanut-containing foods as early as 4 to 6 months of age may help prevent a peanut allergy. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends introducing potentially allergenic foods when other complementary foods are introduced to an infant’s diet. Parents with concerns about food allergies should discuss how to include these foods with their pediatrician.
Current evidence does not indicate needing to wait beyond 4 to 6 months before introducing potential allergy-causing foods such as eggs, dairy, soy, peanuts and fish. In fact, introducing peanut-containing foods as early as 4 to 6 months of age may help prevent a peanut allergy. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends introducing potentially allergenic foods when other complementary foods are introduced to an infant’s diet. Parents with concerns about food allergies should discuss how to include these foods with their pediatrician.
Don’t feed your baby solid foods from a bottle. It can be a choking hazard and despite a popular misconception, putting cereal in a baby's bottle won't help with sleeping through the night. Other foods that are considered to be choking hazards are listed below.
Do supervise your child while eating. Infants should be able to sit upright and face forward when you first introduce solid foods. This makes swallowing easier and choking less likely.
Don’t feed directly from the jar of food but instead spoon some food into a separate dish first. Feeding directly from the jar may introduce bacteria from your baby's mouth to the spoon and back into the food, creating a food safety issue.
Don’t feed honey to children under 12 months of age due to the risk of foodborne illness.
Examples of appropriate solid foods listed by age:
6 months:
- Well-cooked and pureed meat, poultry or beans
- Ground, cooked, single-grain cereal or infant cereal with breast milk or formula
- Cooked and pureed vegetables
- Mashed banana or avocado
9 months:
- Well-cooked, minced or finely chopped meat, poultry or beans
- A variety of cooked vegetables cut into small, ½ inch pieces, such as squash and green beans
- Sliced and quartered bananas or small pieces of other soft fruits
12 months:
- Soft, shredded meat, poultry or fish
- Small pieces of cooked vegetables
- Small pieces of soft, easy to chew fruits
- Mixed food dishes the family is eating in appropriately sized pieces
Not recommended for those under 4 years of age due to the risk of choking:
- Popcorn and whole kernel corn
- Nuts and seeds
- Large chunks of meat, poultry and cheese
- Candy, gum drops and jelly beans
- Hard, raw fruits or vegetables such as apples, celery and carrots
- Whole grapes and cherry tomatoes, unless cut into quarters
- Hot dogs, unless cut into strips and age appropriate, bite-size pieces
- Sticky foods, such as peanut butter, which can get stuck in the back of the mouth – peanut butter is okay if spread thinly on bread
For toddlers and preschoolers, chop grapes, meat, poultry, hot dogs and raw vegetables and fruits into small pieces (about ½ inch or smaller).
Nurturing Healthy Relationships with Food
Establishing a positive feeding relationship during infancy can have lifetime benefits. Keep in mind that children are responsible for how much and whether they eat so always wait for your baby to pay attention to each spoonful before you feed them. Don't be afraid to let your baby touch the food in the dish and on the spoon. You wouldn't want to eat something if you didn't know anything about it, would you? In addition, know the cues that your baby is done eating. A common cue babies are full is head turning.
Whatever happens, don't get discouraged and enjoy the experience. With a little patience and creativity, you can make your baby's first solid food eating experience fun for everyone involved!
Tags
Find a Nutrition Expert
Looking for credible nutrition information and recommendations? The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics' network of credentialed food and nutrition practitioners are ready to help!
See Directory
When to Start Baby Food
Starting solids is an exciting and important milestone in baby’s development—one that not only opens them up to a brand-new world of flavors and textures, but also puts them on the right path to growing healthy and strong. Here’s what you need to know about how and when to start baby food for a smooth transition.
Here’s what you need to know about how and when to start baby food for a smooth transition.
In this article:
When to start baby food
How to start baby on solids
Best first foods for baby
Introducing allergenic foods
When to Start Baby Food
Knowing when to start baby food is both crucial and tricky. Starting baby on solids too early means you might increase the risk of choking, obesity and bellyaches, but introducing solids too late means you might slow baby’s growth and encourage an aversion to solid foods, among other conditions. Fortunately, doctors have zeroed in on a sweet spot for starting baby food, which is sometime between 4 and 6 months of age—though, ideally, baby should be receiving their nutrition exclusively from breast milk until the six-month mark, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). How to tell if it’s time for starting solids for your little one? Baby will give you clues, including:
• Baby can sit in a high chair comfortably on their own. This is a major sign in terms of when to start baby food, says Lauren Kupersmith, MD, a pediatrician at Hassenfeld Children’s Hospital at NYU Langone in New York City. It means baby can hold their head up and doesn’t need to be propped up to stay in the upright position, which is important to avoid choking.
This is a major sign in terms of when to start baby food, says Lauren Kupersmith, MD, a pediatrician at Hassenfeld Children’s Hospital at NYU Langone in New York City. It means baby can hold their head up and doesn’t need to be propped up to stay in the upright position, which is important to avoid choking.
• Baby looks interested at mealtime. Babies likes to mimic what we do, so if your child likes to sit up like a big kid and watch you eat, then by all means let them try eating too.
• Baby can move food to the back of their throat to swallow. But if baby tends to push the food out of their mouth—not because they don’t like it, but because they can’t seem to get the food to where it needs to go—hold off on starting solids.
How to Start Baby on Solids
At 4 to 6 months, most of baby’s nutrition will still come from breast milk or formula, so don’t worry if baby doesn’t like eating food right away. Introducing solids is a gradual process, and every baby learns in their own time.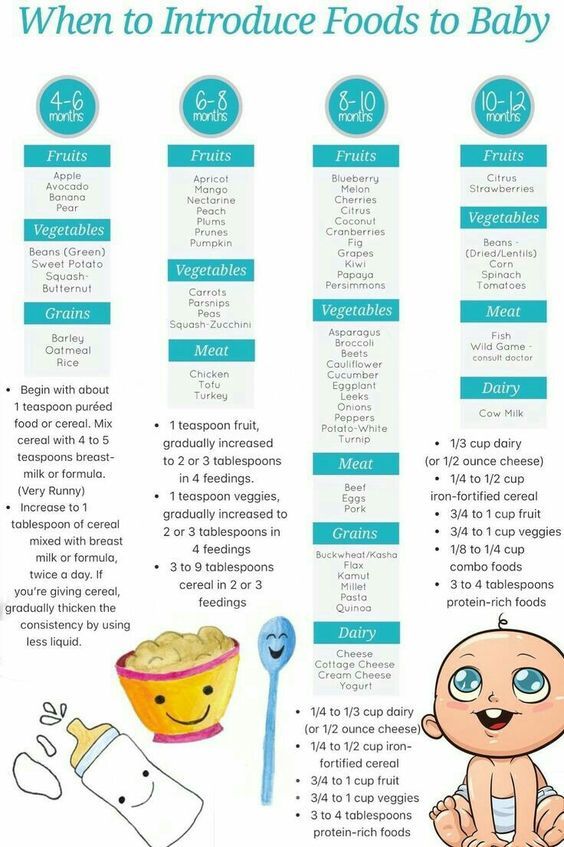 Here are some general guidelines for how to start baby on solids:
Here are some general guidelines for how to start baby on solids:
• Feed baby with a spoon. Letting your child go at it with their hands may seem tempting (and super-cute), but it’s best that they learn the right way from the get-go. (And even then, be prepared to clean up more than a few messes!) Also, never put cereal (or any other food) in baby’s bottle—it’s a choking hazard.
• Start slowly. When introducing solids, a half spoonful will do at first—you may even want to talk baby through it (“Yummy!”). To make it easier for baby to get accustomed to the idea of swallowing solids, start mealtime with a little breast milk or formula, then offer some food (again, no more than a half teaspoon at a time) and finish off with more breast milk or formula. If baby cries or turns away when you present the spoon, try again some other time. Start off with introducing solids at one meal a day, then slowly work your way up. The morning is a good place to start, since baby is often hungriest at that time. When starting solids, baby typically won’t eat more than an ounce or two in one sitting.
When starting solids, baby typically won’t eat more than an ounce or two in one sitting.
• Try new foods more than once. Since babies’ tastes will evolve, you may need to try a food 20 times before a baby actually likes it, says Kupersmith.
• Stick with the same food for three days before trying another one. This makes it easy to track whether baby is allergic to a particular food.
• Try foods in different forms. If baby doesn’t like pureed food, try it mashed. After all, baby is learning about new textures as well as new tastes. It may be a case of trial and error until you find a winner.
Best First Foods for Baby
Got baby safely strapped into the high chair and bib? You’re ready to finally start feeding baby solids! There aren’t any official food rules for babies starting solids, and there’s no scientific evidence suggesting you should introduce one type of food before another, assuming the foods aren’t choking hazards. Nevertheless, baby cereal (such as oatmeal, rice and barley) is an “easy training food,” says Kupersmith, which is why it’s often recommended as baby’s first food; you can always mix it with more milk to build up to a thicker consistency. Many doctors also recommend starting vegetables before fruits, but there’s no evidence that this would make babies like vegetables more when they grow up—babies innately love sweets, and the order of introducing solids to baby doesn’t change that.
Nevertheless, baby cereal (such as oatmeal, rice and barley) is an “easy training food,” says Kupersmith, which is why it’s often recommended as baby’s first food; you can always mix it with more milk to build up to a thicker consistency. Many doctors also recommend starting vegetables before fruits, but there’s no evidence that this would make babies like vegetables more when they grow up—babies innately love sweets, and the order of introducing solids to baby doesn’t change that.
So why not simply start introducing solids with something you think baby will like? Here are a few common first foods for baby that are healthy and easy to eat (and, in the case sweet potato and banana, also easy to digest). Whatever you decide to feed baby, mash it with a fork or puree before serving whenever introducing solids.
- Baby cereal, such as oatmeal, rice, barley
- Sweet potato
- Banana
- Avocado
- Apples
- Pears
- Green beans
- Butternut squash
If your child has been breastfeeding, check with your pediatrician about getting a jump on pureed chicken or beef when you’re starting solids. These foods contain easily absorbable forms of iron and zinc, which baby needs by 4 to 6 months, according to the AAP.
These foods contain easily absorbable forms of iron and zinc, which baby needs by 4 to 6 months, according to the AAP.
At around 9 months, baby should have already worked their way up to a variety of foods, including cereal, vegetables, fruits, meats, eggs and fish (see below regarding the last two). (Keep in mind, though, that baby will still get the majority of their nutrients from breast milk or formula until age one.) By now, baby will probably settle on three meals a day along with two snacks. Let them consume about 4 ounces of solids at each meal (equivalent to a small jar of strained baby food) and about half that amount for each snack.
Save honey and cow’s milk for after baby’s first birthday—there’s a risk for infant botulism with honey (a type of bacterial poisoning), and baby’s tummy isn’t prepared to digest large amounts of cow’s milk until they’re about one year old. Avoid adult processed foods and foods that are choking hazards (such as sticky foods, like large gobs of peanut butter; hard foods that are difficult to gum, like raw vegetables, nuts, seeds and popcorn; and round, slippery foods that haven’t been cut up, like grapes and cherry tomatoes). Instead, the first foods for baby, and those in the months that follow, should be soft and served mashed, pureed or (once baby seems ready to move up from the really mushy stuff) cut up into really little bits. “There’s pretty much free reign at that point,” Kupersmith says.
Instead, the first foods for baby, and those in the months that follow, should be soft and served mashed, pureed or (once baby seems ready to move up from the really mushy stuff) cut up into really little bits. “There’s pretty much free reign at that point,” Kupersmith says.
Introducing Solids Chart
Hesitant about improvising your first foods for baby? That’s okay too. If you prefer an “introducing solids chart” to help you plan out baby’s path, the guide below can come in handy.
Image: The Bump
Introducing Allergenic Foods
Much of the confusion around when to start baby food stems from questions concerning allergenic foods. These are foods that babies are most often allergic to. The major culprits include dairy, eggs, fish, peanuts and tree nuts. In the past, parents were advised to hold off on exposing baby to these foods, but now doctors recommend introducing them early, often and in age-appropriate format, which means starting off with purees and soft textures.
“Dairy is an easy starting point, given options such as yogurt and cheese,” says David Stukus, MD, director of the Food Allergy Treatment Center at Nationwide Children’s Hospital and a spokesperson for the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology. You can also try scrambled eggs in small amounts, although baby may not be too pleased with the texture at first.
As far as peanut products go, the National Institutes of Health issued new guidelines in 2017 that encourage parents of children at high risk for peanut allergies to incorporate them into baby’s diet at 4 to 6 months of age. Giving these babies peanut products before the age of one actually decreases their risk of developing a peanut allergy before age 5 by 81 percent, compared to kids who are introduced to peanuts later in life. Parents of kids without the food allergy risk can start peanut products whenever they’d like, as long as the nuts are in an age-appropriate form: Peanut butter can be thinned out with water or mixed into a fruit or vegetable puree, and peanut powder can also be mixed into cereal and fruits. Don’t give whole peanuts or pieces of peanuts, since they’re a choking risk.
Don’t give whole peanuts or pieces of peanuts, since they’re a choking risk.
Allergic reactions to food are never just a fluke; they will happen with every exposure. Symptoms can range from mild (such as a rash or vomiting) to severe (such as trouble breathing). If baby has a food allergy, you’ll notice a reaction within minutes or up to two hours after eating the problematic food, Stukus says. If the symptoms are severe, call 911 right away. Otherwise, talk to your pediatrician; she can help confirm whether it’s an allergy or some other type of condition (such as a viral illness).
Expert bios:*
Lauren Kupersmith, MD, IBCLC, is a pediatrician and clinical instructor at Hassenfeld Children’s Hospital at NYU Langone in New York City, as well as a certified lactation consultant. She earned her medical degree from New York Medical College in 2005.
David Stukus, MD, is the director of the Food Allergy Treatment Center at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, an associate professor of pediatrics in the division of allergy and immunology and a spokesperson for the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology. He earned his medical degree from University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine in 2002.
He earned his medical degree from University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine in 2002.
Updated January 2020
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
How to properly feed your baby
Elena Gvozdetskaya
Pediatrician GMS Clinic
Ask two mothers how to properly feed their baby and you will get two different answers. This is indeed a delicate and difficult issue. But let's look into it together with expert pediatrician GMS Clinic Elena Gvozdetskaya. The doctor spoke about the principles of nutrition for babies, gave recommendations on the choice of products, the method of preparation, and much more. nine0006
What are the 3 main principles of feeding children
- Safety.

- Variety.
- Regularity.
Does the number of feeds depend on the child's age?
Yes, it depends. The younger the child, the more meals should be. After all, the small stomachs of children cannot digest a lot of food at a time. For example, babies are fed every 3-4 hours, and preschoolers - 3 to 5 times a day.
A young child's serving size can be measured with their fists. He should eat 12 such "cams" of food, of which 2-3 are main meals, 1-2 are snacks. Plus, there should be 2-3 servings of dairy products per day. nine0006
Why do you need breakfast, lunch and dinner?
Food is a source of energy and nutrients. It must be done regularly so that the baby is active, grows and develops properly. Complete breakfasts, lunches and dinners are the key to children's health.
Also, thanks to the diet, you can think over the diet for the day so that the child gets the required amount of calories from healthy food. Parents often plan in advance what meals to cook as main meals. nine0006
nine0006
Is it okay to have snacks between main meals?
Yes, it is necessary. Long breaks between meals can lead to fatigue, fatigue, low blood sugar and concentration, memory.
It is important that snacks include healthy foods such as vegetables, fruits, grains or protein. For example, you can make dried fruit bars, sandwiches with bread and eggs.
Is it necessary to give porridge for breakfast? Which are the best to choose? nine0010
No, not required. Porridge can be replaced with sugar-free cereal or a sandwich made from whole grain bread. During the day, the child should eat 5-6 "cams" of cereals.
You can choose any porridge for breakfast: oatmeal, rice, buckwheat, corn, millet. Be sure to cut out sugar. Instead, fruits, dried fruits are added to some dishes, and honey can be given to children over 1 year old.
How to replace cereals for breakfast to diversify the diet?
Any healthy product will do. The main thing is that the first meal gives satiety for at least 2. 5 hours - before a snack. Breakfast usually includes: nine0006
5 hours - before a snack. Breakfast usually includes: nine0006
- cereals: porridge, cereals, muesli, granola, healthy pastries;
- protein: scrambled eggs, meat, fish;
- dairy products: yoghurt, milk, cheese, syrniki;
- vegetables or fruits.
These products can be combined in various ways. For example, this morning offer your child cheesecakes with strawberries, and tomorrow - an omelette with whole grain bread and cheese.
Remember that according to statistics, children who do not eat breakfast eat sweets more often and drink carbonated drinks. Because of this, they have an increased risk of obesity, the development of cardiovascular diseases and caries. nine0006
Does the child really need soups?
Actually, no. Some parents often prepare soup for their children because it is easier for babies to chew and it passes through the esophagus to the stomach faster. After all, there is already liquid in the dish. This is more convenient than chewing dry food for a long time and carefully so that the required amount of saliva is released.
This is more convenient than chewing dry food for a long time and carefully so that the required amount of saliva is released.
Soup is water, vegetables and meat. It will be just as helpful if the child eats them simply sliced, chewed thoroughly, and drinks enough liquid throughout the day. The main thing is to make sure that the meal includes different food groups. It doesn't matter if it's borscht or vinaigrette. nine0006
What is the ideal dinner for a child?
The main thing is that the child does not experience hunger at night. So choose foods that saturate well. For example:
- cereals: buckwheat, rice, bulgur;
- proteins: chicken, turkey;
- vegetables.
For example, buckwheat with boiled turkey and broccoli is a great dinner option. Or bulgur with steamed chicken cutlets and cucumber and tomato salad.
Toddlers can have a second dinner 20-30 minutes before bedtime. Choose foods such as kefir, yogurt or some kind of fruit. Just don't forget to brush your child's teeth afterwards. nine0006
Just don't forget to brush your child's teeth afterwards. nine0006
Do kids only need freshly prepared food, or is yesterday's soup okay too?
Food that has been stored for more than two hours at 6 to 8 °C is no longer safe for the baby. We do not recommend giving it, because pathogenic bacteria begin to multiply there and toxins are released. If you want to store the dish for about two days, you need rapid cooling to 6 degrees and below.
How to prepare food?
The best methods are steaming or boiling. The latter is considered the best option for killing harmful bacteria because the entire surface of the product is in hot water. And steaming preserves the maximum of vitamins. nine0006
Food can also be baked and fried, but with a little oil. But the formation of a black crust should not be allowed - the rarer the dishes of this method of preparation in the child's diet, the better.
What kind of meat and fish to choose for children?
Our recommendation:
- red meat - 1 portion three times a week: beef, pork, lamb;
- white meat - 1 serving per day: chicken, turkey, rabbit;
- fish - 2 times a week: hake, cod, perch, red fish.
 nine0013
nine0013
Please note! Do not give your child the meat of large predatory fish, such as shark, tuna. After all, they can accumulate mercury and other harmful substances.
What is the norm of fruits and vegetables for a child per day?
Recommended for young children: 2-3 "fist" fruits and vegetables per day. Remember that dried fruits and baked foods also count.
Cooked vegetables, fruit purees and some raw fruits such as avocado, mango, peach, banana can be given at the start of complementary foods. After a year, we recommend starting to introduce soft-skinned fruits into the diet - this is good for digestion. nine0006
Milk in the diet of children - for or against?
If the child is not lactose intolerant or allergic to cow's milk protein, he can drink it and eat dairy products.
When parents notice that their children are consuming too much of this micronutrient-rich drink, it is important to find the cause. Perhaps the baby is not enough from the diet of any substances. Offer a healthy substitute - you need the child to eat a variety of foods and get the whole set of nutrients from different foods. nine0006
Offer a healthy substitute - you need the child to eat a variety of foods and get the whole set of nutrients from different foods. nine0006
What drinks are good for babies and schoolchildren?
Give preference to the following drinks:
- pure water;
- mors;
- compote;
- natural juice or smoothie in small quantities;
- fermented milk drinks;
- milk.
All of these drinks should be free of sugar. When buying in a store, read the ingredients, even if it says "specially for children." nine0006
We do not recommend giving children the following:
- sugary drinks (packed juices, sodas) up to 3 years;
- tea, coffee, other caffeinated drinks up to 5 years;
- healing mineral water.
There are special children's teas, often containing sugar and herbal extracts. Therefore, we do not recommend giving them to a baby until he is 2 years old. Keep in mind that herbal drinks can cause an allergic reaction and reduce iron absorption, and are also not recommended for babies under 2 years of age. nine0006
nine0006
At what age can sweets be given to children? What exactly?
Follow these guidelines:
- no added sugar until two years of age;
- from 2 to 4 years of age, sweets may be limited;
- Ages 5 to 7 - 3-4 teaspoons of sugar per day is acceptable, including candies, cookies, sugary cereals, juices.
From the age of 5, all sweets can be given in moderation, such as marshmallows, marmalade, marshmallows, ice cream, cereal bars, chocolate. nine0006
What is the effect of dry eating in children?
Poorly chewed dry, dense food moves down the esophagus worse, takes longer to digest, creates discomfort in the stomach and a feeling of "lump". It's not harmful, but it's uncomfortable. To avoid this, it is enough to chew food thoroughly and drink liquids throughout the day.
At what age can children be transferred to a common table?
Usually a year old, the child already eats pieces of most complementary foods, from this age it is possible to eat one meal with everyone. nine0006
nine0006
It is only important to adapt the baby plate:
- make meals without salt, salt separately for adults;
- cook until completely done or boiled, do not give raw;
- lettuce can be cut into small pieces: the baby should chew the pieces one at a time, adults should season with sauces in a separate plate;
- the child's meat must be divided into fibers;
- meatballs and cutlets - finely chop for children, for adults pour sauce separately (the same with pasta and cereals). nine0013
If you are in doubt about whether your baby can take a product, it is best to consult your pediatrician.
What should I do if my child refuses to eat healthy food and asks for sausages and biscuits?
If your child only asks for sausages and cookies, don't buy them. Keep healthy alternatives at home, explain, show by example healthy proper nutrition.
Sausages can be replaced with your baby's favorite type of meat, and biscuits can be replaced with fruit or homemade cakes made from healthy ingredients. nine0006
nine0006
How can I instill healthy eating habits in my child?
You can't explain to a child that "chips are bad" if dad eats them with pleasure. The kid will not understand that broccoli is healthy if mom has fried potatoes in her plate. The family and environment of children should lead a healthy lifestyle, eat a varied and balanced diet, and maintain a sufficient level of physical activity. Only in this way will you set a worthy example and be able to instill the right eating habits.
COMPLETE FOOD: TO GROW YOUR BABY HEALTHY. PEDIATRIC ADVICE
Doctor, when is the best time to introduce complementary foods? What are the dangers of introducing complementary foods too early or too late?
In fact, there are no universal recommendations regarding the introduction of complementary foods, - says Solomiya Maksimchuk, - because each baby has its own characteristics, so the approach should be individual. Therefore, answering the first question - when it is advisable to introduce complementary foods, I cannot name a specific figure, because in fact complementary foods are introduced at 3 months, and at 4, and at 6, and at 8 - depending on the indications. In my medical practice, there were children who were one year old, and no matter how we tried to introduce complementary foods, everything was in vain - the kids did not show any food interest, especially those who were breastfed. They had a good weight gain, psychomotor development, but they did not show food interest, and this is not very good, because the children did not form and did not prepare the gastrointestinal tract for the perception of other foods. What, then, can be advised to a mother who is faced with this problem? In this case, I am more guided not by my professional experience, but by the experience of the mother, understanding how difficult it is to force a child to eat if he does not want to. nine0006
In my medical practice, there were children who were one year old, and no matter how we tried to introduce complementary foods, everything was in vain - the kids did not show any food interest, especially those who were breastfed. They had a good weight gain, psychomotor development, but they did not show food interest, and this is not very good, because the children did not form and did not prepare the gastrointestinal tract for the perception of other foods. What, then, can be advised to a mother who is faced with this problem? In this case, I am more guided not by my professional experience, but by the experience of the mother, understanding how difficult it is to force a child to eat if he does not want to. nine0006
In which case is it advisable to introduce complementary foods earlier, in which case - adhering to standard norms?
In the case of breastfeeding (if the baby is completely healthy), I start talking about this when the baby is 6 months old. With artificial feeding, we are talking about the introduction of complementary foods when the baby is 4 months old. Some mothers are of the opinion that breast milk contains all the necessary micronutrients, so you should not rush to complementary foods. Of course, this is true - if the mother adheres to the right diet, she eats fully. But in fact, complementary foods help prepare the baby’s herbal system - the child learns different tastes, because it’s no secret that when a baby receives only breast milk, some digestive juices are released, and in the case of complementary foods, completely different ones, therefore, introducing complementary foods, we gradually prepare an enzymatic system. nine0006
With artificial feeding, we are talking about the introduction of complementary foods when the baby is 4 months old. Some mothers are of the opinion that breast milk contains all the necessary micronutrients, so you should not rush to complementary foods. Of course, this is true - if the mother adheres to the right diet, she eats fully. But in fact, complementary foods help prepare the baby’s herbal system - the child learns different tastes, because it’s no secret that when a baby receives only breast milk, some digestive juices are released, and in the case of complementary foods, completely different ones, therefore, introducing complementary foods, we gradually prepare an enzymatic system. nine0006
Which products are the first to be introduced into complementary foods, because there are different views on this issue - someone advises fermented milk products, someone vegetable purees or juice?
It all depends on the specific situation. If complementary foods are introduced at 3 months, indications are necessary for this - these are digestive disorders of the baby, the child's tendency to constipation.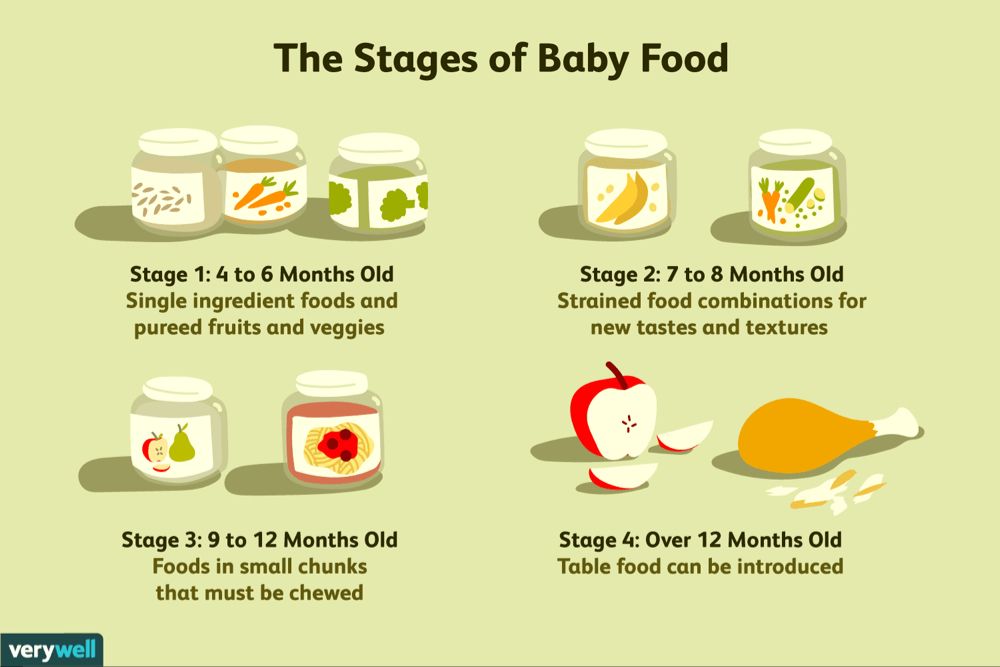 In this case, I recommend giving fermented milk products to the child at the first stage of the introduction of complementary foods. For children who are bottle-fed and have digestive problems, I recommend fermented milk mixtures (horses are considered the first complementary foods). If we are talking about a completely healthy child, first of all, I advise you to introduce vegetable puree - it is easily digested by the children's gastrointestinal tract. Usually, this is a puree of zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower, parsnips, parsley, white carrots, potatoes. Unfortunately, in our area there is not a wide variety of products. Pediatricians should take this into account when advising the mother what to choose at the beginning of complementary foods in winter, because if we advise a zucchini in February, will we find it on the shelves, and if so, will this exotic product benefit the baby? nine0006
In this case, I recommend giving fermented milk products to the child at the first stage of the introduction of complementary foods. For children who are bottle-fed and have digestive problems, I recommend fermented milk mixtures (horses are considered the first complementary foods). If we are talking about a completely healthy child, first of all, I advise you to introduce vegetable puree - it is easily digested by the children's gastrointestinal tract. Usually, this is a puree of zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower, parsnips, parsley, white carrots, potatoes. Unfortunately, in our area there is not a wide variety of products. Pediatricians should take this into account when advising the mother what to choose at the beginning of complementary foods in winter, because if we advise a zucchini in February, will we find it on the shelves, and if so, will this exotic product benefit the baby? nine0006
The first complementary foods start with a small amount - a teaspoon per day. Prepare, for example, zucchini puree. We give the baby half a teaspoon of puree once a day - at lunchtime, and every next day we increase the amount of the product. On average, in 14 days it is possible to increase the amount of complementary foods to 50-70 grams - it all depends on how the child perceives the new food. When a child eats more - up to 100 grams of vegetables, we can diversify the menu - add boiled broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini. When a child eats mostly 2-3 vegetables, we can introduce the next complementary foods (mashed potatoes based on several vegetables are considered one complementary food). The next step is the introduction of fruit puree. Provided that the child responds well to the first complementary foods, after 3 weeks, vegetable complementary foods in the amount of 100 grams can be introduced. And then at 6.5-7 months you can introduce fruits - apples of green or yellow varieties in a baked form. nine0006
We give the baby half a teaspoon of puree once a day - at lunchtime, and every next day we increase the amount of the product. On average, in 14 days it is possible to increase the amount of complementary foods to 50-70 grams - it all depends on how the child perceives the new food. When a child eats more - up to 100 grams of vegetables, we can diversify the menu - add boiled broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini. When a child eats mostly 2-3 vegetables, we can introduce the next complementary foods (mashed potatoes based on several vegetables are considered one complementary food). The next step is the introduction of fruit puree. Provided that the child responds well to the first complementary foods, after 3 weeks, vegetable complementary foods in the amount of 100 grams can be introduced. And then at 6.5-7 months you can introduce fruits - apples of green or yellow varieties in a baked form. nine0006
At the same time, we add a certain amount of fat - olive or sunflower oil - to the prepared vegetable mixture. After the introduction of vegetables and fruits, depending on the age, we introduce the yolk or meat. Regarding when it is worth introducing fruit juices - at one time pediatricians focused considerable attention on this. Today, if a child is breastfed, we do not insist on a drinking regimen or suggest adding water or herbal decoctions from chamomile, dill, fennel to drinking. Fruit juices must be administered concurrently when the child consumes a certain amount of fruit. It can be apple juice - by no means multivitamin or citrus. nine0006
After the introduction of vegetables and fruits, depending on the age, we introduce the yolk or meat. Regarding when it is worth introducing fruit juices - at one time pediatricians focused considerable attention on this. Today, if a child is breastfed, we do not insist on a drinking regimen or suggest adding water or herbal decoctions from chamomile, dill, fennel to drinking. Fruit juices must be administered concurrently when the child consumes a certain amount of fruit. It can be apple juice - by no means multivitamin or citrus. nine0006
What should I do if my baby does not like a certain food?
If rashes appear on the baby’s skin, the baby is worried about intestinal disorders, anxiety associated with abdominal pain, or if there is a tendency to constipation-diarrhea due to the introduction of a certain product, we leave in the diet products of all previous stages of complementary foods, but the one that provoked disorders, cancel. If it is difficult for the mother to understand which particular product caused the disorders, it is necessary to return to the initial level for a certain time - breastfeeding, which at the same time will encourage the mother to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet or a balanced diet. If the baby is on artificial feeding, it is necessary to return to the use of the mixture, without complementary foods. Then, at a slightly more intense pace, you need to take the same steps to introduce complementary foods as before, carefully observing the reaction of the baby. nine0006
If the baby is on artificial feeding, it is necessary to return to the use of the mixture, without complementary foods. Then, at a slightly more intense pace, you need to take the same steps to introduce complementary foods as before, carefully observing the reaction of the baby. nine0006
At what stages of complementary feeding do we introduce cereals, meat, fish, egg yolk? What foods do we start introducing when teeth are erupting in a baby?
After vegetables and fruits, we introduce the yolk into complementary foods, then meat or cereals, followed by sour-milk complementary foods. However, I want to note that the presence of teeth has nothing to do with the introduction of complementary foods, because in fact, children do not chew for a long time. The purpose of complementary foods and the task of the child is to be able to form a food lump in the oral cavity. Then, when the baby swallows liquid food, he hardly retains it in his mouth. And complementary foods make it possible to retain food, enveloping it with saliva and then swallowing it in small portions. In some babies, teething happens even a year, but they have complete complementary foods. nine0006
In some babies, teething happens even a year, but they have complete complementary foods. nine0006
Regarding the timing of complementary foods - meat is given to the baby after about 7 months. Rabbit meat, turkey fillet, beef, quail are best suited. I am often asked whether it is possible to give a child chicken meat during the complementary feeding period. If you are sure that the chicken is home grown without the addition of hormones, chicken is also suitable for the baby's diet.
I recommend eating fish after 10 months - in any case, not red varieties (red fish can be given to a child only after two years of life). The best option is white sea fish of low-fat varieties. When introducing cereals into the diet, it must be remembered that they must be adapted by age - it is these cereals that contain the destroyed grain shell, which contains the most harmful carbohydrates, in particular, gluten. Once upon a time, parents ground rice or buckwheat, but because of these products, the baby had problems with digestion, because there was a certain load on his body. At the beginning of complementary foods, it is better to give free-flowing adapted dairy-free cereals - we breed them in water. When the child has taken this complementary food well, we can introduce milk porridge. For children who are breastfed and are underweight after 4 months, there are other recommendations. As a breastfeeding aficionado, my advice is to stimulate a mother's lactation by reviewing her diet. At the same time, it is advisable to introduce dairy-free cereals, since they provide more calories than vegetables. There are also cases when a child is one year old and mothers replace breastfeeding with formula milk from a bottle. In fact, the baby does not need additional nutrients, moreover, there is no need for supplementation or feeding from a bottle - this is a step back. nine0006
At the beginning of complementary foods, it is better to give free-flowing adapted dairy-free cereals - we breed them in water. When the child has taken this complementary food well, we can introduce milk porridge. For children who are breastfed and are underweight after 4 months, there are other recommendations. As a breastfeeding aficionado, my advice is to stimulate a mother's lactation by reviewing her diet. At the same time, it is advisable to introduce dairy-free cereals, since they provide more calories than vegetables. There are also cases when a child is one year old and mothers replace breastfeeding with formula milk from a bottle. In fact, the baby does not need additional nutrients, moreover, there is no need for supplementation or feeding from a bottle - this is a step back. nine0006
Were there cases of anemia among children under one year of age? How to prevent this problem?
Although not often, there are cases of anemia in the practice of a pediatrician.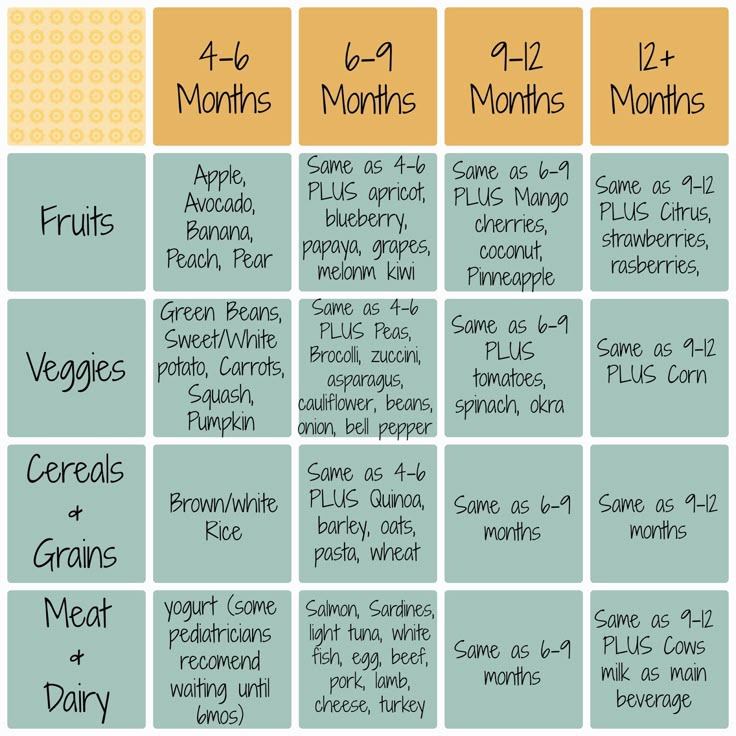 Iron deficiency anemia in a baby occurs in the majority in the absence of a child’s nutritional interest, when it is not possible to adequately introduce complementary foods. But it is necessary to take into account the fact that if the child has low hemoglobin, then the mother has it even lower, because the baby receives everything that is possible during lactation. Therefore, first of all, we work with mom's diet. At the same time, we are taking more intensive steps in replacement feeding - introducing red meats, in particular beef, if age permits (at 8-9months), offal: boiled beef tongue, beef, turkey, rabbit liver, apples, buckwheat for children under one year of age.
Iron deficiency anemia in a baby occurs in the majority in the absence of a child’s nutritional interest, when it is not possible to adequately introduce complementary foods. But it is necessary to take into account the fact that if the child has low hemoglobin, then the mother has it even lower, because the baby receives everything that is possible during lactation. Therefore, first of all, we work with mom's diet. At the same time, we are taking more intensive steps in replacement feeding - introducing red meats, in particular beef, if age permits (at 8-9months), offal: boiled beef tongue, beef, turkey, rabbit liver, apples, buckwheat for children under one year of age.
Up to what age is it best to breastfeed a baby?
When it comes to the formation of immunity, breastfeeding up to 6 months of a child's life is most appropriate, because the baby needs the protection that he receives from his mother. After 6 months of life, the child's immune system independently forms antibodies.